The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks on Industrial Development: Evidence from the Automobile Manufacturing Industry in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Geography of Knowledge Spillovers
2.2. Research on Urban Innovation Networks
2.3. Relationships between Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks and Industrial Development
3. Materials and Methods
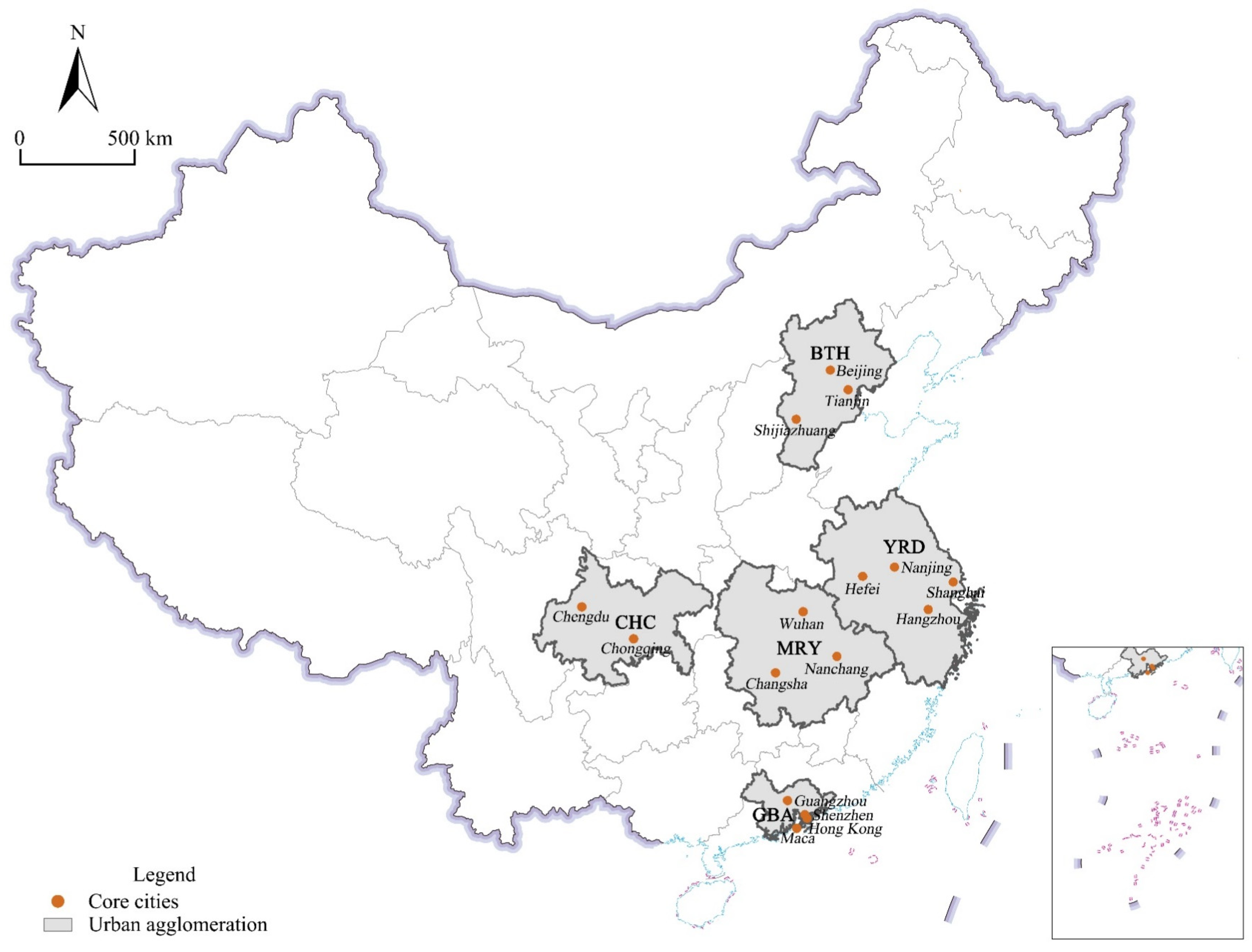
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Materials
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Constructing Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks
3.3.2. Model
4. Results
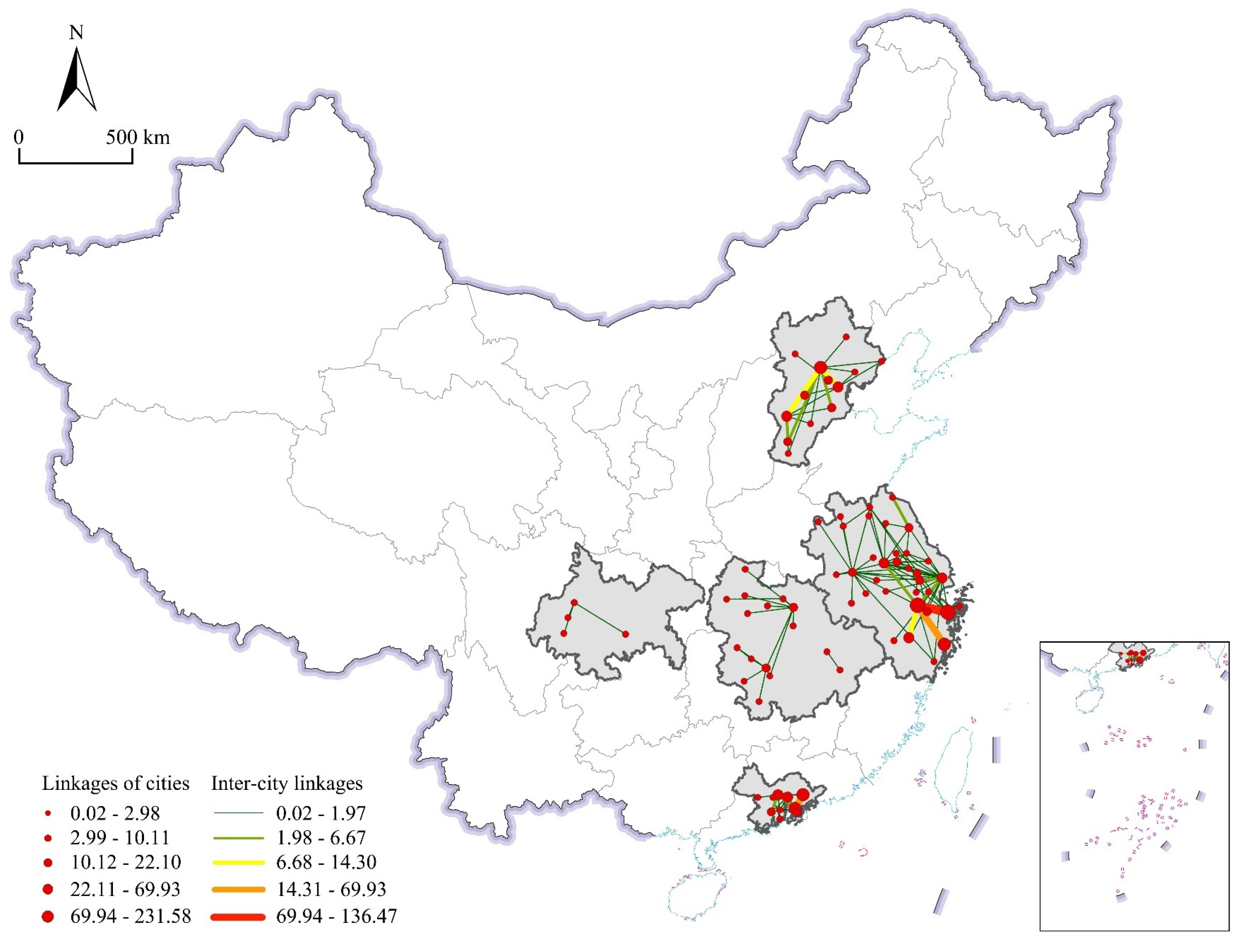
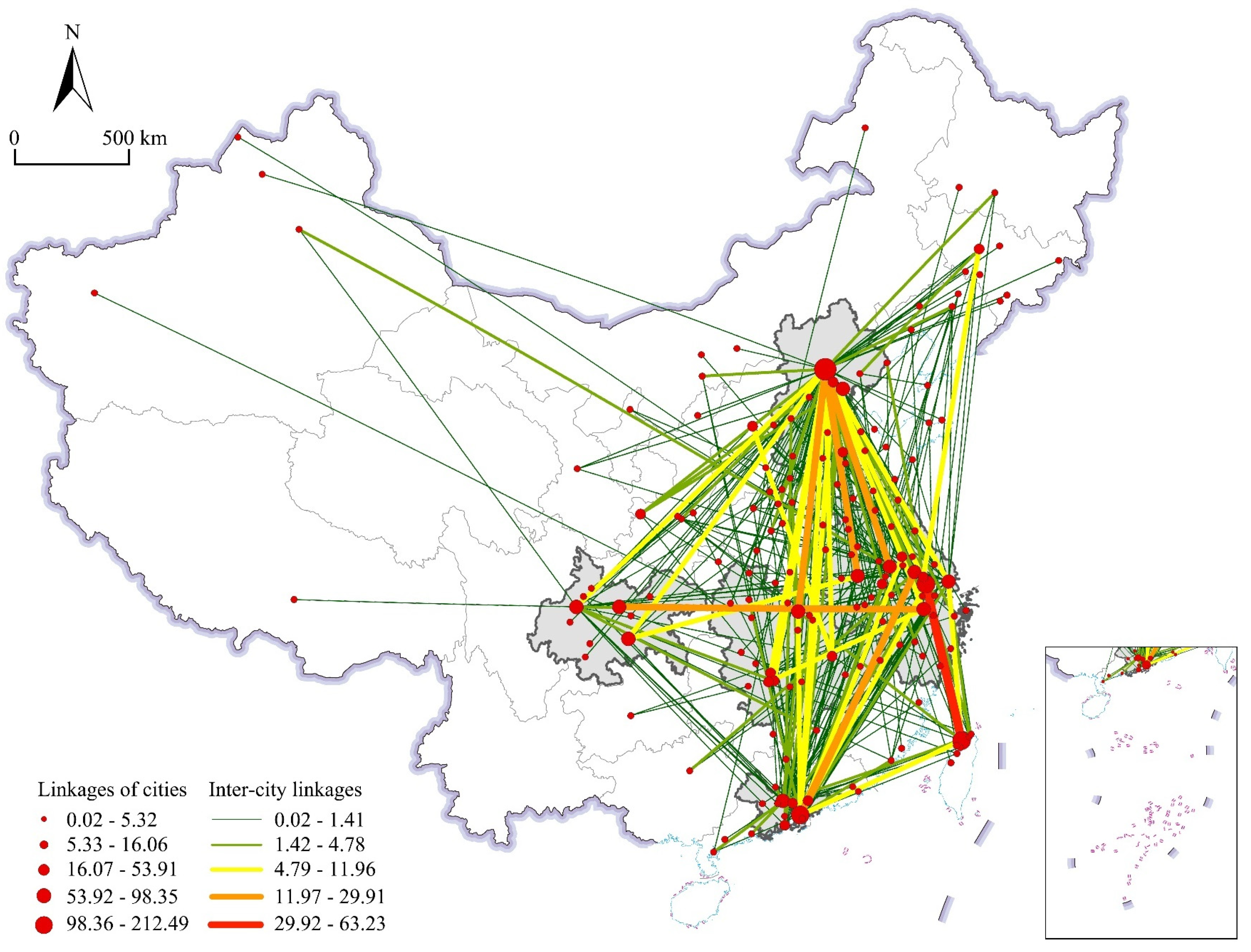
4.1. Characteristics of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks in the Automobile Manufacturing Industry of Five Urban Agglomerations
4.2. The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Innovation Networks on the Development of Automobile Manufacturing Industry
4.3. Robustness Tests
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucas, R.E. On the Mechanics of Economic-Development. J. Monet. Econ. 1988, 22, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.M. Increasing Returns and Long-Run Growth. J. Polit. Econ. 1986, 94, 1002–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.V. Understanding Knowledge Spillovers. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2007, 37, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; Miguelez, E. A Relational Approach to the Geography of Innovation: A Typology of Regions. J. Econ. Surv. 2012, 26, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Trajtenberg, M.; Henderson, R. Geographic Localization of Knowledge Spillovers as Evidenced by Patent Citations. Q. J. Econ. 1993, 108, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Feldman, M.P. R&D Spillovers and the Geography of Innovation and Production. Am. Econ. Rev. 1996, 86, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, G.; Juhasz, S.; Elekes, Z.; Lengyel, B. Repeated Collaboration of Inventors across European Regions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2021, 29, 2252–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wouden, F.; Youn, H. The Impact of Geographical Distance on Learning through Collaboration. Res. Policy 2023, 52, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H.; Malmberg, A.; Maskell, P. Clusters and Knowledge: Local Buzz, Global Pipelines and the Process of Knowledge Creation. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2004, 28, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekezi, O.; Dall’Erba, S.; Kang, D. The Role of Interregional and Inter-Sectoral Knowledge Spillovers on Regional Knowledge Creation across US Metropolitan Counties. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2022, 17, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournakis, I.; Tsionas, M. Productivity with Endogenous FDI Spillovers: A Novel Estimation Approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 251, 108546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bathelt, H. Spatial Knowledge Strategies: An Analysis of International Investments using Fuzzy Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA). Econ. Geogr. 2021, 97, 366–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, C.M.; Goncalves, E.; Freguglia, R.D.S. Knowledge Diffusion Channels in Brazil: The Effect of Inventor Mobility and Inventive Collaboration on Regional Invention. Growth Chang. 2021, 52, 909–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zheng, S.; Kahn, M.E. The Role of Transportation Speed in Facilitating High Skilled Teamwork across Cities. J. Urban Econ. 2020, 115, 103212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, M.A.; Uberti, T.E.; Usai, S. Treating Patents as Relational Data: Knowledge Transfers and Spillovers across Italian Provinces. Ind. Innov. 2011, 18, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, M.S.; Levitte, Y.M. Local Nodes in Global Networks: The Geography of Knowledge Flows in Biotechnology Innovation. Ind. Innov. 2005, 12, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippl, M.; Toedtling, F.; Lengauer, L. Knowledge Sourcing beyond Buzz and Pipelines: Evidence from the Vienna Software Sector. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 85, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Derudder, B.; Dai, L.; Peng, Z. ‘Buzz-and-pipeline’ Dynamics in Chinese Science: The Impact of Interurban Collaboration Linkages on Cities’ Innovation Capacity. Reg. Stud. 2022, 56, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, F.; Mancusi, M.L.; Montobbio, F. Innovation, International R&D Spillovers and the Sectoral Heterogeneity of Knowledge Flows. Rev. World Econ. 2013, 149, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. ‘Buzz-and-Pipeline’ Dynamics of Urban Dual Innovation: Evidence from China’s Biomedical Industry. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 158, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, C.F.; Loof, H.; Nabavi, P.; Stephan, A. A New Approach to Estimation of the R&D-Innovation-Productivity Relationship. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2017, 26, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ji, Y. Patent Actor-Network Formation from Regional Innovation to Open Innovation: A Comparison between Europe and China. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2023, 31, 925–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Albert, C.; Rubio, F.; Valero, F. Impact of Digital Transformation on the Automotive Industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 162, 120343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, A.B. Real Effects of Academic Research. Am. Econ. Rev. 1989, 79, 957–970. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Varga, A.; Acs, Z. Local Geographic Spillovers between University Research and High Technology Innovations. J. Urban Econ. 1997, 42, 422–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autant-Bernard, C.; LeSage, J.P. Quantifying Knowledge Spillovers using Spatial Econometric Models. J. Reg. Sci. 2011, 51, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R.A. Proximity and Innovation: A Critical Assessment. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balland, P.; Boschma, R. Complementary Interregional Linkages and Smart Specialisation: An Empirical Study on European Regions. Reg. Stud. 2021, 55, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, C.W.; Schwarz, A.W.; Find, S. The Top-Level Global Research System, 1997-1999: Centres, Networks and Nodality. an Analysis Based on Bibliometric Indicators. Urban Stud. 2002, 39, 903–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, C.W.; Schwarz, A.W.; Find, S. World Cities of Scientific Knowledge: Systems, Networks and Potential Dynamics. An Analysis Based on Bibliometric Indicators. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1879–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breschi, S.; Lenzi, C. Co-Invention Networks and Inventive Productivity in US Cities. J. Urban Econ. 2016, 92, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balland, P.; Boschma, R.; Crespo, J.; Rigby, D.L. Smart Specialization Policy in the European Union: Relatedness, Knowledge Complexity and Regional Diversification. Reg. Stud. 2019, 53, 1252–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Phelps, N. Megalopolis Unbound: Knowledge Collaboration and Functional Polycentricity within and beyond the Yangtze River Delta Region in China, 2014. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Phelps, N.A. Megalopolitan Glocalization: The Evolving Relational Economic Geography of Intercity Knowledge Linkages within and beyond China’s Yangtze River Delta region, 2004-2014. Urban Geogr. 2019, 40, 1310–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, X. Proximity and the Evolving Knowledge Polycentricity of Megalopolitan Science: Evidence from China’s Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, 1990–2016. Urban Stud. 2021, 58, 2405–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Phelps, N.; Tu, M. Closed or Connected? The Economic Geography of Technological Collaboration between Special Economic Zones in China’s Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou Metropolitan Area. Urban Geogr. 