Abstract
We usually hope that social norms discourage injustice. However, we are all witnesses to harmful norms enforced by governments, such as xenophobia, which need to be contested and changed. Previous studies have concluded that it is possible to change a harmful norm through contestation by powerless actors if suitable structural conditions exist. However, these structural conditions have not been sufficiently studied and, as such, are the focus of this paper. Our paper begins with a review of well-established micro-level theories of social identity theory (SIT), recast as a set of 42 discrete theoretical statements. These statements are then re-expressed in the form of a systems-level theory of macro-changes in societal norms using the system dynamics approach. The over-time dynamic behavior simulated using this structure is compared to events in two well-known case studies of changes in societal norms: women’s suffrage between 1830 and 1920, and the emergence of more tolerant lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) norms in the US between 1950 and 2018. Further simulations of the model explore the roles of anger and social outrage, foreshadowing the ability of simulation-based experiments, such as the one presented here, to explore in a robust way a wide range of (undemocratic) regimes under counter-factual conditions.
1. Introduction: How Committed Social Action Can Drive Large-Scale Changes in Social Norms
“Never underestimate the power of a small group of committed people to change the world. In fact, it is the only thing that ever has.” As this opening quote from Margaret Mead suggests, many large-scale social changes, such as shifts in national norms, can and do start from the committed action of small groups of people. This paper is devoted to understanding the connection between micro social identity theory and large-scale macro changes in social norms.
Norms are an important concept for many disciplines in the social and policy sciences. A typical definition characterizes a norm as “a standard of appropriate behavior for actor/actors with a given identity” [1,2,3]. Behaviors become norms through reinforcement and punishment by peers, organizational settings, and government [4,5]. We usually expect norms to be beneficial for society and to discourage violence and/or injustice. However, sometimes harmful and restrictive norms are enforced by governments and social groups; these harmful norms include xenophobia and religious and ethnic discrimination, alongside many others that need to be changed. As governments are generally unwilling to change the laws associated with these harmful norms, it is mainly up to small groups of committed individuals to contest (Wiener defined contestation as a “social practice [that] entails objection to specific issues that matter to people”; in “international relations, contestation ... involves the range of social practices which discursively express disapproval of norms.”) and challenge them.
The constructivist school of thought is linked to a significant body of literature on norm contestation and how it challenges or results in the decay of old norms. Previous work has assumed that the power of the actor (i.e., those who contest an old norm) is the main reason for norm decay; therefore, the structural factors behind norm decay or new norm emergence have not received enough attention. To date, the literature on contesting harmful norms has tended to focus on powerful state and non-state actors [6,7], showing that a powerful state can change a harmful norm. For example, Sandholtz [8] studied the wartime plunder norm and the ways in which contestation changed it. While plundering was acceptable for centuries, Great Britain contested that norm after Napoleon’s defeat—maybe because it was never conquered by France—and argued against it. Great Britain used its diplomatic power to effect this change. Later, an anti-plunder norm became institutionalized after WWII, and Western states’ opposition to Soviet plundering of Germany entrenched it further. Sandholtz’s study proved that sometimes, norm contestation behavior can change an existing harmful norm. In his case study, the norm violator was a prominent and powerful actor in IR.
The constructivist literature on power norm contestation is not limited to the international level. There are also studies that offer domestic analyses. Just as strong states such as the United Kingdom or China can contest and challenge a global norm at the international level, there are powerful actors, including elites and government officials, who can challenge or change a dominant norm at the domestic level. Barnes [6] investigated how the Bush administration tried to revise the norm of torture and use it to its benefit. However, this study showed that torture remains taboo in the United States, and the Bush administration’s attempt was unsuccessful. Sikkink [7] discussed how, during the Iraq war, a “relatively small group of powerful political operators” inside the United States sought to undermine the norm of torture to make these actions legitimate. In another study, scholars examined how governmental actors challenged the global norm of human rights after the 9/11 attacks by giving priority to the norm of counterterrorism [9].
It is not surprising that strong actors can change norms, but questions remain regarding the role of less powerful actors. This aspect of norm study has mostly been ignored until recently. Acharya [10] developed a theory based on Slaughter’s idea of “norm subsidiarity” and considered the agency of weak states such as those in the Middle East, Latin America, and Africa [11]. This proved that sometimes, non-prominent state actors can contest and develop new regional rules and norms which become established and provide another way to understand the global norm (e.g., Pan-Arabism in the Middle East, as opposed to the global norm). His work showed that contestations by weak states matter, and that such states have the potential to make changes; this contrasts with the dominant belief in the field.
Another important study of weak state contesters, known as “rogue states”, provided norm researchers with some new insights. In “Rogue States as Norm Entrepreneurs”, Wunderlich [12] investigated when such states can be recognized as rational norm entrepreneurs (creators). This further demonstrates that contester power levels at the international scale are not the sole determining factor that shapes whether a contestation is successful, as has traditionally been assumed: there are other factors that play important roles, and those conditions need much more attention and research.
At the domestic level, it is not difficult to find examples of relatively powerless actors revising and establishing norms. Obvious examples include LGBTQ rights in most western countries, abortion laws in Canada, Ireland, and elsewhere, and “marry the rapist” laws in many western and non-western countries. These examples prove that the committed actions of small group of people can matter. Indeed, these examples support scholars’ claims that an actor’s level of power is not the only determining factor in changing a norm: under suitable structural conditions, even powerless actors can challenge and ideally change a harmful norm [13]. However, those structural conditions have been insufficiently studied. This study seeks to contribute to our understanding of norms by exploring the structural conditions and mechanisms under which the actions of relatively powerless actors can bring about changes in norms and behaviors at the domestic level.
This paper develops a system dynamics simulation model which captures existing causal theories to replicate observed real-world conditions. Some aspects of the model are well known from the literature, but this does not detract from the insights associated with the specific findings and hypotheses which emerged from our model. For example, we explore circumstances in which unjustified punishments administered by governments cause feelings of anger among those who violate norms, which increases the violation and contestation of harmful norms. In other words, under the right conditions, government punishment facilitates the emergence of new norms rather than prohibiting it.
The paper proceeds as follows. The next section explains how we build on the assumptions of social identity theory to create a system dynamic computational simulation model. Next, the paper “exercises” the simulation model to generate a set of results concerning the conditions under which the contestation of a norm by a relatively powerless actor can begin a process that leads to the replacement of the old norm with a new one. The subsequent sections validate our model results with two examples: the LGBTQ rights and Women’s Suffrage movements. Finally, a conclusion is presented.
2. Materials and Method: Extracting System Structures from Social Identity Theory
This study views the macro process of societal norm changes as a generic system that can be examined using the system dynamics method. A central tenet of the system dynamics method is that the over-time dynamic behavior of a system is determined by the structure of that system. In turn, this structure is understood to be a set of system stocks or state variables that are connected via a web of feedback effects, all of which may be captured by equations within a simulation model.
For example, in his foundational studies, Forrester [14] conceptualized generic industrial production systems as stocks of workers, capital equipment, and raw materials being transformed into finished products, all of which are connected in a web of feedback relationships, which is defined by the rules governing a firm’s operations. The structural rules governing production were gleaned through qualitative interviews with the managers of the firm. Similarly, Forrester [15] conceptualized cities in the US as urban systems consisting of stocks of workers, housing, and industrial job-producing structures connected via a web of feedback relationships, which the author came to know by interviewing a small set of knowledgeable informants, identified to him by John Collins, the mayor of Boston. When simulated, these urban feedback-oriented structures generated generic patterns of growth, overshoot, and eventual urban stagnation characteristic of many US cities in the middle decades of the 20th century.
Qualitative methods for identifying and mapping system structures have come a long way since Forrester’s initial interviews [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26], but the overall method of conceptualizing a system structure as a small set of stocks connected via a web of controlling feedback loops has remained a core aspect of system dynamics. In this study, the source of the system structure is well-established, and based on previously published micro theories of individual norm formation, collected under the broad rubric of “Social Identity Theory” (SIT). Elements of SIT, including “self-categorizing theory”, as well as a cost-and-benefits-oriented theory of personal risk, coupled with theories of the emotional aspects of decision-making associated with anger and outrage, were systematically coded into 42 succinct propositions; these were then reassembled into a generic system dynamics structure that presents a macro-level theory of society-level norm change.
This study first presents the over-time behavior that emerges from this generic structure as graphs of key variables emerging from a formal simulation model. Next, these plots of key system variables over time are compared to events associated with two well-known cases of large-scale shifts in societal norms within a democratic society—women’s suffrage between 1830 and 1920, and the emergence of more tolerant LGBTQ norms in the US between 1950 and 2018. Further simulation experiments with the model explore additional topics, including the roles of anger and social outrage, as well as the role of antipreneurs in determining overall system behavior.
2.1. Social Identity Theory Forms the Basis for a Simulation Experiment
Our formal model begins with concepts and insights from social identity theory (SIT). Social identity theory explains how individuals’ norms and behaviors are shaped through their interactions. To SIT scholars, social norms and social identity should be considered key motivational factors in attempts to explain individuals’ behaviors. In this context, social norms are informal rules that groups adopt [27], while social identity is part of an individual’s self-conception which derives from one’s knowledge of one’s membership of a social group, together with the value and emotional significance attached to that membership. According to Turner, group identity is basically a cognitive mechanism whose adaptive function is to make “group behavior” possible [28]. This approach is mostly used by social psychologists and anthropologists. From this perspective, there is an inevitable connection between members’ social identity and group behavior. Thus, this approach shows how group norms change individuals’ norms and behavior (an experimental study on the correlation between norms and behavior is described in [29]). SIT fits well with this study, as it shows how a new norm can spread among other group members with shared interests, such that it might eventually evolve, strengthen, or weaken the dominant norm. All 42 of the claims and assumptions derived from SIT, on which this model is based, are summarized in Table A1. Our review of the theoretical background below highlights some of the key elements.
