2.1. Taiwanese Textile Industry
Taiwan’s textile industry has played a crucial economic and social development. In the early stages, the industry was mainly cotton spinning, but with government support for petrochemical downstream raw materials in the 1960s, it shifted toward chemical fibers and blended products. After fulfilling domestic demand, Taiwan’s cotton textile industry turned to export markets, and by the 1970s, vertical integration from raw materials, textiles, to apparel established Taiwan’s position in the global supply chain. From 1967 to 2003, textiles were Taiwan’s largest foreign exchange earner for 37 consecutive years, averaging around US
$10 billion annually, contributing significantly to the economy and livelihoods [
12].
Over the past six decades, continuous product innovation and investment in production equipment have enabled Taiwan to build one of the world’s most complete textile production systems. Taiwan has become a global hub for functional textiles, supplying advanced materials to the international sportswear and fashion markets. The industry continues to develop toward smart textiles, sustainability, and functional applications, maintaining its leading global position [
12].
However, the industry has faced notable challenges in recent years. Between 2005 and 2021, Taiwan’s textile and apparel production value declined by 30.7%, from NT
$498.9 billion to NT
$345.6 billion. Within this period, apparel and made-ups contracted 62.1%, artificial fibers decreased by 52.3%, and textiles fell by 15%. Both manufacturers and employment levels also shrank significantly. These structural shifts highlight the need for strategic transformation, as developing a well-defined strategy is essential for outperforming competition and achieving sustainable growth [
13].
2.2. Dynamic Capabilities Theory
Since Teece et al. [
14] advanced the concept of “the firm’s ability to integrate, build, and reconfigure internal and external competences to address rapidly changing environments,” Dynamic Capabilities Theory has come to be seen as one of the important foundations for explaining the ability of firms to maintain competitiveness in contexts of extreme uncertainty. The value of the theory lies in answering questions related to the “why” and “how” firms survive and grow in continuously transforming conditions [
15]. The theory emphasizes that organizations create value in the three capacities of sensing, seizing, and transforming [
5,
6]. Helfat et al. [
7] further specified that dynamic capability, as defined in the context of organizations, refers to an organization’s ability to purposefully create, extend, and modify its base of resources, which is not a static stock of resources but ongoing and evolving.
The operational mechanisms of dynamic capabilities are derived from perspectives encompassing two main streams. Specifically, on the one hand, Mele et al. [
16] shared that dynamic capabilities are a set of identifiable, path dependent processes that may be regarded as cross-firm “best practices.” On the other hand, Zhang et al. [
17] described them as higher-order routines delivered from experiential accumulation and organizational learning. This mechanism encompasses not only routines, inertia, and endogenous change [
17], but also the role of managerial awareness and motivation in devoting capability evolution [
18]. Teece and Pisano [
19] highlighted the idea of “dynamic” as the dynamic environment, while “capabilities” focus on the importance of management, especially with respect to integration and reconfiguration of resources. Thus, the theoretical framework has emerged as a necessary theory to understand how firms use innovation to address problems in the market [
20].
Dynamic Capabilities Theory is particularly relevant to understanding risk management capability, technological innovation investment, and competitiveness. Teece [
14] mentioned that dynamic capabilities can develop technological innovation into managerial innovation. Li and Liu [
21] noted that companies can see threats and opportunities, act quickly, and develop systems to solve problems. This means that firms that consistently build dynamic capabilities can maximize their ability to identify and respond to risks, and spur technological innovation investment through resource reconfiguration [
22]. Further, under the condition of a digital transformation and an industrial revolution, dynamic capabilities are considered to be crucial and integral drivers of firms’ ability to continuously create new knowledge and new value [
23,
24].
Therefore, the current study will adopt dynamic capabilities as the primary linking mechanism for explaining how technological resources, competitive pressure observations, and innovation attitudes impact the risk management capability and technological innovation investment that affects competitiveness. The theoretical premise for explaining the causal relationships among these variables is based on the three functions of dynamic capabilities (sensing, seizing and transforming). The sensing function helps firms recognize external threats and opportunities, the seizing function enables firms to allocate and invest in the resources for innovation effectively, and the transforming function ensures that the firm adjusts its organizational structure and processes to the external environment change. This theoretical premise will be used to formulate an integrative framework, that can demonstrate the mediating and driving role of dynamic capabilities in the relationship between technological innovation and company competitiveness in the textile industry.
