Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Analysis and Hypotheses
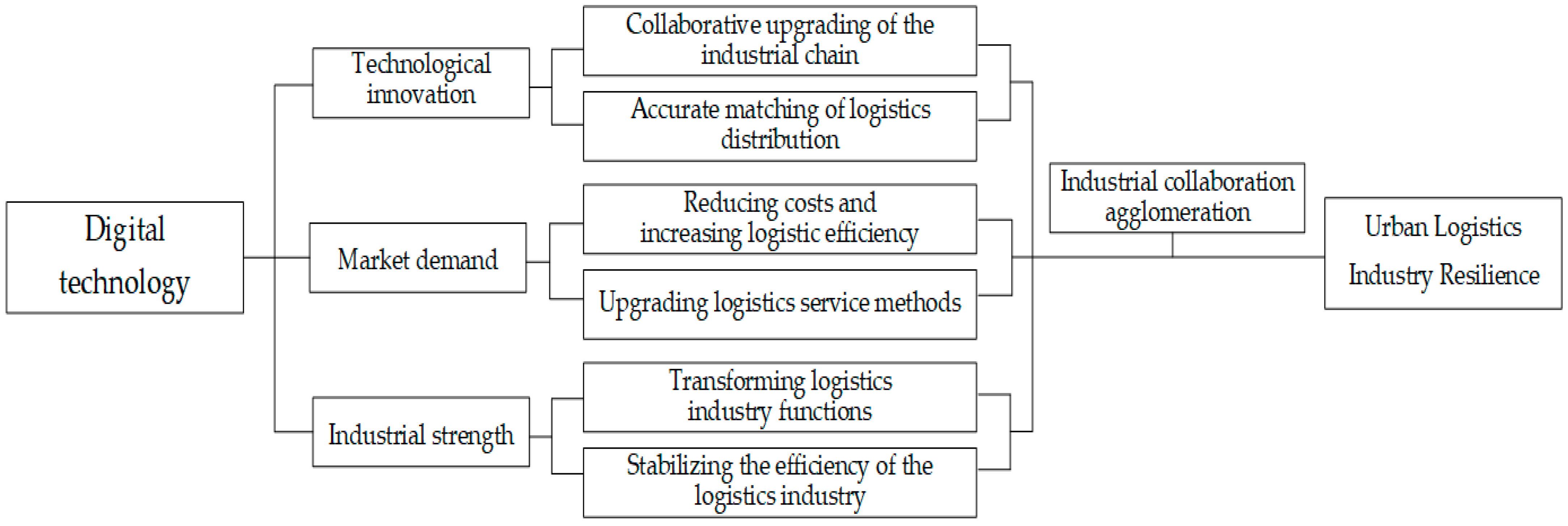
3.1. Direct Effects of Digital Technology on Logistics Industry Resilience
3.2. Mediating Effects of Digital Technology on Logistics Industry Resilience
3.3. Threshold Effects of Digital Technology on Logistics Industry Resilience
4. Research Design
4.1. Model Construction
4.1.1. Baseline Regression
4.1.2. The Mediation Effect
4.1.3. Threshold Effect
4.2. Indicator Selection
4.2.1. Index System of Logistics Industry Resilience
4.2.2. Indicator System for Digital Technology
4.2.3. The Mediating Effect of Industrial Collaboration Agglomeration
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Data Collection and Description
5. Empirical Analysis
5.1. Baseline Regression
5.2. Robustness Test
5.2.1. 2SLS Test
5.2.2. Replace the Dependent Variable
5.2.3. Remove Outliers
5.3. Mediation Analysis
5.4. Threshold Effect
5.5. Heterogeneity Test
5.6. Further Research Based on the “Broadband China” Policy
5.6.1. Background and Model Specification
5.6.2. Empirical Test Results
5.7. Discussions
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Recommendations
6.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | “The China Logistics Yearbook” is a book published by China Fortune Publishing House in 2023, compiled by the China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing; “The China Statistical Yearbook” is an informative annual publication compiled and printed by the National Bureau of Statistics (https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/, accessed on 23 July 2024). “The China Third Industry Statistical Yearbook” is a book compiled by the National Bureau of Statistics and published by China Statistics Publishing House; “The China Electronic Information Industry Statistical Yearbook” is a book published by the Electronic Industry Press. “The China City Statistical Yearbook” is a descriptive term compiled by each city government to comprehensively reflect the economic and social development of Chinese cities. It is an annual publication that is compiled and published separately for each city. “Digital Inclusive Finance Index” is a report compiled by the “Peking University Digital Inclusive Finance Index” research group. |
| 2 | See Note 1 above. |
References
- Li, M.; Huang, K.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y. Dynamic evolution, regional differences and influencing factors of high-quality development of China’s logistics industry. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Qadri, M.A.; Suman, R. Understanding the role of digital technologies in education: A review. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2022, 3, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Qian, F.; Ding, H.; Zhang, X. Digitalization of logistics for transition to a resource-efficient and circular economy. Resour. Policy 2023, 83, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrings, C. Ecological Resilience in the Sustainability of Economic Development. Économie Appliquée 1995, 48, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, A.; Graaff, T.D.; Nijkamp, P. Resilience: An evolutionary approach to spatial economic systems. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2002, 2, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C. What determines the economic resilience of Chinese cities amid pandemic crisis: An economic operating state perspective. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 104, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; He, B. Does foreign direct investment affect wage inequality in Chinese manufacturing sector? Appl. Econ. Lett. 2023, 30, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S. The impact of digital finance on regional economic resilience. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2024, 85, 102353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; He, B. Does Digital Infrastructure Improve Urban Economic Resilience? Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chong, W.K.; Li, D. A systematic literature review of the capabilities and performance metrics of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 4541–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambulkar, S.; Blackhurst, J.; Grawe, S. Firm’s resilience to supply chain disruptions: Scale development and empirical examination. J. Oper. Manag. 2014, 33–34, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Review of quantitative methods for supply chain resilience analysis. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 125, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiao, Z. Research on spatio-temporal heterogeneity of global cross-border e-commerce logistics resilience under the impact of the COVID-19epidemic. Geogr. Res. 2021, 12, 3333–3348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S. Innovation of Resilient Logistics Leading Strategy from the Perspective of Green Economic Development in Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Nantong Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 1, 11–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Yang, B.; Ma, H. Calculation of Logistics Resilience in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Stat. Decis. 