1. Introduction
Advances in virtual reality (VR) technology have facilitated a new level of immersive experience in art and cultural heritage exhibitions. VR redefines relationships with exhibits by overcoming the limitations of physical space and providing users with new ways of interacting with them [
1,
2]. This transformation strengthens the relationship between exhibits and users and enriches the exhibition experience through deeper immersion. Museum exhibition experiences through VR are an important research topic as they do not simply provide information but allow users to take an active role in interacting with exhibits and creating their own experiences [
3]. Presence refers to a user’s sense of reality within a virtual environment and the sense that they are present in the environment, which is an important factor in increasing engagement [
4,
5]. Previous studies have demonstrated that interactivity plays an important role in enhancing presence, which, in turn, increases user engagement and satisfaction [
1]. For example, Kim et al. [
6] analyzed the impact of user interaction on immersion and satisfaction in VR environments and found that immersion was an important mediating factor for satisfaction [
4]. These results suggest that strategies for enhancing interactivity are important for designing VR exhibition experiences.
Museum exhibitions utilizing VR technology are significant because, unlike traditional exhibitions, they go beyond the physical environment to provide globally accessible and interactive experiences. Flavián et al. [
7] found that immersive technologies, such as VR, lead to a richer and more immersive user exhibition experience [
4]. Additionally, Han et al. [
8] identified the positive impact of interactivity on user engagement and satisfaction through a user experience model in VR exhibitions [
3].
The essence of VR comprises three pillars: presence, interaction, and immersion [
9]. Based on existing research, this study aims to systematically analyze the effects of interaction and presence on museum exhibition experiences through VR. By confirming the effects of interaction on presence and examining whether it has a significant impact on immersion and satisfaction, we aim to provide practical implications for designing VR exhibition experiences. In the context of exhibiting artwork, this study makes a significant academic contribution by focusing on whether providing the same level of immersion and satisfaction in a virtual environment as in a physical exhibition is possible.
2. Related Studies
2.1. Virtual Exhibition Experience
With the advancement of VR technology, exhibition spaces are no longer bound by physical constraints and can explore new possibilities. Virtual exhibitions transcend time and space, creating immersive experiences for visitors and revolutionizing the cultural sector.
Traditional exhibitions are primarily visual and convey one-way information, while virtual exhibitions actively engage visitors and stimulate their senses to create richer experiences. With VR technology, visitors feel they are physically present in the exhibition space, interact directly with the exhibits, and actively explore them.
The key concepts of virtual exhibitions are presence and immersion. Presence refers to the psychological state of the feeling that a user is physically present in a virtual environment, whereas immersion occurs when a user is completely focused on a specific activity and loses track of time and space. Virtual exhibitions maximize both presence and immersion to create an unforgettable experience for visitors.
A study found that VR had a greater impact on learning and enjoyment than traditional environments [
10], while another reported that VR experiences had a positive impact on visitor satisfaction and intention to return. Specifically, they found that the presence and authenticity of the VR experience play an important role in satisfaction [
11].
Another important finding reports that VR technology increases motivation to learn and makes complex information easier to understand. VR allows visitors to experience various visual elements and simulations, enabling new ways of communicating and understanding information [
12,
13]. VR exhibits have also been proven to enhance learning by providing greater immersion and interactivity than traditional exhibition methods [
14,
15].
However, the use of VR does not always result in positive effects. Some users experience dizziness from wearing headsets [
16], and the level of immersion and comfort can vary significantly depending on the VR display method. Additionally, users may encounter difficulties with the operation or interface of the technological devices [
17].
However, the study of the virtual exhibition experience is still in its infancy, and since it is a complex phenomenon with many interacting variables, further research is needed. In particular, an in-depth analysis of different types of virtual exhibitions, the development of personalized virtual exhibition systems, and the social impact of virtual exhibitions are necessary.
Virtual exhibitions provide a new level of exhibition experience beyond the constraints of time and space and have the potential to contribute to the development of the cultural field. With further research, we expect virtual exhibitions to be developed to provide richer and more meaningful experiences for visitors.
2.2. Elements of Experience (4Es) in VR
The 4Es in VR refer to the four main elements of experience: education, entertainment, escape, and aesthetics, which play important roles in the VR exhibition experience. These elements were developed based on the Experience Economy theory proposed by Pine and Gilmore [
18] and have been recognized as key factors in increasing user immersion and interaction. In virtual exhibitions, the 4Es serve as important criteria for evaluating and improving the overall quality of visitor experiences.