While much of the existing literature has applied Dynamic Capabilities Theory to issues of transformation and innovation, several gaps remain. First, the findings of most studies, although theoretically informed, develop conceptual or theoretical frameworks or models. For instance, Zhang et al. [
17] combined various perspectives from different schools of thought to develop an evolution-based framework while Mele et al. [
16] conducted a literature review on knowledge-based dynamic capabilities as a foundation for a research agenda. However, much of the literature remains in macro-level theory and has rarely considered related questions of how firms reconcile “innovation investment” and “risk management”.
Second, some studies have examined specific contexts, for example, Komkowski et al. [
20] looked at German manufacturing experts views of lean management in the context of Industry 4.0, or Liu et al. [
25] conducted an empirical analysis of CSR on innovation, and reported on the moderating effect of digital transformation on effects observed. However, again, the studies emphasized investments in innovation, CSR or digital transformation, and rarely examined the role of “risk management capability,” or interactions with technological innovation investment.
Third, some studies report challenges for survival in start-ups (e.g., [
26]) or developed capability lists, implementation roadmaps for Industry 4.0 (e.g., [
27]) but are essentially about addressing resource allocation to respond to environmental challenges, with little focus on how traditional industries, under competitive pressure, respond by investing in innovation to increase competitiveness by developing “risk management capability”.
As a result, existing studies have consistently failed to consider the interactive role of “risk management capability” and technological innovation investment in transforming traditional industries, or to provide empirical tests of their mediation effects. The research questions that are addressed in the study sought to verify the effects of technological resources, competitive pressure and innovation attitudes on “risk management capability” and “innovation investment”, in order to explore how “risk management capability” and “innovation investment” can promote competitiveness, and to test if “risk management capability” and “innovation investment” can have a positive mediation effect; thereby filling the inquiry created by the existing studies not addressing the interactive roles of innovation and risk management and their implications.
Table 1 listed Literature Summary of Dynamic Capabilities Theory.
2.3. Technological Resources
Technological resources refer to the various technologies and related knowledge that an organization or company possesses and utilizes [
28]. These resources include hardware, software systems, technical expertise, patents, and other technology-related assets [
29]. These resources are key factors in corporate innovation and enhancing competitiveness [
29,
30]. First, technological resources can improve production efficiency and reduce costs through automation and technological upgrades [
30]. Secondly, technological resources are the foundation for product and service innovation, helping companies develop new products and services to meet market demands [
31]. In summary, possessing and effectively utilizing technological resources can place companies in an advantageous position in market competition, establishing competitive barriers and preventing imitation by competitors.
Technological resources are a primary driver of economic growth and development [
32]. Technological progress makes production more efficient, thereby improving overall economic benefits [
33]. Moreover, the effective management of technological resources can help achieve environmental sustainability, such as reducing pollution and resource consumption through technological innovation [
34]. Additionally, companies with strong technological resources can adapt more quickly to market changes, seize new opportunities, and respond to challenges [
35]. Finally, companies that leverage technological resources for innovation and improvement can significantly enhance their market performance and financial results, as technological resources can moderate the relationship between diversification and performance [
36].
Taiwan’s textile companies need to place great emphasis on technological resources as they can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. Advanced technological equipment and automated production lines can improve production speed and product quality, reduce labor and time costs, thereby boosting overall competitiveness [
8]. Secondly, facing intense international market competition, Taiwan’s textile companies must continuously innovate to develop new products and improve product quality, in order to meet market demands and consumer preferences [
8]. Moreover, with the growing awareness of environmental protection and increasingly stringent regulations, Taiwan’s textile companies must focus more on environmental protection and social responsibility during the production process. Technological resources can assist companies in developing and applying environmentally friendly technologies, reducing pollution and resource consumption in the production process, and achieving green production [
37]. Lastly, technological resources enable companies to respond more flexibly to market changes and technological advancements, allowing them to maintain market adaptability [
8].
