A Study of the Strategic Interaction in Environmental Regulation Based on Spatial Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Approach (ESDA)
2.1.2. Setting of the Econometric Model
- 1.
- The spatial lag panel data model:
- 2.
- The spatial error panel data model:
2.2. Data Description and Variable Selection
2.2.1. Variables
- (1)
- Environmental regulation
- (2)
- Decentralized indicators (FD)
- (3)
- Public demand for environmental protection (LETTER)
- (4)
- Other variables
2.2.2. Data
3. Empirical Results and Analysis of the Spatial Effects
3.1. Spatial Correlation
3.1.1. Global Spatial Correlation
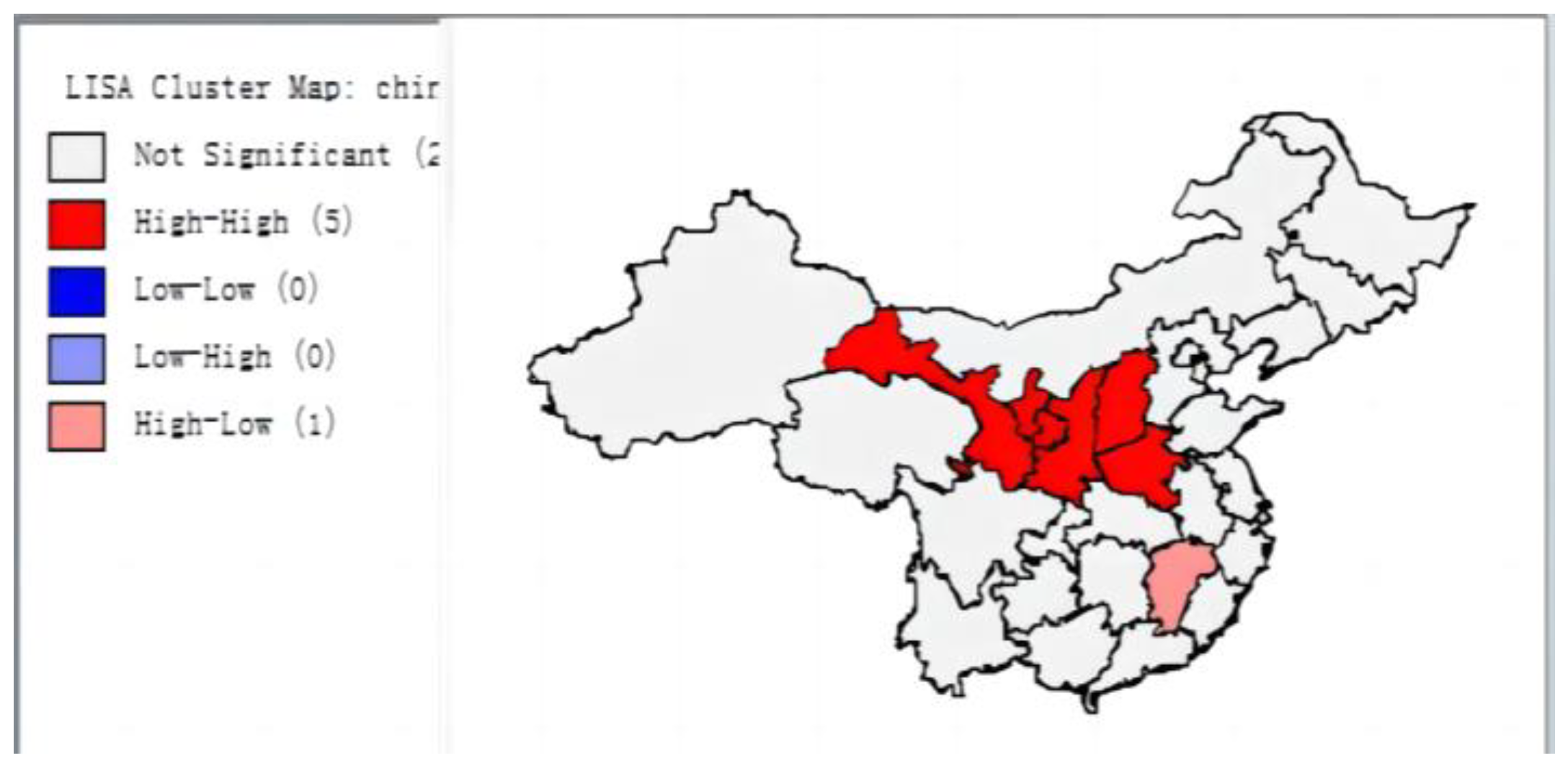
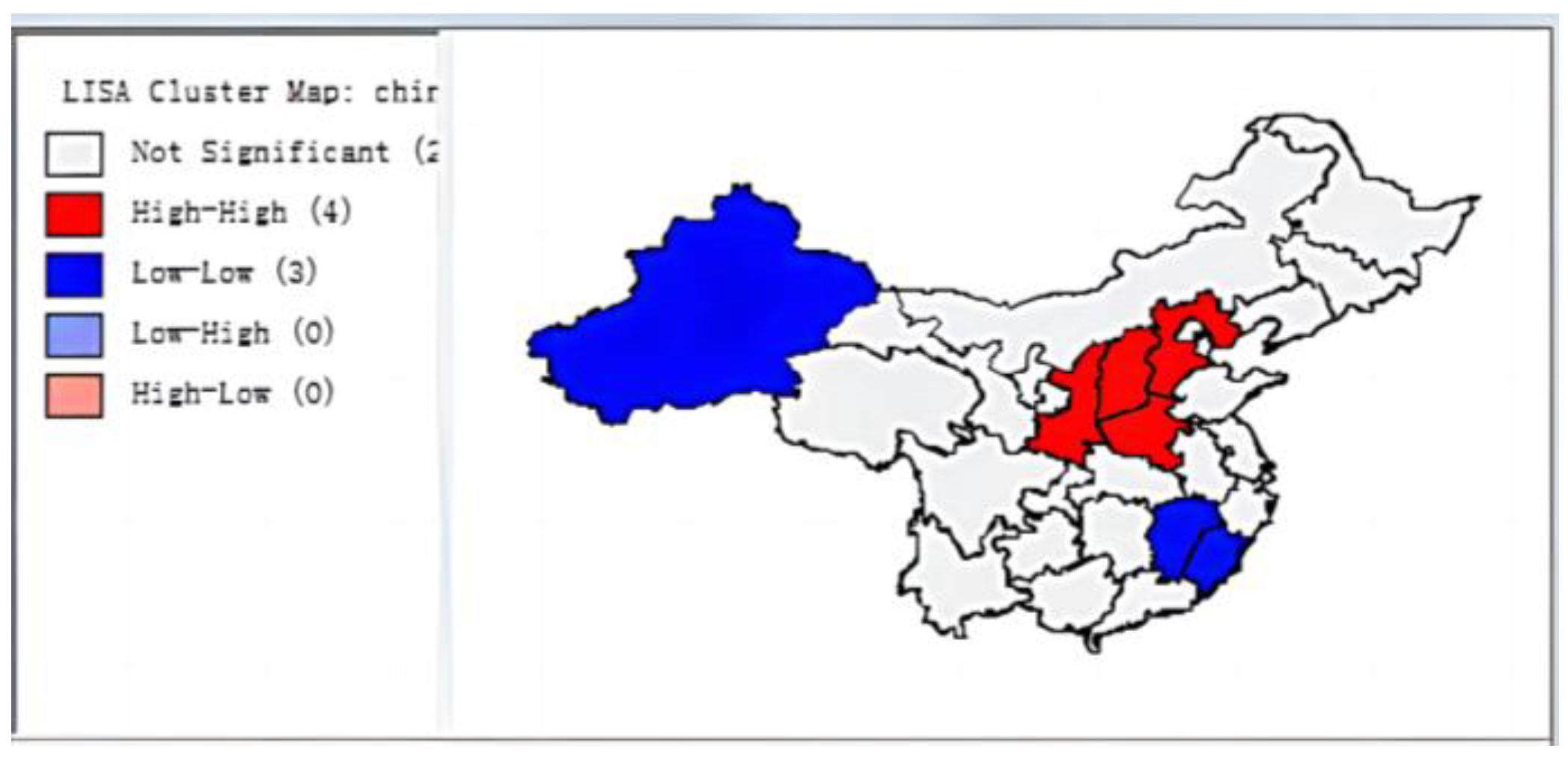
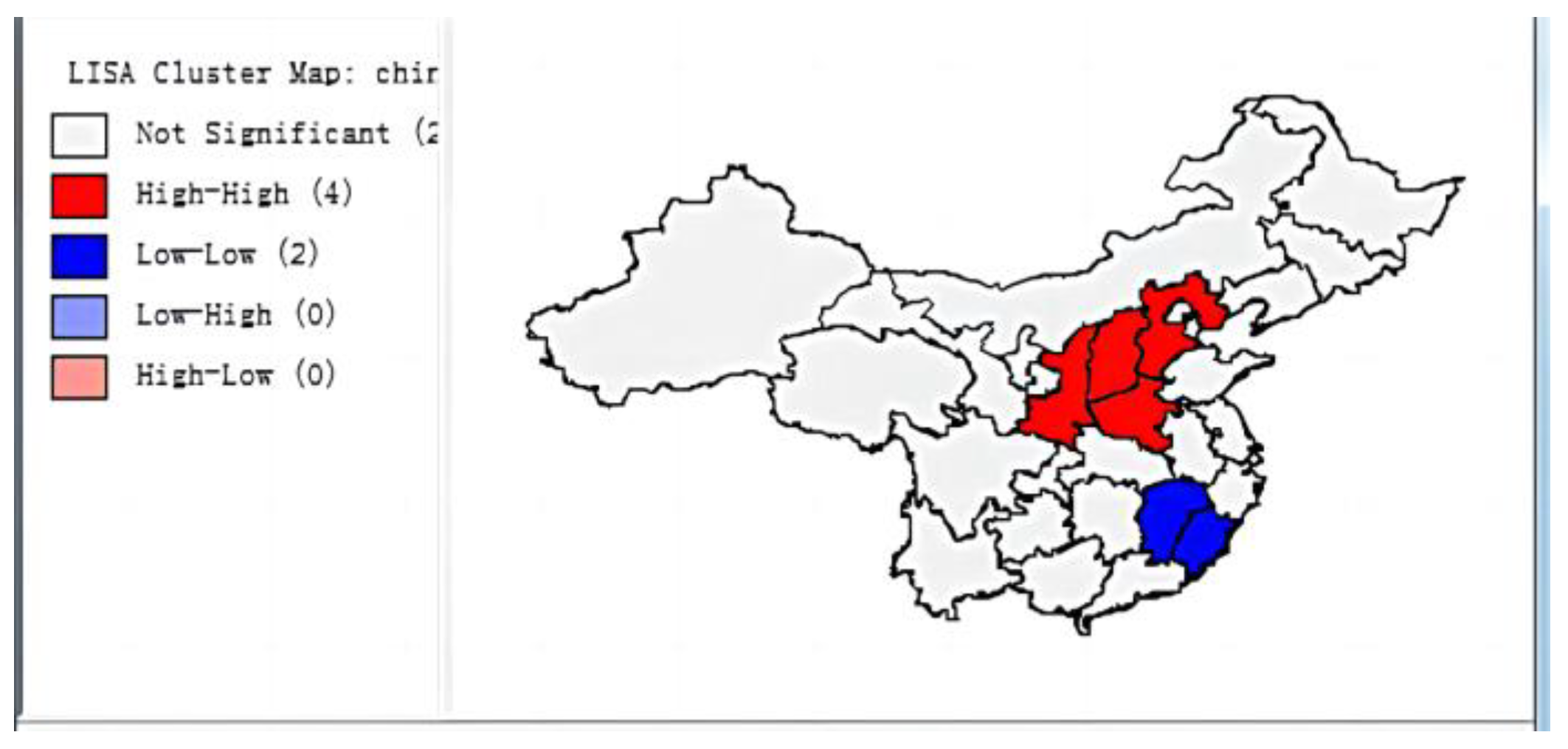
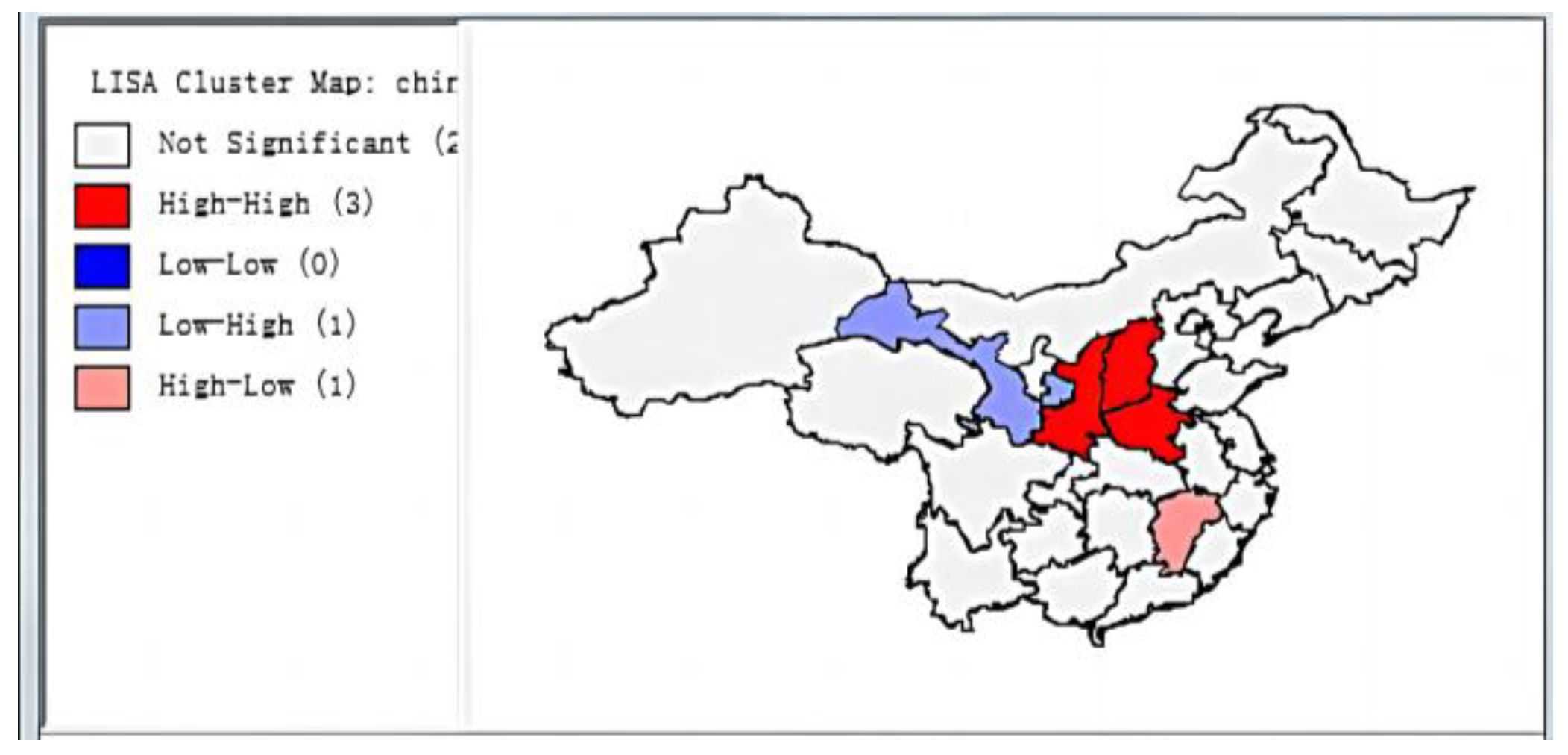
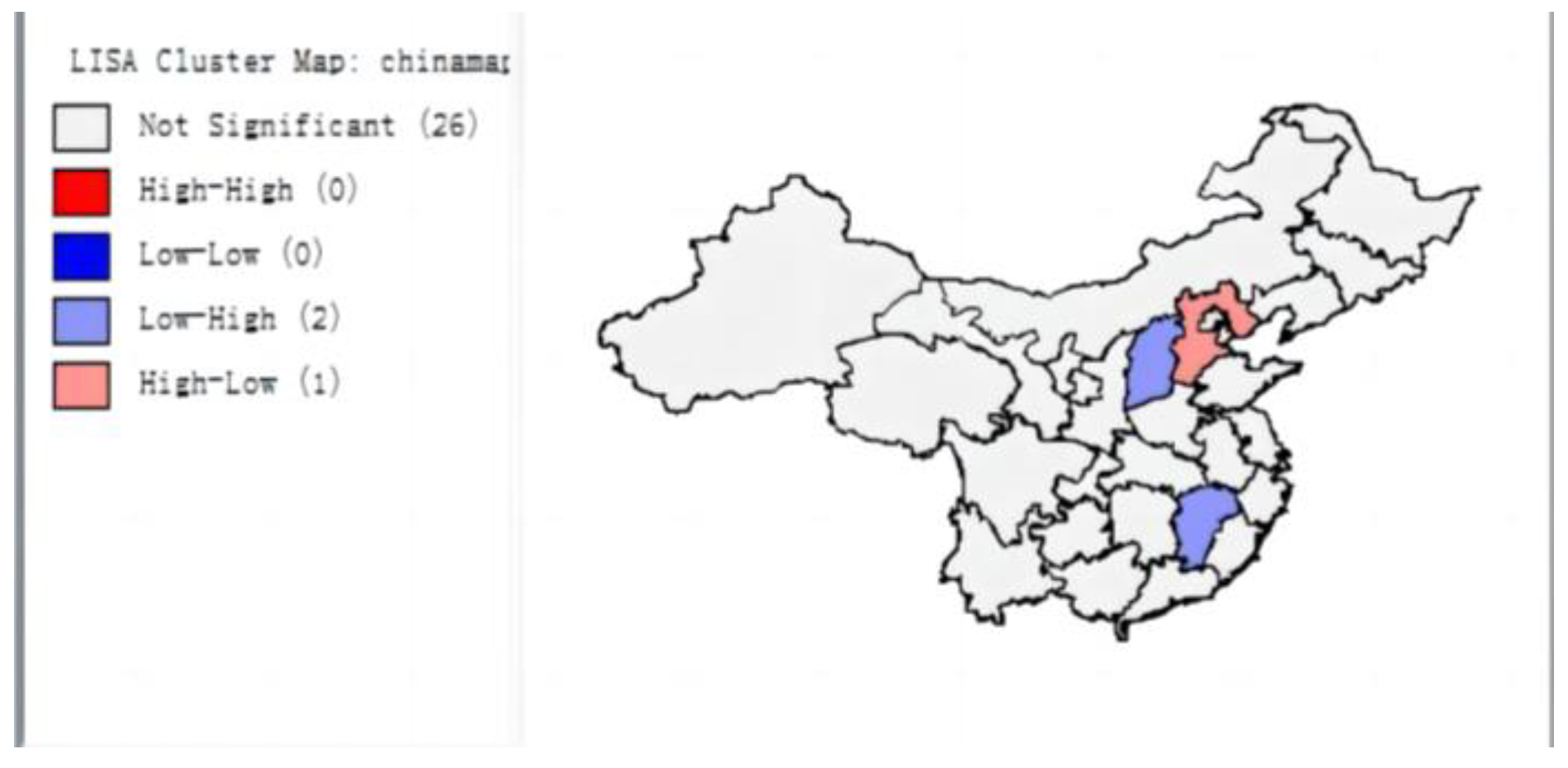
3.1.2. Local Spatial Correlation
3.2. Spatial Spillover Effects
- (1)
- Environmental regulation
- (2)
- Fiscal decentralization (FD)
- (3)
- Public environmental demands (LETTER)
