Use of System Dynamics Modelling for Evidence-Based Decision Making in Public Health Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
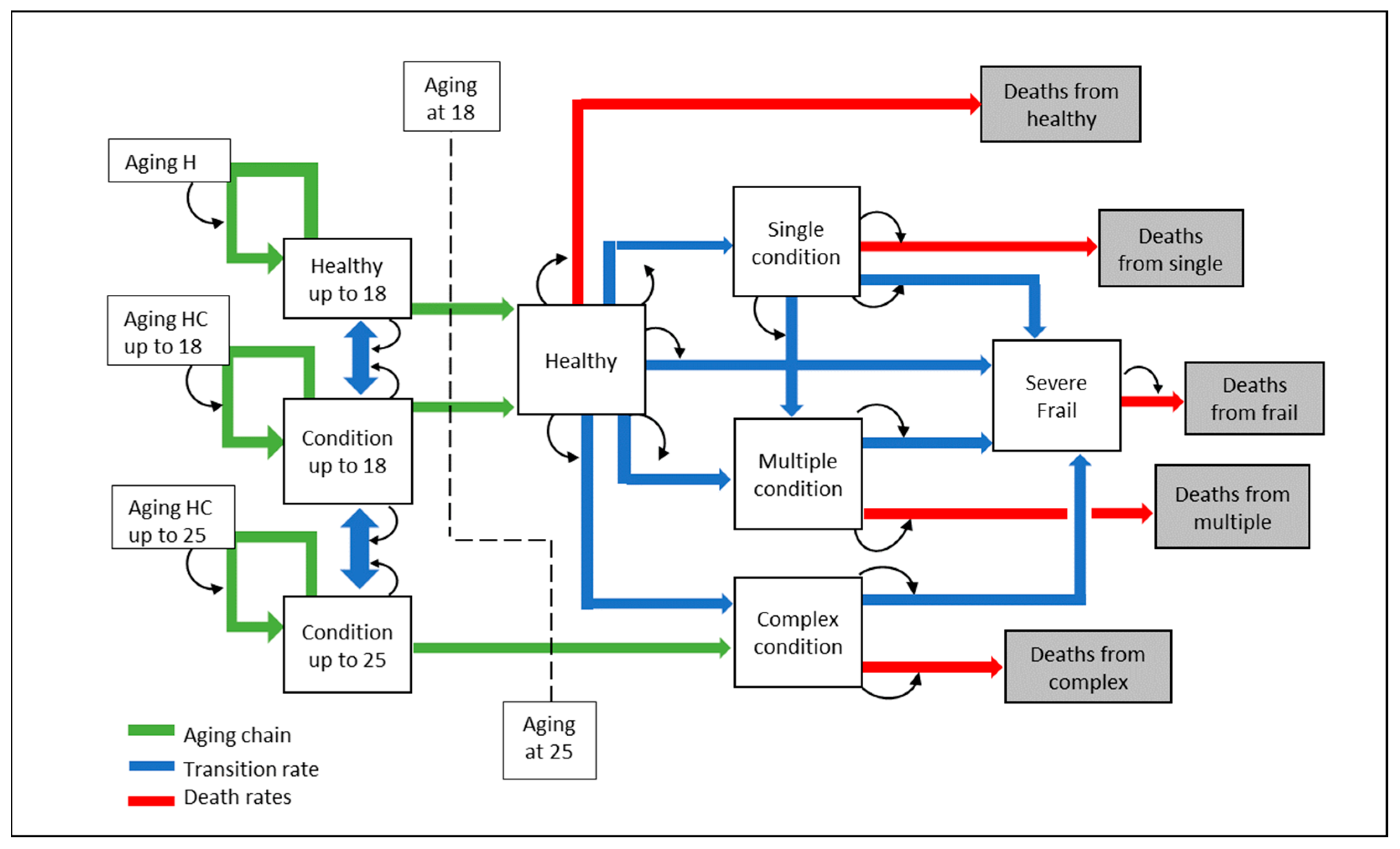
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Main Finding
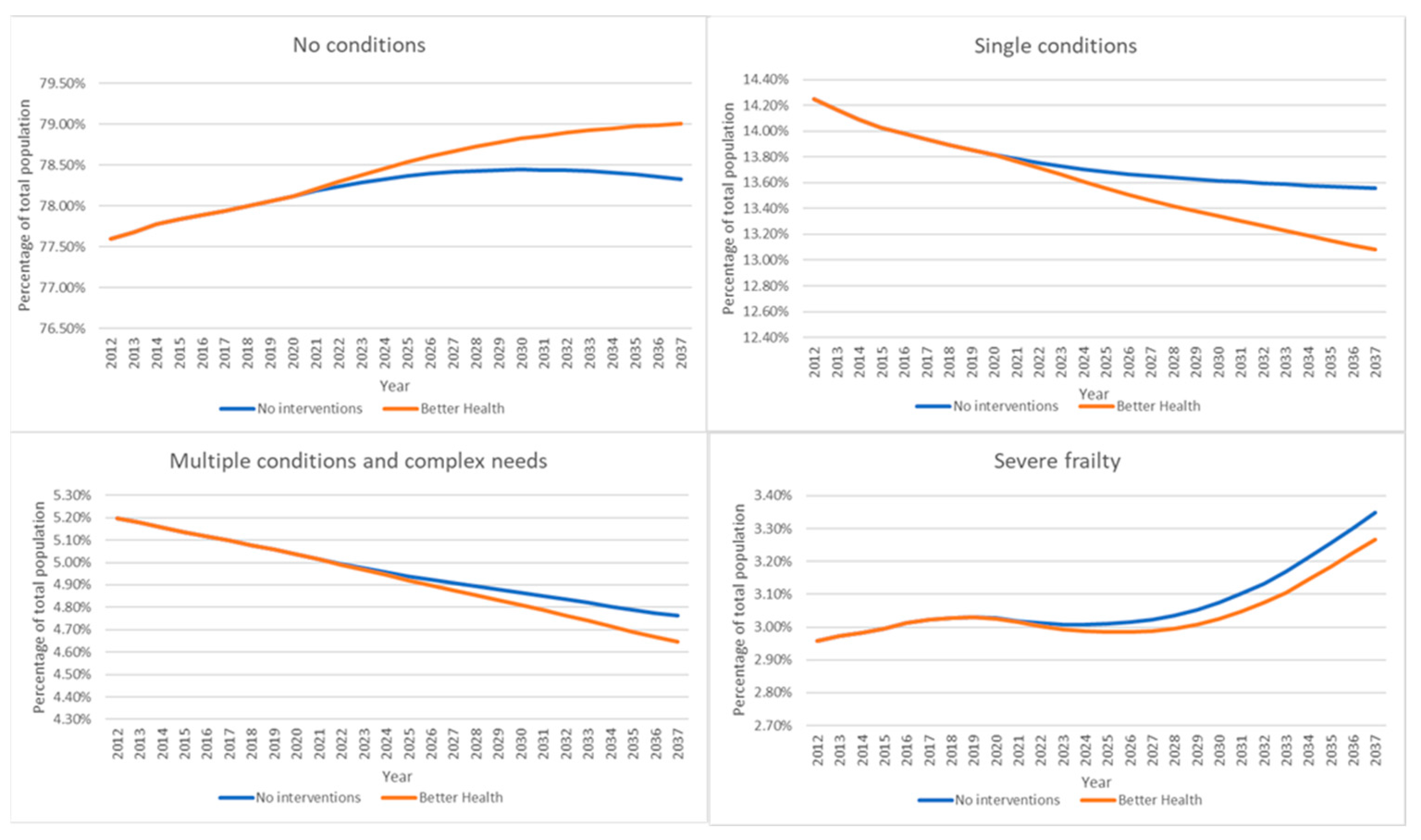
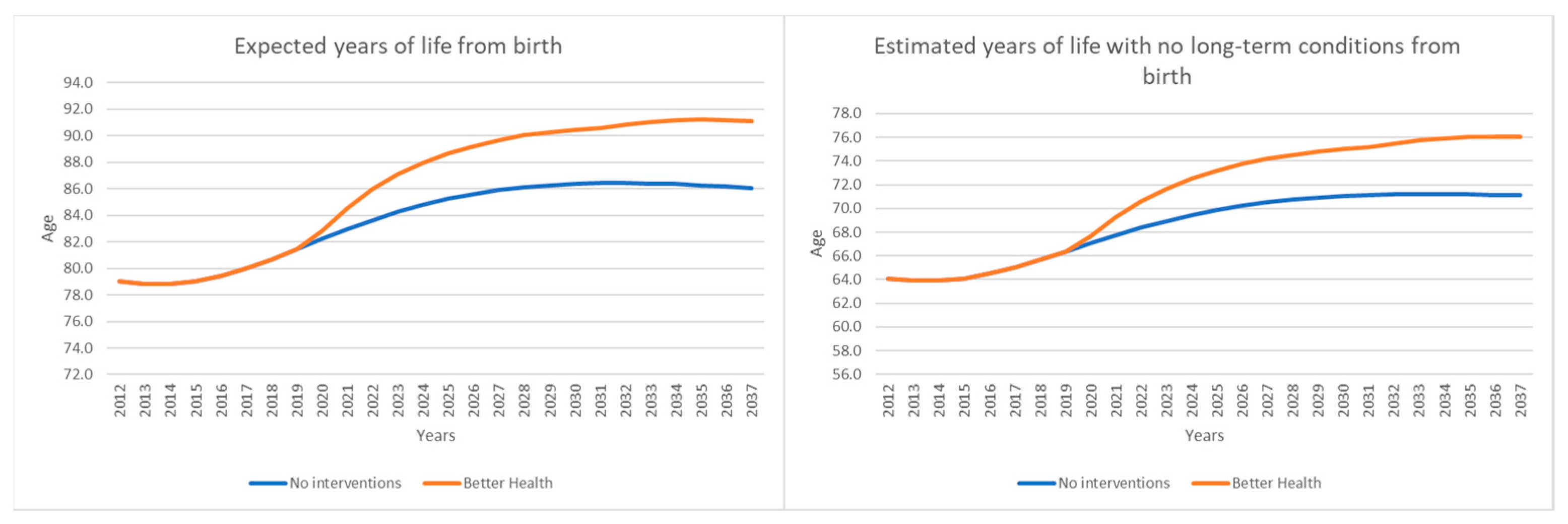
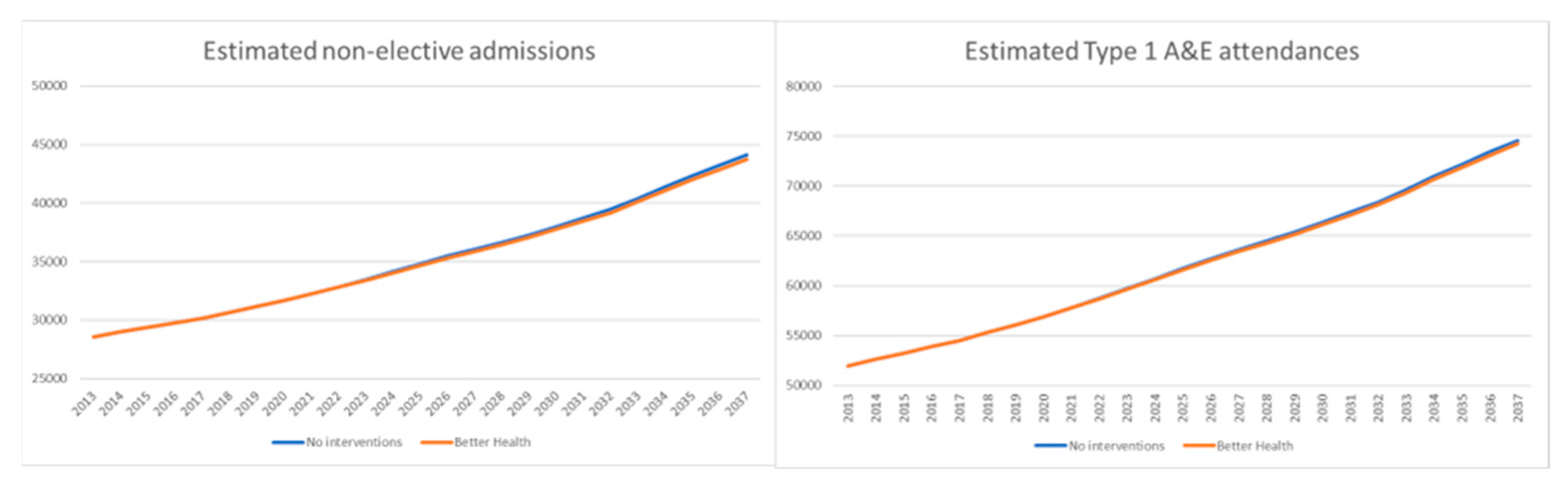
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oxford Brookes University: Protecting Older People Population Information. Available online: https://www.poppi.org.uk (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Lepenioti, K.; Bousdekis, A.; Apostolou, D.; Mentzas, G. Prescriptive analytics: Literature review and research challenges. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England: Health Economics: Evidence Resource. Available online: www.gov.uk/government/publications/health-economics-evidence-resource (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Bauer, G.R. Incorporating intersectionality theory into population health research methodology: Challenges and the potential to advance health equity. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 110, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, E.; Er, V.; Penney, T.; Egan, M.; White, M.; Meier, P.; Whitehead, M.; Lock, K.; de Cuevas, R.A.; Smith, R.; et al. Evaluation of public health interventions from a complex systems perspective: A research methods review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 272, 113697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadeja, N.; Zhu, N.J.; Lebcir, R.M.; Sassi, F.; Holmes, A.; Ahmad, R. Using system dynamics modelling to assess the economic efficiency of innovations in the public sector—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, J.B.; Hirsch, G.B. System dynamics modeling for public health: Background and opportunities. Am. J. Public Health 2006, 96, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnoff, B.; Bradley, C.; Honeycutt, A.A.; Soler, R.E.; Orenstein, D. Estimating the relative impact of clinical and preventive community-based interventions: An example based on the Community Transformation Grant Program. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2019, 16, 180594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, H.; Savona, N.; Glonti, K.; Bibby, J.; Cummins, S.; Finegood, D.T.; Greaves, F.; Harper, L.; Hawe, P.; Moore, L.; et al. The need for a complex systems model of evidence for public health. Lancet 2017, 390, 2602–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J.; Smith, C.; Jagals, P. The application of system dynamics modelling to environmental health decision-making and policy—A scoping review. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davahli, M.R.; Karwowski, W.; Taiar, R. A System Dynamics Simulation Applied to Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, G.; Miskolczi, P. Dynamics of participation: System dynamics and participation—An empirical review. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2019, 36, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, Y.; Lich, H.K.; Lemke, M.K. Complex Systems and Population Health: A Primer; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Health and Social Care. Joint Strategic Needs Assessment and Joint Health and Wellbeing Strategies Explained. 2011. Available online: www.gov.uk/government/publications/joint-strategic-needs-assessment-and-joint-health-and-wellbeing-strategies-explained (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Statistical Bulletin. 2021 Mid-Year Population Estimates: Age and Sex Profile. Kent Analytics. January 2023. Available online: https://www.kent.gov.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/14725/Mid-year-population-estimates-age-and-gender.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- ONS. Census 2021: Total Population Change between 2011 and 2021. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigration/populationestimates (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Data Resource: The Kent Integrated Dataset (KID). Available online: https://ijpds.org/article/view/427 (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Kent County Council (KCC) Housing Led Forecasts 2021. Available online: www.kent.gov.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/59806/KCC-housing-led-summary.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- ONS, Deaths Broken Down by Age, Sex, Area and Cause of Death. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/deaths (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- ONS, General Lifestyle Survey: 2011. Available online: www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/personalandhouseholdfinances/incomeandwealth/compendium/generallifestylesurvey/2013-03-07 (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Health Survey for England. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/health-survey-for-england (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- General Household Survey. Available online: https://www.data.gov.uk/dataset/138ca035-a90c-4e37-80f5-4c73eeb6ae04/general-household-survey (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Maternity and Breastfeeding. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/statistics/statistical-work-areas/maternity-and-breastfeeding/ (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Statistics on Women’s Smoking Status at Time of Delivery: England. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/statistics-on-women-s-smoking-status-at-time-of-delivery-england (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- National Child Measurement Programme. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/national-child-measurement-programme (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- English Indices of Deprivation 2010. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/english-indices-of-deprivation-2010 (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Millennium Cohort Study. Available online: https://cls.ucl.ac.uk/cls-studies/millennium-cohort-study/ (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- NHS Long Term Plan 2019. Available online: www.longtermplan.nhs.uk (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Lacey, P. Strategic Workforce Planning (SWiPe) Derbyshire Re-shaping Community Workforce, Child health and wellbeing services Draft report—July 2016. (Unpublished report July 2016). 20 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Outcomes Based Healthcare. Available online: https://outcomesbasedhealthcare.com/segmentation-approaches (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA). Available online: www.elsa-project.ac.uk (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- NHS Electronic Frailty Index (EFI). Available online: www.england.nhs.uk/ourwork/clinical-policy/older-people/frailty/efi/ (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Lewington, S.; Clarke, R.; Qizilbash, N.; Peto, R.; Collins, R.; Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002, 360, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogers, R.P.; Hoogenveen, R.T.; Boshuizen, H.; Woodward, M.; Knekt, P.; Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Visscher, T.L.S.; Menotti, A.; Thorpe, R.J.; et al. Overweight and obesity increase the risk of coronary heart disease: A pooled analysis of 30 prospective studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 107. [Google Scholar]
- James, W.P.T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Mhurchu, C.N.; Kalamara, E.; Shayeghi, M.; Rigby, N.J.; Nishida, C.; Rodgers, A. Overweight and obesity (high body mass index). In Comparative Quantification of Risk Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; Ezatti, M., Lopez, A.D., Rodgers, A., Murray, C.J.L., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 497–596. [Google Scholar]
