A Spatiotemporal Atlas of the Gut Microbiota in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus: Implications for Health and Environment
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Detection
2.3. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
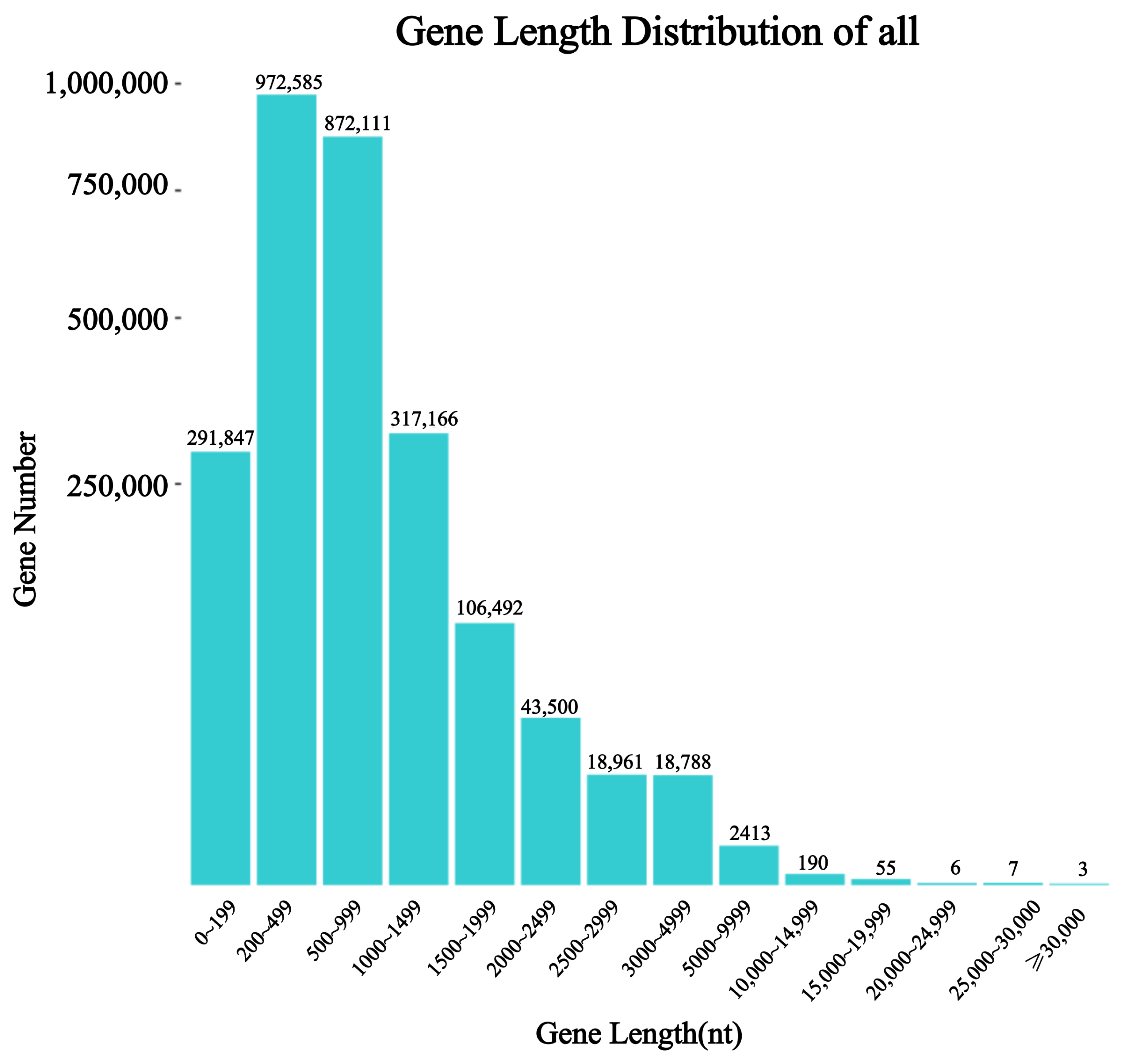
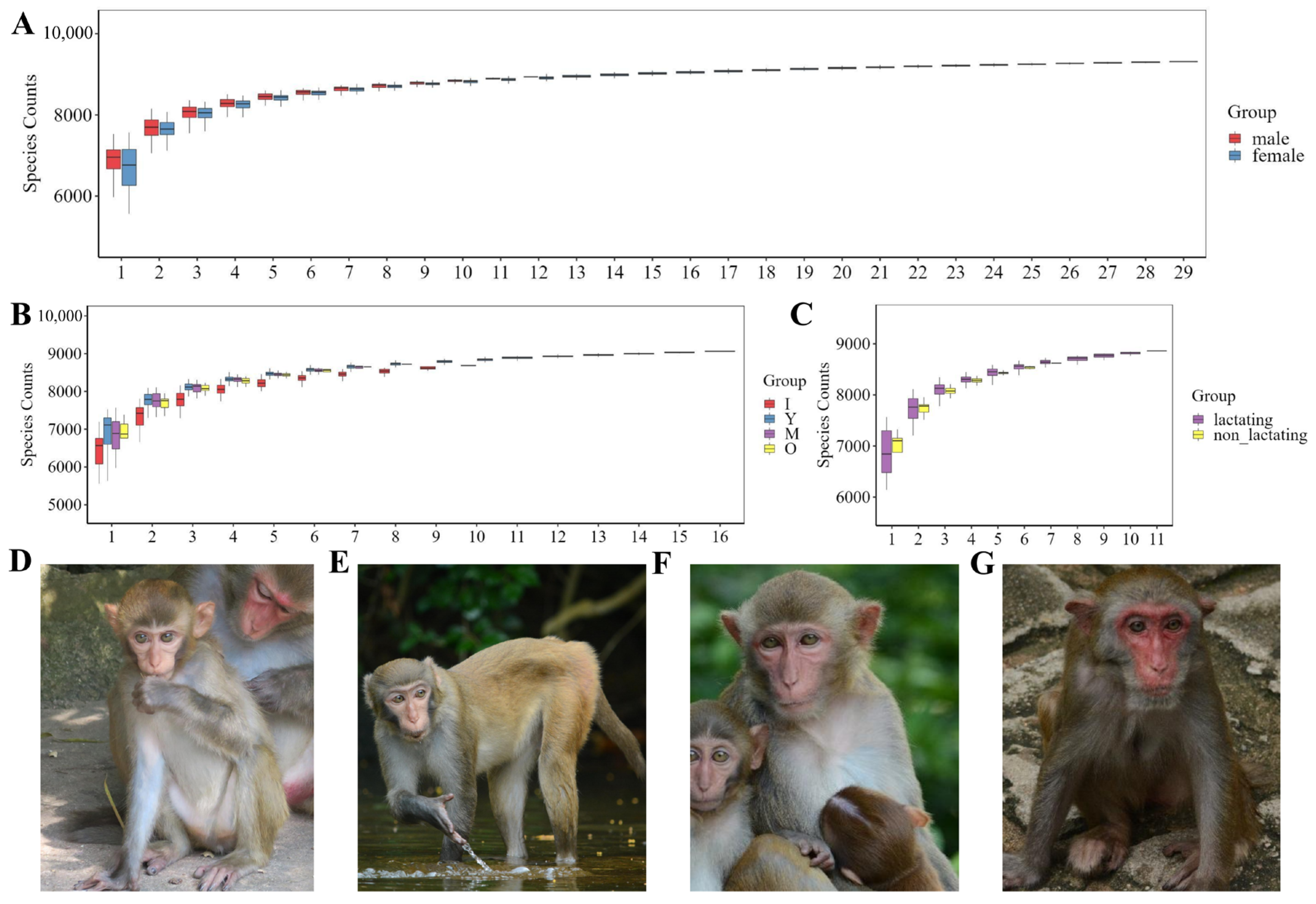
3.1. Sequencing and Observation
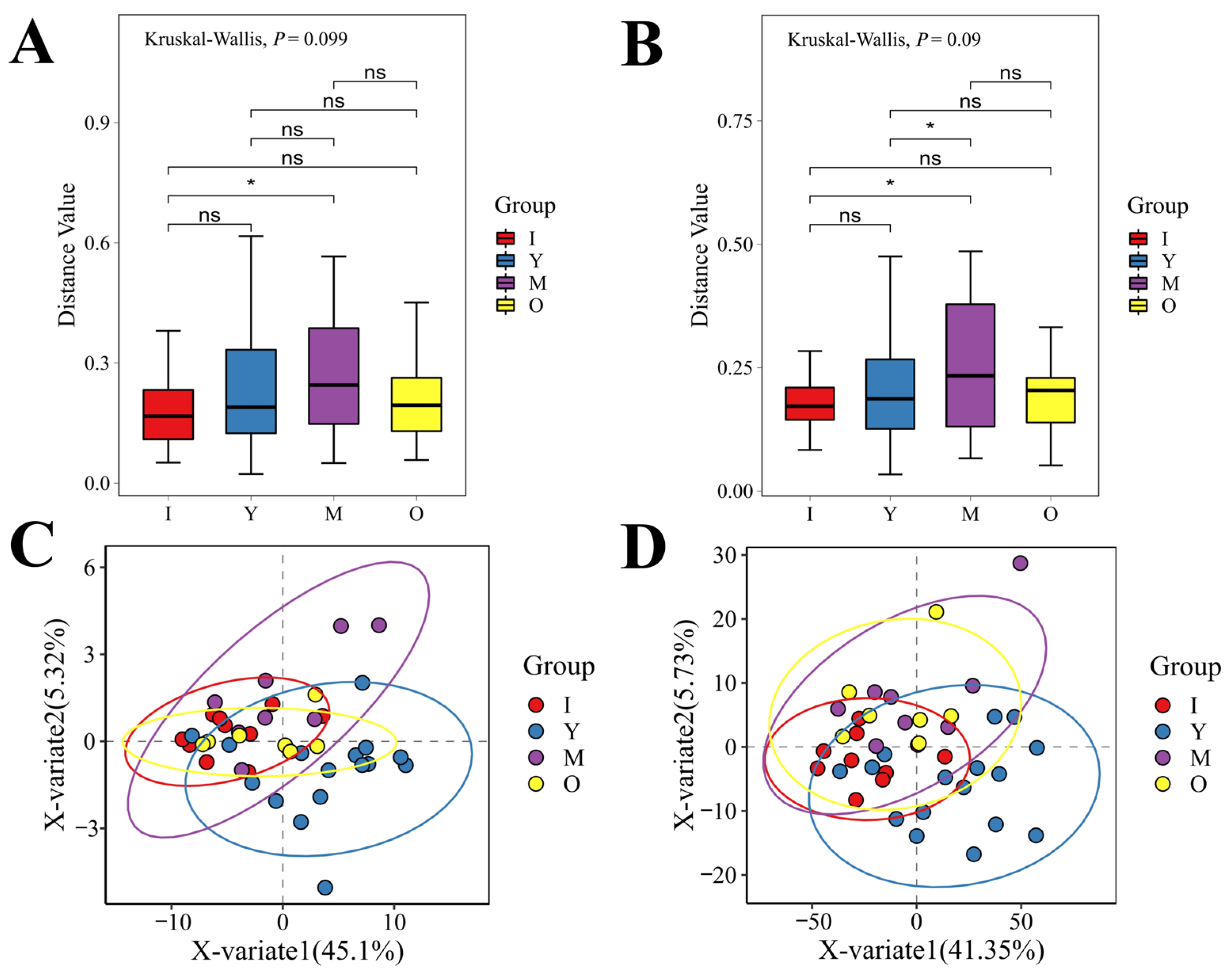
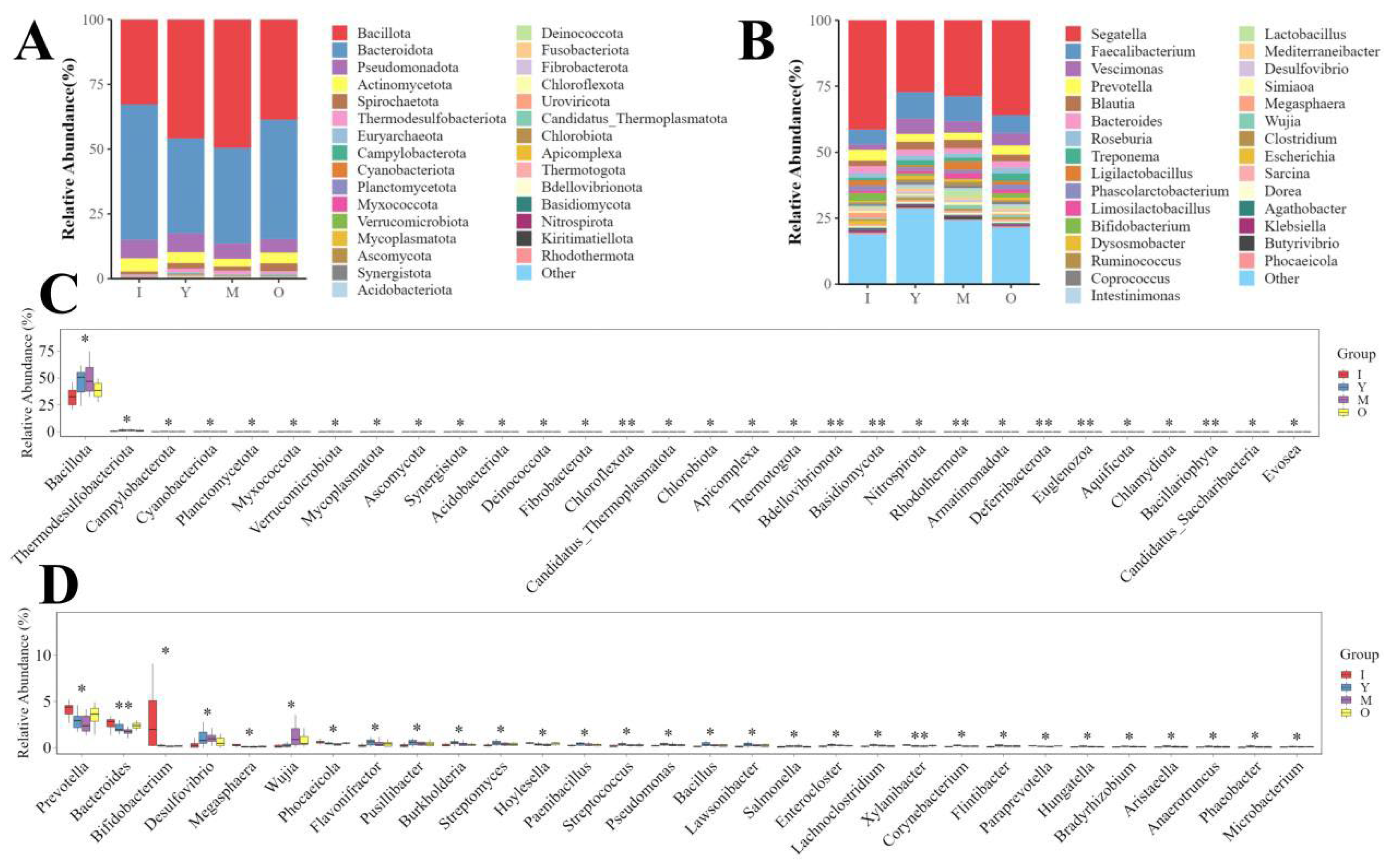
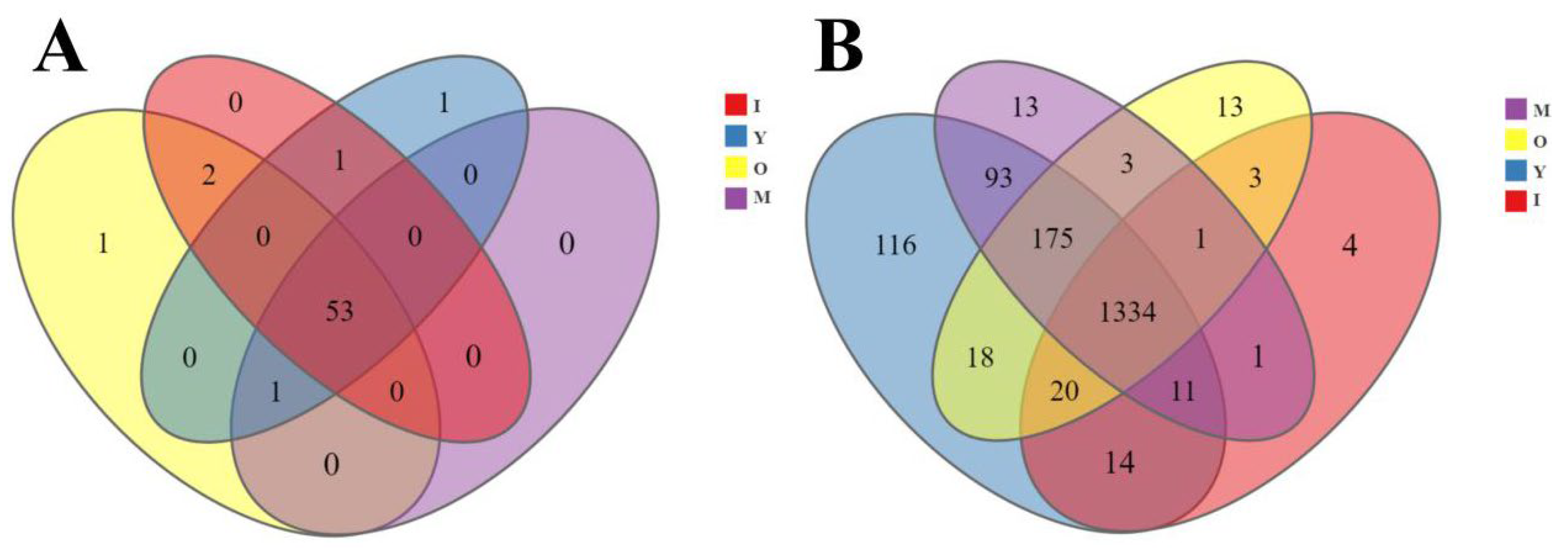
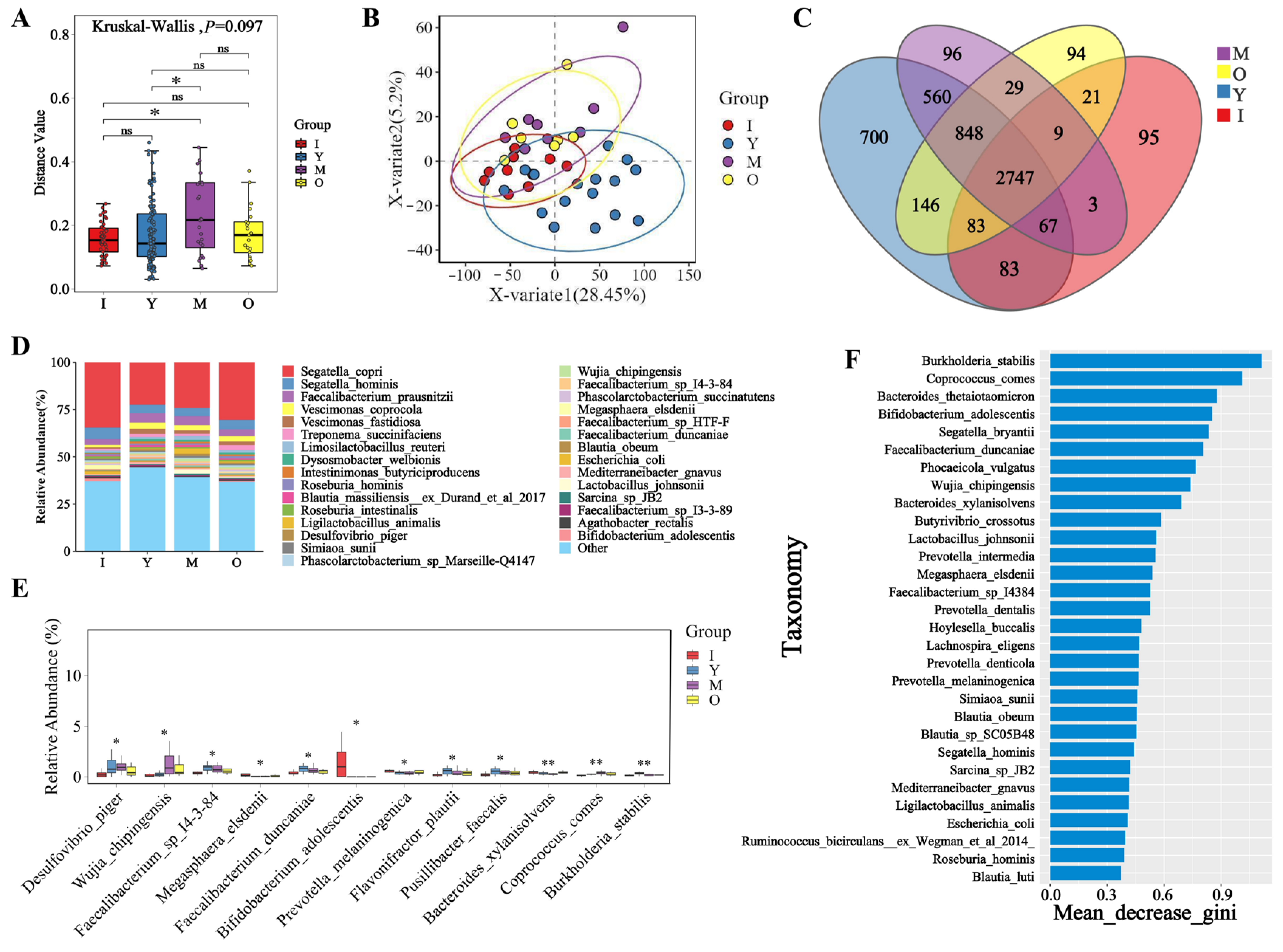
3.2. Microbial Diversity Across Different Age Groups of Macaques
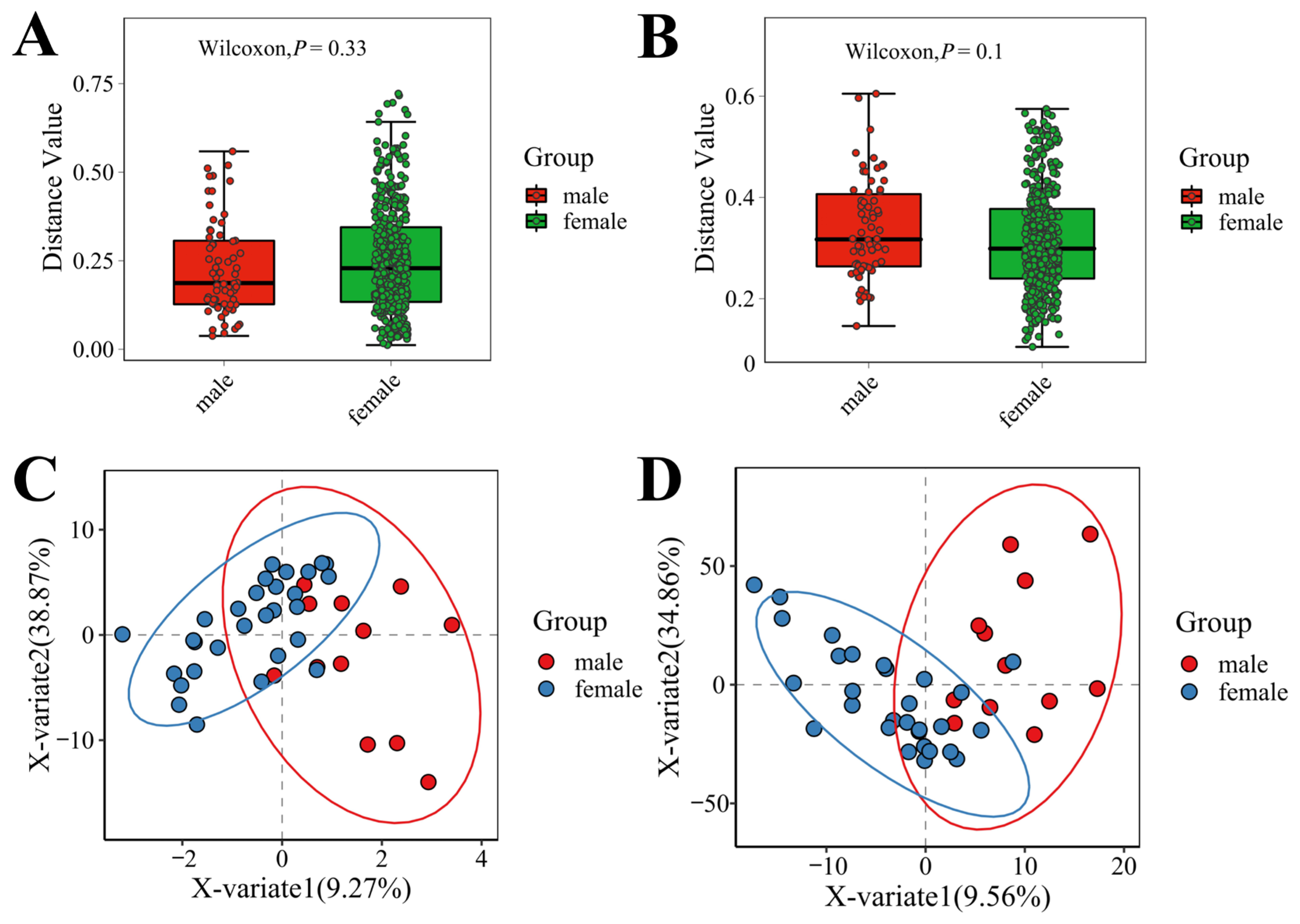
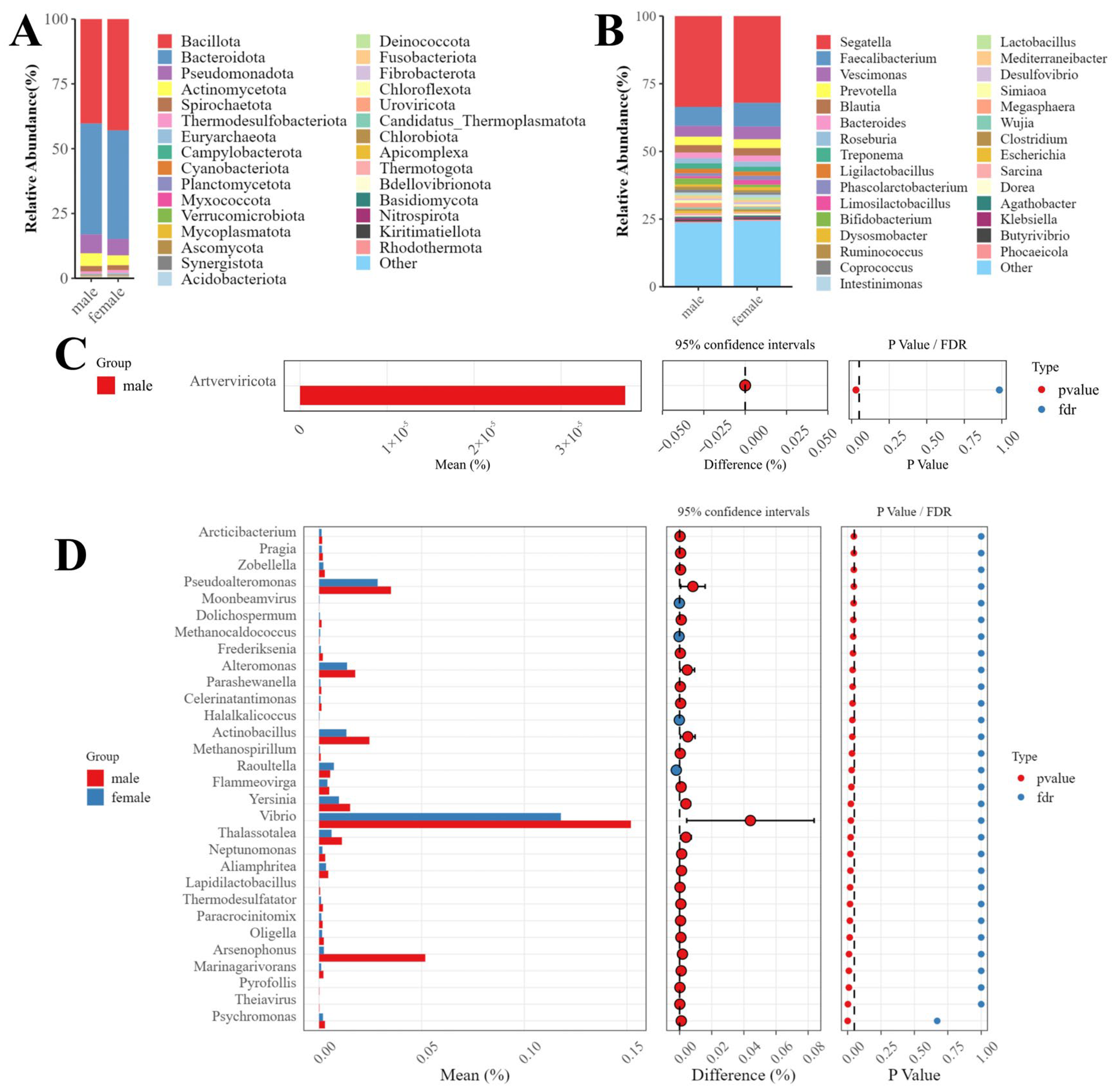
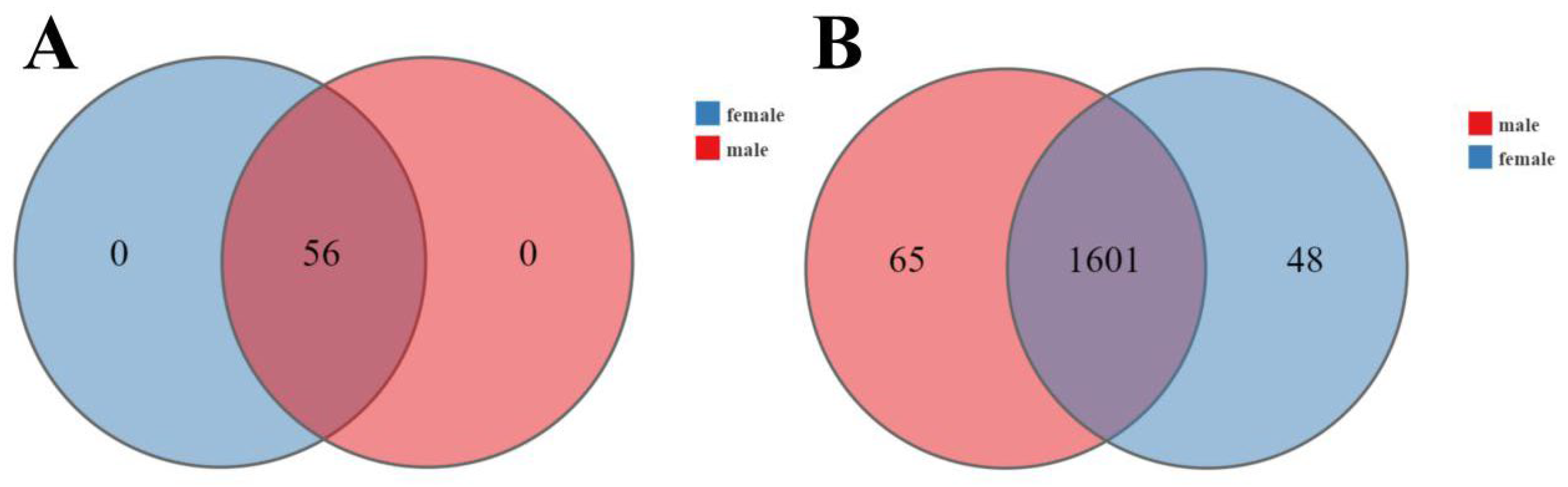
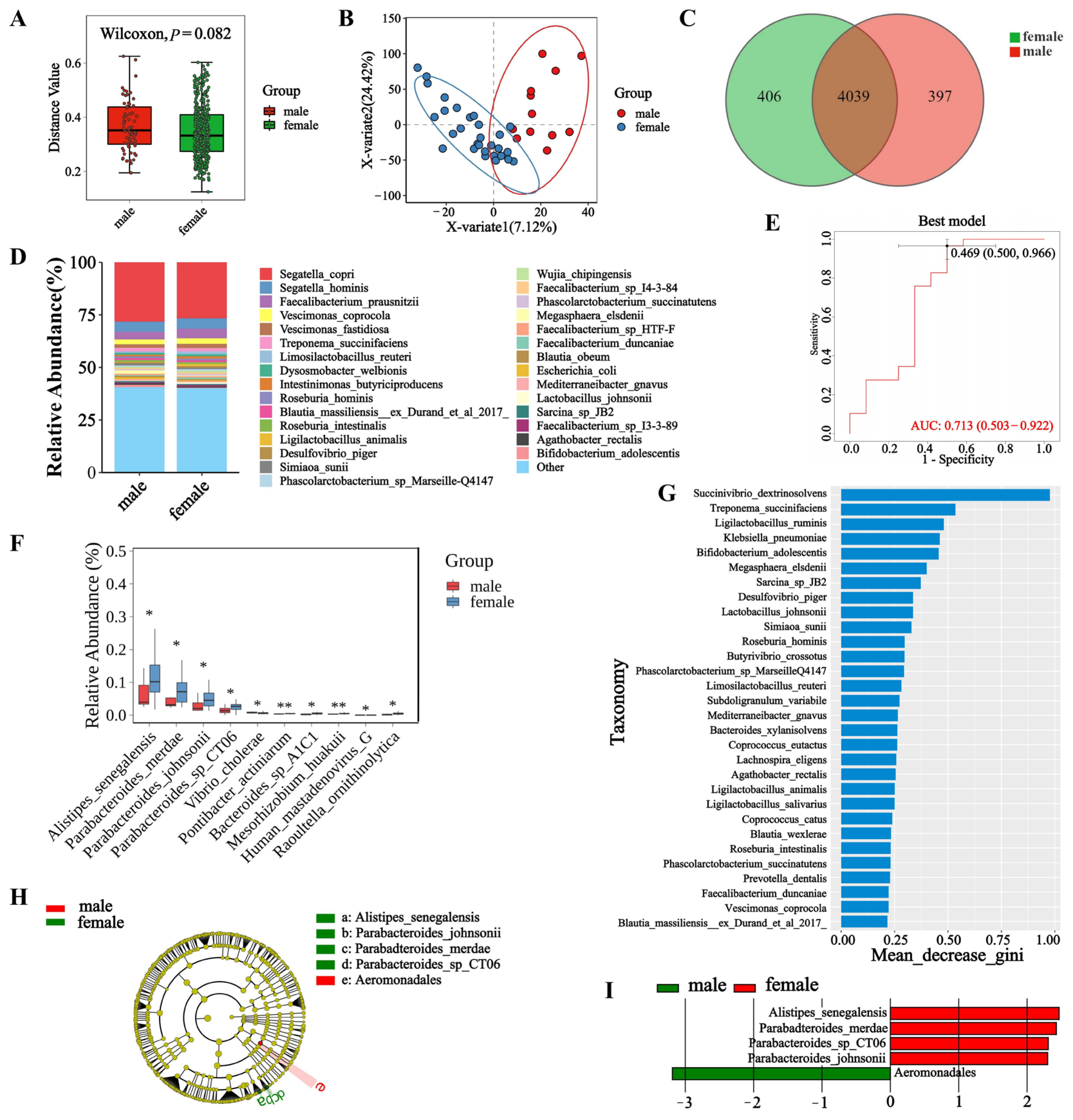
3.3. Microbial Diversity in Male and Female Macaques
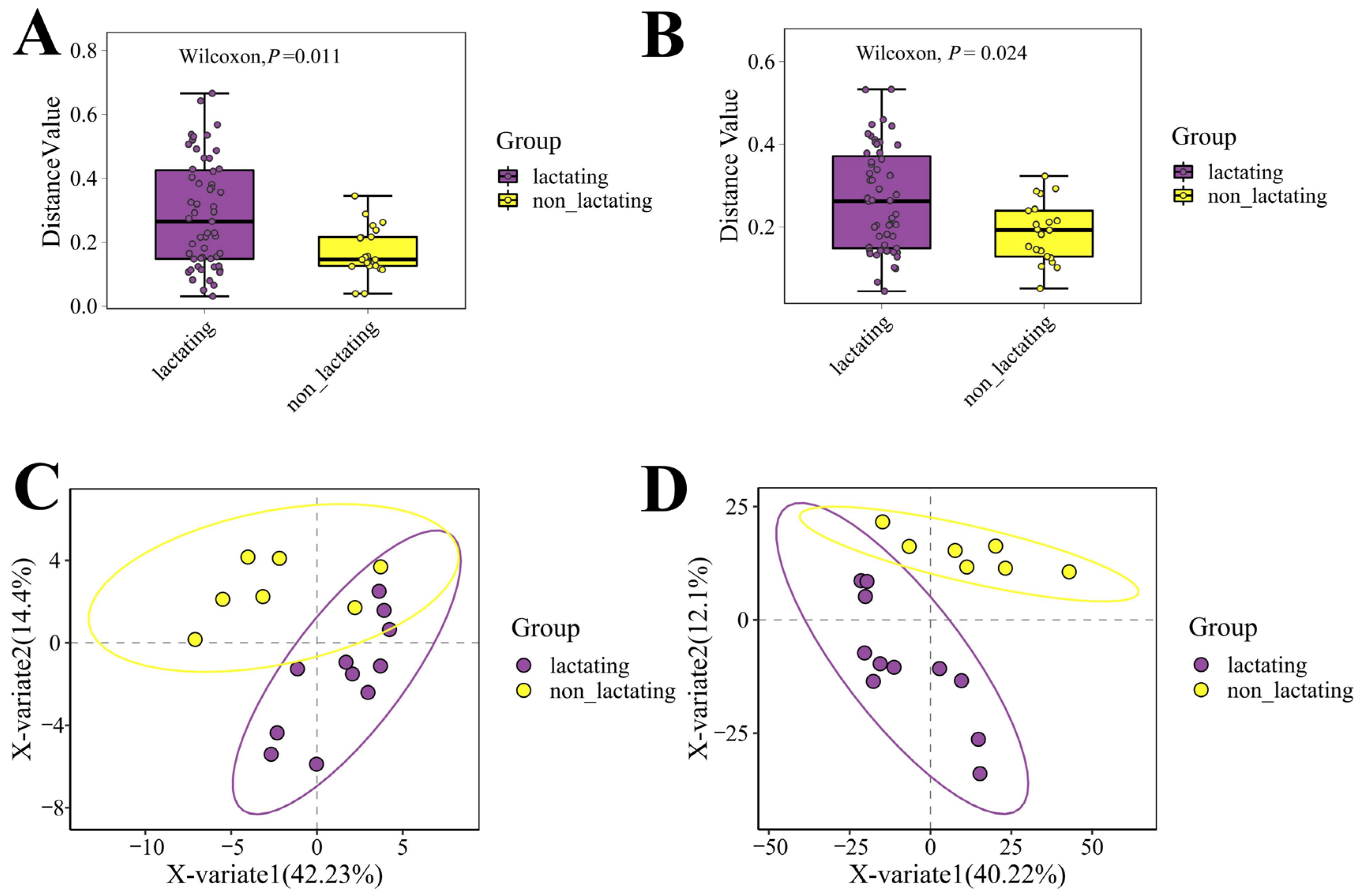
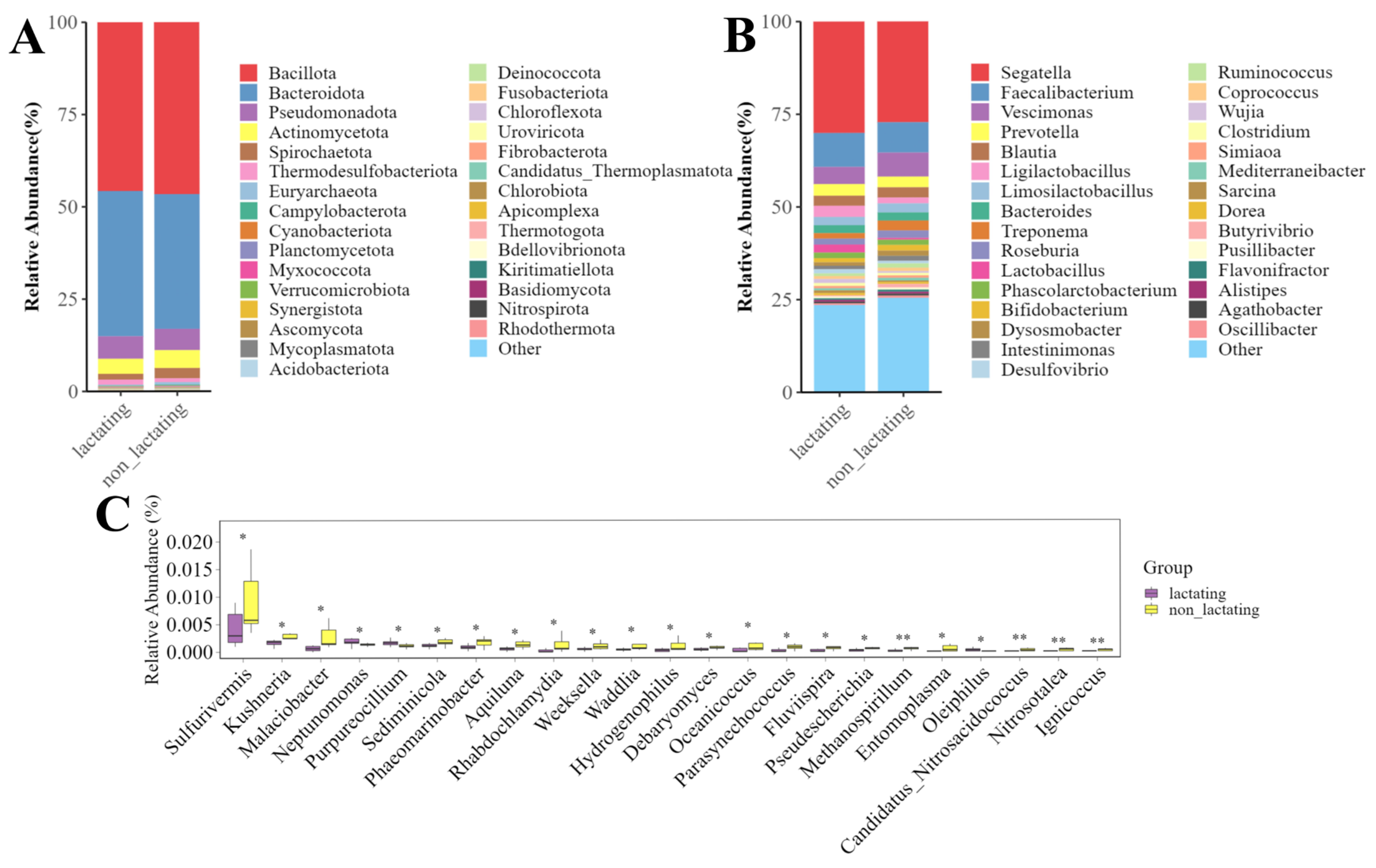
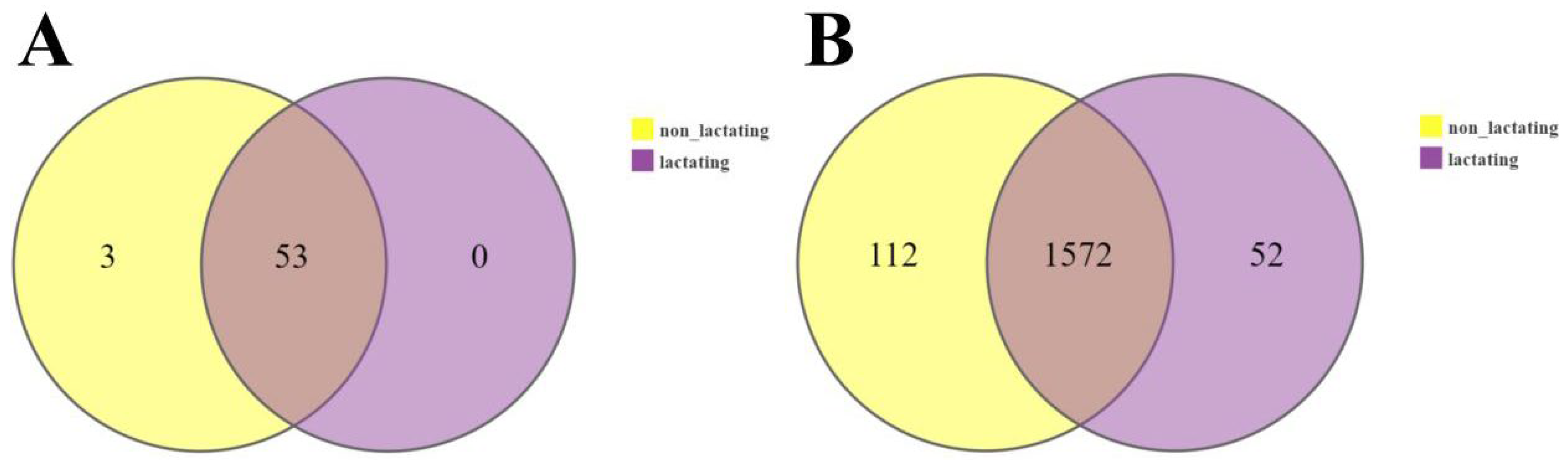
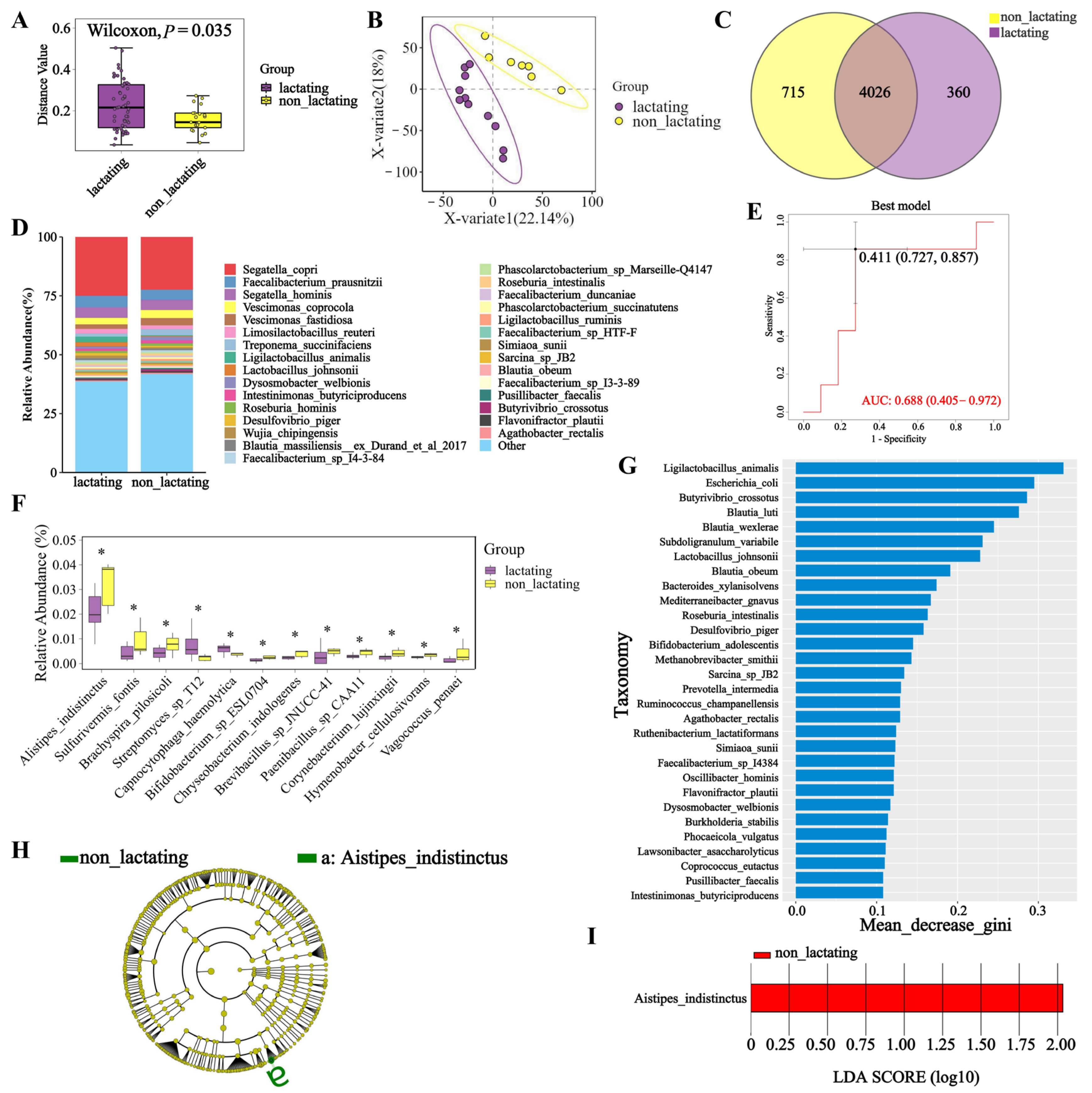
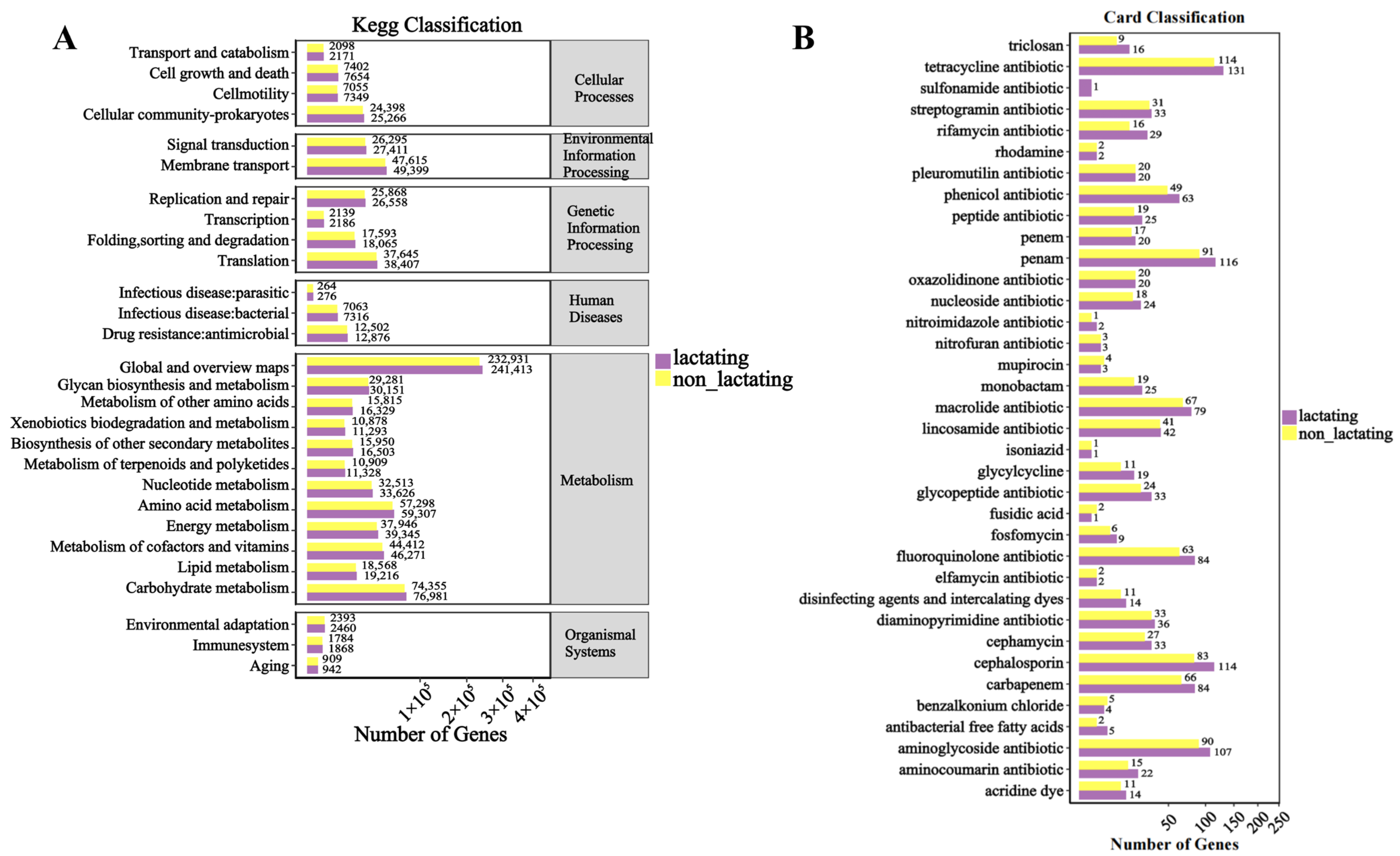
3.4. Microbial Diversity During Lactation and Non-Lactation Periods in Macaques
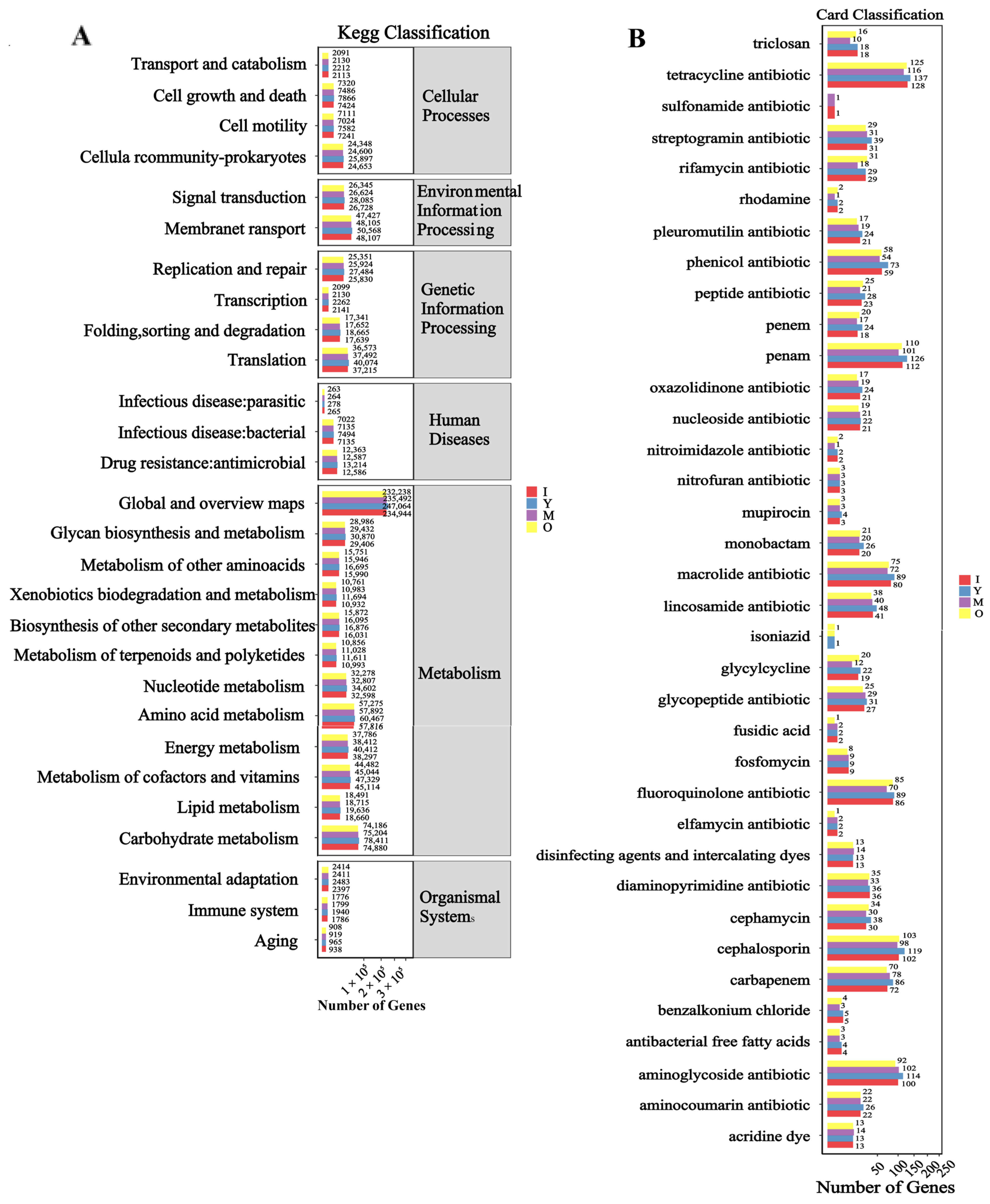
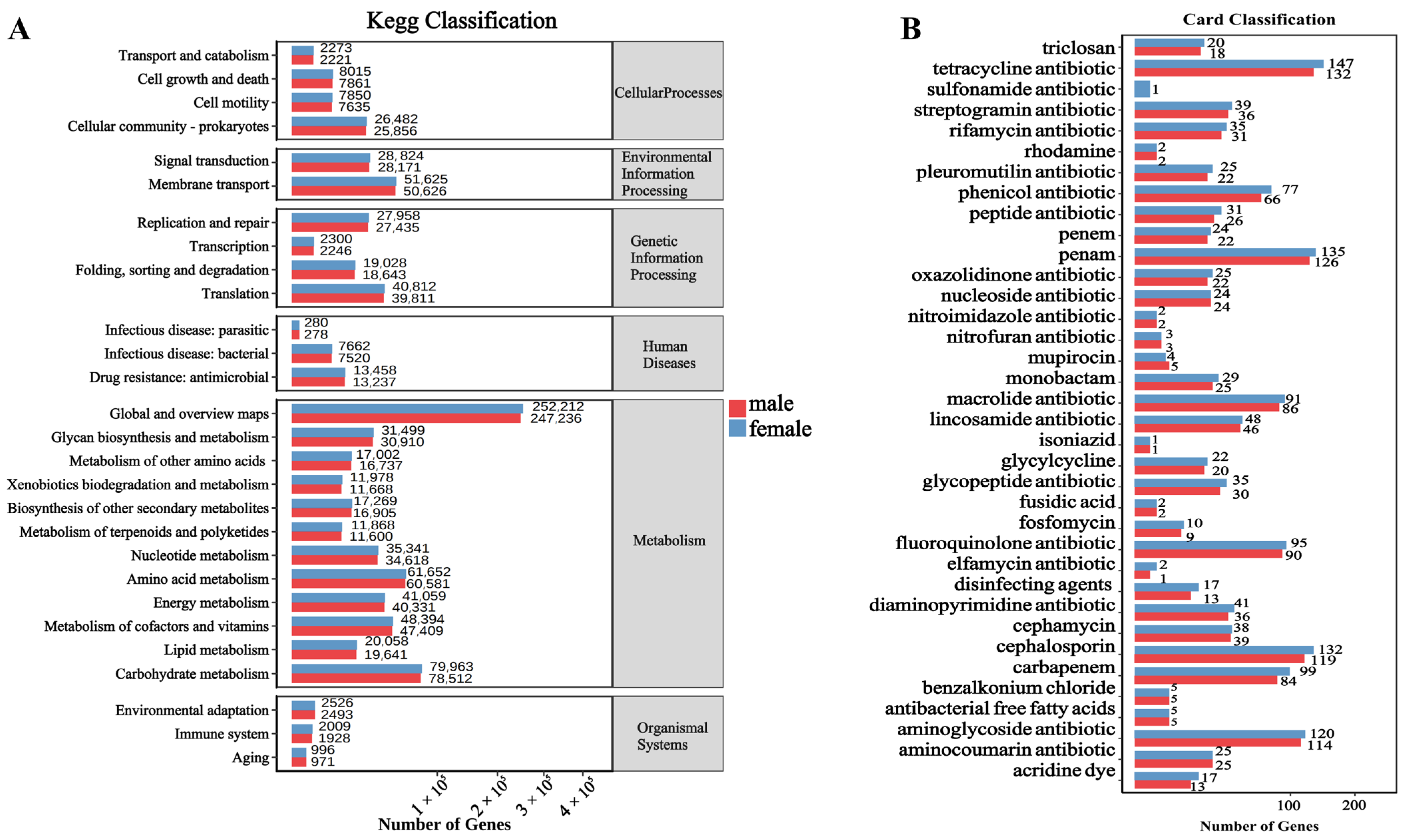
3.5. Functional Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Contig Number | Assembly Length (bp) | N50 (bp) | N90 (bp) | Max Length (bp) | Min Length (bp) | Average Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 167,569.32 | 232,460,365.68 | 2446.41 | 564.78 | 333,851.73 | 300.00 | 1402.73 |
References
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhou, J.; Luo, J.; Zhu, W.; Lai, Y.; Long, E.; et al. Metagenomic comparison of intestinal microbiota between normal and liver fibrotic rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurgaia, M.A. Characteristics of Escherichia Serogroup O132:K Isolated in Intestinal Diseases in Monkeys. Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 1982, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Hayakawa, T.; Kiyono, M.; Yamabata, N.; Enari, H.; Enari, H.S.; Fujita, S.; Kawazoe, T.; Asai, T.; Oi, T.; et al. Diet-related factors strongly shaped the gut microbiota of Japanese macaques. Am. J. Primatol. 2023, 85, e23555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnegan, P.M.; Garber, P.A.; McKenney, A.C.; Bicca-Marques, J.C.; De la Fuente, M.F.; Abreu, F.; Souto, A.; Schiel, N.; Amato, K.R.; Mallott, E.K.; et al. Group membership, not diet, structures the composition and functional potential of the gut microbiome in a wild primate. mSphere 2024, 9, e0023324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold, G.L.; Smith, M.; Grange, C.; Watt, E.R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Mukhopadhya, I. Role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: What have we learnt in the past 10 years? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1192–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, M.A.; Schloss, P.D. Schloss, Erratum for Sze and Schloss, “Looking for a Signal in the Noise: Revisiting Obesity and the Mi-crobiome”. mBio 2017, 8, e01995-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvallet, C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Irizarry, R.A.; Alm, E.J. Meta-analysis of gut microbiome studies identifies disease-specific and shared responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, R. Pharmacologic and Nonpharmacologic Therapies for the Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2019, 43, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kadyan, S.; Hochuli, N.; Salazar, G.; Laitano, O.; Chakrabarty, P.; Efron, P.A.; Zafar, M.A.; Wilber, A.; Nagpal, R. An Enteric Bacterial Infection Triggers Neuroinflammation and Neurobehavioral Impairment in 3xTg-AD Transgenic Mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230 (Suppl. S2), S95–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salia, S.; Burke, F.F.; Hinks, M.E.; Randell, A.M.; Matheson, M.A.; Walling, S.G.; Swift-Gallant, A. Gut microbiota transfer from the preclinical maternal immune activation model of autism is sufficient to induce sex-specific alterations in immune response and behavioural outcomes. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2025, 123, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Seasonal variation in the gut microbiota of rhesus macaques inhabiting limestone forests of southwest Guangxi, China. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, A.M.; Allen, J.M.; Jaggers, R.M.; Bailey, M.T. A descriptive analysis of gut microbiota composition in differentially reared infant rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) across the first 6 months of life. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackelmann, G.; Gillingham, M.A.F.; Schmid, J.; Heni, A.C.; Wilhelm, K.; Schwensow, N.; Sommer, S. Human encroachment into wildlife gut microbiomes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Seasonal variations in gut microbiota of semiprovisioned rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) living in a limestone forest of Guangxi, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 951507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tan, X.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S.; Yan, Z.; Xu, H.; Ren, B.; Zhang, P.; et al. Population genomics of wild Chinese rhesus macaques reveals a dynamic demographic history and local adaptation, with implications for biomedical research. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.R.; Leigh, S.R.; Kent, A.; Mackie, R.I.; Yeoman, C.J.; Stumpf, R.M.; Wilson, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; White, B.A.; Garber, P.A. The role of gut microbes in satisfying the nutritional demands of adult and juvenile wild, black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra). Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2014, 155, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lyu, M.; Wu, C.; Chu, Y.; Han, N.; Yang, D.; Hu, K. Variation in body mass and morphological characters in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus from Hainan, China. Am. J. Primatol. 2016, 78, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.F.; Wang, F.J.; Yu, L.; Ye, H.H.; Yang, G.B. Metagenomic comparison of the rectal microbiota between rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) and cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis). Zool. Res. 2019, 40, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z. Gut microbiota are associated with sex and age of host: Evidence from semi-provisioned rhesus macaques in southwest Guangxi, China. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8096–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cleary, D.W. Convergent and Divergent Age Patterning of Gut Microbiota Diversity in Humans and Nonhuman Primates. mSystems 2022, 7, e0151221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriansjach, J.; Baum, S.T.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Van Der Pol, W.J.; Buford, T.W.; Colman, R.J.; Masternak, M. Age-Related Differences in the Gut Microbiome of Rhesus Macaques. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2020, 75, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoughi, B.; Schneider, D.; Daniel, R.; Schülke, O.; Ostner, J. Aging gut microbiota of wild macaques are equally diverse, less stable, but progressively personalized. Microbiome 2022, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.-Y.; Rao, J.-H.; Tang, M.-T.; Zhao, G.-A.; Li, Q.-C.; Wu, L.-M.; Liu, S.-Q.; Li, B.-H.; Xiao, B.-Q.; Liu, X.-Y.; et al. Characterization of Changes and Driver Microbes in Gut Microbiota During Healthy Aging Using a Captive Monkey Model. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yin, B.; Li, W.; Chai, T.; Liang, W.; Huang, Y.; Tan, X.; Zheng, P.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Age-related changes in microbial composition and function in cynomolgus macaques. Aging 2019, 11, 12080–12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, M.C.; Montague, M.J.; Villamil, C.I.; Stock, M.K.; Trujillo, A.E.; DePasquale, A.N.; Orkin, J.D.; Surratt, S.E.B.; Gonzalez, O.; Platt, M.L.; et al. Age and sex-associated variation in the multi-site microbiome of an entire social group of free-ranging rhesus macaques. Microbiome 2021, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzà, S.; Schneider, D.; Daniel, R.; Heistermann, M.; Sangmaneedet, S.; Ostner, J.; Schülke, O. The long-term gut bacterial signature of a wild primate is associated with a timing effect of pre- and postnatal maternal glucocorticoid levels. Microbiome 2023, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, D.N.; Lubach, G.R.; Lyte, M.; Phillips, G.J.; Gosain, A.; Pierre, J.F.; Vlasova, R.M.; Styner, M.A.; Coe, C.L. Proteobacteria abundance during nursing predicts physical growth and brain volume at one year of age in young rhesus monkeys. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyimo, B.; Hugho, E.; Mathew, C.; Mayenga, C.; Lukambagire, A.H.; Lyimo, S.; Munuo, L.; Byukusenge, M.; Withall, J.; Ashford, R.T.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors for brucellosis amongst livestock and humans in a multi-herd ranch system in Kagera, Tanzania. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1478494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, U.; Girdhar, Y.; Kaur, M.; Kapoor, P.; Ahlawat, S.; Vijh, R.K. Buffalo milk transcriptome: A comparative analysis of early, mid and late lactation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, D.; Rekowska, A.K.; Grunwald, A.; Bień, K.