- (4)
- Other variables
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fredriksson, P.G.; Millimet, D.L. Strategic Interaction and the Determination of Environmental Policy Across US States. J. Urban Econ. 2002, 51, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, N.D. Interstate Competition and Environmental Regulation: A Test of the Race-to-the-bottom Thesis. Soc. Sci. Q. 2006, 87, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, W. Analysis of local fiscal expenditure preferences under Chinese style fiscal decentralization. Econ. Manag. Res. 2010, 7, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Chen, S.L. Local government competition and environmental policy: Evidence from Chinese provincial data. Financ. Econ. Res. 2019, 4, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z. The game behavior of local government competition and river basin water environmental protection. Econ. Issues 2014, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M. A study on the strategic interaction of market segmentation among regions in China. China Ind. Econ. 2014, 2, 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, P. An empirical study of local environmental expenditures. Econ. Res. 2010, 5, 82–94. [Google Scholar]
- Konisky, D.M. Regulatory Competition and Environmental Enforcement: Is There a Race to the Bottom. Am. J. Political Sci. 2007, 51, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q. Research on environmental governance under the fiscal decentralization system. Financ. Econ. Politics Law 2011, 3, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.C.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.Y. Fiscal decentralization and environmental pollution: A carbon emission perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2011, 10, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, J. Environmental regulation and its assessment in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2010, 9, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner, J. Strategic interaction among governments: An overview of empirical studies. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Elliott, R. Determining the trade environment composition effect: The role of capital, labor and environmental regulations. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, B. Direct regulation of a mobile polluting firm. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 45, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J. Spatial panel data models. In Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis; Fischer, M.M., Getis, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 377–407. [Google Scholar]
- Horrace, W.C.; Schnier, K.E. Estimation a Production Function for Highly-Mobile Technologies; Department of Economics, Syracuse University: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, D.; Train, K.E. Mixed MNL models of discrete response. J. Appl. Econom. 2000, 15, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, G.R.; Hauber, A.B. Spatial boundaries and choice set definition on a random utility model of recreation demand. Land Econ. 1998, 74, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, J.; Hardman, I.; Shimshack, J.; Voorheis, J. Disparities in PM2.5 air pollution in the United States. Science 2020, 369, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, K.; Downey, L. Inter-Neighborhood Migration, Race, and Environmental Hazards: Modeling Micro-Level Processes of Environmental Inequality. Am. J. Sociol. 2010, 115, 1110–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatter-Götz, H.; Mohai, P.; Haas, W.; Plutzar, C. Environmental Inequality in Austria: Do Inhabitants’ Socioeconomic Characteristics Differ Depending on Their Proximity to Industrial Polluters? Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jia, J. Strategic Interaction Behavior, Fiscal Spending Competition and Regional Economic Growth among Local Governments. Manag. World 2009, 10, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Gong, Q. Public