Organization of Serotonergic Cell Populations in the Brain and Spinal Cord of the Short-Lived African Turquoise Killifish
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Immunofluorescence
2.2. Specificity of the Primary Antibody
2.3. Imaging
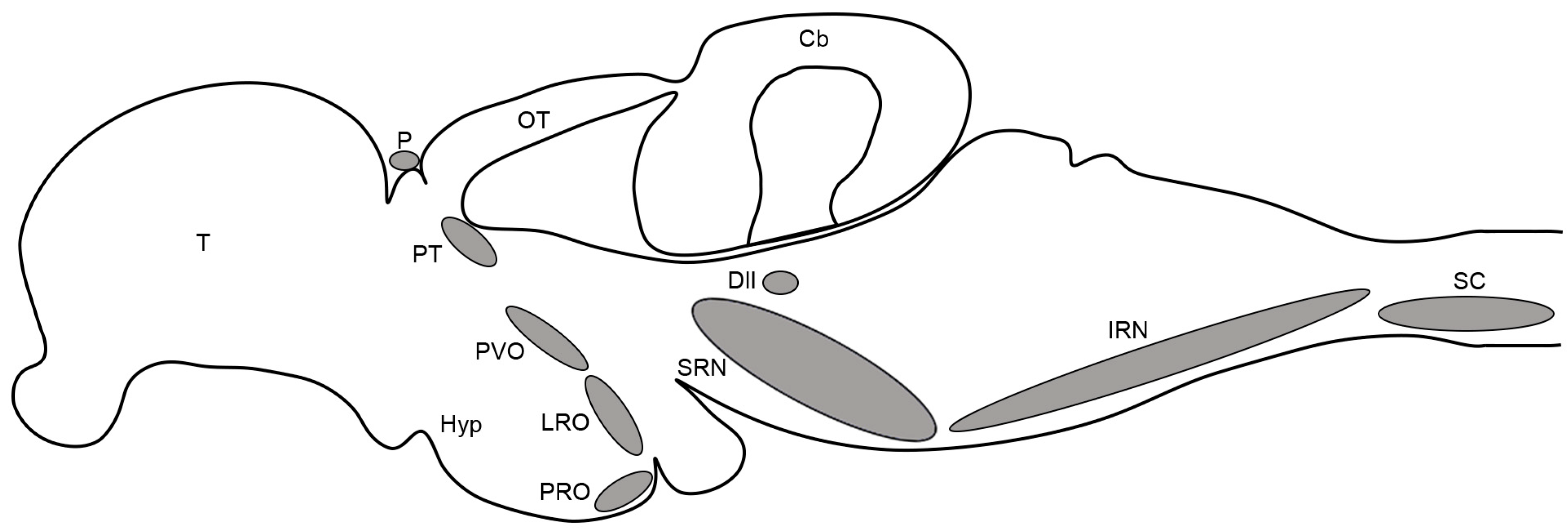
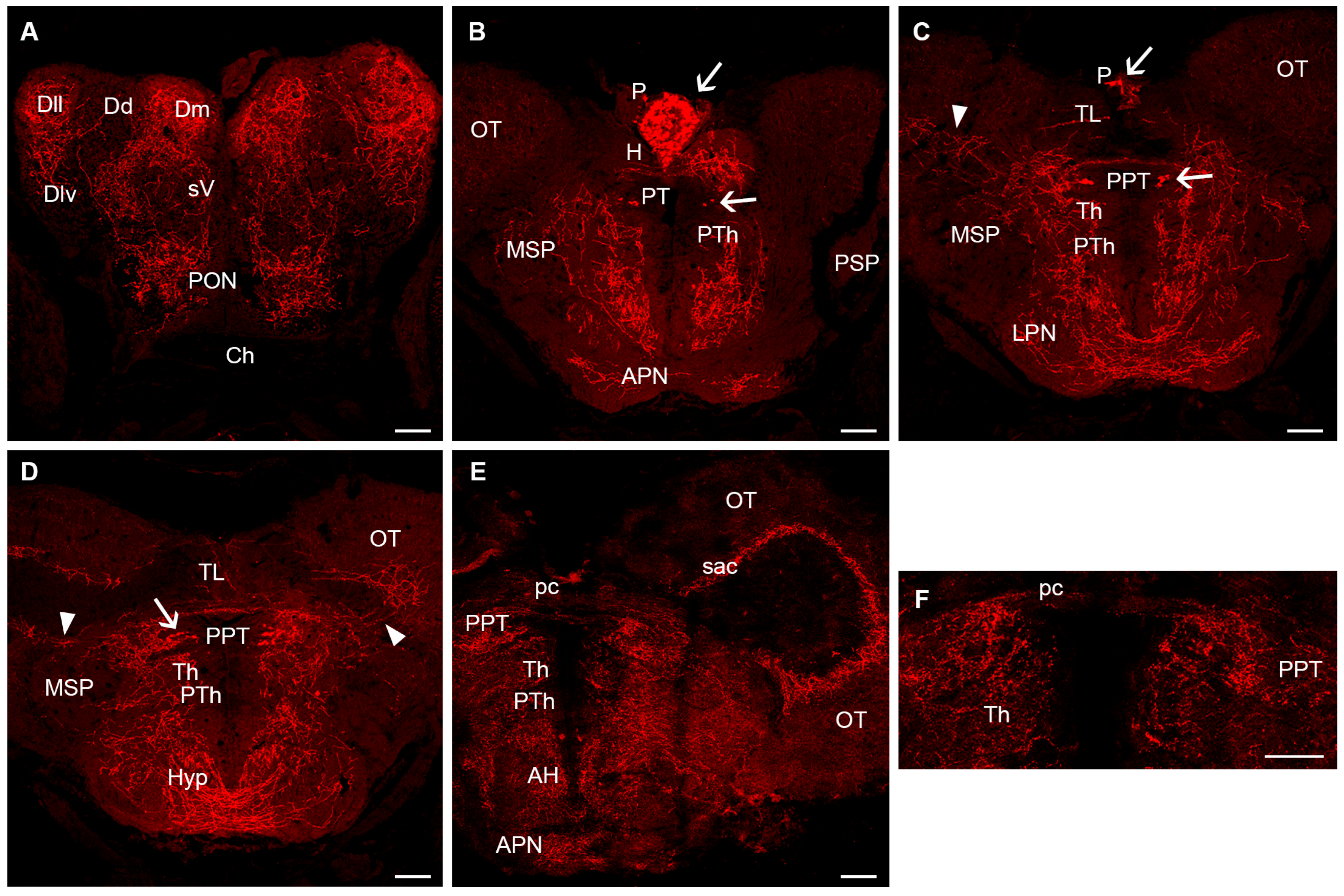
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Neuroanatomy of the Serotonergic System in Fishes
4.2. Some Considerations on the Serotonergic System in Aging Killifish
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AH | anterior hypothalamus |
| APN | anterior preglomerular nucleus |
| ATN | anterior tuberal nucleus |
| Cb | Cerebellum |
| Ch | optic chiasm |
| CON | caudal octavolateralis nucleus |
| D | dorsal telencephalic area (pallium) |
| Dd | dorsal zone of D |
| DIL | diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobes |
| DlI | dorsolateral isthmus |
| Dll | latero-lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon |
| Dlv | ventro-lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon |
| Dm | medial zone of dorsal telencephalon |
| FN | funicular nucleus |
| GN | glomerular nucleus |
| H | habenula |
| Hy | hypophysis |
| Hyp | hypothalamus |
| IO | inferior olive |
| IRN | inferior raphe nucleus |
| III | oculomotor nucleus |
| ll | lateral leminiscus |
| LPN | lateral preglomerular nucleus |
| LRO | lateral recess organ |
| LTN | lateral tuberal nucleus |
| LX | vagal lobe |
| MSP | magnocellular superficial pretectal nucleus |
| Nh | neurohypophysis |
| NMLF | nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle |
| OT | optic tectum |
| P | pineal organ (epiphysis) |
| pc | posterior commissure |
| PLL | posterior lateral line nerve |
| PON | preoptic nucleus |
| PRO | posterior recess organ |
| PSP | parvocellular superficial pretectal nucleus |
| PT | pretectum |
| PPT | periventricular pretectum |
| PTh | prethalamus (ventral thalamus) |
| PTu | posterior tubercle |
| PVO | paraventricular organ |
| sac | stratum album centrale (of the OT) |
| SC | spinal cord |
| sp | stratum periventriculare (of the OT) |
| SRN | superior raphe nucleus |
| T | telencephalon |
| Teg | tegmentum |
| Th | thalamus (dorsal thalamus) |
| TL | torus longitudinalis |
| TS | torus semicircularis |
| V | ventral telencephalic area (subpallium) |
| VC | valvula cerebelli |
| sV | subcommissural zone of V |
| X | vagal nerve |
| Xm | vagal motor nucleus |
References
- Parey, E.; Louis, A.; Montfort, J.; Bouchez, O.; Roques, C.; Iampietro, C.; Lluch, J.; Castinel, A.; Donnadieu, C.; Desvignes, T.; et al. Genome structures resolve the early diversification of teleost fishes. Science 2023, 379, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Near, T.J.; Thacker, C.E. Phylogenetic Classification of Living and Fossil Ray-Finned Fishes (Actinopterygii). Bull. Peabody Mus. Nat. Hist. 2024, 65, 3–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Sánchez, A.; Almaida-Pagán, P.F.; Mendiola, P.; de Costa, J. Nothobranchius as a model for aging studies. A Rev. Aging Dis. 2013, 5, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, M.; Englert, C. Nothobranchius furzeri: A Model for Aging Research and More. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, H.; Krug, J.; Singer, P.; Englert, C. The African turquoise killifish Nothobranchius furzeri as a model for aging research. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2018, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzibasi Tozzini, E.; Cellerino, A. Nothobranchius annual killifishes. EvoDevo 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, M.M.; Grenn, A.A.; Page, I.H. Serum vasoconstrictor, serotonin; isolation and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 176, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesaar, C. The serotonergic system in fish. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, J.; Repérant, J.; Ward, R.; Vesselkin, N.P.; Rio, J.P.; Miceli, D.; Kratskin, I. The serotoninergic system of the brain of the lamprey, Lampetra fluviatilis: An evolutionary perspective. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1992, 5, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalo, X.M.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Meléndez-Ferro, M.; Pérez-Costas, E.; Anadón, R.; Rodicio, M.C. Development of the serotonergic system in the central nervous system of the sea lamprey. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 34, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro-Iglesias, A.; Villar-Cerviño, V.; Anadón, R.; Rodicio, M.C. Development and organization of the descending serotonergic brainstem-spinal projections in the sea lamprey. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 36, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro-Iglesias, A.; Villar-Cerviño, V.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Anadón, R.; Rodicio, M.C. Neurochemical characterization of sea lamprey taste buds and afferent gustatory fibers: Presence of serotonin, calretinin, and CGRP immunoreactivity in taste bud bi-ciliated cells of the earliest vertebrates. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro-Iglesias, A.; Cornide-Petronio, M.E.; Anadón, R.; Rodicio, M.C. Serotonin and GABA are colocalized in restricted groups of neurons in the larval sea lamprey brain: Insights into the early evolution of neurotransmitter colocalization in vertebrates. J. Anat. 2009, 215, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornide-Petronio, M.E.; Ruiz, M.S.; Barreiro-Iglesias, A.; Rodicio, M.C. Spontaneous regeneration of the serotonergic descending innervation in the sea lamprey after spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2535–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, T.C.; Livingston, C.A.; Hughes, M.G.; McAdoo, D.J.; Leonard, R.B. The distribution of serotonin in the CNS of an elasmobranch fish: Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies in the Atlantic stingray, Dasyatis sabina. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 221, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Honma, Y.; Ueda, S.; Sano, Y. Immunohistochemical demonstration of serotonin neuron system in the central nervous system of the Japanese dogfish, Scyliorhinus torazame (Chondrichthyes). J. Hirnforsch. 1990, 31, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Stuesse, S.L.; Cruce, W.L.; Northcutt, R.G. Localization of serotonin, tyrosine hydroxylase, and leu-enkephalin immunoreactive cells in the brainstem of the horn shark, Heterodontus francisci. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 308, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuesse, S.L.; Stuesse, D.C.; Cruce, W.L. Raphe nuclei in three cartilaginous fishes, Hydrolagus colliei, Heterodontus francisci, and Squalus acanthias. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 358, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, I.; Molist, P.; Anadón, R.; Rodríguez-Moldes, I. Development of the serotoninergic system in the central nervous system of a shark, the lesser spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 804–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.M.; González, A. Organization of the serotonergic system in the central nervous system of two basal actinopterygian fishes: The Cladistians Polypterus senegalus and Erpetoichthys calabaricus. Brain Behav. Evol. 2014, 83, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrio, F.; Anadón, R.; Rodríguez-Moldes, I. Distribution