Coenzyme-A-Independent Transacylation System; Possible Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in Transacylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Diversity of Fatty Acids in Glycerophospholipids
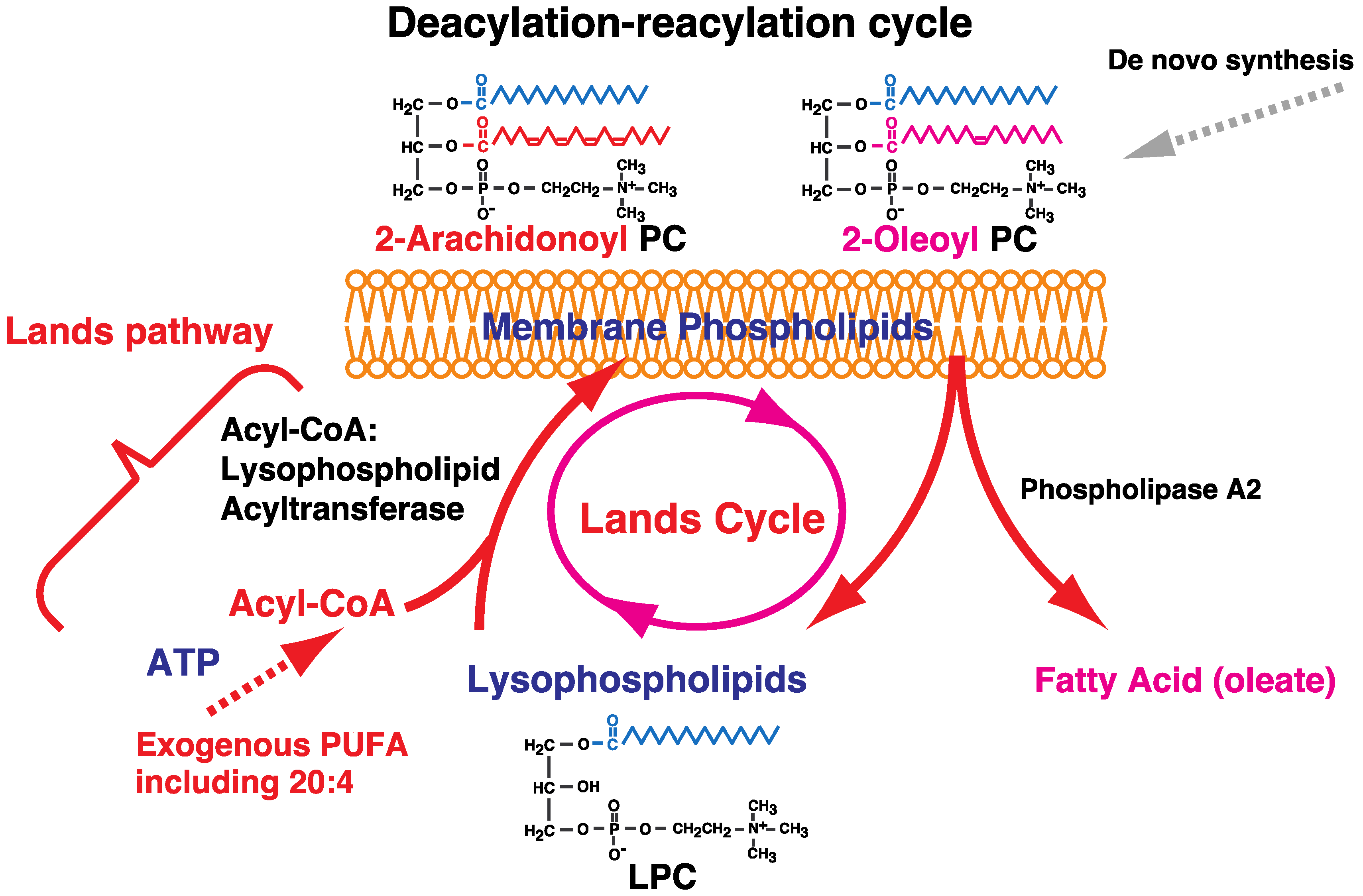
2. Fatty Acid Remodeling System of Glycerophospholipids
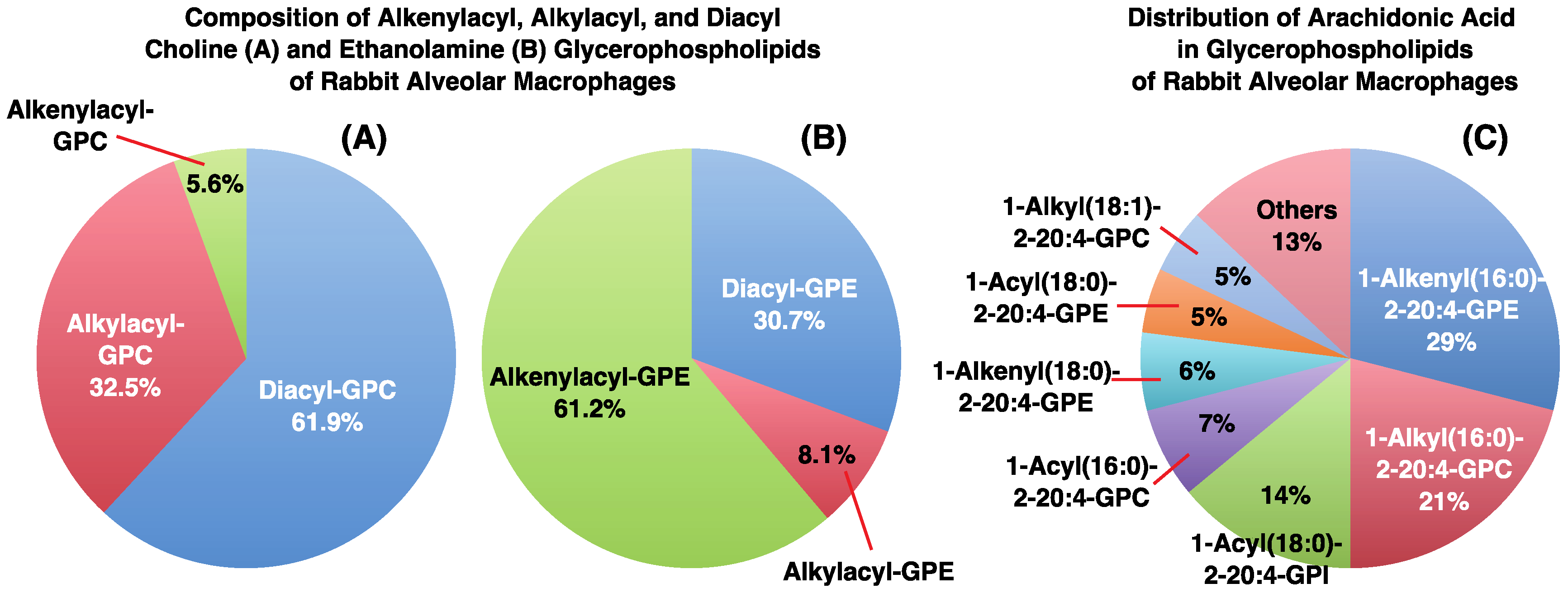
3. Alkyl- or Alkenyl-Type Glycerophospholipids Contain Large Amounts of PUFAs, Such as Arachidonic Acid
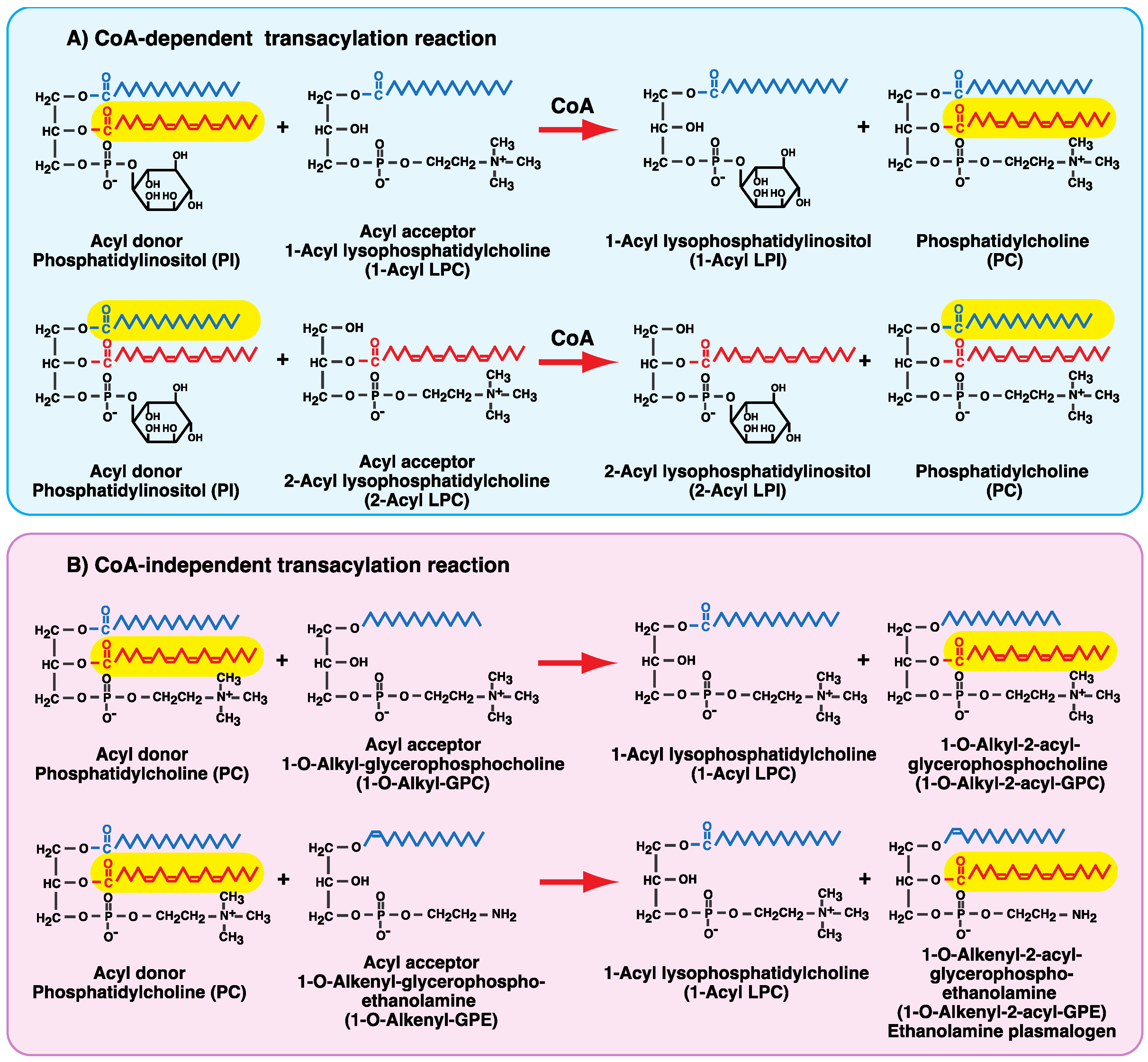
4. CoA-Independent Transacylation Activity between Diacyl Phospholipids and Ether-Linked Lysophospholipids
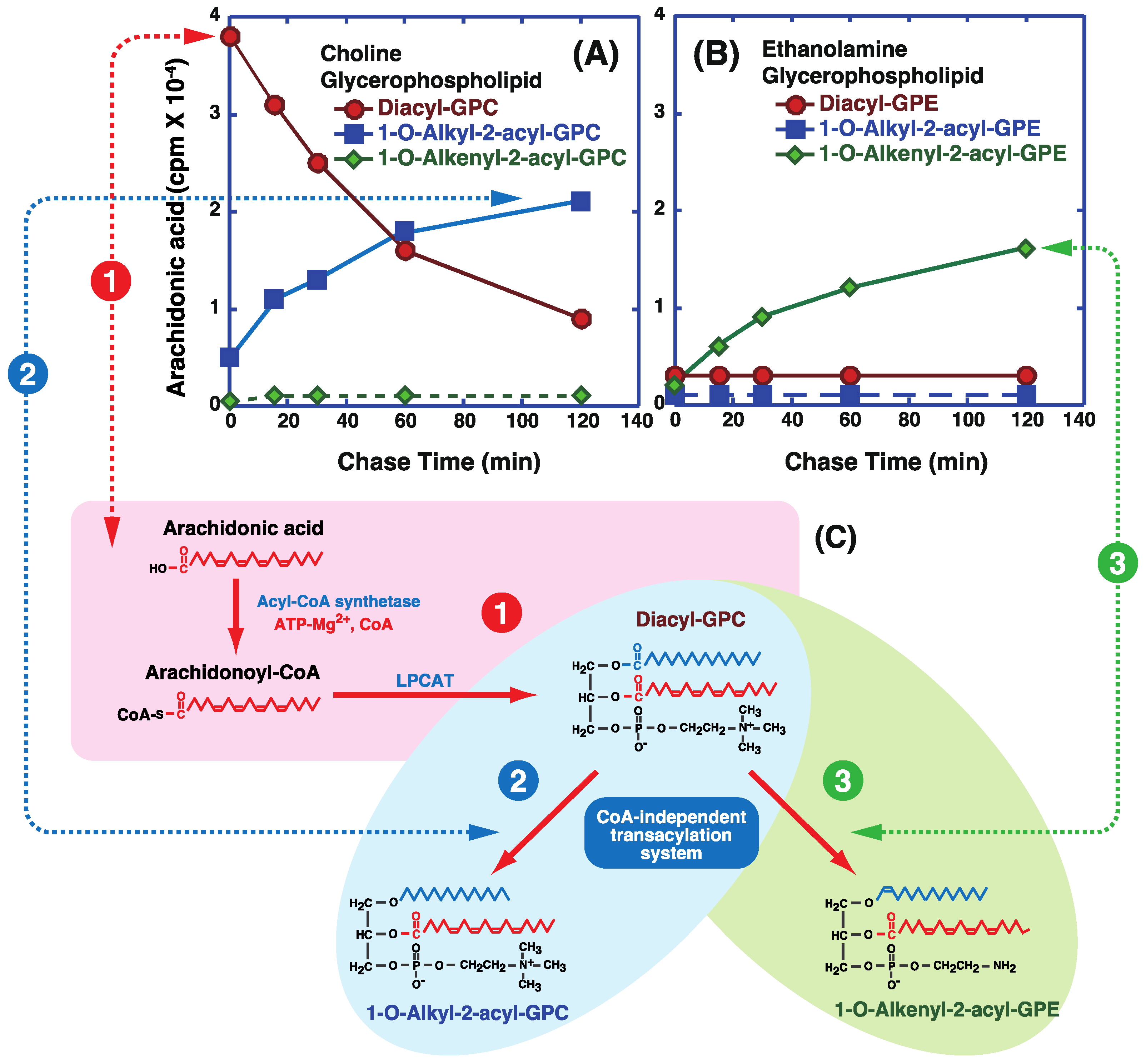
5. Incorporation and Mobilization of Arachidonic Acid in Lipid Subclasses via Acyl-CoA Acyltransferases and CoA-Independent Transacylation
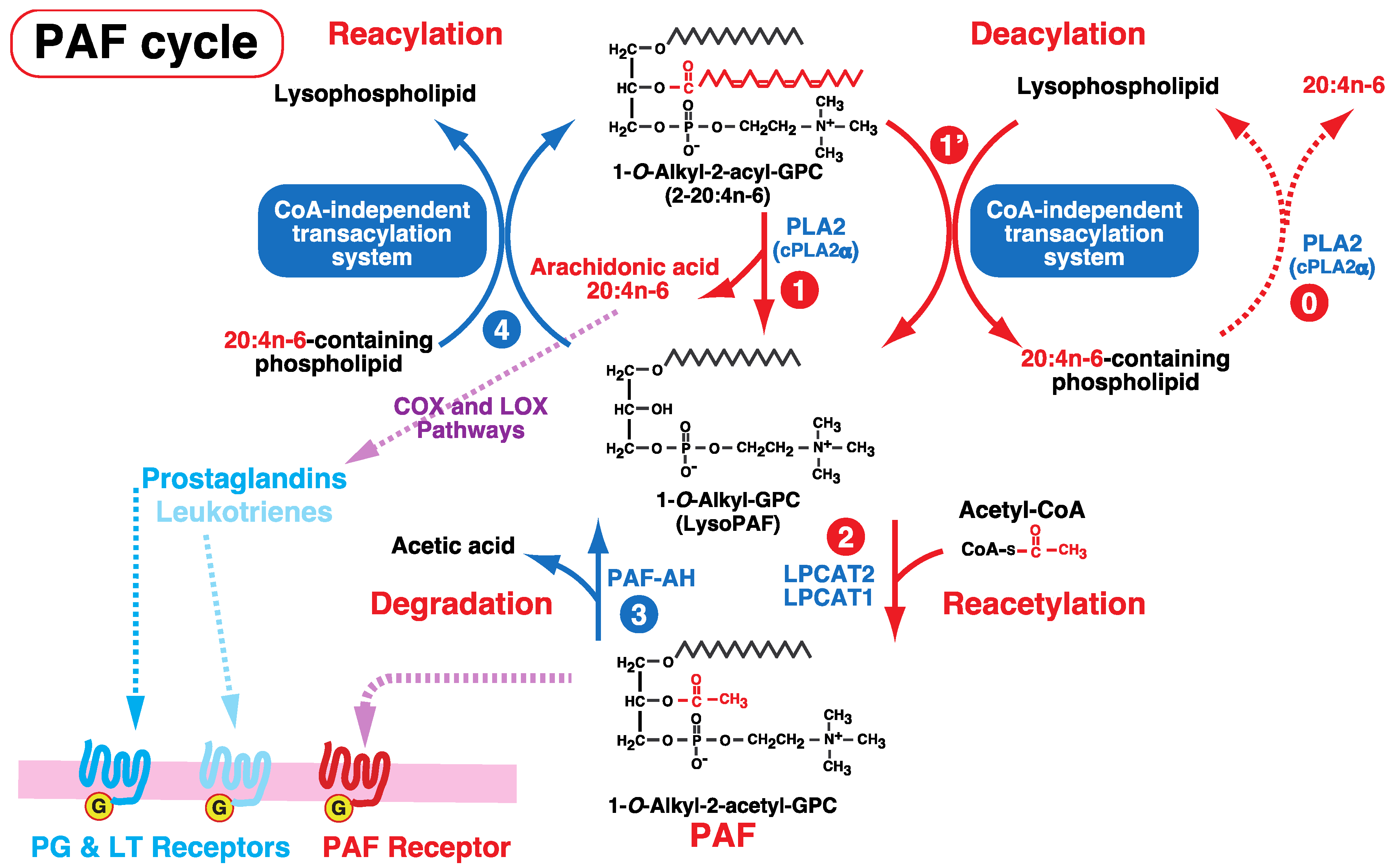
6. Involvement of the CoA-Independent Transacylation System in PAF Metabolism
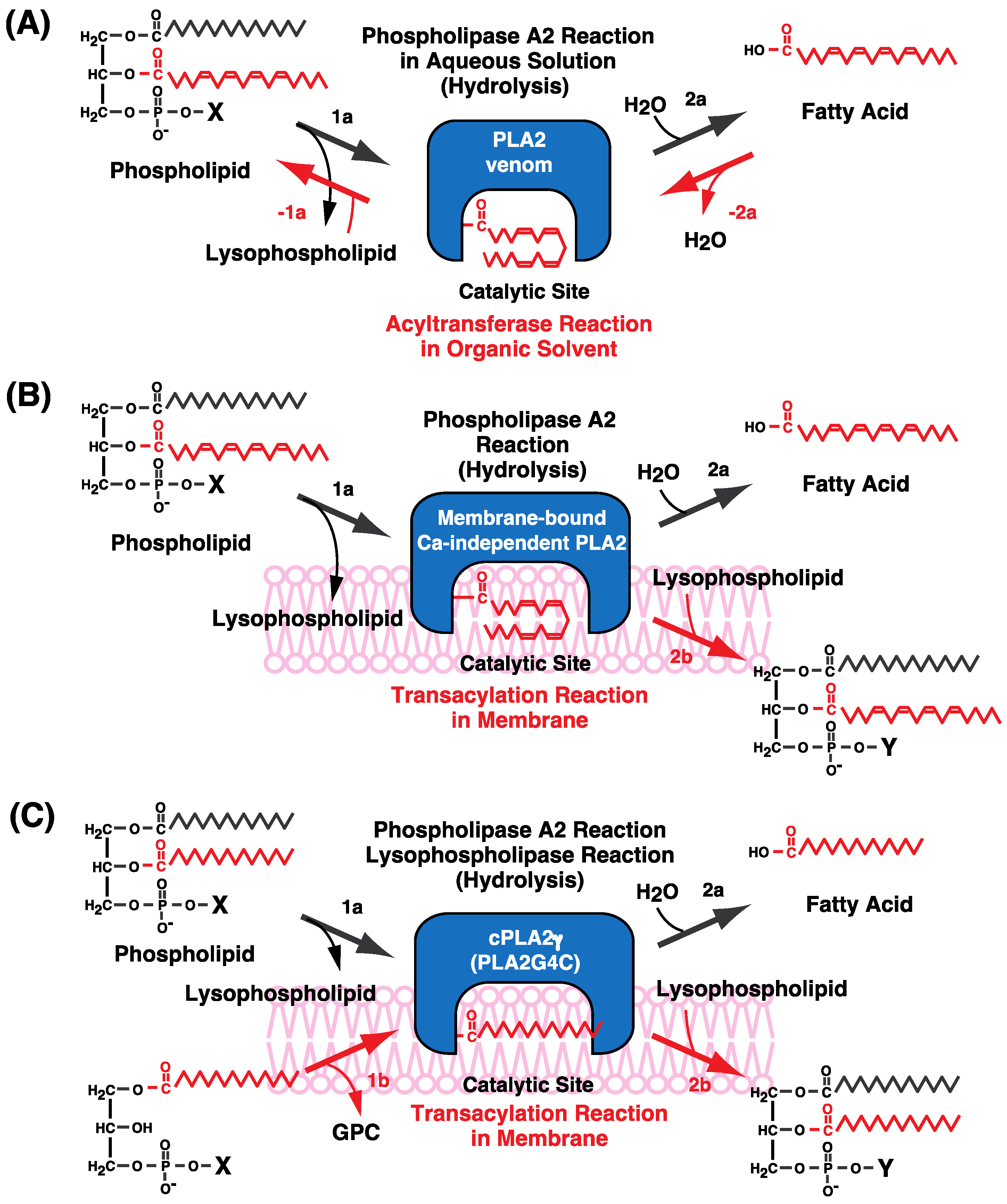
7. Possible Molecular Mechanisms of CoA-Independent Transacylation Reactions
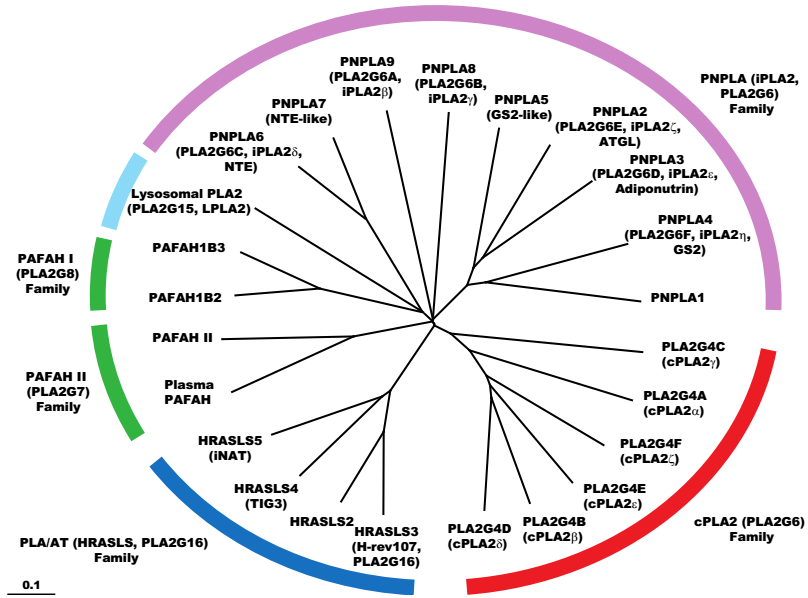
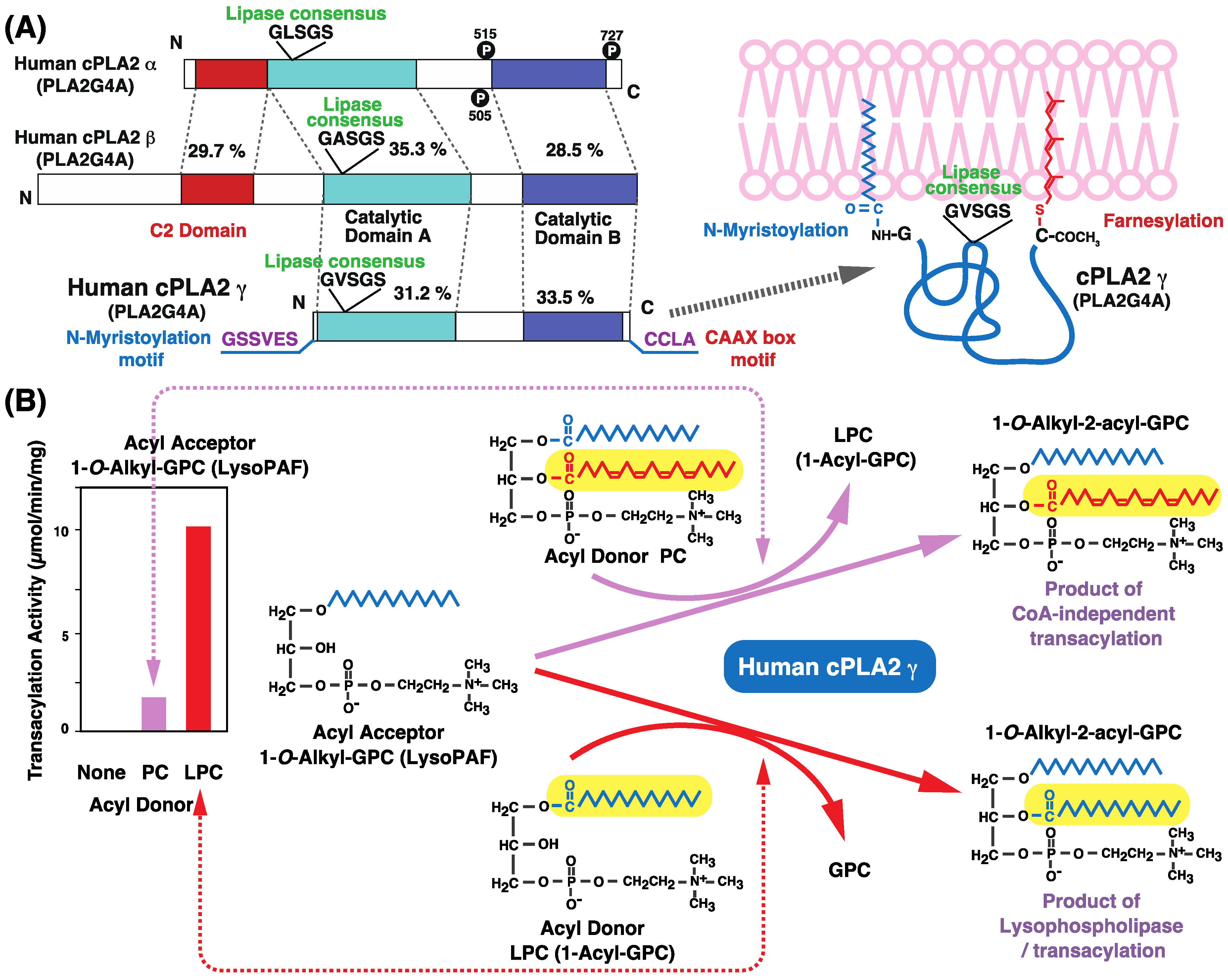
8. Intracellular PLA2
9. cPLA2γ Catalyzes CoA-Independent Transacylation Reactions that Transfer Arachidonic Acid to Ether-Linked Lysophospholipids
10. cPLA2γ Exhibits High Lysophospholipase/Transacylation Activity
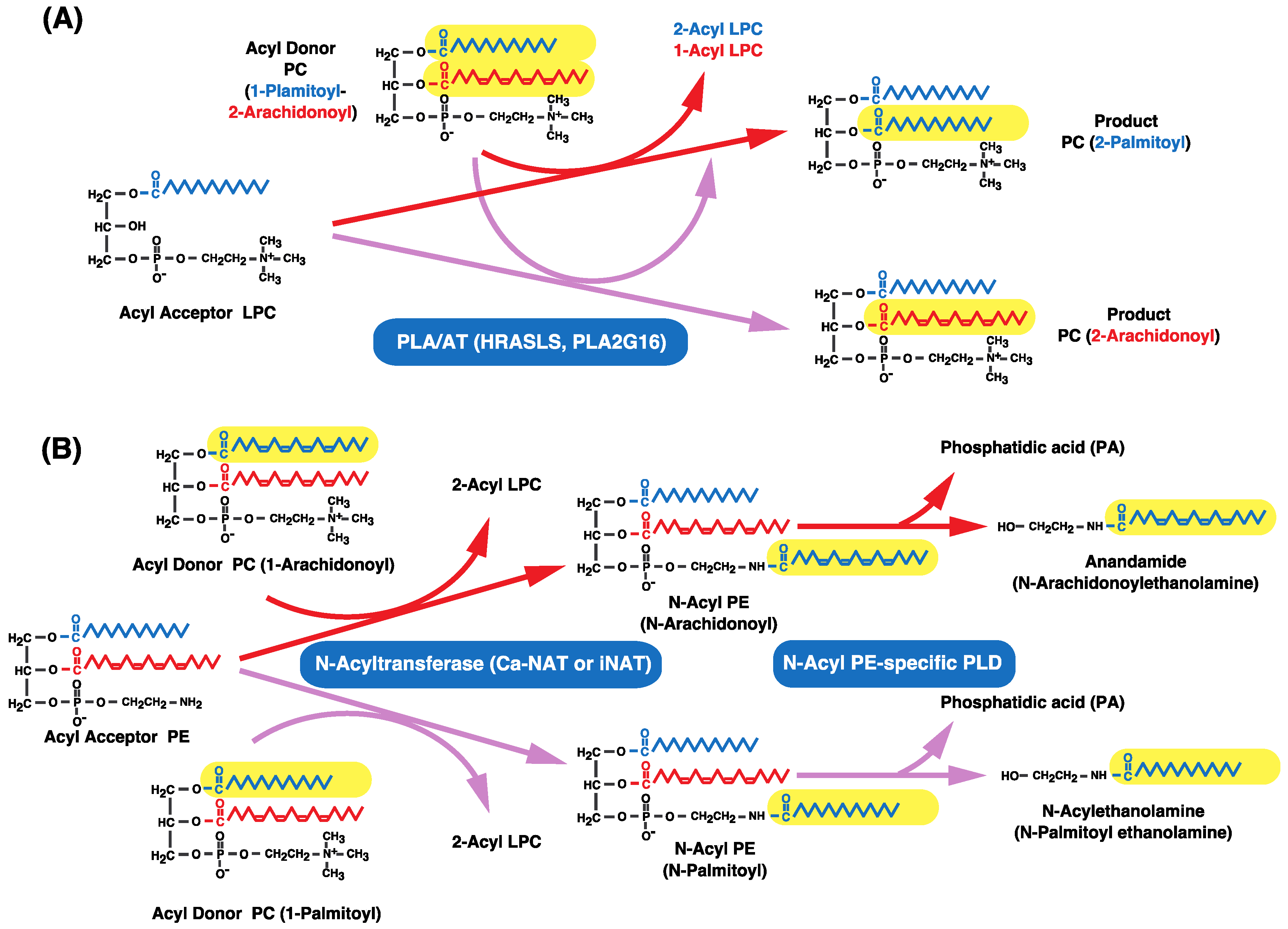
11. Other Enzymes that Catalyze Transacylation Reactions
12. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dowhan, W. Molecular basis for membrane phospholipid diversity: Why are there so many lipids? Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 199–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holub, B.J.; Kuksis, A. Metabolism of molecular species of diacylglycerophospholipids. Adv. Lipid Res. 1978, 16, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Composition of alkyl ether-linked phospholipids in mammalian tissues. In Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators; Snyder, F., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 55–85. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T. Lipid mediators in health and disease: Enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumura, A. A family of phospholipid autacoids: Occurrence, metabolism and bioactions. Prog. Lipid Res. 1995, 34, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Waku, K. The metabolism of glycerophospholipid and its regulation in monocytes and macrophages. Prog. Lipid Res. 1989, 28, 205–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Acyltransferases and transacylases involved in fatty acid remodeling of phospholipids and metabolism of bioactive lipids in mammalian cells. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1997, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Ito, M.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. Acyltransferases and transacylases that determine the fatty acid composition of glycerolipids and the metabolism of bioactive lipid mediators in mammalian cells and model organisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 18–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, J.S.; Sprecher, H. Phospholipid fatty acid remodeling in mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1084, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, F.; Lee, T.C.; Blank, M.L. The role of transacylases in the metabolism of arachidonate and platelet activating factor. Prog. Lipid Res. 1992, 31, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Coenzyme A-independent acyltransferase. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 209, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Shimizu, T. Acyl-CoA:lysophospholipid acyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Hishikawa, D.; Harayama, T.; Yuki, K.; Shimizu, T. Recent progress on acyl CoA:lysophospholipid acyltransferase research. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S46–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lands, W.E. Metabolism of glycerolipids: A comparison of lecithin and triglyceride synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 231, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lands, W.E. Metabolism of glycerolipids. II. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irvine, R.F.; Dawson, R.M. Transfer of arachidonic acid between phospholipids in rat liver microsomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 91, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Masuzawa, Y.; Waku, K. Coenzyme A-dependent transacylation system in rabbit liver microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 17490–17498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Masuzawa, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Waku, K. Transacylation of lyso platelet-activating factor and other lysophospholipids by macrophage microsomes. Distinct donor and acceptor selectivities. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; Blank, M.L.; Snyder, F. Acylation of lysophospholipids by rabbit alveolar macrophages. Specificities of CoA-dependent and CoA-independent reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 7889–7895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flesch, I.; Ecker, B.; Ferber, E. Acyltransferase-catalyzed cleavage of arachidonic acid from phospholipids and transfer to lysophosphatides in macrophages derived from bone marrow. Comparison of different donor- and acceptor substrate combinations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 139, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, R.M.; Pritzker, C.R.; Deykin, D. Coenzyme A-mediated arachidonic acid transacylation in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 2403–2406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colard, O.; Breton, M.; Bereziat, G. Induction by lysophospholipids of CoA-dependent arachidonyl transfer between phospholipids in rat platelet homogenates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 793, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Sato, K.; Watanabe, M.; Tokudome, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Induction of coenzyme A-dependent transacylation activity in rat liver microsomes by administration of clofibrate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1211, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kudo, N.; Ojima, T.; Mabuchi-Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. Coenzyme A-dependent cleavage of membrane phospholipids in several rat tissues: ATP-independent acyl-CoA synthesis and the generation of lysophospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1255, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kudo, N.; Ojima, T.; Kondo, S.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. Coenzyme A-dependent modification of fatty acyl chains of rat liver membrane phospholipids: Possible involvement of ATP-independent acyl-CoA synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Kawagishi, N.; Miyashita, T.; Nagatsuka, T.; Sugiura, T.; Kume, K.; Shimizu, T.; Waku, K. ATP-independent fatty acyl-coenzyme A synthesis from phospholipid Coenzyme A-dependent transacylation activity toward lysophosphatidic acid catalyzed by acyl-coenzyme A: Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26745–26752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, K.; Miyashita, T.; Nagatsuka, T.; Kondo, H.; Kawagishi, N.; Nakanishi, H.; Kamata, R.; Sugiura, T.; et al. Reverse reaction of lysophosphatidylinositol acyltransferase functional reconstitution of coenzyme A-dependent transacylation system. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30382–30393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. The molecular species composition of diacyl-, alkylacyl- and alkenylacylglycerophospholipids in rabbit alveolar macrophages. High amounts of 1-O-hexadecyl-2-arachidonyl molecular species in alkylacylglycerophosphocholine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 833, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ojima-Uchiyama, A.; Masuzawa, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K.; Saito, H.; Yui, Y.; Tomioka, H. Phospholipid analysis of human eosinophils: High levels of alkylacylglycerophosphocholine (PAF precursor). Lipids 1988, 23, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Nakajima, M.; Sekiguchi, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Waku, K. Different fatty chain compositions of alkkenylacyl, alkylacyl and diacyl phospholipids in rabbit alveolar macrophages. High amounts of arachidonic acid in ether phospholipids. Lipids 1983, 18, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, K. Is the high propensity of ethanolamine plasmalogens to form non-lamellar lipid structures manifested in the properties of biomembranes? Chem. Phys. Lipids 1996, 81, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.O.; Kuchenbecker, J.; Rothhaar, T.L.; Grösgen, S.; Hundsdörfer, B.; Burg, V.K.; Friess, P.; Müller, U.; Grimm, H.S.; Riemenschneider, M.; et al. Plasmalogen synthesis is regulated via alkyl-dihydroxyacetonephosphate-synthase by amyloid precursor protein processing and is affected in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Singh, J.; Singh, I. Plasmalogen deficiency in cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy and its modulation by lovastatin. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1766–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgas, K.; Teigler, A.; Komljenovic, D.; Just, W.W. The ether lipid-deficient mouse: Tracking down plasmalogen functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, R.M.; Deykin, D. Arachidonoyl transacylase in human platelets. Coenzyme A-independent transfer of arachidonate from phosphatidylcholine to lysoplasmenylethanolamine. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 13806–13811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, R.M.; Patton, G.M.; Pritzker, C.R.; Deykin, D. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor in human platelets. Transacylase-mediated synthesis of 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 13316–13320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. CoA-independent transfer of arachidonic acid from 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine to 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso platelet-activating factor) by macrophage microsomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 127, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Masuzawa, Y.; Waku, K. Transacylation of 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso platelet-activating factor) and 1-O-alkenyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine with docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 ω3). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 133, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, F.H.; Murphy, R.C. Remodeling of arachidonate-containing phosphoglycerides within the human neutrophil. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 7771–7777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chilton, F.H.; Hadley, J.S.; Murphy, R.C. Incorporation of arachidonic acid into 1-acyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine of the human neutrophil. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 917, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colard, O.; Breton, M.; Bereziat, G. Arachidonyl transfer from diacyl phosphatidylcholine to ether phospholipids in rat platelets. Biochem. J. 1984, 222, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojima, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Masuzawa, Y.; Waku, K. Selective transacylation of 1-O-alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine by docosahexaenoate and arachidonate in rat brain microsomes. J. Neurochem. 1987, 48, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzawa, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Sprecher, H.; Waku, K. Selective acyl transfer in the reacylation of brain glycerophospholipids. Comparison of three acylation systems for 1-alk-1′-enylglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, 1-acylglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine and 1-acylglycero-3-phosphocholine in rat brain microsomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1005, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.V.; Schmid, H.H. Selectivity of acyl transfer between phospholipids: Arachidonoyl transacylase in dog heart membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 129, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.L.; Wykle, R.L.; Snyder, F. The retention of arachidonic acid in ethanolamine plasmalogens of rat testes during essential fatty acid deficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 316, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, Y.; Okano, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ojima, A.; Waku, K. Selective acylation of alkyllysophospholipids by docosahexaenoic acid in Ehrlich ascites cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 876, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waku, K.; Lands, W.E. Acyl coenzyme A: 1-alkenyl-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine acyltransferase action in plasmalogen biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waku, K.; Nakazawa, Y. Acyltransferase activity to 1-O-alkyl-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biochem. 1970, 68, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waku, K.; Nakazawa, Y. Regulation of the fatty acid composition of alkyl ether phospholipid in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. The substrate specificities of 1-O-alkylglycerol 3-phosphate and 1-O-alkylglycero-3-phosphorylcholine acyltransferases. J. Biochem. 1977, 82, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, M.; Colard, O. Protein kinase C promotes arachidonate mobilization through enhancement of CoA-independent transacylase activity in platelets. Biochem. J. 1991, 280, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.D.; Sung, C.M.; Huang, L.; Chilton, F.H. CoA-independent transacylase activity is increased in human neutrophils after treatment with tumor necrosis factor-α. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1215, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.D.; Fonteh, A.N.; Sung, C.M.; Heravi, J.D.; Nixon, A.B.; Chabot-Fletcher, M.; Griswold, D.; Marshall, L.A.; Chilton, F.H. Effects of CoA-independent transacylase inhibitors on the production of lipid inflammatory mediators. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 274, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.D.; Eris, T.; Sung, C.M.; Chabot-Fletcher, M.; Mayer, R.J.; Surette, M.E.; Chilton, F.H. Inhibitors of coenzyme A-independent transacylase induce apoptosis in human HL-60 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 279, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Katayama, O.; Fukui, J.; Nakagawa, Y.; Waku, K. Mobilization of arachidonic acid between diacyl and ether phospholipids in rabbit alveolar macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1984, 165, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Kurihara, K.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Heterogeneity in the metabolism of the arachidonoyl molecular species of glycerophospholipids of rabbit alveolar macrophages. The interrelationship between metabolic activities and chemical structures of the arachidonoyl molecular species. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 153, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colard, O.; Breton, M.; Bereziat, G. Arachidonate mobilization in diacyl, alkylacyl and alkenylacyl phospholipids on stimulation of rat platelets by thrombin and the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. Biochem. J. 1986, 233, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Blank, M.L.; Snyder, F. An arachidonoyl (polyenoic)-specific phospholipase A2 activity regulates the synthesis of platelet-activating factor in granulocytic HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12363–12371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takayama, H.; Kroll, M.H.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Schafer, A.I. Turnover of eicosanoid precursor fatty acids among phospholipid classes and subclasses of cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 1989, 258, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wey, H.E.; Jakubowski, J.A.; Deykin, D. Incorporation and redistribution of arachidonic acid in diacyl and ether phospholipids of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 878, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, J.; Henson, P.M.; Cochrane, C.G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets: The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 136, 1356–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demopoulos, C.A.; Pinckard, R.N.; Hanahan, D.J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9355–9358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, J.; Tencé, M.; Varenne, P.; Bidault, J.; Boullet, C.; Polonsky, J. Semi-synthesis and proposed structure of platelet-activating factor (P.A.F.): PAF-acether an alkyl ether analog of lysophosphatidylcholine. C. R. Seances Acad. Sci. D 1979, 289, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.L.; Snyder, F.; Byers, L.W.; Brooks, B.; Muirhead, E.E. Antihypertensive activity of an alkyl ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 90, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Z.; Nakamura, M.; Miki, I.; Minami, M.; Watanabe, T.; Seyama, Y.; Okado, H.; Toh, H.; Ito, K.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from guinea pig lung. Nature 1991, 349, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Kudo, I.; Kim, D.K.; Nagata, K.; Nozawa, Y.; Inoue, K. Purification and characterization of human platelet phospholipase A2 which preferentially hydrolyzes an arachidonoyl residue. FEBS Lett. 1991, 282, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, R.M.; Roberts, E.F.; Manetta, J.; Putnam, J.E. The Ca2+-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a 100-kDa protein in human monoblast U937 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5268–5272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.D.; Lin, L.L.; Kriz, R.W.; Ramesha, C.S.; Sultzman, L.A.; Lin, A.Y.; Milona, N.; Knopf, J.L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca2+-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell 1991, 65, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wykle, R.L.; Malone, B.; Snyder, F. Enzymatic synthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, a hypotensive and platelet-aggregating lipid. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 10256–10260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Hishikawa, D.; Nakanishi, H.; Harayama, T.; Ishii, S.; Taguchi, R.; Shimizu, T. A single enzyme catalyzes both platelet-activating factor production and membrane biogenesis of inflammatory cells cloning and characterization of acetyl-CoA: Lyso-PAF acetyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6532–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harayama, T.; Shindou, H.; Ogasawara, R.; Suwabe, A.; Shimizu, T. Identification of a novel noninflammatory biosynthetic pathway of platelet-activating factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11097–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Fukuda, T.; Masuzawa, Y.; Waku, K. Ether lysophospholipid-induced production of platelet-activating factor in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1047, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, Y.; Lee, T.C.; Snyder, F. A coenzyme A-independent transacylase is linked to the formation of platelet-activating factor (PAF) by generating the lyso-PAF intermediate in the remodeling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 8268–8272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.L.; Venable, M.E.; Bauldry, S.A.; Greene, D.G.; Kennedy, M.; Bass, D.A.; Wykle, R.L. Evidence that hydrolysis of ethanolamine plasmalogens triggers synthesis of platelet-activating factor via a transacylation reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 18699–18706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, K.; Inoue, K. Overview of PAF-degrading enzymes. In Enzymes; Inoue, K., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 38, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Karasawa, K. Clinical aspects of plasma platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, K.; Harada, A.; Satoh, N.; Inoue, K.; Setaka, M. Plasma platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH). Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, M.; Masuzawa, Y.; Yazawa, K. Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on the generation of platelet-activating factor by eosinophilic leukemia cells, Eol-1. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 3525–3533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pernas, P.; Olivier, J.L.; Legoy, M.D.; Bereziat, G. Phospholipid synthesis by extracellular phospholipase A2 in organic solvents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 168, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.D.; McCarte-Roshak, A.; Huang, L.; Sung, C.M.; Bolognese, B.; Marshall, L.A. Biochemical and pharmacological comparison of a cytosolic, high molecular weight phospholipase A2, human synovial fluid phospholipase A2 and CoA-independent transacylase. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal. 1994, 10, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaloske, R.H.; Dennis, E.A. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, Y.; Ohto, T.; Uozumi, N.; Shimizu, T. Biochemical properties and pathophysiological roles of cytosolic phospholipase A2s. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Tucker, D.E.; Burchett, S.A.; Leslie, C.C. Properties of the group IV phospholipase A2 family. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Taketomi, Y.; Miki, Y.; Sato, H.; Hirabayashi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Recent progress in phospholipase A2 research: from cells to animals to humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 152–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uozumi, N.; Kume, K.; Nagase, T.; Nakatani, N.; Ishii, S.; Tashiro, F.; Komagata, Y.; Maki, K.; Ikuta, K.; Ouchi, Y.; et al. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in allergic response and parturition. Nature 1997, 390, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Underwood, K.W.; Song, C.; Kriz, R.W.; Chang, X.J.; Knopf, J.L.; Lin, L.L. A novel calcium-independent phospholipase A2, cPLA2-γ, that is prenylated and contains homology to cPLA2. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 21926–21932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, R.T.; Strifler, B.A.; Kramer, R.M.; Sharp, J.D. Molecular cloning of two new human paralogs of 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8823–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohto, T.; Uozumi, N.; Hirabayashi, T.; Shimizu, T. Identification of novel cytosolic phospholipase A2s, murine cPLA2δ, ϵ, and ζ, which form a gene cluster with cPLA2β. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24576–24583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Ghosh, M.; Spencer, D.M.; Leslie, C.C. Enzymatic properties of human cytosolic phospholipase A2γ. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29526–29536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.M.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Mancuso, D.J.; Sims, H.F.; Muslin, A.J.; Gross, R.W. Purification of recombinant human cPLA2γ and identification of C-terminal farnesylation, proteolytic processing, and carboxymethylation by MALDI-TOF-TOF analysis. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11798–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, K.; Hirabayashi, T.; Houjou, T.; Uozumi, N.; Taguchi, R.; Shimizu, T. Human group IVC phospholipase A2 (cPLA2γ). Roles in the membrane remodeling and activation induced by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8809–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Masuda, S.; Kudo, I. Arachidonate release and prostaglandin production by group IVC phospholipase A2 (cytosolic phospholipase A2γ). Biochem. J. 2003, 372, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Kamata, R.; Kawagishi, N.; Nakanishi, H.; Suzuki, H.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Roles of C-terminal processing, and involvement in transacylation reaction of human group IVC phospholipase A2 (cPLA2γ). J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Tanaka, K.; Kamata, R.; Kumazawa, T.; Suzuki, N.; Koga, H.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. Subcellular localization and lysophospholipase/transacylation activities of human group IVC phospholipase A2 (cPLA2γ). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsinde, J.; Bianco, I.D.; Ackermann, E.J.; Conde-Frieboes, K.; Dennis, E.A. Inhibition of calcium-independent phospholipase A2 prevents arachidonic acid incorporation and phospholipid remodeling in P388D1 macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8527–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsinde, J. Roles of various phospholipases A2 in providing lysophospholipid acceptors for fatty acid phospholipid incorporation and remodelling. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbes, H.; Drevet, S.; Pageaux, J.F.; Lagarde, M.; Laugier, C. Involvement of calcium-independent phospholipase A2 in uterine stromal cell phospholipid remodelling. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 7118–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Dennis, E.A. Antisense inhibition of group VI Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 blocks phospholipid fatty acid remodeling in murine P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29317–97321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.M.; Mancuso, D.J.; Yan, W.; Sims, H.F.; Gibson, B.; Gross, R.W. Identification, cloning, expression, and purification of three novel human calcium-independent phospholipase A2 family members possessing triacylglycerol lipase and acylglycerol transacylase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48968–48975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienesberger, P.C.; Oberer, M.; Lass, A.; Zechner, R. Mammalian patatin domain containing proteins: A family with diverse lipolytic activities involved in multiple biological functions. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S63–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazen, S.; Ford, D.; Gross, R. Activation of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 during rabbit myocardial ischemia which is highly selective for plasmalogen substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5629–5633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McHowat, J.; Creer, M. Lysophosphatidylcholine accumulation in cardiomyocytes requires thrombin activation of Ca2+-independent PLA2. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, H1972–H1980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, D.J.; Abendschein, D.R.; Jenkins, C.M.; Han, X.; Saffitz, J.E.; Schuessler, R.B.; Gross, R.W. Cardiac ischemia activates calcium-independent phospholipase A2β, precipitating ventricular tachyarrhythmias in transgenic mice: rescue of the lethal electrophysiologic phenotype by mechanism-based inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22231–22236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Jenkins, C.M.; Han, X.; Mancuso, D.J.; Sims, H.F.; Yang, K.; Gross, R.W. The highly selective production of 2-arachidonoyl lysophosphatidylcholine catalyzed by purified calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ: Identification of a novel enzymatic mediator for the generation of a key branch point intermediate in eicosanoid signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26669–26679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.S.; Swenson, L.; Derewenda, U.; Serre, L.; Wei, Y.; Dauter, Z.; Hattori, M.; Adachi, T.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; et al. Brain acetylhydrolase that inactivates platelet-activating factor is a G-protein-like trimer. Nature 1997, 385, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Wilder, C.; Eberhardt, C.; Stafforini, D.M.; Dietsch, G.; Schimpf, B.; Hooper, S.; Le Trong, H.; Cousens, L.S.; Zimmerman, G.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature 1995, 374, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, A.; Hattori, K.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Protection against oxidative stress-induced cell death by intracellular platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase II. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32315–32320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellors, A.; Tappel, A.L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids by a lysosomal enzyme. J. Lipid Res. 1967, 8, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.H.; Okamoto, Y.; Morishita, J.; Tsuboi, K.; Tonai, T.; Ueda, N. Discovery and characterization of a Ca2+-independent phosphatidylethanolamine N-acyltransferase generating the anandamide precursor and its congeners. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3614–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.H.; Uyama, T.; Wang, J.; Okamoto, Y.; Tonai, T.; Ueda, N. cDNA cloning and characterization of human and mouse Ca2+-independent phosphatidylethanolamine N-acyltransferases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyama, T.; Morishita, J.; Jin, X.H.; Okamoto, Y.; Tsuboi, K.; Ueda, N. The tumor suppressor gene H-Rev107 functions as a novel Ca2+-independent cytosolic phospholipase A1/2 of the thiol hydrolase type. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyama, T.; Jin, X.H.; Tsuboi, K.; Tonai, T.; Ueda, N. Characterization of the human tumor suppressors TIG3 and HRASLS2 as phospholipid-metabolizing enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, B.E.; Corr, P.B.; Robison, A.K.; Goldstein, R.A.; Witkowski, F.X.; Klein, M.S. Accumulation of lysophosphoglycerides with arrhythmogenic properties in ischemic myocardium. J. Clin. Investig. 1978, 62, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, R.Y.; Lederman, C.L. Effect of reduced calcium on lysophosphatidylcholine-induced cardiac arrhythmias. Pharmacology 1985, 31, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, R.Y. Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced arrhythmias and its accumulation in the rat perfused heart. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.J.; Hughes, L.L.; Louis, A.I.; Kramer, R.M.; Dennis, E.A. Metal ion and salt effects on the phospholipase A2, lysophospholipase, and transacylase activities of human cytosolic phospholipase A2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1167, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupan, L.A.; Steffens, D.L.; Berry, C.A.; Landt, M.; Gross, R.W. Cloning and expression of a human 14-3-3 protein mediating phospholipolysis. Identification of an arachidonoyl-enzyme intermediate during catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 8707–8710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogura, Y.; Parsons, W.H.; Kamat, S.S.; Cravatt, B.F. A calcium-dependent acyltransferase that produces N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamines. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Tonegawa, T.; Nakane, S.