Turner and Hogg [30] proposed the “self-categorization theory”, which is a foundation on which to build a formal model. Based on this theory, individuals have personal norms which shape their identities and interests. Individuals perceive similarity with others based on a given set of interests or characteristics (factors of interest might include history or gender, among many others. This perception of similarity is a key element in shaping a new category or group. In this study, we use the terms “category” and “group” interchangeably. By joining a particular category, group members learn and assign a group norm [30]. The authors believe that joining a group makes individuals perceive similarities with other members and experience a sense of solidarity. In other words, people perceive themselves primarily based on their reference group and its norm and goals. Those shared goals provide trust (in both its emotional and cognitive dimensions) and cooperation among group members, and thereby function as a deep assumption underwriting the social order. Thus, if a person perceives that their goals are different from those of the group, they distrust the group norms and perceive dissimilarity with other members, leading them to begin performing dissimilarity-focused comparisons and detach from the group [31]. Social judgment is based on the comparison mechanism; in other words, we compare targets with comparison standards regarding a set of interests [32].
Based on this theory, group norm activation and peer influence cause individuals to depersonalize and self-stereotype. Depersonalization is a cognitive redefinition of the self from unique attributions to shared category membership and associated stereotypes [33]. Self-stereotyping happens when people identify with a category’s stereotypes and clichés [33], which leads to internalization, whereby people assign the norms and attributes of the category to themselves, as when a norm is taken for granted [34]. Those who internalize a norm begin to behave in a manner which is in line with that norm. This is a concise explanation of the self-categorization theory which, as we mentioned earlier, is a foundation upon which to build a formal model.
It should be noted that this theory mainly explains the emergence of group/social norms which do not contest the dominant norms. According to this theory, once they internalize a norm, group members begin to behave in a way that is based upon that norm. However, this is not the case in this study. Thus, this paper expands the theory based on the existing literature of collective action, and adds a distinct variable of risk taking, which requires further explanation.
Risk taking depends on the perceived cost and benefit of a particular action. In other words, individuals in a society take risks based on a cost–benefit calculation [35,36]. In this study, the cost is considered to comprise negative emotions, and the benefit comprises positive emotions. These emotions are defined as temporary good or bad states which arises based on a situation: in other words, a positive or negative feeling, which could be conscious or unconscious [37,38], which is experienced in the process of performing a particular action. Psychologists have argued that humans have five main basic emotions, fear, sadness, anger, joy, and disgust, which shape their behavior and risk-taking decisions. For the purposes of this study, we define negative feelings as the sum of fear, which could be the fear of losing a job or money, or being arrested, with the feeling of disgust due to being abandoned by peers [4,35,39]. A positive feeling is the sum of anger, due to unjustified government punishment, and pro-category emotion. We define pro-category emotion as the sum of the feeling of sadness of having shared grievances with violators, and the feeling of joy while violating norms and receiving admiration [40,41,42]. Here, risk-taking individuals may fulfill interests such as improving their status in the group or receiving more admiration. In other words, risk is a cultural value [40].
It should be noted that this framework provides for a potential reversal of the traditional pattern of emotions associated with norm violation. Traditionally, violators of a dominant norm are punished by the government or by their peers when their behavior causes negative feelings among the group [43,44,45]. The key difference here is that if violation of a norm arises through membership in a transgressive group, then government punishment is potentially not an obstacle but, instead, a facilitator that intensifies the contestation of a harmful norm. Such a phenomenon may have been observed at the Stonewall Inn riots: a foundational moment in the LGBTQ rights movement, when a police attack on a gay bar caused a significant increase in the number of contesters. In fact, contestation of a norm sometimes results in positive feelings, as happened in Iran after an “Inqilab Girl”—a woman who removed her scarf in one of the most populated streets in Tehran to oppose the norm of compulsory hijab—contested a harmful norm.
Eventually, after internalizing the group norm, group members take risks based on the calculation of their cost and benefit, and behave against the dominant norm. It should be noted that this practicing of a new norm contrasts with existing norms and laws and, as a result, there are punishments associated with it [4,5].
2.2. Forty-Two Propositions That Bridge Social Identity Theory and the System Simulation
Our work views the theoretical literature on Social Identity Theory as the basic evidence that can be used to structure a system dynamics simulation model. In order to establish a consistent logic about the phenomenon of norm emergence within this huge body of literature, and to show their dynamic relations and the interpretations of these relations, we extracted 42 key propositions based on existing SIT to be used as the basis for constructing our simulator. While more complete details of this process have been presented elsewhere [46], here we review several examples of this work. Claims are statements which are explicitly supported by at least one citation within the norm emergence literature. Logical extensions of claims are called assumptions.
Based on the literature, shared interests cause the perception of similarity and, as a consequence, can lead to the formation of a new group. We show this as a claim in Table 1. Or, as another example, while much of the literature considers punishment to be a primary tool in the enforcement of norms, we assume that governments’ unjustified punishments result in feelings of anger and may increase instances of norm violation, as happened during the Stonewall Inn Riot. We repeated this process 42 times and created a consistent logic among the norm emergence variables from the literature.

Table 1.
Example of Propositions.
To depict the logical relationships between norm emergence variables, we use Causal Loop Diagrams (CLDs). The CLDs are used both to depict the propositions and to build the simulation model. The CLDs for this model shape reinforcing loops (R1–R17) and balancing loops (B1–B11). Reinforcing and balancing loops, respectively, cause positive and negative effects. Each loop starts at a variable and moves forward in the direction that leads back to the starting variable. We review an example loop below; full details of this process can be found elsewhere, as can details of other loops [46].
Figure 1 shows one example of the cause–effect relationship between variables for norm emergence, based on Social Identity Theory and the claims and assumptions table.
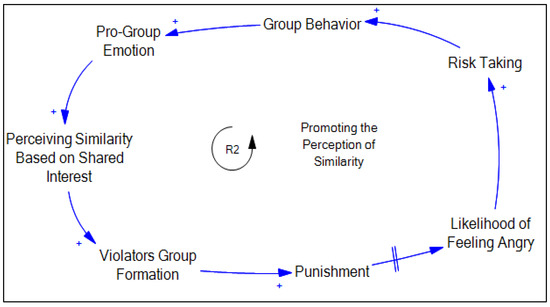
Figure 1.
Promoting perception of similarity, R2.
Loop Legend: Promoting the perception of similarity, R2 ([4,5,34,47,48,49]), is illustrated. The perception of similarity based on shared interests results in the formation of a violator group, which in turn triggers government punishment. There is a likelihood that punishment increases feelings of anger. As a result, people take more risks, and that increases the incidence of group behavior. The increased incidence of violating behaviors in a group increases pro-group feeling, which later strengthens the perception of similarity.
2.3. Telling the Story of the Emergence of Norm Contestation
This short section aims to develop some premises for the model presented in the next section by telling the story of one possible path through the model: a path in which an old norm is replaced. This is the brief story of the stock and flow system dynamic model, but it is important to remember that the emergence of a new norm is not the only story that the model developed in the next section can tell, and there is a possibility that it does not emerge.
When a person or a few people who believe in a new norm begin to contest the (harmful) old norm, not only to show their personal opposition but to draw attention to the problem, it is hard for other members of the society who have a shared interest with those violators not to join them. As a result, the old norm begins to transform into the new norm, with an increasing number of people joining the violators’ group. However, these people have not fully rejected the old norm; there is a likelihood that they may find that the old norm fulfills their interests better, and therefore resist change and return to the general population. The next step during a move toward the new norm is to have violators internalize the new norm through education. This internalization is necessary because, while it is true that they do not believe in the old norm, they still do not believe in any other norm: they are a population that might be convinced to follow other norms. The increase in the number of people who internalize the new norm means the society faces more violations of the old norm. But violating the old norm is harder and riskier in the early stages of a collective behavior due to punishment both from the government and from peers. People are likely to be afraid they will lose their jobs, lives, reputations, and even their friends and families. With time and the persistence of the violating behavior, a new norm gains more popularity. This shift in the dominant views of the population makes risk taking easier and, as a consequence, the violating behavior happens more openly until the new norm eventually gains sufficient followers to have enough power to change the old norm through institutional change. Nevertheless, this new norm itself is always in danger of being challenged, weakened, and replaced by another norm when people find that another norm fulfills their goals and interests better. Real-world examples of this story include the paths that LGBTQ rights and the women’s suffrage movements followed in the US, which we explain in detail later.
2.4. Simulation Model
Our simulation model was formulated as a system dynamics model and created within a Vensim simulation environment (vensim.com, accessed on 15 July 2022). As is the case with all system dynamics models, this model is a state-determined system that aggregates the population into homogeneous classes and model dynamics that are controlled by a network of feedback loops. In mathematical terms, the simulation can be characterized as a set of non-linear simultaneous differential equations.
The simulation model was built around four main population stocks, which in sum are equal to the total population of the society. (A fully detailed explanation of the model is available elsewhere [46].) Figure 2 shows these stocks and respective flows. Each of those four stocks represent one state of the population which can be transferred to another state. In other words, stocks are changed from the old norm population to the violators’ group population, to a population that has internalized the new norm, to a new norm followers’ population, and finally to any of the other states. In this study, we assume that, when the new norm population reaches a majority, then public opinion will affect institutions and is capable of changing the harmful norm. (This assumption has its root in the constructivist claim that people’s values and opinions have a direct influence on government officials and their policy [50].) Thus, by studying peoples’ opinions, we can, in some ways, predict their political behavior. After talking to experts in the field, we selected a 100-year window of time to determine whether this transition would happen.
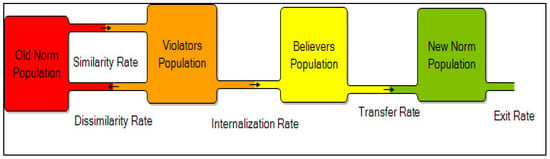
Figure 2.
Model’s main stocks and flows.