2.4. Risk Management Capabilities
Corporate risk management is regarded as an integrated mechanism that adopts a unified risk supervision approach to help firms cope with multidimensional risks [
38]. These risks may include market risk, operational risk, financial risk, legal risk, environmental risk, and more [
39]. Risk management capabilities involve the establishment of systematic methods and processes to reduce the impact of risks on the achievement of corporate objectives. First, companies should systematically identify and assess the various risks they face and prioritize them based on their likelihood and potential impact [
40,
41]. Secondly, for the identified risks, companies should develop corresponding risk response strategies and plans, including risk avoidance, reduction, transfer, and acceptance [
42]. Finally, companies should continuously monitor risk conditions and promptly report changes in risk levels so that management can respond quickly and make informed decisions [
43].
Effective risk management capabilities can help companies identify potential threats and opportunities, thereby improving the quality of decision-making. Through systematic risk assessments, companies can more accurately predict market changes and develop more robust business strategies [
41]. Secondly, risk management capabilities can assist companies in responding to emergencies and uncertainties, ensuring stable operations. For instance, when faced with natural disasters, economic crises, or legal changes, companies can swiftly take action to mitigate the impact on their business [
39]. Furthermore, strong risk management capabilities can enhance a company’s competitiveness. By identifying and managing risks, companies can maintain an advantageous position in the face of competition, seize opportunities, and avoid potential losses and failures [
42]. Finally, effective risk management can increase investor and stakeholder confidence in the company. When a company can demonstrate effective risk management strategies and capabilities, investors are more likely to trust its business and management, which in turn facilitates capital inflow [
44].
Technological resources, including advanced technical equipment and data analysis tools, can help companies more accurately identify and predict potential risks [
45,
46]. For example, through big data analytics and artificial intelligence technologies, companies can analyze market trends and consumer behaviors, identifying market risks and changes in demand in advance, thereby developing corresponding response strategies [
47]. Additionally, technological resources can provide the technical support and resource assurance that companies need when facing risks. For instance, automation equipment and intelligent systems can improve a company’s flexibility and response speed during the production process, helping them quickly respond to unexpected events and uncertainties in production [
48]. Moreover, technological resources support companies in developing contingency plans and risk management systems, enhancing their risk response capabilities. Sufficient technological resources contribute to building and improving internal risk management systems, including risk identification, assessment, monitoring, and response management [
43]. Companies can utilize technological resources to develop risk management information systems, enabling real-time monitoring and dynamic management of various risks, thereby improving the systematicness and effectiveness of risk management [
49].
In summary, technological resources positively impact the risk management capabilities of Taiwan’s textile companies by improving risk identification and forecasting abilities, supporting the implementation of risk response measures, and promoting the construction of internal risk management systems. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