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. Enzymatic synthesis of anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, through N-acylphosphatidyl- ethanolamine pathway in testis: involvement of Ca2+-dependent transacylase and phosphodiesterase activities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Tonegawa, T.; Nakane, S.; Yamashita, A.; Ishima, Y.; Waku, K. Transacylase-mediated and phosphodiesterase-mediated synthesis of N-arachidonoylethanolamine, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, in rat brain microsomes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 240, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Tonegawa, T.; Kondo, S.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. N-Arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide), an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand and related lipid molecules in the nervous system. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal. 1996, 14, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Kodaka, T.; Nakane, S.; Yamashita, A.; Kishimoto, S.; Waku, K.; Ishima, Y. Biosynthesis and Action of Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, Endogenous Cannabimimetic Molecules. In Essential Fatty Acids and Eicosanoids; Riemersma, R.A., Armstrong, R., Kelly, R.W., Eds.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998; pp. 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.C.; Uemura, Y.; Snyder, F. A novel CoA-independent transacetylase produces the ethanolamine plasmalogen and acyl analogs of platelet-activating factor (PAF) with PAF as the acetate donor in HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 19992–20001. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.C.; Ou, M.C.; Shinozaki, K.; Malone, B.; Snyder, F. Biosynthesis of N-acetylsphingosine by platelet-activating factor: Sphingosine CoA-independent transacetylase in HL-60 cels. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, K.; Qiu, X.; Lee, T. Purification and characterization from rat kidney membranes of a novel platelet-activating factor (PAF)-dependent transacetylase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of PAF, formation of PAF analogs, and C2-ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8655–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.; Longobardi, L.; Karasawa, K.; Malone, B.; Inoue, T.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K.; Lee, T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF)-dependent transacetylase and its relationship with PAF acetylhydrolases. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26704–26709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsoukatos, D.C.; Liapikos, T.A.; Tselepis, A.D.; Chapman, M.J.; Ninio, E. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase and transacetylase activities in human plasma low-density lipoprotein. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, A.; Shayman, J.A.; Radin, N.S. A novel enzyme that catalyzes the esterification of N-acetylsphingosine metabolism of C2-ceramides. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14383–14389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abe, A.; Shayman, J.A. Purification and characterization of 1-O-acylceramide synthase, a novel phospholipase A2 with transacylase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8467–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, M.; Abe, A.; Shayman, J.A. Cloning and characterization of a lysosomal phospholipase A2, 1-O-acylceramide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10090–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
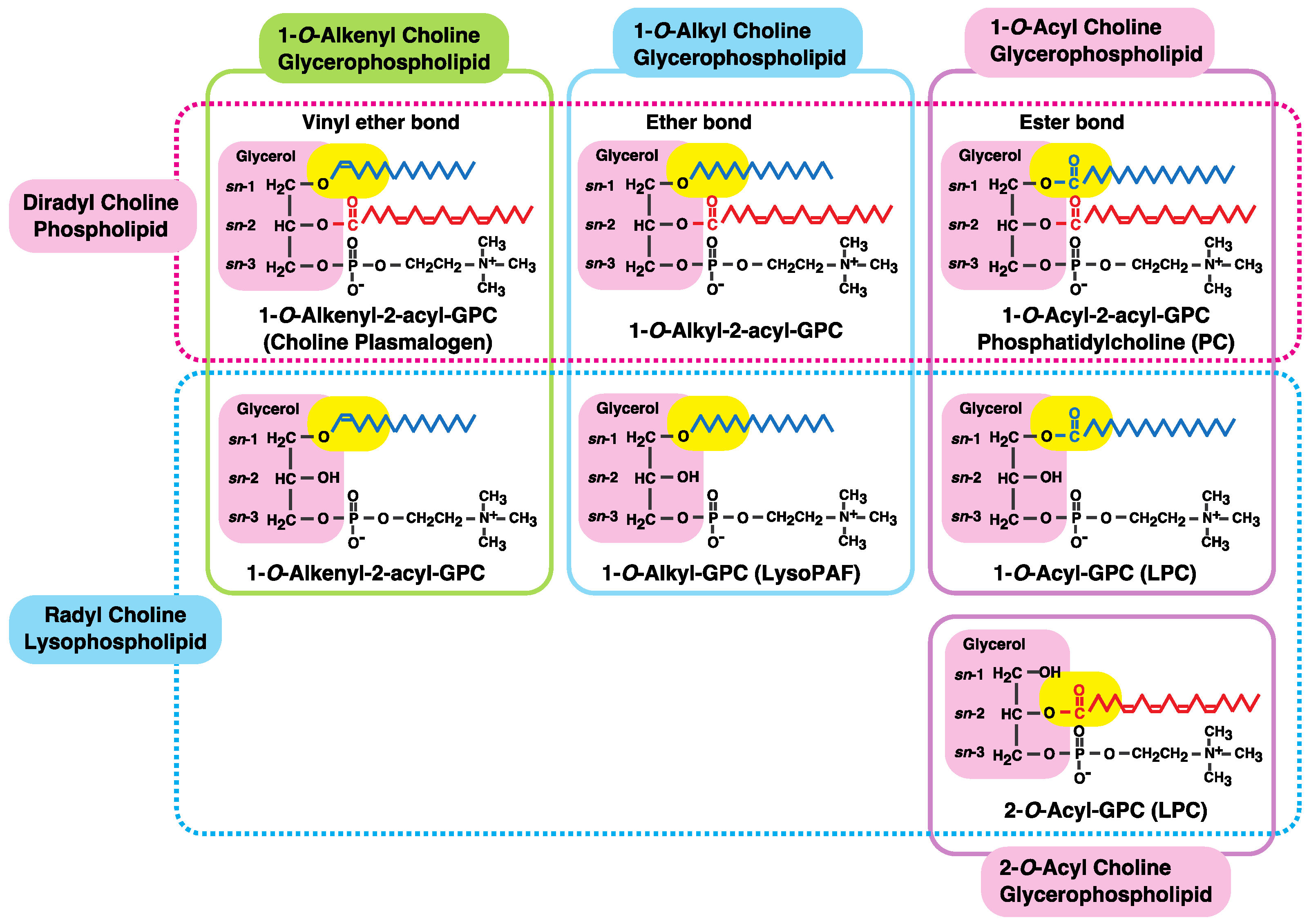
| Class | Subclass | Chemical | Other Names |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diradyl glycerophospholipid | |||
| Choline glycero-phospholipid | 1, 2-Diacyl | 1, 2-Diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1,2-Diacyl-GPC) | Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
| 1-O-Alkyl-2-acyl | 1-O-Alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1-Alkyl-2-acyl-GPC) | Plasmanylcholine | |
| Alkyl phosphatidylcholine | |||
| 1-O-Alkenyl-2-acyl | 1-O-Alkenyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1-Alkenyl-2-acyl-GPC) | Plasmenylcholine | |
| Alkenyl phosphatidylcholine | |||
| Choline plasmalogen | |||
| Ethanolamine glycero-phospholipid | 1, 2-Diacyl | 1, 2-Diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (1,2-Diacyl-GPE) | Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| 1-O-Alkyl-2-acyl | 1-O-Alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-ethanolamine (1-Alkyl-2-acyl-GPE) | Plasmanylethanolamine | |
| Alkyl phosphatidylethanolamine | |||
| 1-O-Alkenyl-2-acyl | 1-O-Alkenyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-ethanolamine (1-Alkenyl-2-acyl-GPE) | Plasmenylethanolamine | |
| Alkenyl phosphatidyethanolamine | |||
| Ethanolamine plasmalogen | |||
| Serine glycero- phospholipid | 1, 2-Diacyl | 1, 2-Diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (1,2-Diacyl-GPS) | Phosphatidylserine (PS) |
| Inositol glycerol-phospholipid | 1, 2-Diacyl | 1, 2-Diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol (1,2-Diacyl-GPI) | Phosphatidylinositol (PI) |
| Radyl lysophospholipid | |||
