Abstract
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in programming assistance has garnered researchers’ attention for its potential to reduce learning costs for users, increase work efficiency, and decrease repetitive coding tasks. However, given the novelty of AI Coding Assistant Tools (AICATs), user acceptance is currently limited, and the factors influencing this phenomenon are unclear. This study proposes an expanded model based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) that incorporates the characteristics of AICAT users to explore the key factors affecting college students’ willingness to use AICATs. Utilizing a survey methodology, 303 Chinese participants completed the questionnaire. Factor analysis and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) results indicate that users’ dependence worry (DW) about AICATs positively affects perceived risk (PR), which in turn negatively impacts perceived usefulness (PU) and perceived ease of use (PEOU), thus reducing user willingness to use. Dependence concerns also negatively impact perceived trust (PT), while PT positively affects PU and PEOU, thereby enhancing willingness to use. Additionally, a user’s self-efficacy (SE) negatively impacts DW and positively affects PEOU. This study discusses the potential significance of these findings and offers suggestions for AICAT developers to foster and promote widespread use.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) has become a focal point in the computer science field. With the current wave of AI technology applications, numerous tech companies have released a variety of AI tools for generating text, images, music, code, and even videos, sparking a global “AI storm” [1]. For instance, the text-generating ChatGPT reached one million registered users within five days of its launch and one hundred million in just two months [2]. In the AI-generated content (AIGC) sector, tools like the image generators Midjourney and Stable Diffusion, the code generator Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, and OpenAI’s latest AI video generation model, Sora, represent the current phase of AI in enhancing user work efficiency, offering new possibilities for projects that are traditionally high-barrier, complex, and time-consuming.
In the programming realm, AI Coding Assistant Tools (AICATs), such as OpenAI Codex, DeepMind AlohaCode, and Amazon CodeWhisper, have become a focal point of interest in recent years [3]. As the demand for software developers to quickly generate code continues to grow, there has been a significant increase in interest in tools that programming productivity [4]. Previous research has shown that AI-assisted programming can improve the efficiency of software engineers [5], especially when dealing with complex algorithms or extensive code. Moreover, as programming becomes more widespread, learning to code has emerged as a popular trend. Coding basics are now being incorporated into K-12 education in many countries [6,7], with Microsoft founder Bill Gates advocating coding as a “basic skill that every student should learn in the 21st century” [8], leading to an expanding demographic of learners. However, learning to code is challenging [9,10], with beginners often struggling with complex logic and tedious fundamentals, spending considerable time and effort. The emergence of AI-assisted programming tools has begun to make learning and applying programming easier [11]. The OpenAI Codex model has been shown to perform well in solving programming tasks presented in simple English, with researchers finding that AI tools like Codex can achieve excellent results in various introductory programming tests [12,13]. Recent studies focusing on the use of AI-assisted programming tools among beginners have found that groups using AICATs perform better [14], significantly improving task completion rates, accuracy scores, reducing encountered errors, and shortening task completion times.
While AI-assisted programming tools have been validated for their positive effects on learning and applying programming, societal concerns have emerged regarding the use of such tools. These include complex ethical issues encountered during the use of AI-assisted programming tools [15], problems related to users’ over-reliance [11], and the sustainability of programming education [3]. Developers of AI-assisted programming tools also express concerns that their models could be misused, highlighting the need to guard against potential risks and harms [11,16]. In the future, whether users will choose to use AICATs will become a focal point for developers. Users’ willingness to use is influenced by multiple factors, necessitating further research and surveys to clarify the key factors impacting their willingness. Effective studies on user acceptance can provide insights for the development and updates of AI programming tools.
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), proposed by Davis based on the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), hypothesizes that external variables influence users’ usage intentions through perceived usefulness and ease of use, ultimately leading to actual usage behavior [17]. The TAM model is one of the most commonly used models for studying user acceptance and has been found to successfully predict behavioral intentions. In the field of AI user acceptance research, the TAM model is the most flexible of all research models, allowing for the extension of its external variables or model structure through modifications [18].
Current research on AICATs primarily focuses on the tools’ algorithms and functionalities. In terms of user use, studies often compare whether using AI-assisted programming tools has an effect [14] on users or verifies the usability [19] of such tools, with relatively less research on users’ willingness to use. Users’ willingness to use is directly related to their actual usage behavior, making it an important area of research in the user experience domain of AI-assisted programming tools. Therefore, based on the widespread use of AICATs in colleges, this study aims to explore a model based on the TAM to study the factors influencing college students’ willingness to use AI-assisted programming tools and to investigate the key factors affecting users’ willingness to use. Overall, this study will focus on addressing the following questions: (1) What are the primary determinants affecting university students’ readiness to adopt AI-enhanced coding tools? (2) How do these primary determinants correlate with university students’ readiness to adopt AI-enhanced coding tools? (3) What revelations can be derived for the refinement and advancement of AI-enhanced coding tools?
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Development and Application of AI Coding Assistant Tools
People have always been seeking effective and feasible methods to simplify the programming process and facilitate programming work for users. In recent years, with the development of AI-generated content technology, attention has turned to the possibility of using artificial intelligence to drive code generation. AI Coding Assistant Tools have gradually started to be applied in actual work scenarios. Many conversational AI models also support code generation, making AI-assisted programming tools more accessible to the general public. Meanwhile, code-completion AI programming tools, represented by GitHub Copilot, have begun to be used in programming work in a more tool-oriented form. These AI-assisted programming tools, trained on vast amounts of data, make more efficient and convenient programming possible. Codex, for instance, was trained on over 50 million GitHub repositories, covering the vast majority of GitHub’s code [11]. AlphaCode, released in 2022, was trained on over 715 GB of GitHub code, including programs written in C++, C#, Java, and other languages [16]. AI-assisted programming tools can customize programming tutorials for users outside the computer field, visualize complex code data, make it easier for users to take over and inherit legacy code, and learn new programming languages [20]. While AI-assisted programming tools have good code interpretation capabilities, especially for learners, they may also lead to low-quality code containing errors or security vulnerabilities [21]. This is because most AI-assisted programming tool models include risky and erroneous code [11] data in their training. For example, Copilot is based on a large language model trained on open-source code, including some unsafe codes, thus there is a possibility of generating code with these errors [22]. Therefore, the current stage of AI-assisted programming tool use entails both convenience and risk for users.