demands, officials’ incentives and regional environmental governance. Zhejiang Soc. Sci. 2014, 5, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Aldeco, L.; Barrage, L.; Turner, M.A. Equilibrium Particulate Exposure; Technical Report; Brown University: Providence, RI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.; Arkolakis, C. Trade and the Topography of the Spatial Economy. Q. J. Econ. 2014, 129, 1085–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
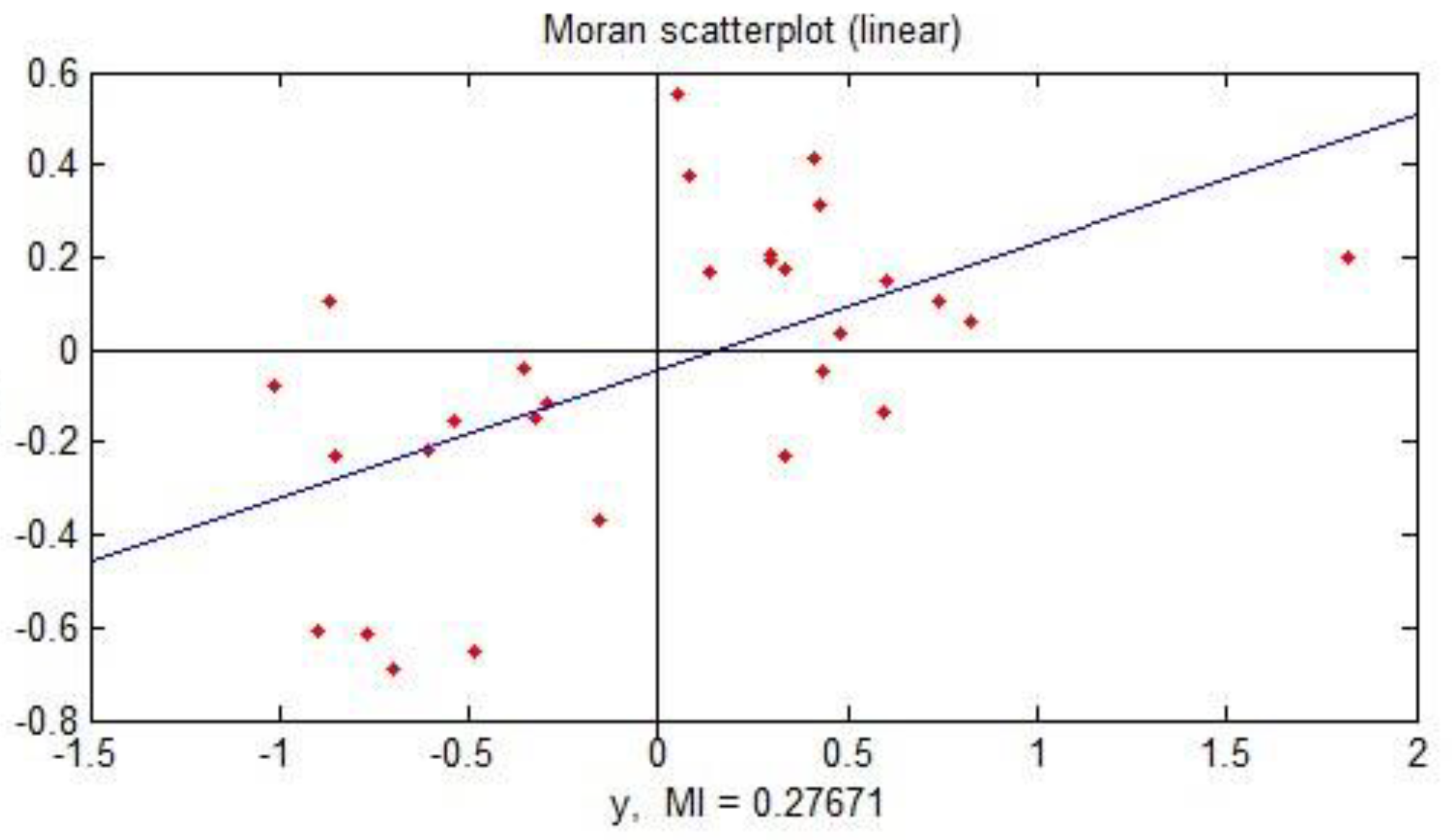

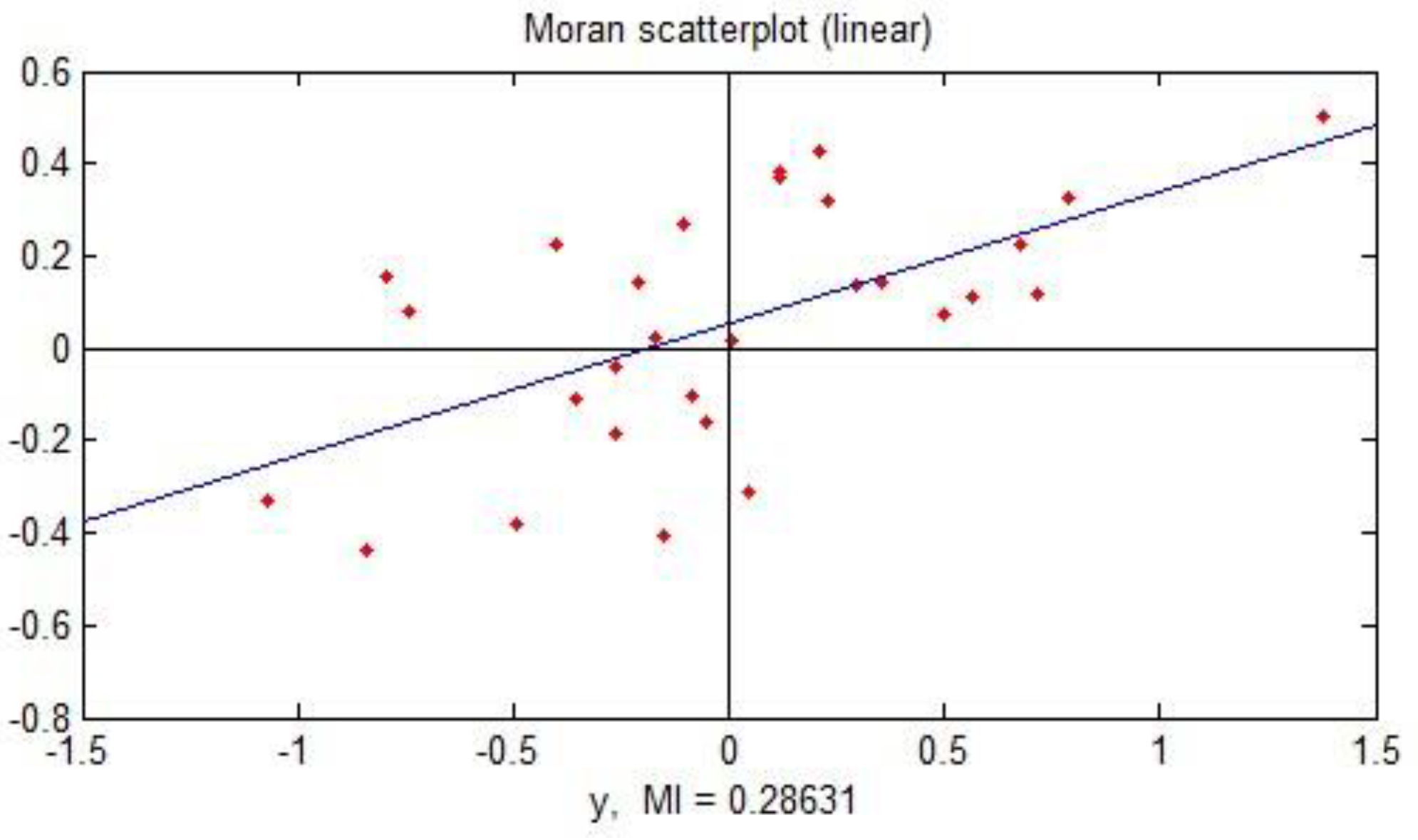
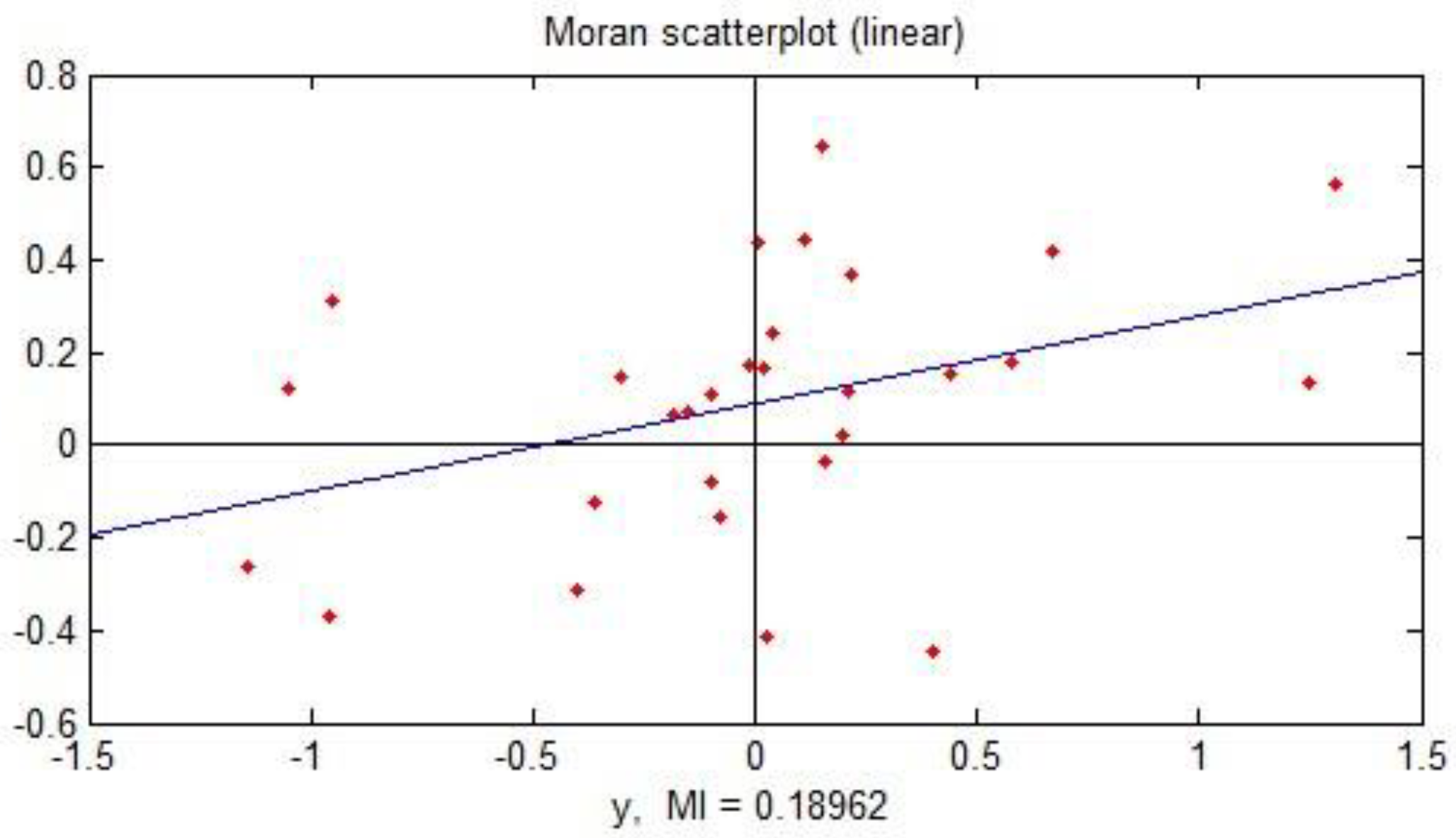
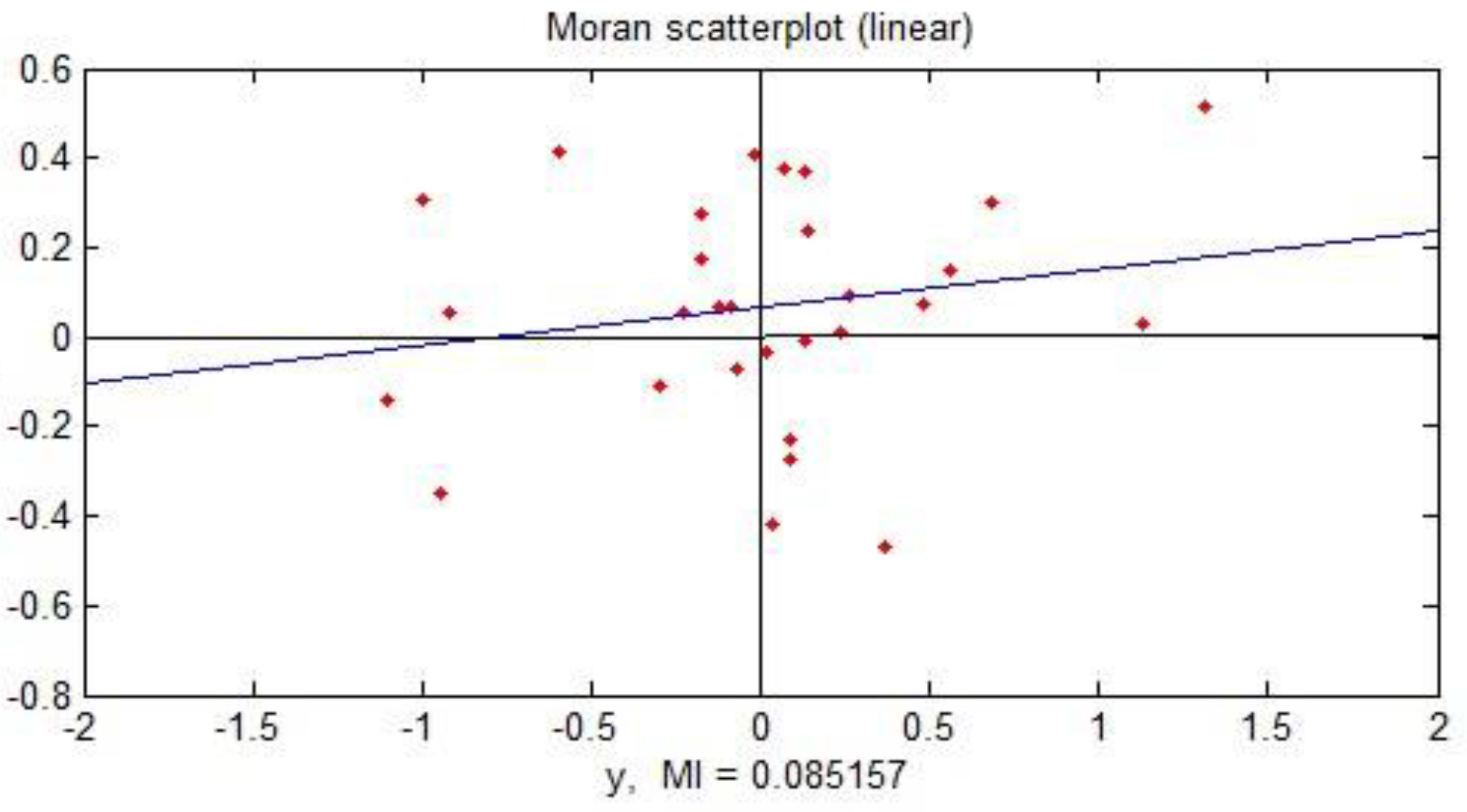
| Year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.085 |
| Basic Panel Data Model | Spatial Lag Panel Data Model | Spatial Error Panel Data Model | ||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | |
| Pooled OLS | Fixed effects ML estimation | Fixed effects ML estimation | Random effects ML estimation | Fixed effects ML estimation | Random effects ML estimation | |