| Choline glycerol-phospholipid | 1-Acyl | 1-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1-Acyl-GPC) | Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) |
| 1-Acyl lysoPAF | |||
| 1-O-Alkyl | 1-O-Alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1-Alkyl-GPC) | 1-Alkyl lysophosphatidylcholine (1-Alkyl LPC) | |
| Lyso platelet activating factor (LysoPAF) | |||
| 1-O-Alkenyl | 1-O-Alkenyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (1-Alkenyl-GPC) | 1-Alkenyl lysophosphatidylcholine (1-Alkenyl LPC) | |
| Choline lysoplasmalogen | |||
| Ethanolamine glycerol-phospholipid | 1-Acyl | 1-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (1-Acyl-GPE) | 1-Acyl lysophosphatidylethanolamine (1-Acyl LPE) |
| 1-O-Alkyl | 1-O-Alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (1-Alkyl-GPE) | 1-Alkyl lysophosphatidylethanolamine (1-Alkyl LPE) | |
| 1-O-Alkenyl | 1-O-Alkenyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (1-Alkenyl-GPE) | 1-Alkenyl lysophosphatidylethanolamine (1-Alkenyl LPE) | |
| Ethanolamine lysoplasmalogen | |||
| Serine glycerol-phospholipid | 1-Acyl | 1-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (1-Acyl-GPS) | 1-Acyl lysophosphatidylserine (1-Acyl LPS) |
| 2-Acyl | 2-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (2-Acyl-GPS) | 2-Acyl lysophosphatidylserine (2-Acyl LPS) | |
| Inositol glycerol-phospholipid | 1-Acyl | 1-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol (1-Acyl-GPI) | 1-Acyl lysophosphatidylinositol (1-Acyl LPI) |
| 2-Acyl | 2-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol (2-Acyl-GPI) | 2-Acyl lysophosphatidylinositol (2-Acyl LPI) | |
| Acyltransferases and Transacylation Systems | Cofactor | Acyl Donor | Acyl Acceptor | Fatty Acid Transferred | Enzyme(s) Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acyl-CoA:Lysophospholipid Acyltransferase | Acyl-CoA | LPC, LPE, LPS, LPI | AGPAT family | ||
| MBOAT family | |||||
| CoA-Independent Transacylation System | None | Phospholipids | 1-O-alkyl-GPC | C20, C22 PUFA at sn-2 | Not Identified |
| PC, PE | 1-O-Alkenyl-GPE | ||||
| CoA-Dependent Transacylation System | CoA | Phospholipids | LPC, LPE, LPS, LPI | 20:4, 18:2 at sn-2 18:0 at sn-1 | Involvement of Acyl-CoA Acyltransferases |
| PI > PC, PE | |||||
| Lysophospholipase/Transacylation | None | LPC, LPE | LPC, LPE | cPLA2γ (PLA2 G4C) |
| Family | Candidates | Cofactor | Reactions | Acyl Donor | Acyl Acceptor | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cPLA2 (PLA2G4) | cPLA2γ (PLA2 G4C) | None | CoA-independent transacylation | Phospholipids PC, PE | 1-O-alkyl-GPC1-O-Alkenyl-GPE | Low activity? |
| Lysophospholipase/transacylation | LPC, LPE | LPC, LPE 1-O-alkyl-GPC1-O-Alkenyl-GPE | Clearance of lysophospholipid? | |||
| cPLA2α (PLA2 G4A) | None | Lysophospholipase/transacylation | Phospholipids PC, PE | LPC, LPE | ||
| cPLA2ε (PLA2G4E) | Ca2+ | N-acyltransferase | PC, PE | PE | Anandamide synthesis | |
| iPLA2 (PNPLA, PLA2G6) | iPLA2ε (PNPLA3) | None | Triacylglycerol lipase/transacylase | Triacylglycerol | Acylglycerol | Triacylglycerol degaradation/synthesis |
| iPLA2ζ (PNPLA2) | ||||||
| iPLA2η (PNPLA4) | ||||||
| PLA/AT (HRASLS, PLA2G16) | HRASLS5 (iNAT) | None | N-acyltransferase | PC, PE | PE | Anandamide synthesis |
| HRASLS3 (H-Rev107) | ||||||
| HRASLS2 | CoA-independent transacylation | PC, PE | LPC, LPE | Preference to sn-1 fatty acid than sn-2 ones as acyl donor | ||
| HRASLS4 (TIG3) | ||||||
| 14-3-3 protein family | 30 kDa PLA2 | None | Transacylation reaction? | Phospholipids PC, PE | ||
| PAFAH II (PLA2G7) | PAF-AH II | None | Transacetylation | PAF, Oxidized Phospholipid | 1-O-Alkenyl-GPE, sphigosine | Transfer of short chain fatty acid |
| Plasma PAF-AH | None | Transacetylation | LPC, LPE | LPC, LPE | Transfer of short chain fatty acid | |
| Lysosomal PLA2 | LPLA2 (PLA2G15) | None | Transacylation | PC | 1-O-Alkenyl-GPE, ceramide |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamashita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Koizumi, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Sugiura, T. Coenzyme-A-Independent Transacylation System; Possible Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in Transacylation. Biology 2017, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6020023
Yamashita A, Hayashi Y, Matsumoto N, Nemoto-Sasaki Y, Koizumi T, Inagaki Y, Oka S, Tanikawa T, Sugiura T. Coenzyme-A-Independent Transacylation System; Possible Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in Transacylation. Biology. 2017; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamashita, Atsushi, Yasuhiro Hayashi, Naoki Matsumoto, Yoko Nemoto-Sasaki, Takanori Koizumi, Yusuke Inagaki, Saori Oka, Takashi Tanikawa, and Takayuki Sugiura. 2017. "Coenzyme-A-Independent Transacylation System; Possible Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in Transacylation" Biology 6, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6020023
APA StyleYamashita, A., Hayashi, Y., Matsumoto, N., Nemoto-Sasaki, Y., Koizumi, T., Inagaki, Y., Oka, S., Tanikawa, T., & Sugiura, T. (2017). Coenzyme-A-Independent Transacylation System; Possible Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in Transacylation. Biology, 6(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6020023





