The BVES Gene Regulates the Homeostasis of Deer Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Wnt Signaling
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Expression of the BVES Gene in Antler Tissue at Different Growth Stages
2.2.2. Cloning of the CDS Region of the BVES Gene from the Antler of the Tarim Red Deer and Construction of an Overexpression Vector
2.2.3. BVES Protein Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2.4. Isolation of Deer Antler MSCs
2.2.5. BVES Overexpressing Lentivirally Transfected Antler MSCs
2.2.6. Transfection of Antler MSCs by siRNA
2.2.7. Assay for Cell Count
2.2.8. Cell Proliferation Capacity Assay
2.2.9. Detection of Genes Related to the Wnt Pathway
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
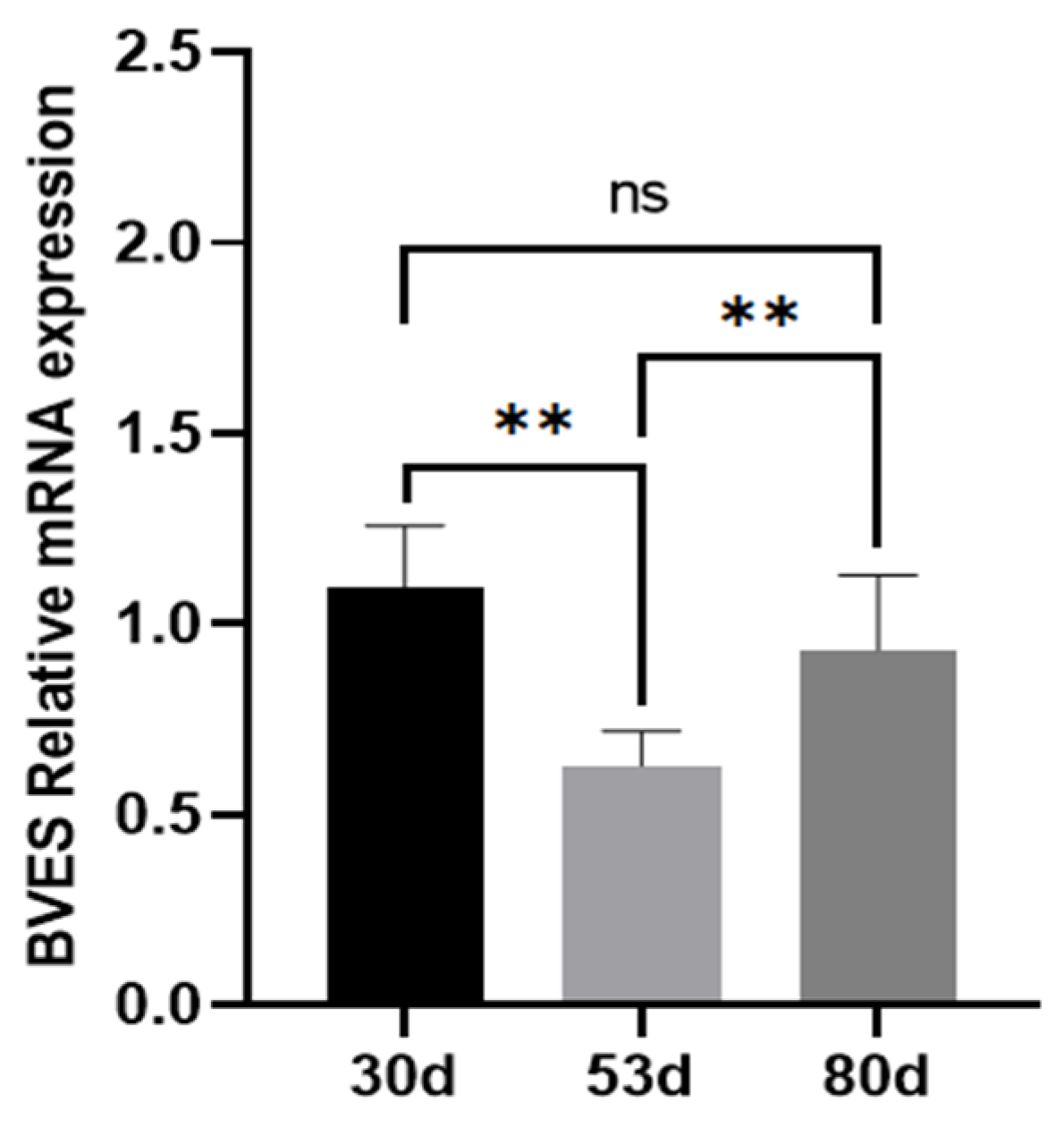
3.1. Expression of the BVES Gene in Antler Tissue at Different Growth Stages
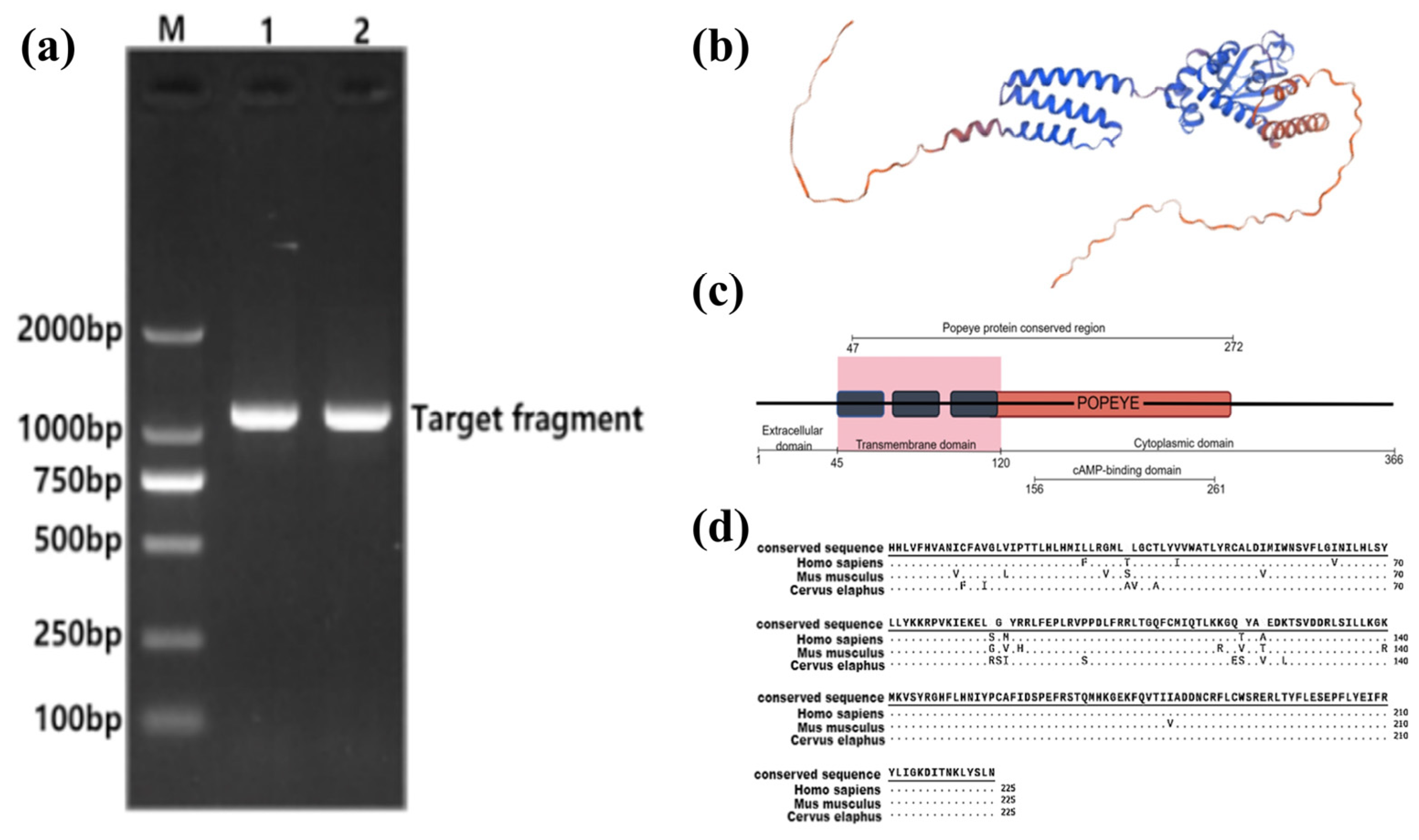
3.2. Construction and Protein Structure Prediction of the BVES Overexpression Vector in Tarim Red Deer Antler
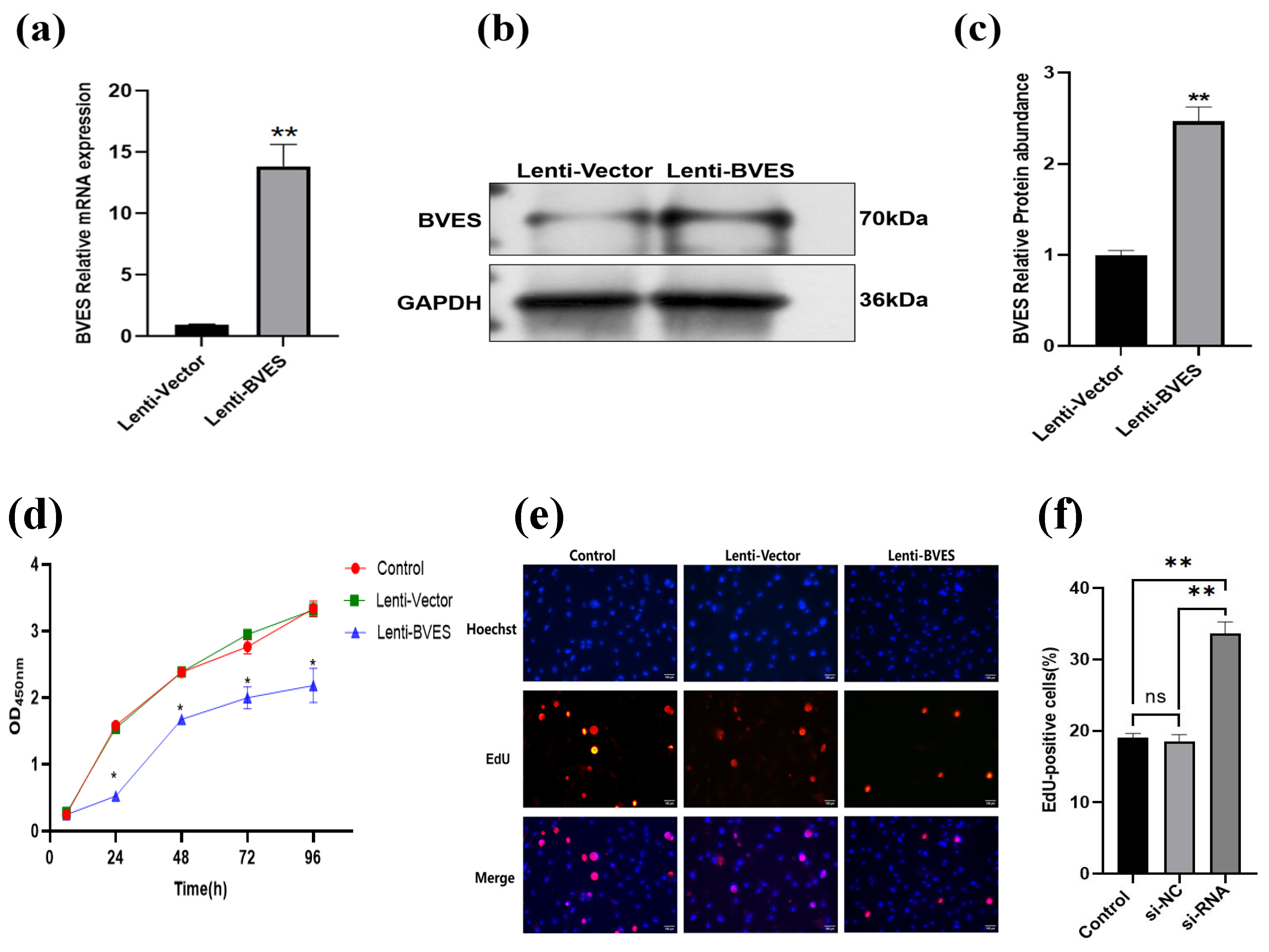
3.3. Effect of BVES Overexpression on the Proliferative Capacity of Antler MSCs
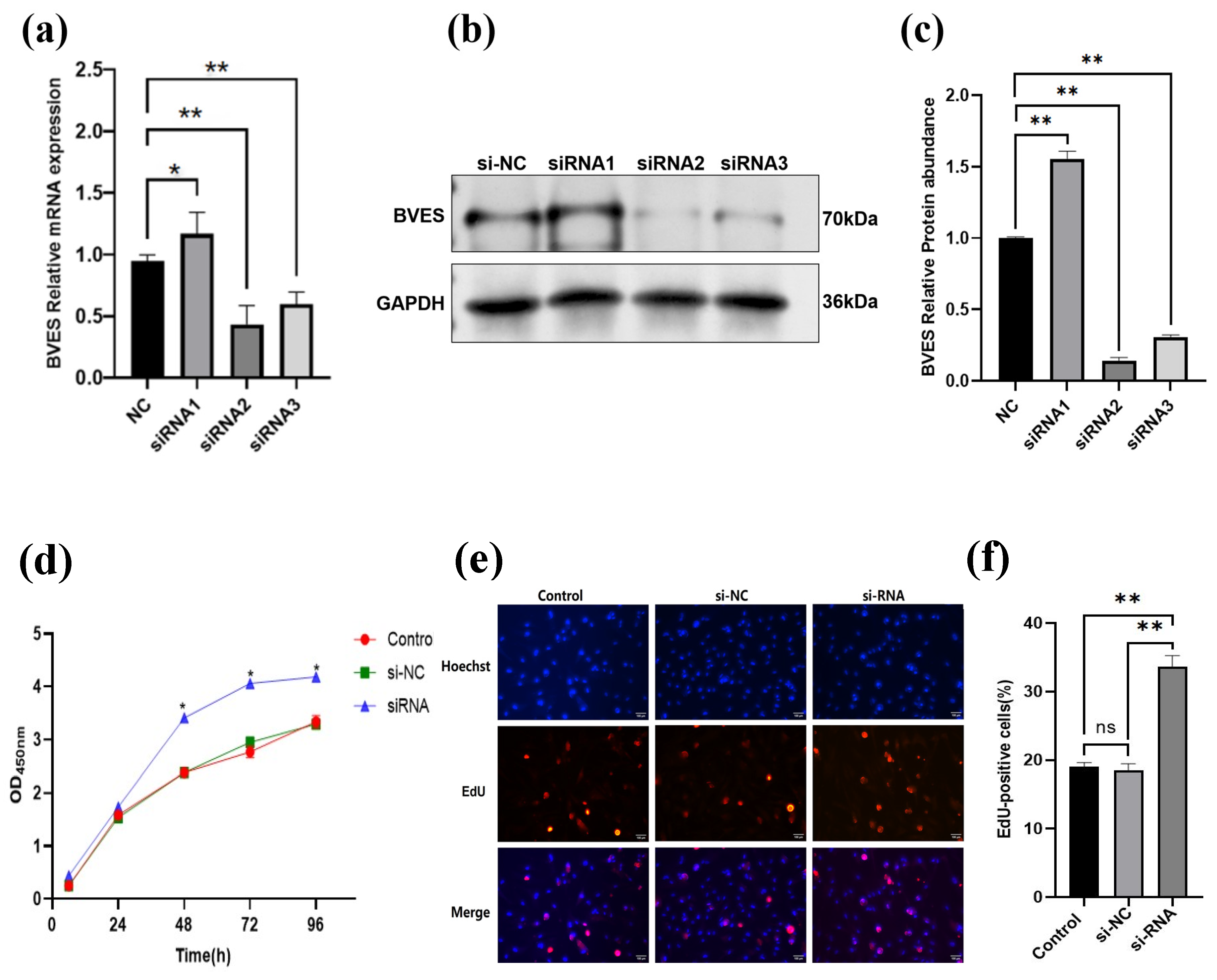
3.4. The Effect of Interfering with BVES on the Proliferation Ability of Deer Antler MSCs
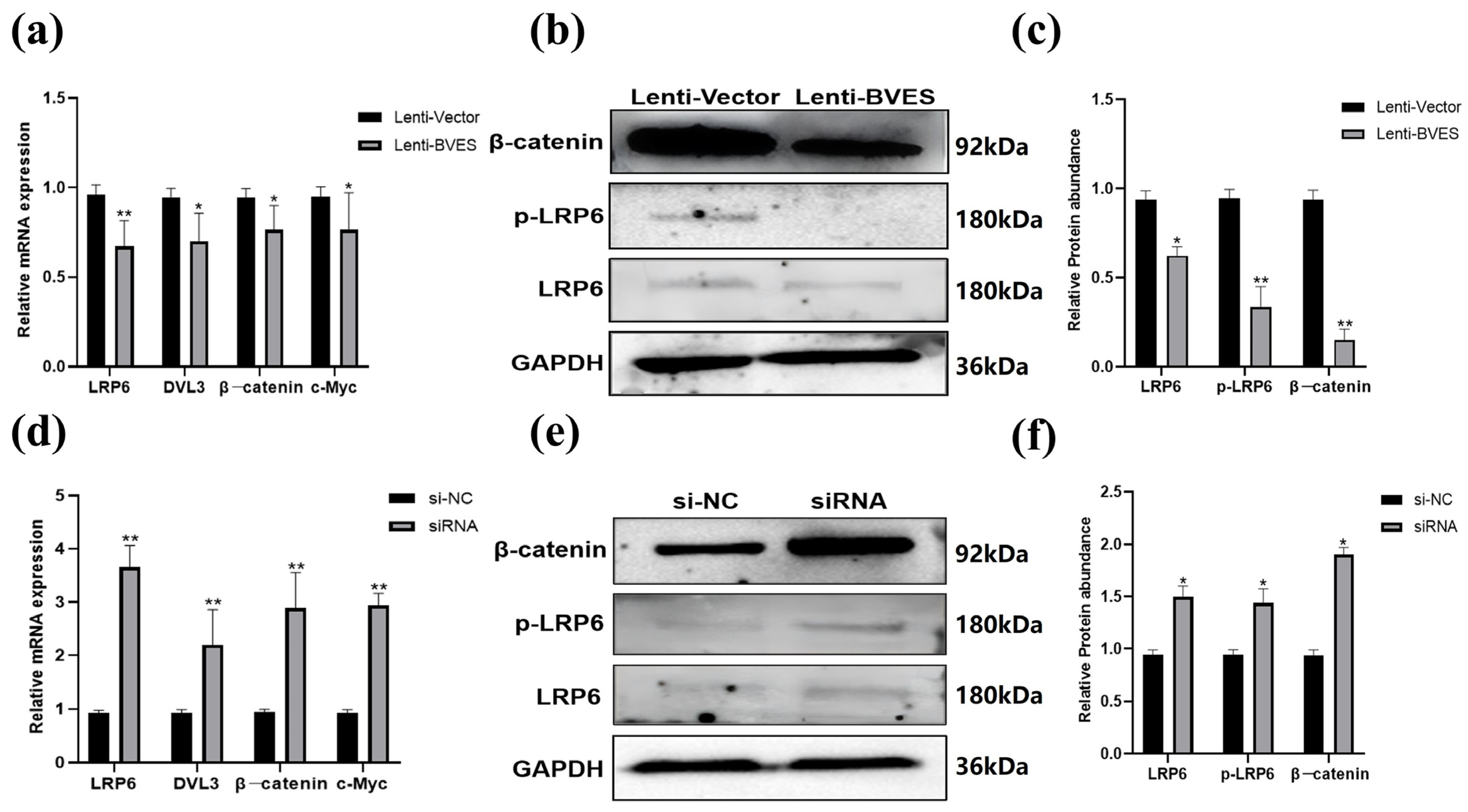
3.5. Effect of the BVES Gene on Wnt Signaling in Deer Antler MSCs Proliferation
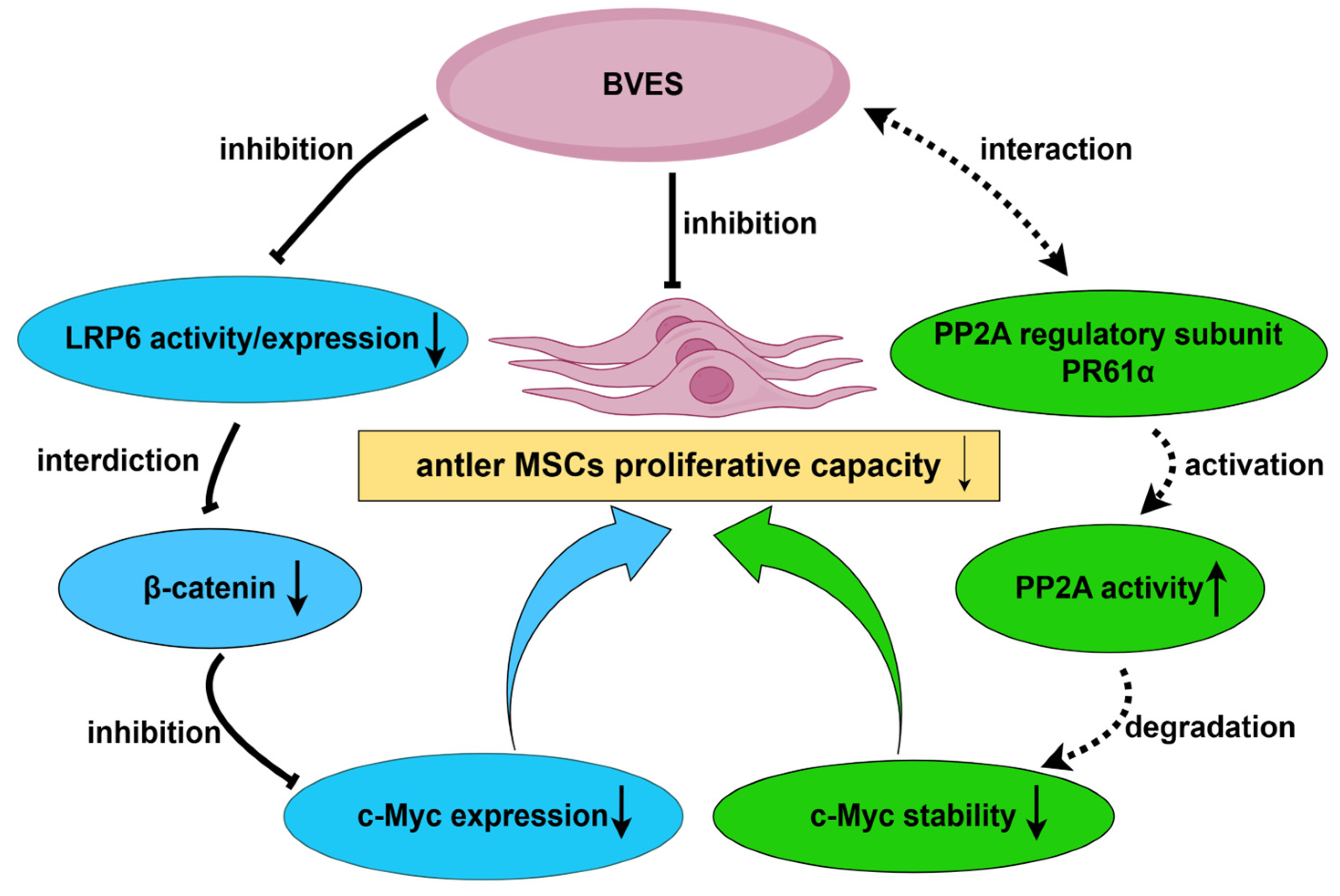