| C | 0.260 | 3.749 | ||||
| 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||
| FD | −0.345 | −0.511 *** | −0.415 *** | 0.081 * | −0.529 *** | 0.108 |
| (0.823) | (0.000) | (0.002) | (0.216) | (0.000) | (0.160) | |
| LNGDP | 0.556 *** | 0.246 | 0.156 | 0.442 *** | 0.158 | 0.826 *** |
| (0.000) | (0.119) | (0.359) | (0.000) | (0.353) | (0.000) | |
| LETTER | 0.019 | 0.037 ** | 0.029 * | 0.709 *** | 0.039 ** | 0.029 |
| (0.000) | (0.021) | (0.100) | (0.269) | (0.052) | (0.156) | |
| LN PEOPLE | 0.087 *** | −2.300 ** | −2.363 ** | −0.096 | −2.455 ** | −0.157 ** |
| (0.006) | (0.015) | (0.019) | (0.212) | (0.025) | (0.044) | |
| LNFDI | 0.0275 | −0.2271 *** | −0.0545 | −0.257 | 0.00527 | −0.0880 |
| (0.267) | (0.082) | (0.6632) | (0.264) | (0.277) | (0.400) | |
| δ | 0.227 ** | 0.264 *** | ||||
| (0.023) | (0.000) | |||||
| λ | 0.213 ** | 0.171 | ||||
| (0.045) | (0.161) | |||||
| Rsquare | 0.209 | 0.471 | 0.853 | 0.798 | 0.846 | 0.772 |
| LM-Lag | Robust LM-Lag | LM-Error | Robust LM-Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.442 | 2.56 | 2.565 | 0.683 |
| 0.035 | 0.01 | 0.109 | 0.409 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. A Study of the Strategic Interaction in Environmental Regulation Based on Spatial Effects. Systems 2023, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11020062
Gao H, Li F, Zhang J, Sun Y. A Study of the Strategic Interaction in Environmental Regulation Based on Spatial Effects. Systems. 2023; 11(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hewen, Fei Li, Jinhua Zhang, and Yu Sun. 2023. "A Study of the Strategic Interaction in Environmental Regulation Based on Spatial Effects" Systems 11, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11020062
APA StyleGao, H., Li, F., Zhang, J., & Sun, Y. (2023). A Study of the Strategic Interaction in Environmental Regulation Based on Spatial Effects. Systems, 11(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11020062







