Laboratory Diagnostics of Rickettsia Infections in Denmark 2008–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Study Population
2.2. Rickettsia Antibody Detection
2.3. Detection of Rickettsia spp. DNA by PCR Assay and Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Diagnostic Samples
3.2. Samples Tested for Rickettsia Antibodies
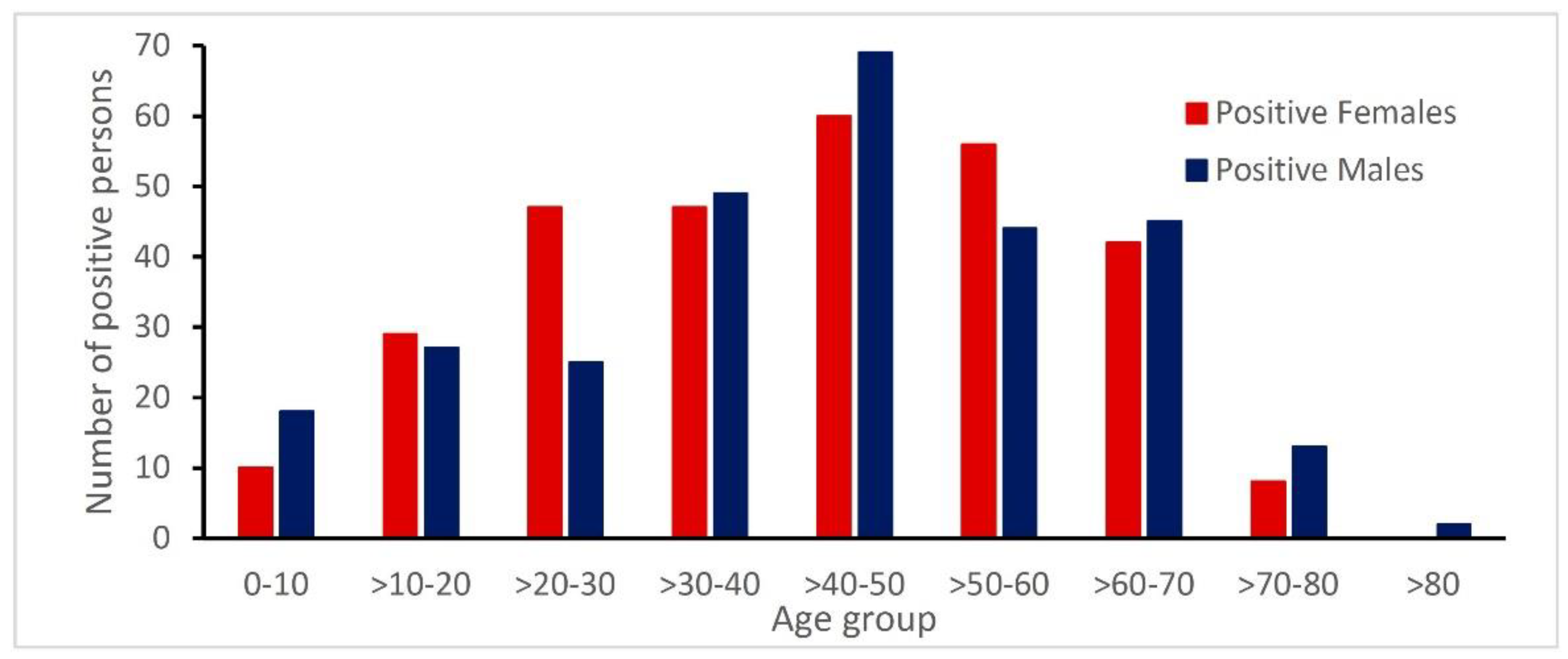
3.3. Age and Gender Distribution of Patients with Rickettsia Antibodies
3.4. Geographical Distribution of Danish Cases
3.5. Seroprevalence of Rickettsia spp. in Denmark
3.6. Concordance Between PCR and Serology
3.7. Co-Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drexler, N.A.; Dahlgren, F.S.; Massung, R.F.; Behravesh, C.B.; Heitman, K.N.; Paddock, C.D. National surveillance of spotted fever group rickettsioses in the United States, 2008–2012. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouqui, P.; Bacellar, F.; Baranton, G.; Birtles, R.; Bjöersdorff, A.; Blanco, J.-R.; Caruso, G.; Cińco, M.; Fournier, P.; Francavilla, E.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 1108–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocias, L.F.; Jensen, B.B.; Villumsen, S.; Lebech, A.-M.; Skarphedinsson, S.; Dessau, R.B.; Krogfelt, K. Rickettsioses in Denmark: A retrospective survey of clinical features and travel history. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, S.A.M.; Rajapakse, R.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Nanayakkara, D.; Budagoda, S.; Weerakoon, K.G.; Edirisinghe, J.; Premaratna, R. Rickettsioses in the central hills of Sri Lanka: Serological evidence of increasing burden of spotted fever group. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e988–e992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, S.A.M.; Gawarammana, I. Validity of the Weil-Felix test in the diagnosis of acute rickettsial infections in Sri Lanka. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.M.; Storgaard, M.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Obel, N. Rickettsiosis after a stay in South Africa. Ugeskr. Laeger 2004, 166, 902–904. [Google Scholar]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Al Marai, D.; Andersen, L.O.; Krogfelt, K.; Jensen, J.S.; Larsen, K.S.; Nielsen, H. Babesia spp. and other pathogens in ticks recovered from domestic dogs in Denmark. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantsø, B.; Svendsen, C.B.; Jensen, P.M.; Vennestrøm, J.; Krogfelt, K. Seasonal and habitat variation in the prevalence of Rickettsia helvetica in Ixodes ricinus ticks from Denmark. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarphedinsson, S.; Lyholm, B.F.; Ljungberg, M.; Søgaard, P.; Kolmos, H.J.; Nielsen, L.P. Detection and identification of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi, and Rickettsia helvetica in Danish Ixodes ricinus ticks. APMIS 2007, 115, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarphedinsson, S.; Jensen, P.M.; Kristiansen, K. Survey of tickborne infections in Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.; Fournier, P.-E.; Pedersen, I.S.; Krarup, H.; Ejlertsen, T.; Raoult, D. Serological and molecular evidence of Rickettsia helvetica in Denmark. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 36, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiellerup, P.; Dyhr, T.; Rolain, J.-M.; Christensen, M.; Damsgaard, R.; Fisker, N.; Andersen, N.F.; Raoult, D.; Krogfelt, K. No serological evidence for Rickettsial diseases among Danish elite Orienteerers. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, C.B.; Milman, N.; Dziegiel, M.H.; Krogfelt, K.; Høier-Madsen, M. Determination of rickettsial and antinuclear antibodies in Danish patients with sarcoidosis. Clin. Respir. J. 2008, 2, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, J.A.; Thybo, S. African Tick Bite Fever upon game hunting in South Africa. Ugeskr. Laeger 2011, 173, 2572–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Kibsgaard, L.; Lindberg, J.; Villumsen, S.; Larsen, C.S. Rickettsiosis should be considered as a differential diagnosis in patients having fever related to travelling. Ugeskr. Laeger 2012, 174, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ECDC. Epidemiological Situation of Rickettsioses in EU/EFTA Countries; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, H.M.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bradley, K.K.; Dahlgren, F.S.; Drexler, N.A.; Dumler, J.S.; Folk, S.M.; Kato, C.Y.; Lash, R.R.; Levin, M.L.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Tickborne Rickettsial diseases: Rocky mountain spotted fever and other spotted fever group Rickettsioses, Ehrlichioses, and Anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2016, 65, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantsø, B.; Svendsen, C.B.; Jørgensen, C.S.; Krogfelt, K. Evaluation of serological tests for the diagnosis of rickettsiosis in Denmark. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 76, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Hindersson, P.; Pedersen, N.S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenos, J.; Unsworth, N.B.; Graves, S.R. A highly sensitive and specific real-time PCR assay for the detection of spotted fever and typhus group Rickettsiae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, K.; Elfving, K.; Påhlson, C. Rickettsia helveticain Patient with Meningitis, Sweden, 2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, H.; Artsob, H. Spotted fever group Rickettsiae: A brief review and a Canadian perspective. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Dunaj, J.; Swiecicka, I.; Zambrowski, G.; Chmielewska-Badora, J.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Zajkowska, J.; Czupryna, P.; Kondrusik, M.; Grygorczuk, S.; et al. Co-infections with Borrelia species, Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Babesia spp. in patients with tick-borne encephalitis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welc-Falęciak, R.; Hildebrandt, A.; Siński, E. Co-infection with Borrelia species and other tick-borne pathogens in humans: Two cases from Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2010, 17, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krause, P.J.; McKay, K.; Thompson, C.A.; Sikand, V.K.; Lentz, R.; Lepore, T.; Closter, L.; Christianson, D.; Telford, S.R.; Persing, D.; et al. Disease-specific diagnosis of Coinfecting Tickborne Zoonoses: Babesiosis, human granulocytic Ehrlichiosis, and lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumler, J.S.; Walker, D.H. Ehrlichia chaffeensis (human Monocytotropic Ehrlichiosis), Anaplasma phagocytophilum (human Granulocytotropic Anaplasmosis), and other Anaplasmataceae. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.; Blanton, L. Rickettsia rickettsii and other spotted fever group Rickettsiae (Rocky Mountain spotted fever and other spotted fevers). In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.T.; Satjanadumrong, J.; Hughes, T.; Stenos, J.; Blacksell, S.D. Diagnosis of spotted fever group Rickettsia infections: The Asian perspective. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adem, P.V. Emerging and re-emerging rickettsial infections. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrel, R.N.; Berenger, J.-M.; Laroche, M.; Ayhan, N.; Bitam, I.; Delaunay, P.; Parola, P. Neglected vector-borne bacterial diseases and arboviruses in the Mediterranean area. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 26, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total No of Samples | General Practitioners | Medical Specialists | Hospitals | Others 2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tested | n (%) 3) | Tested | n (%) | Tested | n (%) | Tested | n (%) | Tested | n (%) | ||
| by analysis | Single 1) | 1248 | 427 (34) | 157 | 53 (34) | 15 | 2 (13) | 1068 | 368 (34) | 1248 | 2 (19) |
| Combined | 1156 | 299 (26) | 459 | 129 (28) | 74 | 17 (23) | 607 | 150 (25) | 16 | 2 (19) | |
| PCR | 415 | 43 (10) | 63 | 13 (21) | 7 | 0 | 338 | 30 (9) | 7 | 0 | |
| by year | 2008 | 29 | 11 (38) | 9 | 2 (22) | 2 | 2 (100) | 18 | 7 (39) | 0 | 0 |
| 2009 | 469 | 114 (24) | 196 | 53 (27) | 20 | 4 (20) | 250 | 55 (22) | 3 | 2 (67) | |
| 2010 | 411 | 91 (22) | 132 | 30 (23) | 7 | 1 (4) | 268 | 59 (22) | 4 | 1 (25) | |
| 2011 | 404 | 101 (25) | 85 | 24 (28) | 10 | 0 | 302 | 77 (25) | 7 | 0 | |
| 2012 | 354 | 125 (35) | 67 | 31 (46) | 3 | 1 (33) | 280 | 91 (33) | 4 | 2 (50) | |
| 2013 | 332 | 142 (43) | 58 | 23 (40) | 6 | 4 (67) | 265 | 115 (43) | 3 | 0 | |
| 2014 | 418 | 98 (23) | 74 | 19 (26) | 16 | 5 (31) | 325 | 74 (23) | 3 | 0 | |
| 2015 | 402 | 87 (22) | 58 | 13 (22) | 32 | 2 (6) | 305 | 70 (23) | 7 | 2 (29) | |
| Total | 2819 | 770 (27) | 679 | 195 (29) | 96 | 19 (20) | 2013 | 548 (27) | 31 | 7 (23) | |
| SFG | TG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) 1) | n (%) | |||
| Positive | 484 | (86) | 40 | (7) |
| IgM | 401 | (83) | 18 | (46) |
| IgM and IgG | 44 | (9) | 1 | |
| IgG | 39 | (8) | 21 | (54) |
| No. of Co-Infections | Rickettsia (R) | B. henselae B. quintana2) | B. burgdorferi2) | Ehrlichia3) | F. tularensis3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 197 | ||||
| 1 | 72 | 17 | 32 | 15 | 8 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Total | 279 | 22 | 40 | 20 | 10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schjørring, S.; Jepsen, M.T.; Sørensen, C.A.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Kantsø, B.; Petersen, R.F.; Skovgaard, O.; Krogfelt, K.A. Laboratory Diagnostics of Rickettsia Infections in Denmark 2008–2015. Biology 2020, 9, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9060133
Schjørring S, Jepsen MT, Sørensen CA, Valentiner-Branth P, Kantsø B, Petersen RF, Skovgaard O, Krogfelt KA. Laboratory Diagnostics of Rickettsia Infections in Denmark 2008–2015. Biology. 2020; 9(6):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9060133
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchjørring, Susanne, Martin Tugwell Jepsen, Camilla Adler Sørensen, Palle Valentiner-Branth, Bjørn Kantsø, Randi Føns Petersen, Ole Skovgaard, and Karen A. Krogfelt. 2020. "Laboratory Diagnostics of Rickettsia Infections in Denmark 2008–2015" Biology 9, no. 6: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9060133
APA StyleSchjørring, S., Jepsen, M. T., Sørensen, C. A., Valentiner-Branth, P., Kantsø, B., Petersen, R. F., Skovgaard, O., & Krogfelt, K. A. (2020). Laboratory Diagnostics of Rickettsia Infections in Denmark 2008–2015. Biology, 9(6), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9060133