Previous research has mostly focused on the usability testing and verification of AI-assisted programming tools [12], providing insights into the benefits and issues of using these tools. However, there is almost no research exploring AI-assisted programming tools with a focus on user willingness to use them. As AI-assisted programming continues to develop, AICATs will provide significant help to users. What factors users will base their use or rejection of AICATs on, and what aspects AICATs should be updated and developed in to gain broader use, will be issues of concern in the field of AICAT user experience research for some time to come, and are the themes of this paper.
2.2. The Technology Acceptance Model
The Technology Acceptance Model is widely used to explain research on the adoption or acceptance behavior of information technology. According to TAM, perceived ease of use and usefulness are seen as two important factors that explain usage intention [23]. Furthermore, since its inception, many external variables have been added to TAM to better explain and predict the acceptance and use intentions of information technology systems [24]. By considering various external influencing factors on users, the TAM model can better understand users’ acceptance of new technologies. In the field of user acceptance of AI products, the TAM model has a broad base of use [25]. For example, Svenja Mohr et al. [26] introduced factors such as property rights over business data and personal innovativeness to extend TAM, exploring the behavioral factors affecting the acceptance of AI in German agriculture. Kang [27] introduced learning motivation as an intermediary variable to extend the TAM model, investigating the determinants affecting university students’ use of artificial intelligence systems. Xu [28] and colleagues proposed an expanded model based on TAM to study the factors affecting users’ use of AI painting systems.
However, although the TAM model has been widely applied in the field of AI, no research has been found applying the TAM model in the discussion of user acceptance of AICATs. Therefore, this study aims to propose an expanded model based on TAM, combined with the characteristics of users using AICATs, to explore the key factors influencing users’ willingness to use AI-assisted programming tools. It offers suggestions for the development and update direction of AICATs and expands the application of the TAM model in the field of AI.
3. Research Hypotheses and Research Model
3.1. Research Hypotheses
3.1.1. Perceived Trust (PT)
Perceived trust encompasses users’ belief about the reliability and credibility of technology [29]. This trust convinces users that employing the technology will meet their objectives [30]. It has been established as a crucial factor affecting users’ adoption of new technologies [31]. As artificial intelligence technology develops widely, users’ trust in artificial intelligence technology plays a significant role in their acceptance of it [32]. Previous research on users’ willingness to adopt AI technology, identified trust as a fundamental precondition for usage behavior. This element has been integrated into the Technology Acceptance Model to predict behavioral intentions. In the context of using AICATs, the quality of the code generated depends heavily on the accuracy and stability of its underlying large language model (LLM) [21,33]. Consequently, AI-generated code might also suffer from quality issues, which raises concerns among users. Based on these observations, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1a (H1a).
Users’ perceived trust in AICATs will positively affect their perceived usefulness of AICATs.
Hypothesis 1b (H1b).
Users’ perceived trust in AICATs will positively affect their perceived ease of use of AICATs.
3.1.2. Perceived Risk (PR)
Perceived risk refers to users’ beliefs [34] about potential and uncertain negative effects. Perceived risk is an important predictor of users’ acceptance of technology and systems [35]. In previous research, perceived risk was considered an important condition affecting the acceptance of innovative technologies [36]. While AI-assisted programming brings convenience, it also raises concerns. AI code generation has introduced security issues, with Codex developers noting that their tool “brings significant security adjustments, does not always generate code that meets users’ intentions, and could be misused.” [11]. The use of AI to automatically generate code has also raised ethical issues regarding academic integrity and code reuse [3]. Unauthorized use of copyright-protected code also raises fairness issues regarding AICAT development [37]. These aspects bring potential risks to users of AICATs. In past findings, perceived risk has been proven to be negatively related to the attitude towards using technology [38]. Therefore, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2a (H2a).
Users’ perceived risk of AICATs will negatively affect their perceived trust in AICATs.
Hypothesis 2b (H2b).
Users’ perceived risk of AICATs will negatively affect their perceived usefulness of AICATs.
Hypothesis 2c (H2c).
Users’ perceived risk of AICATs will negatively affect their perceived ease of use of AICATs.
3.1.3. Dependence Worry (DW)
In this study, dependence worry refers to users’ concerns about becoming overly reliant on AICATs to the point of being unable to make correct judgments and considerations. A study from Microsoft Research [39] suggests that an important goal in the design of AI systems is to foster appropriate reliance on AI. In this context, over-dependence on artificial intelligence is defined as users accepting incorrect AI advice, leading to subjective judgment errors. Over-dependence often occurs when users are uncertain about the extent to which they should trust AI. One of the main risks of AI-generated code in practice is users’ over-reliance [11]. In the process of using AICATs, due to the convenience of AI-generated code, students, especially novices, can easily become overly dependent and reflexively copy and paste it into their projects without questioning its correctness [20]. This phenomenon is detrimental to the learning and sustainable development of programming skills. At the educational level, it has become habitual for university students to use AICAT products, which raises concerns among educators. Earlier studies have also noted that students and educators are particularly prone to over-reliance on artificial intelligence, speaking to concerns about higher education [40]. This dependence on artificial intelligence could also lead to a loss of cognitive abilities and a decrease in enthusiasm among students [41]. These negative effects of overreliance on AI products may lead to skepticism and apprehensive attitudes towards using these products, especially among users who are programming learners. Therefore, from the perspective of sustainable development and skill training, concerns about over-reliance on AICATs might lead to a decrease in users’ trust in AICATs or an increased perception of the risks associated with sustainability issues in use, thus refusing to use the technology. Hence, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 3a (H3a).
