Epiphytic Terrestrial Algae (Trebouxia sp.) as a Biomarker Using the Free-Air-Carbon Dioxide-Enrichment (FACE) System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- to study the mid-term exposure of increased CO2 on changes in the density of epiphytic terrestrial algae using the FACE system;
- (2)
- to assess the relationship between algal density and the distance from the CO2 source.
2. Methodology
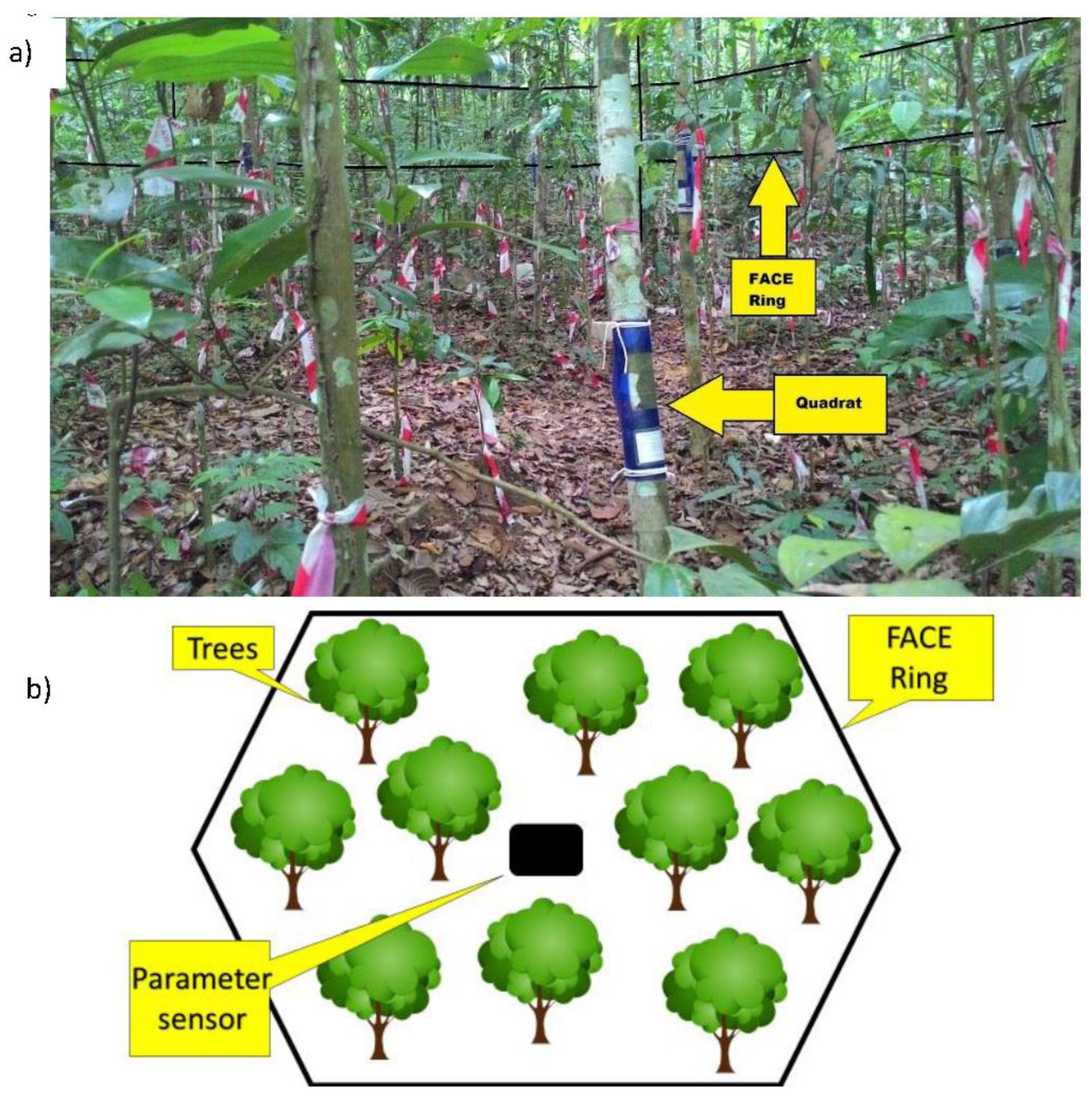
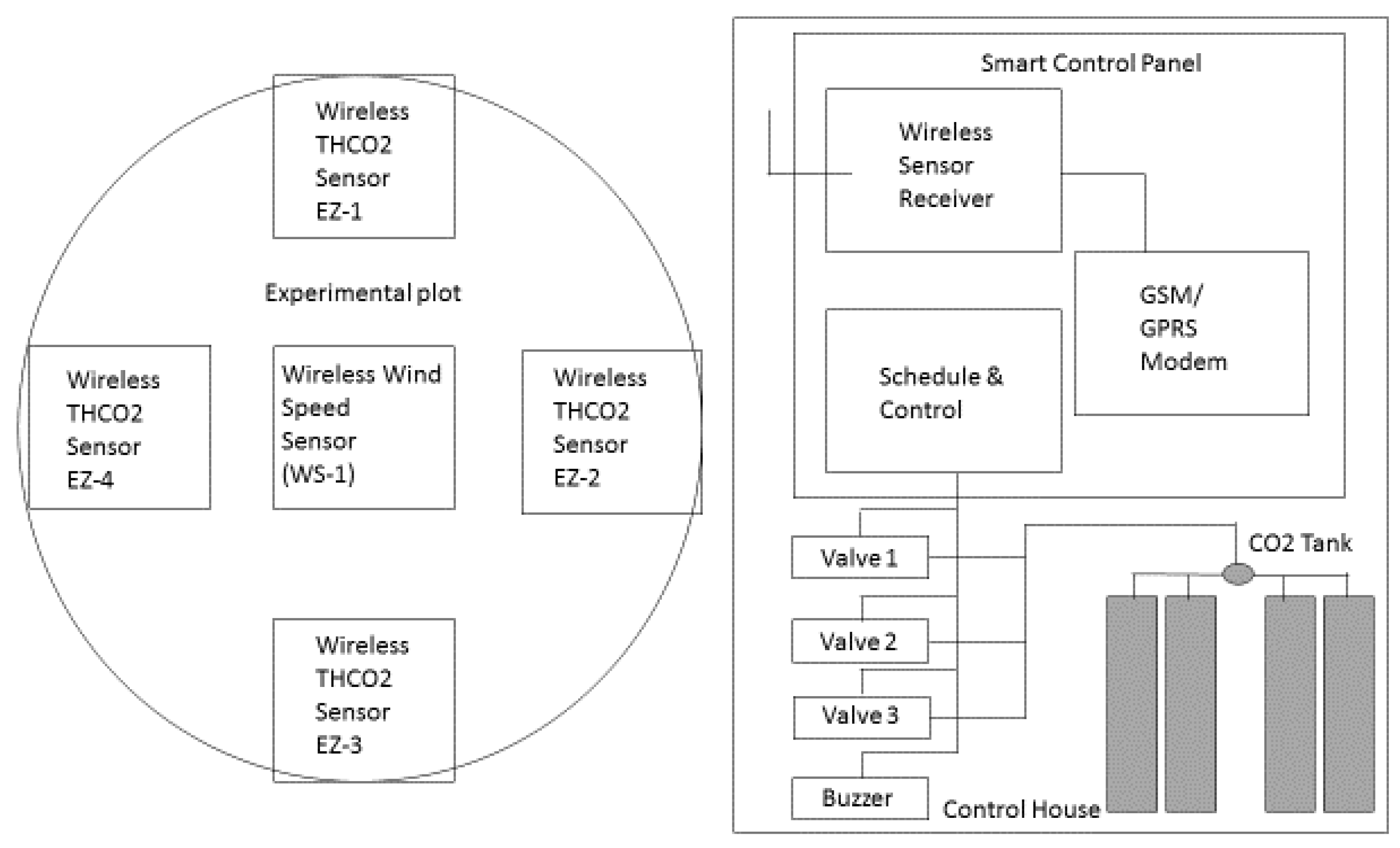
2.1. Site and Environmental Parameter Description
2.2. Systematic Algal Collection and Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
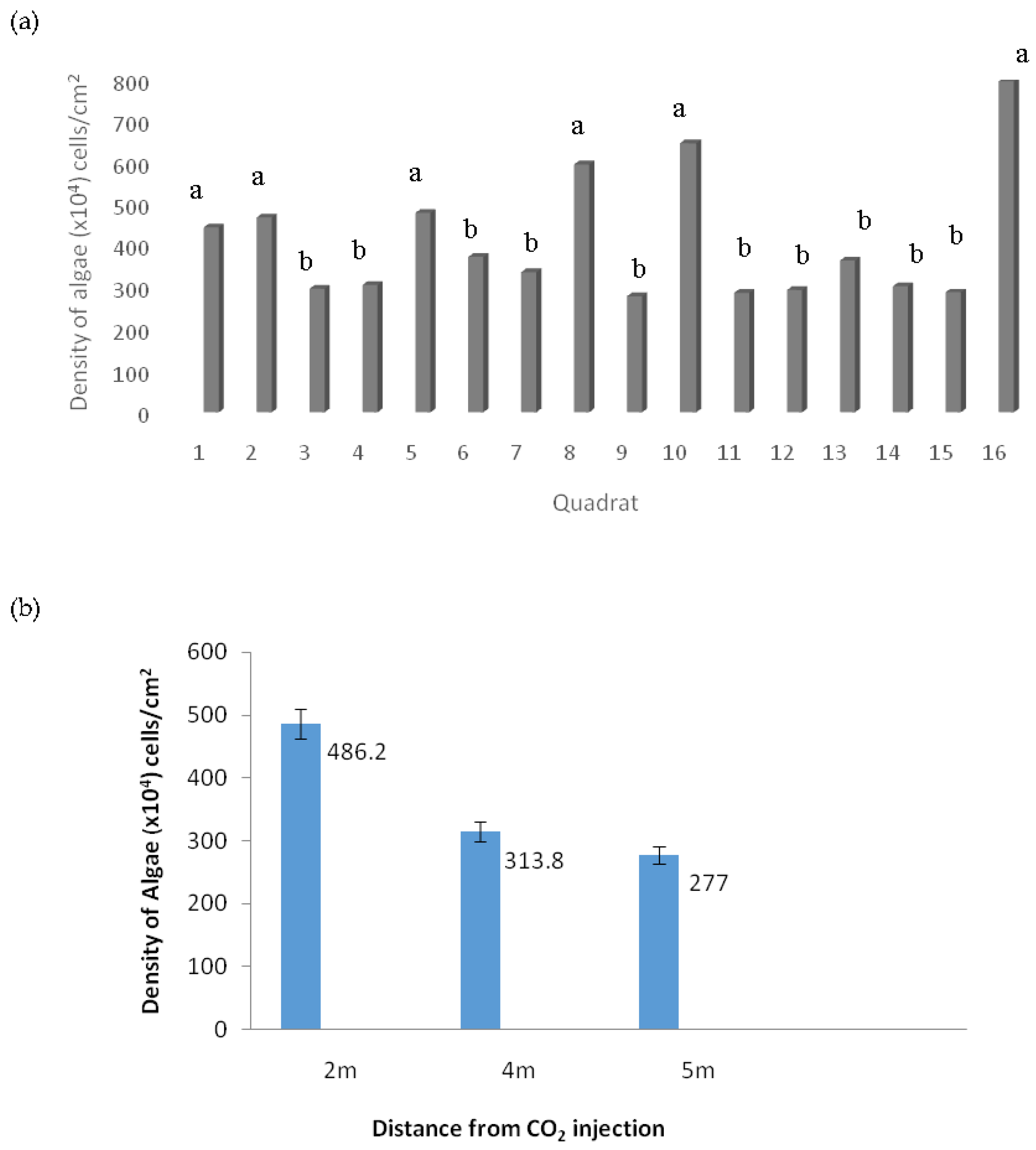
3.1. Density of Algae after CO2 Exposure
3.2. The Relationship between Algal Density and the Distance of CO2 Source
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidari, H.; Katircioğlu, S.T.; Saeidpour, L. Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and energy consumption in the five ASEAN countries. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. The Little Green Data; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, D.; Pires, J.C.M. Atmospheric CO2 capture by algae: Negative carbon dioxide emission path. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrelly, D.J.; Everard, C.D.; Fagan, C.C.; McDonnell, K.P. Carbon sequestration and the role of biological carbon mitigation: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 712–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) Biomarkers and Risk Assessment: Concepts and Principles; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, D.B.; Walker, C.H. The role of biomarkers in environmental assessment (3). Vertebrates Ecotoxicol. 1994, 3, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, H.W.; Bold, H.C. Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algae species. In Phycological Studies; University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 1963; Volume 44, pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, M. Algal capture of carbon dioxide; biomass generation as a tool for greenhouse gas mitigation with reference to New Zealand energy strategy and policy. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 3428–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, O.; von Caemmerer, S.; Ziska, L.H.; Conroy, J.P. The growth response of C4 partial pressure: A reassessment. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, B.A.; Kelly, M.G. Use of algae and other plants for monitoring rivers. Aust. J. Ecol. 1995, 20, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.; Tripathi, R.D.; Rai, U.N.; Pal, A.; Siugh, S.P. Physico-chemical characteristics and pollution level of Lake Nainital (U.P. India): Role of macrophytes and phytoplankton in biomonitoring and phytoremediation of toxic metl ions. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 2171–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volterra, L.; Conti, M.E. Algae as biomarkers, bioaccumulators and toxin producers. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 13, 92–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, K. Characterization of diurnal photosynthetic rhythms in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum grown in synchronous culture under ambient and elevated CO2. Funct. Plant Biol. 2004, 31, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Aruga, Y.; Asada, K.; Kiyohara, M. Influence of enhanced CO2 on growth and photosynthesis of the red algae Gracilaria sp. and G. chilensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, A.; Marzuki, S.D.; Mohd