2023, 44, 1995–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, E.; Kumar, A. Too Much of a Good Thing? Network Brokerage within and between Regions and Innovation Performance. Reg. Stud. 2023, 57, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida, R.; Adler, P.; Mellander, C. The City as Innovation Machine. Reg. Stud. 2017, 51, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H.; Zhao, J. Conceptualizing Multiple Clusters in Mega-City Regions: The Case of the Biomedical Industry in Beijing. Geoforum 2016, 75, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H.; Cohendet, P. The Creation of Knowledge: Local Building, Global Accessing and Economic Development-toward an Agenda. J. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 14, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, W.R. Breakthrough Inventions and Migrating Clusters of Innovation. J. Urban Econ. 2010, 67, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.; Rabellotti, R.; Zirulia, L. When Do Global Pipelines Enhance the Diffusion of Knowledge in Clusters? Econ. Geogr. 2013, 89, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H. Buzz-and-Pipeline Dynamics: Towards a Knowledge-Based Multiplier Model of Clusters. Geogr. Compass 2007, 1, 1282–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, S.; Liu, F. A Foot in Two Camps or Your Undivided Attention? The Impact of Intra- and Inter-Community Collaboration on Firm Innovation Performance. Technol. Anal. Strat. 2020, 32, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R.A.; Wal, A.L.J.T. Knowledge Networks and Innovative Performance in an Industrial District: The Case of a Footwear District in the South of Italy. Ind. Innov. 2007, 14, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, C.; Schiffauerova, A. Who’s Right, Marshall or Jacobs? The Localization Versus Urbanization Debate. Res. Policy 2009, 38, 318–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, H.L.F.; Poot, J.; Smit, M.J. Which Agglomeration Externalities Matter Most and Why? J. Econ. Surv. 2016, 30, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acs, Z.J.; Anselin, L.; Varga, A. Patents and Innovation Counts as Measures of Regional Production of New Knowledge. Res. Policy 2002, 31, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, T. Knowledge Structure, Network Structure, Exploitative and Exploratory Innovations. Technol. Anal. Strat. 2020, 32, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Ke, S. The Effects of Factor Proximity and Market Potential on Urban Manufacturing Output. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 39, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, F. Technological Upgrading in Chinese Cities: The Role of FDI and Industrial Structure. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2020, 56, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H.; Turi, P. Local, Global and Virtual Buzz: The Importance of Face-to-Face Contact in Economic Interaction and Possibilities to Go beyond. Geoforum 2011, 42, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storper, M.; Venables, A.J. Buzz: Face-to-Face Contact and the Urban Economy. J. Econ. Geogr. 2004, 4, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Industry Codes and Types | The Four-Digit Code Patent Types |