Users’ dependence worry about AICATs will negatively affect their perceived trust in AICATs.
Hypothesis 3b (H3b).
Users’ dependence worry about AICATs will positively affect their perceived risk of AICATs.
3.1.4. Self-Efficacy (SE)
Self-efficacy refers to the confidence of users in their knowledge and skills to complete tasks using the technology and to overcome any difficulties [42]. Historically, self-efficacy has been applied in research related to learning [43,44]. Self-efficacy reflects individuals’ beliefs in their capability to successfully execute tasks [45]. The acceptance and use of technology are significantly influenced by self-efficacy. In programming learning, novices often feel overwhelmed by complex coding tasks [46], leading to feelings of frustration and demoralization, especially in the early stages of learning, where repeated failures can reduce learners’ self-efficacy in programming [47]. Compared to traditional programming tools, AICAT often helps users enhance their programming efficiency and complete complex code generation. Studies on the support effect of AI code generators for novices have found that using AI code generation can significantly improve task completion rates, increase correctness scores, reduce errors, and shorten the time to complete tasks [14]. For proficient programmers, AICAT provides a more efficient coding experience and eliminates many tedious and basic tasks. Professionals find using AICAT intuitive and enjoy this productive approach [48]. Amid the widespread concern about dependency on AICAT, users with high self-efficacy usually possess advanced programming skills and concerns about not mastering programming independently or needing AICAT are typically unfounded. Therefore, they have fewer concerns about the negative impacts of over-reliance on AICAT. At the same time, while AICAT is easier to use and more accessible for beginners compared to traditional programming tools, it still requires a basic understanding of programming knowledge and logical thinking. As such, users with low self-efficacy are likely to be learners or beginners in programming. These users often have a stronger need and goal to master programming skills, hence they may experience more intense concerns about dependency while using AICAT. Thus, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 4a (H4a).
Users’ self-efficacy regarding AICATs will negatively affect their dependence worry about AICATs.
Hypothesis 4b (H4b).
Users’ self-efficacy regarding AICATs will positively affect their perceived ease of use of AICATs.
3.1.5. Perceived Usefulness (PU)
Perceived usefulness refers to the extent to which a person believes that using a specific system will enhance his/her job performance [23]. Previous research has demonstrated that perceived usefulness has a direct impact on users’ behavioral intention to use a technology [49]. Perceived usefulness is considered one of the most motivational factors in IT adoption [50]. Hence, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
Users’ perceived usefulness of AICATs will positively affect their intention to use AICATs.
3.1.6. Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU)
Perceived ease of use refers to the degree to which a user believes that using a specific system will be effort-free [23]. AI-assisted programming makes it easier for novice and non-professional users to get started with operating systems and features, providing a simple and understandable programming experience, thereby enhancing users’ propensity to use the technology. Previous research has shown that perceived ease of use has a positive impact on perceived usefulness [24]. Perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use, as two core constructs in the TAM model, have been widely studied and are considered to influence users’ attitudes and behavioral intentions to adopt new technologies [51]. Therefore, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 6a (H6a).
Users’ perceived ease of use of AICATs will positively affect their perceived usefulness of AICATs.
Hypothesis 6b (H6b).
Users’ perceived ease of use of AICATs will positively affect their behavioral intention to use AICATs.
3.2. Research Model
Based on the aforementioned hypotheses (see Table 1), this study proposes a research model focused on users’ willingness to use AICATs, with perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and behavioral intention as the basic variables. Through literature review and analysis of past research, four external variables were derived and established: perceived trust, perceived risk, self-efficacy, and dependence worry. Taking into account the characteristics of AICATs, an integrated framework for studying user willingness to use was constructed, as shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Research hypotheses.
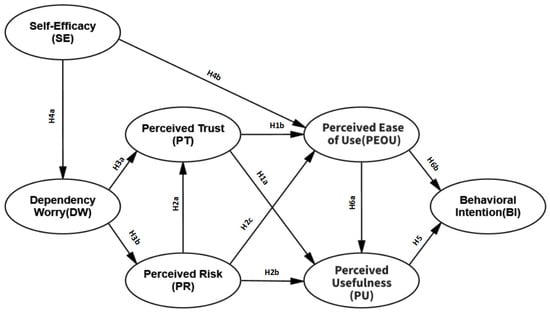
Figure 1.
Proposed conceptual model.
4. Methods
4.1. Questionnaire Design
To empirically validate the research model we proposed, we chose to conduct further studies through an online survey. At the beginning of the questionnaire, we briefly introduced the respondents to AICATs. The questionnaire for this study is divided into two parts. The first part collects basic information about the respondents, including gender, age, grade, academic major, familiarity with programming, awareness of AICATs, and usage situations. We have surveyed the nine most common AICATs currently available on the market. By investigating how users interact with these AICATs, we aim to gain further insight into the general usage patterns of AICATs and the users’ familiarity with them. Additionally, it should be noted that the focus of this survey is specifically on the programming assistance features of these AICAT products, not their other functionalities. The second part of the questionnaire consists of scales. The scales mix 5-point and 7-point Likert scales, and the items are randomly ordered. This questionnaire includes 7 variables, with 3–5 measurement items for each variable, totaling 25 items. The questionnaire scale section is adapted and modified based on the previous literature, with detailed content and references provided in Table 2. To ensure that the questionnaire is clear, understandable, and unambiguous in both its questioning style and content, a small-scale pre-test was conducted before the official survey. A total of 30 pre-test questionnaires were collected, and follow-up was conducted with the respondents, leading to further adjustments and modifications to the questionnaire scales. This pilot test also indicates that the questionnaire is suitable for larger-scale surveys. We assured participants that all data would be used solely for academic research, and their identity information would remain confidential.