- Lewington, S.; Whitlock, G.; Clarke, R.; Sherliker, P.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Peto, R.; Collins, R. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: A meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55000 vascular deaths. Lancet 2007, 370, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics on Smoking, England—2013. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/statistics-on-smoking/statistics-on-smoking-england-2013 (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Bull, F.; Armstrong, T.P.; Dixon, T.; Ham, S.; Neiman, A.; Pratt, M. Physical inactivity. In Comparative Quantification of Risk Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; Ezatti, M., Lopez, A.D., Rodgers, A., Murray, C.J.L., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 729–881. [Google Scholar]
- Joubert, J.; Norman, R.; Lambert, E.V.; Groenewald, P.; Schneider, M.; Bull, F. Estimating the burden of disease attributable to physical inactivity in South Africa in 2000. SAMJ S. Afr. Med. J. 2007, 97, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathers, C.; Vos, T.; Stevenson, C. The Burden of disease and injury in Australia, (AIHW Catalogue No. PHE 17). In Comparative Quantification of Risk Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; Ezatti, M., Lopez, A.D., Rodgers, A., Murray, C.J.L., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tackling Obesity in England. Available online: https://www.nao.org.uk/reports/tackling-obesity-in-england/ (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Livingston, G.; Sommerlad, A.; Orgeta, V.; Costafreda, S.G.; Huntley, J.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet Comm. 2017, 390, 2673–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezatti, M.; Lopea, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Murray, C.J.L. (Eds.) Comparative Quantification of Risk. Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Unal, B.; Critchley, J.A.; Capewell, S. Explaining the Decline in Coronary Heart Disease Mortality in England and Wales Between 1981 and 2000. Circulation 2004, 109, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England, QoF Data: Public Health Profiles—OHID. Available online: www.phe.org.uk (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Yarnoff, B.; Honeycutt, A.; Bradley, C.; Khavjou, O.; Bates, L.; Bass, S.; Kaufmann, R.; Barker, L.; Briss, P. Validation of the prevention impacts simulation model (PRISM). Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, 200225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H.; He, X. Research on supply and demand of aged services resource allocation in China: A system dynamics model. Systems 2022, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONS, Population Projections. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigration/populationprojections (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Hekimoğlu, M.; Barlas, Y. Sensitivity analysis for models with multiple behavior modes: A method based on behavior pattern measures. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2016, 32, 332–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isee Systems, Stella Architect. Available online: https://www.iseesystems.com/store/products/stella-architect.aspx (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; França, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysina, D.; Fergusson, D.M.; Leve, L.D.; Horwood, J.; Reiss, D.; Shaw, D.S.; Elam, K.K.; Natsuaki, M.N.; Neiderhiser, J.M.; Harold, G.T. Maternal Smoking During Pregnancy and Offspring Conduct Problems. Evidence From 3 Independent Genetically Sensitive Research Designs. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, K.; Heron, J.; Smith, G.D.; Thapar, A. Maternal and Paternal Smoking During Pregnancy and Risk of ADHD Symptoms in Offspring: Testing for Intrauterine Effects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Levitan, E.B.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal smoking during pregnancy and child overweight: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.; Butt, S.; Tomaszewski, W. The Dynamics of Bad Housing: The Impact of Bad Housing on the Living Standards of Children; National Centre for Social Research: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Boardman, B. Fixing Fuel Poverty: Challenges and Solutions; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Wales. Welsh Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study: Adverse Childhood Experiences and Their Impact on Health-Harming Behaviours in the Welsh Adult Population; Public Health Wales: Cymru, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Kuang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X. Applications of system dynamics models in Chronic disease prevention: A systematic review. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, 210175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyo, H.K.; Batcher, C.; Wile, K.; Huang, P.; Orenstein, D.; Milstein, B. From model to action. Health Promot. Pract. 2012, 14, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHS England. Population Health and the Population Health Management Programme. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/integratedcare/what-is-integrated-care/phm (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Interdisciplinary Association for Population Health Science. County Health Ranking Model. Available online: https://iaphs.org/institutional-member-highlight-university-of-wisconsin (accessed on 23 March 2023).