Initially, most of the population is in the old norm population (shaded red in Figure 2). The process of potential norm transformation begins when there is an initial group of norm contesters who find a norm harmful and act to change it for the benefit of society. These individuals form the beginning of the violators’ population (shaded orange). Their norm contestation acts as a triggering phenomenon for the rest of the society (the old norm population), setting off a process in which contestation potentially continues to lead to growth in the number of contesters who believe in a new norm (shaded yellow), ultimately producing a new norm population (shaded green). We use the following integral form of a differential equation to formulate the old norm population with a 100-year window of time:
There will come a time in a society when the old norm population (shaded red) are unhappy about the old norm and their situation; this is when the initial contestation of the norm provides motivation and encouragement among the old norm population. They come to think that the contesters’ norm possibly better fulfills their goals, and thus decide to join them. We named this group the violators’ population. However, there are two possibilities for this group: members may either find the old norm better and go back to it, or learn and subscribe to the new norm and begin internalizing it. We refer to the group that is internalizing the new norm as the believers’ population (shaded yellow in Figure 2). As the new norm becomes the normative behavior, believers transition into the new norm population (shaded green). Finally, there is always the possibility that a competing norm will challenge the new norm as time goes on, and the number of people following the new norm will decrease. This is modeled through the exit rate. Each of the boxes in Figure 2 is a stock; mathematically, they use the same logic to be formulated in the simulation model. Full details on the simulation model’s structure and equations can be found in the published work by Salimi [46].
Using the Literature to Operationalize the Dissimilarity and Internalization Rates in the Simulation Model
Here, we offer examples of our claims and assumptions in our model structure. We start from the Dissimilarity Rate and Internalization Rate, which are shown in Figure 3. The violators’ population might learn that the new norm is incompatible with their own interests and goals. That perception of an incompatible goal causes distrust toward the new norm. Trust is the main factor in gathering a group together to act towards a common goal. Thus, losing trust in a group norm results in people returning to the old norm population.
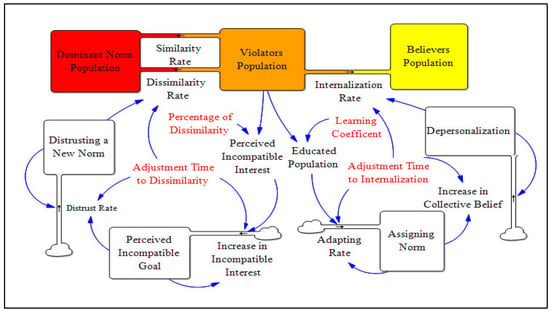
Figure 3.
Perception of dissimilarity and new norm internalization.
On the other hand, the violators’ population can receive education and learn and subscribe to the new norm. This education is based on the educational resources that are available and varies across different cultures. Thus, we define the learning coefficient as a constant to show accessibility to resources. When adopting a new norm, members of the violators’ group may start to depersonalize themselves or, in other words, increasingly define themselves as similar to other members of the new norm population. Thus, the emphasis is on us and our goals, rather than me and my goals [51]. This process results in shaping a collective belief or identity among the group, and moves this population toward the believers’ population. Unlike the colorful box these are not cumulative—rather, they are arithmetic, and we use the equation given below to implement the internalization rate in the simulation model and other rates that have similar logic.
Internalization Rate = (Depersonalization − Believers Population)/(Adjustment Time to Internalization/3)
Figure 3 depicts one part of a simulation model, which we call Sub Models 2 and 3: “Perception of Dissimilarity” and “ Internalization Rate”, respectively. In the Appendix A and Appendix B we illustrate the same process, using claims and assumptions to operationalize the simulation model three more times. Sub model 1: “Perception of Similarity” represents the process by which people percieve their similarity with violators. Sub Model 4: “Emergence of New Norm” explains how people move toward the new norm from the believer population. Sub Model 5: “Exit from the New Norm” explains how the followers of the new norm exit the new norm population. See Appendix B (Stock-and-Flow-Diagrams, Table A2 and Table A4) for more documentation of the model.
After the simulation model was developed, we put it through a series of validation tests to the greatest extent possible. System dynamics researchers have developed a series of rigorous structural and behavioral tests, such as dimensional consistency, boundary adequacy, sensitivity analysis, extreme conditions, and behavior reproduction tests [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]. For a full explanation of our model structural and behavioral tests, see [46] (pp. 109–115).
3. Exercising the Simulation Model
In this section, we describe how a system dynamics model allows us to simulate and evaluate the effects of different variables and conditions on the emergence of new norms. This is where the payoff from building a simulation model of the theory emerges. This section contains a discussion of base run behavior for a democratic culture only. Simulations for non-democratic cultures have been completed by Salimi in her dissertation work [35], and we intend to present these results in future publications.
Base Run Behavior for a Democratic Culture
To address the main questions of this study, we begin with a base simulation run to determine the conditions that result in the emergence of a new norm in democratic cultures (See Table A5 for a description of the conditions). The base run results are shown in Figure 4, which depicts the key populations and their expected behaviors.
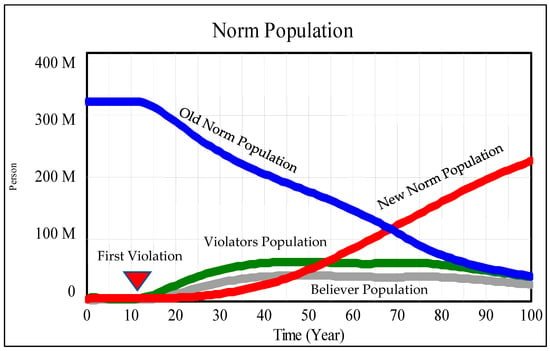
Figure 4.
New norm emergence results in a democratic culture.
As shown in the Figure 4, the first violation happens at year 10. We consider this an “initial disturbance” or critical juncture [62,63]; it triggers a powerful response in the society and moves the system in a new direction. (The so-called first violation, which in the literature is also known as critical juncture, is assumed to happen at year 10 in the current run but it might also happen later, when enough people in the society come to a shared understanding about the old norm. For example, the desegregation movement began in the early 1900s and had some achievements at this time, but the critical juncture for the movement was Rosa Parks’ violation of segregation laws in 1955 when she refused to vacate her seat on the public bus, which later resulted in the Montgomery bus boycott that catapulted Martin Luther King to national prominence. In other words, that event was a foundation for the Civil Right Movement.) Thus, it is crucial that the first violation happens at the appropriate time, when an adequate amount of people in the society have come to a shared intersubjective understanding and shared feeling about the old norm. We showed shared understanding and feeling as a parameter called pro-category emotion. It is important to note that these critical juncture events are contingent, and often happen at the intersection of two or more independent sequences of events. (For more information, see [62,64,65].)
Figure 4 shows the emergence of a new norm in a democratic society. The blue line here shows the number of people who follow the old norm; the red line shows the number of people who follow the new norm; the green line shows the number of people who violate the old norm but still are neutral and might either move toward a new norm or go back to the old norm; finally, the grey line shows the number of people who believe in the new norm. We consider a country like the US, with a population of around 330 million, and assume that 97 percent of the population follow the old norm at the beginning of the simulation/at time zero. We study a society in which one percent of the population has already violated the old norm, one percent believe in the new norm, and one percent already behave based on the new norm. Then, this society faces a violation at year 10, which can be considered a critical juncture based on the literature of path dependance, and that violation moves the system in the new direction. Or, in other words, people begin violating the old norm. Violating the old norm begins at year 10, but following a new norm does not happen until later; the intervening period is the time that people and society need to be educated and unified toward a new norm. Based on the results shown in Figure 4, there is a crossing point/cross over at around year 68, which Finnemore and Sikkink [3] called the tipping point. (Dynamics modelers usually reserve the term tipping point to refer to a shift in loop dominance.) At this time, an old norm has lost the majority of its followers and its robustness overtly shrinks. The transfer of power between followers of two groups begins, and there is a shift between new norm opponents and proponents [66].
In the following section, we have chosen to examine LGTBQ rights and the women’s suffrage movement in the US, and we argue that the stories that those cases tell are the same as that of our model. It is important to mention that, in comparing the case studies’ graphs to the model’s results graph, we emphasize the face validity of simulation calibration. In principle, the quantitative calibration of data which we collected from real world cases—LGBTQ rights and Women Suffrage—with the data generated by the simulation model is not possible, since they comprise theoretical statements from the literature. Since quantitative and point-precise isomorphic calibration is not possible, then the best we can do here is qualitative calibration. As such, we can observe that our general theoretical model rebuilds a specific case’s pattern, such as that of LGBTQ rights or women’s suffrage. The similarity of the patterns indicates face validity and expert validity.
4. Discussion
4.1. Case Examplar #1: The LGBTQ Rights Movement and Same Sex Marriage
The LGBTQ rights movement was not significant before the 1969 Stonewall Inn riot, though gays and lesbians were systematically suppressed in society. In other words, they mainly used the strategy of duck and cover. The Mattachine Society and the daughters of Bilitis were the two main gay rights societies, and were organizations of a few hundred members. However, the Stonewall Inn Riot in June 1969 changed everything for the movement. On 28 June 1969, police stormed the inn and arrested cross-dressers. Angry people participated in a three-day public opposition of the police attack and publicly violated the law. The Stonewall Inn riot is considered a critical juncture for this movement, which we called the first violation in our model. The Stonewall Inn Riot totally changed the movement’s scope and direction [67]. Although there were 205 people in the bar, records show that around 600 people participated in the riot—some of whom were not gay. This means that the riot not only acted as a public violation of law, but it successfully attracted attention from across society and triggered people to transform from old norm toward the new norm, as shown in Figure 5A. Based on our model, at this point, a small number of committed people start challenging the old norm and society faced a group of violators: this was a time for public education to promote a single goal or shared identity. After the riot, activists put significant efforts into the movement to educate people and attract more attention to the cause. For example, in 1970, LGBTQ rights activists organized and launched the first gay pride parade to commemorate the Stonewall Riot. It began in New York City and spread across the US very rapidly. Figure 5B represents how fast the pride parade spread across the movement’s membership in San Francisco. The movement, meanwhile, gained financial support from the Lambda Legal Defense Fund, and eventually they even formed the LGBTQ Rights National Lobby. As predicted/explained by our model, through educational resources and across time, the movement gained more followers across society.