The first element is educational experience. Users can explore the content of VR exhibits in various ways. Rather than solely obtaining information, they can become learning agents. The educational experience not only expands the viewer’s knowledge of the exhibit but also helps them understand and analyze it more deeply [
19]. In virtual exhibitions, interactive content and immersive environments allow users to actively acquire knowledge.
The second element is the entertainment experience. VR exhibits not only inform visitors but also entertain and excite them. This is important, as an immersive experience makes an exhibit more interesting to the audience. Exhibitions utilizing VR technology have been proven to provide greater immersion and interactivity than traditional exhibition methods, thereby enhancing both learning and entertainment experiences [
10,
13,
14].
The third element is the escapist experience. One of the greatest advantages of VR technology is that it immerses users in a virtual environment, allowing them to escape their daily routines and experience a new world. The escapist experience allows the user to escape the constraints of the real world and freely explore the virtual space within an exhibit, which is an important factor in increasing the immersion and intensity of the experience [
20].
The final element is the aesthetic experience. The aesthetic experience in VR exhibits refers to the beauty and sensory pleasure that visitors experience in the visual elements and spatial arrangement of the exhibit. Virtual environments can offer unique aesthetic elements that differ from traditional exhibits and can elicit emotional responses from visitors. An aesthetic experience leads to an evaluation of how visually appealing and harmonious virtual exhibit spaces are [
21].
In VR exhibits, the 4Es interact with each other rather than acting independently, thereby enriching the overall experience of visitors. For example, a combination of educational and entertainment elements can increase the fun of learning, whereas a combination of escape and aesthetics can provide a stronger sense of immersion. Thus, the 4Es play an important role in the multidimensional evaluation of the user experience of VR exhibits.
Recent studies have explored how the 4Es in VR affect visitors’ immersive experiences, specifically analyzing the impact of each element on visitors’ psychological responses and cognitive engagement [
22]. However, these studies are still in their infancy, and more in-depth research is required to understand how each of the 4Es interacts with VR exhibition experiences.
In conclusion, the 4Es—education, entertainment, escape, and aesthetics—are key elements in VR exhibit experiences that significantly impact user experience, and further research is needed to understand how each element enriches visitor experience. In particular, analyzing the impact of the 4Es on user experience in VR exhibit experiences is crucial for better exhibition design and user experience.
2.3. The Relationship Between Virtual Exhibition Experience, Interaction, and Presence
Research on experience (the 4Es) and interactions has been conducted across various fields. Jeong et al. [
23] revealed that website characteristics influence Pine and Gilmore’s 4Es (entertainment, escapism, aesthetics, and education), which in turn affect users’ intentions to use websites through emotional factors such as pleasure and arousal. Li et al. [
24] pointed out that while visual authenticity was high in online museum tours, behavioral authenticity was lacking, and they emphasized the need to enhance interaction, which may be related to the qualitative improvement of the sense of presence.
Blunden’s [
25] work addresses how the interaction of text and artifacts in an exhibition shapes a visitor’s experience, explaining that these factors serve to capture the visitor’s attention and provide meaning. Conversely, Macdonald [
26] analyzed visitor experience in terms of cognitive, emotional, and physical dimensions and suggested that exhibit design can actively engage visitors. Chirico et al. [
27] suggested that VR is effective in improving the emotional well-being among patients with cancer and related it to the entertainment and educational aspects of the experience.
Experiential exhibitions have been used as tools to enhance visitor engagement through the experience of presence. Seol and Joo [
28] reported the effects of presence: (1) the more similar the viewing experience, the more positive the presence effect, and (2) the higher the presence experience, the greater the arousal and emotion.
Blunden’s research explains that the interaction of text and artifacts in an exhibition contributes to shaping the visitor experience, which in turn increases presence [
25]. Meanwhile, Pimentel et al. [
29] examined the impact of interactivity and social presence on emotional outcomes in a 360-degree video and found that high interactivity increases presence, providing users with greater immersion.
This study builds on the findings of previous studies to examine how interactivity affects presence while viewing VR exhibits.