of serotonin (5HT)-immunoreactive structures in the central nervous system of two chondrostean species (Acipenser baeri and Huso huso). J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 407, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, D.; González, A.; López, J.M. Neuroanatomical Distribution of the Serotonergic System in the Brain and Retina of Holostean Fishes, The Sister Group to Teleosts. Brain Behav. Evol. 2020, 95, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, O.; Chambolle, P. Serotonin in the brain of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. An immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1983, 234, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenhuis-van den Heuvel, T.H.; Nieuwenhuys, R. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the diencephalon and mesencephalon of the trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cellbodies, fibres and terminals. Anat. Embryol. 1984, 169, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, P.; Van Veen, T. Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the brain of the teleost Gasterosteus aculeatus L. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 226, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, P.; Ebbesson, S.O. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of sockeye salmon fry. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1989, 2, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Meek, J.; Joosten, H.W. Distribution of serotonin in the brain of the mormyrid teleost Gnathonemus petersii. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 281, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.A.; Maler, L.; Tinner, B. The distribution of serotonin in the brain of Apteronotus leptorhynchus: An immunohistochemical study. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1990, 3, 429–465. [Google Scholar]
- Batten, T.F.; Berry, P.A.; Maqbool, A.; Moons, L.; Vandesande, F. Immunolocalization of catecholamine enzymes, serotonin, dopamine and L-dopa in the brain of Dicentrarchus labrax (Teleostei). Brain Res. Bull. 1993, 31, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, F.J.; Rendón-Unceta, M.C.; Sarasquete, C.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Distribution of serotonin in the brain of the Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis: An immunohistochemical study. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2000, 18, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesaar, C.; Stigloher, C.; Tannhäuser, B.; Wullimann, M.F.; Bally-Cuif, L. Axonal projections originating from raphe serotonergic neurons in the developing and adult zebrafish, Danio rerio, using transgenics to visualize raphe-specific pet1 expression. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 10, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, M.; Forlano, P.M. Serotonin distribution in the brain of the plainfin midshipman: Substrates for vocal-acoustic modulation and a reevaluation of the serotonergic system in teleost fishes. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020, 15, 3451–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.K.; Ganesh, C.B. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine)-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of the viviparous fish Gambusia affinis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 118, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biradar, A.; Ganesh, C.B. Serotonin-immunoreactivity in the brain of the cichlid fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Anat. Rec. 2024, 307, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.M.; González, A. Comparative analysis of the serotonergic systems in the CNS of two lungfishes, Protopterus dolloi and Neoceratodus forsteri. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunin, M.A.; Wightman, R.M. Quantitative evaluation of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) neuronal release and uptake: An investigation of extrasynaptic transmission. J. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 4854–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Miguel, F.F.; Trueta, C. Synaptic and extrasynaptic secretion of serotonin. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengod, G.; Vilaró, M.T.; Cortés, R.; López-Giménez, J.F.; Raurich, A.; Palacios, J.M. Chemical Neuroanatomy of 5-HT Receptor Subtypes in the Mammalian Brain. In The Serotonin Receptors; Roth, B.L., Ed.; The Receptors; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 319–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Gray, J.A.; Roth, B.L. The expanded biology of serotonin. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.; Lillesaar, C. Probing the diversity of serotonin neurons. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 5, 2382–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro-Iglesias, A.; Mysiak, K.S.; Scott, A.L.; Reimer, M.M.; Yang, Y.; Becker, C.G.; Becker, T. Serotonin Promotes Development and Regeneration of Spinal Motor Neurons in Zebrafish. Cell Rep. 2015, 3, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winberg, S.; Thörnqvist, P.O. Role of brain serotonin in modulating fish behavior. Curr. Zool. 2016, 62, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrido-Cameán, D.; Robledo, D.; Sánchez, L.; Rodicio, M.C.; Barreiro-Iglesias, A. Serotonin inhibits axonal regeneration of identifiable descending neurons after a complete spinal cord injury in lampreys. Dis. Models Mech. 2019, 20, dmm037085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo, S.; Ivanov, D.K.; Wood, S.H. Serotonin: From top to bottom. Biogerontology 2013, 14, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Luijtelaar, M.G.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Tonnaer, J.A. Aberrant morphology of serotonergic fibers in the forebrain of the aged rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 95, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Luijtelaar, M.G.; Tonnaer, J.A.; Steinbusch, H.W. Aging of the serotonergic system in the rat forebrain: An immunocytochemical and neurochemical study. Neurobiol. Aging 1992, 13, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, J.A.; de la Roza, C.; Machado, A.; Cano, J. The effect of age on the monoamines of the hypothalamus. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1995, 13, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Ueda, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsushita, H.; Sawada, T.; Kawata, M. Vulnerability to aging in the rat serotonergic system. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 96, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis-Nunno, H.; Halpern-Sebold, L.; Schreibman, M.P. Immunocytochemical changes in serotonin in the forebrain and pituitary of aging fish. Neurobiol. Aging 1986, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evsiukova, V.; Antonov, E.; Kulikov, A.V. Effects of Sex and Group Size on Behavior and Brain Biogenic Amines in Short-Lived Turquoise Killifish (Nothobranchius furzeri). Zebrafish 2021, 18, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evsiukova, V.S.; Arefieva, A.B.; Sorokin, I.E.; Kulikov, A.V. Age-Related Alterations in the Level and Metabolism of Serotonin in the Brain of Males and Females of Annual Turquoise Killifish (Nothobranchius furzeri). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 6, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonovo, J.; Allende-Castro, C.; Medinas, D.B.; Cárdenas, D.; Cuevas, M.P.; Hetz, C.; Concha, M.L. Immunohistochemical characterisation of the adult Nothobranchius furzeri intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 2024, 395, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.K.; Brunet, A. The African turquoise killifish: A research organism to study vertebrate aging and diapause. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurling, P.; Rodríguez, E.M. The paraventricular and posterior recess organs of elasmobranchs: A system of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons containing immunoreactive serotonin and somatostatin. Cell Tissue Res. 1990, 259, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antri, M.; Auclair, F.; Albrecht, J.; Djeudjang, N.; Dubuc, R. Serotoninergic modulation of sensory transmission to brainstem reticulospinal cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, J.L.; Uy, N.; Maruska, K.P.; Carpenter, R.E.; Fernald, R.D. Social status differences regulate the serotonergic system of a cichlid fish, Astatotilapia burtoni. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217 Pt 15, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, E.; Chagnaud, B.P.; Wullimann, M.F. Serotonin systems in three socially communicating teleost species, the grunting toadfish (Allenbatrachus grunniens), a South American marine catfish (Ariopsis seemanni), and the upside-down catfish (Synodontis nigriventris). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 104, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonovo, J.; Ahumada-Galleguillos, P.; Oñate-Ponce, A.; Allende-Castro, C.; Henny, P.; Concha, M.L. Organization of the Catecholaminergic System in the Short-Lived Fish Nothobranchius furzeri. Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 728720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornide-Petronio, M.E.; Anadón, R.; Rodicio, M.C.; Barreiro-Iglesias, A. The sea lamprey tryptophan hydroxylase: New insight into the evolution of the serotonergic system of vertebrates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 218, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuesse, S.L.; Cruce, W.L.; Northcutt, R.G. Serotoninergic and enkephalinergic cell groups in the reticular formation of the bat ray and two skates. Brain Behav. Evol. 1991, 38, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, U.; König, B. Serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of Eigenmannia lineata (Gymnotiformes, Teleostei). J. Hirnforsch. 1990, 31, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Corio, M.; Peute, J.; Steinbusch, H.W. Distribution of serotonin- and dopamine-immunoreactivity in the brain of the teleost Clarias gariepinus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1991, 4, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Thomas, P. Immunocytochemical localization of serotonin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone in the brain and pituitary gland of the Atlantic croaker Micropogonias undulatus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1993, 91, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzini, E.T.; Baumgart, M.; Battistoni, G.; Cellerino, A. Adult neurogenesis in the short-lived teleost Nothobranchius furzeri: Localization of neurogenic niches, molecular characterization and effects of aging. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellipanni, G.; Rink, E.; Bally-Cuif, L. Cloning of two tryptophan hydroxylase genes expressed in the diencephalon of the developing zebrafish brain. Mech. Dev. 2002, 119 (Suppl. S1), S215–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivite, M.; Leal, E.; Míguez, J.M.