Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Six Camellia sinensis Accessions: Genetic Divergence, Adaptive Evolution, and Molecular Marker Development
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.2. IR Boundary and Codon Usage Bias Analysis
2.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Nucleotide Diversity, Sequence Similarity, and Synteny Analysis
2.6. Molecular Marker Development and Validation
3. Results
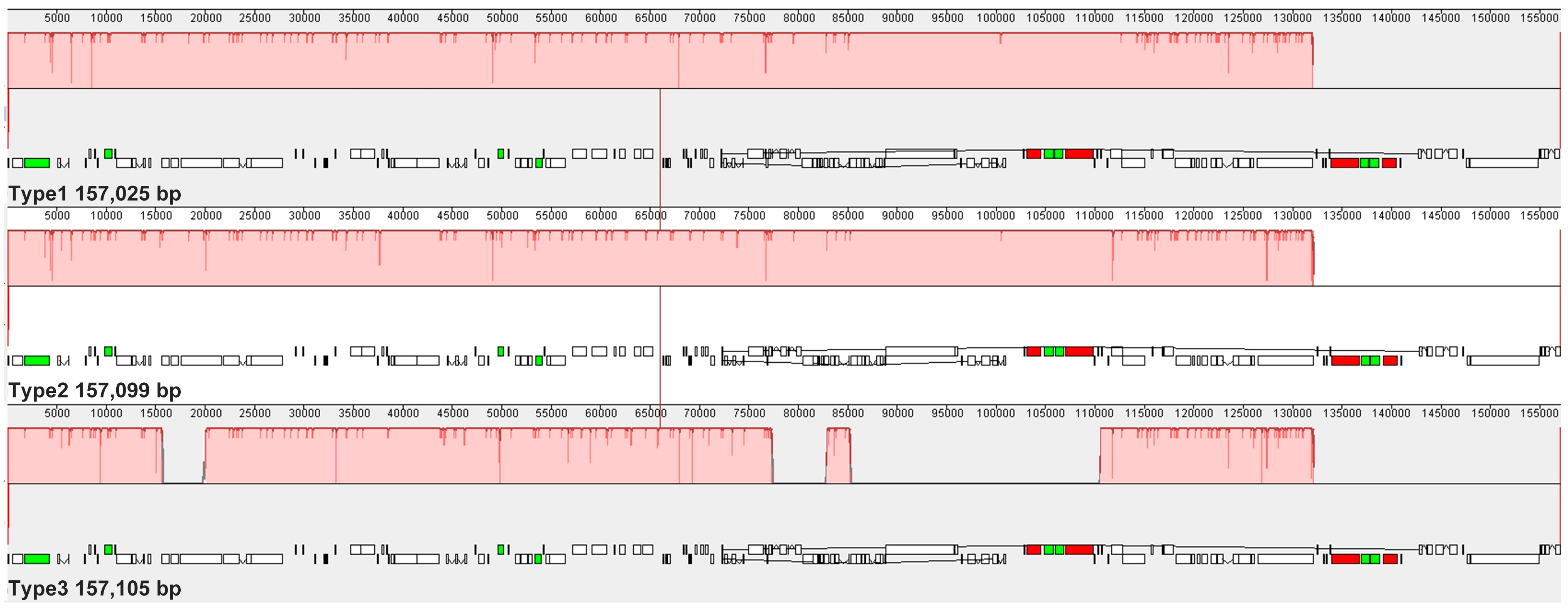
3.1. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Annotation
3.2. IR Boundary Dynamics
3.3. Codon Usage Bias Analysis
3.4. Repeat Sequence Analysis
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.6. Nucleotide Diversity Analysis
3.7. Molecular Marker Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SSR | Simple sequence repeat |
| ML | Maximum-likelihood |
| BI | Bayesian inferences; |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| PCGs | Protein-coding gene sequences |
References
- Chowaniak, M.; Niemiec, M.; Zhu, Z.; Rashidov, N.; Gródek-Szostak, Z.; Szeląg-Sikora, A.; Sikora, J.; Kuboń, M.; Fayzullo, S.A.; Mahmadyorzoda, U.M. Quality assessment of wild and cultivated green tea from different regions of China. Molecules 2021, 26, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Fang, Z.; Hao, T. Genome resequencing reveals an independently originated Camellia sinensis variety–Hainan tea. Agrobiodiversity 2024, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-M.; Meegahakumbura, M.K.; Wambulwa, M.C.; Burgess, K.S.; Möller, M.; Shen, Z.-F.; Li, D.-Z.; Gao, L.-M. Genetic analyses of ancient tea trees provide insights into the breeding history and dissemination of Chinese Assam tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica). Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingjie, Z.; Yajie, Z.; Jinghong, Z.; Jing, Y.; Shaowu, L. Climatic Characteristics and the Condition of Climate Health Recuperation in Wuzhishan County. Nat. Sci. Hainan Univ. 2022, 40, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, C.; Pan, X.; Liang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Assembly and comparative analysis of the first complete mitochondrial genome of Camellia sinensis var. assamica ‘Hainan Dayezhong’, endemic to Hainan Province, China. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Feng, H.; Chang, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Hao, X.; Li, A.l.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; Cui, P. Population sequencing enhances understanding of tea plant evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kan, S.; Liao, X.; Zhou, J.; Tembrock, L.R.; Daniell, H.; Jin, S.; Wu, Z. Plant organellar genomes: Much done, much more to do. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Mao, S.-Y.; Gao, L.-Z. Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: Genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Chen, H.; Xuan, L.; Yang, Y.; Chong, X.; Li, M.; Yu, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, F. Novel molecular markers for Taxodium breeding from the chloroplast genomes of four artificial Taxodium hybrids. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1193023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Pan, L.; Huang, Q.; Hao, Z. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes in Carica species reveals evolutionary relationships of papaya and the development of efficient molecular markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1686914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Duan, W.; Zhao, J.; Jing, Y.; Feng, M.; Kuang, B.; Wei, N.; Chen, B.; Yang, X. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome in Saccharum spp. and related members of ‘Saccharum Complex’. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Cai, P.; Huo, D.; Hong, Y. Comparative chloroplast genomes: Insights into the evolution of the chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis and the phylogeny of Camellia. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W65–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.E.; Searle, S.; Harris, N.; Gibson, M.; Iyer, V.; Richter, J.; Wiel, C.; Bayraktaroglu, L.; Birney, E.; Crosby, M. Apollo: A sequence annotation editor. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7762–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z. Determination of the evolutionary pressure on Camellia oleifera on Hainan Island using the complete chloroplast genome sequence. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tong, W.; Zhao, H.; Ge, R.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Mallano, A.I.; Deng, W. Comparative transcriptomic analysis unveils the deep phylogeny and secondary metabolite evolution of 116 Camellia plants. Plant J. 2022, 111, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Kong, X.; Xia, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Shan, R.; Chen, Z.; You, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y. Genomic analysis of 1,325 Camellia accessions sheds light on agronomic and metabolic traits for tea plant improvement. Nat. Genet. 2025, 57, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Q.; Gong, H.; Yang, Y.; Ye, J.; Jia, X. Unveiling the Molecular Mechanisms of Browning in Camellia hainanica Callus through Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, N.; Johnson, B.S.; Bates, P.D. Metabolically distinct pools of phosphatidylcholine are involved in trafficking of fatty acids out of and into the chloroplast for membrane production. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2768–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Cai, X.; Gong, M.; Xia, M.; Xing, H.; Dong, S.; Tian, S.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y. Complete chloroplast genomes provide insights into evolution and phylogeny of Zingiber (Zingiberaceae). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Li, H.-L.; Li, Z.-X.; Guo, Y.; Fu, X.-Q.; Liao, Q.-H.; Zhang, W.-L.; Liu, Y.-Q. Chloroplast genome comparison and phylogenetic analysis of the commercial variety Actinidia chinensis ‘Hongyang’. Genes 2023, 14, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Qin, Y.; Tang, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.-T.; Xiao, L.-Z.; Luo, H. The chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis var. assamica cv. Duntsa (Theaceae) and comparative genome analysis: Mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationships. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2025, 72, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Peng, D. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of three Paraphalaenopsis (Aeridinae, Orchidaceae) species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Species | Type | Cultivar | Region | Length (bp) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. sinensis ‘hainanensis’ | Type 1 | Anji baicha | Total | 157,025 | 37.30 |
| LSC | 86,586 | 35.33 | |||
| IR-A | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| SSC | 18,277 | 30.55 | |||
| IR-B | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| Type 1 | Fuding dahaocha | Total | 157,025 | 37.30 | |
| LSC | 86,586 | 35.33 | |||
| IR-A | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| SSC | 18,277 | 30.55 | |||
| IR-B | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| Type 1 | Fuyun 6 | Total | 157,025 | 37.30 | |