2.4. The Relationship Between Interaction and Presence and Immersion and Satisfaction
Studies of the impact of interactivity on presence have yielded mixed results. Higher interactivity makes users feel more immersed in a virtual environment, which fosters cognitive engagement and enhances their presence [
1]. Interactivity has also been demonstrated to trigger emotional responses in users, making the experience of presence more vivid [
2]. However, some studies have indicated that overly complex interactions can increase the user’s cognitive load, which can decrease presence [
3]. These studies suggest that interactions are an important factor in enhancing presence and play an important role in immersion and satisfaction.
Li et al. [
1] reported that interaction in VR environments is a key factor in enhancing the user immersion experience, which also has a positive impact on user satisfaction. Similarly, Gorini et al. [
30] argued that immersion and narrative enhance the quality of the VR experience by providing a strong sense of presence to the user and emphasized that interactive elements can further enhance this immersion.
Specifically, highly interactive VR environments allow users to experience a deeper sense of immersion, which is an important factor in improving the quality of VR experiences. For example, systems that increase interactivity through real-time prediction (i.e., a technology that reduces delays by analyzing and preparing user behavior in advance.) and rendering optimization (i.e., technology that improves the quality of VR experiences by efficiently processing high-quality graphics.) improve user experience and increase immersion, whereas systems that provide haptic feedback enrich user experience and contribute to immersion. The relationship between interactivity and immersion enhances immersion by allowing users to experience life-like sensations in the virtual world, which plays an important role in increasing user satisfaction and the quality of experience. These findings highlight the importance of interaction as VR technology evolves and suggest that proper interaction design is necessary to maximize immersion.
Furthermore, interactivity is an important factor in increasing user satisfaction in VR environments. Kim et al. found that gaze-based interfaces in mobile VR environments increased satisfaction through user interactions [
31]. Lee et al. [
9] revealed that gait interaction can improve immersion and minimize VR motion sickness while increasing user satisfaction.
Studies on the impact of presence on immersion have found that presence plays an important role in enhancing immersive experiences and improving the quality of the user experience. Presence makes users feel as if they are physically present in the virtual environment, which increases immersion and results in a more realistic and emotionally rich experience. Personalized avatars and highly immersive environments provide users with a stronger sense of body ownership and presence, enhancing their immersion. Furthermore, the interaction between immersion and narrative significantly enhanced presence, providing users with a deeper sense of engagement. Higher levels of immersion increase presence, which is an important factor in many applications.