2022, 4, 102–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, H. The influencing factors and improvement paths of digital logistics resilience under the background of green development. J. Commer. Econ. 2023, 14, 71–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N.V. Digital Business Strategy: Toward a Next Generation of Insights. MIS Q. 2013, 1, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adner, R.; Puranam, P.; Zhu, F. What is Different About Digital Strategy? From Quantitative to Qualitative Change. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2022, 4, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Z. Does the development of digital technology contribute to the innovation performance of China’s high-tech industry? Technovation 2023, 124, 102738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, D.; Stead, D. Impact of Information and Communications Technology on Transport. Transp. Rev. 2004, 5, 611–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, K.; Shan, Y.G. Leveraging corporate digitalization for green technology innovation: The mediating role of resource endowments. Technovation 2024, 133, 102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hong, J.; Lau, K.H. Impact of supply chain digitalization on supply chain resilience and performance: A multi-mediation model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 259, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shee, H.K.; Miah, S.J.; De Vass, T. Impact of smart logistics on smart city sustainable performance: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 821–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumzej, R. Intelligent logistics systems in E-commerce and transportation. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 20, 2348–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-García, J.A.; Elias-Giordano, C.; Quiroz-Flores, J.C.; Nallusamy, S. Profitability enhancement by digital transformation and canvas digital model on strategic processes in post-COVID-19 in logistics SMEs. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2024, 9, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. R&D and Firm Resilience During Bad Times. Soc. Sci. Res. Netw. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Piran, M.J. A crowdsourcing logistics solution based on digital twin and four-party evolutionary game. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 130, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfadel, A.; Hörl, S.; Tapia, R.J.; Politaki, D.; Kureshi, I.; Tavasszy, L.; Puchinger, J. A conceptual digital twin framework for city logistics. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 103, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCarthy, B.L.; Ivanov, D. The Digital Supply Chain; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Ilıcak, Y. Smart urban logistics: Literature review and future directions. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 81, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Zhang, S. Research on Distribution Dynamics, Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Intelligent Development of China’s Logistics Industry. China Bus. Mark. 2023, 3, 17–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Singh, R.K.; Papadopoulos, T. Linking Digital Orientation and Data-Driven Innovations: A SAP–LAP Linkage Framework and Research Propositions. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.; Fan, Z.; Day, C.; Barlow, C. Digital Twin: Enabling Technologies, Challenges and Open Research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 108952–108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, J.L.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Alberti, A.M. Convergence of Distributed Ledger Technologies with Digital Twins, IoT, and AI for fresh food logistics: Challenges and opportunities. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023, 31, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhaus, S.; Grosse, E.H. Logistics 4.0: A systematic review towards a new logistics system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, F.R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Logistics: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 4250–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarabady, N.J.; Durst, S. A systematic literature review on the economic impact of digitalization technologies in transport logistics. Transp. Econ. Manag. 2024, 2, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Research on consumers’ personal information security and perception based on digital twins and Internet of Things. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinqin, W.; Qalati, S.A.; Hussain, R.Y.; Irshad, H.; Tajeddini, K.; Siddique, F.; Gamage, T.C. The effects of enterprises’ attention to digital economy on innovation and cost control: Evidence from A-stock market of China. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, P. Enterprise digital transformation, financial information disclosure and innovation efficiency. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 59, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, A.; Shamina, L.; Niu, J.; Yadykin, V. Transformation of Distribution Logistics Management in the Digitalization of the Economy. J. Open Innov. 2021, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, Q. Research on value creation path of logistics platform under the background of digital ecosystem: Based on SEM and fsQCA methods. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2024, 67, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, S.; Joshi, K.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sethuraman, K. Reflecting on an empirical study of the digitalization initiatives for sustainability on logistics: The concept of sustainable logistics 4.0. Clean. Logist. Supply Chain 2022, 4, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L. Digital economy, industrial structure upgrading, and residents’ consumption: Empirical evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 92, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, J. The future of cities in the digital economy era: A study on the impact of internet on the agglomeration of producer services in Chinese Cities. China Econ. Q. Int. 2024, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wan, X.; Jahanger, A.; Li, M.; Murshed, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Does the digital economy reduce air pollution in China? A perspective from industrial agglomeration. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 3625–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.W.; Fan, B.; Chang, Y.J. CSR, Digital Transformation, and Internal Control: Three-Way Interaction Effect on the Firm Value of Chinese Listed Companies. Systems 2024, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Aguayo, J.; McFarlane, D.; Schönfuß, B.; Salter, L. A catalogue of digital solution areas for logistics SMEs. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Liu, M. How does the digital transformation drive digital technology innovation of enterprises? Evidence from enterprise’s digital patents. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 204, 123428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, F.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhao, Q. Inclusive digital economy, resource dependence and changes in the urban energy mix: City level analysis from China. Resour. Policy 2024, 92, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucc, D.; Saldanha, N.; Deng, X. A Meditation on Mediation: Evidence that Structural Equations Models Perform Better Than Regressions. J. Consum. Psychol. 2007, 2, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Sunley, P. On the Notion of Regional Economic Resilience: Conceptualization and Explanation. J. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 1, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, L. Digital finance and regional economic resilience: Theoretical framework and empirical test. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 55, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, L.; Proverbs, D.; Wei, J. Intelligent Storage Location Allocation with Multiple Objectives for Flood Control Materials. Water 2019, 11, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y. Integrating equity and efficiency into urban logistics resilience under emergency lockdowns. Transportation Research. Part E, Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 183, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chan, H.K.; Thadani, D.R.; Chan FK, S.; Peng, Y. The role of digital techniques in organisational resilience and performance of logistics firms in response to disruptive events: Flooding as an example. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 266, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.S.; Ramanathan, U. The role of digital technologies in supply chain resilience for emerging markets’ automotive sector. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Gong, Y.; Yang, B.; Xu, X. Resilience, efficiency fluctuations, and regional heterogeneity in disaster: An empirical study on logistics. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2024, 93, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Yadav, A.K.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Khan, S.A.; Sharma, S.C. Strategies to overcome barriers to innovative digitalisation technologies for supply chain logistics resilience during pandemic. Technol. Soc. 2022, 69, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, M.C. A Complex Adaptive Systems View of Resilience in a Project Team. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2012, 29, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiapa, M.; Batsiolas, I. Firm resilience in regions of Eastern Europe during the period 2007–2011. Post-Communist Econ. 2018, 31, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Yang, L.; Huo, B. The impact of information technology usage on supply chain resilience and performance: An ambidexterous view. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 232, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbeto, D.L.; Hon AH, Y. Market turbulence and service innovation in hospitality: Examining the underlying mechanisms of employee and organizational resilience. Serv. Ind. J. 2020, 40, 1119–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ritchie, B.W.; Verreynne, M. Building tourism organizational resilience to crises and disasters: A dynamic capabilities view. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2019, 21, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroson, E.V.; Breen, L.; Hou, J.; Sowter, J. Advancing the understanding of pharmaceutical supply chain resilience using complex adaptive system (CAS) theory. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Du, A.M.; Liang, J. The digital economy and entrepreneurial dynamics: An empirical analysis of urban regions in China. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2024, 71, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cai, H. The impacts on regional “resource curse” by digital economy: Based on panel data analysis of 262 resource-based cities in China. Resour. Policy 2024, 95, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Digital Economy and Urban Entrepreneurial Activity. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 66, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, K.; Dong, X.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Assessing the digital economy and its carbon-mitigation effects: The case of China. Energy Econ. 2022, 113, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xu, L. Digitalization and innovation: How does the digital economy drive technology transfer in China? Econ. Model. 2024, 136, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Research on the impact of Industrial Collaborative Agglomeration on Regional Economic Growth: Based on the Perspective of Scale Effect and Congestion Effect. Econ. Rev. 2023, 2, 43–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, X. Effect of the logistics industry on the promotion of China’s position in the global value chain: An international trade perspective. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 86, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q. Spatial impact of the digital economy on low-carbon logistics efficiency in RCEP countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, J. Impact of technological innovation on carbon emissions in China’s logistics industry: Based on the rebound effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S. Internet Development and Productivity Growth in Manufacturing Industry: Internal Mechanism and China Experiences. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 8, 5–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Xu, D.; Nan, G.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Does the cross-border e-commerce comprehensive pilot zones policy affect the urban–rural income gap in China? Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 2024. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstykh, T.; Shmeleva, N.; Boev, A.; Guseva, T.; Panova, S. System Approach to the Process of Institutional Transformation for Industrial Integrations in the Digital Era. Systems 2024, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary | Secondary | Tertiary | Attributes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics Resilience | Resistance and Recovery Capacity | Total wages of employees in transportation, warehousing, and postal services (in billion CNY) | + | [14] |
| Freight volume by waterway, railway, and air transport (10,000 tons) | + | [55] | ||
| Road freight volume (10,000 tons) | + | [56] | ||
| Logistics warehouse area (square kilometers) | + | [54] | ||
| Total volume of express delivery services (Hundred million pieces) | + | [55] | ||
| The proportion of the tertiary industry output value to the GDP (%) | + | [57] | ||
| Adaptation and Adjustment Capacity | Per capita regional GDP (in CNY) | + | [14,15] | |
| Total retail sales of consumer goods (In CNY ten thousand) | + | [58] | ||
| Volume of import and export trade (In CNY hundred million) | + | [59] | ||
| Total fiscal expenditure of the logistics industry (In CNY 100 million) | + | [60] | ||
| Number of mobile subscribers at the end of the year (in 10,000 households) | + | [61] | ||
| [62] | ||||
| Total sales of goods in wholesale and retail trade above designated size (in CNY 10,000) | + | [63] | ||
| Innovation and Transformation Capacity | Number of R&D personnel (in 10,000 persons) | + | [16] | |
| Number of patents granted | + | [15] | ||
| Number of university students per 10,000 persons | + | [64] | ||
| Proportion of education expenditure to local financial budgetary expenditure (%) | + | [65] |
| Primary | Secondary | Tertiary | Attributes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Technology | Internet Penetration Rate | Number of Broadband Internet Access Users per 100 persons | + | [66] |