| LSC | 86,586 | 35.33 | |||
| IR-A | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| SSC | 18,277 | 30.55 | |||
| IR-B | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| Type 1 | Zhongcha 108 | Total | 157,025 | 37.30 | |
| LSC | 86,586 | 35.33 | |||
| IR-A | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| SSC | 18,277 | 30.55 | |||
| IR-B | 26,081 | 42.95 | |||
| Type 2 | Fuding dabaicha | Total | 157,099 | 37.30 | |
| LSC | 86,643 | 35.32 | |||
| IR-A | 26,090 | 42.95 | |||
| SSC | 18,276 | 30.56 | |||
| IR-B | 26,090 | 42.95 | |||
| Type 3 | dayecha | Total | 157,105 | 37.29 | |
| LSC | 86,632 | 35.32 | |||
| IR-A | 26,094 | 42.94 | |||
| SSC | 18,285 | 30.51 | |||
| IR-B | 26,094 | 42.94 |
| Group of Genes | Name of Genes |
|---|---|
| Subunits of NADH-dehydrogenase | ndhA, ndhB(×2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK |
| Subunits of photosystem Ⅰ | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Subunits of photosystem Ⅱ | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ, ycf3 |
| Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petB, petD, petG, petL, petN |
| Subunits of ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF, atpH, atpI |
| Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL |
| Small subunit of ribosome | rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(×2), rps8, rps11, rps12(×2), rps14, rps15, rps16, rps18, rps19 |
| Large subunit of ribosome | rpl2(×2), rpl14, rpl16, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(×2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| DNA dependent RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2 |
| rRNA genes | rrn4.5S(×2), rrn5S(×2), rrn16S(×2), rrn23S(×2) |
| tRNA genes | trnA-UGC(×2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnfM-CAU, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU(×2), trnI-GAU(×2), trnK-UUU, trnL-CAA(×2), trnL-UAA, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(×2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(×2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-CGU, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(×2), trnV-UAC, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA |
| Maturase | matK |
| c-type cytochrom synthesis gene | ccsA |
| Envelope membrane protein | cemA |
| Protease | clpP |
| Subunit of Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase | accD |
| Translational initiation factor | infA |
| Genes of unknown functions Open Reading | ycf1(×2), ycf2(×2), ycf4, ycf15(×2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Pan, L.; Du, X.; Hao, Z. Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Six Camellia sinensis Accessions: Genetic Divergence, Adaptive Evolution, and Molecular Marker Development. Biology 2026, 15, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010007
Fu Y, Pan L, Du X, Hao Z. Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Six Camellia sinensis Accessions: Genetic Divergence, Adaptive Evolution, and Molecular Marker Development. Biology. 2026; 15(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yanli, Lei Pan, Xiaoxi Du, and Zhigang Hao. 2026. "Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Six Camellia sinensis Accessions: Genetic Divergence, Adaptive Evolution, and Molecular Marker Development" Biology 15, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010007
APA StyleFu, Y., Pan, L., Du, X., & Hao, Z. (2026). Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Six Camellia sinensis Accessions: Genetic Divergence, Adaptive Evolution, and Molecular Marker Development. Biology, 15(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology15010007