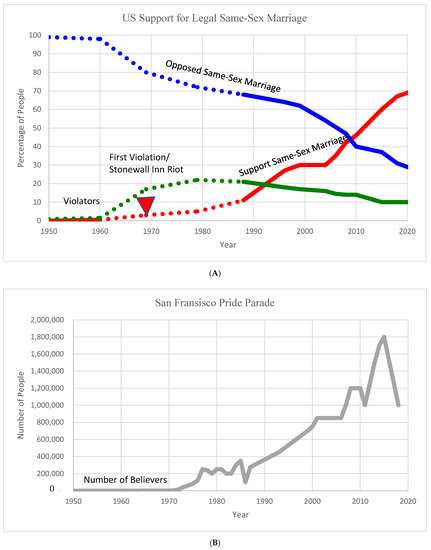
Figure 5.
(A) Change over time in the US of people’s opinions about same-sex marriage. (B) Change over time in the number of people who participate in Pride parades. The red triangle depicts the time that Stonewall riot happened.
As expected, any opposition of the law results in different kinds of punishments, and LGBTQ rights followers and advocates were no exception. For example, from 1980 to 1986, the movement faced significant obstacles as social conservatives slowed down the movement. However, through continued educational efforts and advocacy, LGBTQ rights activists were successful in establishing relevant narratives at the judicial level, which facilitated opinion change among opponents.
Public contestation of the laws and consistent education resulted in a significant increase in the percentage of the US population that believed in the legalization of same-sex marriage. Eventually, with an increase in the number of supporters and a decrease in the number of opponents, the movement reached a tipping point in 2010, as predicted by the model. In 2011, for the first time, the majority of the population supported same-sex marriage. In the same year, President Barack Obama’s view evolved from support of civil unions (a middle-ground stance) to full support of marriage equality. Finally, in 2015, same-sex marriage was officially legalized in the US through a Supreme Court decision. However, it took almost 60 years for this gay rights norm to be accepted by half of the population, as is shown in Figure 5A. We reconstruct this figure based on the data published by GALLUP at https://news.gallup.com/poll/311672/support-sex-marriage-matches-record-high.aspx from 1996 to 2020 (accessed on 1 June 2020). Additionally, we found data from as far back as 1988 and also from 2004, 2006, 2008, and 2010, in the General Social Survey (NORC/University of Chicago), for people who agree, disagree, and those who are neither agree nor disagree, and combined these data with others from GALLUP. Based on the available resources, there were around 600 people who participated in the Stonewall Inn riot, and we interpolated the rest of the figure. The blue line here represents the percentage of people who were opposed to same-sex marriage, which, in Figure 4, we called old norm followers. The red line represents the percentage of society that supports same-sex marriage, shown in Figure 4 and referred to as new norm followers. The green line shows the neutral people, whom we referred to as violators in Figure 4. To build the green line, we used data from NORC and subtracted the percent of supporters from opposers, based on the data available from GALLUP. Finally, the grey line is the number of people who internalized the new norm: in other words, the believers. We collect data for that line based on the San Francisco Pride Committee Website from 2001 to 2015, and from the San Francisco Chronicle.) It took less than a decade to reach 70 percent acceptance in the society; this is to be expected, as behavior changes faster after the tipping point.
There exists similar pattern of behavior between our model’s results and the case of LGBTQ rights, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5A,B. The blue line in Figure 5 represents people who disagree with same-sex marriage being legalized, which is the old norm in Figure 4; in both figures, this blue line declines gradually after the first violation. In contrast, the red lines in Figure 4 and Figure 5A, which represent the number of new norm followers or people who agree with the same-sex marriage being legalized, gradually increases. As was the case with our model results, in Figure 5A, the movements reach the tipping point and society then faces a shift of power from opponents of the movement towards proponents of the movement; finally, same-sex marriage was legalized, and an old norm has changed. The green and grey lines in Figure 5A,B at first increased and then, as the harmful norm changed, declined; this shows a pattern of behavior similar to our model’s result. This is a brief explanation of the movement, offered for the purposes of testing our model and applying it to a real-world example; for more details on the movement, see [68]. In this case study, we observe a similar pattern of behavior to that predicted by our model. As mentioned earlier, quantitative calibration is not possible here, and, as such, we conducted a qualitative calibration.
4.2. Case Examplar #2: The Women’s Suffrage Movement
In the United States, the women’s suffrage movement comprised around 100 years of struggles, starting from the 1820s and 1830s and ending in 1920 when women won the right to vote. The movement existed from the early 19th century, but the Seneca Falls Convention in 1948 significantly changed the direction and scope of the movement. The convention was the first of its kind, and around 300 people participated, including men and women. For the first time, they signed a declaration that included women’s suffrage, legitimizing the movement for equal rights for women. That event attracted significant attention across the US and, in the folllowing year, it turned into the first women’s right national convention, with almost 900 participants. The main goal of the first national convention was to promote the goal of the movement. The convention’s speeches were printed and distributed across the nation; following this, women’s rights activists and many students in several states, including Ohio and Massachusetts, began lecturing on women’s rights to popularize the issue and educate more people.
The convention in 1848, which was followed by another in 1850, attracted significant attention and shifted people away from an old norm toward a new norm, beginning in 1860 when more than 1000 people attended the convention. We reconstruct Figure 5 based on the data available in [69] for the blue and red lines. They provide a list of all 48 states and the year each state granted women suffrage. The blue line represents the number of states which opposed granting suffrage (old norm followers) and the red line is the number of states that supported granting suffrage to women (new norm followers). The green dots in Figure 5 show the number of people who attended women’s rights conferences and/or conventions during the years 1848, 1850, 1860, and 1890. We refer to this group as violators in our model. Data are collected from the National Park Service archive at https://www.nps.gov/articles/us-suffrage-timeline-1648-to-2016.htm (accessed on 4 August 2020), the American Bar association at https://www.americanbar.org/groups/public_education/programs/19th-amendment-centennial/toolkit/suffrage-timeline/ (accessed on 30 July 2019), Thoughtco.com at https://www.thoughtco.com/national-womans-rights-conventions-3530485 (accessed on 17 March 2018), Lewis, Jone Johnson, “National Woman’s Rights Conventions”, ThoughtCo, thoughtco.com/national-womans-rights-conventions-3530485 (accessed on 16 February 2021). Finally, data for the grey line (which represents believers and advocates of the movements) were collected according to the number of people who signed the women’s suffrage petition during the years 1848, 1866, 1893, and 1915. Data were collected from The Conversation at https://theconversation.com/how-17-000-petitions-helped-deliver-votes-for-women-91093 (accessed on 5 February 2018), from Bridgit Williams’ book at https://www.bwb.co.nz/books/womens-suffrage-petition-1893/ (accessed on 15 May 2017), from the American Bar association at https://www.americanbar.org/groups/public_education/programs/19th-amendment-centennial/toolkit/suffrage-timeline/ (accessed on 30 July 2019), and from the National Park Service archive at https://www.nps.gov/articles/us-suffrage-timeline-1648-to-2016.htm (accessed on 4 August 2020) (which was built based on the data available in Lott and Kenny’s work [69], and other data available through newspaper and archives, consistent with our model’s results. As shown in Figure 6, in the early stages of the movement, due to the high risk of both government and peer punishment, the transfer from the old norm toward the new one is slow. It took almost 20 years until the state of Wyoming granted suffrage to women in 1969. The movement also encountered several critical moments. For example, the Civil War brought the movement to a halt. Nevertheless, the movement’s activists made significants efforts toward public education and awareness of the issues. Even Stanton and Anthony, advocates of the movement, published The Revolution in 1868 and discussed the exclusion of women in order to further popularize the problem. Eventually, through public violation of norms and consistant education the first state granted suffrage to women in 1869, followed by Utah in 1870.
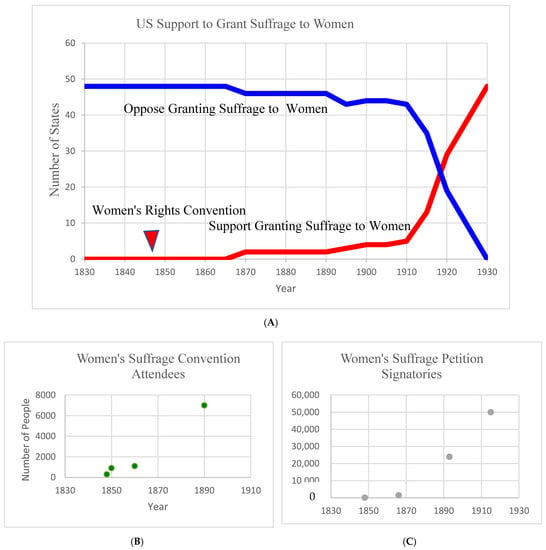
Figure 6.
(A) The USA’s behavior change, by state across time, regarding women’s right to vote. Respectively, from left to right, (B,C) depict the change over time in the number of people who attended women’s suffrage conventions to show their opposition to unjust laws; and change over time in the number of people who signed and supported the suffrage petition. The red triangle represents the first violation in the Women’s Suffrage Movement.
The division of violators in the movement into different groups, such as the National Woman Suffrage Association (NWSA) or its rival, the American Woman Suffrage Association (AWSA), significantly slowed down the movement; this phenomenon supports our model’s emphasis on the importance of education and having shared goals and identities. This movement had several challenges and was in danger of being destroyed at some points, but in 1888 the National Council of Women was established to promote and popularize equal rights for women and, in 1890, those groups fighting for women’s rights eventually merged to form the National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA), with an initial membership of 117,000. This union and its activities resulted in suffrage being granted to women at the state level, and, in 1893, Colorado granted voting rights to women, followed by Idaho in 1896. After that, the consistent transformation of the old norm into a new norm began. After this union was created, the progressive era began, and followers of the old norm decreased in number. Women of all classses entered public life. It is imporant to note that, in 1912, the movement gained the support of former President Theodore Roosevelt, bolstering the movement significantly. In 1913, activists organized a parade in Washington, DC. Additionally, during this period, Alice Paul orgainzed the National Woman’s Party, and the arrests, violence, and force-feedings endured by its members “shocked the nation and brought attention and support to their cause.” By 1920, the majority of the states had granted suffrage to women and, through a constitutional amendment, women won the right to vote across all states.
