Nanogel Loaded with Perilla frutescens Leaf-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Indomethacin for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Animals
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of PFE
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of PFE-GEL, IND-GEL, and PFE-IND-GEL
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.7. Rat IA Model and Treatment
2.8. Inflammatory Cytokine Measurement
2.9. Histopathological Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
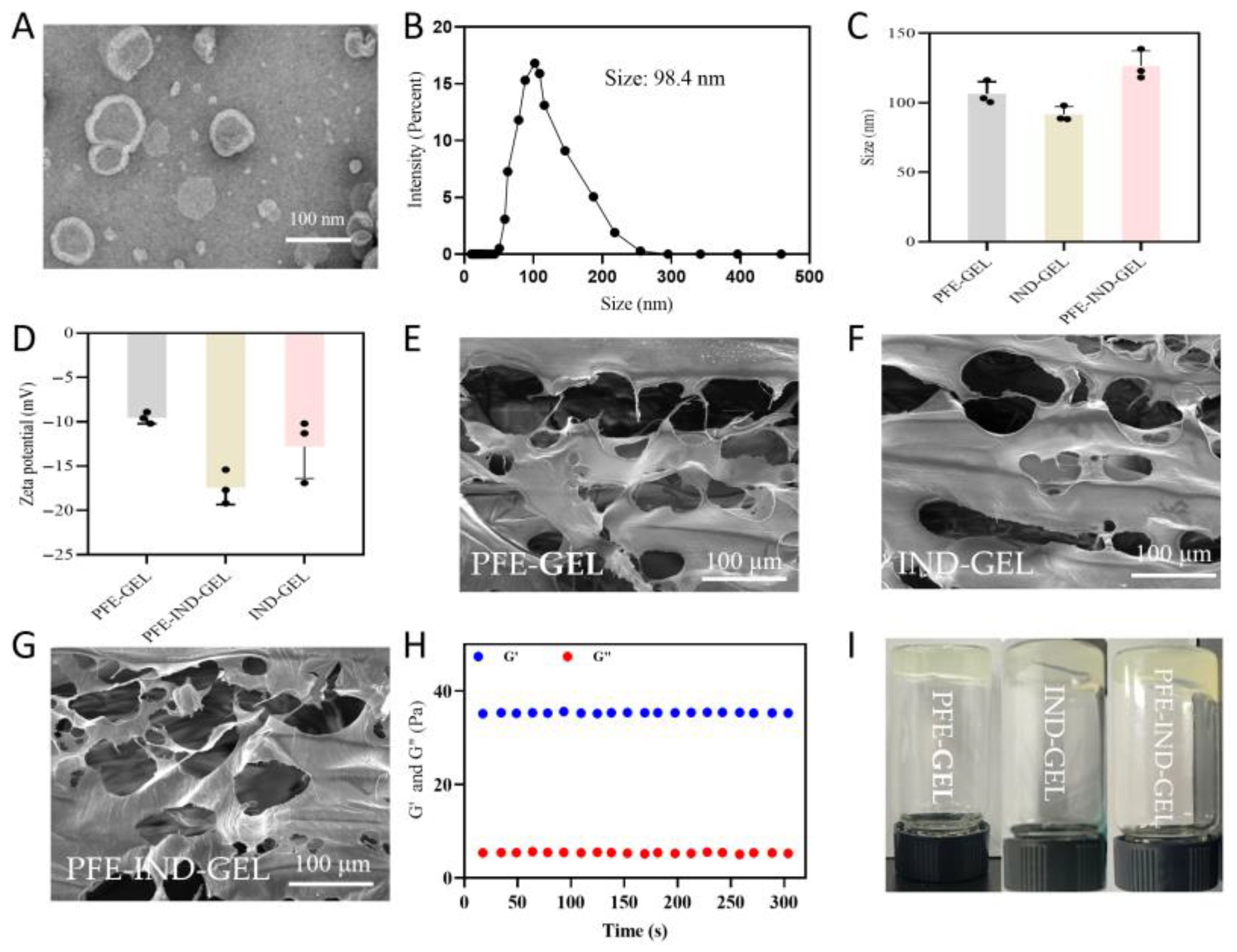
3.1. Characterization of PFE, PFE-GEL, IND-GEL, and PFE-IND-GEL
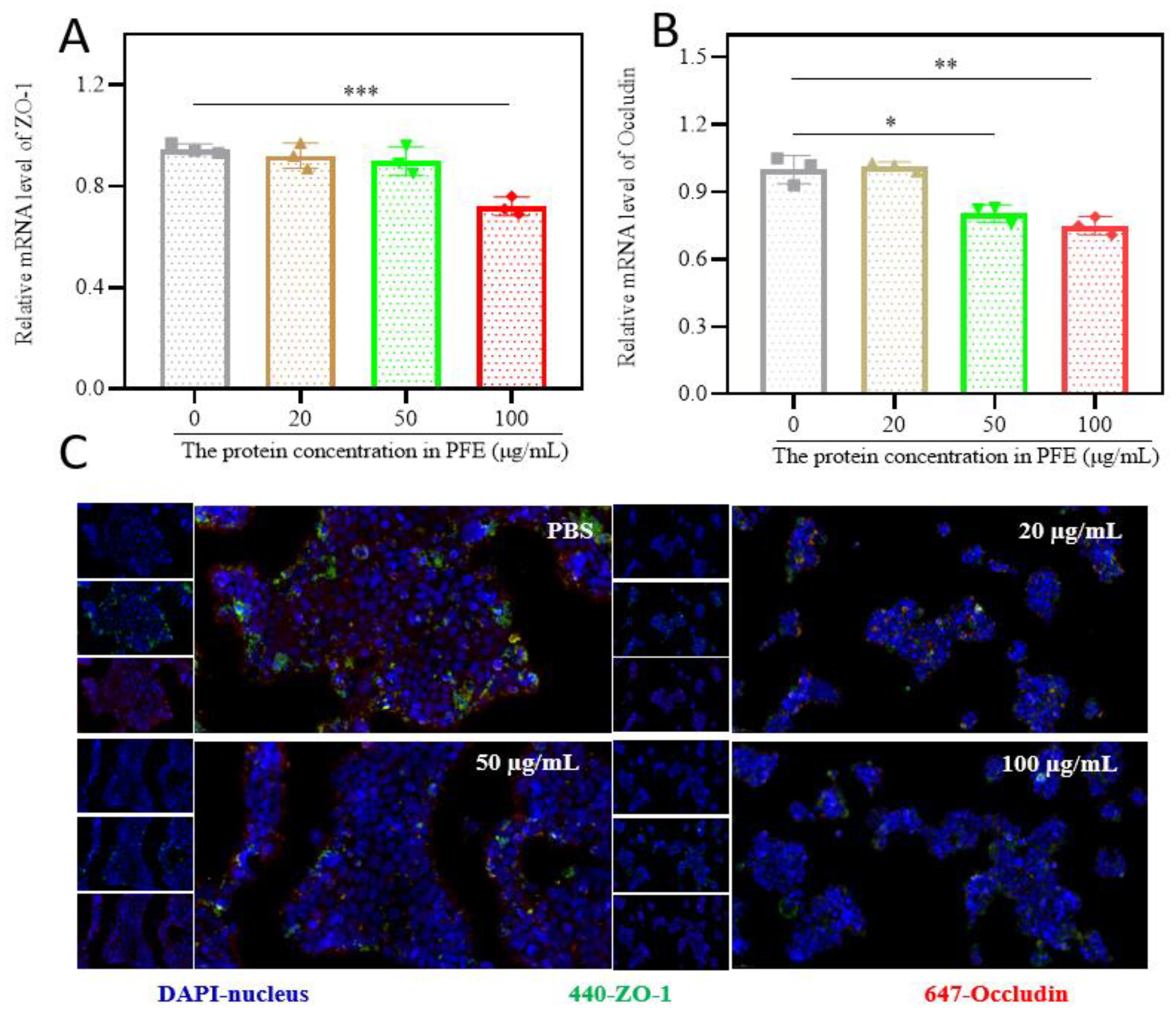
3.2. PFE Reduces Tight Junction Protein Expression in HaCaT Cells
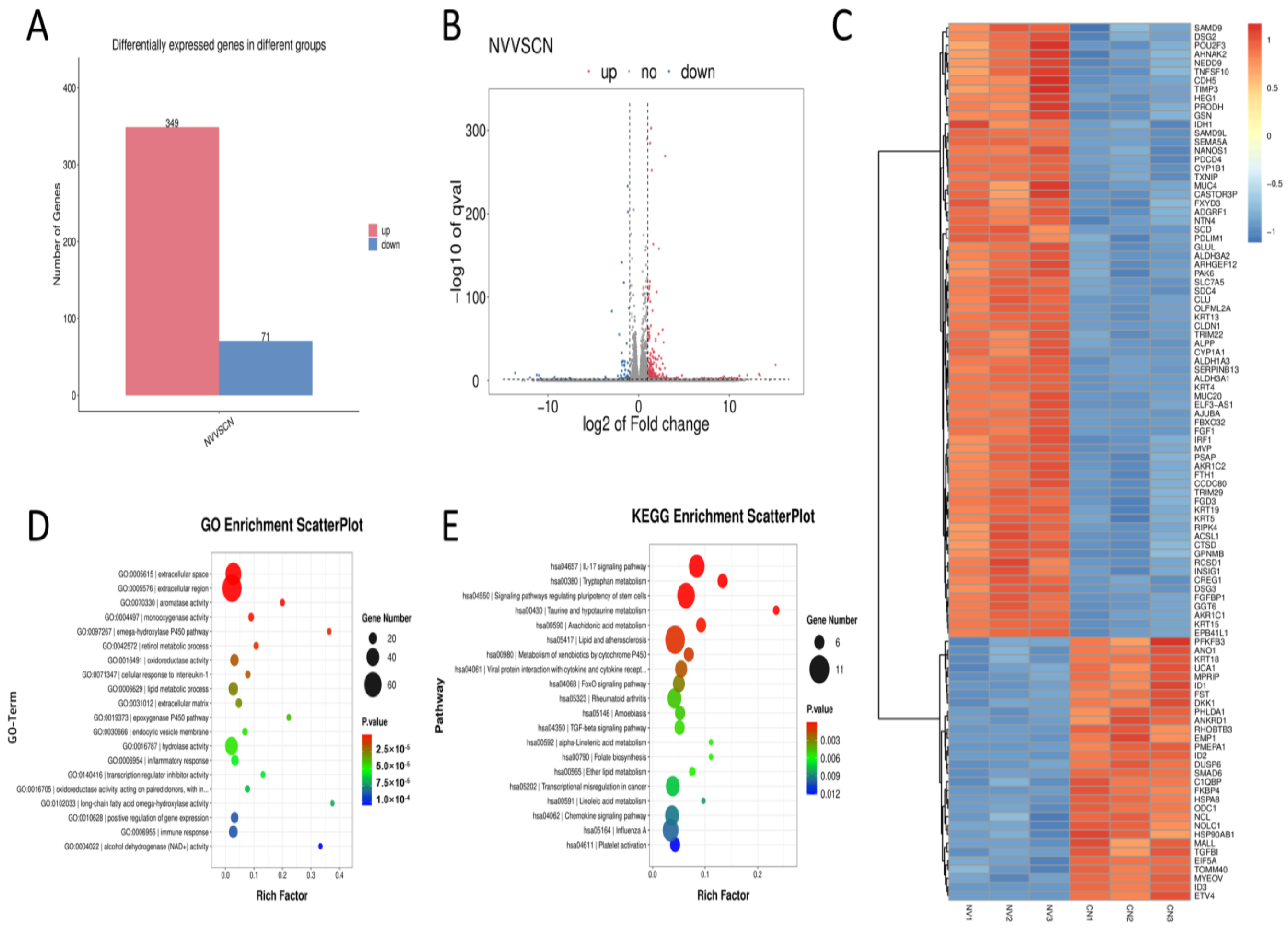
3.3. Transcriptomic Profiling of PFE-Treated HaCaT Cells
3.4. Therapeutic Efficacy of PFE-IND-GEL in Arthritic Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IA | Inflammatory arthritis |
| IND | Indomethacin |
| PFE | Perilla Frutescens leaf-derived exosome-like nanovesicles |
| PFE-IND-GEL | PFE loaded with IND and developed into a nanogel designed |
| TDDS | Topical drug delivery systems |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
References
- Wedderburn, L.R.; Ramanan, A.V.; Croft, A.P.; Hyrich, K.L.; Dick, A.D. Towards molecular-pathology informed clinical trials in childhood arthritis to achieve precision medicine in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.M.; Primdahl, J.; Bremander, A.; Eggen, L.; Christensen, J.R. Developing a complex vocational rehabilitation intervention for patients with inflammatory arthritis: The WORK-ON study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursum, J.; Nielen, M.M.; Twisk, J.W.; Peters, M.J.; Schellevis, F.G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Korevaar, J.C. Increased risk for chronic comorbid disorders in patients with inflammatory arthritis: A population-based study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2013, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Ge, G.