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Impact of Maternal Body Composition, Hydration, and Metabolic Health on Breastfeeding Success: A Comprehensive Review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e945591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Cui, Z.; Ma, K.; Wu, D.; Luo, J.; Li, F.; Xiong, W.; Rao, S.; Xiang, Q.; et al. Lachnospiraceae -derived butyrate mediates protection of high fermentable fiber against placental inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itell, H.L.; Kaur, A.; Deere, J.D.; Barry, P.A.; Permar, S.R. Rhesus monkeys for a nonhuman primate model of cytomegalovirus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.P.V.; Paster, B.J.; Grimaldi, G.; Lourenço, T.G.B.; Teva, A.; Campos-Neto, A.; McCluskey, J.; Kleanthous, H.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Stashenko, P. Clinical and microbiological parameters of naturally occurring periodontitis in the non-human primate Macaca mulatta. J. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 9, 1403843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rera, M.; Azizi, M.J.; Walker, D.W. Organ-specific mediation of lifespan extension: More than a gut feeling? Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shute, A.; Bihan, D.G.; Lewis, I.A.; Nasser, Y. Metabolomics: The Key to Unraveling the Role of the Microbiome in Visceral Pain Neurotransmission. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 917197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lan, Y.; Yue, B.; He, M.; Zhang, A.; Li, J. Assembly of novel microbial genomes from gut metagenomes of rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta). Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2188848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Xiong, J.; Yang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.; Qian, W.; Hu, S.; Wang, Q.; Aleem, M.T.; Miao, W.; et al. Metagenome of Gut Microbiota Provides a Novel Insight into the Pathogenicity of Balantioides coli in Weaned Piglets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, O.; Bartuv, R.; Vetcos, M.; Medina, S.; Jiang, J.; Freilich, S. NetCom: A Network-Based Tool for Predicting Metabolic Activities of Microbial Communities Based on Interpretation of Metagenomics Data. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, R.M.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Stepanauskas, R.; Harmon-Smith, M.; Doud, D.; Reddy, T.B.K.; Schulz, F.; Jarett, J.; Rivers, A.R.; Eloe-Fadrosh, E.A.; et al. Minimum information about a single amplified genome (MISAG) and a metagenome-assembled genome (MIMAG) of bacteria and archaea. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A. McCormick, Aging, Frailty, and the Microbiome-How Dysbiosis Influences Human Aging and Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.A.; Supali, T.; Gankpala, L.; Djuardi, Y.; Sartono, E.; Zhou, Y.; Fischer, K.; Martin, J.; Tyagi, R.; Bolay, F.K.; et al. Differential human gut microbiome assemblages during soil-transmitted helminth infections in Indonesia and Liberia. Microbiome 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretler, T.; Weisberg, H.; Koren, O.; Neuman, H. The effects of antipsychotic medications on microbiome and weight gain in children and adolescents. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.E.B.; Rubel, M.A.; Bailey, A.G.; Ranciaro, A.; Thompson, S.R.; Campbell, M.C.; Beggs, W.; Dave, J.R.; Mokone, G.G.; Mpoloka, S.W.; et al. Population structure of human gut bacteria in a diverse cohort from rural Tanzania and Botswana. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mouali, Y.; Tawk, C.; Huang, K.D.; Amend, L.; Lesker, T.R.; Ponath, F.; Vogel, J.; Strowig, T. The RNA landscape of the human commensal Segatella copri reveals a small RNA essential for gut colonization. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1910–1926.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, A.; Huang, K.D.; Asnicar, F.; Fehlner-Peach, H.; Pasolli, E.; Karcher, N.; Armanini, F.; Manghi, P.; Bonham, K.; Zolfo, M.; et al. The Prevotella copri Complex Comprises Four Distinct Clades Underrepresented in Westernized Populations. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 666–679.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lesker, T.R.; Gronow, A.; Gilbert, B.; Raemy, E.; Lamacchia, C.; Gabay, C.; Finckh, A.; Strowig, T. Prevotella copri in individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.M.; Adebayo, A.S.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Freidin, M.B.; Finckh, A.; Strowig, T.; Lesker, T.R.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Gilbert, B.; Kirkham, B.; et al. Associations between gut microbiota and genetic risk for rheumatoid arthritis in the absence of disease: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e418–e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Jia, D.; et al. Heat-inactivated Bifidobacterium adolescentis ameliorates colon senescence through Paneth-like-cell-mediated stem cell activation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, J.; Ge, Q.; Fan, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hou, T.; et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis regulates catalase activity and host metabolism and improves healthspan and lifespan in multiple species. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qie, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mi, K.; Pei, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The landscape in the gut microbiome of long-lived families reveals new insights on longevity and aging—Relevant neural and immune function. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Jing, Y.; Qi, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. Author Correction: Deep insights into the gut microbial community of extreme longevity in south Chinese centenarians by ultra-deep metagenomics and large-scale culturomics. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Yu, K.; Song, S.; et al. Male-Biased Gut Microbiome and Metabolites Aggravate Colorectal Cancer Development. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Stavropoulou, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Current Insights in Microbiome Shifts in Sjogren’s Syndrome and Possible Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Shang, X.; Liu, J.; Chi, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, T. The gut microbiota in osteoarthritis: Where do we stand and what can we do? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.H.; Camilleri, M.; Crowe, S.E.; El-Omar, E.M.; Fox, J.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Malfertheiner, P.; McColl, K.E.; Pritchard, D.M.; Rugge, M.; et al. The stomach in health and disease. Gut 2015, 64, 1650–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansour, O. Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) in the Arab World: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e65421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Gimenez, G.; Laiger, J.C.; Robert, C.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Genome sequence and description of Alistipes senegalensis sp. nov. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2012, 6, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.-X.; Zheng, K.-Y.; Wang, Y.-G. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key mucosal barrier modulators in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5555–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Hao, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Bi, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y. Quantitative and dynamic profiling of human gut core microbiota by real-time PCR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Shi, B.; Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Hong, L.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, M.; Yan, S. Artemisia annua L. polysaccharide improves the growth performance and intestinal barrier function of broilers challenged with Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guan, K.; Su, Q.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Kuang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, B. Change of Gut Microbiota in PRRSV-Resistant Pigs and PRRSV-Susceptible Pigs from Tongcheng Pigs and Large White Pigs Crossed Population upon PRRSV Infection. Animals 2022, 12, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Shao, L.; Sun, S.-H.; Wu, J.; Song, Q.-H.; Zou, H.-S.; Ling, Z.-X. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Chinese children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: An observational study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2394–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaddar, N.; El Roz, A.; Ghssein, G.; Ibrahim, J.-N. Emergence of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis among Lebanese Pregnant Women: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Species Distribution. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 2019, 5016810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszka, K.; Wahli, W. Enteric Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis from the Perspective of Nuclear Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dellatore, P.; Douard, V.; Qin, L.; Watford, M.; Ferraris, R.P.; Lin, T.; Shapses, S.A. High fat diet enriched with saturated, but not monounsaturated fatty acids adversely affects femur, and both diets increase calcium absorption in older female mice. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, S.; Gras-Leguen, C.; Le Vacon, F.; Potel, G.; de La Cochetiere, M.-F. Development of intestinal microbiota in infants and its impact on health. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezirtzoglou, E.; Stavropoulou, E. Immunology and probiotic impact of the newborn and young children intestinal mi-croflora. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leser, T.D.; Mølbak, L. Better living through microbial action: The benefits of the mammalian gastrointestinal microbiota on the host. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2194–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-X.; Liu, L.-D.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhu, S.-S.; Ye, B.-Q.; Yang, J.-L.; Huang, J.-Y.; Huang, Z.-H.; You, Y.; Li, W.-K.; et al. Alistipes indistinctus-derived hippuric acid promotes intestinal urate excretion to alleviate hyperuricemia. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 366–381.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, R.; Nugent, M.; Cai, W.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Chaves, L.D.; Abyad, S.; Honan, A.M.; Thomas, S.A.; Zheng, W.; Valiyaparambil, S.A.; et al. Advanced glycation end products dietary restriction effects on bacterial gut microbiota in peritoneal dialysis patients; a randomized open label controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Cai, T.; Dong, L.; Liang, S.; Zhu, L.; Song, X.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Administration of Alistipes indistinctus prevented the progression from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by enhancing the gut barrier and increasing Lactobacillus spp. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 741, 151033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The Genus Alistipes: Gut Bacteria With Emerging Implications to Inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, F.; Morotomi, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Sakon, H.; Tanaka, R. Alistipes indistinctus sp. nov. and Odoribacter laneus sp. nov., common members of the human intestinal microbiota isolated from faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kajiura, S.; Hirai, Y.; Watanabe, T. Capnocytophaga haemolytica sp. nov. and Capnocytophaga granulosa sp. nov., from Human Dental Plaque. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciantar, M.; Spratt, D.A.; Newman, H.N.; Wilson, M. Capnocytophaga granulosa and Capnocytophaga haemolytica: Novel species in subgingival plaque. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2001, 28, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Martin, M.A.; Araji, O.A.; Barquero, J.M.; Velázquez, C.; García-Borbolla, M.; Gallego, P.; Infantes, C.A. Aortic Valve Endocarditis by Capnocytophaga Haemolytica. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idate, U.; Bhat, K.; Kulkarni, R.D.; Kotrashetti, V.; Kugaji, M.; Kumbar, V. Comparison of culture and polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism for identification of various Capnocytophaga species from subgingival plaque samples of healthy and periodontally diseased individuals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2022, 26, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaseñor-Aranguren, M.; Rosés, C.