There exists similar patterns of behavior in our model results and in the case of the Women’s Suffrage Movement; these patterns are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 6A–C. The blue line in Figure 6A represents people who opposed granting suffrage to women, which is the old norm in Figure 4; in both Figures, this blue line declines gradually after first violation. In contrast, the red lines in Figure 4 and Figure 6A, which represent the number of new norm followers or people who agree with granting suffrage to women, gradually increase. The green and grey lines in Figure 6B,C increase until the old norm changes. Again, we can observe a similarity between the behavior patterns predicted by our model and those observed in the case of the Women’s Suffrage Movement. As mentioned earlier, quantitative calibration is not possible here; instead, we conducted a qualitative calibration.
4.3. Effect of Anger on the Emergence of a New Norm
Previous scholars have studied how police intervention affects political participation, as in the case of the minority civilian [70]. One of the main arguments of this study, which is depicted in Figure 7, is:
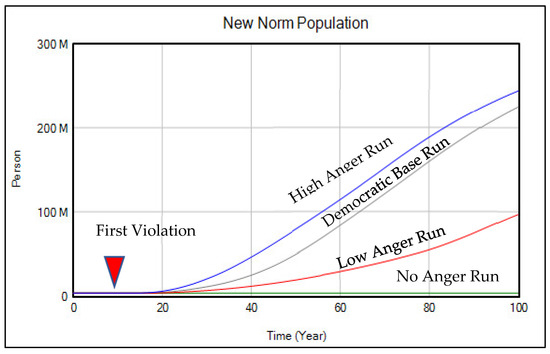
Figure 7.
New norm emergence under asymmetric feelings of anger.
Government punishment might increase anger among those who are oppressed or depressed by the old norm, which, in turn, increases risk taking, rather than decreasing risk taking as intended. This encourages more people to violate the norm. As a consequence, it increases both the number of people whose behaviors are based on the new norm, and those who perceive themselves to be similar to violators.
To dynamically test the implications of this assumption, we formulate “feeling of anger”; in this experiment, we keep all other variables the same, and only change the value for the effect of anger on positive feelings to see how it affects the growth of the new norm population. In other words, the feeling of anger reacts slowly over time to the effect of punishment. We capture this phenomenon in the simulation model using the Smooth function.
In terms of the specific parameter values in the simulation model, the initial value for this variable in the base run is 0.7. The other runs here change that initial value to 0 when there is no anger; 0.4 when anger is low; and 1 when anger reaches its maximum effect. The results are shown in Figure 7. The grey line shows the democratic base run in which the old norm will be replaced by the new norm; the green line shows no feelings of anger, and as a result the increase in the new norm followers happens very slowly. The red line depicts the new norm population when there is low anger, and finally the blue line depicts the population when feelings of anger reach their height.
As is shown in Figure 7, when feelings of anger are low and/or when anger does not exist, the new norm will not emerge. However, in other instances, government punishment that triggers anger can accelerate norm change. This is arguably what happened through the Stonewall Inn Riots concerning LGBTQ rights [71], and the actions of the National Woman’s Party in the fight for suffrage. (For more details, see “Tactics and Techniques of the National Woman’s Party Suffrage Campaign” in Women of Protest: Photographs from the Records of the National Woman’s Party, Manuscript Division, Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA. Downloaded from https://www.loc.gov/static/collections/women-of-protest/images/tactics.pdf, accessed on 10 August 2022). (See Table A6 for a description of conditions).
The reason why increasing feelings of anger result in the more rapid growth of the contesting norm population can explained by looking at the graphs in Figure 8. An increase in feelings of anger increases positive feelings, which, in turn, increase the benefit of taking risks and, consequently, of engaging in violating behaviors. If those feelings of anger are suppressed, we see the opposite results. An increase in violating behavior has another side effect. It causes more people from outside the group to notice the ongoing violation and, due to emotional ties, perceive similarity. As a result, they join the violators’ group, which further weakens the old norm.
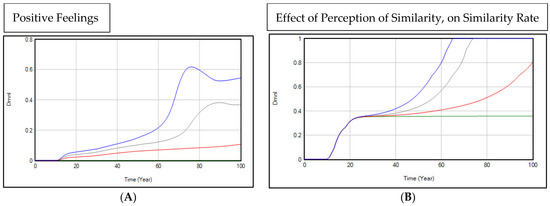
Figure 8.
Respectively, (A) and (B) represent positive feelings and the effect of perceived similarity on similarity rates under asymmetric feelings of anger. (It should be noted that the variable “Effect of Perception of Similarity on Similarity Rate” depicts how changes in the perception of similarity based on shared interests within a society affect the transition from the old norm toward the violators’ population. Here, we investigate how different levels of anger can affect the perception of similarity between other people and the violators’ population. Here, we study how different levels of anger affect the variable perception of similarity and, as a consequence, the effect of the perception of similarity on the similarity rate. See Appendix B for further details.) The blue line show positive feeling and the effect of the perception of similarity on the transfer rate during a high anger run. Similarly, the grey lines represent positive feelings and the effect of the perception of similarity on the transfer rate for the democratic base run; the red lines depict positive feelings and the effect of the perception of similarity on the transfer rate for the low anger run; finally, the green lines show positive feelings and the effect of the perception of similarity on the transfer rate for a situation when there are no feelings of anger.
The results in Figure 8 show a counterfactually generated hypothesis based on different levels of anger in the society. It is evident that, when anger is high among people who are suppressed due to punishment by the government, the rate of violating behavior increases in society. This happened both during the Stonewall Inn Riots during the LGBTQ rights movement, when the police raid on a gay club caused a significant increase in the number of contesters, and in the suffrage movement as a result of the National Woman’s Party’s actions, arrests, hunger strikes, and force-feedings. But what if government punishment in fact causes few feelings of anger? The grey lines in Figure 8 show this scenario. As we can see, low levels of anger result in less positive feeling towards violators and lower rates of violating behavior; as a consequence, new norm followers do not grow to even half of the population.
This hypothesis emphasizes that governments potentially need to be cautious when it comes to punishing violators. If punishing violators would be perceived as unjustified, or the punishment considered illegitimate, triggering anger, then the punishment could backfire. Thus, governments usually seek a policy to justify their punishments and reduce the feelings of anger.
5. Summary of Dynamics of Norm Change within a Democratic Culture
This study began with the question: under what conditions does powerless individual actors’ contestation of harmful dominant norms cause the emergence of new norms which result in changes in states’ behavior? The simulation model, which is built based on existing causal theories, produces results concerning the necessary structural conditions under which contesting a harmful norm by individual powerless actors results in the emergence of a new norm. Among these structural conditions are education [72], dissatisfaction with the old norm, and anger at the tactics used to enforce the old norm.
A major contribution of this paper is its ability to demonstrate how a systems-level theory of shifts in overall societal norms can be created from micro-level theories of social identity theory. This generic systems theory of changes in societal norms generates simulated-over-time behavior that is compared and found to be quite similar to actual events from two well-known cases of changing societal norms. Finally, the simulation model introduces new counterfactually generated hypotheses, which need to be further tested empirically, as discussed below.
The results can be summarized in the following statements. In democratic societies, whenever a sufficient population of a given society comes to a shared understanding that an old restrictive norm is not beneficial for them and there exist other norms which can better fulfill their goals and interests, there is an opportunity for their committed action and for an initial contestation to spark a transformation of the norm. An initial violation can be generated at a critical juncture and move the system in a new direction, in the sense that some portion of the people in each society feel positive about that contestation and even identify themselves with the violators and join them.
After the violators’ group forms, there is a need for educational resources to make it possible for a considerable percentage of the violators to be educated and to learn and accept the new norm, and eventually internalize that norm. This force acting in the model is not the only necessary factor to have a significant number of violators internalize the new norm; at the same time, it is necessary to have an insignificant percentage of the violators’ population perceive different goals and dissimilarity regarding the new norm. Those people who internalize the norm shape the believers who probably contest an old norm publicly. For believers, there is always a risk of being punished by government and their peers when they begin to explicitly behave based on the new norm. However, for them, the benefits behind changing an old norm clearly outweigh the risks of being punished. Through consistent public contestation and education, an increasing share of the society will join the new group over time, and public opinion will force states to change the law and their behaviors.
The above paragraphs summarize what our model predicts as the appropriate structural conditions under which a new norm can emerge due to the committed action of small groups. The two case studies of LGBTQ rights and Women Suffrage are two examples among many others that prove how the committed action of small groups can bring about societal change under the appropriate structural conditions. This validates Margaret Mead’s assertion.
5.1. Future Work Can Use the Simulator to Explore “What If” Scenarios
The purpose of this paper has been to describe the process of social norm transformation using the lens of Social Identity Theory, interpreted as a system dynamics simulation model. The work presented above is limited to exploring social norm transformation within a democratic culture. However, the same framework can readily be applied to the study of transforming social norms in non-democratic cultures and in the presence of various counter-factual circumstances. These include, but are not limited to: “what if” anger is higher or lower (as explored in this paper), or “what if” antipreneurs are more (or less) active (norm antipreneurs are a group of people who try to maintain the status quo; in other words, they promote the old norm [73]). Because this work is based on a system dynamics model, the changes needed to implement such “what if” simulations can be readily accomplished by changing model parameters or adding one or more feedback effects to the aggregate simulation model. Indeed, much of this work has already been started by Salimi [46]. For example, such future publications will explore:
- The effects of democratic versus non-democratic cultures. The feedback effects in the basic model of democratic norm change can be parametrically altered to represent alternative non-democratic cultures, setting up a comparative discussion of similarities in outcomes between these two very different cultures.
- The effects of various levels and types of antipreneurial behaviors. While entrepreneurs work to create forces that promote changing norms, antipreneurs are those actors who work to preserve old norms through their systematic activities. Our theory can be used to explore the relative effectiveness of various antipreneurial strategies.