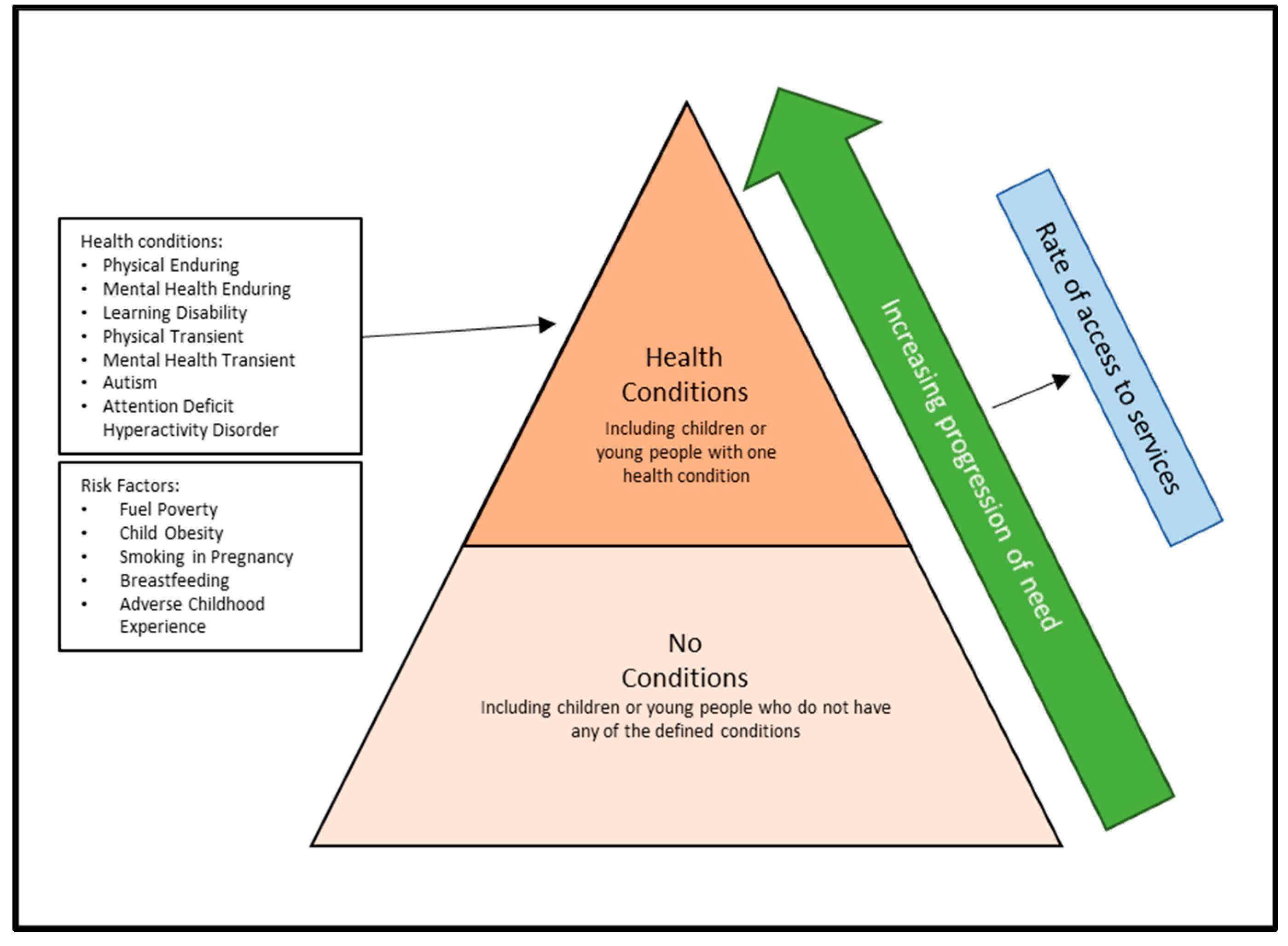

| Intervention | Title | Baseline | Impact (%) | Number | Start | End | Target | Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Increase breastfeeding at 6–8 weeks | 45.2 | 20 | NA | 2019 | 2024 | 65.2 | absolute |
| 2 | Reduce smoking in pregnancy | 13.9 | 6 | NA | 2019 | 2025 | 7.9 | absolute |
| 3 | Reduce child obesity | 16.5 | 20 | NA | 2019 | 2025 | 13.2 | proportional |
| 4 | Reduce fuel poverty in children | 17.4 | 20 | NA | 2019 | 2022 | 13.9 | proportional |
| 5 | Reduce ACE in childhood | 24 | 20 | NA | 2020 | 2030 | 19.2 | proportional |
| 6 | Improve recognition and treatment of hypertension | 40 | 30 | NA | 2020 | 2025 | 28 | proportional |
| 7 | Improve recognition and treatment of CVD risk | 50 | 30 | NA | 2020 | 2025 | 65 | proportional |
| 8 | Improve smoking cessation | 20 | 8 | NA | 2019 | 2024 | 28 | absolute |
| 9 | Increase weight management | 25 | 10 | NA | 2019 | 2024 | 27.5 | proportional |
| 10 | Alcohol screening | NA | Screening | 50,000 | 2019 | 2025 | NA | absolute |
| 11 | Alcohol treatment | NA | Treatment | 5000 | 2019 | 2030 | NA | absolute |
| 12 | Reduce fuel poverty for older people | 11.5 | 20 | NA | 2019 | 2024 | 9.2 | proportional |
| 13 | Reduce ACE at 15 years | 7.5 | 20 | NA | 2020 | 2030 | 6 | proportional |
| Long-Term Condition | 2012 | No Interventions | Better Health | Difference between Better Health and No Interventions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2037 | Percentage Difference | 2037 | Percentage Difference | |||
| Asthma | 6.83% | 5.95% | −12.90% | 5.88% | −13.90% | −1.00% |
| CHD | 1.92% | 1.59% | −17.23% | 1.51% | −21.48% | −4.25% |
| COPD | 0.75% | 0.63% | −15.79% | 0.57% | −23.92% | −8.13% |
| Diabetes | 2.76% | 3.25% | 18.02% | 3.07% | 11.35% | −6.66% |
