Sediment Carbon Accumulation in Southern Latitude Saltmarsh Communities of Tasmania, Australia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
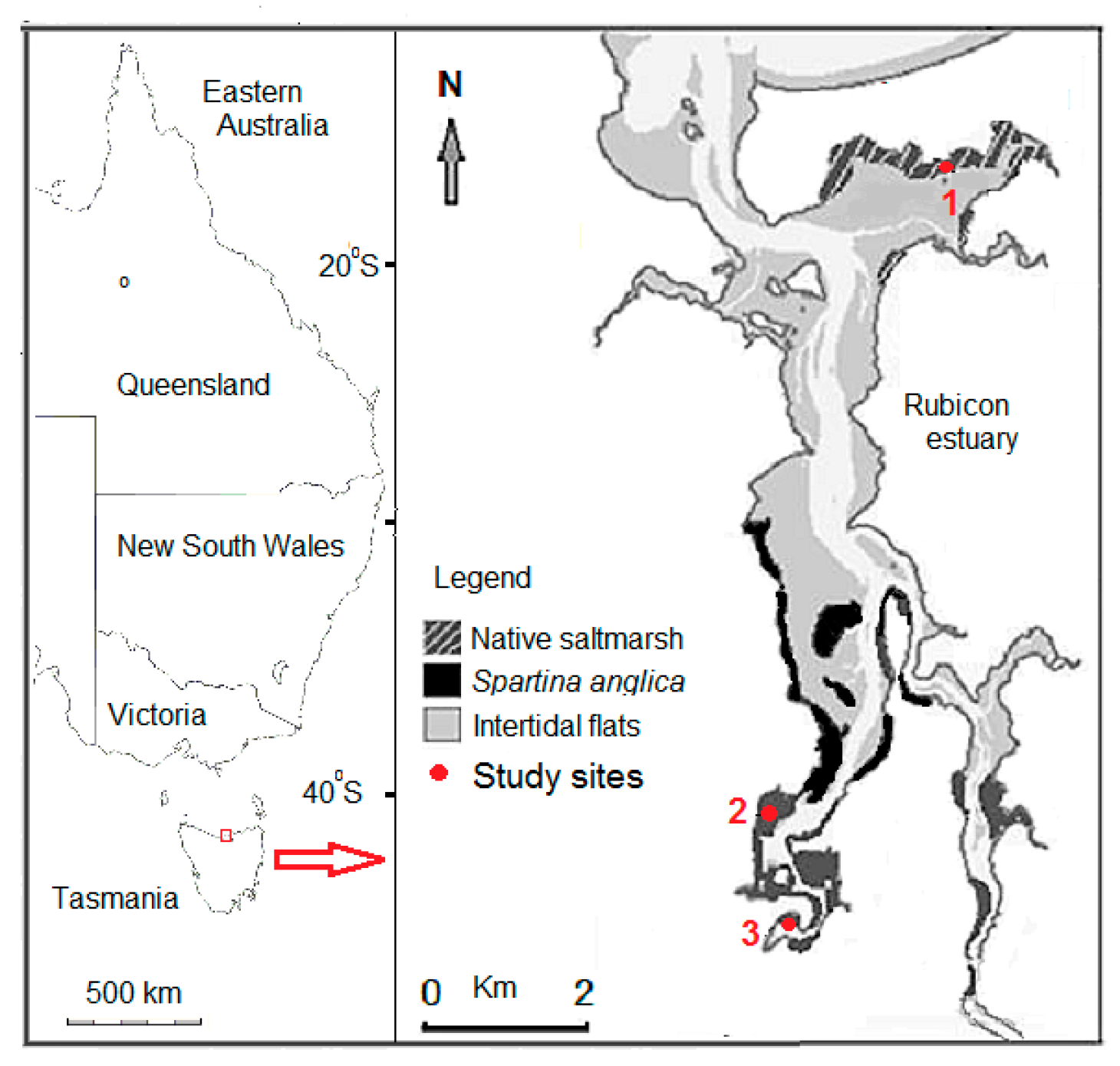
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analyses
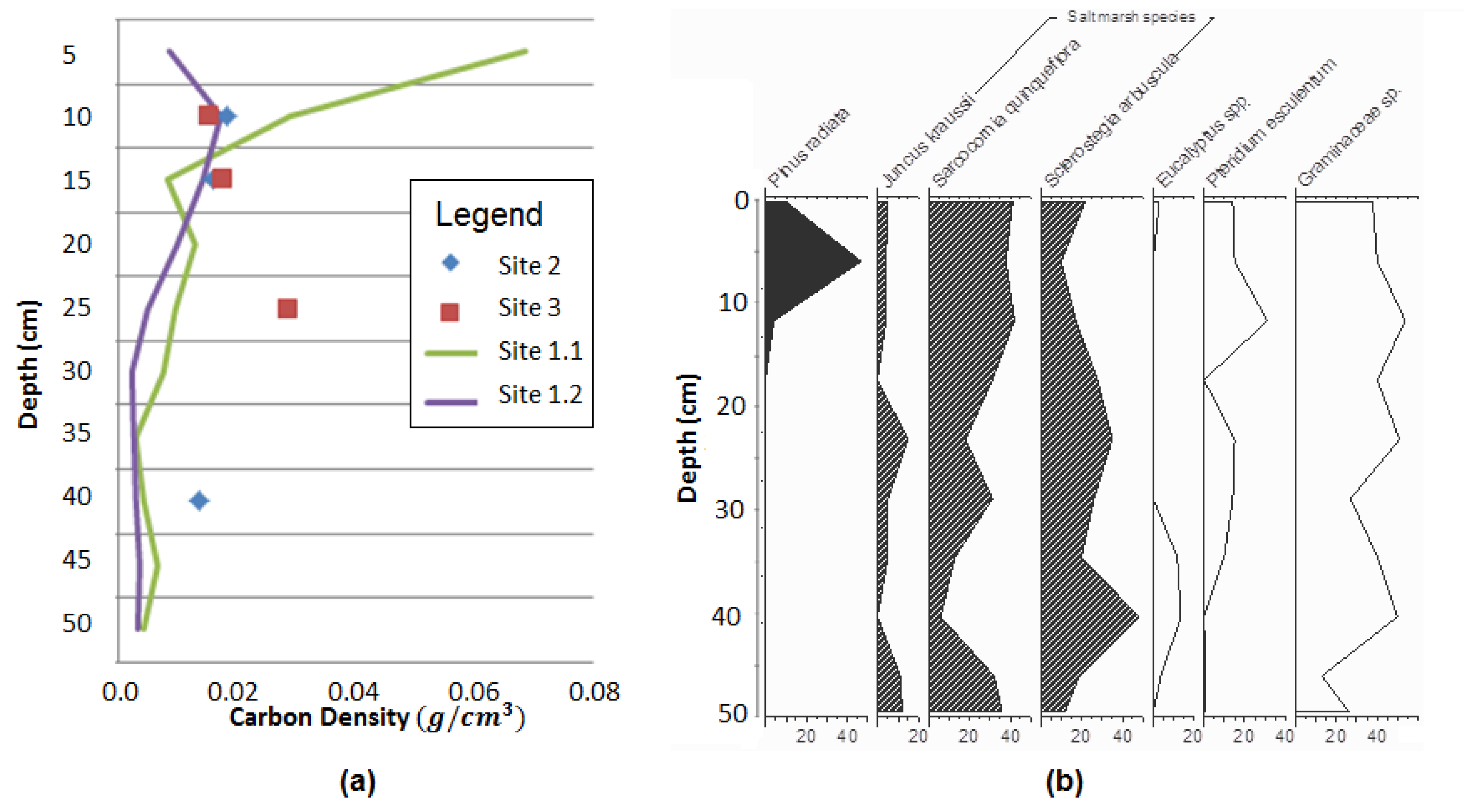
2.3. Vertical Accretion
3. Results
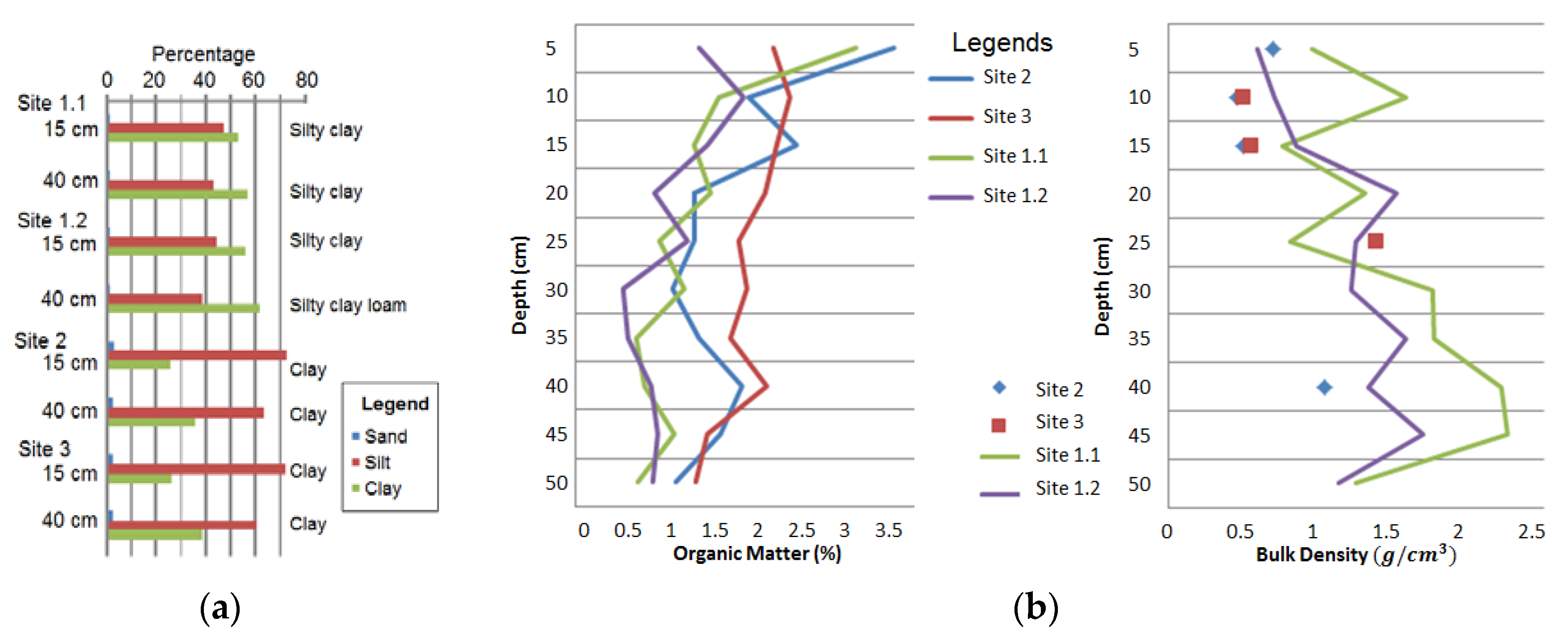
3.1. Grain Size and Organic Matter
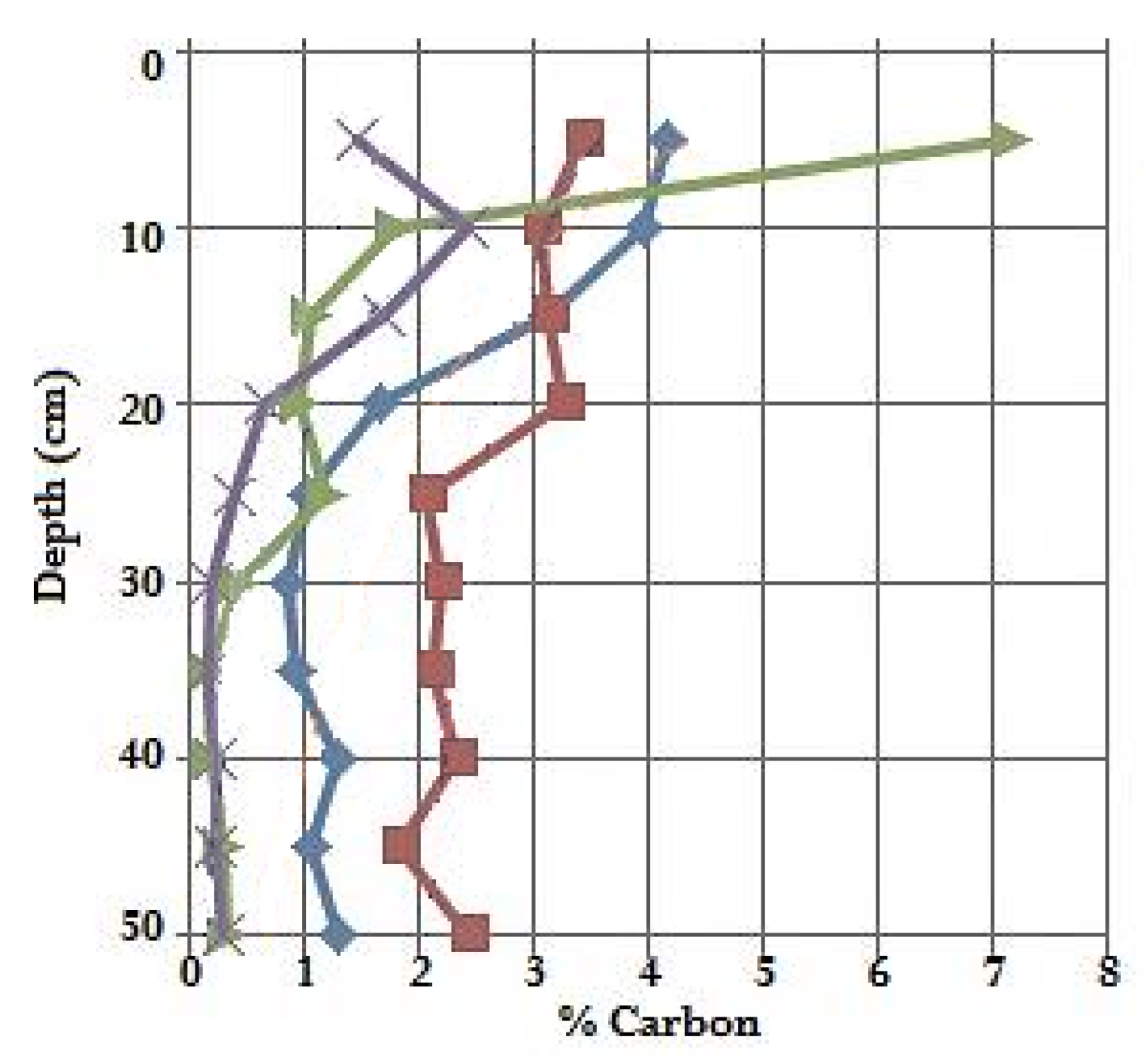
3.2. Sediment Carbon Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boorman, L.A. Salt marshes-present functioning and future change. Mangroves Saltmarshes 1999, 3, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmura, G.L. What do we need to assess the sustainability of the tidal salt marsh carbon sink? Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Losada, I.J.; Hendriks, I.E.; Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Wassmann, R.; Vlek, P. An appraisal of global wetland area and its organic carbon stock. Curr. Sci. 2005, 8, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleway, J.J.; Saintilan, N.; Macreadie, P.I.; Ralph, P.J. Sedimentary factors are key predictors of carbon storage in SE Australian saltmarshes. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Bernal, B.; Nahlik, A.M.; Mander, Ü.; Zhang, L.; Anderson, C.J.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Brix, H. Wetlands, carbon, and climate change. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmura, G.L.; Anisfeld, S.C.; Cahoon, D.R.; Lynch, J.C.; Laffoley, D.; Baxter, J. Global carbon sequestration in tidal, saline wetland soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, S.; Borges, A.V.; Castaneda-Moya, E.; Diele, K.; Dittmar, T.; Duke, N.C.; Kristensen, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Marchand, C.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Mangrove production and carbon sinks: A revision of global budget estimates. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Kauffman, J.B.; Murdiyarso, D.; Kurnianto, S.; Stidham, M.; Kanninen, M. Mangroves among the most carbon-rich forests in the tropics. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, C. Freshwater input structures soil properties, vertical accretion, and nutrient accumulation of Georgia and U.S. tidal marshes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, M.R.; Ellison, J.C. Intertidal morphology change following Spartina anglica introduction, Tamar Estuary, Tasmania. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 149, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, A.J.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Saco, P.M. Surface evolution and carbon sequestration in disturbed and undisturbed wetland soils of the Hunter estuary, southeast Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsey-Quirk, T.; Seliskar, D.M.; Sommerfield, C.K.; Gallagher, J.L. Salt marsh carbon pool distribution in a Mid-Atlantic lagoon, USA: Sea level rise implications. Wetlands 2011, 31, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, S.C.; Sax, D.F.; Palmer, M.E.; Booth, H.S.; Deegan, L.A.; Bertness, M.D.; Leslie, H.M. Salt marsh persistence is threatened by predicted sea-level rise. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, R.F.; Chmura, G.L.; Beecher, C.B. Carbon accumulation in Bay of Fundy saltmarshes: Implications for restoration of reclaimed marshes. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidgeon, E. Carbon sequestration by coastal marine habitats: Important missing sinks. In The Management of Natural Coastal Carbon Sinks; Laffoley, D., Grimsditch, G., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 47–51. ISBN 978-2-8317-1205-5. [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Ollivier, Q.R.; Kelleway, J.J.; Serrano, O.; Carnell, P.E.; Lewis, C.E.; Atwood, T.B.; Sanderman, J.; Baldock, J.; Connolly, R.M.; et al. Carbon sequestration by Australian tidal marshes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleway, J.J.; Saintilan, N.; Macreadie, P.I.; Baldock, J.A.; Ralph, P.J. Sediment and carbon deposition vary among vegetation assemblages in a coastal salt marsh. Biogeoscience 2017, 14, 3763–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Conrad, S.; Akkerman, K.; Fairfax, S.; Fredericks, J.; Hanrio, E.; Sanders, L.M.; Scott, E.; Skillington, A.; Tucker, J.; et al. Seagrass, mangrove and saltmarsh sedimentary carbon stocks in an urban estuary; Coffs Harbour, Australia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.A.; Jesse, A.; Hawke, B.; Baldock, J.; Tabet, B.; Lockington, D.; Lovelock, C.E. Dynamics of sediment carbon stocks across intertidal wetland habitats of Moreton Bay, Australia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4222–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.J.E.; Carnell, P.E.; Sanderman, J.; Baldock, J.A.; Macreadie, P.I. Variability and vulnerability of coastal ‘Blue Carbon’ stocks: A case study from Southeast Australia. Ecosystems 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zann, L.P. Our Sea, Our Future: Major Findings of the State of the Marine Environment Report for Australia; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, Australia, 1995; ISBN 9780642173911. [Google Scholar]
- Short, A.D. Beaches of the Tasmanian Coast and Islands; Sydney University Press: Sydney, Australia, 2006; ISBN 1-920898-12-3. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, G.J.; Barrett, N.S.; Graddon, D.J. A Classification of Tasmanian Estuaries and Assessment of Their Conservation Significance Using Ecological and Physical Attributes, Population and Land Use; Marine Research Laboratories, University of Tasmania: Hobart, Australia, 1999; ISBN 07246 4754 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Meteorology. Available online: www.bom.gov.au/climate/averages/tables/cw_091126.shtml (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Cotching, W.E. A review of the challenges for long term management of krasnozems in Australia. Aust. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1995, 8, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, C.; Cotching, W. Turbidity and sediment loads from selected catchments in north-west Tasmania. Nat. Res. Manag. J. 2000, 3, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, P. Australian saltmarshes in global context. In Australian Saltmarsh Ecology; Saintalin, N., Ed.; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 1999; pp. 1–22. ISBN 9780643093713. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, M.E.; MacFarlane, G.R. Effects of salinity and temperature on the germination of Phragmites australis, Juncus kraussii, and Juncus acutus: Implications for estuarine restoration initiatives. Wetlands 2006, 26, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, M.R.; Ellison, J.C. Tidal marsh erosion and accretion trends following invasive species removal, Tamar Estuary, Tasmania. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.E. Engineering Properties of Soils and Their Measurement, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, C.B.; Seneca, E.D.; Broome, S.W. Loss on ignition and Kjeldahl Digestion for estimating organic carbon and total Nitrogen in estuarine marsh Soils: Calibration with dry combustion. Estuaries 1991, 14, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments; Office of Research and Development, US. Environmental Protection Agency: Las Vegas, CA, USA, 2002.