|---|---|
| 36 Automobile manufacturing industry | B60K, B62D, F02B, F02D, F02M, A01D, A61G, A62C, B60F, B60P, B60V, B64D, B65F, F41H, B60L, B60M, B61D, F16F, B60B, B60D, B60G, B60J, B60N, B60R, B60S, B60T, B60W, H01R |
| Variables | Label | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Urban industrial development level | DEV | Economic census yearbooks for China and related provinces including Hebei, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Guangdong, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, and Sichuan in 2018 |
| Innovation linkages of intra-city innovation network | CITY | The CNIPA database |
| Innovation linkages of inter-city innovation networks within urban agglomerations | MEG | |
| Innovation linkages of innovation networks between cities within and beyond urban agglomerations | COU | |
| Urban industrial agglomeration level | EPAMI | Economic census yearbooks for China and related provinces including Hebei, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Guangdong, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, and Sichuan in 2018 |
| Urban economic development level | PGDP | China Urban Statistical Yearbook in 2018 |
| S&T and education investment | SE | |
| Urban industrialization level | SGDP | |
| Foreign investment | FDI |
| Geographical Scales | City | Innovation Linkages | Urban Agglomerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-city innovation networks | Beijing | 203.46 | BTH |
| Shanghai | 125.00 | YRD | |
| Hangzhou | 66.63 | YRD | |
| Shenzhen | 54.93 | GBA | |
| Chongqing | 44.20 | CHC | |
| Changzhou | 28.33 | YRD | |
| Guangzhou | 22.95 | GBA | |
| Zhuhai | 21.65 | GBA | |
| Nanjing | 19.52 | YRD | |
| Suzhou | 17.75 | YRD | |
| Tianjin | 11.89 | BTH | |
| Changsha | 11.76 | MRY | |
| Wuhan | 9.75 | MRY | |
| Foshan | 8.50 | GBA | |
| Huizhou | 8.46 | GBA | |
| Ningbo | 7.77 | YRD | |
| Dongguan | 7.75 | GBA | |
| Yancheng | 7.69 | YRD | |
| Hefei | 7.49 | YRD | |
| Zhenjiang | 6.73 | YRD | |
| Inter-city innovation networks within urban agglomerations | Hangzhou | 231.58 | YRD |
| Ningbo | 138.52 | YRD | |
| Taizhou | 69.93 | YRD | |
| Shenzhen | 64.64 | GBA | |
| Beijing | 49.57 | BTH | |
| Huizhou | 48.05 | GBA | |
| Shanghai | 22.10 | YRD | |
| Shijiazhuang | 21.61 | BTH | |
| Guangzhou | 18.83 | GBA | |
| Tianjin | 14.86 | BTH | |
| Nanjing | 13.47 | YRD | |
| Jinhua | 12.33 | YRD | |
| Dongguan | 12.07 | GBA | |
| Suzhou | 10.11 | YRD | |
| Hong Kong | 8.65 | GBA | |
| Xingtai | 6.74 | BTH | |