| HF | 0.02% | 0.02% | −10.74% | 0.02% | −10.96% | −0.22% |
| Stroke | 0.67% | 0.59% | −12.52% | 0.49% | −27.56% | −15.04% |
| Frail moderate | 1.30% | 1.53% | 17.88% | 1.55% | 19.27% | 1.39% |
| Multiple | 3.89% | 3.51% | −9.61% | 3.42% | −12.01% | −2.40% |
| SE MI | 0.54% | 0.46% | −14.18% | 0.44% | −18.27% | −4.09% |
| Neuro | 0.18% | 0.19% | 4.82% | 0.19% | 5.17% | 0.35% |
| Dementia | 0.32% | 0.34% | 8.12% | 0.34% | 7.60% | −0.52% |
| LD | 0.28% | 0.26% | −7.46% | 0.26% | −7.59% | −0.13% |
| Frail severe | 2.96% | 3.35% | 13.21% | 3.27% | 10.45% | −2.76% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
George, A.; Badrinath, P.; Lacey, P.; Harwood, C.; Gray, A.; Turner, P.; Springer, D. Use of System Dynamics Modelling for Evidence-Based Decision Making in Public Health Practice. Systems 2023, 11, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050247
George A, Badrinath P, Lacey P, Harwood C, Gray A, Turner P, Springer D. Use of System Dynamics Modelling for Evidence-Based Decision Making in Public Health Practice. Systems. 2023; 11(5):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050247
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorge, Abraham, Padmanabhan Badrinath, Peter Lacey, Chris Harwood, Alex Gray, Paul Turner, and Davinia Springer. 2023. "Use of System Dynamics Modelling for Evidence-Based Decision Making in Public Health Practice" Systems 11, no. 5: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050247
APA StyleGeorge, A., Badrinath, P., Lacey, P., Harwood, C., Gray, A., Turner, P., & Springer, D. (2023). Use of System Dynamics Modelling for Evidence-Based Decision Making in Public Health Practice. Systems, 11(5), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050247







