Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage
Abstract
:1. gp130 Cytokines
2. Oncostatin M
3. OSM Modulation of Adipocyte Differentiation
4. OSM is an Adipokine
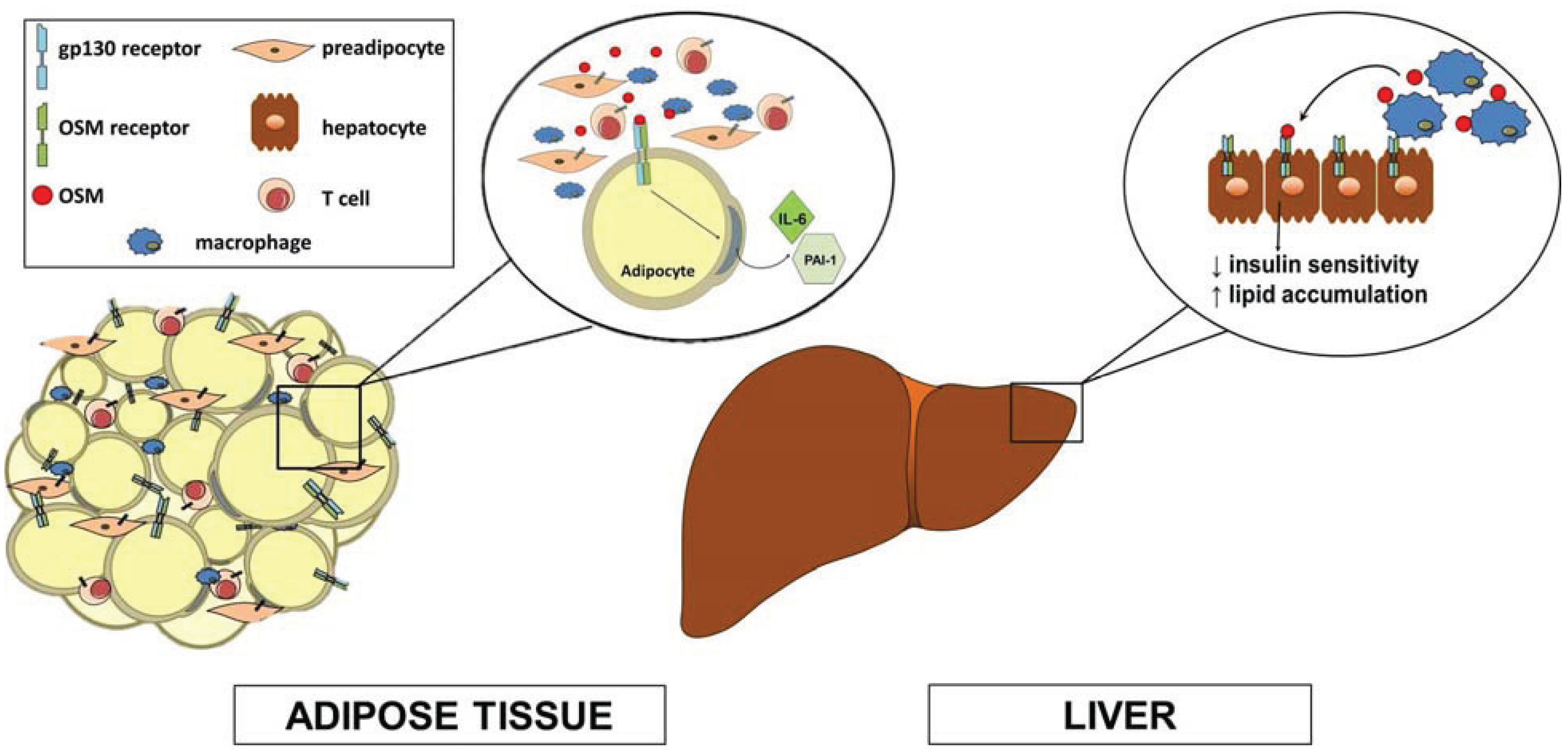
5. Hepatic Effects of OSM
6. Metabolic Studies in OSMRβ Knockout Mice
7. Summary and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fasnacht, N.; Muller, W. Conditional gp130 deficient mouse mutants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, A.; Sahin, S.; Koc, F.; Karayakali, M.; Sahin, M.; Benli, I.; Kadi, H.; Burucu, T.; Ceyhan, K.; Erkorkmaz, U.; et al. Cardiotrophin-1 plasma levels are increased in patients with diastolic heart failure. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, CR25–CR31. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D.; Dendale, P.; Beelen, M.; Jonkers, R.A.; Mullens, A.; Corluy, L.; Meeusen, R.; van Loon, L.J. Plasma adipokine and inflammatory marker concentrations are altered in obese, as opposed to non-obese, type 2 diabetes patients. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.A.; Ranganathan, S.; Li, C.; Wood, L.; Ranganathan, G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E745–E751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez, B.; Gonzalez, A.; Querejeta, R.; Barba, J.; Diez, J. Association of plasma cardiotrophin-1 with stage C heart failure in hypertensive patients: Potential diagnostic implications. J. hypertens. 2009, 27, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natal, C.; Fortuno, M.A.; Restituto, P.; Bazan, A.; Colina, I.; Diez, J.; Varo, N. Cardiotrophin-1 is expressed in adipose tissue and upregulated in the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E52–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, A.R.; S, T.M.; Garima, G.; Raju, A. Serum levels of oncostatin M (a gp 130 cytokine): An inflammatory biomarker in periodontal disease. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slevin, M.; Krupinski, J.; Mitsios, N.; Perikleous, C.; Cuadrado, E.; Montaner, J.; Sanfeliu, C.; Luque, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; et al. Leukaemia inhibitory factor is over-expressed by ischaemic brain tissue concomitant with reduced plasma expression following acute stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Febbraio, M.A. Gp130 receptor ligands as potential therapeutic targets for obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenius, V.; Wallenius, K.; Ahren, B.; Rudling, M.; Carlsten, H.; Dickson, S.L.; Ohlsson, C.; Jansson, J.O. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gregorio, G.B.; Hensley, L.; Lu, T.; Ranganathan, G.; Kern, P.A. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in mice with a targeted mutation in the IL-6 gene: Absence of development of age-related obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E182–E187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, V.; Nagaev, I.; Smith, U. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3t3-l1 adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45777–45784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloaguen, I.; Costa, P.; Demartis, A.; Lazzaro, D.; di Marco, A.; Graziani, R.; Paonessa, G.; Chen, F.; Rosenblum, C.I.; van der Ploeg, L.H.; et al. Ciliary neurotrophic factor corrects obesity and diabetes associated with leptin deficiency and resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6456–6461. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, P.D.; Anderson, K.D.; Sleeman, M.W.; Wong, V.; Tan, J.; Hijarunguru, A.; Corcoran, T.L.; Murray, J.D.; Thabet, K.E.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; et al. Ciliary neurotrophic factor activates leptin-like pathways and reduces body fat, without cachexia or rebound weight gain, even in leptin-resistant obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4652–4657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sleeman, M.W.; Garcia, K.; Liu, R.; Murray, J.D.; Malinova, L.; Moncrieffe, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Wiegand, S.J. Ciliary neurotrophic factor improves diabetic parameters and hepatic steatosis and increases basal metabolic rate in db/db mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14297–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, M.P.; Littlejohn, T.W.; Schwartz, S.L.; Weiss, S.R.; McIlwain, H.H.