Ferroptosis-Linked Six-Gene Panel Enables Machine Learning-Assisted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. Variance-Stabilising Transformation and Gene Symbol Annotation
2.4. Curation of Ferroptosis-Related Genes
2.5. Wilcoxon Analysis of Ferroptosis-Related Gene Expression
2.6. Survival Analysis and Prognostic Gene Selection
2.7. Pathway Activity Scoring and Correlation with Prognostic Genes
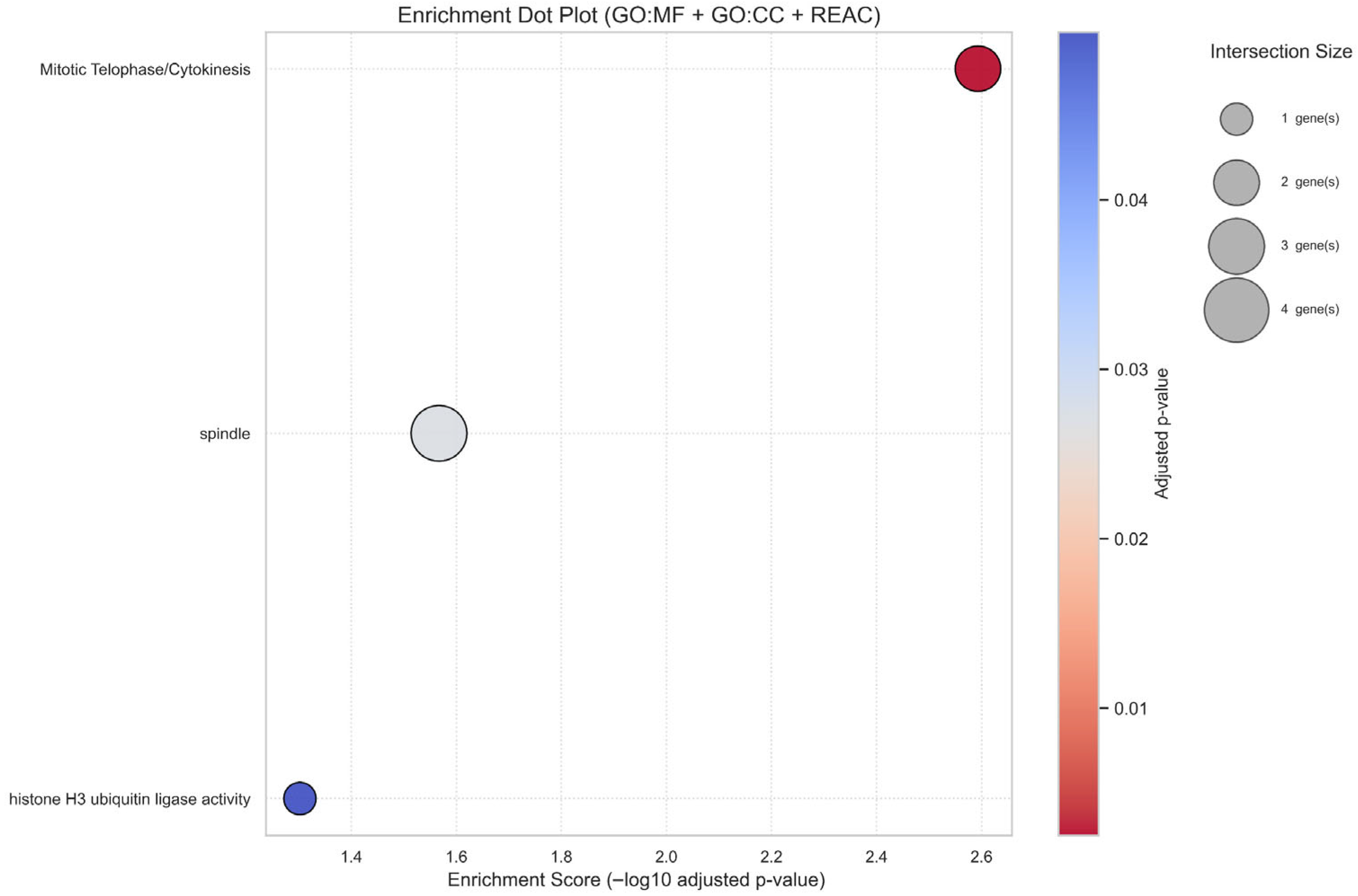
2.8. Functional Enrichment Analysis
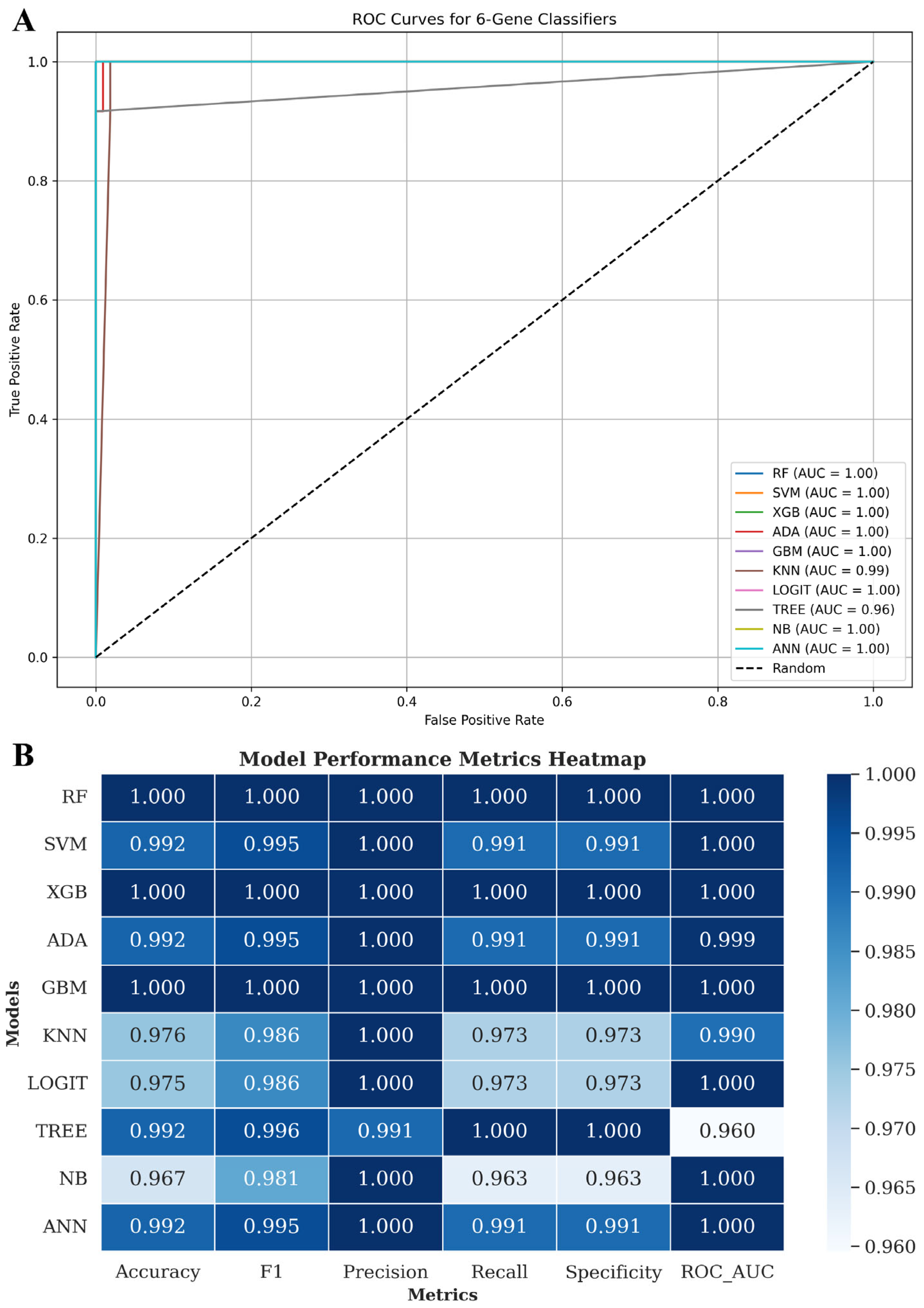
2.9. Machine Learning Classification Using Six-Gene Signature
2.10. Targeted Drug Prediction and Gene–Drug Correlation Analysis
3. Results
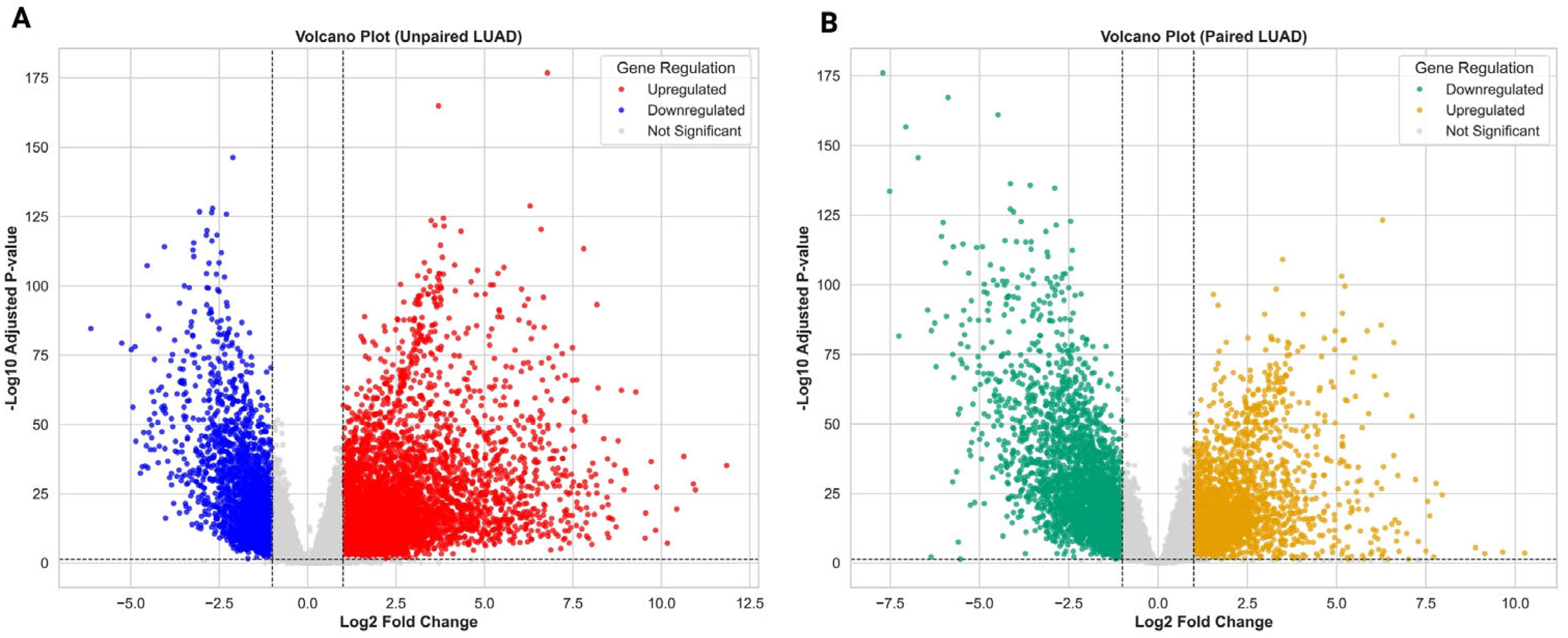
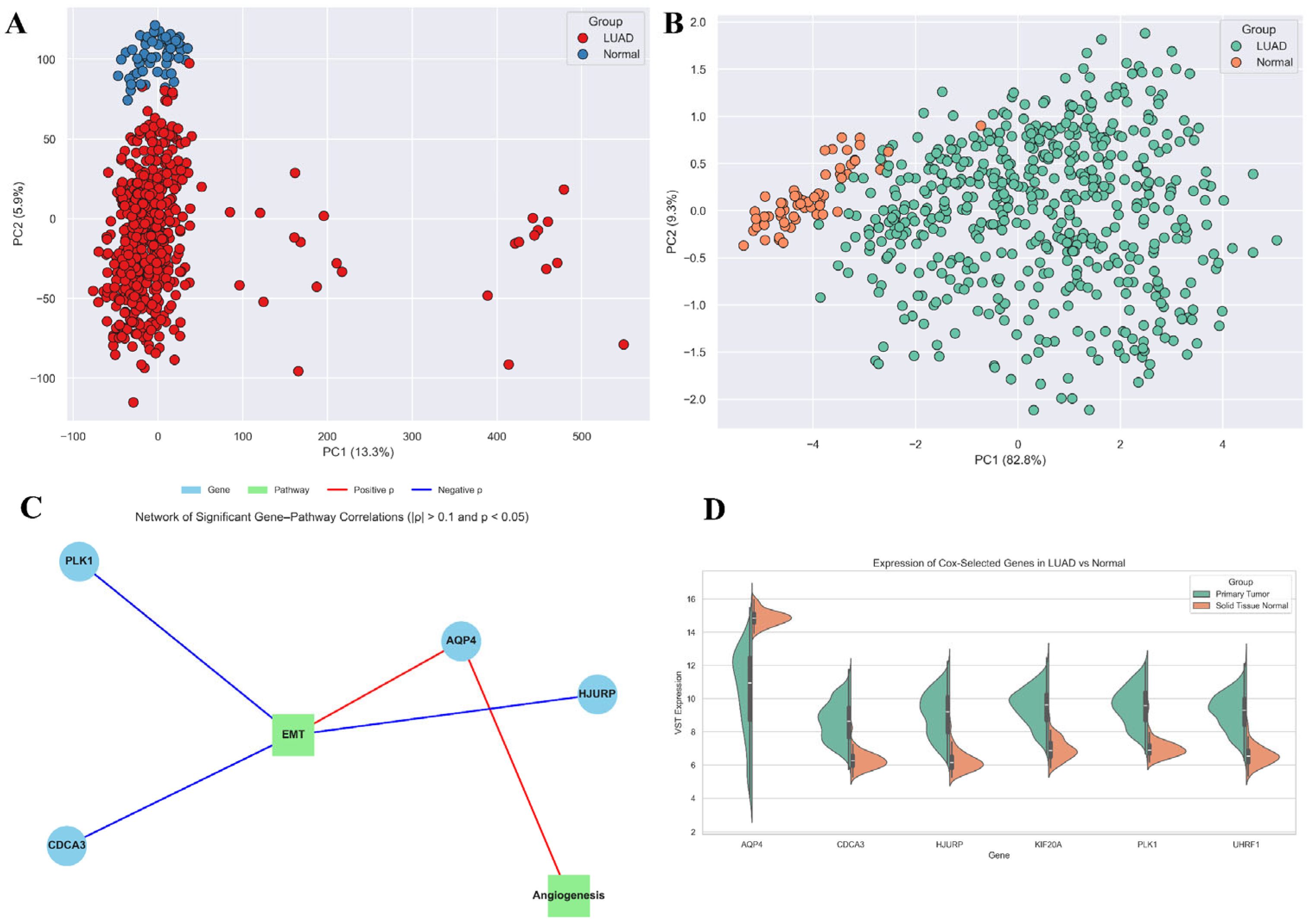
3.1. Transcriptomic Landscape of LUAD Reveals Widespread Dysregulation
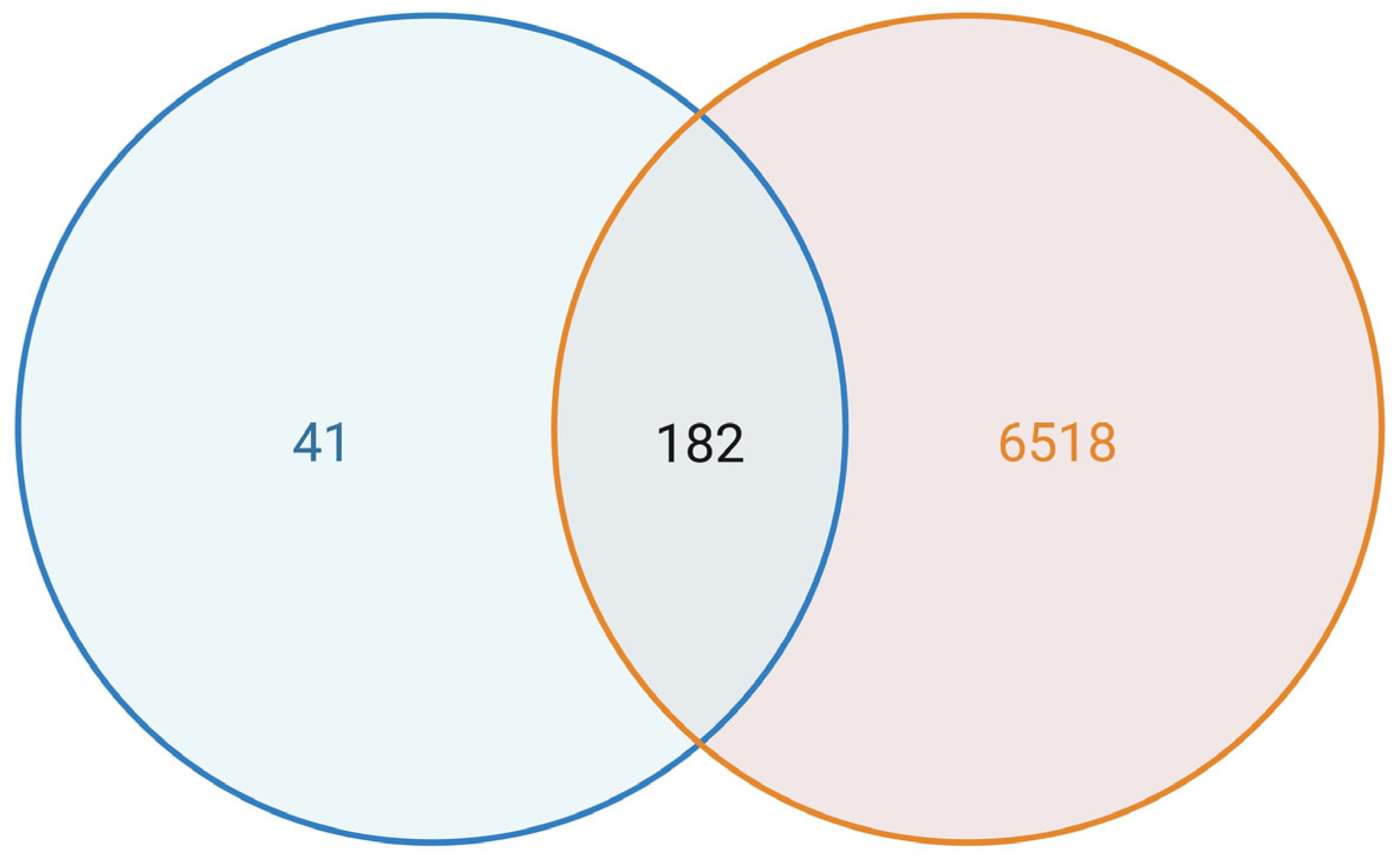
3.2. Normalisation and Ferroptosis Gene Annotation Reveal a Refined Expression Matrix for LUAD
3.3. Dysregulation of Ferroptosis-Related Genes in LUAD Tumours
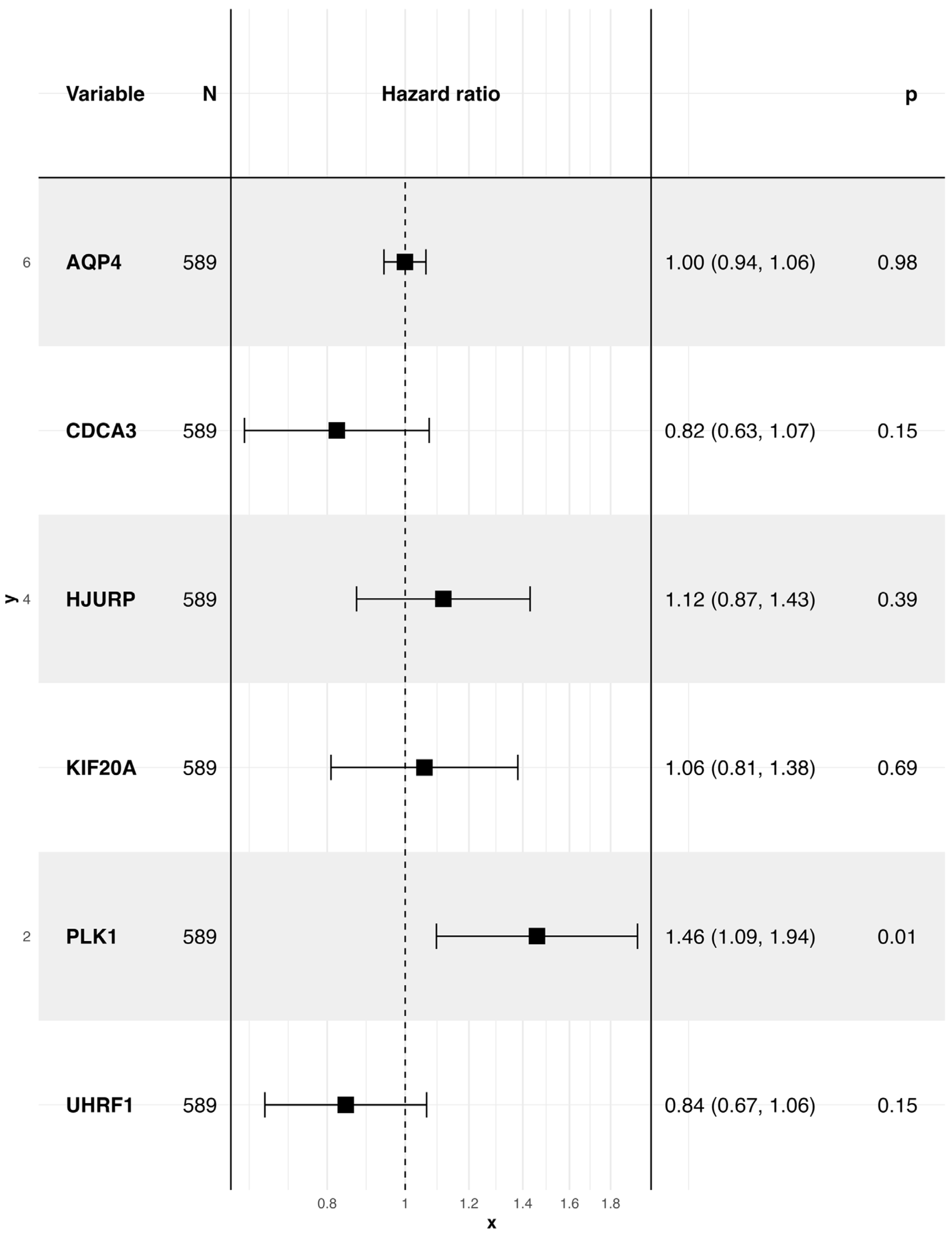
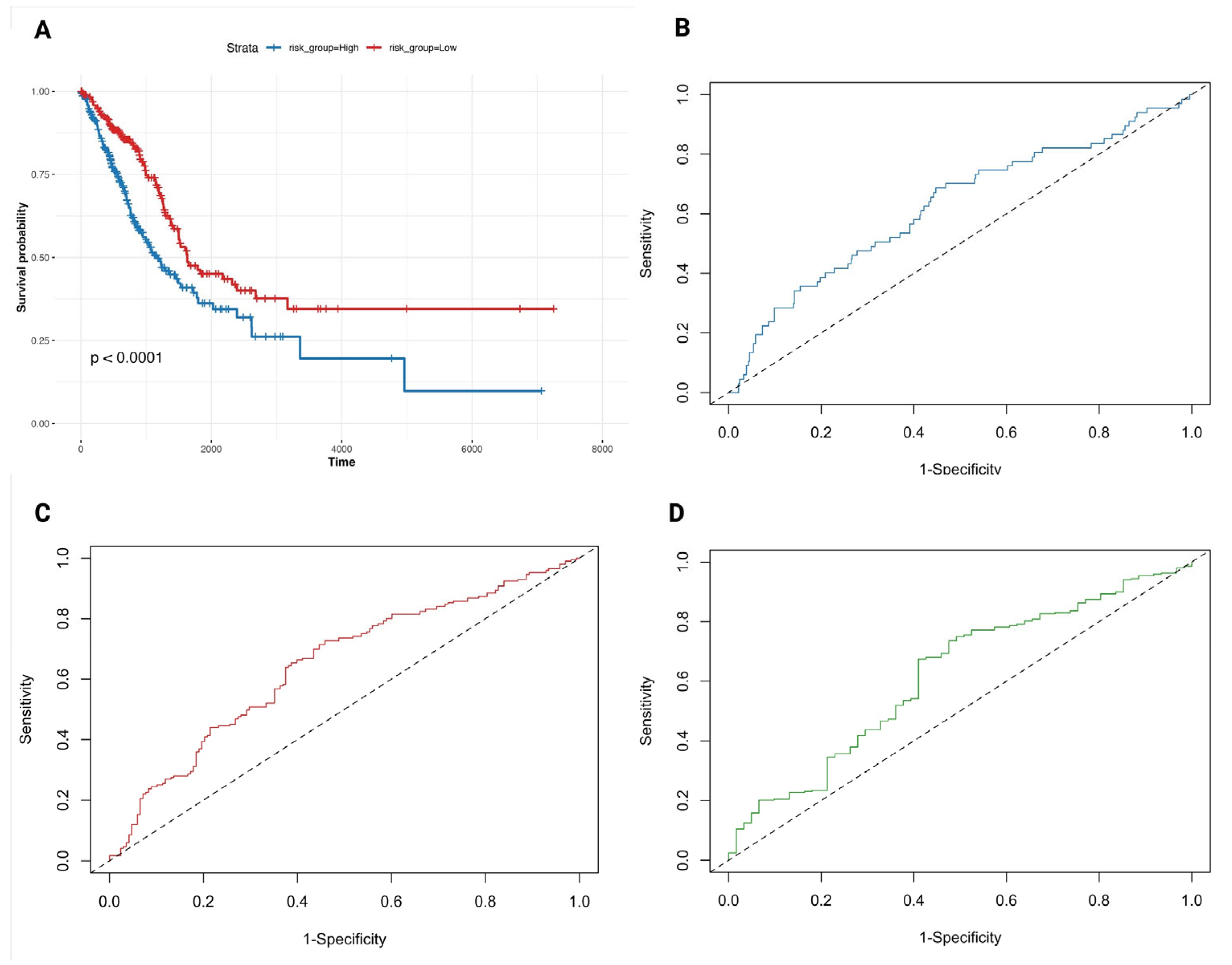
3.4. A Ferroptosis-Derived Signature Stratifies LUAD Patients by Survival Risk
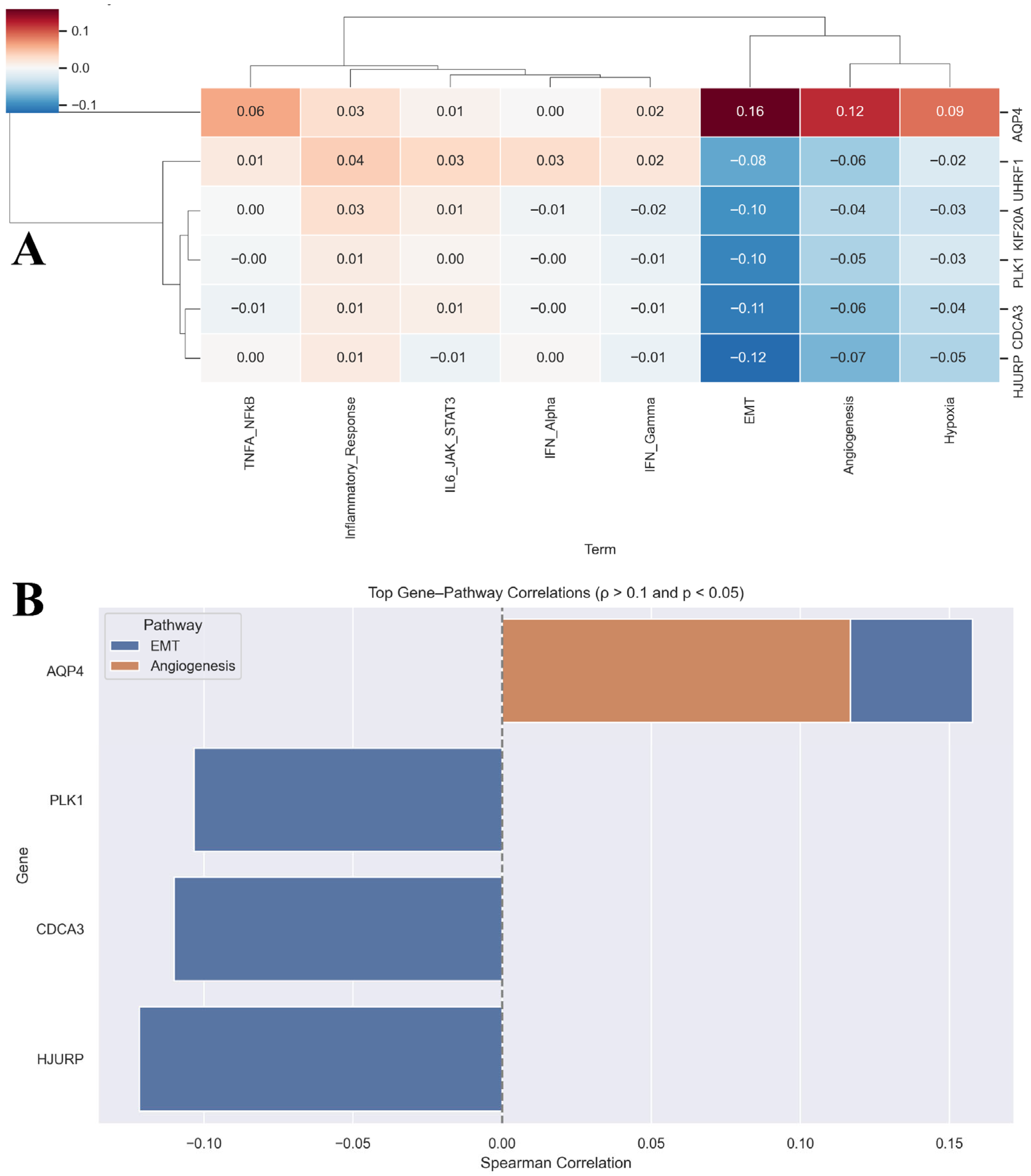
3.5. Prognostic Ferroptosis Genes Associate with LUAD Hallmark Pathways