Presence makes users feel present in a virtual environment, which increases immersion and, in turn, increases user satisfaction. Furthermore, it is an important aspect of the user experience and has been indicated to work more effectively when immersion and narratives are combined to increase user satisfaction.
Presence has also been shown to influence emotional responses and behavioral intentions, which positively impact overall satisfaction with the user experience.
Lee and Kim [
32] found that presence experiences had a static effect on engagement and attitude, whereas Kim and Yoon [
33] found a direct effect on user engagement and enjoyment.
Therefore, this study aims to test the relationship between the effects of VR virtual exhibition experiences on presence, interaction, engagement, and satisfaction, based on the results of previous studies.
3. Research Model and Hypothesis Setting
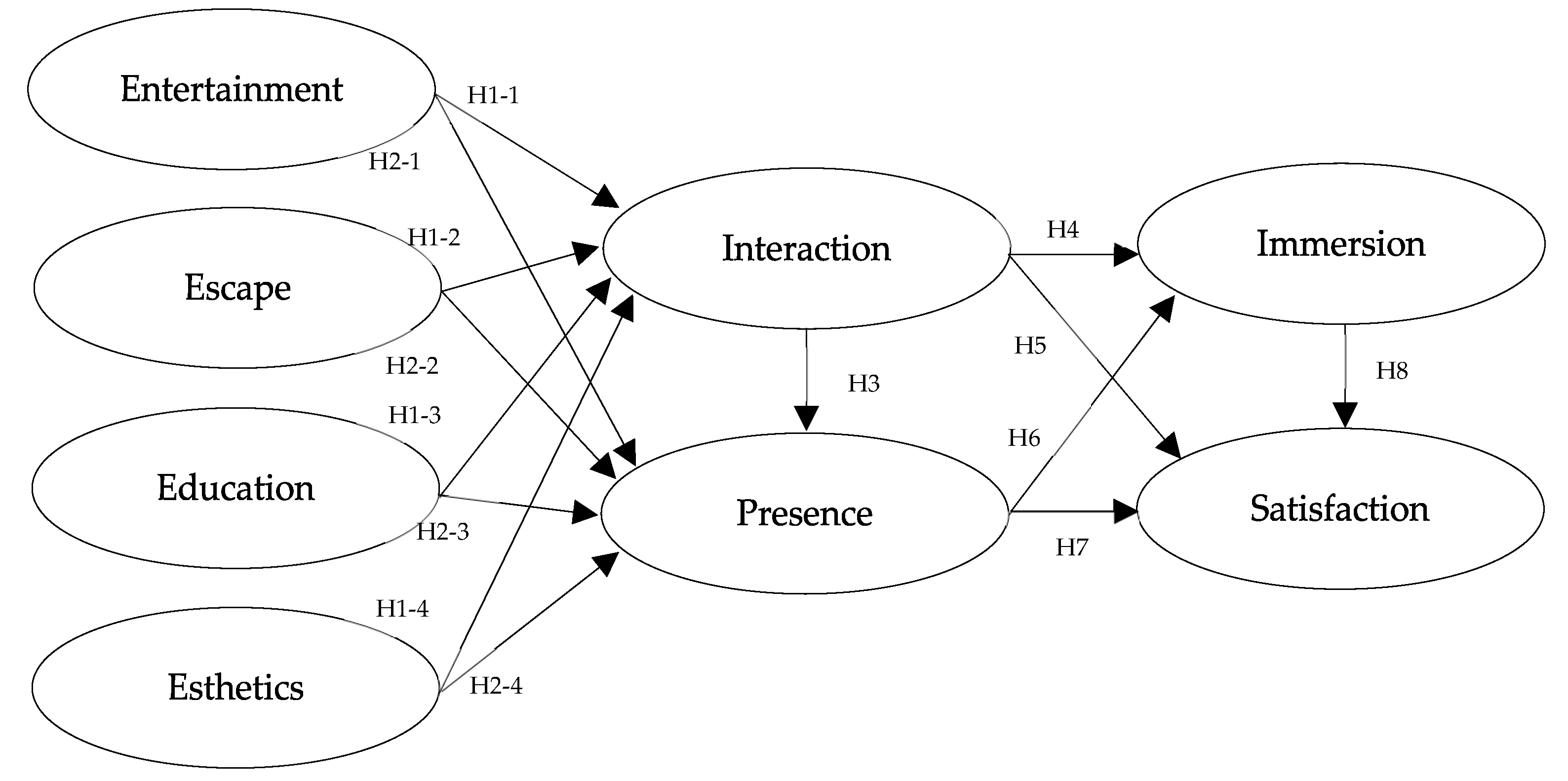
This study divided the experience factors of the virtual exhibition center into entertainment, deviant, educational, and aesthetic experience factors and constructed a research model to test the relationship between interaction, presence, immersion, and satisfaction, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
4. Method
4.1. Research Subjects and Data Collection
For the study, we selected “Pinnacle of Property: The Uigwe, Records of the State Rites of the Joseon Dynasty”, a 360-degree VR exhibition created by the National Museum of Korea, a representative museum operated by the Korean government, and viewed the exhibition using HMD (Head Mounted Display), which is highly realistic, interactive, and immersive, to meet the purpose of this study.
The study was conducted through a survey targeting 194 students enrolled at C University in Cheongju, Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea from 12 June to 24 July 2024. Prior to the survey, participants were given instructions on how to operate the device and experience the VR content. They then wore the VR device (Meta Quest 2) and spent approximately 5 min mastering its operation. Once they were ready, participants experienced a VR exhibition (
https://www.museum.go.kr/museum/2023/uigwe_virtualtour, accessed on 6 April 2024) thoroughly. After the experience, the purpose and method of the survey were explained, and the questionnaires were distributed. The data were collected using a self-administered survey method, where respondents completed the questionnaires independently.
Out of the 194 participants, responses that were invalid or insincere (e.g., marking all answers in a single column or failing to complete the survey) were excluded, resulting in 181 valid responses used for the final analysis. The experiment was conducted in the same experimental environment as shown in
Figure 2.
The analysis revealed the following characteristics of the participants: the majority were female (78.6%), significantly higher than males (21.4%), with an average age of 22.3 years. Regarding VR usage experience in the past year, 71.1% had used VR between 1 and 5 times, the highest proportion. Monthly VR usage was less than 2 times for 89.7% of respondents, followed by 3–4 times at 4.1%.