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; McMahon, C. Deer antler—A novel model for studying organ regeneration in mammals. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 56, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, D.; Bader, D. Cloning and expression of hbves, a novel and highly conserved mRNA expressed in the developing and adult heart and skeletal muscle in the human. Mamm. Genome 1999, 10, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, D.; Zavaljevskib, M.; Streiff, N.; Bader, D. bves: A novel gene expressed during coronary blood vessel development. Dev. Biol. 1999, 209, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrée, B.; Hillemann, T.; Kessler-Icekson, G.; Schmitt-John, T.; Jockusch, H.; Arnold, H.-H.; Brand, T. Isolation and characterization of the novel popeye gene family expressed in skeletal muscle and heart. Dev. Biol. 2000, 223, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parang, B.; Thompson, J.J.; Williams, C.S. Blood Vessel Epicardial Substance (BVES) in junctional signaling and cancer. Tissue Barriers 2018, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, T.; Simrick, S.L.; Poon, K.L.; Schindler, R.F.R. The cAMP-binding Popdc proteins have a redundant function in the heart. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, T. POPDC proteins and cardiac function. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Hawes, S.E.; Stern, J.E.; Wiens, L.; Lu, H.; Dong, Z.M.; Jordan, C.D.; Kiviat, N.B.; Vesselle, H. DNA Methylation in Tumor and Matched Normal Tissues from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Che, X. MBNL1-AS1 