Exosome Proteome of U-87MG Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Exosomes
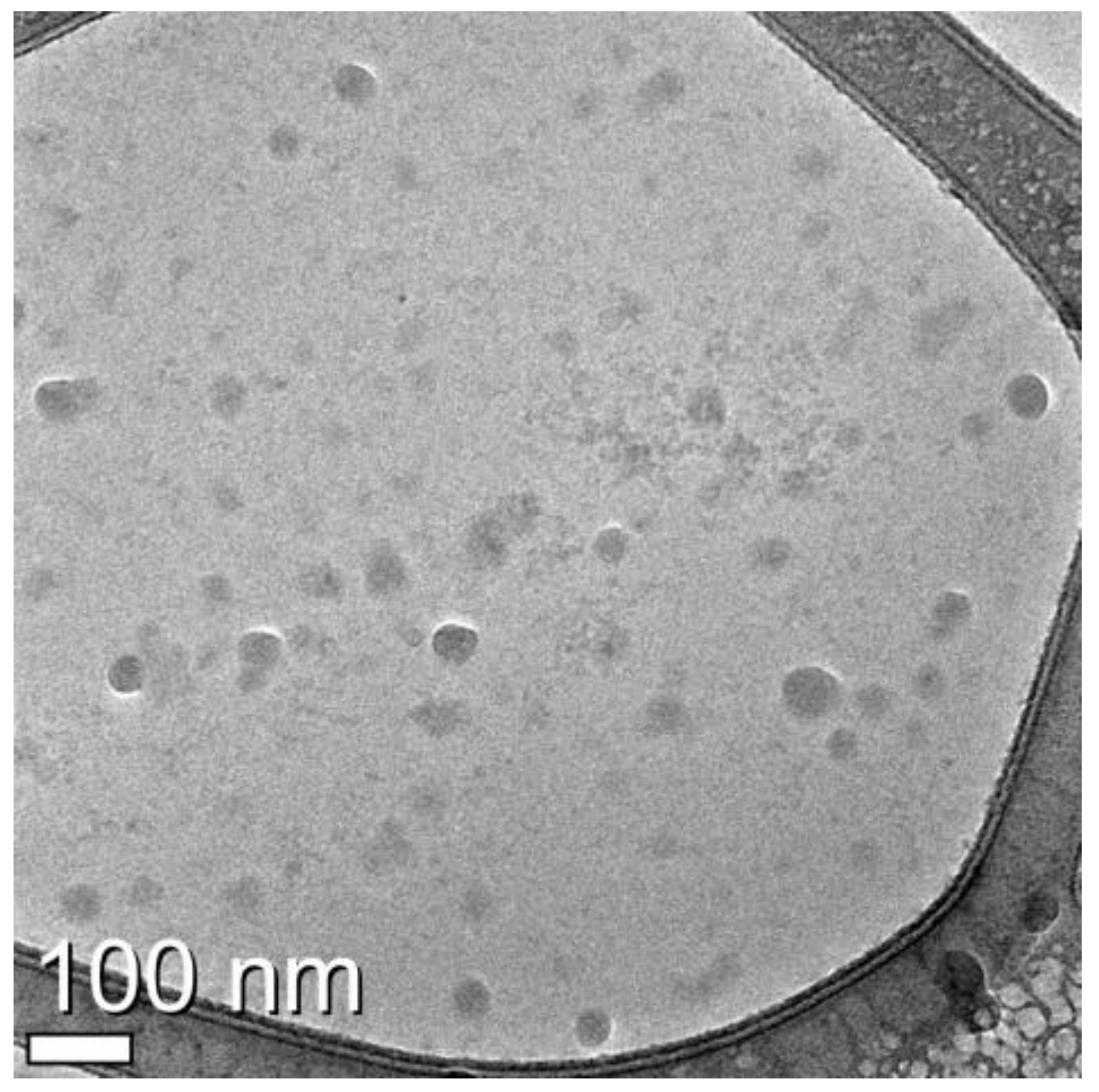
2.3. Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis (2-DE) and Gel Image Analysis
2.5. In-Gel Enzymatic Digestion and MALDI-TOF-MS
2.6. Mascot Database Search
2.7. Western Blotting Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Exosomes
3.2. Identification of Exosomes from U-87MG Cell Culture Medium by Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.3. Protein Analysis of U-87MG Exosomes by Immunoblotting
3.4. Characterization of Exosomal Proteins by Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
3.5. Proteome Analysis by MALDI-TOF-MS and Mascot Search
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratajczak, J.; Wysoczynski, M.; Hayek, F.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Membrane-derived microvesicles: Important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, A.; Seetharam, L.; Yamaguchi, S.; Gotoh, N.; Takahashi, T.; Neufeld, G.; Shibuya, M. A new communication system between hepatocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver through vascular endothelial growth factor and Flt tyrosine kinase receptor family (Flt-1 and KDR/Flk-1). Oncogene 1994, 9, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Dejana, E. Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Immunol. Today 1989, 10, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidulescu, C.; Clejan, S.; O’Connor, K.C. Vesicle traffic through intercellular bridges in DU 145 human prostate cancer cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2004, 8, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, H.; Sadler, P.J. Transferrin as a metal ion mediator. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2817–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.J.; Jensen, S.S.; Lim, J.W.E. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: Current perspectives. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4083–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.J.; Oh, S.O.; Ahn, S.M.; Lee, B.H.; Moon, M.H. Proteomic analysis of exosomes from human neural stem cells by flow field-flow fractionation and nanoflow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3475–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Pol, E.; Hoekstra, A.G.; Sturk, A.; Otto, C.; Van Leeuwen, T.G.; Nieuwland, R. Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Vancells, J.; Rodriguez-Suarez, E.; Embade, N.; Gil, D.; Matthiesen, R.; Valle, M.; Elortza, F.; Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Characterization and comprehensive proteome profiling of exosomes secreted by hepatocytes. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 5157–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Simoesexosome, S.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobiecka, M. Exosome and microvesicles: Extracellular frontiers of intercellular communication. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, 3rd ed.; Somasundaran, P., Ed.; Taylor & Francis, CRC Press: Oxfordshire, UK, 2016; pp. 2632–2644. [Google Scholar]
- Vella, L.J.; Sharples, R.A.; Lawson, V.A.; Masters, C.L.; Cappai, R.; Hi, A.F. Packing of prions into exosomes is associated with a novel pathway of PrP processing. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadiu, I.; Narayanasamy, P.; Dash, P.K.; Zhang, W.; Gendelman, H.E. Biochemical and biologic characterization of exosomes and microvesicles as facilitators of HIV-1 infection in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, L.; Honsho, M.; Zahn, T.R.; Keller, P.; Geiger, K.D.; Verkade, P.; Simons, K. Alzheimer’s disease β-amyloid peptides are released in association with exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11172–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B lymphocytes secrete antigen—Presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wubbolts, R.; Leckie, R.S.; Veenhuizen, P.T.M.; Schwarzmann, G.; Möbius, W.; Hoernschemeyer, J.; Slot, J.W.; Geuze, H.J.; Stoorvogel, W. Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B Cell-derived exosomes potential implications for their function and multivesicular body formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10963–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cell. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laulagnier, K.; Motta, C.; Hamdi, S.; Roy, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Pageaux, J.F.; Kobayashi, T.; Salles, J.P.; Perret, B.; Bonnerot, C.; et al. Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Boussac, M.; Véron, P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Garin, J.; Amigorena, S. Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: A secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7309–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, N.; Lankar, D.; Faure, F.; Regnault, A.; Dumont, C.; Raposo, G.; Hivroz, C. TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the TCR/CD3/zeta complex. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3235–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijnen, H.F.G.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; Raposo, G.; Candalh, C.; Boussac, M.; Hershberg, R.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Heyman, M. Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevrier, B.; Vilette, D.; Archer, F.; Loew, D.; Faigle, W.; Vidal, M.; Laude, H.; Raposo, G. Cells release prions in association with exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9683–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, F.; Schartz, N.E.C.; Chaput, N.; Flament, C.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S.; Angevin, E.; Zitvogel, L. Tumor-derived exosomes: A new source of tumor rejection antigens. Vaccine 2002, 20, A28–A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauré, J.; Lachenal, G.; Court, M.; Hirrlinger, J.; Chatellard-Causse, C.; Blot, B.; Grange, J.; Schoehn, G.; Goldberg, Y.; Boyer, V.; et al. Exosomes are released by cultured cortical neurones. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 31, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lässer, C.; Alikhani, V.S.; Ekström, K.; Eldh, M.; Paredes, P.T.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Gabrielsson, S.; Lötvall, J.; Valadi, H. Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: Uptake by macrophages. J. Transl. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, M.P.; Hegmans, J.P.; Hemmes, A.; Luider, T.M.; Willemsen, R.; Severijnen, L.A.A.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Burgers, S.A.