| Hefei | 6.61 | YRD | |
| Langfang | 5.69 | BTH | |
| Yancheng | 5.54 | YRD | |
| Baoding | 5.43 | BTH | |
| Innovation networks between cities within and beyond urban agglomerations | Beijing | 212.49 | BTH |
| Shenzhen | 98.35 | GBA | |
| Suzhou | 86.44 | YRD | |
| Hangzhou | 53.91 | YRD | |
| Changzhou | 43.23 | YRD | |
| Wuhan | 34.56 | MRY | |
| Nanchong | 29.91 | CHC | |
| Shanghai | 28.69 | YRD | |
| Nanjing | 26.75 | YRD | |
| Hefei | 24.08 | YRD | |
| Guangzhou | 23.86 | GBA | |
| Chengdu | 23.55 | CHC | |
| Chongqing | 21.32 | CHC | |
| Tianjin | 20.91 | BTH | |
| Huizhou | 16.06 | GBA | |
| Nanchang | 15.10 | MRY | |
| Changsha | 14.08 | MRY | |
| Wuxi | 11.17 | YRD | |
| Langfang | 10.00 | BTH | |
| Zhuzhou | 9.33 | MRY |
| Geographical Scales | City Pairs | Innovation Linkages | Urban Agglomerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inter-city innovation networks within urban agglomerations | Hangzhou–Ningbo | 136.47 | YRD |
| Hangzhou–Taizhou | 69.93 | YRD | |
| Shenzhen–Huizhou | 46.94 | GBA | |
| Beijing–Shijiazhuang | 14.30 | BTH | |
| Beijing–Tianjin | 13.56 | BTH | |
| Hangzhou–Jinhua | 12.31 | YRD | |
| Hong Kong–Shenzhen | 8.60 | GBA | |
| Guangzhou–Dongguan | 6.67 | GBA | |
| Beijing–Langfang | 5.69 | BTH | |
| Shanghai–Suzhou | 5.45 | YRD | |
| Shenzhen–Dongguan | 4.46 | GBA | |
| Shanghai–Hangzhou | 4.32 | YRD | |
| Beijing–Baoding | 4.06 | BTH | |
| Beijing–Xingtai | 3.74 | BTH | |
| Guangzhou–Shenzhen | 3.52 | GBA | |
| Beijing–Cangzhou | 3.33 | BTH | |
| Nanjing–Hangzhou | 3.06 | YRD | |
| Shijiazhuang–Xingtai | 2.99 | BTH | |
| Guangzhou–Foshan | 2.70 | GBA | |
| Guangzhou–Jiangmen | 2.45 | GBA | |
| Innovation networks between cities within and beyond urban agglomerations | Suzhou–New Taipei | 63.23 | YRD–Other |
| Hangzhou–Nanchong | 29.91 | YRD–CHC | |
| Shenzhen–Changzhou | 23.26 | GBA–YRD | |
| Changzhou–Huizhou | 16.06 | YRD–GBA | |
| Beijing–Wuhan | 15.59 | BTH–MRY | |
| Beijing–Hefei | 14.94 | BTH–YRD | |
| Beijing–Nanjing | 14.39 | BTH–YRD | |
| Beijing–Shenzhen | 11.96 | BTH–GBA | |
| Beijing–Changsha | 10.46 | BTH–MRY | |
| Beijing–Chongqing | 9.54 | BTH–CHC | |
| Shenzhen–Langfang | 9.50 | GBA–BTH | |
| Shenzhen–New Taipei | 9.26 | GBA–Other | |
| Beijing–Suzhou | 9.18 | BTH–YRD | |
| Hangzhou–Xiangtan | 8.16 | YRD–MRY | |
| Beijing–Chengdu | 8.02 | BTH–CHC | |
| Beijing–Hangzhou | 7.66 | BTH–YRD | |
| Wuxi–Changchun | 7.60 | YRD–Other | |
| Chongqing–Hefei | 7.21 | CHC–YRD | |
| Shenzhen–Suzhou | 7.09 | GBA–YRD | |
| Nanchang–Taiyuan | 6.79 | MRY–Other |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CITY | 0.453 * | 0.332 ** | 0.358 ** | 0.457 ** | 0.566 *** | 0.389 ** | 0.827 *** | 0.287 * | 0.278 * |
| (0.235) | (0.163) | (0.170) | (0.184) | (0.214) | (0.166) | (0.275) | (0.171) | (0.156) | |
| MEG | 0.206 * | 0.642 *** | 0.203 * | 0.363 *** | 0.208 * | 0.424 *** | 0.227 ** | 0.666 *** | 0.236 ** |
