Management Economic Systems and Governance to Reduce Potential Risks in Digital Silk Road Investments: Legal Cooperation between Hainan Free Trade Port and Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Privacy, Security Risks, and Threat of Cyberterrorism
2.2. The Hainan FTP’s Role in Supporting Africa’s Growth
2.3. Conflicts of the Relationship between National Initiatives and Commercial Need
2.4. Digital Investment and the B&R
2.5. Digital Investment and Governance Mechanisms
2.6. Digital Investment and Technology Transfer
2.7. Digital Investment and International Cooperation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Data Source
3.3. Results
3.3.1. Digital Investment Cooperation between China and Ethiopia
3.3.2. WJP and ROL
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Paths to Resolve Risks in DSR Investment
4.2. Digital Investment, Governance Mechanisms, Cross-Border Transactions, and Technology
4.3. The Hainan FTP to Solving Future Development Prospects for African Nations
5. Conclusions
5.1. Implications
5.2. Study of Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China’s Digital Silk Road: A Game Changer for Asian Economies. Available online: https://thediplomat.com/2019/04/chinas-digital-silk-road-a-game-changer-for-asian-economies/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Moynihan, H.; Patel, C. Restrictions on Online Freedom of Expression in China. Research Paper. 2021. Available online: https://ccn.unistra.fr/websites/ccn/documentation/Cybersecurite/2021-03-17-restrictions-online-freedom-expression-china-moynihan-patel.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Sen, G.; Bingqin, L. The Digital Silk Road and the Sustainable Development Goals. 2019, Volume 50. Available online: https://bulletin.ids.ac.uk/index.php/idsbo/article/view/3061 (accessed on 8 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Khaskheli, M.B. Innovation Helps with Sustainable Business, Law, and Digital Technologies: Economic Development and Dispute Resolution. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Belt and Road Initiative: A Key Pillar of the Global Community of Shared Future—The Third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation. Available online: http://www.beltandroadforum.org/english/n101/2023/1010/c124-895.html (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- “Chinese Digital Silk Road” Dominates the Western Balkans—GreekReporter.Com. Available online: https://greekreporter.com/2021/10/24/china-balkans-digital-silk-road/ (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Chaisse, J.; Bauer, C. Cybersecurity and the Protection of Digital Assets: Assessing the Role of International Investment Law and Arbitration. Vanderbilt J. Entertain. Technol. Law 2018, 21, 549. [Google Scholar]
- Khaskheli, M.B.; Wang, S.; Yan, X.; He, Y. Innovation of the Social Security, Legal Risks, Sustainable Management Practices and Employee Environmental Awareness in the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethio-Telecom Partners with Huawei to Launch Pilot 5G Services in Ethiopia—China.Org.Cn. Available online: http://www.china.org.cn/business/2022-05/11/content_78212025.htm (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Ethiopia—Adoption of Telecommunication Services Law|Investment Policy Monitor|UNCTAD Investment Policy Hub. Available online: https://investmentpolicy.unctad.org/investment-policy-monitor/measures/3411/ethiopia-adoption-of-telecommunication-services-law (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Ethiopia Postpones Privatization Process of Ethio-Telecom Company. Available online: https://www.ena.et/web/eng/w/en_34381 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Cheney, C. China’s Digital Silk Road: Strategic Technological Competition and Exporting Political Illiberalism; Council on Foreign Relations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Freedom on the Net 2018—The Rise of Digital Authoritarianism/Reports and Papers/Resources/Media Freedom in Europe—Resource Centre by OBCT—Resource Centre. Available online: https://www.rcmediafreedom.eu/Resources/Reports-and-papers/Freedom-on-the-Net-2018-The-Rise-of-Digital-Authoritarianism (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Van der Lugt, S. Exploring the Political, Economic, and Social Implications of the Digital Silk Road into East Africa; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2021; pp. 315–346. [Google Scholar]