3.6. Prognostic Ferroptosis Genes Converge on Cell Cycle and Genomic Integrity Pathways
3.7. Six-Gene Proliferation-Linked Signature Discriminates LUAD from Normal Tissue Across Machine Learning Models
3.8. Gene-Drug Correlations Highlight Candidate Vulnerabilities but Require LUAD-Specific Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| NSCLC | Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| ssGSEA | Single-Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| VST | Variance-Stabilising Transformation |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| XGB | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| ADA | Adaptive Boosting |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| KNN | k-Nearest Neighbours |
| LOGIT | Logistic Regression |
| NB | Naïve Bayes |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| APC | Article Processing Charge |
| PLK1 | Polo-Like Kinase 1 |
| DAMPs | Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandara, D.R.; Hammerman, P.S.; Sos, M.L.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Hirsch, F.R. Squamous cell lung cancer: From tumor genomics to cancer therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.L.; Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. ALK-positive lung cancer: A moving target. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguet, J.; Smith, K.H.; Bramlage, P. Targeted therapies for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer—Recent advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanton, C.; Govindan, R. Clinical implications of genomic discoveries in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzyz, P. Methyl groups sink into phospholipids and histones. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 342–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Vanden Berghe, T. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Santos, M.J.; García-Martín, S.; Fustero-Torre, C.; Di Domenico, T.; Gómez-López, G.; Al-Shahrour, F. Bioinformatics roadmap for therapy selection in cancer genomics. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3881–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Dong, X. Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Green, M.; Choi, J.E.; Gijón, M.; Kennedy, P.D.; Johnson, J.K.; Liao, P.; Lang, X.; Kryczek, I.; Sell, A.; et al. CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 569, 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpman, D.; Tontanahal, A. Extracellular vesicles in renal inflammatory and infectious diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Guo, W.; Lv, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Tan, F.; Li, N.; Xue, Q.; Gao, Y.