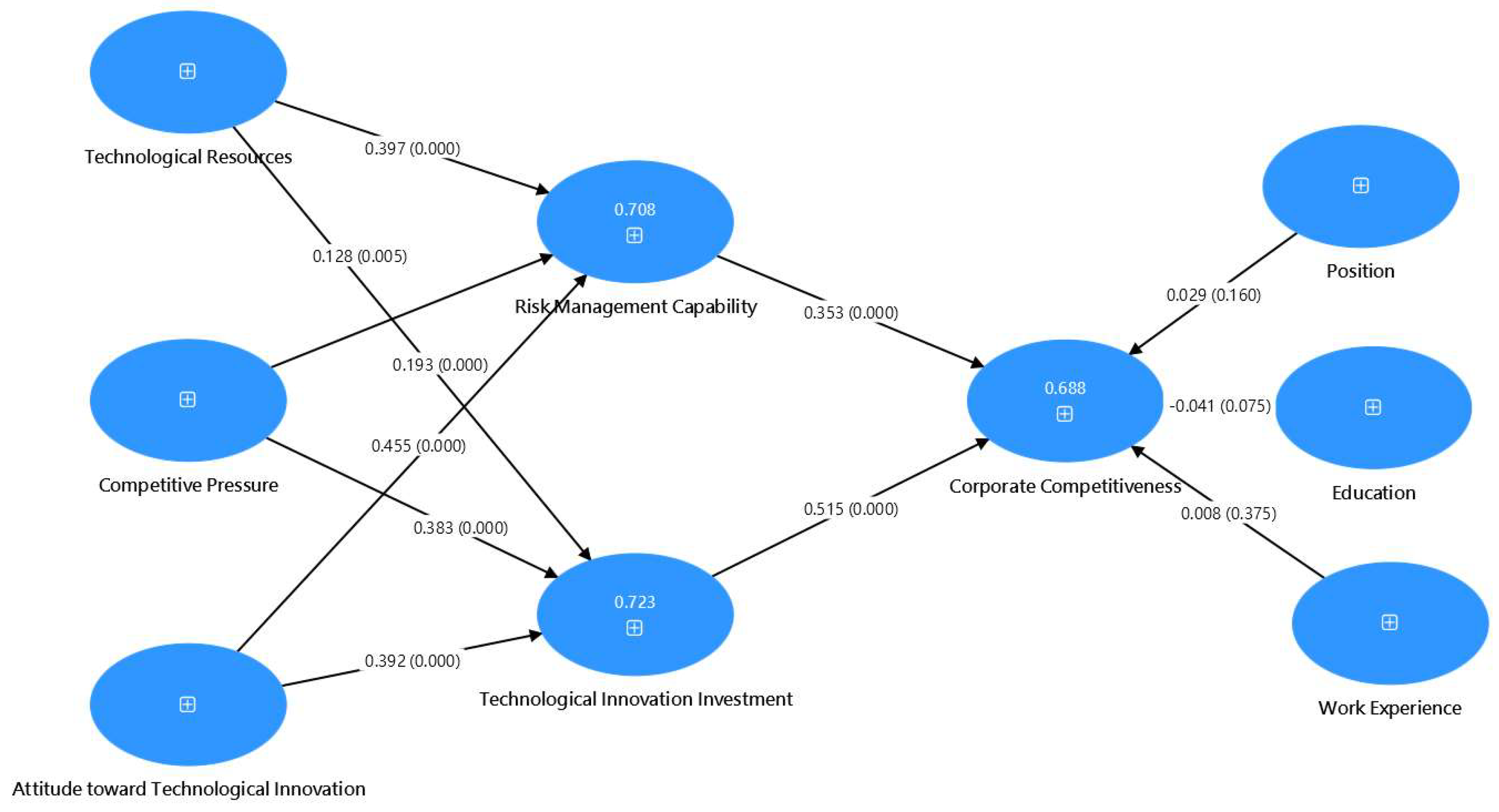
H1. The technological resources of Taiwan’s textile companies have a positive impact on their risk management capabilities.
2.5. Investment in Technological Innovation
Investment in technological innovation refers to the funds and resources that a company dedicates to activities such as technology research and development, technology acquisition, equipment upgrades, and other related initiatives [
46]. The purpose of these investments is to enhance the company’s innovation capabilities, develop new products, or improve existing products to maintain market competitiveness [
50]. Through technological upgrades and the introduction of automated equipment, companies can increase production efficiency and reduce production costs [
51]. Moreover, investment in technological innovation can help companies improve the quality of existing products, enhancing their market competitiveness and customer satisfaction [
52]. Furthermore, continuous investment in technological innovation allows companies to maintain a competitive edge in rapidly changing markets, preventing them from being surpassed by competitors [
53]. Finally, technological innovation contributes to the development of environmentally friendly technologies and products, promoting sustainable development and meeting society’s demands for environmental sustainability [
54].
As companies increase their investment in technological resources, they are better positioned to make further investments in technological innovation, creating a positive feedback loop. Research shows a significant positive correlation between a company’s technological resources and innovation investments; the more technological resources a company possesses, the more it invests in innovation [
54]. Companies with abundant technological resources are better equipped to respond to market competition and technological changes, which motivates them to make more innovation investments. These companies can leverage technological resources to improve market responsiveness and product competitiveness, thereby driving further innovation investments [
55].
In summary, the technological resources of Taiwan’s textile companies have a significant positive impact on their investment in technological innovation. As companies accumulate more technological resources, their investment in technological innovation also increases. This is primarily because technological resources enhance a company’s innovation capabilities, innovation outcomes, and market competitiveness, creating a positive cycle of technological innovation investment. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H2. The technological resources of Taiwan’s textile companies have a positive impact on their investment in technological innovation.
2.6. Competitive Pressure
Competitive pressure refers to the challenges a company faces in the market from other businesses, including competition from market rivals, product substitutes, supplier bargaining power, and customer bargaining power [
56]. Competitive pressure compels companies to continuously improve their products, services, and processes to maintain or enhance their market position. First, competitive pressure drives companies to innovate technologically and develop new products to meet consumer demands and stand out in the market [
57]. Secondly, competitive pressure forces companies to seek more efficient operational models and management methods to reduce costs and improve production efficiency [
58]. Finally, by responding to competitive pressure, companies can enhance their market competitiveness, strengthen their market position, and achieve sustained growth [
59].