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bray, G.A.; Roberts, W.G.; Heyman, E.R.; Stambler, N.; et al. Recombinant variant of ciliary neurotrophic factor for weight loss in obese adults: A randomized, dose-ranging study. JAMA 2003, 289, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Bluher, S.; Moschos, S.; Bullen, J., Jr.; Kokkotou, E.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Wiegand, S.J.; Sleeman, M.W.; Mantzoros, C.S. Ciliary neurotrophic factor ax15 alters energy homeostasis, decreases body weight, and improves metabolic control in diet-induced obese and ucp1-dta mice. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvonic, S.; Cornelius, P.; Stewart, W.C.; Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. The regulation and activation of ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling proteins in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, S.; Turpin, S.M.; Ke, F.; Kemp, B.E.; Watt, M.J. Metabolic remodeling in adipocytes promotes ciliary neurotrophic factor-mediated fat loss in obesity. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2546–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balhoff, J.P.; Stephens, J.M. Highly specific and quantitative activation of stats in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenney, R.; Stansfield, K.; Pekala, P.H. Interleukin 11 signaling in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, J.M.; Lumpkin, S.J.; Fishman, J.B. Activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 and 3 by leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin-m, and interferon-gamma in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31408–31416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvonic, S.; Hogan, J.C.; Arbour-Reily, P.; Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. Effects of cardiotrophin on adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47572–47579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, U.A.; Stewart, W.C.; Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. Neuropoietin attenuates adipogenesis and induces insulin resistance in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22505–22512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.M.; Lagrou, M.J.; Fransson, I.; Werelius, B.; Delattre, O.; Thomas, G.; de Jong, P.J.; Todaro, G.J.; Dumanski, J.P. The genes for oncostatin M (OSM) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) are tightly linked on human chromosome 22. Genomics 1993, 17, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.M.; Bruce, A.G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8641–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarling, J.M.; Shoyab, M.; Marquardt, H.; Hanson, M.B.; Lioubin, M.N.; Todaro, G.J. Oncostatin M: A growth regulator produced by differentiated histiocytic lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 9739–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, B.; de Imus, C.; Friend, D.; Boiani, N.; Thoma, B.; Park, L.S.; Cosman, D. Dual oncostatin M (OSM) receptors. Cloning and characterization of an alternative signaling subunit conferring OSM-specific receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 32635–32643. [Google Scholar]
- Gearing, D.P.; Comeau, M.R.; Friend, D.J.; Gimpel, S.D.; Thut, C.J.; McGourty, J.; Brasher, K.K.; King, J.A.; Gillis, S.; Mosley, B.; et al. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: An oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the lif receptor. Science 1992, 255, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara, M.; Hara, T.; Kim, H.; Murate, T.; Miyajima, A. Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor do not use the same functional receptor in mice. Blood 1997, 90, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, R.A.; Juan, T.S.; Welcher, A.A.; Sun, Y.; Cupples, R.; Guthrie, B.; Fletcher, F.A. Cloning and characterization of a specific receptor for mouse oncostatin M. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, U.A.; Stewart, W.C.; Stephens, J.M. Gp130 cytokines exert differential patterns of crosstalk in adipocytes both in vitro and in vivo. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011, 19, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Lioubin, M.N.; Marquardt, H. Purification and characterization of cytostatic lymphokines produced by activated human T lymphocytes. Synergistic antiproliferative activity of transforming growth factor beta 1, interferon-gamma, and oncostatin M for human melanoma cells. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 2977–2983. [Google Scholar]