- Jasuma, N.B.; Paksi, A.K. China’s Digital Silk Road: The Loss for Indonesia. Nation State J. Int. Stud. 2021, 4, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, B. Challenge and Perspective for Digital Silk Road. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2020, 7, 1804180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M. Combatting the Seen and Unseen Threats of China’s Digital Silk Road. Network for Strategic Analysis, Queen’s Iniversity. 2022. Available online: https://ras-nsa.ca/combatting-the-threats-of-chinas-digital-silk-road/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Malena, J. The Extension of the Digital Silk Road to Latin America: Advantages and Potential Risks. Brazilian Center for International Relations. 2021. Available online: https://cdn.cfr.org/sites/default/files/pdf/jorgemalenadsr.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Shandler, R.; Kostyuk, N.; Oppenheimer, H. Public Opinion and Cyberterrorism. Public Opin. Q. 2023, 87, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ma, Z.; Rashwan, A.K.; Khaskheli, M.B.; Abdelrady, W.A.; Abdelaty, N.S.; Hassan Askri, S.M.; Zhao, P.; Chen, W.; Haider Shamsi, I. Exploring the Interplay of Food Security, Safety, and Psychological Wellness in the COVID-19 Era: Managing Strategies for Resilience and Adaptation. Foods 2024, 13, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sustainable Development and Economic Impact of China’s Belt and Road Initiative in Ethiopia|East Asia. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12140-023-09402-y (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Understanding China’s Belt and Road Infrastructure Projects in Africa|Brookings. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/understanding-chinas-belt-and-road-infrastructure-projects-in-africa/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Omoruyi, E.M.M.; Zhexi, W.; Bing, Z.; Kai, W.; Xin, X. China’s Infrastructure Development and Its Impact on Africa Economic Growth. Int. J. Afr. Asian Stud. 2016, 23, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, L.T.N. The Adjustment of China’s Foreign Investment Policy and Law—Lessons for Vietnam. VNU J. Sci. Leg. Stud. 2022, 38, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H. Building a Digital Silk Road? Situating the Internet in China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Int. J. Commun. 2018, 12, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Borodyna, O. China’s Investment in Digital Infrastructure along the Belt and Road. 2021. Available online: https://odi.cdn.ngo/media/documents/Emerging_analysis_Chinas_investment_in_digital_infrastructure_along_Belt_and_R_aoPN2lL.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Yean, T.S. The Digital Free Trade Zone (DFTZ): Putting Malaysia’s SMEs onto the Digital Silk Road. 2018. Available online: https://www.iseas.edu.sg/wp-content/uploads/pdfs/ISEAS_Perspective_2018_17@50.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Bosetti, R. The Digital Silk Road: Towards a China-Centred Eurasian Tech Ecosystem? 2020. Available online: https://digitalcommons.fiu.edu/srhreports/cybersecurity/cybersecurity/39/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Hussain, F.; Imran, A.; Hussain, Z.; Khan, M.I. Infrastructure Development for the Digital Silk Road (DSR) and Its Implications for China Under the Belt and Road Initiative. Asia-Pac. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2023, 23, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, L.; Bansal, R.; Pruthi, N.; Khaskheli, M.B. Impact of Social Media Influencers on Customer Engagement and Purchase Intention: A Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Yang, X.; Song, H. The Impact of Scientific and Technological Information Resource Utilization on Breakthrough Innovation in Enterprises: The Moderating Role of Strategic Aggressiveness. Systems 2024, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Chan, J.H. China’s Digital Silk Road: Implications for India. Inst. South Asian Stud. Insights 2018, 521, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nouwens, M.; Lons, C.; Shehab, N.; Malcomson, S.; Neill, A. China’s Digital Silk Road: Integration into National IT Infrastructure and Wider Implications for Western Defence Industries. 