attenuates tumor cell proliferation by regulating the miR-29c-3p/BVES signal in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 50, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.S.; Zhang, B.; Smith, J.J.; Jayagopal, A.; Barrett, C.W.; Pino, C.; Russ, P.; Presley, S.H.; Peng, D.; Rosenblatt, D.O.; et al. BVES regulates EMT in human corneal and colon cancer cells and is silenced via promoter methylation in human colorectal carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4056–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayagopal, A.; Yang, J.; Haselton, F.R.; Chang, M.S. Tight Junction–Associated Signaling Pathways Modulate Cell Proliferation in Uveal Melanoma. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.K.; Short, S.P.; Barrett, C.W.; Mittal, M.K.; Keating, C.E.; Thompson, J.J.; Harris, E.I.; Revetta, F.; Bader, D.M.; Brand, T.; et al. BVES Regulates Intestinal Stem Cell Programs and Intestinal Crypt Viability after Radiation. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salik, B.; Yi, H.; Hassan, N.; Santiappillai, N.; Vick, B.; Connerty, P.; Duly, A.; Trahair, T.; Woo, A.J.; Beck, D.; et al. Targeting RSPO3-LGR4 Signaling for Leukemia Stem Cell Eradication in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 263–278.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleas, J.P.; D’ARcangelo, E.; Huang, L.; Karoubi, G.; Nostro, M.C.; McGuigan, A.P.; Waddell, T.K. Assembly of lung progenitors into developmentally-inspired geometry drives differentiation via cellular tension. Biomaterials 2020, 254, 120128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Weng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ni, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, P.; et al. The lncRNA NEAT1 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression via interacting with DDX5. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tang, S. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Lv, H.; Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Gao, Q.; Han, C. Screening of Transcriptional Differential Genes in Antler After Top Pruning and Expression Characteristics of BVES Gene. Pak. J. Zool. 2024, 56, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Cong, S.; Tan, J.; Hou, W.; Ma, F.; Zheng, L. Establishment of a neutralization assay for Nipah virus using a high-titer pseudovirus system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussau, S.; Lytvyn, V.; Simoneau, M.; Guilbault, C.; Leclerc, M.; Nazemi-Moghaddam, N.; Coulombe, N.; Elahi, S.M.; McComb, S.; Gilbert, R. Packaging cells for lentiviral vectors generated using the cumate and coumermycin gene induction systems and nanowell single-cell cloning. Mol. Ther.—Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 29, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.S.; Allen, S.; Faucheux, C.; Althnaian, T.; Mount, J.G. Deer antlers: A zoological curiosity or the key to understanding organ regeneration in mammals? Am. J. Anat. 2005, 207, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Clark, D.E.; Lord, E.A.; Stanton, J.A.L.; Suttie, J.M. Sampling technique to discriminate the different tissue layers of growing antler tips for gene discovery. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmova, E.; Bartos, L.; Kotrba, R.; Bubenik, G.A. Effect of different factors on proliferation of antler cells, cultured in vitro. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, D.; Pang, X.; Guo, J.; Li, T.; Song, J.; Peng, Y. Deer antler stem cells immortalization by modulation of hTERT and the small extracellular vesicles characters. Front. Veter. Sci. 2024, 11, 1440855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. Induction of Chondrogenic Differentiation and Expression of c-Myc Gene in Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Tarim Deer Antler. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cegielski, M.; Izykowska, I.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Gworys, B.; Zabel, M.; Dziegiel, P. Histological studies of growing and mature antlers of red deer stags (Cervus elaphus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2009, 38, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyurjan, I.; Molnar, A.; Borsy, A.; Steger, V.; Hackler, L.J.; Zomborszky, Z.; Papp, P.; Duda, E.; Deak, F.; Lakatos, P.; et al. Gene expression dynamics in deer antler: Mesenchymal differentiation toward chondrogenesis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2006, 277, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.K.; Li, C.; Asher, G.; Wells, D.N.; Oback, B. Red Deer Cloned from Antler Stem Cells and Their Differentiated Progeny1. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, W.; Zhai, J.; Wang, W.; He, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, C. High quality repair of osteochondral defects in rats using the extracellular matrix of antler stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2024, 16, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C. The Mechanism of the Influence of Oncogene c-Myc on the Regulation of Deer Antler Development. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, A.; Breher, S.S.; Waldeyer, C.; Schindler, R.F.R.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Rinné, S.; Wischmeyer, E.; Schlueter, J.; Becher, J.; Simrick, S.; et al. Popeye domain containing proteins are essential for stress-mediated modulation of cardiac pacemaking in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Tian, R.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Peng, F.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, F.; et al. The expression of BVES in gallbladder cancer and its inhibitory effect on the proliferation and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells by overexpression. Tumori 2018, 38, 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Pan, W.; Farr, G.R.; Flynn, C.; Yuan, H.; Takada, S.; Kimelman, D.; Li, L.; et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5 binds to Axin and regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, J.G.; Muzylak, M.; Allen, S.; Althnaian, T.; McGonnell, I.M.; Price, J.S. Evidence that the canonical Wnt signalling pathway regulates deer antler regeneration. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.J.; Short, S.P.; Parang, B.; Brown, R.E.; Li, C.; Ng, V.H.; Saito-Diaz, K.; Choksi, Y.A.; Washington, M.K.; Smith, J.J.; et al. Blood vessel epicardial substance reduces LRP6 receptor and cytoplasmic β-catenin levels to modulate Wnt signaling and intestinal homeostasis. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parang, B.; Kaz, A.M.; Barrett, C.W.; Short, S.P.; Ning, W.; Keating, C.E.; Mittal, M.K.; Naik, R.D.; Washington, M.K.; Revetta, F.L.; et al. BVES regulates c-Myc stability via PP2A and suppresses colitis-induced tumourigenesis. Gut 2016, 66, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorth, P. A modular misexpression screen in Drosophila detecting tissue-specific phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12418–12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, J.A.; Freedman, N.J.; Lefkowit, R.J. G protein–coupled receptor kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 653–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence | Annealing Temperature | Fragment Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| BVES-1 | F: ATGCGAGGAATTTTCAAGATGAATTATACT | 63 | 1098 |
| R: AGGCCACTGACGAACTTTAAATGTATTTG | |||
| BVES | F: TGACGACCGTCTGAGTATTCTCCTG | 61 | 133 |
| R: TCACCTTTGTGCATCTGGGTTGATC | |||