Competitive pressure is a key driver of technological progress, as companies must continuously innovate in order to maintain a technological edge in the face of competition [
60]. Secondly, in response to competitive pressure, companies need to improve product quality and service levels to attract and retain customers [
61]. Furthermore, competitive pressure stimulates market vitality, prompting companies to constantly seek new market opportunities and business models to maintain their competitiveness [
57]. Lastly, competitive pressure pushes companies to enhance their ability to adapt to market changes, increasing their resilience when facing uncertainty [
62].
In highly competitive markets, companies must continuously enhance their risk management capabilities to cope with the ever-changing market environment and challenges from competitors [
59]. When companies face greater competitive pressure, they are more likely to adopt advanced risk management methods and technologies to ensure stability and sustainable development. Effective risk management helps companies quickly respond to market fluctuations and uncertainties, allowing them to take appropriate measures to maintain their competitive advantage [
63]. Under high competitive pressure, companies need greater resilience to face various market challenges. Strong risk management capabilities enable companies to better predict and respond to potential risks, thereby increasing their resilience and adaptability [
64].
In summary, as companies face greater competitive pressure, their risk management capabilities improve. This is because competitive pressure drives companies to continuously enhance their risk management capabilities in order to maintain market competitiveness and achieve sustainable development. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H3. Competitive pressure faced by Taiwan’s textile companies has a positive impact on their risk management capabilities.
Under high competitive pressure, companies are more strongly motivated to innovate. Competitive pressure pushes companies to constantly seek innovation opportunities to avoid being eliminated from the market [
65]. This means that when companies face competitive pressure, they are more inclined to invest resources in technological innovation to secure their market position. When faced with competitive pressure, companies increase R&D investment to ensure the competitiveness of their technologies and products. Research has found a significant positive correlation between competitive pressure and investment in technological innovation, with companies’ innovation investments increasing as competitive pressure rises [
66].
In conclusion, the greater the competitive pressure a company faces, the more it invests in technological innovation. This is because competitive pressure stimulates companies’ innovation motivation and R&D investment, driving them to continuously innovate in order to maintain market competitiveness and technological leadership. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H4. Competitive pressure faced by Taiwan’s textile companies has a positive impact on their investment in technological innovation.
2.7. Attitude Toward Technological Innovation
A company’s attitude toward technological innovation refers to its overall perspective and behavior regarding innovation activities, including the adoption of new technologies, investment in R&D, and the formulation and implementation of innovation strategies [
50]. This attitude reflects the importance a company places on technological advancement and innovation [
67]. In rapidly changing market environments, a proactive attitude toward technological innovation can help companies adapt more quickly to market changes and consumer demands, thereby maintaining their market competitiveness [
68]. Continuous investment in technological innovation is the foundation for long-term growth and sustainable development. A positive attitude toward technological innovation promotes continuous progress in the technological field, ensuring a company’s leading position in the market [
69]. A supportive attitude toward innovation can also unlock employees’ innovative potential, encouraging them to propose creative solutions in their work, thus enhancing the company’s overall innovation capacity [
70].
Also, a company’s proactive attitude toward technological innovation drives its investment in R&D and the adoption of new technologies, which in turn enhances its risk management capabilities. Research has shown that there is a close connection between knowledge management capabilities and risk management capabilities, with a positive innovation environment helping companies manage market risks [
71]. Managerial innovation and technological innovation are closely related, and this relationship has a significant impact on a company’s risk management capabilities. Companies at higher stages of technological capability demonstrate a stronger connection between risk management and technological innovation, indicating that a proactive attitude toward innovation enhances risk management capabilities [
72].
Overall, the more positive a company’s attitude toward technological innovation, the better its risk management capabilities. This is because a proactive innovation attitude fosters the collaborative development of knowledge management and risk management, enhancing a company’s adaptability and market competitiveness. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H5. The attitude toward technological innovation in Taiwan’s textile companies has a positive impact on their risk management capabilities.
