Start-Ups as Adaptable Stable Systems Based on Synchronous Business Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Action Research Methodology
3. Literature Review
3.1. Internal Models
3.2. Synchronization for Adaptable Stability
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. The EU and Nature-Based Solutions. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/research-andinnovation/research-area/environment/nature-based-solutions_en (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Calheiros, C.S.; Nikolaou, I. Nature-based solutions as a tool in the new circular economic model for climate change adaptation. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfeld, C.; Ivanova, M. Special Issue: First Principles in Science, Introduction: First principles in science—Their status and justification. Synthese 2021, 198, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, M.J.; de Paula, R.C.; Campoe, O.C.; Carneiro, R.L. Adaptability and stability of eucalypt clones at different ages across environmental gradients in Brazil. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 454, 117631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.Q.; Partelli, F.L.; Golynski, A.; de Sousa Pimentel, N.; Ferreira, A.; de Oliveira Bernardes, C.; Ribeiro-Barros, A.I.; Ramalho, J.C. Adaptability and stability of Coffea canephora genotypes cultivated at high altitude and subjected to low temperature during the winter. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 252, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, P.E.; Farias, F.J.C.; de Carvalho, L.P.; Ribeiro, L.P.; Nascimento, M.; Azevedo, C.F.; Cruz, C.D.; Bhering, L.L. Adaptability and stability of cotton genotypes regarding fiber yield and quality traits. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.C.B.; Damasceno-Silva, K.J.; de Moura Rocha, M.; Oliveira, G.C.X. Evolution of methodology for the study of adaptability and stability in cultivated species. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 990–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Lekevičius, E.; Loreau, M. Adaptability and functional stability in forest ecosystems: A hierarchical conceptual framework. Ekologija 2012, 58, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, K.A. The three faces of ecological fitness. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. C Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 42, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, V.R.; Annila, A. Natural selection for least action. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2008, 464, 3055–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laland, K.N.; Uller, T.; Feldman, M.W.; Sterelny, K.; Müller, G.B.; Moczek, A.; Jablonka, E.; Odling-Smee, J. The extended evolutionary synthesis: Its structure, assumptions and predictions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruineberg, J.; Rietveld, E.; Parr, T.; van Maanen, L.; Friston, K.J. Free-energy minimization in joint agent-environment systems: A niche construction perspective. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 455, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S. Synchronous generative development amidst situated entropy. Entropy 2022, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alana, J.E.; Slater, T.; Bucknam, A. Action Research for Business, Nonprofit, and Public Administration—A Tool for Complex Times; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lewin, K. Action research and minority problems. J. Soc. Issues 1946, 2, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillinger, A.-S.; Els, C.; Schäfer, B.; Bender, B. Business model risk and uncertainty factors: Toward building and maintaining profitable and sustainable business models. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y.; Clark, T. Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, J. Open Innovation Business Modeling: Gamification and Design Thinking Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.J. Business Model Design Compass: Open Innovation Funnel to Schumpeterian New Combination Business Model Developing Circle; Springer: Singapore, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Manninen, K.; Huiskonen, J. Sustainability goal setting with a value-focused thinking approach. In Sustainable Business Models; Aagaard, A., Ed.; Palgrave Studies in Sustainable Business in Association with Future Earth; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 89–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs, W.; Cocklin, C. Conceptualizing a “sustainability business model”. Organ. Environ. 2008, 21, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Daunizeau, J.; Kilner, J.; Kiebel, S.J. Action and behavior: A free-energy formulation. Biol. Cybern. 2010, 102, 227–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, S.A. Answering Schrödinger’s “What Is Life?”. Entropy 2020, 22, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CB Insights. The Top 20 Reasons Startups Fail. Available online: https://conferences.law.stanford.edu/vcs2019/wp-content/uploads/sites/63/2018/09/001-top-10.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- McKenzie, D.; Sansone, D. Predicting entrepreneurial success is hard: Evidence from a business plan competition in Nigeria. J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 141, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P. The Second Law; Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Montévil, M.; Mateo, M. Biological organization and constraint closure. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 372, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.A.; Nayak, P.R. Strategic sourcing: A progressive approach to the make-or-buy decision. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 1992, 6, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew, N.; Sarasvathy, S.D. Exaptation and niche construction: Behavioral insights for an evolutionary theory. Ind. Corp. Chang. 2016, 25, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Vrba, E.S. Exaptation—A missing term in the science of form. Paleobiology 1982, 8, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Nelson, R. Creating something from nothing: Resource construction through entrepreneurial bricolage. Adm. Sci. Q. 2005, 50, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roli, A.; Kauffman, S.A. Emergence of organisms. Entropy 2020, 22, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. Synergetics. In Self-Organizing Systems; Yates, F.E., Garfinkel, A., Walter, D.O., Yates, G.B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 417–434. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, C.J.; Smith, R. The predictive global neuronal workspace: A formal active inference model of visual consciousness. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 199, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luksha, P. Niche construction: The process of opportunity creation in the environment. Strateg. Entrep. J. 2008, 2, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitzman, L.; Foster, R. Seasons of Life: The Biological Rhythms That Enable Living Things to Thrive and Survive; Profile Books: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Senge, P.; Kleiner, A.; Roberts, C.; Ross, R.; Roth, G.; Smith, B. The Dance of Change: The Challenges to Sustaining Momentum in Learning Organizations; Doubleday: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, S. Accessing active inference theory through its implicit and deliberative practice in human organizations. Entropy 2021, 23, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoni, G.; Balasubramanian, V.; Gold, J.I. What is optimal in optimal inference? Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 29, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, R.C.; Ashby, W.R. Every good regulator of a system must be a model of that system. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1970, 1, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, D.; Balcetis, E. Wishful seeing: How preferences shape visual perception. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 22, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurse, M.S.; Grant, W.J. I’ll see it when I believe it: Motivated numeracy in perceptions of climate change risk. Environ. Commun. 2020, 14, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitek, D.J.; Sherlock, G. Whole genome, whole population sequencing reveals that loss of signaling networks is the major adaptive strategy in a constant environment. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydow, J.; Schreyögg, G.; Koch, J. Organizational path dependence: Opening the black box. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2009, 34, 689–709. [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy, S.P.; Hantula, D.A. Inherently irrational? A computational model of escalation of commitment as Bayesian updating. Behav. Process. 2016, 127, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staw, B.M.; Sandelands, L.E.; Dutton, J.E. Threat rigidity effects in organizational behavior: A multilevel analysis. Adm. Sci. Q. 1981, 26, 501–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelopoulos, N.C. Perceptual inference. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 55, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, C.; Koechlin, E. A neural representation of prior information during perceptual inference. Neuron 2008, 59, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, G.T.W. The psychology of prejudice. Pop. Sci. M. 1890, 36, 440. [Google Scholar]
- Nairne, J.S.; Pandeirada, J.N.; Gregory, K.J.; Van Arsdall, J.E. Adaptive memory: Fitness relevance and the hunter-gatherer mind. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 20, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobfoll, S.E. Conservation of Resources Theory: Its Implication for Stress, Health, and Resilience. In The Oxford Handbook of Stress, Health, and Coping; Folkman, S., Ed.; Oxford Library of Psychology: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 127–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, I.; Kozusznik, M.W.; Peiró, J.M.; Tordera, N. Individual, co-active and collective coping and organizational stress: A longitudinal study. Eur. Manag. J. 2019, 37, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. The resilience of terrestrial ecosystems: Local surprise and global change. In Sustainable Development of the Biosphere; Clark, W.C., Munn, R.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1986; pp. 292–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E.; Goerner, S.J.; Lietaer, B.; Gomez, R. Quantifying sustainability: Resilience, efficiency and the return of information theory. Ecol. Complex. 2009, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, G.N.; Calderone, D.; Morales, L.J. Brain entropy and human intelligence: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissner-Gross, A.D.; Freer, C.E. Causal entropic forces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 168702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Schwartenbeck, P.; Parr, T.; Friston, K. An active inference approach to modeling structure learning: Concept learning as an example case. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, B.; Kumaran, D.; Seymour, B.; Dolan, R.J. Frames, biases, and rational decision-making in the human brain. Science 2009, 313, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowem, M.M.; Mowen, J.C. An empirical examination of the biasing effects of framing business decisions. Decis. Sci. 1986, 17, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigerenzer, G. Why heuristics work. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 3, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.M.C.; Gigerenzer, G. Simple heuristics and rules of thumb: Where psychologists and behavioural biologists might meet. Behav. Process. 2005, 69, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P. The Principle of Least Action in Quantum Mechanics. Ph.D. Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, I. Elegance in Science: The Beauty of Simplicity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.P.; Eisenhardt, K.M.; Bingham, C.B. Optimal structure, market dynamism, and the strategy of simple rules. Adm. Sci. Q. 2009, 54, 413–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Fields, C.; Hoffman, D.D.; Prentner, R.; Singh, M. Fact, fiction, and fitness. Entropy 2020, 22, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessey, I. Cognitive fit: A theory-based analysis of the graphs versus tables literature. Decis. Sci. 1991, 22, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Bertels, S.; Ewert, T.; MacConnachie, P.; O’Brien, J. Bridging the research-practice gap. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 26, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelle, J.; Berthold, K. Effects of comparing contrasting cases on learning from subsequent explanations. Cogn. Instr. 2015, 33, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. Arrival of the Fittest: Solving Evolution’s Greatest Puzzle; Penguin: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, S. Future-proofing startups: Stress management principles based on adaptive calibration model and active inference theory. Entropy 2021, 23, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picken, J.C. From startup to scalable enterprise: Laying the foundation. Bus. Horiz. 2017, 60, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A. Digital startups and the adoption and implementation of Lean Startup Approaches: Effectuation, bricolage and opportunity creation in practice. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurti, E.; Salavati, S.; Mirijamdotter, A. Using systems thinking to illustrate digital business model innovation. Systems 2021, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S. Dismantling the box—Applying principles for reducing preconceptions during ideation. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 2016, 20, 1650049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, H.Y.; Fauvel, C. Criticisms, variations and experiences with business model canvas. Eur. J. Agric. For. Res. 2013, 1, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rompho, N. Operational performance measures for startups. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2018, 22, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbus, A.; Lussier, R.N. Entrepreneurs use a balanced scorecard to translate strategy into performance measures. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2006, 44, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute-Wenig, S.; Refflinghaus, R. Quality management for microenterprises and start-ups: Is the ISO 9001 suitable? Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2020, 12, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, L.; Tucci, C.; Afuah, A. A critical assessment of business model research. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2017, 11, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.P.; Garnett, R. The entropic basis of collective behaviour. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, L.J.; Repenning, N.P. Why firefighting is never enough: Preserving high-quality product development. Syst. Dyn. Rev. J. Syst. Dyn. Soc. 2001, 17, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, K.; Matschinsky, F. Translation of Ludwig Boltzmann’s paper ‘On the relationship between the second fundamental theorem of the mechanical theory of heat and probability calculations regarding the conditions for thermal equilibrium’. Sitzungberichte der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften. Mathematisch-Naturwissen Classe. Abt. II, LXXVI 1877, pp 373–435 (Wien. Ber. 1877, 76, 373–435). Reprinted in Wiss. Abhandlungen, Vol. II, reprint 42, p. 164–223, Barth, Leipzig, 1909. Entropy 2015, 17, 1971–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Clausius, R. The Mechanical Theory of Heat: With Its Applications to the Steam Engine and to the Physical Properties of Bodies; John van Voorst: London, UK, 1867. [Google Scholar]
- de Maupertuis, P.L.M. Les loix du mouvement et du repos déduites d’un principe métaphysique. In Histoire de l’Academie Royale des Sciences et des Belles-Lettres de Berlin; Haude: Berlin, Germay, 1746; pp. 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K. Life as we know it. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, R. Global desertification vulnerability to climate change and human activities. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.I.; Rathburn, S.L.; Cfapps, D.M. Landslide response to climate change in permafrost regions. Geomorphology 2019, 340, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, M.M.; de Dios, V.R.; Bradstock, R.A. Unprecedented burn area of Australian mega forest fires. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Xu, B. Impact of climate change on human infectious diseases: Empirical evidence and human adaptation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, F.R.; Ibrahim, Q.S.U.; Bari, M.S.; Alam, M.J.; Dunachie, S.J.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Patwary, M.I. The association between temperature, rainfall and humidity with common climate-sensitive infectious diseases in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrathall, D.J.; Mueller, V.; Clark, P.U.; Bell, A.; Oppenheimer, M.; Hauer, M.; Abel, K. Meeting the looming policy challenge of sea-level change and human migration. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

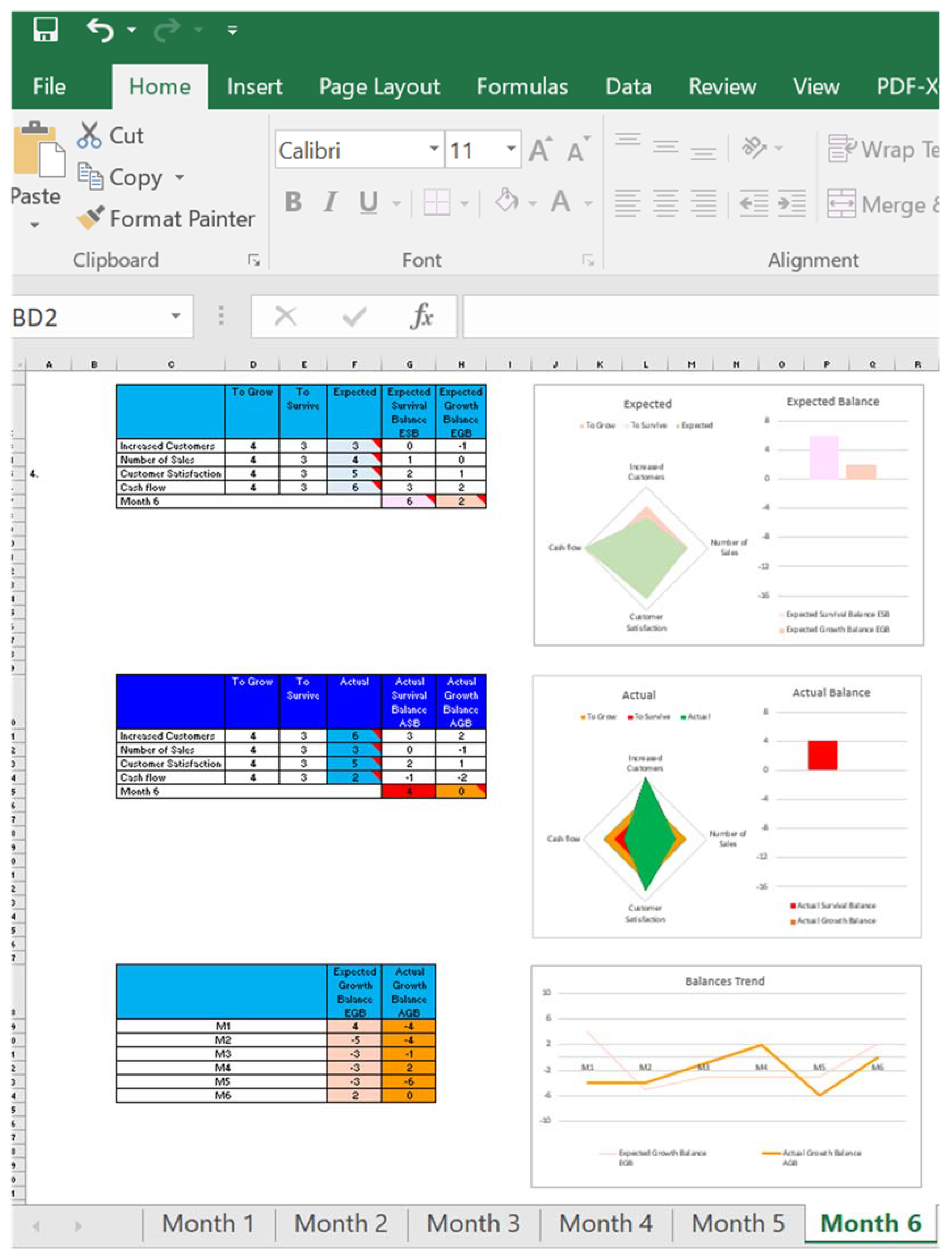



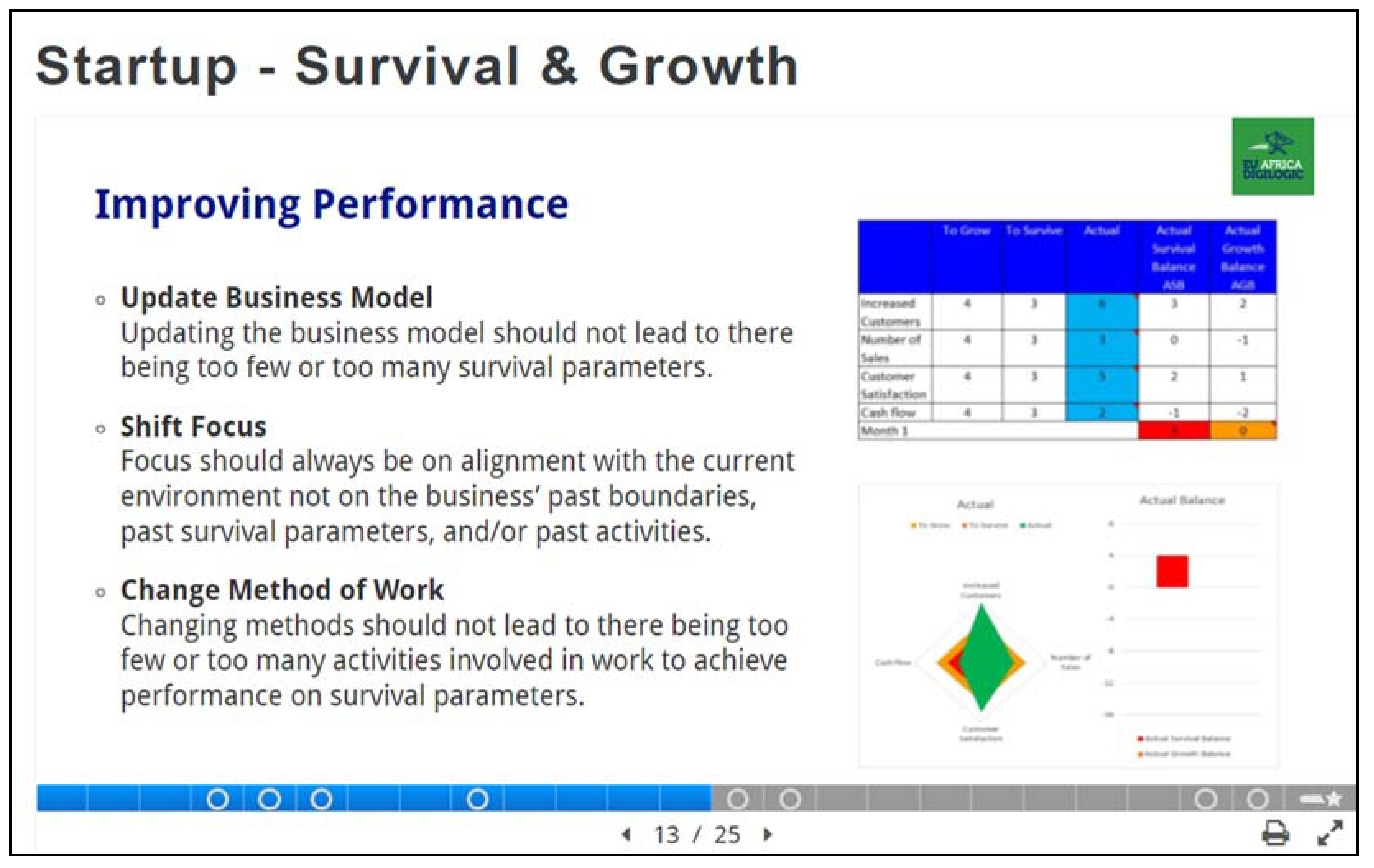

| Maladaptation | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Underfitting | Increase survival parameters and inter-relationships between them |
| Overfitting | Reduce survival parameters and inter-relationships between them |
| No fitting | Change boundaries, survival parameters, and inter-relationships |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fox, S.; Vahala, P. Start-Ups as Adaptable Stable Systems Based on Synchronous Business Models. Systems 2022, 10, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10030081
Fox S, Vahala P. Start-Ups as Adaptable Stable Systems Based on Synchronous Business Models. Systems. 2022; 10(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleFox, Stephen, and Päivi Vahala. 2022. "Start-Ups as Adaptable Stable Systems Based on Synchronous Business Models" Systems 10, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10030081
APA StyleFox, S., & Vahala, P. (2022). Start-Ups as Adaptable Stable Systems Based on Synchronous Business Models. Systems, 10(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10030081