- Bengtsson, L.; Enell, M. Chemical analysis. In Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology; Berglund, E.B., Ed.; The Blackburn Press: Caldwell, NJ, USA, 1986; Volume 13, pp. 423–455. ISBN 978-1930665804. [Google Scholar]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, V. Atlas of Coastal Saltmarsh Wetlands in the Cradle Coast Region of Tasmania; Cradle Coast NRM: Burnie, Tasmania, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prahalad, V. Coastal Saltmarsh Wetland Asset Mapping: Technical Report; Cradle Coast NRM: Burnie, Tasmania, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chmura, G.L.; Coffey, A.; Crago, R. Variation in surface sediment deposition on salt marshes in the Bay of Fundy. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, J.C. Pollen evidence of Late Holocene mangrove development in Bermuda. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. Lett. 1996, 196, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.P.; Cornejo, B. Is the first flowering event and corresponding maturity phase in trees related to radial wood density changes? Trees 2016, 30, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, J.C. Long-term retrospection on mangrove development using sediment cores and pollen analysis. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice Grass Advisory Group. Strategy for the Management of Rice Grass (Spartina anglica) in Tasmania, Australia; Department of Primary Industries, Water and Environment: Hobart, Australia, 2002.
- Jiménez, J.J.; Lal, R.; Rosso, R.O.; Leblanc, H.A. The soil organic carbon in particle-size separates under different regrowth forest stands of northeastern Costa Rica. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, L.A.; Belbin, K.; Doyle, R.B. Organic carbon in the silt + clay fraction of Tasmanian soils. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 22, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, M.J.; Craft, C.B. Carbon sequestration and nutrient (nitrogen, phosphorus) accumulation in river-dominated tidal marshes, Georgia, USA. Wetland Soils 2010, 74, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.J.; Jacoby, C.A. Biomass and above-ground productivity of saltmarsh plants in South-eastern Australia. Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1994, 45, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, W.H.; DeLaune, R.D. Subsidence, accretion, and sea level rise in south San Francisco Bay marshes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 36, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.J.; Dargie, G.; Dooling, G.P.; Gee, C.; Holden, J.; Kelly, T.; McKendrick-Smith, K.A.; Morris, P.J.; Noble, A.; Palmer, S.M.; et al. Questioning ten common assumptions about peatlands. Mires Peat 2017, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, J.C. Biogeomorphology of mangroves. In Coastal Wetlands: An Ecosystem Integrated Approach; Wolanski, E., Cahoon, D., Perillo, G.M.E., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, P.I.; Allen, T.; Rosengren, N.; Sinclair, S.; White, M.; Yugovic, J. Coastal wetlands of Victoria, south-eastern Australia: Providing the inventory and condition information needed for their effective management and conservation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2014, 25, 454–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laegdsgaard, P. Ecology, disturbance and restoration of coastal saltmarsh in Australia: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 14, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property | Site 1.1 | Site 1.2 | Site 2 | Site 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation type | J. kraussii | S. quinqueflora | Spartina | Spartina |
| Organic matter (%) | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.13 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.47 ± 0.17 | 1.19 ± 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.08 | 0.8 ± 0.16 |
| Sediment carbon (%) | 1.37 ± 0.63 | 0.78 ± 0.24 | 1.95 ± 0.39 | 2.6 ± 0.17 |
| Carbon density (g/cm3) | 0.023 ± 0.006 | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.020 ± 0.002 |
| Vertical accretion (mm/year) | 0.42 | 18 | 20 | 30 |
| Carbon accretion (g/cm2/year) | 0.015 | 0.022 | 0.034 | 0.055 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellison, J.C.; Beasy, K.M. Sediment Carbon Accumulation in Southern Latitude Saltmarsh Communities of Tasmania, Australia. Biology 2018, 7, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology7020027
Ellison JC, Beasy KM. Sediment Carbon Accumulation in Southern Latitude Saltmarsh Communities of Tasmania, Australia. Biology. 2018; 7(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology7020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllison, Joanna C., and Kim M. Beasy. 2018. "Sediment Carbon Accumulation in Southern Latitude Saltmarsh Communities of Tasmania, Australia" Biology 7, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology7020027
APA StyleEllison, J. C., & Beasy, K. M. (2018). Sediment Carbon Accumulation in Southern Latitude Saltmarsh Communities of Tasmania, Australia. Biology, 7(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology7020027