As for the purpose of VR use, gaming accounted for the highest proportion at 92.4%, followed by content development at 3.1%.
4.2. Operational Definitions and Measurement Tools of Variables
4.2.1. VR Experience Factors
For the study, we selected “Pinnacle of Property: The Uigwe, Records of the State Rites of the Joseon Dynasty”, a 360-degree VR exhibition created by the National Museum of Korea, a representative.
This study defined the VR exhibition experience as presented in
Table 1 based on the research of Lee and Lee (2023) and Lee and Kim (2018) and refined the items to fit the purpose of this study. Each item was measured using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1 = not at all, 5 = very much).
The answers for each element were as follows. Recreational experience: ① the experience in the virtual space was enjoyable; ② the experience in the virtual space was entertaining; ③ the experience in the virtual space was exciting; and ④ the experience in the virtual space was fun. Educational experience: ① the virtual reality experience was educational; ② I was able to acquire knowledge or skills through the virtual reality experience; ③ I gained new information through the virtual reality experience; and ④ the virtual reality experience stimulated my intellectual curiosity. Deviant experience: ① I felt like I was in a different time and place during the virtual reality experience; ② I felt like I was a different person during the virtual reality experience; ③ I felt like I was out of reality during the virtual reality experience; ④ I forgot about my daily life during the virtual reality experience; and ⑤ I felt like I was in another world during the virtual reality experience. Aesthetic experience: ① the space on the screen was attractive during the virtual reality experience; ② the design on the screen was eye-catching during the virtual reality experience; ③ the items on the screen were eye-catching during the virtual reality experience; and ④ the space on the screen was eye-catching during the virtual reality experience.
4.2.2. Interaction
This study defines interaction based on the description of Lee (2020): “the degree to which certain actions occurred because of the occurrence of an event between a person and a machine under physical conditions”. To measure it, the items used in the studies of Park and Yoo [
38] and Park and Kim [
39] were modified and supplemented to fit the context of this study. The items were measured using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1 = not at all; 5 = very much), with a total of four items. The answers were as follows: ① I was able to make adjustments as I wanted; ② I obtained information and reacted exactly as I typed; ③ I was free to operate as I wanted; and ④ it responded quickly to my commands.
4.2.3. Presence
This study defines presence based on the descriptions of Kim and Bocca [
40], Ardura and Artola [
41], and So [
42]: “the degree to which a person feels as if he or she is present in the exhibition hall when experiencing VR content.” The measurement tool for measuring presence was adapted from the studies of the same authors. Each item was measured using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1 = not at all, 5 = very much). The items were as follows: ① I felt as if I was inside the virtual space; ② I felt as if I was traveling; ③ I felt as if I was immersed in the virtual environment world while I was in the virtual space; ④ I experienced a virtual world and it disappeared as soon as I finished viewing it; ⑤ I felt like I was in a virtual space during the virtual experience; ⑥ I felt like I was in a virtual world during the virtual experience; ⑦ The virtual world was more real and took precedence over the real world during the virtual experience; and ⑧ I was constantly forgetting that I was participating in an experiment during the virtual experience.
4.2.4. Immersion
This study defined immersion based on the description of Yoon et al. [
43]: “the degree of temporal and spatial immersion in a VR experience.” The tools to measure it are modified from the items used in the studies of Hudson et al. [
44], Jennett et al. [
45], and Yoon et al. [
44]. Each item was measured using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1 = not at all, 5 = very much). The items were as follows: ① I felt disconnected from the outside world while experiencing the VR exhibit; ② I felt completely immersed while experiencing the VR exhibit; and ③ I forgot about things I usually cared about while experiencing the VR exhibit.
4.2.5. Satisfaction
This study defined satisfaction based on the description of Kim and Noh [
46]: “the overall degree of satisfaction with the virtual exhibition experience.” The instrument used to measure it was adapted from the studies of Stavrianea and Kamenidou [
47], Kim and Noh [
46], and Koo and Heo [
48]. Each item was measured using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1 = not at all true, 5 = very true). The answers were as follows: ① overall satisfaction with VR exhibits; ② experiencing VR exhibits was a satisfying experience; and ③ willingness to invest time, money, and effort to experience VR exhibits.
4.3. Validation of Measurement Variables and Reliability
A confirmatory factor analysis was conducted to verify the validity of the variables and measurement items in this study.
