Contribution of Neurotrophins to the Immune System Regulation and Possible Connection to Alcohol Addiction
Abstract
1. Introduction: Neurotrophin Signaling
2. Neurotrophin Receptors and Signaling Pathways
2.1. NGF Pathway
2.2. BDNF Pathway
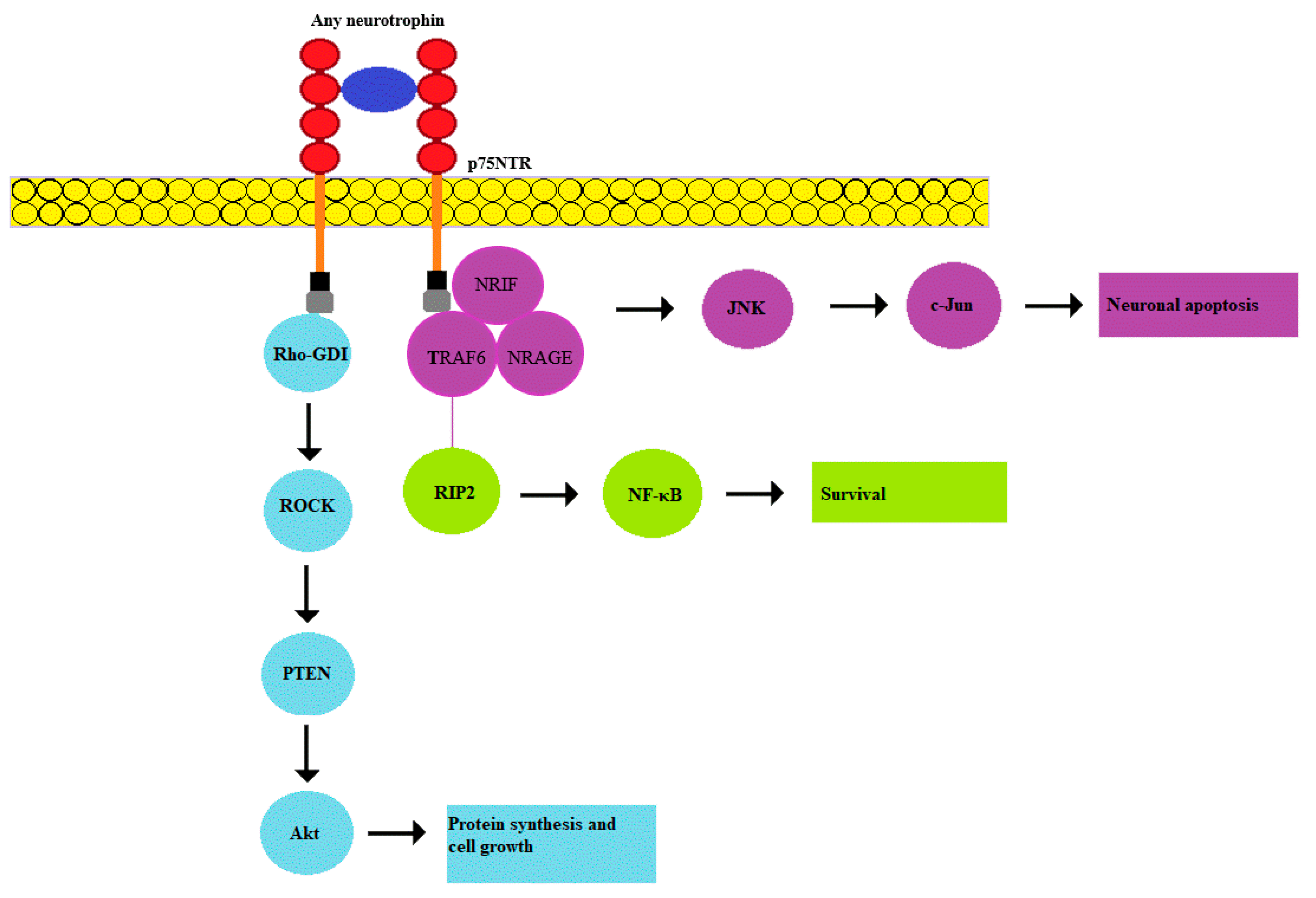
2.3. p75NTR Pathway
3. Possible Role of Neurotrophins in Alcohol Addiction
4. Role of Neurotrophins in the Immune System Regulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dechant, G.; Barde, Y.A. The neurotrophin receptor p75 (NTR): Novel functions and implications for diseases of the nervous system. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Pang, P.T.; Woo, N.H. The yin and yang of neurotrophin action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloe, L.; Rocco, M.L.; Bianchi, P.; Manni, L. Nerve growth factor, from the early discoveries to the potential clinical use. J. Trans. Med. 2012, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnone, G.; De Benedetti, F.; Bracci-Laudiero, L. NGF and its receptors in the regulation of inflammatory response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempstead, B.L. Deciphering proneurotrophin actions. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 220, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer, A.; Lee, R.; Teng, K.K.; Jansen, P.; Madsen, P.; Nielsen, M.S.; Jacobsen, C.; Kliemannel, M.; Schwarz, E.; Willnow, T.E.; et al. Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature 2004, 427, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, L.; Bonsignore, F.; Gobbo, F.; Amodeo, R.; Calvello, M.; Jacob, A.; Signore, G.; Schirripa Spagnolo, C.; Porciani, D.; Mainardi, M.; et al. Fast-diffusing p75NTR monomers support apoptosis and growth cone collapse by neurotrophin ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21563–21572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, F.E.; Stanley, E.M.; Carter, B.D. Neurotrophin responsiveness of sympathetic neurons is regulated by rapid mobilization of the p75 receptor to the cell surface through TrkA activation of Arf6. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 5606–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.L.; Bailey, S.; Matusica, D.; Nicholson, I.; Muyderman, H.; Pagadala, P.C.; Neet, K.E.; Zola, H.; Macardle, P.; Rush, R.A. ProNGF mediates death of Natural Killer cells through activation of the p75NTR-sortilin complex. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 226, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Lim, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Fu, D.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhong, J.H.; Xiao, Z.C.; Zhou, X.F. ProBDNF and its receptors are upregulated in glioma and inhibit the growth of glioma cells in vitro. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waskow, M.; Steliga, A.; Morys, J. BDNF, a key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Lim, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.-H.; Zhou, X.-F. Precursor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF) forms a complex with Huntingtin-associated protein-1 (HAP1) and sortilin that modulates proBDNF trafficking, degradation, and processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16272–16284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xiong, J.; Ruan, C.S.; Ruan, Y.; Liu, D.; Bao, J.J.; Zhou, X.F. ProBDNF/p75NTR/sortilin pathway is activated in peripheral blood of patients with alcohol dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.C.; Choi, I.G.; Kim, Y.K.; Ham, B.J.; Yang, B.H.; Roh, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, D.Y.; Chai, Y.G. Relation between plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in the male patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol 2009, 43, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Noronha, A.; Warren, K.R.; Koob, G.F.; Sinha, R.; Thakkar, M.; Matochik, J.; Crexs, F.T.; Chandler, L.J.; Pfefferbaum, A.; et al. Brain pathways to recovery from alcohol dependence. Alcohol 2015, 49, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, C.F. Neurotrophin-4, the odd one out in the neurotrophin family. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proenca, C.C.; Song, M.; Lee, F.S. Differential effects of BDNF and neurotrophin 4 (NT4) on endocytic sorting of TrkB receptors. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, S.; Wahle, P. Developmental changes of neurotrophin mRNA expression in the layers of rat visual cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors, roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 609–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogłodek, E.A.; Just, M.J.; Szromek, A.R.; Araszkiewicz, A. Assessing the serum concentration levels of NT-4/5, GPX-1, TNF-α, and l-arginine as biomediators of depression severity in first depressive episode patients with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Pharm. Rep. 2017, 69, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahnestock, M.; Yu, G.; Michalski, B.; Mathew, S.; Colquhoun, A.; Ross, G.M.; Coughlin, M.D. The nerve growth factor precursor proNGF exhibits neurotrophic activity but is less active than mature nerve growth factor. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, M.; Fahnestock, M. ProNGF, but not NGF, switches from neurotrophic to apoptotic activity in response to reductions in TrkA receptor levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.P.; Barker, P.A. Neurotrophin signaling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors, a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Thrimawithana, T.; Little, P.J.; Xu, J.; Feng, Z.P.; Zheng, W. The nerve growth factor signaling and its potential as therapeutic target for glaucoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 759473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.R.; West, A.E. Mechanisms of specificity in neuronal activity-regulated gene transcription. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 94, 259–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secondo, A.; Esposito, A.; Petrozziello, T.; Boscia, F.; Molinaro, P.; Tedeschi, V.; Pannaccione, A.; Ciccone, R.; Guida, N.; Di Renzo, G.; et al. Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 1 on nuclear envelope controls PTEN/Akt pathway via nucleoplasmic Ca2+ regulation during neuronal differentiation. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, A.S.; Hargreaves, A.J.; Dickenson, J.M. Activation of transglutaminase 2 by nerve growth factor in differentiating neuroblastoma cells, a role in cell survival and neurite outgrowth. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 820, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasia, A.; Deinhardt, K.; Chao, M.V.; Will, N.E.; Irmady, K.; Lee, F.S.; Hempstead, B.L.; Bracken, C. Val66Met polymorphism of BDNF alters prodomain structure to induce neuronal growth cone retraction. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kairisalo, M.; Korhonen, L.; Sepp, M.; Pruunsild, P.; Kukkonen, J.P.; Kivinen, J.; Timmusk, T.; Blomgren, K.; Lindholm, D. NF-κB-dependent regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revest, J.; Le Roux, A.; Roullot-Lacarrière, V.; Kaouane, N.; Vallee, M.; Kasanetz, F.; Rouge-Pont, F.; Tronche, F.; Desmedt, A.; Piazza, P.V. BDNF-TrkB signaling through Erk1/2MAPK phosphorylation mediates the enhancement of fear memory induced by glucocorticoids. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydyuk, M.; Xu, B. BDNF signaling and survival of striatal neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Voleti, B. Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression, novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, J.; He, F.; Xiao, W.; Hu, X.; Luo, Z. CaMKII-mediated CREB phosphorylation is involved in Ca2+-induced BDNF mRNA transcription and neurite outgrowth promoted by electrical stimulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Karelina, K.; Obrietan, K. CREB, a multifaceted regulator of neuronal plasticity and protection. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Moya-Alvarado, G.; Gonzalez-Billaut, C.; Bronfman, F.C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating neuronal growth by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2016, 73, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, C.; Simi, A. p75 neurotrophin receptor signaling in nervous system injury and degeneration, paradox and opportunity. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, R.B.; Williams, K.S. The p75 neurotrophin receptor, at the crossroad of neural repair and death. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Kenchappa, R.S.; Simi, A.; Karaca, E.; Reversi, A.; Choi, S.; Bothwell, M.; Minfarro, I.; Friedman, W.J.; et al. Activation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor through conformational rearrangement of disulphide-linked receptor dimers. Neuron 2009, 62, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotthibundhu, A.; Li, Q.X.; Thangnipon, W.; Coulson, E.J. Aβ1–42 stimulates adult SVZ neurogenesis through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccanti, M.; Coccurello, R.; Carito, V.; Ciafrè, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Giacovazzo, G.; Mancinelli, R.; Tirassa, P.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Pascale, E.; et al. Paternal alcohol exposure in mice alters brain NGF and BDNF and increases ethanol-elicited preference in male offspring. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carito, V.; Ceccanti, M.; Ferraguti, G.; Coccurello, R.; Ciafre, S.; Tirassa, P.; Fiore, M. NGF and BDNF alterations by prenatal alcohol exposure. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Ra, Y.; Han, C.; Kim, D.-J. Decreased serum level of NGF in alcohol-dependent patients with declined executive function. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boschen, K.E.; Klintsova, A.Y. Neurotrophins in the brain, interaction with alcohol exposure during development. Vitam. Horm. 2017, 104, 197–242. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, S.M.; Miller, M.W. Nerve growth factor neuroprotection of ethanol-induced neuronal death in rat cerebral cortex is age-dependent. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Warnault, V.; Darcq, E.; Morisot, N.; Phamluong, K.; Wilbrecht, L.; Massa, S.M.; Longo, F.M.; Ron, D. The Bdnf Val68 to met polymorphism increases compulsive alcohol drinking in mice which is reversed by TrkB activation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Patel, P.D.; Sant, G.; Meng, C.X.; Teng, K.K.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lee, F.S. Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type BDNF in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4401–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003, 112, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C. A critical role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in alcohol consumption. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Vasudevan, D.M. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol metabolism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, M.B.; Moore, D.B.; Paiva, M.; Madorsky, I.; Mayer, J.; Shaw, G. The role of neurotrophic factors, apoptosis-related proteins, and endogenous antioxidants in the differential temporal vulnerability of neonatal cerebellum to ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D. Nerve growth factor, a neuroimmune crosstalk mediator for all seasons. Immunology 2017, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Fang, J. Peripheral immune activation by lipopolysaccharide decreases neurotrophins in the cortex and hippocampus in rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnydrig, S.; Korner, L.; Landweer, S.; Ernst, B.; Walker, G.; Otten, U.; Kunz, D. Peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration transiently affects expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, corticotropin and proopiomelanocortin in mouse brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 429, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.A.; García-Suárez, O.; Hannestad, J.; Pérez-Pérez, M.; Germanà, A. Neurotrophins and the immune system. J. Anat. 2003, 203, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Herbruggen, O.; Braun, A.; Rochlitzer, S.; Jockers-Scherubl, M.; Hellweg, R. Neurotrophic factors—A tool for therapeutic strategies in neurological, neuropsychiatric and neuroimmunological diseases? Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, K. Current perspectives on the link between neuroinflammation and neurogenesis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 30, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siiskonen, H.; Harvima, I. Mast cells and sensory nerves contribute to neurogenic inflammation and pruritus in chronic skin inflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschensteiner, M.; Gallmeier, E.; Behrens, L.; Vargas Leal, V.; Misgeld, T.; Klinkert, W.E.F.; Kolbeck, R.; Hoppe, E.; Oropeza-Wekerle, R.; Bartke, I.; et al. Activated human T cells, B cells, and monocytes produce brain-derived neurotrophic factor in vitro and in inflammatory brain lesions, a neuroprotective role of inflammation? J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobbo, B.L.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Bromberg, E.; De Vries, E.F.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders, focus on neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orekhov, A.N.; Poznyak, A.V.; Sobenin, I.A.; Nikiforov, N.N.; Ivanova, E.A. Mitochondrion as a selective target for treatment of atherosclerosis, role of mitochondrial DNA mutations and defective mitophagy in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and chronic inflammation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and age-related diseases, role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, G.T.; Sheedy, D.; Kril, J.J. Using autopsy brain tissue to study alcohol-related brain damage in the genomic age. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunck, R.V.; Torres, I.L.; Laste, G.; de Souza, A.; Macedo, I.C.; Valle, M.T.; Salomon, J.L.; Moreira, S.; Kuo, J.; Arbo, M.D.; et al. Protracted alcohol abstinence induces analgesia in rats, possible relationships with BDNF and interleukin-10. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.; Wiegand, S.J.; Siuciak, J.A.; Lindsay, R.M.; Rudge, J.S. Effects of BDNF infusion on the regulation of TrkB protein and message in adult rat brain. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 145, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuciak, J.A.; Wong, V.; Pearsall, D.; Wiegand, S.J.; Lindsay, R.M. BDNF produces analgesia in the formalin test and modifies neuropeptide levels in rat brain and spinal cord areas associated with nociception. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1995, 7, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasala, S.; Barr, T.; Messaoudi, I. Impact of alcohol abuse on the adaptive immune system. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2015, 37, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, G.; Saha, B. Alcohol’s effect on host defense. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Neurotrophin | Effect | Possible mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol consumption | |||
| NGF | Increased level of NGF; possible protective function | Prevents alcohol-induced neuronal death in rats | [43,44,45,46,47] |
| BDNF | Pro-BDNF increased, while mBDNF decreased; controls alcohol consumption | Polymorphisms in BDNF gene associated with the risk of alcoholism development; promotes survival of neurons | [48,49,50,51] |
| NT-4 | Not clear yet | Possible role in alcohol-induced oxidative stress | [52] |
| Immune system regulation | |||
| NGF | Pro-inflammatory | Promotes survival of immune cells | [4,55] |
| BDNF | Produced by activated immune cells; analgesic effect | Promotes survival of neurons | [56,57] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozlov, E.M.; Grechko, A.V.; Chegodaev, Y.S.; Wu, W.-K.; Orekhov, A.N. Contribution of Neurotrophins to the Immune System Regulation and Possible Connection to Alcohol Addiction. Biology 2020, 9, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040063
Kozlov EM, Grechko AV, Chegodaev YS, Wu W-K, Orekhov AN. Contribution of Neurotrophins to the Immune System Regulation and Possible Connection to Alcohol Addiction. Biology. 2020; 9(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozlov, Evgenii M., Andrey V. Grechko, Yegor S. Chegodaev, Wei-Kai Wu, and Alexander N. Orekhov. 2020. "Contribution of Neurotrophins to the Immune System Regulation and Possible Connection to Alcohol Addiction" Biology 9, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040063
APA StyleKozlov, E. M., Grechko, A. V., Chegodaev, Y. S., Wu, W.-K., & Orekhov, A. N. (2020). Contribution of Neurotrophins to the Immune System Regulation and Possible Connection to Alcohol Addiction. Biology, 9(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040063