| (0.113) | (0.219) | (0.115) | (0.119) | (0.112) | (0.111) | (0.097) | (0.212) | (0.097) | |
| COU | 0.243 ** | 0.238 ** | 0.521 *** | 0.263 ** | 0.341 *** | 0.384 *** | 0.292 ** | 0.300 ** | 0.831 *** |
| (0.121) | (0.119) | (0.190) | (0.123) | (0.129) | (0.127) | (0.116) | (0.119) | (0.232) | |
| CITY × CITY | −0.033 | ||||||||
| (0.052) | |||||||||
| MEG × MEG | −0.094 ** | ||||||||
| (0.041) | |||||||||
| COU × COU | −0.078 * | ||||||||
| (0.044) | |||||||||
| CITY × MEG | −0.086 ** | ||||||||
| (0.043) | |||||||||
| CITY × COU | −0.090 ** | ||||||||
| (0.044) | |||||||||
| MEG × COU | −0.118 *** | ||||||||
| (0.039) | |||||||||
| CITY × EPAMI | 0.200 ** | ||||||||
| (0.085) | |||||||||
| MEG × EPAMI | 0.162 ** | ||||||||
| (0.077) | |||||||||
| COU × EPAMI | 0.196 *** | ||||||||
| (0.067) | |||||||||
| EPAMI | 0.881 *** | 0.875 *** | 0.862 *** | 0.856 *** | 0.858 *** | 0.835 *** | 0.808 *** | 0.771 *** | 0.759 *** |
| (0.081) | (0.076) | (0.081) | (0.078) | (0.080) | (0.077) | (0.092) | (0.109) | (0.092) | |
| PGDP | 0.337 | 0.246 | 0.341 | 0.326 | 0.329 | 0.333 | 0.293 | 0.298 | 0.304 |
| (0.249) | (0.252) | (0.238) | (0.246) | (0.245) | (0.244) | (0.239) | (0.235) | (0.238) | |
| SE | 0.807 | 0.639 | 1.040 | 0.834 | 0.960 | 0.982 | 0.756 | 0.886 | 0.748 |
| (0.722) | (0.693) | (0.706) | (0.715) | (0.706) | (0.696) | (0.700) | (0.701) | (0.692) | |
| SGDP | 0.581 | 0.760 | 0.352 | 0.391 | 0.274 | 0.261 | 1.104 * | 0.859 | 1.055 * |
| (0.586) | (0.536) | (0.535) | (0.547) | (0.553) | (0.523) | (0.565) | (0.523) | (0.535) | |
| FDI | 0.149 * | 0.160 ** | 0.143 * | 0.148 * | 0.146 * | 0.149 * | 0.126 | 0.152 * | 0.123 |
| (0.081) | (0.078) | (0.081) | (0.079) | (0.080) | (0.078) | (0.082) | (0.083) | (0.080) | |
| Cons | 3.222 | 2.984 | 4.253 * | 3.846 | 4.550 * | 4.395 * | 1.259 | 2.397 | 1.104 |
| (2.624) | (2.513) | (2.504) | (2.495) | (2.535) | (2.467) | (2.418) | (2.477) | (2.470) | |
| Megalopolis FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 |
| R2 | 0.848 | 0.854 | 0.851 | 0.852 | 0.852 | 0.857 | 0.854 | 0.853 | 0.856 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVCITY | 0.848 ** | 0.427 * | 0.491 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.922 *** | 0.569 ** | 1.141 *** | 0.349 | 0.343 |
| (0.349) | (0.216) | (0.234) | (0.275) | (0.319) | (0.231) | (0.421) | (0.257) | (0.237) | |
| AVMEG | 0.211 | 1.082 *** | 0.210 | 0.527 *** | 0.221 | 0.612 *** | 0.260 ** | 0.915 *** | 0.272 ** |
| (0.153) | (0.322) | (0.161) | (0.148) | (0.154) | (0.127) | (0.123) | (0.309) | (0.130) | |
| AVCOU | 0.299 * | 0.286 * | 0.933 *** | 0.365 ** | 0.535 *** | 0.604 *** | 0.411 ** | 0.418 ** | 1.132 *** |
| (0.174) | (0.159) | (0.239) | (0.169) | (0.171) | (0.170) | (0.160) | (0.168) | (0.353) | |
| AVCITY × AVCITY | −0.130 | ||||||||