We removed items with low factor loadings and applied modification indices to improve the structural model fit.
We checked convergent and discriminant validity to verify the validity of the measurement variables. First, average variance extracted (AVE) and conceptual reliability (CR) were checked to confirm convergent validity. As presented in
Table 2, the AVE value was 0.863~0.938 (≥0.5 is appropriate) and the CR value was 0.959~0.984 (≥0.7 is appropriate), confirming convergent validity.
To test discriminant validity, we used the mean variance extracted and squared correlation value. The results of this test are presented in
Table 3. The highest correlation was between “immersion” and “satisfaction” with a correlation coefficient of 0.493, and the smallest value of 0.929, the root mean square value of AVE, exceeded it; therefore, discriminant validity was confirmed. Finally, hypothesis testing was conducted centering on the structural model.
5. Research Result
The results of the structural model analysis for hypothesis testing are as follows: first, the model fit indices are χ
2 = 551.405 (df = 442),
p = 0.000 (
p ≥ 0.05 is desirable), GFI = 0.844 (≥0.80 is acceptable), AGFI = 0.814 (≥0.80 is acceptable), RMR = 0.021 (<0.05 is acceptable), TLI = 0.978 (≥0.90 is acceptable), CFI = 0.981 (≥0.90 is acceptable), and RMSEA = 0.037 (≤0.06 is good), indicating that the model fit indices exceed all recommended values and the model is evaluated as suitable. The hypothesis-testing results according to the research model are presented in
Table 4 and
Figure 3.
The results of the path analysis indicate that H1, which states that “VR exhibition experience (entertainment, escapism, education, and aesthetics) has a positive effect on interaction”, was supported for all factors except educational experience. Specifically, entertainment experience (β = 0.172, t = 2.322, p < 0.05), escapism experience (β = 0.332, t = 4.233, p < 0.001), and aesthetic experience (β = 0.190, t = 2.588, p < 0.05) positively influenced interaction (H1-1, H1-2, H1-4). Next, H2, which states that “VR exhibition experience (entertainment, escapism, education, and aesthetics) has a positive effect on presence”, was supported for all factors except aesthetic experience. Specifically, entertainment experience (β = 0.192, t = 2.575, p < 0.05), escapism experience (β = 0.161, t = 1.998, p < 0.05), and educational experience (β = 0.162, t = 2.347, p < 0.05) positively influenced presence (H2-1, H2-2, H2-3). H3, stating that “interaction has a positive effect on presence”, was also supported (β = 0.201, t = 2.114, p < 0.001). Furthermore, H4, stating that “interaction has a positive effect on immersion” (β = 0.177, t = 2.114, p < 0.05), and H5, stating that “interaction has a positive effect on satisfaction” (β = 0.272, t = 3.606, p < 0.001), were both supported. H6, which states that “presence has a positive effect on immersion”, was supported (β = 0.174, t = 2.107, p < 0.05), while H7, stating that “presence has a positive effect on satisfaction”, does not have a significant effect (β = 0.136, t = 1.868, p > 0.05). Finally, H8, which states that “immersion has a positive effect on satisfaction”, was supported (β = 0.201, t = 2.114, p < 0.001).
6. Results and Discussion
This study explored the intricate relationships between interaction, presence, immersion, and satisfaction within VR exhibition environments, aiming to provide actionable insights for VR designers and researchers. The findings underscore the multifaceted nature of user experiences in VR and reveal the distinct roles played by different experiential factors.
Influence of Experiential Factors on Interaction
The results show that recreational, escapist, and aesthetic experiences significantly enhance interaction. Recreational experiences, by eliciting positive emotions such as joy and curiosity, enable users to engage more actively with VR content. This supports findings by Mandryk et al. (2006) and Tan (2008), highlighting the importance of emotionally driven design in fostering interaction [
49,
50]. Similarly, escapist experiences, characterized by their ability to transport users out of their daily realities, were found to promote deeper user engagement. This aligns with research by Bai et al. (2021), which indicates that escapist experiences not only immerse users but also encourage proactive participation [
51].
Aesthetic experiences enriched the interaction by enhancing users’ sensory engagement. When VR environments are visually appealing and artistically designed, users are more likely to interact with their surroundings in meaningful ways, as suggested by Gotthardt (2023) and Gulhan et al. (2023). These findings highlight the importance of curating visually cohesive and immersive environments that enhance interaction while also contributing to overall user satisfaction [
52,
53].