- The effects of various levels of faux activists on New Norm Emergence. While activists work to attract public opinion in favor of the ongoing collective action, faux activists are those who work for governments or other rival groups to turn public opinion against an ongoing collective action by showing extreme violent action. Our theory can be used to explore the relative effectiveness of various faux activists’ strategies.
- The effects of punishment. While punishment is the main mechanism used to enforce a norm, there are times when governments reduce pressure and levels of punishment. Our theory can be used to explore the relative effectiveness of various punishment strategies.
5.2. Limitations of This Study
Even with the contributions that this study makes to the understanding of norm change, the basic model presented in this study has some limitations and can be improved in some ways by future work. First, at present, the flow rate “Percentage of Dissimilarity” represents the change in the population who return from the violators’ group to the old norm population. Arguably this is too simplistic. The direction of this flow rate could be changed to include a percentage of violators who perceive dissimilarity with the new norm, and instead of returning to the old norm population form another group of violators with a different goal. A similar situation applies to the “Exit Rate”. Finally, most of the initial values used in the model runs are derived from the extant literature. They are necessarily imprecise approximations and, at times, extrapolations. Using more real-world data would enable the optimization of the model for particular norms and scenarios. This would provide better insights into different conditions and policies. Thus, another area for future research is to collect additional empirical data with which to calibrate the model to fit different instances or situations.
Author Contributions
This paper is an original manuscript from the doctoral dissertation of K.S., titled “Norm Contestation and its Affect in Emergence of a New Norm”. The other authors (J.T.R., R.K., G.P.R. and D.A. mainly contribute to the review and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All details about the model, including its description, formulation, and codes, can be found at [35].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Model’s claims and assumptions/propositions.
Table A1.
Model’s claims and assumptions/propositions.
| Model Variables | Claim/ Assumption | Number of Claims/ Assumptions | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Values | Claim | 1 | Individuals’ values have their roots in the societies’ culture, religion, social media, rules, and normative structure | [74,75,76,77] |
| Personal Value | Assumption | 2 | Contesting a norm affects personal values | Logical extension of claim #1 |
| Personal Value | Assumption | 3 | The dominant norm affects personal values | Logical extension of claim #1 |
| Personal Norm | Claim | 4 | Personal values shape personal norms; a norm is a tool to achieve goals | [78,79] |
| Pro-Group Emotion | Claim | 5 | Personal norms shape personal emotions | [80] |
| Pro-Group Emotion | Claim | 6 | Violation of a norm causes pro-category emotions among those who have a shared feeling of grievance and, indeed, among those who see violators as brave and risk takers and admire them | [40,41,42] |
| Pro-Group Emotion | Claim | 7 | Group violations cause pro-emotion among others | [49] |
| Personal Identity | Claim | 8 | Personal norms shape personal identity | [81] |
| Violators’ Group Formation | Claim | 9 | Perception of similarity based on shared interest shapes a new group | [35] |
| Risk Taking | Claim | 10 | Anger increases risk taking | [47,48] |
| Risk Taking | Claim | 11 | Pro-group emotion increases risk-taking | [47,82] |
| Risk Taking | Claim | 12 | Fear decreases risk taking | [83] |
| Risk Taking | Assumption | 13 | Peer pressure decreases risk taking | Logical extension of claim #12 |
| Likelihood of Feeling Angry | Assumption | 14 | Punishment might cause anger among people who perceive the same grievances | Based on historical evidence |
| Feeling of Fear | Claim | 15 | Punishment causes fear as it challenges individuals’ interests | [4,35] |
| Peer pressure / feelings of disgust | Claim | 16 | Individuals feel in-group peer pressure to behave based on the group norm, otherwise they will be perceived as disgusting and abandoned by their peers | [39,84] |
| Behavior | Claim | 17 | Normative context affects personal behavior | [85] |
| Peer pressure | Assumption | 18 | The dominant norm affects the perception of peer pressure | Logical extension of claim #17 |
| Peer Pressure | Assumption | 19 | The new norm affects perceptions of peer pressure | Logical extension of claim #17 |
| Perceiving Similarity Based on Shared Interests | Claim | 20 | Personal identity shapes personal interests and the perception of similarity | [41,42] |
| Perceiving Similarity Based on Shared Interests | Claim | 21 | The pro-group emotion makes others perceive their similarity with violators based on their shared interests | [41,42] |
| Likelihood of Defining Incompatible Goals | Claim | 22 | There is always a possibility that individuals find their initial goals are not incompatible with a group norm | [86] |
| Undergoing Dissimilarity-Focused Compression | Claim | 23 | Distrust awakens the dissimilarity comparison | [86] |
| Emergence of Distrust Toward Category Norm | Claim | 24 | Incompatible goals cause distrust | [86] |
| Learning and Assigning the Norms of the Group | Claim | 25 | Each group has its own norm and, by joining the distinct category, group members will learn about the norm and start assigning the group norm | [30,33] |
| Depersonalization | Claim | 26 | The more members assign the group norm, the more they depersonalize and self-stereotype | [30] |
| Internalization of the Norm | Claim | 27 | The more individuals self-stereotype, the more they internalize the norm | [30] |
| Group Behavior | Claim | 28 | Group members behave because of norm internalization | [30] |
| Emergence of a New Norm | Claim | 29 | Group behavior will become normative after a while | [30] |
| Group Behavior | Claim | 30 | Punishment decreases the group violating behavior | [4,5] |
| Group Behavior | Claim | 31 | Risk taking increases group members’ riskier behavior or more violating behavior | [40] |
| Emergence of a New Norm | Claim | 32 | Legal norms’ strength weakens the contesting norm | [13] |
| Dominant Norm/Legal Norm | Assumption | 33 | Contesting a norm weakens the legal norm (the population size of either the contesting or legal norm balance each other) | Logical extension of claim #32 |
| Pro-category Emotion | Assumption | 34 | The violation of a dominant norm triggers pro-category emotion | Based on historical evidence like Inqilab Girls |
| Extreme Behavior | Claim | 35 | It is always possible that members lose their awareness and show extreme behavior | [40] |
| Punishment | Claim | 36 | Extreme behavior increases government punishment | [87] |
| Likelihood to Trigger Anti-category Norm Emotion | Claim | 37 | Extreme behavior causes negative emotions among members | [40] |
| Group Violating Behavior | Claim | 38 | Anti-category emotion reduces group violating behaviors | [40] |
| Pro-category Emotion | Assumption | 39 | The violation of a dominant norm triggers pro-category emotion | Based on historical evidence, such as Inqilab Girls |
| Extreme Behavior | Claim | 39 | It is always possible that members lose their awareness and show extreme behavior | [40] |
| Punishment | Claim | 40 | Extreme behavior increases government punishment | [87] |
| Likelihood to Trigger Anti-category Norm Emotion | Claim | 41 | Extreme behavior causes negative emotions among members | [40] |
| Group Violating Behavior | Claim | 42 | Anti-category emotion reduces group violating behavior | [40] |
Appendix B
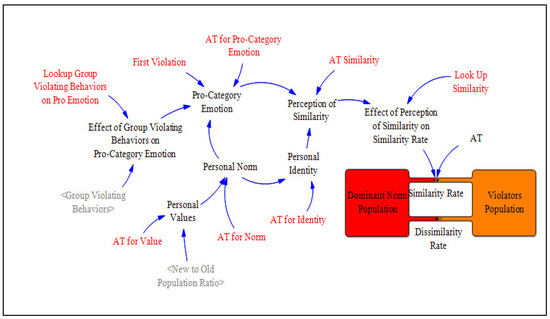
Figure A1.
Sub Model 1: Perception of similarity.
As discussed earlier, the main element that affects the transfer rate from the old population to the violators population is the perception of similarity. The Figure above shows an overview of this process. People perceive similarity based on their shared interests, which could be many different things such as their job, gender, grievances, and many others. As I explain in the formal model, these shared interests have their roots in people’s values.

Table A2.
Perception of similarity sub-model’s parameters report.
Table A2.
Perception of similarity sub-model’s parameters report.
| Variables | Description and Formulation | Type | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant/Old Norm Population | INTEG (“Stage 3. Dissimilarity Rate”-Transfer Rate, Total Population × P1) People who believe in the old norm and are the population with the potential to learn a new norm | Stock | Person |
| Transfer Rate | Transfer Rate: Effect of Perception of Similarity on Transfer Rate × Dominant Norm Population/AD Time to Transfer Change in the number of populations who perceive similarity with and join the violators group | Rate | Person/Year |
| First Violation | First Violation = STEP (0.5, 10) This shows the effect of people or groups of people who initially perceive the old norm to be harmful and violate it before other members of society | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| “Pro-Category Emotion” | “Pro-Category Emotion” = SMOOTH ((Personal Norm × “Effect of Group Violating Behaviors on Pro-Category Emotion”) + First Violation, “AT for Pro-Category Emotion”) It shows when population emotion is in favor of the violating behavior | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Look Up Similarity | S-shaped or logistic growth Relation between the potential population who self-categorize themselves as violators and perception of similarity | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Lookup Group Violating Behaviors on Pro Emotion | This graphical function shows how an increase in group members’ violating behaviors leads to an increase of emotion in favor of the group | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Personal Value | Personal Value: SMOOTH (New to Old Population Ratio, AT for Value) This variable shows the change in values among the population | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Personal Norm | Personal Norm: SMOOTH (Personal Values, AT for Norm) Affected by value, this variable shows the change in norms among the population. | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Personal Identity | Personal Identity: SMOOTH (Personal Norm, AT for Identity) Affected by norm, this variable shows the change in identity among population | Auxiliary | Dmnl |
| Perception of Similarity | This shows the change in perceived similarity based on the shared interest among the population that joins the violators Perception of Similarity: SMOOTH (MAX (“Pro-Category Emotion” + Personal Identity, 0), AT Similarity) | Auxiliary | Dmnl |

Table A3.
Perception of dissimilarity and new norm internalization sub-models’ parameters report.
Table A3.