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, L.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Wei, M.; et al. Prevention and treatment of inflammatory arthritis with traditional Chinese medicine: Underlying mechanisms based on cell and molecular targets. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 89, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuls-Mirete, M.; Ogdie, A.; Guma, M. Micronutrients: Essential Treatment for Inflammatory Arthritis? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinikhah, S.M.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Madry, H.; Arshad, R.; Mohammadzadeh, V.; Cucchiarini, M. Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmunzer, B.J.; Hernandez, I.; Gellad, W.F. The Skyrocketing Cost of Rectal Indomethacin. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, S.; Shehata, M.; Albuhiri, A.; Khairy, A. Combined rectal indomethacin and intravenous saline hydration in post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 23, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.; Song, M.; Kim, M.; Park, H.K.; Kim, D.W.; Pang, C. Bioinspired Suction-Driven Strategies with Nanoscale Skin-Controllable Adhesive Architectures for Efficient Liquid Formulated Transdermal Patches. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 13567–13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, M.; Ren, C.; Li, M.; Liu, M.; You, Z.; Li, P. Therapeutic potential of Lycium barbarum-derived exosome-like nanovesicles in combating photodamage and enhancing skin barrier repair. Extracell. Vesicle 2025, 5, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H. Separation, characterization and anti-inflammatory activities of galactoglycerolipids from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 37, 3610–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, B.R.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Mu, Z.S. Rosmarinic acid in Perilla frutescens L. as a potential adenosine deaminase inhibitor: Preparation, machine learning validation and binding mechanism study. Food Chem. 2025, 485, 144458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Chang, C.J. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of Perilla frutescens-derived extracellular vesicles: Insights from Zebrafish models. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 182, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, M.; Peng, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, T. An improvised one-step OptiPrep cushion ultracentrifugation method for outer membrane vesicles isolation of Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y. Exosomes: Compositions, biogenesis, and mechanisms in diabetic wound healing. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isik, M.; Vargel, I.; Ozgur, E.; Cam, S.B.; Korkusuz, P.; Emregul, E. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes-loaded hybrid hydrogel enhances the calvarial defect regeneration in middle-age rats. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Han, D. GelMA combined with sustained release of HUVECs derived exosomes for promoting cutaneous wound healing and facilitating skin regeneration. J. Mol. Histol. 2020, 51, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Wang, F.; Lin, L.; Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Shang, Y.; Hua, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, B.; Peng, Z. The T-type voltage-gated Ca(2+) channel Ca(V)3.1 involves in the disruption of respiratory epithelial barrier induced by Pasteurella multocida toxin. Virulence 2025, 16, 2466482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manara, M.; Carriero, A.; Congia, M.; Galluzzo, C.; Pandolfi, M.; Salvato, M.; Scriffignano, S.; Cauli, A.; D’Angelo, S.; Lubrano, E.; et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in psoriatic arthritis: Clinical practice suggestions based on scientific evidence and expert opinion. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2025, 43, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Fang, J.; Song, Z.; Geng, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Green and efficient extraction of flavonoids from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. leaves based on natural deep eutectic solvents: Process optimization, component identification, and biological activity. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Formulations | Oxidized Alginate | GelMA | LAP | CaCl2 | PFE | IND | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFE-GEL | 3.75 mL | 5 mL | 0.25 mL | 5 mL | 1 mL | 10 mL | |
| IND-GEL | 3.75 mL | 5 mL | 0.25 mL | 5 mL | 1 g | 11 mL | |
| PFE-IND-GEL | 3.75 mL | 5 mL | 0.25 mL | 5 mL | 1 mL | 1 g | 10 mL |
| Target | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ZO-1 | CGGAAAGGGTGAAGGAGATG | CATTGCCATCCTCTTCATCC |
| Occludin | TGTGGGTTCCTACTGCTGCT | AGCCACAGCCATTGTAGTCC |
| GAPDH | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, W. Nanogel Loaded with Perilla frutescens Leaf-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Indomethacin for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Biology 2025, 14, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080970
Li X, Wang F, Wang R, Cheng Y, Liu J, Luo W. Nanogel Loaded with Perilla frutescens Leaf-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Indomethacin for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Biology. 2025; 14(8):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080970
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianqiang, Fei Wang, Rui Wang, Yanjie Cheng, Jinhuan Liu, and Wanhe Luo. 2025. "Nanogel Loaded with Perilla frutescens Leaf-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Indomethacin for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis" Biology 14, no. 8: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080970
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, F., Wang, R., Cheng, Y., Liu, J., & Luo, W. (2025). Nanogel Loaded with Perilla frutescens Leaf-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Indomethacin for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Biology, 14(8), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080970