| (0.087) | |||||||||
| AVMEG × AVMEG | −0.231 *** | ||||||||
| (0.073) | |||||||||
| AVCOU × AVCOU | −0.217 *** | ||||||||
| (0.071) | |||||||||
| AVCITY × AVMEG | −0.231 *** | ||||||||
| (0.067) | |||||||||
| AVCITY × AVCOU | −0.243 *** | ||||||||
| (0.075) | |||||||||
| AVMEG × AVCOU | −0.303 *** | ||||||||
| (0.064) | |||||||||
| AVCITY × EPAMI | 0.310 ** | ||||||||
| (0.136) | |||||||||
| AVMEG × EPAMI | 0.253 ** | ||||||||
| (0.118) | |||||||||
| AVCOU × EPAMI | 0.277 ** | ||||||||
| (0.108) | |||||||||
| EPAMI | 0.896 *** | 0.891 *** | 0.861 *** | 0.858 *** | 0.858 *** | 0.824 *** | 0.848 *** | 0.816 *** | 0.816 *** |
| (0.085) | (0.079) | (0.084) | (0.082) | (0.084) | (0.082) | (0.094) | (0.106) | (0.096) | |
| PGDP | 0.438 * | 0.351 | 0.421 * | 0.414 * | 0.411 * | 0.394 * | 0.455 * | 0.445 * | 0.460 * |
| (0.248) | (0.253) | (0.231) | (0.242) | (0.240) | (0.235) | (0.236) | (0.230) | (0.234) | |
| SE | 0.922 | 0.678 | 1.279 * | 0.981 | 1.161 * | 1.167 * | 0.927 | 1.072 | 0.895 |
| (0.732) | (0.694) | (0.704) | (0.712) | (0.698) | (0.679) | (0.714) | (0.712) | (0.706) | |
| SGDP | 0.486 | 0.919 | 0.258 | 0.323 | 0.157 | 0.195 | 1.160 * | 0.920 | 1.111 * |
| (0.601) | (0.585) | (0.541) | (0.567) | (0.551) | (0.526) | (0.621) | (0.582) | (0.603) | |
| FDI | 0.145 * | 0.178 ** | 0.120 | 0.146 * | 0.128 | 0.141 * | 0.130 | 0.154 * | 0.130 |
| (0.081) | (0.081) | (0.082) | (0.079) | (0.080) | (0.077) | (0.084) | (0.084) | (0.083) | |
| Cons | 2.906 | 1.614 | 4.190 | 3.566 | 4.555 * | 4.399 * | −0.061 | 1.263 | −0.099 |
| (2.760) | (2.568) | (2.625) | (2.586) | (2.623) | (2.534) | (2.543) | (2.605) | (2.599) | |
| Megalopolis FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 | 107 |
| R2 | 0.841 | 0.851 | 0.849 | 0.850 | 0.849 | 0.858 | 0.845 | 0.844 | 0.846 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, W.; Li, J. The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks on Industrial Development: Evidence from the Automobile Manufacturing Industry in China. Systems 2024, 12, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010005
Xiong W, Li J. The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks on Industrial Development: Evidence from the Automobile Manufacturing Industry in China. Systems. 2024; 12(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Weiting, and Jingang Li. 2024. "The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks on Industrial Development: Evidence from the Automobile Manufacturing Industry in China" Systems 12, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010005
APA StyleXiong, W., & Li, J. (2024). The Knowledge Spillover Effect of Multi-Scale Urban Innovation Networks on Industrial Development: Evidence from the Automobile Manufacturing Industry in China. Systems, 12(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010005