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Barceló, A.M.; Milagro, F.I. Association of the Gut Microbiota with the Host’s Health through an Analysis of Biochemical Markers, Dietary Estimation, and Microbial Composition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, R.X.; Colgan, S.P. Physiologic hypoxia in the intestinal mucosa: A central role for short-chain fatty acids. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2024, 327, C1087–C1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xu, X.; Xia, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, S.; Xiang, X.; Xia, D.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Variation of Gut Microbiome in Free-Ranging Female Tibetan Macaques (Macaca thibetana) across Different Reproductive States. Animals 2020, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuffa, S.; Lay, C.; Wimborne, E.A.; Rodriguez, A.H.; Wu, Y.; Nobrega, F.L.; Bartke, N.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S.; Knol, J.; Roeselers, G.; et al. Milk phospholipid-coated lipid droplets modulate the infant gut microbiota and metabolome influencing weight gain. Microbiome 2025, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L. Microbiome-Metabolomics Insights into the Milk of Lactating Dairy Cows to Reveal the Health-Promoting Effects of Dietary Citrus Peel Extracts on the Mammary Metabolism. Foods 2022, 11, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Number of Individuals in Different Age Groups | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–3 Years | 4–6 Years | 7–12 Years | 13–17 Years | Over 17 Years Old | |||
| Sex | Female | 5 | 11 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 29 |
| Male | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 | |
| Lactation | 0 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 11 | |
| Non-lactation | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 7 | |
| Weight/kg | 2.32 ± 0.07 | 5.69 ± 0.61 | 7.65 ± 0.68 | 7.95 ± 0.63 | 7.97 ± 0.76 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Cai, K. A Spatiotemporal Atlas of the Gut Microbiota in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus: Implications for Health and Environment. Biology 2025, 14, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080980
Yuan J, Sun Z, Sun R, Wang J, Wu C, Liu B, Zhao X, Li Q, Zhao J, Cai K. A Spatiotemporal Atlas of the Gut Microbiota in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus: Implications for Health and Environment. Biology. 2025; 14(8):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080980
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jingli, Zewen Sun, Ruiping Sun, Jun Wang, Chengfeng Wu, Baozhen Liu, Xinyuan Zhao, Qiang Li, Jianguo Zhao, and Keqi Cai. 2025. "A Spatiotemporal Atlas of the Gut Microbiota in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus: Implications for Health and Environment" Biology 14, no. 8: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080980
APA StyleYuan, J., Sun, Z., Sun, R., Wang, J., Wu, C., Liu, B., Zhao, X., Li, Q., Zhao, J., & Cai, K. (2025). A Spatiotemporal Atlas of the Gut Microbiota in Macaca mulatta brevicaudus: Implications for Health and Environment. Biology, 14(8), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080980