Perception of dissimilarity and new norm internalization sub-models’ parameters report.
| Variables | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| “Depersonalization and Self-Stereotyping” | This stock shows the population who are depersonalized. (“Stage 2. Increase in Collective Belief”, 0) | Person |
| Learning and Assigning Norms | This stock shows the population who are learning and assigning a new norm. (“Stage 1. Adapting Rate”, 0) | Person |
| Perceived Incompatible Goal | The population who realizes that they have different goals and interests to those of the group norm (“Stage 1. Increase Rate”, 0) | Person |
| Emergence of Distrust Toward Category Norms | Having different goal results in the emergence of distrust among group members (“Stage 2. Distrust Increase Rate”, 0) | Person |
| Violators Group Population | The population who disobeys a dominant norm (Transfer Rate-“Stage 3. Internalization Rate”-“Stage 3. Dissimilarity Rate”, Total Population × P2) | Person |
| Internalized the Contesting Norm Population | The population who internalizes the new norm (“Stage 3. Internalization Rate”-Emergence of Contesting Norm Rate, Total Population × P3) | Person |
| “Stage 1. Adapting Rate” | “Stage 1. Adapting Rate” = (Potential Population who learning-Learning and Assigning Norm)/(Adjustment Time to Internalization/3) Change in the number of populations who learn and assign the group norm | Person/Year |
| “Stage 1. Increase Rate” | “Stage 1. Increase Rate” = (Potential Population who perceived incompatible goal-Perceived Incompatible Goal)/(Adjustment Time to Dissimilarity/3) Change in the number of populations who perceive their interests to be dissimilar to those of other members | Person/Year |
| “Stage 2. Increase in Collective Belief” | “Stage 2. Increase in Collective Belief” = (Learning and Assigning Norm-“Depersonalization and Self-Stereotyping”)/(Adjustment Time to Internalization/3) Change in the number of populations who have a shared believe in the group norm | Person/Year |
| “Stage 2. Distrust Increase Rate” | “Stage 2. Distrust Increase Rate” = (Perceived Incompatible Goal-Emergence of Distrust Toward Category Norms)/(Adjustment Time to Dissimilarity/3) Change in the number of populations who lose their trust in the group norm | Person/Year |
| “Stage 3. Internalization Rate” | “Stage 3. Internalization Rate” = (“Depersonalization and Self-Stereotyping”-Internalized the Contesting Norm Population)/(Adjustment Time to Internalization/3) Change in the number of populations who internalize the norm through time | Person/Year |
| “Stage 3. Dissimilarity Rate” | “Stage 3. Dissimilarity Rate” = Emergence of Distrust Toward Category Norms/(Adjustment Time to Dissimilarity/3) Change in number of populations who perceive dissimilarity | Person/Year |
| Potential Population Learning the Norm | Those parts of the violator population who learn the norm Learning Coefficient × Violators Group Population | Person |
| Potential Population Who Perceived Incompatible Goal | Potential Population who Perceived Incompatible Goal = Potential Population who learning × Likelihood of defining incompatible goal Those parts of the violator population who realize their goals and interests are different than the group’s | Person |
| Percentage of Dissimilarity | Percentage of violators who, after learning a group norm, perceive dissimilarity between their interests and the group’s interests | Person |
| Learning Coefficient | Potential Population who Perceived Incompatible Goal = Potential Population who learning × Likelihood of defining incompatible goal An exogenous variable which shows the percentage of violators who will be educated in favor of a new norm | Person |
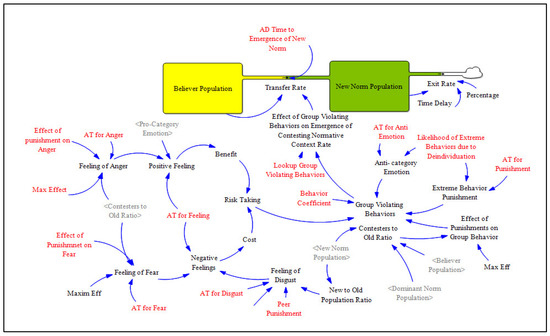
Figure A2.
Sub-models 4 and 5: “Emergence of New Norm Sub-Model” and “Exit from the New Norm”.
Appendix B.1. Sub-Model: “Emergence of New Norm Sub-Model”
This figure above shows the model’s transition from the population that internalizes and believes in the new norm into a population that behaves based on the new norm. As discussed in the formal model, after internalizing and believing in a norm, people start practicing that norm and, after a while, the norm becomes a normative behavior of a society. Thus, group violating behavior and its effects are the main elements which affect this transition.
We use the following equation to implement group violating behavior:
Group Violating Behaviors = ((Risk Taking)/(Extreme Behavior Punishment × “Anti- Category Emotion”
× Effect of Punishments on Group Behavior)) × Behavior Coefficient
× Effect of Punishments on Group Behavior)) × Behavior Coefficient
Appendix B.2. Sub Model: “Exit from the New Norm”
This section shows that, after a period represented by a time delay, some people change their minds and leave the new norm population. This can occur because the new norm no longer fulfills their interests, and/or another norm fits their interests better. Thus, a percentage of the new norm population that encounters this phenomenon through time will exit that population.

Table A4.
New norm emergence sub-model’s parameters report.
Table A4.
New norm emergence sub-model’s parameters report.
| Variables | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| New Norm Population | Population who accepts and behaves based on the new norm New Norm Population = INTEG (Emergence of Contesting Normative Context Rate-Exit Rate, Total Population × P4) | Person |
| Emergence of Contesting Normative Context Rate | Change in the number of populations who behave based on the new norm Emergence of Contesting Normative Context Rate = MIN (Internalized the Contesting Norm Population, Internalized the Contesting Norm Population × Effect of Group Violating Behaviors on Emergence of Contesting Normative Context Rate)/AD Time to Emergence of New Norm | Person/Year |
| Group Violating Behaviors | This auxiliary shows the increase in group violating behaviors Group Violating Behaviors = (Risk Taking × Effect of Peer Punishment on Group Violating Behaviors)/(Extreme Behavior Punishment × “Anti- category Emotion” × Effect of Punishments on Group Behavior) | Dmnl |
| Punishment of Extreme Behavior | Punishment which is executed by governments to suppress extreme behavior during collective action Extreme Behavior Punishment = SMOOTH (Likelihood of Extreme Behaviors × 1.2, AT for Punishment) | Dmnl |
| Likelihood of Extreme Behaviors | This is the likelihood of unacceptable behavior, such as breaking public goods | Dmnl |
| Risk Taking | It shows a population’s risk taking based on their cost and benefit calculations Risk Taking = MIN (Benefit/Cost, 1) | Dmnl |
| Cost | Variable shows the loss and expense of violating behavior. Negative feelings include feelings of disgust and/or shame from peers, and feelings of fear of the government’s punishment, which could be the fear of being arrested, losing one’s job, or economic loss. These are the two main costs associated with reduced risk taking Cost = Negative Feelings | Dmnl |
| Benefit | Variable showing the gains and advantages of violating behaviors Benefit = Positive Feeling | Dmnl |
| Positive Feeling | Feeling which increase the benefit of risk taking SMOOTH3I(“Pro-Category Emotion” × Feeling of Anger, AT for Feeling, 0.1) | Dmnl |
| Negative Feeling | Feeling which increase the cost of risk taking Negative Feelings = SMOOTH (Effect of Fear on Negative Feeling + Effect of Disgust on Negative Feelings, AT for Feeling) | Dmnl |
| “Anti-category Emotion” | The emotion which is triggered by extreme behavior and decreases the group’s behavior “Anti- category Emotion” = SMOOTH (Likelihood of Extreme Behaviors due to Deindividuation, AT for Anti Emotion) | Dmnl |
| Look Up Punishment | This shows the punishment which is executed by governments to suppress norm violators, which is the ratio of the new-to-old norm populations. We define it this way, and assume that governments gain their power from their supporters’ populations; as the number of their supporter/followers’ decreases compared to the contesters’ population, they have less power to punish norm violators. [(0,0)–(20,1)], (0,0.1), (0.1,0.15), (0.25,0.3), (0.5,0.5), (0.75,0.8), (1,1), (1.3,0.8), (2,0.5), (4,0.3), (10,0.15), (20,0.1) | Dmnl |
| Feeling of Anger | The feeling that violators perceive due to governments’ severe and/or unjustified punishments SMOOTH(Effect of punishment on Anger(Contesters to Old Ratio) × Max Effect, AT for Anger) | Dmnl |
| Feeling of Fear | The feelings which violators experience due to government punishments, or fears of losing their jobs or being arrested SMOOTH(Effect of Punishment on Fear(Contesters to Old Ratio) × Maxim Eff, AT for Fear) | Dmnl |
| Lookup Group Violating Behaviors | This shows the relationship between group violating behaviors on transferring from internalizing to new norm | Dmnl |
| Feeling of Disgust | The feeling which violators perceive due to peer pressure SMOOTH (Peer Punishment (New to Old Population Ratio) × Maximum Effect, AT for Disgust) | Dmnl |
| Exit Rate | Change in the new norm population due to no longer behaving based on that norm Exit Rate = (New Norm Population × Percentage)/Time Delay | Person/Year |
Appendix C

Table A5.
Democratic base-run parameters’ initial values.
Table A5.
Democratic base-run parameters’ initial values.
| Parameter | Initial Value |
|---|---|
| Percentage of Dissimilarity | 5% |
| Learning Coefficient | 70% |
| Likelihood of Extreme Behaviors | 0.1 |
| Effect of Anger on Positive Feeling | 0.7 |
| Effect of First Violation on Pro-Category Emotion | 0.5 |

Table A6.
Democratic base run vs. parameter values for asymmetric feelings of anger.
Table A6.