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N. Proteomic analysis of exosomes isolated from human malignant pleural effusions. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.; Ridinger, J.; Rupp, A.K.; Janssen, J.W.G.; Altevogt, P. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, L.J.; Greenwood, D.L.V.; Cappai, R.; Scheerlinck, J.P.Y.; Hill, A.F. Enrichment of prion protein in exosomes derived from ovine cerebral spinal fluid. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 124, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, J.L.; Métayer, S.; Belghazi, M.; Dacheux, F.; Dacheux, J.L. Identification, proteomic profiling, and origin of ram epididymal fluid exosome-like vesicles. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.J.; Homer, N.; O’Connor, B.D.; Chen, Z.; Eskin, A.; Lee, H.; Merriman, B.; Nelson, S.F. U87MG Decoded: The Genomic Sequence of a Cytogenetically Aberrant Human Cancer Cell Line. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.K.; Cho, Y.M.; Bae, S.H.; Zoubaulis, C.C.; Paik, Y.K. Single-step perfusion chromatography with a throughput potential for enhanced peptide detection by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.A. New discoveries on the biology and detection of human chorionic gonadotropin. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenbeck, G.; Harter, C.; Brecht, A.; Herrmann, D.; Lottspeich, F.; Orci, L.; Wieland, F.T. beta’-COP, a novel subunit of coatomer. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2841–2845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayne, R.; Burgeson, R.E. Structure and Function of Collagen Types; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1987; pp. 105–143. [Google Scholar]
- Markoff, A.; Bogdanova, N.; Knop, M.; Rüffer, C.; Kenis, H.; Lux, P.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Todorov, V.; Dworniczak, B.; Horst, J.; et al. Annexin A5 interacts with polycystin-1 and interferes with the polycystin-1 stimulated recruitment of E-cadherin into adherens junctions. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 369, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobiecka, M.; Chalupa, A.; Dworakowska, B. Piezometric biosensors for anti-apoptotic protein survivin based on buried positive-potential barrier and immobilized monoclonal antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 84, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobiecka, M.; Dworakowska, B.; Jakiela, S.; Lukasiak, A.; Chalupa, A.; Zembrzycki, K. Sensing of survivin mRNA in malignant astrocytes using graphene oxide nanocarrier-supported oligonucleotide molecular beacons. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 235, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobiecka, M.; Chalupa, A. DNA Strand replacement mechanism in molecular beacons encoded for the detection of cancer biomarkers. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 4782–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

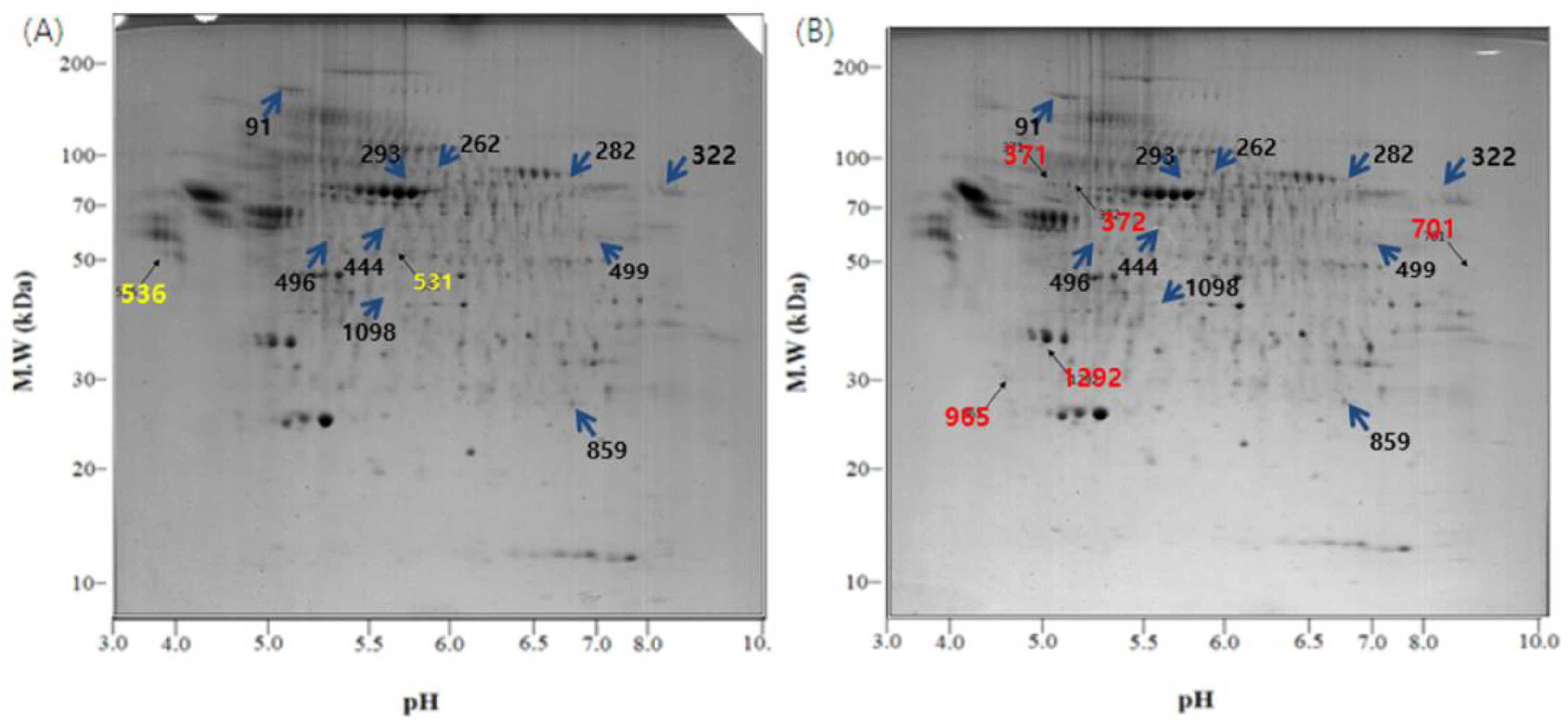
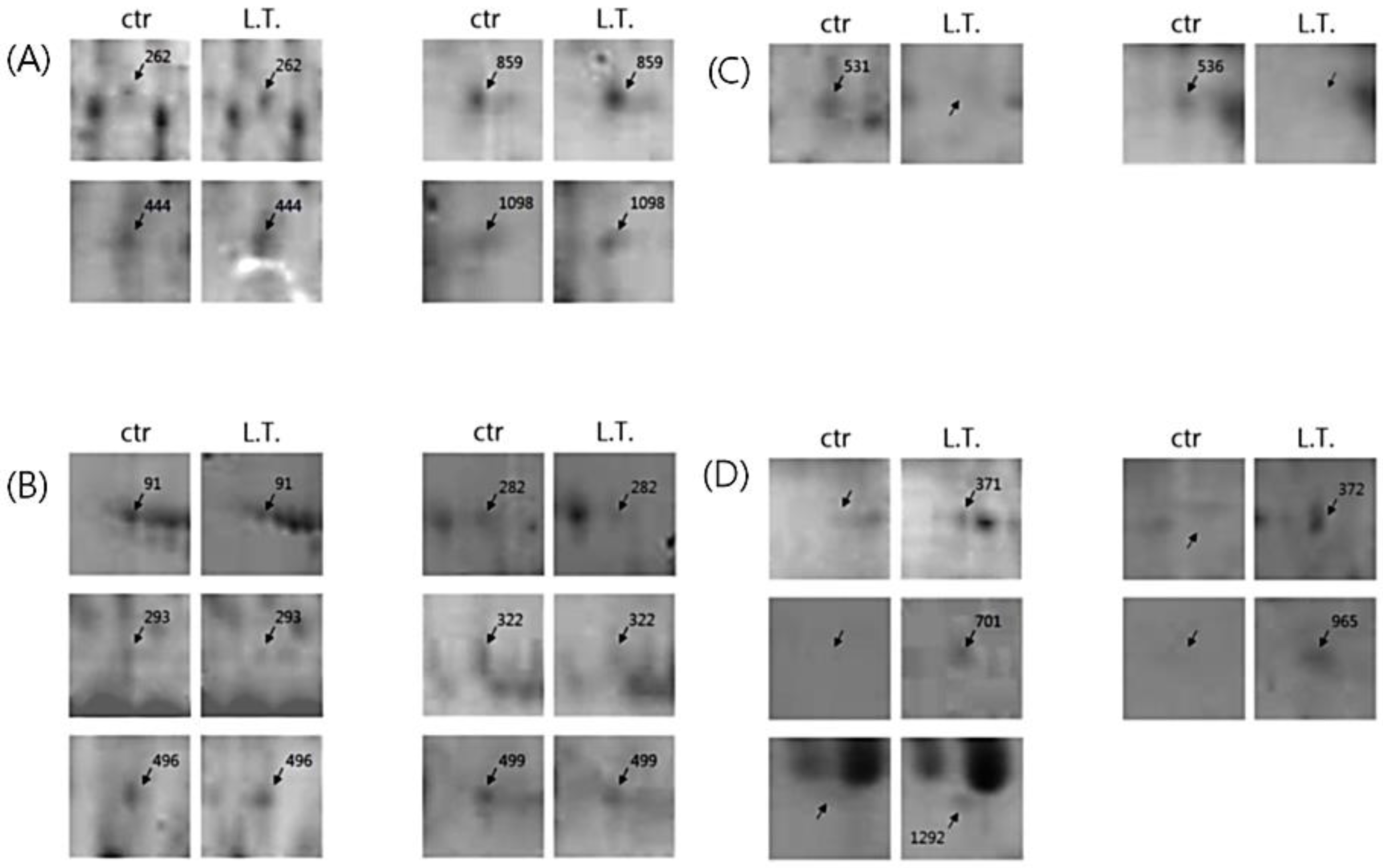
| (A) The proteins whose expression was increased in the L.T. gel. | ||||||||
| Spot ID | Protein Description | Accession No. | Score | MW (Da) | pI | Coverage (%) | Matched Peptides No. | L.T./Ctr Ratio (% vol.) |
| 262 | calcium-dependent secretion activator 2 isoform b | gi|148839284 | 54 | 144,652 | 5.80 | 13 | 14 | 2.0 |
| 444 | hCG1817425 | gi|119590387 | 68 | 15,559 | 8.88 | 63 | 7 | 3.2 |
| 859 | armadillo repeat-containing protein 4 | gi|31657114 | 53 | 117,146 | 7.98 | 17 | 13 | 2.6 |
| 1098 | immunoglobulin heavy variable 5 | gi|371571045 | 54 | 10,996 | 9.10 | 62 | 6 | 2.3 |
| (B) The proteins whose expression was decreased in the L.T. gel. | ||||||||
| Spot ID | Protein Description | Accession No. | Score | MW (Da) | pI | Coverage (%) | Matched Peptides No. | Ctr/L.T. Ratio (% vol.) |
| 91 | collagen, type VI, alpha 1, isoform CRA_b | gi|119629727 | 76 | 109,602 | 5.26 | 24 | 19 | 3.6 |
| 282 | DNA topoisomerase I, mitochondrial isoform 2 | gi|386642871 | 56 | 59,178 | 9.18 | 26 | 10 | 3.4 |
| 293 | titin | gi|407139 | 62 | 524,823 | 8.06 | 8 | 28 | 3.5 |
| 322 | putative RNA-binding protein 15B | gi|54607124 | 66 | 97,432 | 9.86 | 21 | 13 | 2.2 |
| 496 | phosphoserine aminotransferase isoform 2 | gi|10863955 | 59 | 35,508 | 6.23 | 35 | 8 | 2.0 |