However, educational experiences did not significantly impact interaction. This finding is consistent with prior research [
54,
55], which suggests that overly information-driven content can hinder active engagement. Educational experiences in VR often lack the immediate, sensory stimuli required to sustain interaction, as users tend to prefer more dynamic and exploratory forms of engagement. This calls for a rethinking of educational content design, shifting from passive information delivery to more interactive and experiential approaches.
The Complex Role of Presence
Presence, a key factor in VR experiences, was positively influenced by recreational, escapist, and educational experiences. Recreational experiences heightened presence by fostering user engagement, as found in Rudi (2021) [
56]. Escapist experiences, by offering freedom from real-world constraints, contributed to a sense of presence that allowed users to feel fully immersed in the virtual environment [
57]. Educational experiences also enhanced presence by improving user focus and cognitive engagement [
58].
Interestingly, aesthetic experiences, which positively influenced interaction, did not show a significant effect on presence. This aligns with Wang et al. (2023), who noted that excessive visual stimulation can detract from the user’s ability to feel fully present [
59]. This suggests that while aesthetic elements are essential for fostering interaction, their impact on presence may be limited unless carefully moderated.
The findings also reveal the significant role of interaction in enhancing presence. Users who actively engage with VR environments are more likely to experience a heightened sense of realism and immersion. This supports theories by Theodoropoulos et al. (2023) and Jung and Lindeman (2021), emphasizing the importance of interactive elements in creating compelling and believable virtual spaces [
60,
61].
Interaction, Immersion, and Satisfaction
Interaction emerged as a key driver of both immersion and satisfaction. Enhanced interaction through multisensory feedback and intuitive design not only deepened user engagement but also contributed to a more satisfying experience. These findings align with studies by Zhang and Long (2019) and Chang et al. (2018), which suggest that interaction-rich environments provide users with opportunities for exploration and active participation, leading to greater immersion [
62,
63].
Immersion has been shown to significantly increase satisfaction. This is because, as previous studies have shown, immersion in a VR environment allows users to experience the virtual world as reality, contributing to increased emotional connection and satisfaction [
20] and strengthening the psychological connection between users and content. In addition, a high level of immersion significantly increases user satisfaction, and the quality of immersion varies depending on the sensory feedback and interaction design of the VR content [
64]. These results emphasize that it is important to combine multisensory feedback and include narrative and interaction elements to actively encourage users to participate in the virtual environment for immersion and that avoiding overly complex designs and designing VR experiences that allow users to immerse themselves naturally can increase satisfaction.
Balancing Presence and Satisfaction
This study highlights an intriguing paradox: while presence positively influenced immersion, it negatively affected satisfaction when excessive. High levels of presence, by increasing realism, blurred the boundaries between virtual and real environments, which enhanced immersion but occasionally led to user discomfort. This is consistent with findings by Ahn et al. (2014) and Weibel and Wissmath (2011), which suggest that overly realistic experiences in VR can induce fatigue or psychological unease [
65,
66] This underscores the need for designers to balance realism with user comfort, ensuring that presence enhances rather than detracts from overall satisfaction.
Implications for VR Design
Strategic Use of Experiential Elements
Recreational and escapist elements should be prioritized to enhance interaction and presence, while aesthetic elements should be carefully calibrated to avoid overstimulation.
- 2.
Reimagining Educational Content
Educational experiences must move beyond passive information delivery to incorporate interactive and sensory-rich features, aligning with user expectations for dynamic engagement.
- 3.
Designing for Immersion and Satisfaction
Multisensory feedback and narrative integration should be core design strategies to maximize both immersion and satisfaction.
- 4.
Moderating Presence
Designers must ensure that presence is sufficiently strong to enhance immersion but not so excessive as to cause user discomfort.
Toward a Holistic Understanding of VR Experiences
This study contributes to a deeper understanding of how different experiential factors interact to shape user experiences in VR. It underscores the importance of tailoring VR environments to meet diverse user needs, striking a balance between interaction, presence, and satisfaction. By carefully considering these dynamics, VR designers can create more engaging, immersive, and ultimately satisfying virtual experiences. These insights also provide a foundation for future research aimed at optimizing VR environments across various application domains.
7. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive exploration of the interplay between interaction, presence, immersion, and satisfaction in virtual reality (VR) exhibitions, offering critical insights for both theoretical development and practical application in VR design. By focusing on how various experiential factors influence user engagement, the findings contribute to the growing body of research aimed at optimizing VR environments for more meaningful and satisfying user experiences.
The results underline the pivotal role of interaction as a mediator in the relationship between user experiences and outcomes. Recreational, escapist, and aesthetic experiences emerged as significant contributors to interaction. Recreational experiences enhanced interaction through emotional engagement, demonstrating that entertainment-driven elements are fundamental in fostering user involvement. Escapist experiences offered a sense of liberation from real-world constraints, further amplifying user participation. Aesthetic experiences enriched the virtual environment, intensifying both the frequency and depth of user interaction. These findings suggest that VR exhibition designers should strategically integrate these experiential elements to create environments that actively engage users.
In contrast, educational experiences presented a more nuanced dynamic. While they failed to significantly influence interaction, they positively contributed to presence by enhancing focus and comprehension. This highlights the dual nature of educational content in VR; it can deepen cognitive engagement when effectively designed but risks being counterproductive if overly information-heavy or passively structured. This divergence emphasizes the need for educational content in VR to be interactive and sensory-rich, ensuring alignment with user expectations for dynamic engagement.
Presence demonstrated a complex role, serving as both an enhancer of flow and a potential detractor from satisfaction when excessive. Higher levels of presence significantly boosted immersion by blurring the boundaries between virtual and real environments, aligning with theories of environmental realism and cognitive absorption. However, the negative impact of excessive presence on satisfaction underscores the psychological and physiological limits of user tolerance for hyperrealistic experiences. This finding challenges the conventional assumption that maximizing presence is universally beneficial, suggesting instead that a balanced approach is essential to prevent discomfort or fatigue.
Immersion, as a mediator between presence and satisfaction, revealed itself as a critical determinant of positive user outcomes. Deep flow elicited heightened emotional responses, leading to increased satisfaction. The strong alignment of these findings with Csikszentmihalyi’s flow theory suggests that VR experiences designed to sustain a seamless flow state can significantly enhance user enjoyment and perceived value.
Practically, this study underscores the necessity of multisensory and narrative-driven design strategies in VR exhibitions. Interaction should be optimized through engaging and intuitive interfaces that integrate sensory feedback and compelling narratives. Designers must carefully moderate aesthetic elements to avoid overstimulation and maintain user focus. Furthermore, educational content must transition from passive information delivery to formats that encourage exploration and interactivity, ensuring its compatibility with other experiential elements.
From a broader perspective, this study highlights the intricate balance required between presence, immersion, and satisfaction in VR environments. While presence enriches the user experience by enhancing realism and engagement, excessive presence can inadvertently detract from satisfaction. Immersion, on the other hand, consistently reinforces satisfaction by deepening the user’s emotional and cognitive involvement. These findings underscore the importance of tailoring VR experiences to meet diverse user needs, emphasizing flexibility and adaptability in design.
However, despite these meaningful results, the study has the following limitations.
First, because it focused on art exhibitions, it is difficult to generalize to various types of VR exhibitions (e.g., historical exhibitions, educational exhibitions, etc.). The effects of interaction and presence on user immersion and satisfaction may differ in VR exhibitions with different themes or forms. Future studies need to expand the research results by encompassing various types of exhibitions.
Second, although the results of the study showed that educational experiences had a negative effect on interaction, there is a lack of specific reasons or in-depth analysis for this. This does not provide a deeper understanding of how educational experiences are connected to interaction. Future studies need to identify the reasons why educational experiences had a negative effect on interaction.
Third, this study measured presence, interaction, immersion, and satisfaction through a questionnaire, but it lacked various methodological approaches, including physiological responses or behavioral data in addition to these subjective evaluations. In future studies, if more objective and precise analyses are conducted through physiological data (e.g., heart rate, brain waves) generated during VR experiences in addition to the questionnaire, it is expected that more effective VR exhibition experiences can be provided.
Fourth, this study approached VR positively by applying its framework to museum exhibitions and derived meaningful results. However, it is clear that VR also has limitations as a virtual medium, and issues such as high costs, technical complexity, and accessibility were not explored in depth.
Therefore, we hope that this study will be used as basic data to overcome these limitations in follow-up studies and verify the relationships between various variables related to VR exhibition experiences.