| LRP6 | F: CCATCCGCCGCTCCTTCATAG | 58 | 127 |
| R: TCAGTGCCAGTGTCTGTCCAATAG | |||
| DVL3 | F: GAGCACCATCACCTCCACCAGCTCC | 61 | 161 |
| R: TGAGCCACATTCGGTCACGGACCTCT | |||
| β-catenin | F: TGCTGAAGGTGCTGTCTGTCTG | 58 | 133 |
| R: TTCCGTAGAGTCCAAAGGCAGTTC | |||
| c-Myc | F: CAAATGTGCCAGCCCAAGGTTTTC | 65 | 130 |
| R: CTCTGGGATCTGGTCACGAAGAGCA | |||
| GAPDH | F: TGTTTGTGATGGGCGTGAACCA | 55 | 154 |
| R: ATGGCGTGGACAGTGGTCATAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Lin, C.; Xiang, X.; Yang, C.; Han, C.; Gao, Q. The BVES Gene Regulates the Homeostasis of Deer Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Wnt Signaling. Biology 2025, 14, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091210
Chen H, Lin C, Xiang X, Yang C, Han C, Gao Q. The BVES Gene Regulates the Homeostasis of Deer Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Wnt Signaling. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091210
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hong, Chuan Lin, Xin Xiang, Chenchen Yang, Chunmei Han, and Qinghua Gao. 2025. "The BVES Gene Regulates the Homeostasis of Deer Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Wnt Signaling" Biology 14, no. 9: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091210
APA StyleChen, H., Lin, C., Xiang, X., Yang, C., Han, C., & Gao, Q. (2025). The BVES Gene Regulates the Homeostasis of Deer Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Wnt Signaling. Biology, 14(9), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091210