2021. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/1426986/chinas-digital-silk-road/2041591/ (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Hanisch, M.; Goldsby, C.M.; Fabian, N.E.; Oehmichen, J. Digital Governance: A Conceptual Framework and Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 162, 113777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongdo, Q.; Khaskheli, M.B.; Rasheed, R.; Mukhtar, H. The Role of China in Influencing Indo-Pak Relations in Contemporary Era. Eur. J. Econ. Law Politics 2019, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infrastructure: The Most Important Enabler of Organic Growth in Africa|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-13-0179-7_4 (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. World Investment Report 2017: Investment and the Digital Economy; United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) World Investment Report (WIR); UN: New York City, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-92-1-060703-2. [Google Scholar]
- Micheli, M.; Ponti, M.; Craglia, M.; Berti Suman, A. Emerging Models of Data Governance in the Age of Datafication. Big Data Soc. 2020, 7, 2053951720948087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.-C.; Hung, C.-Y. Impact of Digital Service Trade Barriers and Cross-Border Digital Service Inputs on Economic Growth. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. The Role of Technology Transfer and Intellectual Property Protection in Investment in China and Southeast Asia. J. Innov. Dev. 2023, 4, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurasia Group White Paper: The Geopolitics of 5G 5G Special. Prepared by Eurasia Group This Report Is Based on the Opinions of Eurasia Group Analysts and Various in-Country Specialists—[PDF Document]. Available online: https://fdocuments.net/document/eurasia-group-white-paper-the-geopolitics-of-5g-5g-special-prepared-by-eurasia.html (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Nouwens, D.G. Meia Introduction. In The Digital Silk Road; Routledge: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-00-339026-8. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kadi, T.H. The Digital Silk Road and Emerging African Data Governance Frameworks: Evidence from Egypt. Shaping the Future of Africa-ChinaEngagement5. 2024. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_cittion&hl=en&user=jETkBAsAAAAJ&citation_for_view=jETkBAsAAAAJ:ufrVoPGSRksC (accessed on 13 June 2024).
- Yi, S.; Zhang, M.; Huo, Z.; Mao, Y. The Configuration Path of the New Rural Collective Economy to Promote the Common Prosperity of Farmers: Based on Qualitative Comparative Analysis Method and the Rural Cases in Zhejiang, China. Systems 2024, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvant, K.P. A G20 Facility to Rekindle FDI Flows; Columbia University, Columbia Center on Sustainable Investment (CCSI): New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilawal Khaskheli, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shamsi, I.H.; Shen, C.; Rasheed, S.; Ibrahim, Z.; Baloch, D.M. Technology Advancement and International Law in Marine Policy, Challenges, Solutions and Future Prospective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1258924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Nexus between China’s Digital Silk Road and Digital Authoritarianism. ISPI. 2020. Available online: https://www.ispionline.it/en/publication/nexus-between-chinas-digital-silk-road-and-digital-authoritarianism-26071 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Stephenson, M.; Hamid, M.F.S.; Peter, A.; Sauvant, K.P.; Seric, A.; Tajoli, L. More and Better Investment Now! How Unlocking Sustainable and Digital Investment Flows Can Help Achieve the SDGs. J. Int. Bus Policy 2021, 4, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.-X.; Gong, H.-P.; Liu, H.