Democratic base run vs. parameter values for asymmetric feelings of anger.
| Parameter | Initial Value | High Anger | Low Anger | No Anger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of Dissimilarity | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Learning Coefficient | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% |
| Likelihood of Extreme Behaviors | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Effect of Anger on Positive Feeling towards Violators | 0.7 | 1 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Effect of First Violation on Pro-Category Emotion | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
References
- Finnemore, M. National Interests in International Society; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, A. Norms reconstituting interests: Global racial equality and US sanctions against South Africa. Int. Organ. 1995, 49, 451–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnemore, M.; Sikkink, K. International norm dynamics and political change. Int. Organ. 1998, 52, 887–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, R.A.; Rasmusen, E.B. Creating and enforcing norms, with special reference to sanctions. Int. Rev. Law Econ. 1999, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, D.; Sen, S.; Sabater-Mir, J. Of social norms and sanctioning: A game theoretical overview. Int. J. Agent Technol. Syst. (IJATS) 2010, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J. The ‘war on terror’ and the battle for the definition of torture. Int. Relat. 2016, 30, 102–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkink, K. The United States and torture: Does the spiral model work? Camb. Stud. Int. Relat. 2013, 126, 145–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sandholtz, W. Prohibiting Plunder: How Norms Change; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, R.; Kahl, M.; Pisoiu, D. The ‘dark’side of normative argumentation—The case of counterterrorism policy. Glob. Const. 2012, 1, 278–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A. Norm subsidiarity and regional orders: Sovereignty, regionalism, and rule-making in the third world. Int. Stud. Q. 2011, 55, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, A.-M. A New World Order; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich, C. Rogue States as Norm Entrepreneurs; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deitelhoff, N.; Zimmermann, L. Norms under challenge: Unpacking the dynamics of norm robustness. J. Glob. Secur. Stud. 2019, 4, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial dynamics. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Urban dynamics. IMR Ind. Manag. Rev. (Pre-1986) 1970, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, G.P.; Pugh, A.L., III. Introduction to system dynamics modeling with DYNAMO. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.; Hunter, A. Multimethod Research: A Synthesis of Styles; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Babbie, E. The Practice of Social Research, 6th ed.; Woolworth Inc.: Belmont, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, G.; Wright, G. The Delphi technique as a forecasting tool: Issues and analysis. Int. J. Forecast. 1999, 15, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.L. Qualitative Research Methods: Focus Groups as Qualitative Research; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 10, p. 9781412984287. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, G. The Long Interview-Qualitative Research Methods; Series 13; Sage Publications, Inc.: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, G.P.; Andersen, D.F. Teamwork in group model building. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1995, 11, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, A.; Corbin, J. Basics of Qualitative Research; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, H.R.; Bernard, H.R. Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, D.L.; Luna-Reyes, L.F.; Diker, V.G.; Black, L.; Rich, E.; Andersen, D.F. The disconfirmatory interview as a strategy for the assessment of system dynamics models. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2012, 28, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde-Selva, J.A.; Usó-Doménech, J.-L.; Gash, H. What Are Ideological Systems? Systems 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D.C. The development and enforcement of group norms. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajfel, H. Human Groups and Social Categories: Studies in Social Psychology; Cup Archive; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Gu, C.; Yang, C. Examining the Influence of Moral Norms on Dockless Shared Bicycle Users’ Parking Behavior—An Exploratory Study Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior. Systems 2022, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.C.; Hogg, M.A.; Oakes, P.J.; Reicher, S.D.; Wetherell, M.S. Rediscovering the Social Group: A Self-Categorization Theory; Basil Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Dirks, K.T.; Ferrin, D.L. The role of trust in organizational settings. Organ. Sci. 2001, 12, 450–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussweiler, T. Comparison processes in social judgment: Mechanisms and consequences. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 110, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.C. Social identification and psychological group formation. In The Social Dimension: European Developments in Social Psychology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984; Volume 2, pp. 518–538. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.C.; Reynolds, K.J. Self-categorization theory. In Handbook of Theories in Social Psychology; Sage Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 399–417. [Google Scholar]
- Granovetter, M. Threshold models of collective behavior. Am. J. Sociol. 1987, 83, 1420–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, J.; Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Clore, G.L.; Gasper, K.; Garvin, E. Affect as information. In Handbook of Affect and Social Cognition; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 121–144. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, N.; Clore, G.L. Mood, misattribution, and judgments of well-being: Informative and directive functions of affective states. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1983, 45, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.C. Social Influence; Thomson Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth, D.R. Group Dynamics; Cole Publishing Company: Brooks, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, D.A.; Benford, R.D. Master frames and cycles of protest. Front. Soc. Mov. Theory 1992, 133, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, D.A.; Rochford, E.B., Jr.; Worden, S.K.; Benford, R.D. Frame alignment processes, micromobilization, and movement participation. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1986, 51, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, R. An evolutionary approach to norms. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 1986, 80, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keltner, D.; Haidt, J. Approaching awe, a moral, spiritual, and aesthetic emotion. Cogn. Emot. 2003, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.L.y.; Luck, M.; d’Inverno, M. Constraining autonomy through norms. In Proceedings of the 1st International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Part 2, Auckland, NZ, USA, 9–13 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salimi, K. Norm Contestation and Its Effects on Emergence of a New Norm. Ph.D. Thesis, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Vazquez, R.M.; Cuilty, E. The role of emotions on risk aversion: A prospect theory experiment. J. Behav. Exp. Econ. 2014, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tversky, A.; Kahneman, D. Advances in prospect theory: Cumulative representation of uncertainty. J. Risk Uncertain. 1992, 5, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Achieving emotions in collective action: Emotional processes and movement mobilization in the 1989 Chinese student movement. Sociol. Q. 2000, 41, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöstedt, R. The discursive origins of a doctrine: Norms, identity, and securitization under Harry S. Truman and George W. Bush. Foreign Policy Anal. 2007, 3, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.; Morgan, G.P.; Martin, M.K.; Carley, K.M. On the coevolution of stereotype, culture, and social relationships: An agent-based model. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2014, 32, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, Y. Formal aspects of model validity and validation in system dynamics. Syst. Dyn. Rev. J. Syst. Dyn. Soc. 1996, 12, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, Y. Credibility, validity and testing of Dynamic Simulation Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications, Lisbon, Portugal, 29–31 July 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buliali, J.L. A model of reliability, average reliability, availability, maintainability and supportability for services with system dynamics approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Applications (ISITIA), Bali, Indonesia, 30–31 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mudjahidin; Hendrawan, R.A.; Aristio, A.P.; Buliali, J.L.; Yuniarto, M.N. Testing methods on system dynamics: A model of reliability, average reliability, and demand of service. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Andersen, D.F. Building confidence in causal maps generated from purposive text data: Mapping transcripts of the Federal Reserve. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2012, 28, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudrat-Ullah, H.; Seong, B.S. How to do structural validity of a system dynamics type simulation model: The case of an energy policy model. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaninger, M.; Grösser, S. System dynamics modeling: Validation for quality assurance. In System Dynamics: Theory and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Senge, P.M.; Forrester, J.W. Tests for building confidence in system dynamics models. Syst. Dyn. TIMS Stud. Manag. Sci. 1980, 14, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J. Business Dynamics; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tomoaia-Cotisel, A.; Allen, S.D.; Kim, H.; Andersen, D.; Chalabi, Z. Rigorously interpreted quotation analysis for evaluating causal loop diagrams in late-stage conceptualization. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2022, 38, 41–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, J. Path dependence in historical sociology. Theory Soc. 2000, 29, 507–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, P. Increasing returns, path dependence, and the study of politics. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzade, R. Historical sociology and time. Sociol. Methods Res. 1992, 20, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, A.S. Reformulating explanatory standards and advancing theory in comparative politics. In Comparative Politics: Rationality, Culture, and Structure; Lichbach, M., Zuckerman, A.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; pp. 277–310. [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi, F. Who learns from what in policy diffusion processes? Am. J. Polit. Sci. 2010, 54, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D. Stonewall: The Riots that Sparked the Gay Revolution; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman, L.R. Victory: The Triumphant Gay Revolution; Harper Perennial: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lott, J.; John, R.; Kenny, L.W. Did women’s suffrage change the size and scope of government? J. Political Econ. 1999, 107, 1163–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullinix, K.J.; Bolsen, T.; Norris, R.J. The feedback effects of controversial police use of force. Polit. Behav. 2021, 43, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, B. Gay Power!: The Stonewall Riots and the Gay Rights Movement, 1969; Twenty-First Century Books: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, G.P. Can systems thinking be an antidote to extensive evil? Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2021, 38, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, A. Norm antipreneurs and theorising resistance to normative change. Rev. Int. Stud. 2016, 42, 310–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidise, E. The role of civil society in developing and consolidating democracy: Evidence from Israel. In Proceedings of the European Consortium for Political Research Workshop, Uppsala, Sweden, 13–18 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, T.; Shils, E.A. Towards a General Theory of Social Action; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.H. Basic human values: Theory, measurement, and applications. Rev. Française Sociol. 1992, 47, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchieri, C. The Grammar of Society: The Nature and Dynamics of Social Norms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dechesne, F.; Dignum, V.; Tan, Y.-H. Understanding compliance differences between legal and social norms: The case of smoking ban. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–6 May 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vickers, G. Values, Norms, and Policies. Policy Sci. 1973, 4, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, J. Feeling like a state: Social emotion and identity. Int. Theory 2014, 6, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C. Norm structure, diffusion, and evolution: A conceptual approach. Eur. J. Int. Relat. 2018, 24, 638–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.; Noussair, C.N. Risk aversion and emotions. Pac. Econ. Rev. 2014, 19, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, S.; Wormwood, J.; Satpute, A.B. The influence of fear on risk taking: A meta-analysis. Cogn. Emot. 2020, 34, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, K.; Frydenlund, E.; Padilla, J.J.; Haaland, H.; Wallevik, H. How does humanitarianism spread? Modeling the origins of citizen initiatives through norm diffusion. In Proceedings of the 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Gothenburg, Sweden, 9–12 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, E.L.; Rimal, R.N.; Ferrence, R.; Cohen, J.E. Understanding the sources of normative influence on behavior: The example of tobacco. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 115, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posten, A.C.; Mussweiler, T. When distrust frees your mind: The stereotype-reducing effects of distrust. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 105, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marx, G.T. Thoughts on a neglected category of social movement participant: The agent provocateur and the informant. Am. J. Sociol. 1974, 80, 402–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).