Table 2.
Questionnaire for variable items and reference.
4.2. Data Collection
On 4 March 2024, a total of 303 questionnaires were administered using the online platform Qualtrics. The study focused on college students familiar with AICAT, thus surveys from respondents answering “No” to the question “Have you ever heard of AI programming?” were discontinued. Of these, 18 participants unfamiliar with AICAT represented 5.9% of all responses. Criteria for a valid questionnaire included the following: a minimum completion time of 120 s, as quicker responses were deemed unreliable; exclusion of surveys with consistent answers or apparent contradictions, leading to the removal of 52 invalid questionnaires. Consequently, 251 valid questionnaires were obtained, yielding an effective response rate of 83%. All participants provided written informed consent. This study was sanctioned by the Academic and Ethics Committee of Guangdong University of Technology (No. GDUTXS2024100).
Descriptive statistics were applied to the 251 valid questionnaires (Table 3) using SPSS 27. Demographic and academic profiles revealed 162 males (64.5%) and 89 females (35.5%); educationally, 1.6% were below undergraduate level, 95.6% were undergraduates, and 2.4% were postgraduates. By major, 13.5% studied humanities, 50.6% were in non-computer science STEM fields, 23.9% were in computer science, and 12% were in other disciplines. Regarding self-assessed programming proficiency, 50.6% were beginners, 30.3% intermediate, 14.3% familiar, 3.6% proficient, and 1.2% expert.

Table 3.
Demographic characteristics of the respondents.
The respondents’ awareness of AICAT is shown in Table 4, with 13.5% having only heard of AI programming but not having used it, while the rest had used AICAT. Among the AICATs known to the respondents, ChatGPT had the highest proportion at 87.6%, followed by Copilot (including Copilot Chat) at 21.9%, with the rest accounting for less than 10% each (multiple-choice item). Notably, ChatGPT was launched by OpenAI on 30 November 2022. According to Baidu Index data, from its launch date to 14 March 2024, ChatGPT had an average daily search index of 61,204. Copilot was launched by Microsoft on 16 September 2023, and since its launch, the Baidu Index was only 3104, indicating that the distribution of AI programming software samples known to the respondents aligns with reality.

Table 4.
Percentage of exposure to and use of AI programming software.
5. Results
The data analysis of this study is mainly divided into two parts: the first step is to assess the reliability and validity of the measurement model, and the second step is to evaluate the fit of the structural equation model and the path coefficients.
5.1. Common Method Bias Assessment
Since the data for each measurement item in this study came from the same subjects, there might be a common method bias issue. Before conducting reliability and validity analysis, we first conducted Harman’s single-factor test to assess the severity of common method bias in the study. The single-factor model indicators, χ2/df = 5.257, RMSEA = 0.130, SRMR = 0.140, IFI = 0.392, CFI = 0.386, GFI = 0.524, AGFI = 0.461, and TLI = 0.345, did not meet the minimum standards for research and were significantly off the mark [66], indicating that the model fit was quite poor. This suggests that common method bias was not severe in this study. Furthermore, we treated behavioral intention as the dependent variable and the remaining variables as independent variables. We calculated the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) for the independent variables. The results showed that the VIF values for perceived trust were 1.535, perceived risk was 1.339, self-efficacy was 1.311, dependence worry was 1.346, perceived usefulness was 1.838, and perceived ease of use was 1.392. As all VIF values for these 6 independent variables fell between 1 and 10, it indicates the absence of multicollinearity among the independent variables.
5.2. Measurement Model Assessment and Multicollinearity Test
To ensure the quality of data analysis, both Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) and Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) were implemented. The effective sample size for these analyses was 251, exceeding five times the number of scale items, indicating an appropriate sample size.
Initially, reliability was examined by calculating Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and Composite Reliability (CR). As depicted in Table 5, a Cronbach’s alpha exceeding 0.7 denotes high model reliability, and a CR above 0.7 signifies robust construct reliability within the measurement model [67]. Both CR and Cronbach’s alpha values surpassed 0.7, affirming the reliability of the questionnaire.

Table 5.
Reliability and validity analysis.
Subsequently, to evaluate construct validity, the hypothesized seven-factor model was compared against three alternative models, as detailed in Table 6. The hypothesized model displayed superior fit compared to the alternatives, validating that the seven variables analyzed represent distinct constructs and confirming strong structural validity of the questionnaire. To further assess structural validity, EFA was performed, beginning with the KMO and Bartlett’s test of sphericity. The KMO value was 0.862, greater than 0.8, and Bartlett’s test value was less than 0.05 [68], indicating the sample data were suitable for EFA. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Varimax rotation were employed for extraction and rotation, with the results summarized in Table 7.

Table 6.
Multiple model comparison.

Table 7.
The component matrix extracted by PCA and rotated by Varimax method.
Convergent validity was then assessed, showing that the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) [67], except for the variable PEOU at 0.496, exceeded the threshold of 0.5 (as listed in Table 5 AVE column), which is deemed satisfactory given the proximity of PEOU’s AVE to 0.5.