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of ferroptosis regulators in lung adenocarcinomas identifies prognostic and immunotherapy-related biomarkers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 587436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L. A nomogram to predict the cancer-specific survival of stage II–IV Epithelial ovarian cancer after bulking surgery and chemotherapy. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4344–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lercher, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Popa, A.M.; Caldera, M.; Schlapansky, M.F.; Baazim, H.; Agerer, B.; Gürtl, B.; Kosack, L.; Majek, P.; et al. Type I interferon signaling disrupts the hepatic urea cycle and alters systemic metabolism to suppress T cell function. Immunity 2019, 51, 1074–1087.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Shen, J.; Mao, L.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Hongbin, S. Cancer associated fibroblast secreted miR-432-5p targets CHAC1 to inhibit ferroptosis and promote acquired chemoresistance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, K. Bulk RNA-seq and scRNA-seq reveal SLC7A11, a key regulatory molecule of ferroptosis, is a prognostic-related biomarker and highly related to the immune system in lung adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2023, 102, e34876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Chard Dunmall, L.S.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y. Ferroptosis-related genes are potential therapeutic targets and the model of these genes influences overall survival of NSCLC patients. Cells 2022, 11, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X. Ferroptosis in immune cells: Implications for tumor immunity and cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025, 84, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, G.; Xiao, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Cao, X. A ferroptosis-related gene signature associated with immune landscape and therapeutic response in osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1024915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Hu, Q. Ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and identifying potential therapeutic drug in EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Qu, Z.; Li, D.; Bai, F.; Xing, J.