Understanding the Effect of Structural Diversity in WRKY Transcription Factors on DNA Binding Efficiency through Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
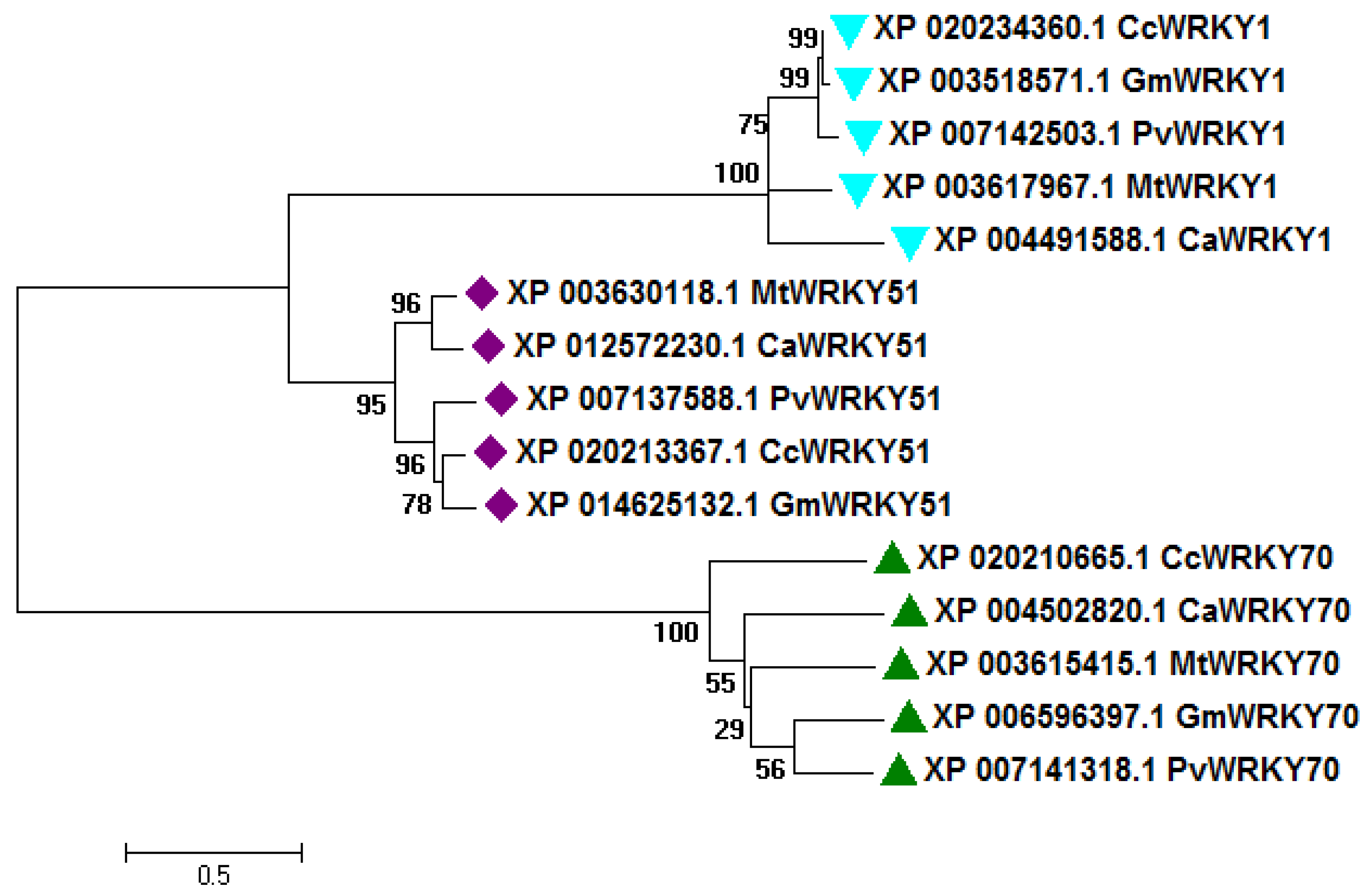
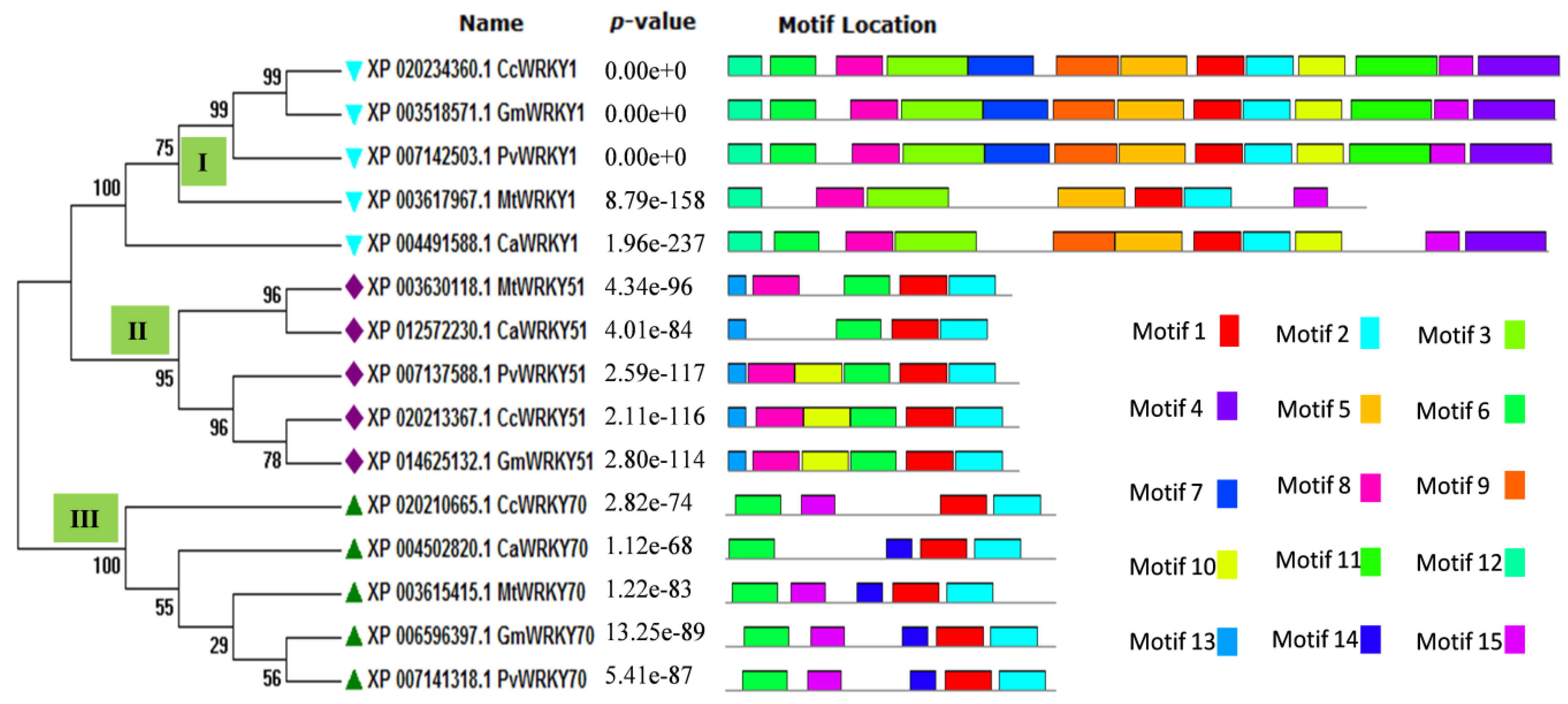
2.1. Sequence Analysis and Comparative Phylogeny
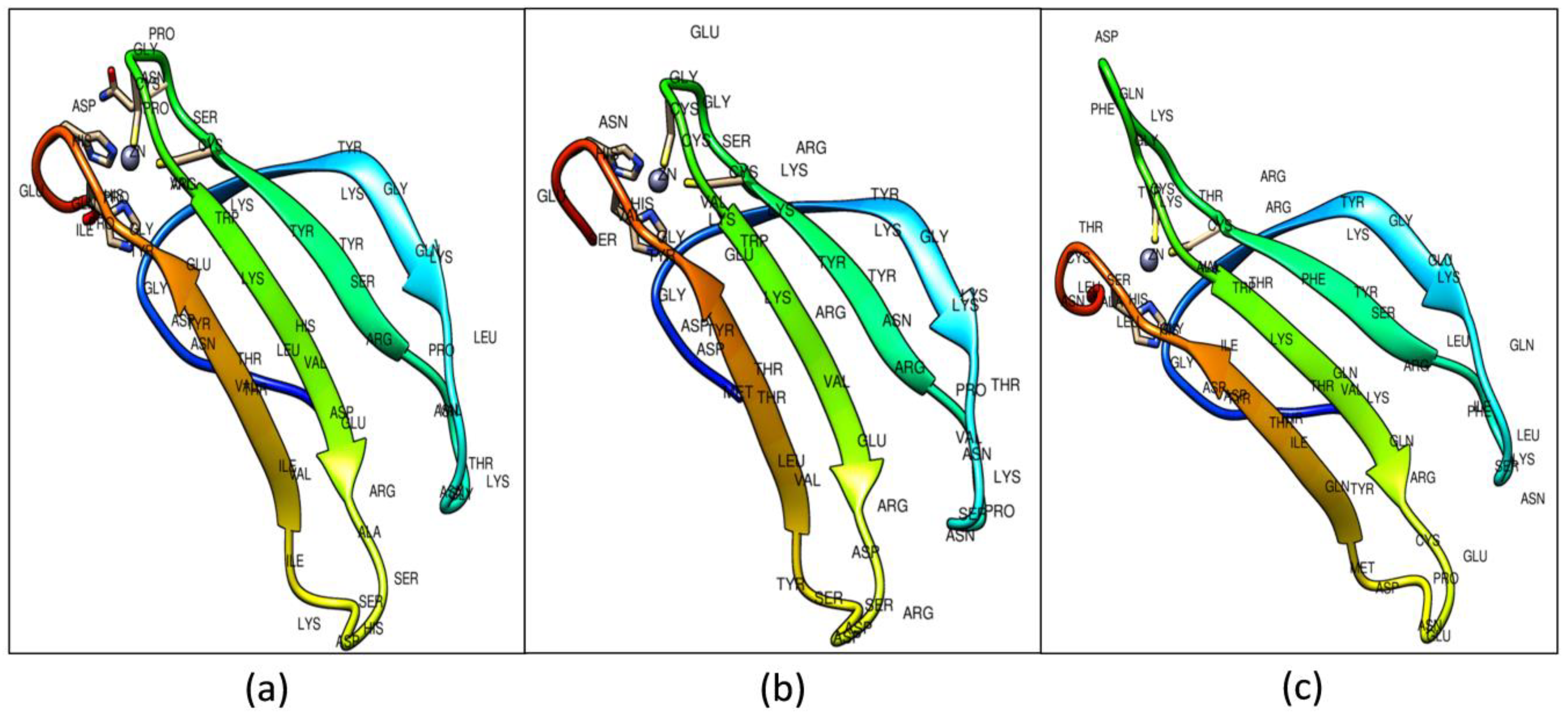
2.2. Construction and Validation of WRKY-DBD Model Variants
2.3. Molecular Docking Analysis of WRKY-DBD Variants with DNA-W-box
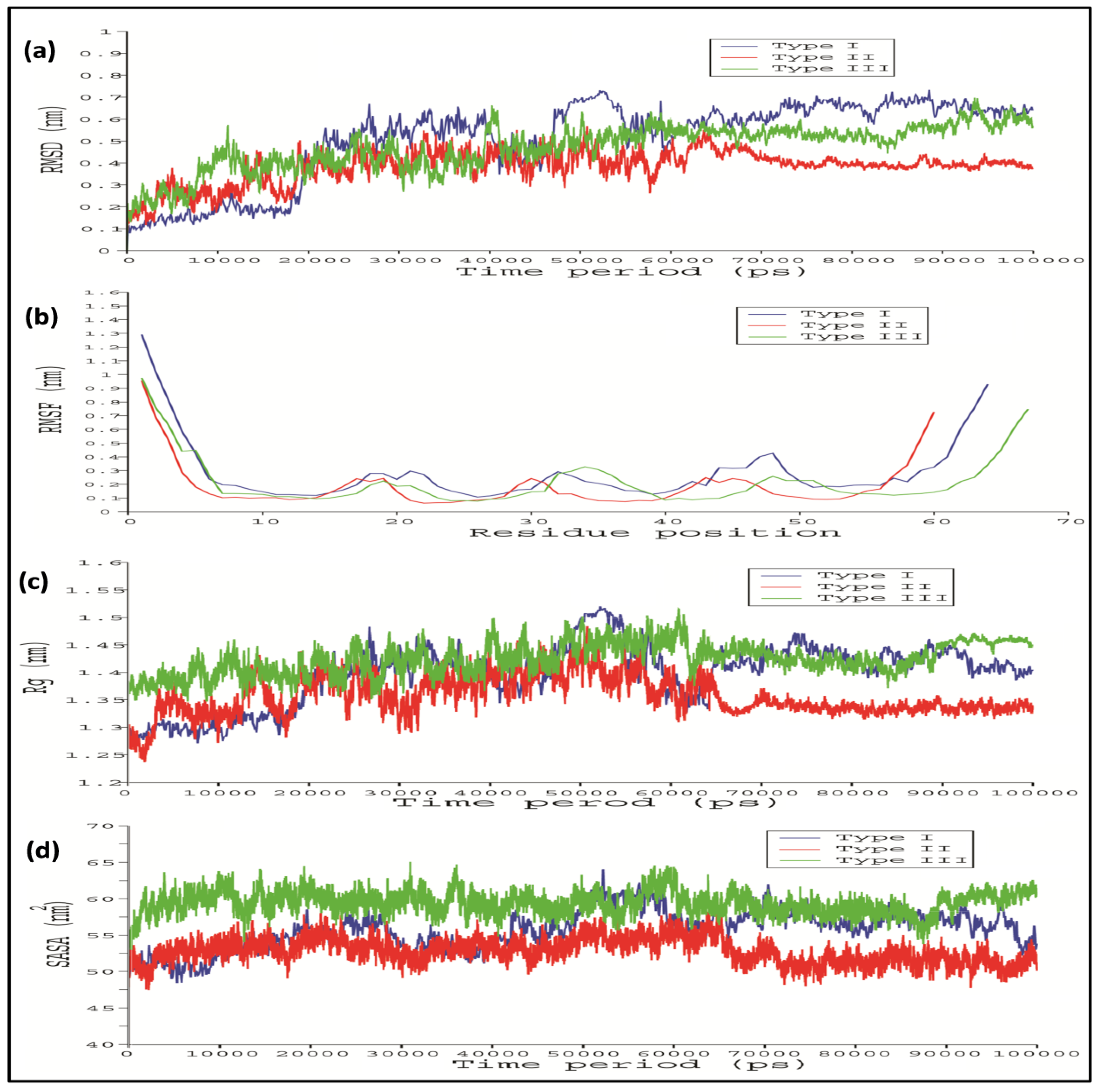
2.4. Comparative Interaction Analysis of Unbound and Bound Complexes Using MD Simulations
2.5. Binding Free Energy Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Retrieval and Analysis
4.2. Primary and Secondary Structure Analysis
4.3. Sequence Alignment, Phylogeny, and Potential Motif Analysis
4.4. Generation of Protein 3D Models
4.5. Evaluation of Structural Models
4.6. Binding Site Prediction
4.7. Protein–DNAInteraction
4.8. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ning, P.; Liu, C.; Kang, J.; Lv, J. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and differential expression under water deficit condition. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, S.; Nakamura, K. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel DNA-binding protein, SPF1, that recognizes SP8 sequences in the 5′ upstream regions of genes coding for sporamin and beta-amylase from sweet potato. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 244, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.A.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Q.J. The WRKY Gene Family in Rice (Oryza sativa). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Hao, B.; Kaushik, S.K.; Pan, Y. WRKY gene family evolution in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetica 2011, 139, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Dong, Q.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, B.; Xiang, Y. Genome-wide survey and characterization of the WRKY gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, B. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in Cucumis sativus. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Jalalahammed, G.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Ruan, M.; Ye, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Feng, K.; Zhou, G.; et al. Putative WRKYs associated with regulation of fruit ripening revealed by detailed expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in pepper. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, J.; Ye, W. Genome-wide investigation and transcriptome analysis of the WRKY gene family in Gossypium. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 290, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.; Kong, N.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, P.; Nan, Y.; Nie, T.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; et al. Genome-wide identification of the potato WRKY transcription factor family. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, P.; Hou, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Xia, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, X.; Wang, X. Global Analysis of WRKY Genes and Their Response to Dehydration and Salt Stress in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Srivastava, V.; Purayannur, S.; Kaladhar, V.C.; Cheruvu, P.J.; Verma, P.K. WRKY domain-encoding genes of a crop legume chickpea (Cicer arietinum): Comparative analysis with Medicago truncatula WRKY family and characterization of group-III gene(s). DNA Res. 2016, 23, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY2 transcription factor mediates seed germination and post germination arrest of development by abscisic acid. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Nolan, T.; Ye, H.; Zhang, M.; Tong, H.; Xin, P.; Chu, J.; Chu, C.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y. Arabidopsis WRKY46, WRKY54 and WRKY70 Transcription Factors Are Involved in Brassinosteroid-Regulated Plant Growth and Drought Response. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.S. TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2, a Trichome and Seed Coat Development Gene of Arabidopsis, Encodes a WRKY Transcription Factor. Plant Cell Online 2002, 14, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.