A proactive attitude toward technological innovation often drives companies to increase investment in R&D and technology acquisition to maintain competitiveness. Research shows that technology acquisition and R&D spending are key indicators of a company’s innovation investment, and a positive attitude toward digital innovation significantly boosts these investments [
50]. Additionally, a positive attitude toward innovation can influence resource allocation strategies, prompting companies to increase investments in science, technology, and innovation activities, thus enhancing overall innovation capacity [
54]. Furthermore, a proactive attitude toward technological innovation helps companies respond to competitive market pressures by continuously investing in innovation to improve product quality and production efficiency, thereby strengthening market competitiveness [
73].
In summary, the more positive a company’s attitude toward technological innovation, the higher its investment in technological innovation. This is because a proactive innovation attitude encourages resource allocation in R&D and technology acquisition, improving the company’s ability to respond to market and environmental pressures, thus increasing its technological innovation investment. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H6. The attitude toward technological innovation in Taiwan’s textile companies has a positive impact on their investment in technological innovation.
2.8. Corporate Competitiveness
Corporate competitiveness is defined as a company’s ability to acquire and maintain an advantage in the market. This competitiveness is demonstrated by a company’s capacity to effectively utilize its resources and capabilities to outperform competitors and achieve sustainable growth and profitability [
74]. The concept of corporate competitiveness encompasses several aspects. First, in terms of resources and capabilities, it includes the management of physical, financial, human, and knowledge resources, as well as organizational and technological capabilities [
75]. Additionally, innovation capability in products, services, processes, and management is a key factor in maintaining competitive advantage [
76]. Furthermore, a company must possess the ability to quickly adapt to market changes and consumer demands, including flexible strategies and efficient operations [
14]. Moreover, brand influence and reputation in the market directly affect consumer choice and loyalty [
77].
In fierce market competition, only companies with strong competitiveness can survive and thrive. By enhancing competitiveness, companies can gain a larger market share, achieve growth and profitability [
74], maintain sustainable development in a constantly changing market environment [
78], and enhance their market value and shareholder interests [
75]. In addition, companies with high competitiveness are better equipped to deal with changes and challenges in the market environment [
14]. Highly competitive companies are also more attractive to investors, as investors tend to favor companies capable of long-term stable growth [
75].
In a globalized and highly competitive market environment, risk management capabilities play a crucial role in corporate competitiveness. Taiwan’s textile companies, when facing various risks (such as market, financial, and supply chain risks), can improve their competitiveness through strong risk management capabilities. Companies with robust risk management capabilities are better able to predict and respond to market fluctuations, ensuring operational stability, which is essential for maintaining and enhancing competitiveness [
39]. Effective risk management improves the efficiency and quality of decision-making, enabling companies to respond quickly to competition and adjust strategies, thereby enhancing their competitive advantage [
44]. A well-executed risk management strategy reduces losses caused by various risks, thereby lowering overall operating costs and boosting competitiveness [
79]. Companies with strong risk management capabilities can effectively handle unexpected events, protect their reputation, and gain greater trust from consumers and investors, all of which significantly enhance competitiveness [
80].
The risk management capabilities of Taiwan’s textile companies have a significant positive impact on their corporate competitiveness. By improving their risk management capabilities, these companies can maintain operational stability, improve decision-making quality, reduce costs and losses, and enhance their reputation, thereby maintaining a competitive advantage in the market. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H7. The risk management capabilities of Taiwan’s textile companies have a positive impact on their corporate competitiveness.
Investment in technological innovation can help companies develop high-quality and differentiated products, thereby gaining a competitive advantage in the market [
81]. Technological innovation can improve production efficiency and reduce costs, enabling companies to offer products at more competitive prices, thus enhancing market competitiveness [
82,
83]. Companies with strong innovation capabilities can quickly respond to changes in market demand, develop new products, and enter new markets, which is crucial for improving competitiveness [
84]. Technological innovation helps enhance a company’s brand image and market recognition, increasing consumer trust and loyalty to the company’s products, thereby boosting competitiveness [
85].
The technological innovation investment of Taiwan’s textile companies has a significant positive impact on their corporate competitiveness. By improving product quality, increasing operational efficiency, promoting market expansion, and enhancing brand image, these companies can stand out in fierce market competition and achieve sustainable growth and development. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H8. The technological innovation investment of Taiwan’s textile companies has a positive impact on their corporate competitiveness.