| Number of Employees in Information Technology Industry | Proportion of Employees in Computer Services and Software Industry to Unit Employees | + | [67] | |
| Output Value of Information Technology Industry | Per Capita Telecommunications Service Volume (in CNY 10,000) | + | [68] | |
| Penetration Rate of Mobile Phones | Number of Mobile Phone Users per 100 People (households) | + | [69] | |
| Development of Digital Finance | China’s Digital Inclusive Finance Index | + | [70] |
| Variable Type | Variable Name | Mean | S. D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent | Resilience of logistics industry (Res) | 0.0007 | 0.658 | −0.670 | 7.550 |
| Core explanatory | Digital technology (Tech) | 0.0009 | 0.756 | −0.830 | 6.960 |
| Mediating | Industrial synergy clustering (ICA) | 2.416 | 0.556 | 0.611 | 4.432 |
| Control | Logistics infrastructure (Pos) | 4.902 | 0.705 | 0.0002 | 7.487 |
| Logistics demand (Dem) | 1.651 | 2.037 | 0.044 | 55.446 | |
| Industrial structure (LnThi) | 3.948 | 0.272 | 2.730 | 4.550 | |
| Level of technological innovation (LnSci) | 4.772 | 0.989 | 0.693 | 7.166 | |
| Number of labor force (Hum) | 4.506 | 3.271 | 0.200 | 34.160 |
| Variables | (1) OLS | (2) RE | (3) FE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tech | 0.431 *** (0.010) | 0.120 *** (0.011) | 0.027 *** (0.010) |
| Pos | 0.027 *** (0.007) | 0.022 *** (0.008) | −0.012 (0.008) |
| Dem | 0.051 *** (0.004) | 0.038 *** (0.003) | 0.032 *** (0.002) |
| LnThi | 0.120 *** (0.026) | 0.191 *** (0.027) | −0.008 (0.031) |
| LnSci | 0.076 *** (0.004) | 0.049 *** (0.005) | 0.011 ** (0.005) |
| Hum | 0.061 *** (0.003) | 0.103 *** (0.004) | 0.120 *** (0.005) |
| Fe | No | No | Yes |
| N | 2750 | 2750 | 2750 |
| R2 | 0.716 | 0.309 | 0.420 |
| Variables | 2SLS | Replace Dependent Variable | Exclude Outliers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Instru | 0.061 *** (0.401) | |||
| Tech | 0.616 *** (0.046) | 0.001 ** (0.001) | 0.035 *** (0.009) | |
| Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2750 | 2750 | 2750 | 2750 |
| R2 | 0.404 | 0.679 | 0.395 | 0.386 |
| F | 69.16 | 196.28 | ||
| Variables | ICA | Res |
|---|---|---|
| Tech | 0.184 *** (0.012) | 0.411 *** (0.010) |
| ICA | 0.107 *** (0.016) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Fe | 1.605 *** (0.150) | −1.946 *** (0.125) |
| N | 2750 | 2750 |
| Method | Delta | Sobel | Monte Carlo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mediation Effect | Indirect Effect | Indirect Effect | Indirect Effect |
| Standard Error | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Z | 6.309 | 6.309 | 6.309 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Conf. Interval | [0.016, 0.030] | [0.016, 0.030] | [0.016, 0.030] |
| Threshold Variable | Model | F | p | Threshold Value | Critical Value | BS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 5% | 1% | ||||||
| Tech | Single | 27.41 | 0.020 | 1.869 | 17.185 | 20.796 | 31.056 | 300 |
| ICA | Single | 24.20 | 0.160 | 2.978 | 29.580 | 41.363 | 99.035 | 300 |
| Double | 28.47 | 0.083 | 3.023 | 26.142 | 36.636 | 79.703 | 300 | |
| Variables | Res | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| Tech·I (Tech ≤ 1.869) | 0.077 *** (0.016) | |
| Tech·I (Tech > 1.869) | 0.032 *** (0.011) | |
| Tech·I (ICA ≤ 2.978) | 0.056 *** (0.012) | |
| Tech·I (2.978 < ICA < 3.023) | 0.191 *** (0.032) | |
| Tech·I (ICA ≥ 3.023) | 0.004 (0.016) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Fe | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2750 | 2750 |
| R2 | 0.312 | 0.320 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | South | North | Northeast | Yellow River Basin | Yangtze River Basin | Southwest | Northwest | |
| Tech | 0.344 ** | −0.068 *** | 0.128 ** | 0.010 | 0.059 *** | 0.084 *** | −0.046 ** | 0.024 |
| (0.147) | (0.018) | (0.050) | (0.008) | (0.021) | (0.019) | (0.022) | (0.028) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 240 | 310 | 270 | 330 | 460 | 520 | 430 | 190 |
| R2 | 0.650 | 0.684 | 0.443 | 0.512 | 0.226 | 0.728 | 0.514 | 0.673 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital | 0.089 *** (0.013) | 0.072 *** (0.012) |
| Controls | No | Yes |
| Fe | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2750 | 2750 |
| R2 | 0.242 | 0.427 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; He, B. Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths. Systems 2024, 12, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080278
Zhang J, Yang Z, He B. Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths. Systems. 2024; 12(8):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080278
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jifeng, Zirui Yang, and Bing He. 2024. "Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths" Systems 12, no. 8: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080278
APA StyleZhang, J., Yang, Z., & He, B. (2024). Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths. Systems, 12(8), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12080278