Ultimately, discriminant validity was verified using the Fornell–Larcker criterion [69]. This criterion is met when the square root of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) for each construct exceeds the correlation coefficients between any pair of variables, indicating robust discriminant validity among the constructs. The AVEs and correlation coefficients for the variables involved in this research are presented in Table 8. The lowest square root of AVE observed was 0.705, while the highest correlation coefficient recorded among the variables was 0.549, thereby meeting the Fornell–Larcker criterion. This analysis underscores significant distinctions among the factors examined, thereby demonstrating strong discriminant validity.

Table 8.
Discriminant validity (Fornell–Larcker criterion).
5.3. Structural Equation Model Assessment
5.3.1. Model Fit Index
The current model’s chi-square/degree of freedom (χ2/df) was 1.506, and other indices—RMSEA at 0.045, SRMR at 0.078, IFI at 0.943, CFI at 0.943, PCFI at 0.826, GFI at 0.889, AGFI at 0.862, and TLI at 0.934—all exceeded the minimum values recommended by previous research [66], indicating the good fit of the model [70] and allowing for analysis of the model test results.
5.3.2. Model Path Analysis
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed for modeling and assessment, analyzed using IBM AMOS 24, with results shown in Table 9. According to the findings, all 12 path hypotheses of the model influencing AI programming usage intention had significant path coefficients (p < 0.05), indicating that the theoretical model’s path assumptions fully match the actual measurement data results. Among these, the path coefficients for “Dependence Worry → Perceived Risk”, “Perceived Risk → Perceived Trust”, “Self-Efficacy → Perceived Ease of Use”, and “Perceived Usefulness → Behavioral Intention” had p values less than 0.001. The path coefficients for “Self-Efficacy → Dependence Worry”, “Perceived Risk → Perceived Usefulness”, and “Perceived Ease of Use → Behavioral Intention” had p values less than 0.01, with the remaining variables’ path coefficients p values less than 0.05.

Table 9.
Path coefficients of the structural equation model.
Finally, we marked the path coefficients and their significance levels on the SEM diagram, as shown in Figure 2.
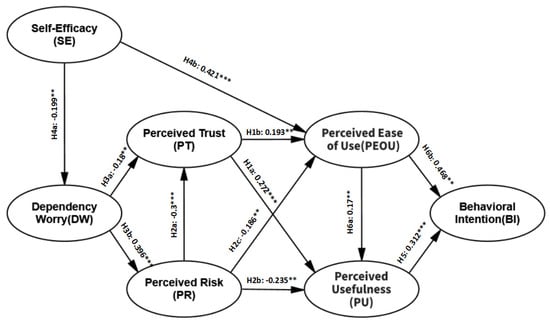
Figure 2.
Results of the structural model test. Note: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
5.3.3. Mediation Effect Analysis
From Figure 2, it is evident that the dependent variable of the model is behavioral intention, and the independent variable is self-efficacy. We aim to investigate the mediating effects from self-efficacy to behavioral intention in order to reveal how users’ sense of self-efficacy specifically influences their behavioral intentions. Therefore, we analyzed all 11 paths from self-efficacy to behavioral intention in Table 10 using the bootstrap method, with 5000 resamples at a 95% confidence level. The results in Table 11 show that the total mediating effect is 0.183. Except for Path 6, where the p-value is greater than 0.05, the p-values for the other paths are all less than 0.05, with confidence intervals that do not cross zero, achieving significance. Among these, Path 1 has the highest mediating effect at 0.132, followed by Path 2 at 0.028, while Paths 10 and 11 have smaller mediating effects, both less than 0.0016.

Table 10.
Mediating effect paths and path names.

Table 11.
Mediating effect analysis.
6. Discussion and Implication
6.1. Discussion of Results
This study aimed to identify the key factors that influence college students’ willingness to adopt AI-assisted programming tools. Firstly, the study found that the external variable perceived trust has a significant positive impact on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use, corroborating prior research [31,71]. In the realm of AI applications, building user trust is vital for promoting their adoption [35]. The greater the trust, the more likely users are to accept AI services [72]. For AI-assisted programming tools, increased user trust translates into greater confidence in the tools’ functionalities, which in turn enhances their willingness to use these tools.
Conversely, perceived risk has a significant negative impact on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use, in line with earlier findings [73]. Users’ apprehensions about the risks associated with using AI-assisted coding tools (AICAT) significantly deter their usage. Security vulnerabilities and the potential low quality of generated code are major concerns, prompting users to prioritize these risks when considering AICAT. Developers can mitigate these concerns by improving the code data purity used in model training, enhancing AICAT function transparency, and making the code’s generation process more interpretable, thus fostering a greater willingness to use AICAT.
Additionally, dependence worry, as a new external variable proposed affecting AICAT use, which has been shown to impact perceived trust and perceived risk positively and negatively, respectively. This view of risk concerns about AICAT aligns with previous research [11]. This situation is more prominent among college students, who have learning and skill needs and may unconsciously rely on tools when using AI-assisted programming tools, which is sometimes detrimental to learners, even though reliance often indicates trust in the product. Therefore, for learners and similar groups, developers can offer more suitable learning modes, respond to users’ needs for code-learning capability enhancement, and reduce users’ dependence worries.
Moreover, self-efficacy has a negative impact on dependence worry and a significant positive impact on perceived ease of use, which also aligns with previous research findings [74,75,76]. Compared to traditional programming learning and development, using AICAT for code work has a lower barrier to entry and is easier to start, resulting in less frustration for users during the process due to higher self-efficacy. When dealing with users who have low self-efficacy, it is often because these users are beginners or have a strong need to learn and master programming skills, which results in greater dependency and anxiety. Therefore, while enhancing the ease of use and convenience of AICAT functions, developers can also adjust the product’s operation mode according to users’ personal demands or familiarity with the code.