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yao, L.; Xu, Q. Identification of a prognostic ferroptosis-related lncRNA signature in the tumor microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kica, P.; Lichołai, S.; Orzechowski, M.; Malawski, M. Accelerating Cloud-Based Transcriptomics: Performance Analysis and Optimization of the STAR Aligner Workflow. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science, Singapore, 7–9 July 2025; pp. 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Smedley, D.; Haider, S.; Ballester, B.; Holland, R.; London, D.; Thorisson, G.; Kasprzyk, A. BioMart–biological queries made easy. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Yuan, X.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Bao, J.; Ning, Y.; Peng, L. FerrDb V2: Update of the manually curated database of ferroptosis regulators and ferroptosis-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D571–D582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R.; Kolde, M.R. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 1.0.12. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/index.html (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Therneau, T.; Lumley, T. survival: Survival Analysis. R package version 3.5-5. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Blanche, P.; Blanche, M.P. timeROC: Time-Dependent ROC Curve and AUC for Censored Survival Data. R package version 0.4. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=timeROC (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, X.; Peltz, G. GSEApy: A comprehensive package for performing gene set enrichment analysis in Python. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g: Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankavaram, U.T.; Varma, S.; Kane, D.; Sunshine, M.; Chary, K.K.; Reinhold, W.C.; Pommier, Y.; Weinstein, J.N. CellMiner: A relational database and query tool for the NCI-60 cancer cell lines. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, V.A.D.; Park, S.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S. Ectopically expressed membrane-bound form of IL-9 exerts immune-stimulatory effect on CT26 colon carcinoma cells. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.-L.; Huang, Z.-J.; Lin, Z.-T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhan, X. Machine learning identifies Pan-cancer landscape of Nrf2 oxidative stress response pathway-related genes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8450087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, N.; Ni, N.; Bai, X.; Liu, N. Lipid peroxidation, GSH depletion, and SLC7A11 inhibition are common causes of EMT and ferroptosis in A549 cells, but different in specific mechanisms. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X. PLK1, a potential target for cancer therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.-F.; Ma, P.C. Emerging insights of tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer targeted therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrumaihi, F. Ferroptosis-Linked Six-Gene Panel Enables Machine Learning-Assisted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology 2025, 14, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091280
Alrumaihi F. Ferroptosis-Linked Six-Gene Panel Enables Machine Learning-Assisted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091280
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrumaihi, Faris. 2025. "Ferroptosis-Linked Six-Gene Panel Enables Machine Learning-Assisted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Biology 14, no. 9: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091280
APA StyleAlrumaihi, F. (2025). Ferroptosis-Linked Six-Gene Panel Enables Machine Learning-Assisted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology, 14(9), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091280