-X.; Gu, M.-H.; Liu, Q.-Q. The WRKY transcription factor OsWRKY78 regulates stem elongation and seed development in rice. Planta 2011, 234, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tang, S.; Zhi, H.; Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Diao, X. Loose Panicle1 encoding a novel WRKY transcription factor, regulates panicle development, stem elongation, and seed size in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Regulation of Specialized Metabolism by WRKY Transcription Factors. Plant Physiol. 2014, 167, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Q.; Tan, X.L.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.F.; Lu, W.J.; Chen, J.Y. BrWRKY65, a WRKY Transcription Factor, Is Involved in Regulating Three Leaf Senescence-Associated Genes in Chinese Flowering Cabbage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1228. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Du, D.; Pan, H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in the Vegetative Buds, Floral Buds and Buds of Chrysanthemum morifolium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. WRKY8 transcription factor functions in the TMV-cg defense response by mediating both abscisic acid and ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1963–E1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, G.; Yang, S.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY57 Functions as a Node of Convergence for Jasmonic Acid- and Auxin-Mediated Signaling in Jasmonic Acid-Induced Leaf Senescence. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Genome-Wide Investigation of WRKY Transcription Factors Involved in Terminal Drought Stress Response in Common Bean. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Hao, L.; Guo, X. The Cotton WRKY Gene GhWRKY41 Positively Regulates Salt and Drought Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.-J.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, Z.-W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhuang, J. Transcriptome-wide identification of Camellia sinensis WRKY transcription factors in response to temperature stress. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 291, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, N.; Sheng, J.; Shen, L. Characterization of WRKY transcription factors in Solanum lycopersicum reveals collinearity and their expression patterns under cold treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslandes, L.; Olivier, J.; Theulieres, F.; Hirsch, J.; Feng, D.X.; Bittner-Eddy, P.; Beynon, J.; Marco, Y. Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis thaliana is conferred by the recessive RRS1-R gene, a member of a novel family of resistance genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chi, Y.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z. Characterization of Soybean WRKY Gene Family and Identification of Soybean WRKY Genes that Promote Resistance to Soybean Cyst Nematode. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Qamar, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Mengiste, T. Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J. 2006, 48, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.U.; Choi, L.M.; Lee, G.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Paek, K.-H. Capsicum annuum WRKY transcription factor d (CaWRKYd) regulates hypersensitive response and defense response upon Tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Sci. 2012, 197, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, C.; Yu, D. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Grover, A.; Sharma, P. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed structural differences among WRKY domain-DNA interaction in barley (Hordeum vulgare). BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: Its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2005, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Xu, Z.-S.; Tian, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.-S. Genomic identification of WRKY transcription factors in carrot (Daucus carota) and analysis of evolution and homologous groups for plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K. Solution Structure of an Arabidopsis WRKY DNA Binding Domain. Plant Cell Online 2005, 17, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwoski, G.; Kothiwale, S.; Meiler, J.; Lowe, E.W. Computational Methods in Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 66, 334–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolinski, A.; Skolnick, J. Monte carlo simulations of protein folding. II. Application to protein A, ROP, and crambin. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 1994, 18, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.; Šali, A. Advances in comparative protein-structure modeling. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.-R.; Nan, J.; Liang, Y.-H.; Mao, P.; Lu, L.; Li, L.; Wei, C.; Lai, L.; Li, Y.; Su, X.-D. DNA binding mechanism revealed by high resolution crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kigawa, T.; Watanabe, S.; Inoue, M.; Yamasaki, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yokoyama, S. Structural Basis for Sequence-specific DNA Recognition by an Arabidopsis WRKY Transcription Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Taylor, I.A.; Peng, Y.-L.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Structural basis of dimerization and dual W-box DNA recognition by rice WRKY domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4308–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Singh, V.K.; Meena, M.; Upadhyay, R.S.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, S. Structural and Functional Insights into WRKY3 and WRKY4 Transcription Factors to Unravel the WRKY–DNA (W-Box) Complex Interaction in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). A Computational Approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, B.; Sharma, P.; Tyagi, C.; Goyal, S.; Grover, A.; Sharma, I. Structural modeling and molecular simulation analysis of HvAP2/EREBP from barley. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 34, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zou, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Z.; Feng, P.; Fan, G.; Wang, W.; Liao, H. In silico analysis on structure and DNA binding mode of AtNAC1, a NAC transcription factor from Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Gupta, D.K.; Jayaswal, P.K.; Mahato, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Singh, S.; Bhutani, S.; Dogra, V.; Singh, B.P.; Kumawat, G.; et al. The first draft of the pigeonpea genome sequence. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, N.K.; Sharma, T.R. PpTFDB: A pigeonpea transcription factor database for exploring functional genomics in legumes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, P.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, N.K.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R.; Sharma, T.R. Understanding the Role of the WRKY Gene Family under Stress Conditions in Pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.). Plants 2019, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Macarthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, R.; Domselaar, G.H.V.; Zhang, H.; Wishart, D.S. SuperPose: A simple server for sophisticated structural superposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W590–W594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zundert, G.V.; Rodrigues, J.; Trellet, M.; Schmitz, C.; Kastritis, P.; Karaca, E.; Melquiond, A.; Dijk, M.V.; Vries, S.D.; Bonvin, A. The HADDOCK2.2 Web Server: User-Friendly Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Wani, S.H.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Dar, Z.A.; Lone, A.A.; Pareek, A.; Singla-Pareek, S.L. Transcription Factors and Plants Response to Drought Stress: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Rahman, M.H.; Deyholos, M.K.; Kav, N.N. Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in canola (Brassica napus L.) in response to fungal pathogens and hormone treatments. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, U.J.; Jeena, G.S.; Shukla, R.K. WRKY Transcription Factors: Molecular Regulation and Stress Responses in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswar, N.; Webb, B.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Madhusudhan, M.; Eramian, D.; Shen, M.-Y.; Pieper, U.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using Modeller. Curr. Protoc. Bioinf. 