Both perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use positively influence user willingness to adopt AICAT, a finding supported by numerous studies [23,77,78,79]. This underscores the importance of these factors in enhancing user engagement with AICAT. Drawing on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), this research integrates specific external factors (perceived trust, perceived risk, self-efficacy) into a model tailored for AICAT user experience research, thereby exploring how these factors interplay and affect user attitudes towards AICAT’s perceived usefulness and ease of use. Going forward, developers should focus on refining AICAT’s usability and ease of use based on these insights to boost user adoption rates. Concurrently, while developing digital business models that adapt to the new technological environment [80,81], further refinement of AICAT’s user service system can be carried out to enhance the product’s user experience. Although AICAT has significantly improved user experience over traditional programming interfaces, it introduces new challenges. Maintaining a balance between ease of programming, product sustainability, and risk management is essential for fostering and enhancing user trust in AICAT. Regarding the implementation of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), this research has effectively integrated the TAM model into user studies concerning AICAT, thus extending the model’s applicability within the realm of artificial intelligence products. This expansion not only underscores the versatility of the TAM model in AI product user research but also offers valuable insights for its potential application in a wider array of AI product studies in the future.
6.2. Implication
This study provides valuable theoretical contributions to the user experience in the domain of AI Coding Assistant Tool (AICAT), providing significant insights for their ongoing development and refinement. Reviewing past research, although TAM theory has been widely applied in the field of AI products, there has been relatively little exploration and analysis specifically for AICAT, which has emerged in recent years. Building on TAM, this research introduces perceived trust and perceived risk with self-efficacy and dependence worry as pivotal external variables, thereby creating a novel user acceptance model for AICAT. The model’s validation revealed that users, particularly college students surveyed in this study, recognize AICAT’s functionality as highly convenient but are also apprehensive about potential sustainability risks, notably those associated with dependence worry. These findings suggest avenues for AICAT’s further refinement, emphasizing the necessity to address users’ educational and long-term development needs alongside their immediate needs for efficient programming. By mitigating users’ fears about becoming overly reliant on AICAT due to concerns about personal skill advancement, this research also informs the broader development of AI products, concentrating on alleviating user anxieties related to dependency on AI technologies. Although this research primarily investigated college students, their patterns of using AICAT closely align with those of the platform’s main user base. Both demographics are unified by their objectives to either acquire or enhance programming skills. Developers can capitalize on the shared characteristics between college and non-college users in their engagement with AICAT. By doing so, they can use these insights to iteratively refine AICAT products, thereby more effectively addressing the needs of their users.
In summary, the results of this study identified key factors influencing college students’ willingness to use AI-assisted programming tools (perceived trust, perceived risk, self-efficacy, and dependence worry), and validated the relationships and impact among these factors. These key factors can be extended to a broader user group, providing suggestions in the user experience dimension for the development and improvement of AICAT. In future developments, AICAT developers can continuously enhance the user experience of AICAT, strengthen users’ trust in AICAT, and gain broader promotion and recognition based on the results of this study and real user feedback.
6.3. Limitation and Future Research
This study presents several limitations. Primarily, the sample is largely composed of college students, who may not accurately represent the core users of AICAT in various contexts. Moreover, the data predominantly originate from China, highlighting the necessity for more heterogeneous samples to affirm the broader applicability of our findings. Future studies should aim to collect data from multiple countries and regions to diversify the study’s participants and enhance the representativeness of the results. Second, this study predominantly utilized an online questionnaire, garnering only 251 valid responses. Subsequent research should increase the quantity of questionnaires and incorporate other research methods, such as interviews or experiments, to gain a deeper understanding of users’ needs and feedback.
7. Conclusions
This study, focusing on college students as the primary research group and based on TAM theory, explored key factors influencing users’ willingness to use AICAT. The findings reveal that users’ willingness to use AICAT is mainly influenced by perceived trust and perceived risk. More specifically, it is affected by users’ self-efficacy and dependence worry. Users’ dependence worry has a positive impact on perceived risk, while perceived risk negatively affects users’ perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. Users’ self-efficacy negatively impacts their dependence worry but positively affects perceived ease of use. This suggests that users’ willingness to use AICAT is often influenced by their trust in the product and their risk assessment, with the sustainability of skill learning also being an important moderating factor for the learner group. Overall, these findings provide suggestions in the user experience dimension for AICAT developers and offer insights for the future development of AICAT.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.P., Z.X. and T.L.; methodology, Z.P.; software, Z.X.; validation, Z.P., Z.X.; formal analysis, Z.X.; investigation, Z.P.; resources, Z.P.; data curation, Z.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.P.; writing—review and editing, T.X. and T.L.; visualization, Z.X.; supervision, T.X.; project administration, Z.P. and T.L.; funding acquisition, T.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the National Social Science Foundation of China (18BYY089), the Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Fund Project of the Ministry of Education (19YJCZH123), and Key Project of Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Strategy Special Fund (University Student Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation, No. pdjh2024a139).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was reviewed and approved by Academic and Ethics Committee of Guangdong University of Technology (approval number: GDUTXS2024100).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the participants to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- OpenAI. ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue. OpenAI. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Harrison Dupré, M. ChatGPT’s Explosive Popularity Makes It the Fastest-Growing App in Human History. Futurism. 3 February 2023. Available online: https://futurism.com/the-byte/chatgpts-fastest-growing-app-human-history (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Becker, B.A.; Denny, P.; Finnie-Ansley, J.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J.; Santos, E.A. Programming Is Hard—Or at Least It Used to Be. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, H.; Ahmad, B.; Tan, B.