2.9. Risk Management Capabilities as Mediator
Technological resources are the foundation for enhancing efficiency and innovation, constituting an important basis for strengthening risk management capability. When firms possess advanced technological equipment and data analytics tools, they are able to more accurately identify and predict potential risks and design effective response measures, thereby promoting the construction and operation of risk management systems [
43,
45,
46]. Enhanced risk management capability enables firms to maintain stable operations and respond quickly in uncertain market environments. This mediating role implies that technological resources not only directly influence corporate competitiveness but also enhance market advantages through the mediating effect of risk management capability [
39].
H9. Technological resources positively influence corporate competitiveness through risk management capability.
Competitive pressure is a critical external force driving firms to continuously improve processes, reduce costs, and pursue innovation. When market challenges intensify, firms adopt more comprehensive risk management approaches to ensure resilience in unstable environments [
59]. Under such conditions, risk management capability becomes indispensable in supporting firms facing intense competition, enabling them to adjust strategies more effectively, mitigate potential losses, and sustain competitive advantages [
63,
64]. Thus, competitive pressure exerts a positive influence on corporate competitiveness through the mediating role of risk management capability.
H10. Competitive pressure positively influences corporate competitiveness through risk management capability.
A firm’s attitude toward technological innovation refers to the degree of emphasis placed on adopting new technologies, investing in R&D, and pursuing innovation strategies. A proactive innovation attitude fosters the integration of knowledge management and technological applications, enhancing the ability to identify, assess, and control risks [
71]. Particularly in contexts of advanced technological capability, the relationship between innovation attitude and risk management is even stronger, indicating that a positive orientation toward innovation improves firms’ risk response capacity [
72]. Consequently, risk management capability is an important mediator between innovation attitude and corporate competitiveness, enabling firms to sustain competitive advantages when facing market challenges.
H11. Attitude toward technological innovation positively influences corporate competitiveness through risk management capability.
2.10. Investment in Technological Innovation as Mediator
Technological resources are the technologies and related knowledge firms can access and use. This can include equipment, know-how, or tech-related assets. Technological resources impact market performance and innovation engagement [
29,
30]. Firms characterized by their abundance of technological resources can also devote more resources to R&D and technology upgrade, thus implementing an innovation investment virtuous cycle [
54,
55]. Investments in technology resources lead to higher production efficiency, lower costs, greater product and service innovation capabilities, and better responsiveness to market demand [
51,
52]. Hence, technological resources amplify sustained competitive advantages in competitive civic markets and enhance overall competitiveness through the mediating mechanism of technological engagement investment [
50,
53].
H12. Technological resources positively influence corporate competitiveness through investment in technological innovation.
Competitive pressure means the challenges firms experience in the marketplace, relative to competitors, substitutes, suppliers, and consumers [
56]. External pressure pushes firms to continuously upgrade products and processes to maintain their position in the marketplace while advancing their growth capabilities [
59]. In highly competitive environments, firms tend to escalate their investment in technological innovation by developing new products and technologies to gain differentiation and meet the customers’ needs [
57,
60]. As such, competitive pressure becomes an important driver of sustainable investment in technological innovation, allowing firms to remain adaptive to market conditions in order not to be outdone by competitors. As firms continuously grow their investment in technological innovation, they will achieve better efficiency and quality, leading them to larger leaps in market competitiveness [
61,
62]. Therefore, competitive pressure promotes corporate competitiveness through the mediating role investment in technological innovation.
H13. Competitive pressure positively influences corporate competitiveness through investment in technological innovation.
Firm attitude toward technological innovation refers to negative adaptive attitude and behavior toward new technologies, R&D investment, and innovation strategies. This reflects how important a firm thinks technological advancement will be to future success [
67,
68]. Firms with a positive adaptive technology innovation attitude are more confident they will engage in D&D, adopt new technologies, and commit resources to investment in technological innovation will later provide them with long-term, market derived advantages [
69,
70]. Research suggests that positive knowledge, innovation, and organizational climate contribute to knowledge management and decision-making, increasing market competitiveness [
71]. Moreover, firms that are high on innovation importance likely have some relationship with technology enhancement capability, continuing to invest in innovation to achieve longer-term market competitiveness [
72]. Therefore, an adaptive attitude built upon innovation distances a firm’s competitive position in competitive markets, which is met through the mediating role of investment in technological innovation.
H14. Attitude toward technological innovation positively influences corporate competitiveness through investment in technological innovation.