-C. An Integrated CREAM for Human Reliability Analysis Based on Consensus Reaching Process under Probabilistic Linguistic Environment. Systems 2024, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Why the World Needs a New Cyber Treaty for Critical Infrastructure. Available online: https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2024/03/why-the-world-needs-a-new-cyber-treaty-for-critical-infrastructure?lang=en¢er=europe (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- China Law Translate. Lawyers’ Practice Code of Conduct (Provisional). China Law Translate. 2017. Available online: https://www.chinalawtranslate.com/en/lawyers-practice-code-of-conduct%EF%BC%88provisional%EF%BC%89/ (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Sustaining the Economic Rise of Africa|Cato Institute. Available online: https://www.cato.org/economic-development-bulletin/sustaining-economic-rise-africa?gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAjw_Na1BhAlEiwAM-dm7II-k2FuY6pqjMToKLko8Um3jwjQq8fUCfYGLtjLaQJ8jcl7-Z8uuhoCS8EQAvD_BwE (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Fan, M.; Liu, J.; Tajeddini, K.; Khaskheli, M.B. Digital Technology Application and Enterprise Competitiveness: The Mediating Role of ESG Performance and Green Technology Innovation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.T.N. Real Property in Chinese Civil Law—The Process of Developing Property Legislation. Vietnam. J. Leg. Sci. 2022, 6, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WJP Rule of Law Index. Available online: https://worldjusticeproject.org/rule-of-law-index (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Rankings. Available online: https://archive.doingbusiness.org/en/rankings (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Bishaw, A.A.; Khaskheli, M.B. Chinese Unprecedented Move Towards Its One-Belt–One-Road Initiative (OBOR): Unfolding the Mythic Realities of Chinese Sphere of Legal Influence in the International Legal Order. Int. Aff. Glob. Strategy 2019, 70, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Zewde, B. A History of Modern Ethiopia, 1855–1991; Ohio University Press: Athens, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gebreluel, G. Ideology, Grand Strategy and the Rise and Decline of Ethiopia’s Regional Status. Int. Aff. 2023, 99, 1127–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGTN China, Ethiopia Establish All-Weather Strategic Partnership. Available online: https://news.cgtn.com/news/2023-10-17/Xi-meets-Ethiopian-Prime-Minister-Abiy-Ahmed-in-Beijing-1nYbDStJBXW/index.html (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Working Paper Series—Ethiopia 2030: A Country Transformed? Options for a Next Generation of Reforms. Available online: https://www.undp.org/ethiopia/publications/working-paper-series-ethiopia-2030-country-transformed-options-next-generation-reforms (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Here’s What Ethiopia Needs to Become Africa’s Next Tech Hub|Center For Global Development. Available online: https://www.cgdev.org/blog/heres-what-ethiopia-needs-become-africas-next-tech-hub (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Tanzania—The Belt and Road Initiative and China-Tanzania Relations—allAfrica.Com. Available online: https://allafrica.com/stories/201705110195.html (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Ghiasy, R.; Krishnamurthy, R. China’s Digital Silk Road. Institute of Peach and Conflict Studies; Leiden Asia Center: New Delhi, India, 2020; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Agbebi, M. China’s Digital Silk Road and Africa’s Technological Future. 2022. Available online: https://www.cfr.org/blog/chinas-digital-silk-road-and-africas-technological-future (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Ethiopia to Become the First African Country to Start Bitcoin Mining. Available online: https://www.forbesafrica.com/crypto/2024/02/22/ethiopia-to-become-the-first-african-country-to-start-bitcoin-mining/ (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Xi, C. Legal and Regulatory Risks of ‘Belt and Road’ Countries: An Index-Based Approach. In Legal and Regulatory Risks of “Belt and Road” Countries: An Index-Based Approach’in Lutz-Christian Wolff and Chao Xi (eds.), Legal Dimensions of China’s One Belt One Road Initiative (Wolters Kluwer, 2016); Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 33–54. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3023194 (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Wang, S.; Maysa, O.; Khaskheli, M.B.; Yang, W. The Power of Digitalization, the Hainan Free Trade Port, and Regulations for Modern Economic Development in Turkmenistan Are Significant. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Q.; Tian, X. Research on Privacy-by-Design Behavioural Decision-Making of Information Engineers Considering Perceived Work Risk. Systems 2024, 12, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Zhang, X.; Khaskheli, M.B.; Hong, F.; King, P.J.H.; Shamsi, I.H. Eco-Efficiency, Environmental and Sustainable Innovation in Recycling Energy and Their Effect on Business Performance: Evidence from European SMEs. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Documentation|Worldwide Governance Indicators. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/worldwide-governance-indicators/documentation#4 (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Sun, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. Big Data-Based Assessment of Political Risk along the Belt and Road. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, F.; Suomi, R.; Kantola, S.-P. Confirming the Links between Socio-Economic Variables and Digitalization Worldwide: The Unsettled Debate on Digital Divide. J. Inf. Commun. Ethics Soc. 2020, 18, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GaoYan, Q. Political Risk Distribution of Chinese Outward Foreign Direct Investment. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2020, 16, 1202–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.; Hefeker, C. Political Risk, Institutions and Foreign Direct Investment. Eur. J. Political Econ. 2007, 23, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X. Navigating Strategic Balance: CEO Big Data Orientation, Environmental Investment, and Technological Innovation in Chinese Manufacturing. Systems 2024, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China-Ethiopia Relations: An Excellent Model for South-South Cooperation—Fahamu. 2014. Available online: https://www.fahamu.org/ep_articles/china-ethiopia-relations-an-excellent-model-for-south-south-cooperation/ (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Ma, R.; Sun, J.; Yin, J. Research on the Impact Mechanism of Smart City Construction on Economic Growth—An Analysis Based on the Schumpeterian Innovation Theory Framework. Systems 2024, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühlig, T. The New Geopolitics of Technical Standardisation: A European Perspective. Future Eur. 2023, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Khaskheli, M.B.; Wang, S. The Requirements for Filing a Consumer Public Interest Litigation in China. MEJM 2024, 11, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehlecke, C.; Wellhausen, R.L. Political Risk and International Investment Law. Annu. Rev. Political Sci. 2022, 25, 485–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellhausen, R.L. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). In Oxford Handbook of International Political Economy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, R. The Impact of Digitalization on International Investment Law: Are Investment Treaties Analogue or Digital? Ger. Law J. 2023, 24, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilawal Khaskheli, M.; Wang, S.; Hussain, R.Y.; Jahanzeb Butt, M.; Yan, X.; Majid, S. Global Law, Policy, and Governance for Effective Prevention and Control of COVID-19: A Comparative Analysis of the Law and Policy of Pakistan, China, and Russia. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1035536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Big Tech and Antitrust: Pay Attention to the Math Behind the Curtain. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/big-tech-and-antitrust-pay-attention-to-the-math-behind-the-curtain/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Micro, Small and Medium Sized Enterprises. 2022. Available online: https://unctad.org/publication/covid-19-pandemic-impact-micro-small-and-medium-sized-enterprises (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Bank, W. Digital Trade for Development. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/099633201042411300/IDU17527e81d18c98144be18acb1c9fc0691b3c8 (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Casalini, F.; González, J.L. Trade and Cross-Border Data Flows; OECD: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Dong, P.; Li, S.; Ju, Y. An Intelligent Cross-Border Transaction System Based on Consortium Blockchain: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.N. Countries of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI); Green Finance & Development Center: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, B. African Special Economic Zones: Lessons and Investments from China; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; ISBN 9789811681042. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, B. The Social and Environmental Impact of Special Economic Zones in Africa. In African Special Economic Zones: Lessons and Investments from China; Robinson, B., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 225–259. ISBN 9789811681059. [Google Scholar]
- April, Y.; Shelton, G. Forum on China-Africa Cooperation: Industrialisation and Agricultural Modernisation; African Books Collective: Oxford, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-0-9783050-4-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Galán, E.; Ilhéu, F.; Zhang, H. The Chinese Special Economic Zones and Foreign Direct Investment in Portuguese-Speaking African Countries: Challenges and Opportunities. In Handbook of Research on Special Economic Zones as Regional Development Enablers; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 287–310. ISBN 978-1-79987-619-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Khaskheli, M.B. The Role of Technology in the Digital Economy’s Sustainable Development of Hainan Free Trade Port and Genetic Testing: Cloud Computing and Digital Law. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-Y.; Narins, T.P.; Sung, W. Developing Information and Communication Technology with the Belt and Road Initiative and the Digital Silk Road. Telecommun. Policy 2023, 47, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaskheli, M.; Bishaw, A.; Mapa, J.; Santos, C. TOW Environmental Migrants in the International Refuge Law and Human Rights: An Assessment of Protection Gaps and Migrants’ Legal Protection. Sci. Jurid. Sci. 2020, 3, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadband Commission. Connecting Africa Through Broadband: A Strategy for Doubling Connectivity by 2021 and Reaching Universal Access by 2030. Broadband Commission Working Group on Broadband for All: A “Digital Infrastructure Moonshot” for Africa. 2019. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/1288883/connecting-africa-through-broadband/1889711/ (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Chiaraviglio, L.; Fiore, M.; Rossi, E.; Marsan, M.A.; Melazzi, N.B.; Buzzi, S. 5G Technology: Which Risks from the Health Perspective. In The 5G Italy Book 2019: A Multiperspective View of 5G; 2019; pp. 2–17. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Luca-Chiaraviglio/publication/337151639_5G_Technology_Which_Risks_From_the_Health_Perspective/links/5dc94572a6fdcc57503e696f/5G-Technology-Which-Risks-From-the-Health-Perspective.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Lemma, A.; Parra, M.M.; Naliaka, L. The AfCFTA: Unlocking the Potential of the Digital Economy in Africa; ODI: London, UK, 2022; Volume 13, Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10855/48749 (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. How to Reshape the Selection Boundaries between Traditional and Digital Supply Chain Finance Based on the Pledge Rate and Default Loss: Two Tripartite Game Models. Systems 2024, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
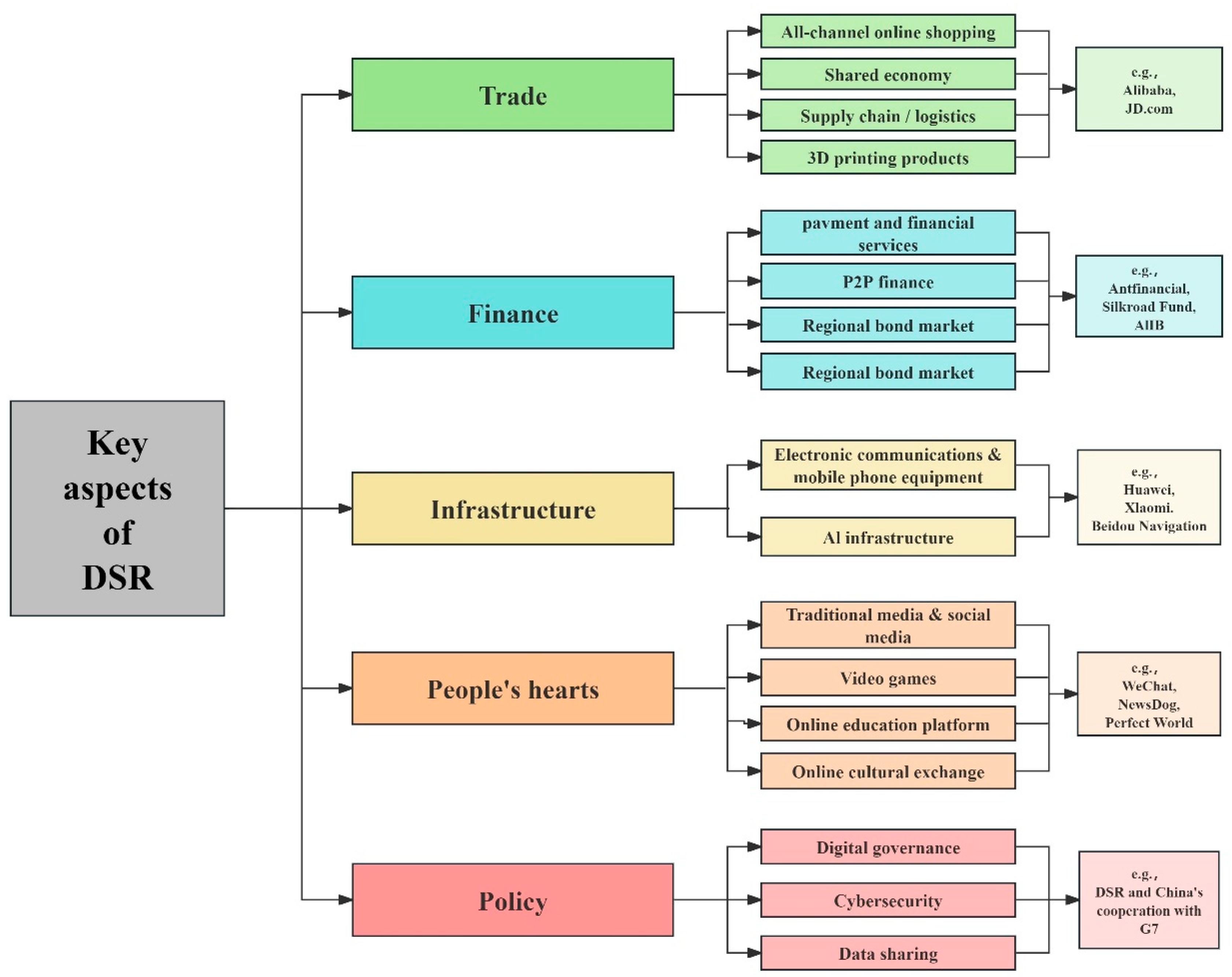
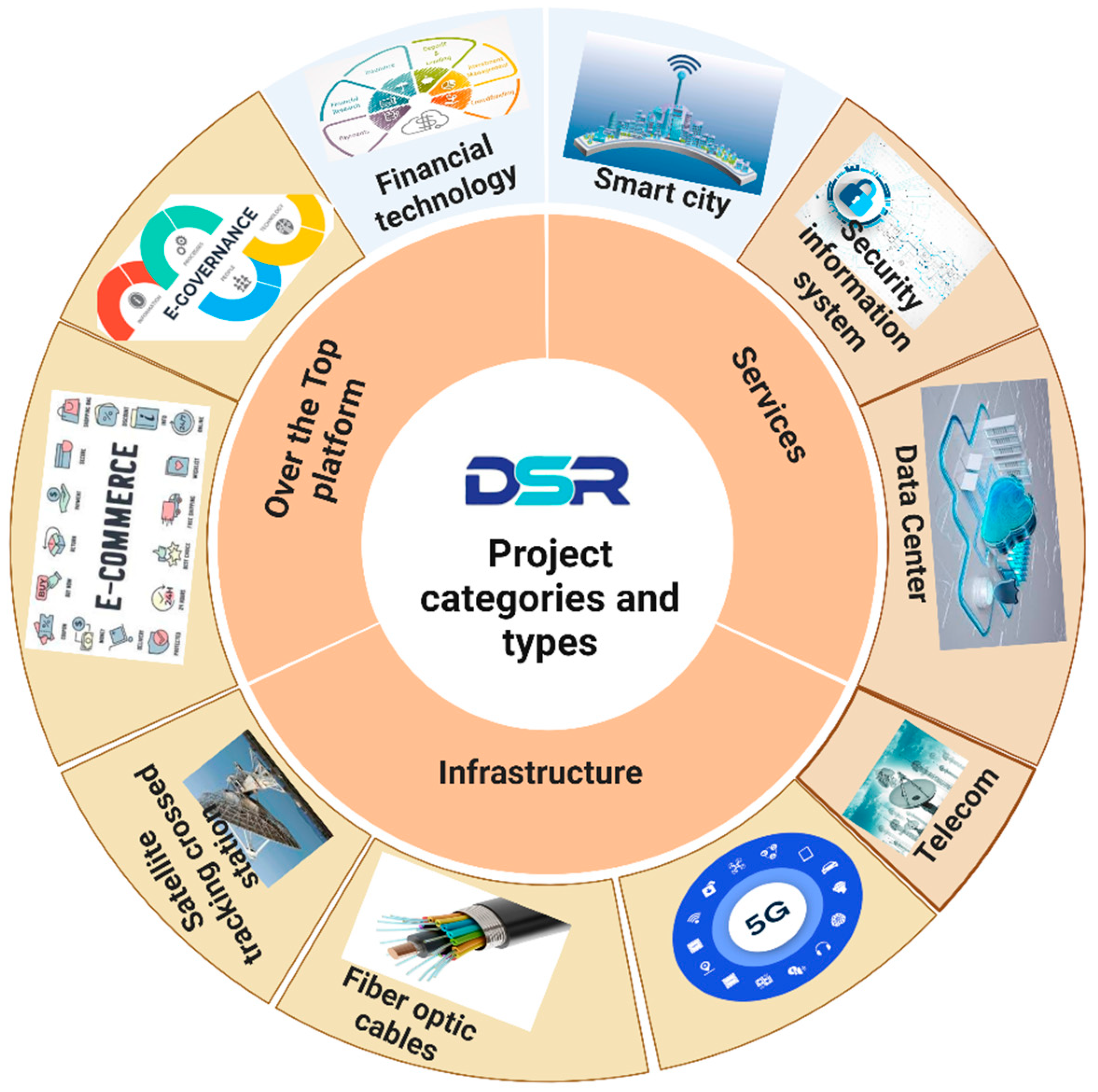
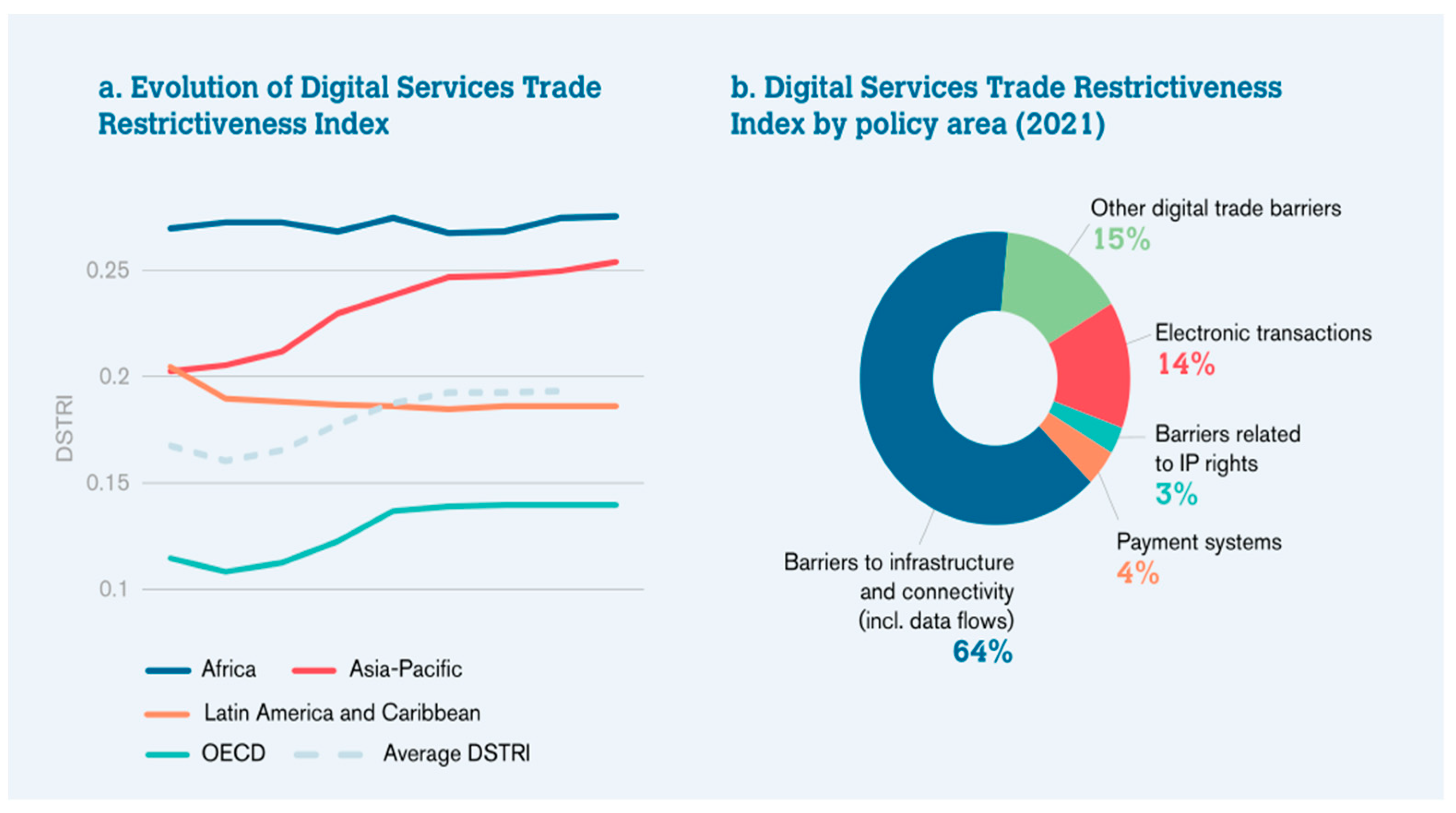
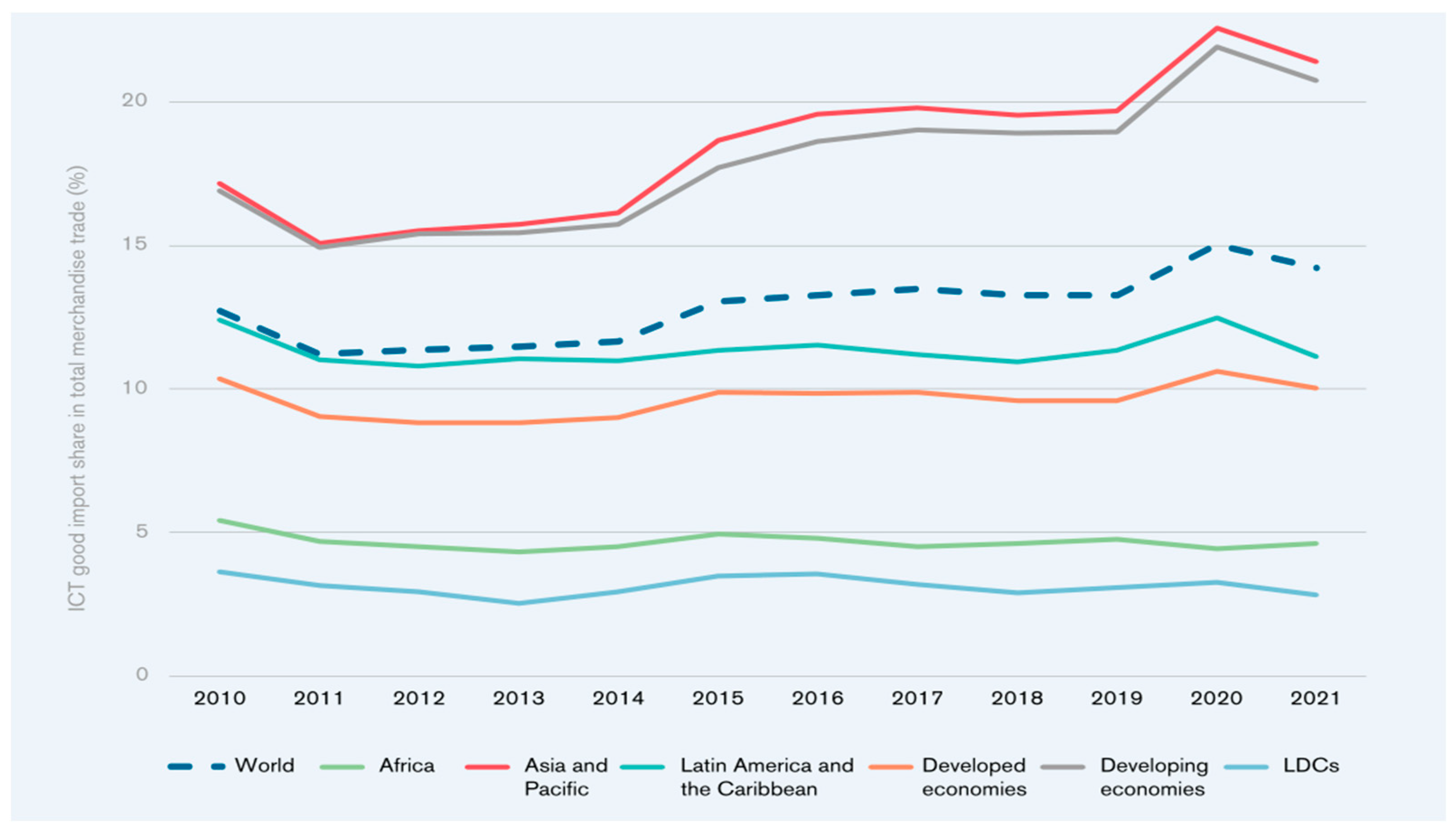
| Year | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China’s stock of direct investment in Ethiopia (USD 10,000) | 91,462 | 113,013 | 200,065 | 197,556 | 256,816 | 255,887 | 299,280 | 281,090 | 262,032 |
| Total stock of foreign direct investment flowing into Ethiopia (USD 10,000) | 726,400 | 1,069,200 | 1,370,000 | 1,851,200 | 2,225,300 | 2,492,300 | 2,735,100 | 3,161,100 | 3,528,100 |
| Percentage of the total stock of direct investment in Ethiopia | 12.6% | 10.6% | 14.6% | 10.7% | 11.5% | 10.3% | 10.9% | 8.9% | 7.4% |