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Karri, R. Asleep at the Keyboard? Assessing the Security of GitHub Copilot’s Code Contributions. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2022; pp. 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A Preliminary Investigation into Computer Assisted Programming; The University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Popat, S.; Starkey, L. Learning to Code or Coding to Learn? A Systematic Review. Comput. Educ. 2019, 128, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.; Davis, N.; Bell, T.; Katz, Y.J.; Reynolds, N.; Chambers, D.P.; Sysło, M.M. Computer Science in K-12 School Curricula of the 2lst Century: Why, What and When? Educ. Inf. Technol. 2016, 22, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, B. Strengthening American Competitiveness for the 21st Century. Yearb. Natl. Soc. Study Educ. 2008, 107, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Boulay, B. Some Difficulties of Learning to Program. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 1986, 2, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lehman, J. Students’ Misconceptions and Other Difficulties in Introductory Programming. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. 2017, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; de Oliveira Pinto, H.P.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G.; et al. Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code. arxiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03374. [Google Scholar]
- Finnie-Ansley, J.; Denny, P.; Becker, B.A.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J. The Robots Are Coming: Exploring the Implications of OpenAI Codex on Introductory Programming. In Proceedings of the 24th Australasian Computing Education Conference, Virtual Event, 14–18 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie-Ansley, J.; Denny, P.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Santos, E.A.; Prather, J.; Becker, B.A. My AI Wants to Know If This Will Be on the Exam: Testing OpenAI’s Codex on CS2 Programming Exercises. In Proceedings of the 25th Australasian Computing Education Conference, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 30 January–3 February 2023; 3 February 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemitabaar, M.; Chow, J.; Carl, M.; Ericson, B.J.; Weintrop, D.; Grossman, T. Studying the Effect of AI Code Generators on Supporting Novice Learners in Introductory Programming. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon; Sheard, J.; Morgan, M.; Petersen, A.; Settle, A.; Sinclair, J.; Cross, G.; Riedesel, C. Negotiating the Maze of Academic Integrity in Computing Education. In Proceedings of the 2016 ITiCSE Working Group Reports, Arequipa, Peru, 9–13 July 2016; pp. 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Choi, D.; Chung, J.; Kushman, N.; Schrittwieser, J.; Leblond, R.; Eccles, T.; Keeling, J.; Gimeno, F.; Dal Lago, A.; et al. Competition-Level Code Generation with AlphaCode. Science 2022, 378, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. A Technology Acceptance Model for Empirically Testing New End-User Information Systems: Theory and Results. Doctoral Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/15192 (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Kelly, S.; Kaye, S.-A.; Oviedo-Trespalacios, O. What Factors Contribute to Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence? A Systematic Review. Telemat. Inform. 2022, 77, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayagopal, D.; Lubin, J.; Chasins, S. Exploring the Learnability of Program Synthesizers by Novice Programmers. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Bend, OR, USA, 29 October—2 November 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.J. Six Opportunities for Scientists and Engineers to Learn Programming Using AI Tools such as ChatGPT. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2023, 25, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler, J.A. Understanding the Limits of AI Coding. Science 2023, 379, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub Copilot Your AI Pair Programmer. GitHub Copilot. Available online: https://copilot.github.com/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Davis, F. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikou, S.A.; Economides, A.A. Mobile-Based Assessment: Investigating the Factors That Influence Behavioral Intention to Use. Comput. Educ. 2017, 109, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.C.; Su, X.; Lin, Z.; He, Y.; Luo, N.; Zhang, Y. Determinants of Technology Acceptance: Two Model-Based Meta-Analytic Reviews. Journal. Mass Commun. Q. 2020, 98, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, S.; Kühl, R. Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence in German Agriculture: An Application of the Technology Acceptance Model and the Theory of Planned Behavior. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 1816–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K. Determinants of College Students’ Actual Use of AI-Based Systems: An Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yoo, C.; Pan, Y. Is Everyone an Artist? A Study on User Experience of AI-Based Painting System. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaci, I. Understanding and Predicting Students’ Intention to Use Mobile Cloud Storage Services. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 58, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asan, O.; Bayrak, A.E.; Choudhury, A. Artificial Intelligence and Human Trust in Healthcare: Focus on Clinicians. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e15154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Tao, D. The Roles of Trust, Personalization, Loss of Privacy, and Anthropomorphism in Public Acceptance of Smart Healthcare Services. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 127, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, H.; David, P.; Ross, A. Trust in AI and Its Role in the Acceptance of AI Technologies. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2022, 39, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.-F.; Guo, S.; Hang, C.-N.; Ho, S.-W.; Tan, C.-W. Natural Language Generation and Understanding of Big Code for AI-Assisted Programming: A Review. Entropy 2023, 25, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, P.-C. The Interrelationship between Intelligent Agents’ Characteristics and Users’ Intention in a Search Engine by Making Beliefs and Perceived Risks Mediators. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 64, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pu, Q.; Liu, N. More Trust or More Risk? User Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence Virtual Assistant. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Ind. 2023, 34, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Shim, J.P. Examining Multi-Dimensional Trust and Multi-Faceted Risk in Initial Acceptance of Emerging Technologies: An Empirical Study of Mobile Banking Services. Decis. Support Syst. 2010, 49, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelty, C.M. Culture’s Open Sources: Software, Copyright, and Cultural Critique. Anthropol. Q. 2004, 77, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Oliveira, T.; Popovič, A. Understanding the Internet Banking Adoption: A Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology and Perceived Risk Application. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2014, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passi, S.; Vorvoreanu, M. Overreliance on AI: Literature Review; Microsoft. 2022. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/overreliance-on-ai-literature-review/ (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Seo, K.; Tang, J.; Roll, I.; Fels, S.; Yoon, D. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Learner–Instructor Interaction in Online Learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Han, H.; Alam, M.M.; Rehmat, M.K.; Irshad, M.; Arraño-Muñoz, M.; Ariza-Montes, A. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Human Loss in Decision Making, Laziness and Safety in Education. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compeau, D.R.; Higgins, C.A. Application of Social Cognitive Theory to Training for Computer Skills. Inf. Syst. Res. 1995, 6, 118–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiyok, E.; Gokcearslan, S.; Kucukergin, K.G. Acceptance of Educational Use of AI Chatbots in the Context of Self-Directed Learning with Technology and ICT Self-Efficacy of Undergraduate Students. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ithriah, S.A.; Ridwandono, D.; Suryanto, T.L.M. Online Learning Self-Efficacy: The Role in E-Learning Success. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1569, 022053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hall, N.C.; Rahimi, S. Self-Efficacy and Causal Attributions in Teachers: Effects on Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Illness, and Quitting Intentions. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2015, 47, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Merrienboer, J.J.G.; Kirschner, P.A.; Kester, L. Taking the Load off a Learner’s Mind: Instructional Design for Complex Learning. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 38, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.; Simon, B. CS Majors’ Self-Efficacy Perceptions in CS1. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop on Computing education research, Providence, RI, USA, 8–9 August 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valový, M.; Buchalcevova, A. The Psychological Effects of AI-Assisted Programming on Students and Professionals. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution, Bogotá, Colombia, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Nicolás, C.; Molina-Castillo, F.J.; Bouwman, H. An Assessment of Advanced Mobile Services Acceptance: Contributions from TAM and Diffusion Theory Models. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, E.; Gumussoy, C.A.; Calisir, F. Examining the Factors Affecting PDA Acceptance among Physicians: An Extended Technology Acceptance Model. J. Healthc. Eng. 2015, 6, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-F.; Yen, S.-N. Towards an Understanding of the Behavioral Intention to Use 3G Mobile Value-Added Services. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2009, 25, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, N. The Acceptance of Smart Home Technology; University of Twente: Enschede, The Nederland, 2018; Available online: https://purl.utwente.nl/essays/75338 (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Lean, O.K.; Zailani, S.; Ramayah, T.; Fernando, Y. Factors Influencing Intention to Use E-Government Services among Citizens in Malaysia. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2009, 29, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A Theoretical Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four Longitudinal Field Studies. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcknight, D.H.; Carter, M.; Thatcher, J.B.; Clay, P.F. Trust in a Specific Technology. ACM Trans. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2011, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherman, M.S.; Pavlou, P.A. Predicting E-Services Adoption: A Perceived Risk Facets Perspective. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Todd, P.A. Understanding Information Technology Usage: A Test of Competing Models. Inf. Syst. Res. 1995, 6, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, A. Understanding Information Systems Continuance: An Expectation-Confirmation Model. MIS Q. 2001, 25, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, S.E. Problematic Internet Use and Psychosocial Well-Being: Development of a Theory-Based Cognitive–Behavioral Measurement Instrument. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2002, 18, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. Online Social Networking and Addiction--a Review of the Psychological Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 3528–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-García, W.C.; Sairitupa-Sanchez, L.Z.; Morales-García, S.B.; Morales-García, M. Development and Validation of a Scale for Dependence on Artificial Intelligence in University Students. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1323898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kozar, K.A.; Larsen, K.R.T. The Technology Acceptance Model: Past, Present, and Future. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, J. Enhancing User Experience with Conversational Agent for Movie Recommendation: Effects of Self-Disclosure and Reciprocity. Int. J. Hum. -Comput. Stud. 2017, 103, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2002388 (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance Structure Analysis: Conventional Criteria versus New Alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling: Rigorous Applications, Better Results and Higher Acceptance. Long Range Plan. 2013, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F. Multivariate Data Analysis; Kennesaw State University: Arlington, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Torrent-Sellens, J.; Jiménez-Zarco, A.I.; Saigí-Rubió, F. Do People Trust in Robot-Assisted Surgery? Evidence from Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Xue, J.; He, M.; Gu, J.; Lin, H.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y. Psychosocial Factors Affecting Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Health Care in China: Cross-Sectional Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e14316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, P. Evaluating Initial Public Acceptance of Highly and Fully Autonomous Vehicles. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2019, 35, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luarn, P.; Lin, H.-H. Toward an Understanding of the Behavioral Intention to Use Mobile Banking. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2005, 21, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Tang, T. Determinants of User Acceptance of Internet Banking: An Empirical Study. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 2003, 14, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Mattila, A.S.; Eva Tao, L. The Role of Post-Training Self-Efficacy in Customers’ Use of Self Service Technologies. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 2008, 19, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Wong, W.-M.; Tam, K.-Y. Determinants of User Acceptance of Digital Libraries: An Empirical Examination of Individual Differences and System Characteristics. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2002, 18, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, E.; Kaarstad, M.; Eitrheim, M.H.R.; Bisio, R.; Reegård, K.; Bloch, M. A Conceptual Model of Trust, Perceived Risk, and Reliance on AI Decision Aids. Group Organ. Manag. 2022, 47, 187–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Workman, J.E. Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Fashion: Are Consumers Ready? Cloth. Text. Res. J. 2019, 38, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, G.; Del Sarto, N.; Piccaluga, A.; Baroncelli, A. Industry 4.0 Base Technologies and Business Models: A Bibliometric Analysis. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2023, 26, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, G.; Crupi, A.; Di Minin, A.; Ritala, P. 50+ Years of R&D Management: A Retrospective Synthesis and New Research Trajectories. R D Manag. 2023, 53, 900–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).