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M. Distribution of two isoforms of tryptophan hydroxylase in the brain of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). An in situ hybridization study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 2265–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, J.; Meissl, H.; Anadón, R. Central projections of the parapineal organ of the adult rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 285, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, J.; Pombal, M.A.; Anadón, R. Afferent and efferent connections of the parapineal organ in lampreys: A tract tracing and immunocytochemical study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 11, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón, J. Photosensitivity and biosynthesis of indole compounds in the cells of the receptor line of the pineal organ of the pike. Ophthalmic Res. 1984, 16, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamotsu, S.; Samejima, M.; Suzuki, N.; Morita, Y. Three-dimensional reconstruction of serotonin-immunoreactive photoreceptors in the pineal organ of the river lamprey, Lampetra japonica. Neurosignals 1997, 6, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pombal, M.A.; Yáñez, J.; Marín, O.; González, A.; Anadón, R. Cholinergic and GABAergic neuronal elements in the pineal organ of lampreys, and tract-tracing observations of differential connections of pinealofugal neurons. Cell Tissue Res. 1999, 295, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, M.; Wada, S.; Kawano-Yamashita, E.; Hara, Y.; Kuraku, S.; Kosaka, S.; Kawakami, K.; Tamotsu, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Shichida, Y.; et al. Diversification of non-visual photopigment parapinopsin in spectral sensitivity for diverse pineal functions. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bégay, V.; Falcón, J.; Cahill, G.M.; Klein, D.C.; Coon, S.L. Transcripts encoding two melatonin synthesis enzymes in the teleost pineal organ: Circadian regulation in pike and zebrafish, but not in trout. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Nam, H.G.; Kim, Y. The core circadian component, Bmal1, is maintained in the pineal gland of old killifish brain. iScience 2020, 9, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.; Clausse, S.; Libouban, S.; Szabo, T. Serotoninergic neurons in the mormyrid brain and their projection to the preelectromotor and primary electrosensory centers: Immunohistochemical study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 1, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.G.; Yang, C.Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Ozawa, H. Fiber connections of the periventricular pretectal nucleus in a teleost, tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Neurosci. Res. 2007, 57, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, J.; Suárez, T.; Quelle, A.; Folgueira, M.; Anadón, R. Neural connections of the pretectum in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 15, 1017–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris-Warrick, R.M.; McPhee, J.C.; Filler, J.A. Distribution of serotonergic neurons and processes in the lamprey spinal cord. Neuroscience 1985, 14, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, T.C.; Roos, L.J.; Williams, B.J.; Leonard, R.B. The descending and intrinsic serotoninergic innervation of an elasmobranch spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 10, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.E.; Wiggin, T.D.; Rivera-Perez, L.M.; Lillesaar, C.; Masino, M.A. Intraspinal serotonergic neurons consist of two, temporally distinct populations in developing zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2016, 76, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.E.; Wahlstrom-Helgren, S.; Wiggin, T.D.; Corwin, B.M.; Lillesaar, C.; Masino, M.A. Intraspinal serotonergic signaling suppresses locomotor activity in larval zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veen, T.; Ekström, P.; Nyberg, L.; Borg, B.; Vigh-Teichmann, I.; Vigh, B. Serotonin and opsin immunoreactivities in the developing pineal organ of the three-spined stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. Cell Tissue Res. 1984, 237, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolliet, V.; Ali, M.A. Immunohistochemical study of the development of serotoninergic neurons in the brain of the brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis. Brain Behav. Evol. 1992, 40, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, D.L.; Fetcho, J.R. Relationship of tyrosine hydroxylase and serotonin immunoreactivity to sensorimotor circuitry in larval zebrafish. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 29, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillesaar, C.; Tannhäuser, B.; Stigloher, C.; Kremmer, E.; Bally-Cuif, L. The serotonergic phenotype is acquired by converging genetic mechanisms within the zebrafish central nervous system. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Llera, L.; Sobrido-Cameán, D.; Quelle-Regaldie, A.; Sánchez, L.; Barreiro-Iglesias, A. An in vivo drug screen in zebrafish reveals that cyclooxygenase 2-derived prostaglandin D2 promotes spinal cord neurogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2024, 57, e13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Kenmochi, N.; Namikawa, K. Age- and α-Synuclein-Dependent Degeneration of Dopamine and Noradrenaline Neurons in the Annual Killifish Nothobranchius furzeri. Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 1727–1733.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, S.; Fronte, B.; Bibbiani, C.; Terzibasi Tozzini, E.; Cellerino, A. Quantification of noradrenergic-, dopaminergic-, and tectal-neurons during aging in the short-lived killifish Nothobranchius furzeri. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, D.E.M.; Valenzano, D.R. Turquoise killifish: A natural model of age-dependent brain degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2023, 90, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhunsel, S.; Bergmans, S.; Beckers, A.; Etienne, I.; Van Houcke, J.; Seuntjens, E.; Arckens, L.; De Groef, L.; Moons, L. The killifish visual system as an in vivo model to study brain aging and rejuvenation. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Llera, L.; Arana, Á.J.; Sánchez, L.; Anadón, R.; Barreiro-Iglesias, A. Organization of Serotonergic Cell Populations in the Brain and Spinal Cord of the Short-Lived African Turquoise Killifish. Biology 2025, 14, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091206
González-Llera L, Arana ÁJ, Sánchez L, Anadón R, Barreiro-Iglesias A. Organization of Serotonergic Cell Populations in the Brain and Spinal Cord of the Short-Lived African Turquoise Killifish. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091206
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Llera, Laura, Álvaro J. Arana, Laura Sánchez, Ramón Anadón, and Antón Barreiro-Iglesias. 2025. "Organization of Serotonergic Cell Populations in the Brain and Spinal Cord of the Short-Lived African Turquoise Killifish" Biology 14, no. 9: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091206
APA StyleGonzález-Llera, L., Arana, Á. J., Sánchez, L., Anadón, R., & Barreiro-Iglesias, A. (2025). Organization of Serotonergic Cell Populations in the Brain and Spinal Cord of the Short-Lived African Turquoise Killifish. Biology, 14(9), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091206