2006, 15, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U. VERIFY3D: Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods Enzymol. Macromol. Crystallogr. Part B 1997, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- UniProt Database. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Database. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- NCBI-Conserved Domain Database. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- ExPASy-ScanProsite Tool. Available online: http://prosite.expasy.org/scanprosite (accessed on 22 January 2019).
- Henson, R.; Cetto, L. The MATLAB bioinformatics toolbox. Encycl. Genet. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2005, 4, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Expasy-ProtParam Tool. Available online: https://web.expasy.org/protparam (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- SOPMA Tool. Available online: https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- PDBsum Web Server. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/pdbsum (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide composition: A novel approach for predicting in vivo stability of a protein from its primary sequence. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MEME Suite 5.0.3. Available online: http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- BLASTP. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Protein-ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UCSF Chimera ver.1.11.2. Available online: http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PyMol ver.3.2. Available online: https://www.pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and Dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E Water Models at 298 K. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9954–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

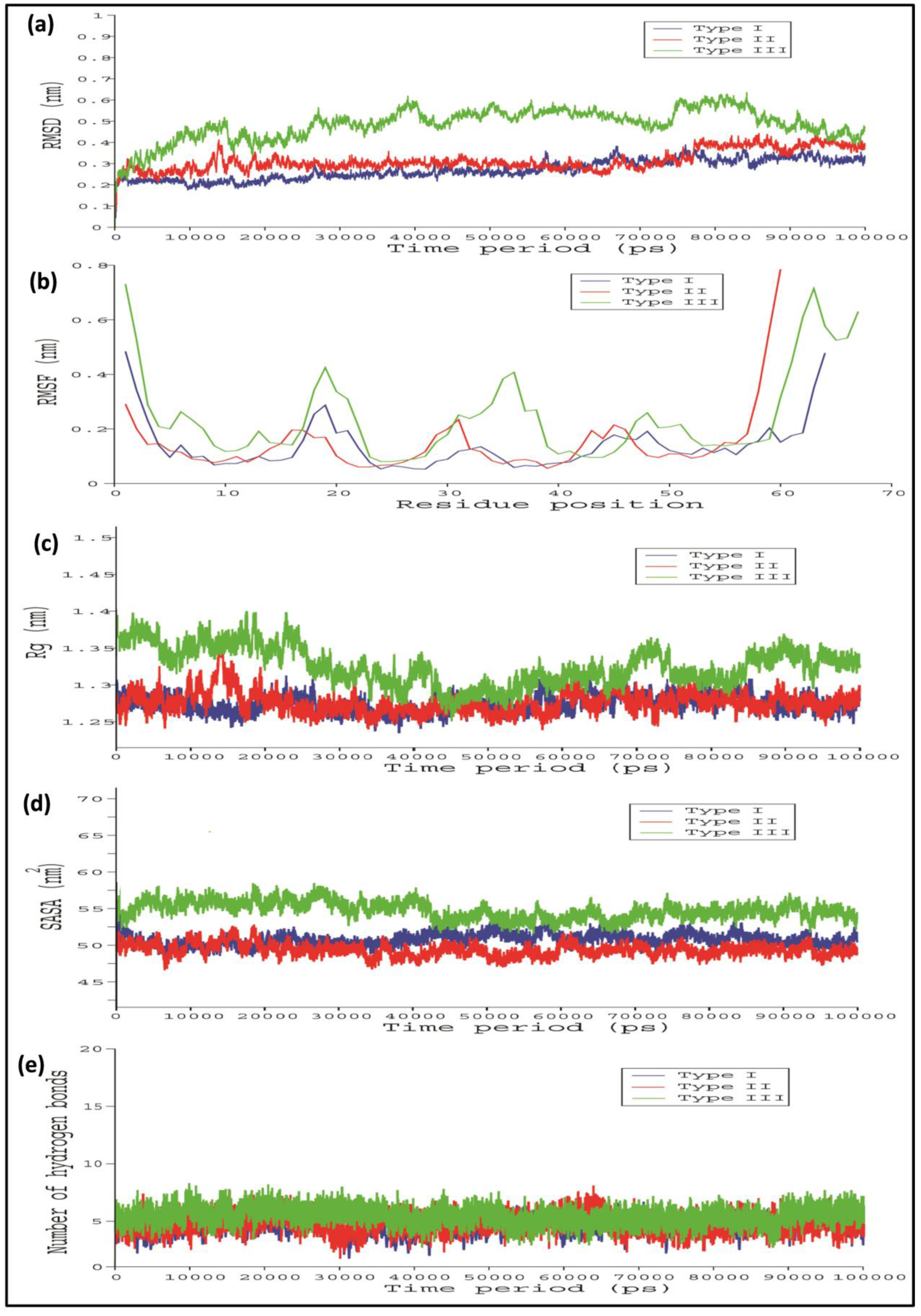
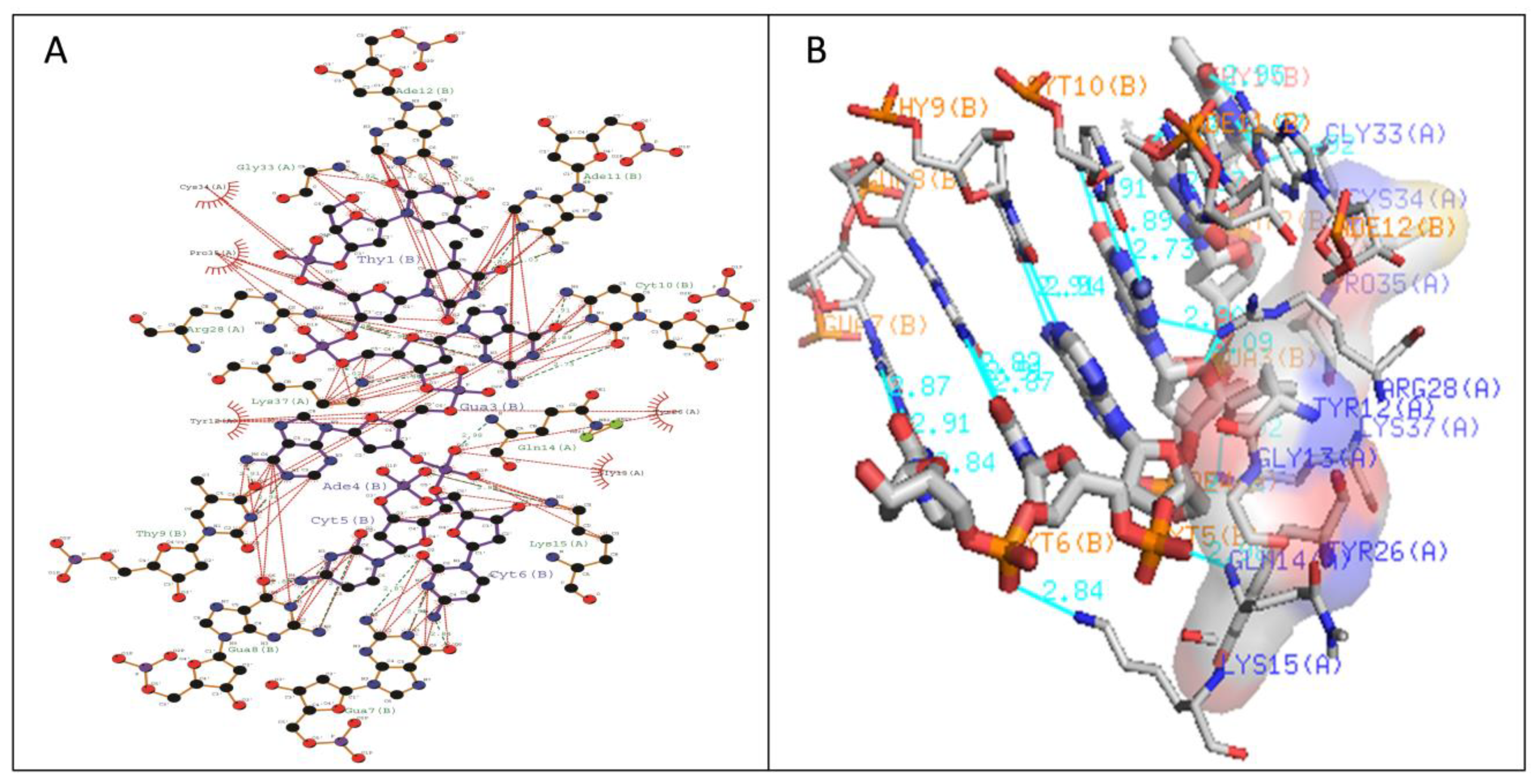
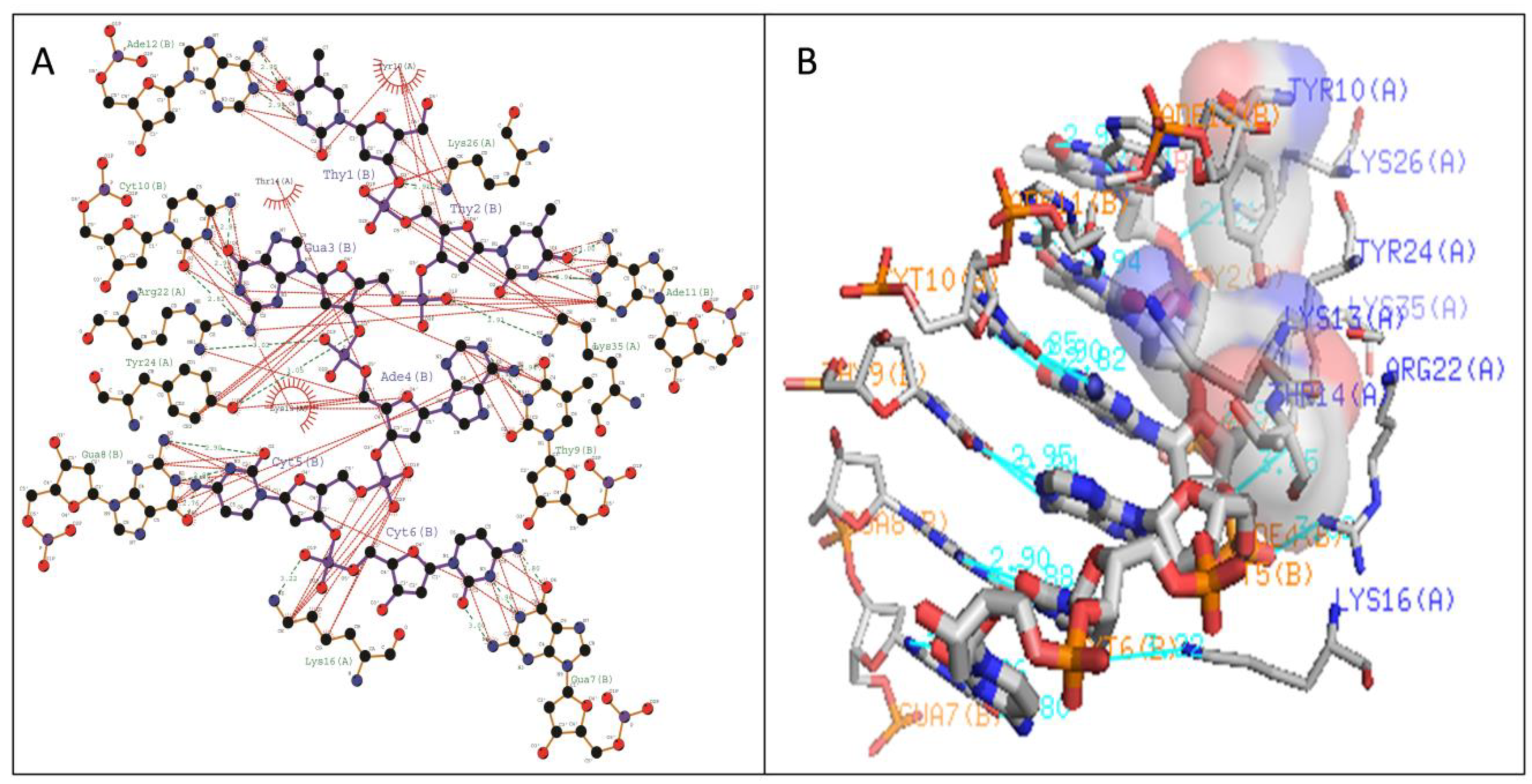
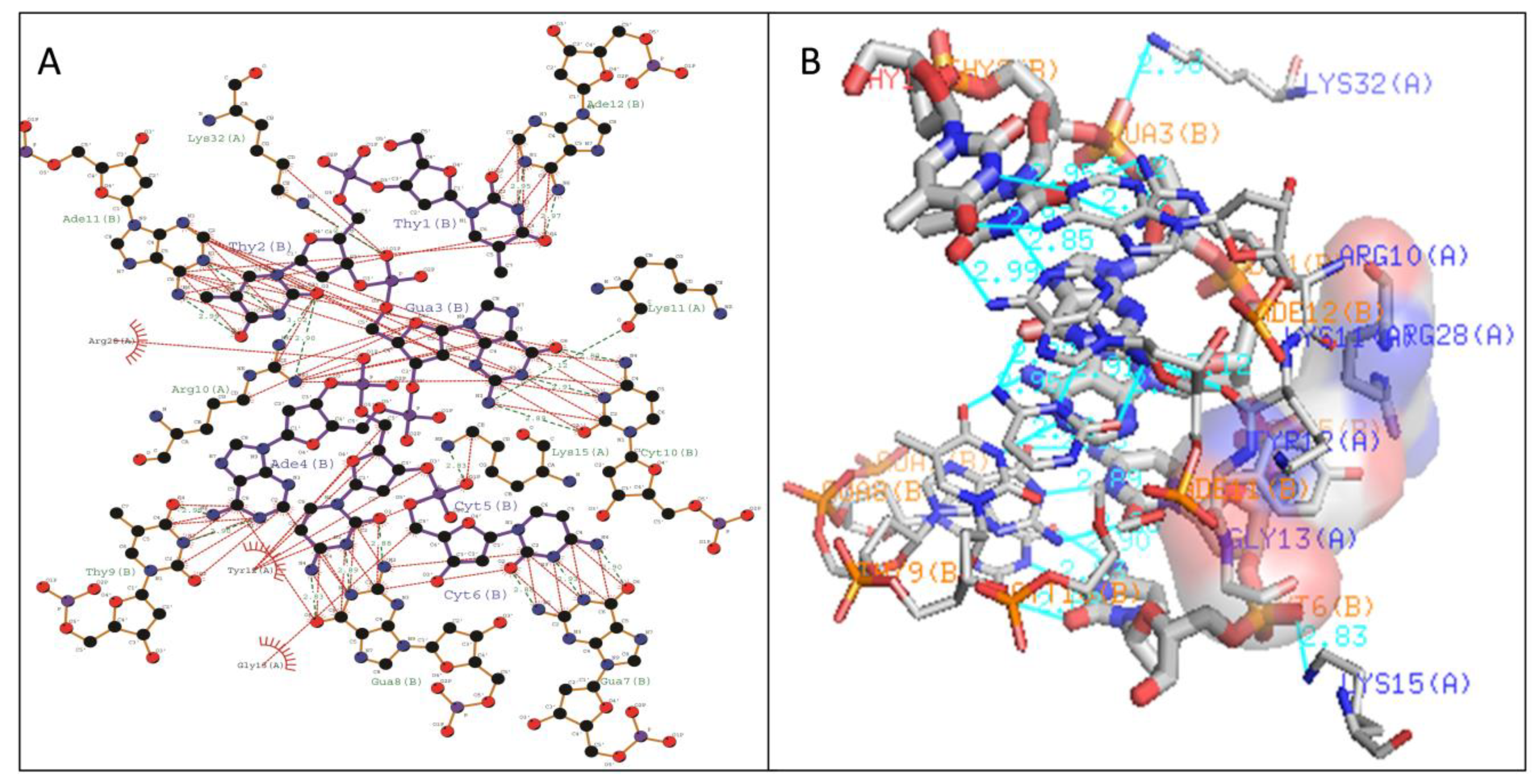
| WRKY Variants | Pre-Simulated WRKY–DNA Docked Complex | Post-Simulated WRKY–DNA Docked Complex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | |
| Type I | Gln14-DC5 (2.98 Å) Arg28-DG3 (2.9 Å) Arg28-DG3 (3.09 Å) Gly33-DT1 (2.92 Å) Lys37-DG3 (3.02 Å) Lys37-DA4 (2.94 Å) | Tyr12, Lys15, Tyr26, Gly33, Cys34, Pro35, Lys37 | Gln14-DC5 (2.98 Å) Arg28-DG3 (2.9 Å) Gly33-DT1 (2.92 Å) Lys37-DG3 (3.02 Å) Lys37-DA4 (2.94 Å) | Tyr12,Gly13, Lys15, Tyr26,Arg28 |
| Type II | Gly11-DA4 (2.87 Å) Lys13-DC6 (2.9 Å) Lys15-DG7 (2.89 Å) Arg22-DT2 (2.8 Å) | Arg10,Lys12,Lys15,Arg22, Tyr25 | Arg10-DT2 (2.9 Å) Lys15-DC6 (2.83 Å) Lys32-DG3 (2.98 Å) | Arg12,Gly14,Lys24,Arg28 |
| Type III | Lys11-DC6 (2.87 Å) Tyr12-DA4 (2.8 Å) Lys15-DC6 (2.83 Å) Lys32-DG3 (2.96 Å) Gln35-DC6 (2.9 Å) | Arg10,Lys11, Gly13, Lys32,Arg45,Tyr53,Gln54 | Lys16-DC6 (2.9 Å) Arg22-DA4 (3.02 Å) Tyr24-DG3 (2.89 Å) Lys35-DG3 (2.91 Å) | Lys11, Tyr12, Lys15, Arg33,Tyr36 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, N.K.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R.; Sharma, T.R. Understanding the Effect of Structural Diversity in WRKY Transcription Factors on DNA Binding Efficiency through Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Biology 2019, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8040083
Singh A, Sharma AK, Singh NK, Sonah H, Deshmukh R, Sharma TR. Understanding the Effect of Structural Diversity in WRKY Transcription Factors on DNA Binding Efficiency through Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Biology. 2019; 8(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Akshay, Ajay Kumar Sharma, Nagendra Kumar Singh, Humira Sonah, Rupesh Deshmukh, and Tilak Raj Sharma. 2019. "Understanding the Effect of Structural Diversity in WRKY Transcription Factors on DNA Binding Efficiency through Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Biology 8, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8040083
APA StyleSingh, A., Sharma, A. K., Singh, N. K., Sonah, H., Deshmukh, R., & Sharma, T. R. (2019). Understanding the Effect of Structural Diversity in WRKY Transcription Factors on DNA Binding Efficiency through Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Biology, 8(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8040083