Yusof, N.B.; Buyong, F.; Mohd Said, M.N.; Sigh, H.R.; Zulkifli, A.R. Epiphytic Terrestrial Algae (Trebouxia sp.) as a Biomarker Using the Free-Air-Carbon Dioxide-Enrichment (FACE) System. Biology 2017, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6010019
Ismail A, Marzuki SD, Mohd Yusof NB, Buyong F, Mohd Said MN, Sigh HR, Zulkifli AR. Epiphytic Terrestrial Algae (Trebouxia sp.) as a Biomarker Using the Free-Air-Carbon Dioxide-Enrichment (FACE) System. Biology. 2017; 6(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Asmida, Sarah Diyana Marzuki, Nordiana Bakti Mohd Yusof, Faeiza Buyong, Mohd Nizam Mohd Said, Harinder Rai Sigh, and Amyrul Rafiq Zulkifli. 2017. "Epiphytic Terrestrial Algae (Trebouxia sp.) as a Biomarker Using the Free-Air-Carbon Dioxide-Enrichment (FACE) System" Biology 6, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6010019
APA StyleIsmail, A., Marzuki, S. D., Mohd Yusof, N. B., Buyong, F., Mohd Said, M. N., Sigh, H. R., & Zulkifli, A. R. (2017). Epiphytic Terrestrial Algae (Trebouxia sp.) as a Biomarker Using the Free-Air-Carbon Dioxide-Enrichment (FACE) System. Biology, 6(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology6010019