| Country | Project | Financier | Borrower | Implementation | Amount | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanzania | National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB) Phase II | Exim bank | Tanzanian government | CITCC, Huawei | USD 100 m | 2010 |
| Cameroon | National Broadband Network Phase I:4G mobile broadband (LTE) | Exim bank | Cameroonian government | Huawei | USD 168 m | 2011 |
| Kenya | National Optic Fibre Backbone Infrastructure (NOFBI). Phase II: E-government | Exim bank | Kenyan government | Huawei | USD 7l m | 2012 |
| Nigeria | Galaxy Backbone project for National Security development system | Exim bank | Nigerian government | Huawei | USD 100 m | 2012 |
| Ethiopia | Telecom Transformation and Expansion (4G network and mobile expansion) 6 Circles—ZTE | Exim bank | Ethiopian government | ZTE | USD 300 m | 2013 |
| Ethiopia | Telecom Transformation and Expansion (4G network and mobile expansion) 7 Circles—Huawei | Exim bank | Ethiopian government | Huawei | USD 800 m | 2013 |
| Tanzania | National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB) Phase III | Exim bank | Tanzanian government | CITCC, Huawei | USD 94 m | 2013 |
| Nigeria | National Information Communication Technology Infrastructure Backbone (NICTIB) Phase I | Exim bank | Tanzanian government | Huawei | USD 100 m | 2013 |
| Guinea | National Backbone fiber optics | Exim bank | Guinean government | Huawei | USD 214.2 m | 2014 |
| Cameroon | National Telecommunications Broadband Network Project Phase II | Exim bank | Cameroonian government | Huawei | USD 337 m | 2015 |
| Ivory Coast | Abidjan Video Surveillance Platform | Exim bank | Ivory Coast government | Huawei | USD 56.7 m | 2016 |
| Cameroon | South Atlantic Inter Link (SAIL) | Exim bank | Cameroonian government | Huawei | USD 85 m | 2017 |
| Nigeria | National Information Communication Technology Infrastructure Backbone (NICTIB) Phase II | Exim bank | Nigerian government | Huawei | USD 334 m | 2018 |
| Sierra Leone | Fibre Optic Backbone Network Phase II | Exim bank | Sierra Leonean government | Huawei | USD 30 m | 2019 |
| Year | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2017–2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Overall Score | Ranking | Overall Score | Ranking | Overall Score | Ranking | Overall Score | Ranking | Overall Score | Ranking | Overall Score | Ranking |
| Ethiopia | 0.38 | 129/142 | 0.39 | 123/140 | 0.41 | 122/139 | 0.41 | 114/128 | 0.39 | 118/126 | 0.38 | 107/113 |
| Area | Country | DB Index | WGI | WJP ROL Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of DB Score | Ease of DB Ranking | Regulatory Quality | Rule of Law | Overall Score | Ranking | ||||
| Estimate of Governance | Percentile Ranking | Estimate of Governance | Percentile Ranking | ||||||
| East Asia | Mongolia | 67.8 | 81 | −0.27 | 42.45 | −0.19 | 45.75 | 0.53 | 64 |
| China | 77.9 | 31 | −0.42 | 36.79 | −0.04 | 52.83 | 0.47 | 97 | |
| Southeast Asia | Brunei | 70.1 | 66 | 1.07 | 82.55 | 0.93 | 80.19 | — | — |
| Indonesia | 69.6 | 73 | 0.21 | 59.43 | −0.19 | 45.28 | 0.53 | 66 | |
| Laos | 50.8 | 154 | −0.99 | 16.04 | −0.18 | 23.58 | — | — | |
| Malaysia | 81.5 | 12 | 0.64 | 72.64 | 0.56 | 68.40 | 0.57 | 55 | |
| Myanmar | 46.8 | 165 | −1.24 | 9.91 | −1.53 | 5.66 | 0.35 | 135 | |
| Philippines | 62.8 | 95 | 0.06 | 53.77 | −0.52 | 33.49 | 0.46 | 100 | |
| Singapore | 86.2 | 2 | 2.21 | 100.00 | 1.78 | 99.06 | 0.78 | 17 | |
| Thailand | 80.1 | 21 | 0.17 | 58.49 | 0.07 | 54.72 | 0.49 | 82 | |
| Vietnam | 69.8 | 70 | −0.43 | 36.32 | −0.16 | 47.64 | 0.49 | 87 | |
| West Asia | Bahrain | 76 | 43 | 0.97 | 78.30 | 0.44 | 65.09 | — | — |
| Iran | 58.5 | 127 | −1.59 | 4.25 | −1.02 | 17.45 | 0.39 | 126 | |
| Iraq | 44.7 | 172 | −1.18 | 11.79 | −1.75 | 3.30 | — | — | |
| Israel | 76.7 | 35 | 1.21 | 86.32 | 0.95 | 81.13 | — | — | |
| Jordan | 69 | 75 | 0.16 | 57.08 | 0.22 | 57.08 | 0.55 | 62 | |
| Kuwait | 67.4 | 83 | 0.21 | 60.38 | 0.28 | 57.55 | 0.58 | 52 | |
| Lebanon | 54.3 | 143 | −1.13 | 13.68 | −1.10 | 13.68 | 0.45 | 107 | |
| Oman | 70 | 68 | 0.43 | 65.57 | 0.50 | 66.51 | — | — | |
| Palestine | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Qatar | 68.7 | 77 | 0.87 | 77.36 | 0.92 | 79.25 | — | — | |
| Saudi Arabia | 71.6 | 62 | 0.42 | 65.09 | 0.29 | 58.02 | — | — | |