| 499 | Chain A, Substrate Induced Remodeling Of The Active Site Regulates HTRA1 Activity | gi|323714490 | 101 | 36,607 | 6.91 | 44 | 12 | 2.1 |
| (C) The protein spots that were only present in the control gel. | ||||||||
| Spot ID | Protein Description | Accession No. | Score | MW (Da) | pI | Coverage (%) | Matched Peptides No. | |
| 531 | coatomer protein complex, subunit beta 2 (beta prime), isoform CRA_b | gi|119599446 | 67 | 99,839 | 5.04 | 22 | 14 | |
| 536 | hypothetical protein FLJ40243, isoform CRA_a | gi|119576413 | 51 | 183,085 | 6.14 | 12 | 17 | |
| (D) The protein spots that were only identified in the L.T. gel. | ||||||||
| Spot ID | Protein Description | Accession No. | Score | MW (Da) | pI | Coverage (%) | Matched Peptides No. | |
| 371 | immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain variable region | gi|5051322 | 63 | 13,695 | 7.94 | 52 | 6 | |
| 372 | nuclear receptor ROR-alpha isoform b | gi|19743901 | 61 | 64,306 | 5.97 | 15 | 10 | |
| 701 | myosin, heavy chain 1, skeletal | gi|109731497 | 127 | 223,975 | 5.62 | 17 | 28 | |
| 701 | muscle, adult | gi|109731497 | 127 | 223,975 | 5.62 | 17 | 28 | |
| 965 | keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | gi|55956899 | 89 | 62,255 | 5.14 | 29 | 12 | |
| 1292 | Chain A, The Effect Of Metal Binding On The Structure Of Annexin V And Implications For Membrane Binding | gi|809185 | 112 | 35,840 | 4.94 | 38 | 14 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chun, S.; Ahn, S.; Yeom, C.-H.; Park, S. Exosome Proteome of U-87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology 2016, 5, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040050
Chun S, Ahn S, Yeom C-H, Park S. Exosome Proteome of U-87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology. 2016; 5(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleChun, Sohyun, Seunghyun Ahn, Chang-Hwan Yeom, and Seyeon Park. 2016. "Exosome Proteome of U-87MG Glioblastoma Cells" Biology 5, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040050
APA StyleChun, S., Ahn, S., Yeom, C.-H., & Park, S. (2016). Exosome Proteome of U-87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology, 5(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5040050