- Suda, T.; Chida, K.; Todate, A.; Ide, K.; Asada, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kuwata, H.; Nakamura, H. Oncostatin M production by human dendritic cells in response to bacterial products. Cytokine 2002, 17, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.F.; Wallace, P.M. Oncostatin M in the anti-inflammatory response. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, Siii75–Siii80. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, W.; Bell, M.; Carroll, G. Detection of oncostatin M in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasanz-Puig, A.; Murray, J.; Preusch, M.; Coan, D.; Namekata, M.; Patel, Y.; Dong, Z.M.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Wijelath, E.S. Oncostatin M is expressed in atherosclerotic lesions: A role for oncostatin M in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2011, 216, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyanets, S.; Kaun, C.; Rychli, K.; Pfaffenberger, S.; Kastl, S.P.; Hohensinner, P.J.; Rega, G.; Katsaros, K.M.; Afonyushkin, T.; Bochkov, V.N.; et al. Oncostatin M-enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells involves pi3k-, p38 mapk-, erk1/2- and stat1/stat3-dependent pathways and is attenuated by interferon-γ. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 217–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Ito, Y.; Matsui, T.; Morikawa, Y.; Senba, E.; Nakashima, K.; Taga, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kishimoto, T.; et al. Fetal liver development requires a paracrine action of oncostatin M through the gp130 signal transducer. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Nonaka, H.; Saito, H.; Tanaka, M.; Miyajima, A. Hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling is impaired after liver injury in oncostatin M receptor knockout mice. Hepatology 2004, 39, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kamiya, A.; Mukouyama, Y.; Hara, T. Role of oncostatin M in hematopoiesis and liver development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000, 11, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, J.; Gartner, D.; Dorn, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Schanze, N.; Elz, S.R.; Puschel, G.P. Oncostatin M produced in kupffer cells in response to pge2: Possible contributor to hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, P.M.; MacMaster, J.F.; Rouleau, K.A.; Brown, T.J.; Loy, J.K.; Donaldson, K.L.; Wahl, A.F. Regulation of inflammatory responses by oncostatin M. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5547–5555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubin, T.; Poling, J.; Kostin, S.; Gajawada, P.; Hein, S.; Rees, W.; Wietelmann, A.; Tanaka, M.; Lorchner, H.; Schimanski, S.; et al. Oncostatin M is a major mediator of cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and remodeling. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 420–432. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Infantes, D.; White, U.A.; Elks, C.M.; Morrison, R.F.; Gimble, J.M.; Considine, R.V.; Ferrante, A.W.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M. Oncostatin M is produced in adipose tissue and is regulated in conditions of obesity and type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocriol. Metab. 2014, 99, E217–E225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Naiki, T.; Miyajima, A. Oncostatin M inhibits adipogenesis through the ras/erk and STAT5 signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37913–37920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarjeant, K.; Stephens, J.M. Adipogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, M. Clinical relevance of adipokines. Diabetes Metab. J. 2012, 36, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danforth, E. Failure of adipocyte differentiation causes type ii diabetes mellitus? Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 13–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, T.; Tanaka, M.; Senba, E.; Miyajima, A.; Morikawa, Y. Lack of oncostatin M receptor β leads to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by switching macrophage phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21861–21875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, T.; Tanaka, M.; Senba, E.; Miyajima, A.; Morikawa, Y. Deficiency of oncostatin M receptor β (OSMRβ) exacerbates high-fat diet-induced obesity and related metabolic disorders in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13821–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Block, T.M.; Wang, M.; Nefsky, B.; Long, R.; Hafner, J.; Mehta, A.S.; Marrero, J.; Gish, R.; Norton, P.A.; et al. Interleukin-6 and oncostatin M are elevated in liver disease in conjunction with candidate hepatocellular carcinoma biomarker gp73. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 11, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Thorat, M.; Ar, P.; Garg, G. Correlation of levels of oncostatin M cytokine in crevicular fluid and serum in periodontal disease. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 2, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Sell, H. Adipokines: A treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteomics. Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed-Ali, V.; Goodrick, S.; Rawesh, A.; Katz, D.R.; Miles, J.M.; Yudkin, J.S.; Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4196–4200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: Depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rega, G.; Kaun, C.; Weiss, T.W.; Demyanets, S.; Zorn, G.; Kastl, S.P.; Steiner, S.; Seidinger, D.; Kopp, C.W.; Frey, M.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and oncostatin M induce plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human adipose tissue. Circulation 2005, 111, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, B.; Verdier, F.; Matak, P.; Deschemin, J.-C.; Mayeux, P.; Vaulont, S. Oncostatin M is a potent inducer of hepcidin, the iron regulatory hormone. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, R.I.; Mazzucco, C.E.; Radka, S.F.; Shoyab, M.; Kiener, P.A. Oncostatin M up-regulates low density lipoprotein receptors in hepg2 cells by a novel mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 18194–18199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanda, J.; Uchiyama, T.; Tomosugi, N.; Higuchi, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Kawabata, H. Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor increase hepcidin expression in hepatoma cell lines. Int. J. Hematol. 2009, 90, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okaya, A.; Kitanaka, J.; Kitanaka, N.; Satake, M.; Kim, Y.; Terada, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Takemura, M.; Fujimoto, J.; Terada, N.; et al. Oncostatin M inhibits proliferation of rat oval cells, oc15-5, inducing differentiation into hepatocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 709–719. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, C.D.; Brown, T.J.; Shoyab, M.; Baumann, H.; Gauldie, J. Recombinant oncostatin M stimulates the production of acute phase proteins in hepg2 cells and rat primary hepatocytes in vitro. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.D.; Kerr, C.; Tanaka, M.; Hara, T.; Miyajima, A.; Pennica, D.; Botelho, F.; Langdon, C.M. Regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in fibroblasts and acute phase proteins in hepatocytes in vitro by mouse oncostatin M, cardiotrophin-1, and il-6. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, M.J.; Jeon, E.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Jung, J.S.; Kim, J.H. Oncostatin M decreases adiponectin expression and induces dedifferentiation of adipocytes by jak3- and mek-dependent pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elks, C.M.; Stephens, J.M. Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage. Biology 2015, 4, 151-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010151
Elks CM, Stephens JM. Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage. Biology. 2015; 4(1):151-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleElks, Carrie M., and Jacqueline M. Stephens. 2015. "Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage" Biology 4, no. 1: 151-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010151
APA StyleElks, C. M., & Stephens, J. M. (2015). Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage. Biology, 4(1), 151-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010151