| Syria | 42 | 176 | −1.82 | 3.77 | −2.07 | 0.94 | — | — | |
| Türkiye | 76.8 | 33 | −0.24 | 43.40 | 0.46 | 36.79 | 0.41 | 117 | |
| The United Arab Emirates | 80.9 | 16 | 1.03 | 82.08 | 0.84 | 78.77 | 0.64 | 37 | |
| Yemen | 31.8 | 187 | −1.92 | 2.83 | −1.85 | 1.89 | — | — | |
| Cyprus | 73.4 | 54 | 0.77 | 75.47 | 0.57 | 68.87 | 0.68 | 31 | |
| Greece | 68.4 | 79 | 0.46 | 67.45 | 0.33 | 59.91 | 0.61 | 47 | |
| Egypt | 60.1 | 114 | −0.71 | 24.53 | −0.26 | 42.45 | 0.35 | 136 | |
| South Asia | Afghanistan | 44.1 | 173 | −1.27 | 8.96 | −1.66 | 5.19 | 0.32 | 140 |
| Bangladesh | 45 | 168 | −0.93 | 17.92 | −0.60 | 29.72 | 0.38 | 127 | |
| Bhutan | 66 | 89 | −0.38 | 38.68 | 0.67 | 71.70 | — | — | |
| India | 71 | 63 | −0.05 | 50.94 | 0.11 | 55.19 | 0.49 | 79 | |
| Maldives | 53.3 | 147 | −0.66 | 26.89 | −0.03 | 53.30 | — | — | |
| Nepal | 63.2 | 94 | −0.65 | 27.83 | −0.45 | 37.74 | 0.52 | 71 | |
| Pakistan | 61 | 108 | −0.89 | 20.28 | −0.67 | 25 | 0.38 | 130 | |
| Sri Lanka | 61.8 | 99 | −0.65 | 27.36 | −0.06 | 52.36 | 0.50 | 77 | |
| Central Asia | Kazakhstan | 79.6 | 25 | −0.01 | 52.83 | −0.47 | 35.85 | 0.53 | 65 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 67.8 | 80 | −0.63 | 28.77 | −1.15 | 12.74 | 0.45 | 103 | |
| Tajikistan | 61.3 | 106 | −1.20 | 11.32 | −1.26 | 10.85 | — | — | |
| Turkmenistan | — | — | −2.07 | 1.89 | −1.49 | 6.13 | — | — | |
| Uzbekistan | 69.9 | 69 | −0.55 | 31.60 | −0.85 | 21.70 | 0.50 | 78 | |
| CIS | Armenia | 74.5 | 47 | −0.02 | 51.89 | −0.14 | 46.23 | — | — |
| Azerbaijan | 76.7 | 34 | −0.10 | 48.11 | −0.62 | 25.94 | — | — | |
| Belarus | 74.3 | 49 | −1.33 | 7.55 | −1.22 | 11.79 | 0.45 | 104 | |
| Georgia | 83.7 | 7 | 1.03 | 81.60 | 0.17 | 56.60 | 0.60 | 48 | |
| Moldova | 74.4 | 48 | 0.10 | 54.72 | −0.29 | 41.98 | 0.53 | 68 | |
| Russia | 78.2 | 28 | −1.14 | 13.21 | −1.20 | 12.26 | 0.44 | 113 | |
| Ukraine | 70.2 | 64 | −0.33 | 40.57 | −0.92 | 18.87 | 0.49 | 89 | |
| Central and Eastern Europe | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 65.4 | 90 | −0.16 | 45.75 | −0.31 | 41.51 | 0.51 | 75 |
| Bulgaria | 72 | 61 | 0.22 | 61.79 | −0.11 | 49.53 | 0.56 | 59 | |
| Croatia | 73.6 | 51 | 0.50 | 68.40 | 0.37 | 61.32 | 0.61 | 45 | |
| Czech Republic | 76.3 | 41 | 1.39 | 88.68 | 1.10 | 83.49 | 0.73 | 20 | |
| Estonia | 80.6 | 18 | 1.56 | 92.92 | 1.42 | 89.62 | 0.82 | 9 | |
| Hungary | 73.4 | 52 | 0.41 | 64.62 | 0.42 | 63.21 | 0.51 | 73 | |
| Latvia | 80.3 | 19 | 1.17 | 84.91 | 0.92 | 79.72 | 0.73 | 22 | |
| Lithuania | 81.6 | 11 | 1.30 | 87.74 | 1.06 | 83.02 | 0.77 | 18 | |
| North Macedonia | 80.7 | 17 | 0.45 | 66.98 | −0.10 | 50.00 | 0.53 | 67 | |
| Montenegro | 73.7 | 50 | 0.54 | 69.34 | −0.13 | 48.58 | 0.56 | 57 | |
| Poland | 76.4 | 40 | 0.72 | 74.53 | 0.43 | 64.15 | 0.64 | 36 | |
| Romania | 73.3 | 55 | 0.36 | 63.68 | 0.40 | 62.26 | 0.63 | 40 | |
| Serbia | 75.7 | 44 | 0.14 | 56.13 | −0.11 | 49.06 | 0.48 | 93 | |
| Slovakia | 75.6 | 45 | 0.85 | 76.89 | 0.62 | 70.28 | 0.66 | 34 | |
| Slovenia | 76.5 | 37 | 0.85 | 76.89 | 0.97 | 82.55 | 0.69 | 27 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Khaskheli, M.B. Management Economic Systems and Governance to Reduce Potential Risks in Digital Silk Road Investments: Legal Cooperation between Hainan Free Trade Port and Ethiopia. Systems 2024, 12, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080305
Wang S, Li Q, Khaskheli MB. Management Economic Systems and Governance to Reduce Potential Risks in Digital Silk Road Investments: Legal Cooperation between Hainan Free Trade Port and Ethiopia. Systems. 2024; 12(8):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080305
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shumin, Qianyu Li, and Muhammad Bilawal Khaskheli. 2024. "Management Economic Systems and Governance to Reduce Potential Risks in Digital Silk Road Investments: Legal Cooperation between Hainan Free Trade Port and Ethiopia" Systems 12, no. 8: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080305
APA StyleWang, S., Li, Q., & Khaskheli, M. B. (2024). Management Economic Systems and Governance to Reduce Potential Risks in Digital Silk Road Investments: Legal Cooperation between Hainan Free Trade Port and Ethiopia. Systems, 12(8), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080305





