Comparative Study of Lefaxin Family in Two Asian Leeches: Hirudinaria manillensis and Whitmania pigra
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA and RNA Sequencing
2.2. Sequence Extraction
2.3. Intraspecific Variation Analysis
2.4. Molecular Evolution Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Protein Biochemical Properties
2.7. Protein Structure Alignment Analysis
2.8. Protein Docking Analysis
2.9. Pichia Pastoris Expression
2.10. Anticoagulation Test
3. Results
3.1. Intraspecific Variation
3.2. Molecular Evolution
3.3. Gene Expression
3.4. Protein Biochemical Properties
3.5. Protein Structure Alignment
3.6. Protein Docking
3.7. Recombinant Protein Synthesis
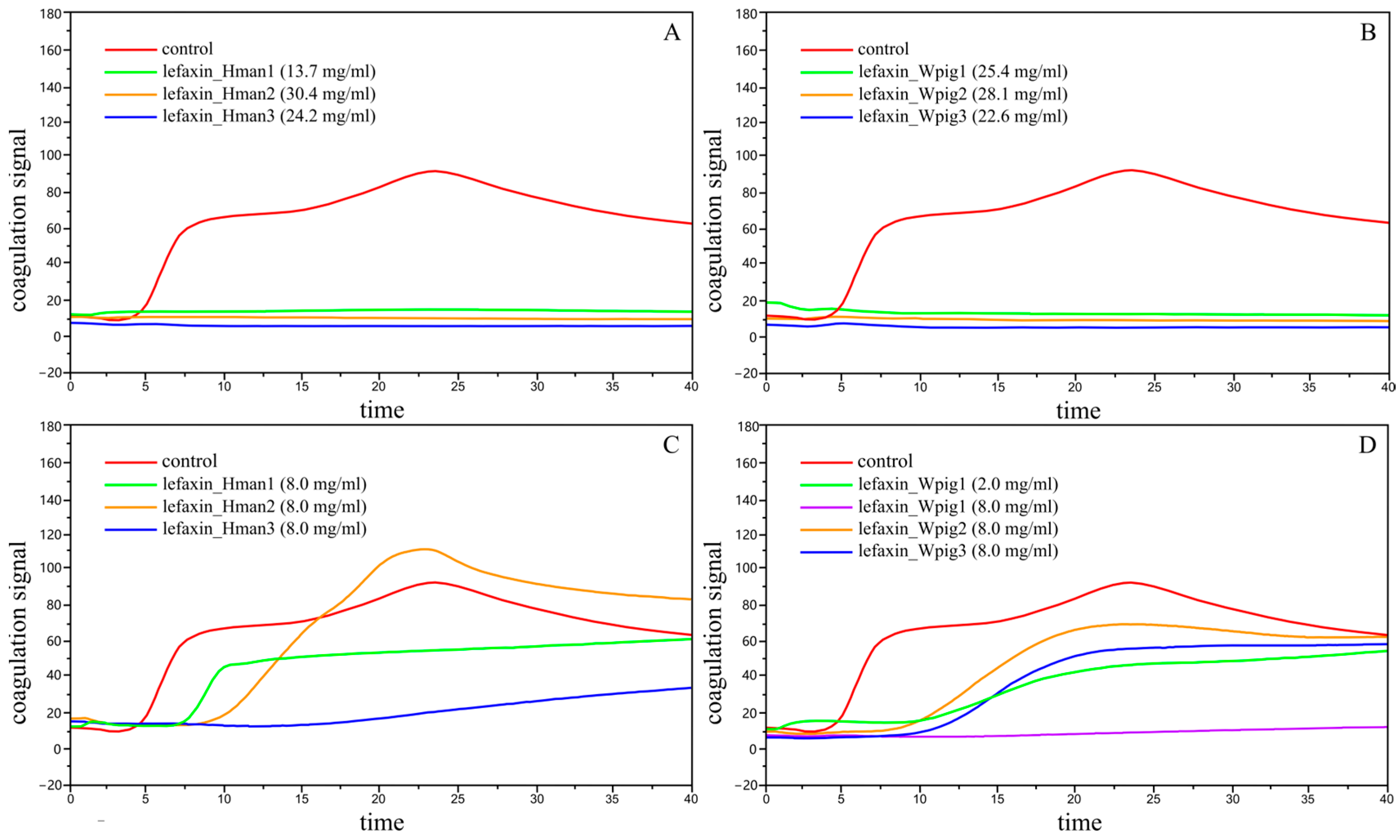
3.8. Anticoagulation of Lefaxins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| VS | number of variable sites |
| HN | number of haplotypes |
| WD | Watterson’s Theta diversity |
| TPM | transcripts per million |
| pI | isoelectric point |
| II | instability index |
| GRAVY | grand average of hydropathy |
| RMSD | root mean square deviation |
| YEPD | Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose |
| ACT | activated clotting time |
| CR | clot rate |
| PF | platelet function |
References
- Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Advances on the application of artificial intelligence in thromboembolic diseases. Chin. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2023, 29, 231–236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. In silico discovery of novel FXa inhibitors by pharmacophore modeling and molecular docking. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2017, 7, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, I.S.; Rao, J.; Izadi, D.; Butler, P.E. Historical Article: Hirudo medicinalis: Ancient origins of, and trends in the use of medicinal leeches throughout history. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 42, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okka, B. Hirudotherapy from past to present. Eur. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.; Jameel, S.; Zaman, F.; Jilani, S.; Sultana, A.; Khan, S.A. A systematic overview of the medicinal importance of sanguivorous leeches. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sig, A.K.; Guney, M.; Uskudar Guclu, A.; Ozmen, E. Medicinal leech therapy-an overall perspective. Integr. Med. Res. 2017, 6, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.P. Therapeutic Potentials of Medicinal Leech in Chinese Medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 52, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, R.L.; Qiu, G.X. Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Thrombotic Diseases in China; Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Shi, P.; You, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Transcriptomic analysis of the salivary gland of medicinal leech Hirudo nipponia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Pan, H. Comparative Study on Differentially Expressed Genes of Hirudinaria manillensis, Hirudo nipponia, and Whitmania pigra. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2024, 43, 1413–1429. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Drug Administration. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Medicine Quality Standards; Guangxi Science and Technology Press: Nanning, China, 2011; Volume 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yunnan Provincial Drug Administration. Yunnan Chinese Medicinal Materials Standard; Yunnan Provincial Drug Administration: Kunming, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.J.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Research progress in the use of leeches for medical purposes. Tradit. Med. Res. 2021, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Ren, K.; Liu, J.; Rehman, S.; Yan, X.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Comprehensive Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis of Hirudinaria manillensis in Different Growth Periods. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 897458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Qi, M.; Yang, X.J. Research Progress on Composition and Breeding Technology of Poecilobdella manillensis. Feed. Ind. 2021, 42, 59–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Kong, W.J.; Yang, M.H.; Ouyang, Z. Advances in the Study of Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Poecilobdella manillensis. Cent. South Pharm. 2013, 11, 750–753. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.T.; Li, J.H. Research Progress in the Analysis of Anticoagulant Active Substances in Leeches and the Extraction and Purification of Hirudin. Acta Neuropharmacol. 2021, 11, 30–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, E.G. Zoogeoraphy of Hirudinidae in China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2007, 46, 100–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Dai, S.-X.; Kong, D.-J.; Yang, P.-P.; Tong, X.; Tong, X.-R.; Bi, X.-X.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-C. The genome of medicinal leech (Whitmania pigra) and comparative genomic study for exploration of bioactive ingredients. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.X.; Li, Z.Y. Extraction and SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis of Anticoagulant Components from Poecilobdella manillensis Lesson in Hainan. J. South China Univ. Trop. Agric. 2019, 10, 204–207. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.Y.; Ren, K.; Ma, X.C.; Shan, H.Q.; Zheng, Y.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhou, W.G.; Zheng, J.H. Comparison on differentially expressed genes in larval, juvenile and adult Hirudo nipponia at different growth stages. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 2714–2724. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Gong, Y.; Yu, X.; Lv, J.Y. Anticoagulant Active Substances Extraction and Anti-Thrombin Activity Analysis of Several Species of Leeches. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2012, 51, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.N.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C.M.; Zhang, Y.Q. Research progress on processing history evolution, chemical constituents, and pharmacological effects of Hirudo. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2022, 47, 5806–5816. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Fan, M.D.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.M. Research Progress on Pharmacological Pechanism of Shuizhi (Hirudo) in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F. Untersuchungen über hirudin. Naturwissenschaften 1955, 42, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montinari, M.R.; Minelli, S. From ancient leech to direct thrombin inhibitors and beyond: New from old. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mory, R.N.; Mindell, D.; Bloom, D.A. The leech and the physician: Biology, etymology, and medical practice with Hirudinea medicinalis. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Law, S.W.; Keller, P.M.; Kniskern, P.J.; Silberklang, M.; Tung, J.-S.; Gasic, T.B.; Gasic, G.J.; Friedman, P.A.; Ellis, R.W. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding antistasin, a leech-derived protein having anti-coagulant and anti-metastatic properties. Gene 1989, 75, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.; Henzel, W.; Nevins, B.; Stults, J.; Lazarus, R. Decorsin. A potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonist and platelet aggregation inhibitor from the leech Macrobdella decora. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10143–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.; Auerswald, E.; Mentele, R.; Eckerskorn, C.; Fritz, H.; Fink, E. Bdellastasin, a serine protease inhibitor of the antistasin family from the medical leech (Hirudo medicinalis) primary structure, expression in yeast, and characterisation of native and recombinant inhibitor. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 253, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manithody, C.; Yang, L.; Rezaie, A.R. Identification of exosite residues of factor Xa involved in recognition of PAR-2 on endothelial cells. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, D.; Bylund, R.; Antonsson, T.; Nilsson, I.; Nyström, J.-E.; Eriksson, U.; Bredberg, U.; Teger-Nilsson, A.-C. A new oral anticoagulant: The 50-year challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, F.; Kelen, E.M.A.; Sampaio, C.A.; Bon, C.; Duval, N.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. A new factor Xa inhibitor (lefaxin) from the Haementeria depressa leech. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Tang, L.Z.; He, B.; Liu, Z.C.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Lin, G.H. Intraspecific variation in the hirudin gene family of the asian buffalo leech (Hirudinaria manillensis). J. Jinggangshan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2024, 45, 38–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Meng, R.; Lin, Y.; Qi, J.; Lin, G. Revisiting the Asian buffalo leech (Hirudinaria manillensis) genome: Focus on antithrombotic genes and their corresponding proteins. Genes 2023, 14, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; He, B.; Liu, K.; Shi, F.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, G. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the non-hematophagous leech Whitmania pigra (Whitman 1884): Identification and expression analysis of antithrombotic genes. Genes 2024, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevreux, B.; Wetter, T.; Suhai, S. Genome Sequence Assembly Using Trace Signals and Additional Sequence Information. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Bioinformatics, Hannover, Germany, 4–6 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X. DAMBE5: A Comprehensive Software Package for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, G. Comparative genomics of three non-hematophagous leeches (Whitmania spp.) with emphasis on antithrombotic biomolecules. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1548006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöver, B.C.; Müller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yang, Z. pamlX: A Graphical User Interface for PAML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2723–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.B.; Salkind, N.J. Using SPSS for Windows and Macintosh; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, L.; Xiao, M.; Yin, J.; Ye, T.; Sun, R.; Ai, R.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; Lin, G. Genetic Variation and Gene Expression of the Antimicrobial Peptide Macins in Asian Buffalo Leech (Hirudinaria manillensis). Biology 2025, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Godzik, A. Flexible structure alignment by chaining aligned fragment pairs allowing twists. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, ii246–ii255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, L.; Weng, Z. ZDOCK: An initial-stage protein-docking algorithm. Proteins 2003, 52, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, S.Y.; Jiang, J.M.; Wang, H.; Wu, G.S.; Li, L.B.; Chen, Q.L.; Du, L.; Wang, F.Y.; Chen, S. Genetic diversity of Hainan cattle population based on whole genome resequencing and screening of candidate genes related to heat adaptation. J. South. Agric. 2024, 55, 3707–3717. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kühnhold, H.; Steinmann, N.; Huang, Y.-H.; Indriana, L.; Meyer, A.; Kunzmann, A. Temperature-induced aerobic scope and Hsp70 expression in the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chak, S.T.; Baeza, J.A.; Barden, P. Eusociality shapes convergent patterns of molecular evolution across mitochondrial genomes of snapping shrimps. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wen, N.; Wang, C.; Cheng, L. A brief review of protein–ligand interaction prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula, V.S.; Sgourakis, N.G.; Francischetti, I.M.; Almeida, F.C.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Valente, A.P. NMR structure determination of Ixolaris and factor X (a) interaction reveals a noncanonical mechanism of Kunitz inhibition. Blood 2019, 134, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, L.; Hu, S.M. A textual research on Whitmania pigra Whitman as the origin of Hirudo. Chin. Med. Her. 2021, 18, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivot, L.; Mathieux, N.; Cosson, A.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Favennec, L.; Gelly, J.-C.; Clain, J.; Coppée, R. CONSTRUCT: An algorithmic tool for identifying functional or structurally important regions in protein tertiary structure. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.-R. Determinants of the rate of protein sequence evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, A.; Jiang, X.e.; Shen, Y.; Lehner, B. Site-saturation mutagenesis of 500 human protein domains. Nature 2025, 637, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeb, M.; Fang, M.C. Assessing bleeding risk in patients taking anticoagulants. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2013, 35, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
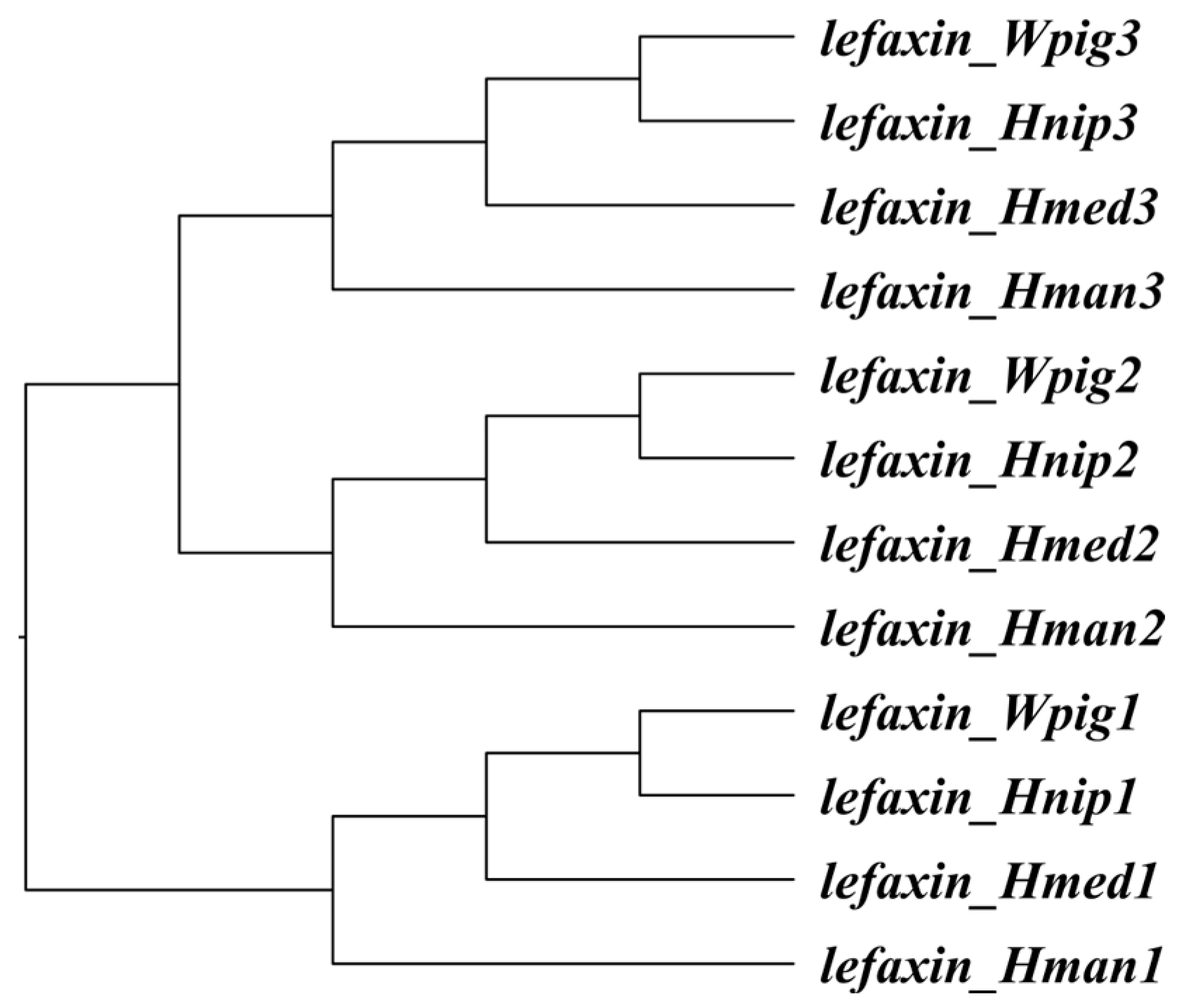
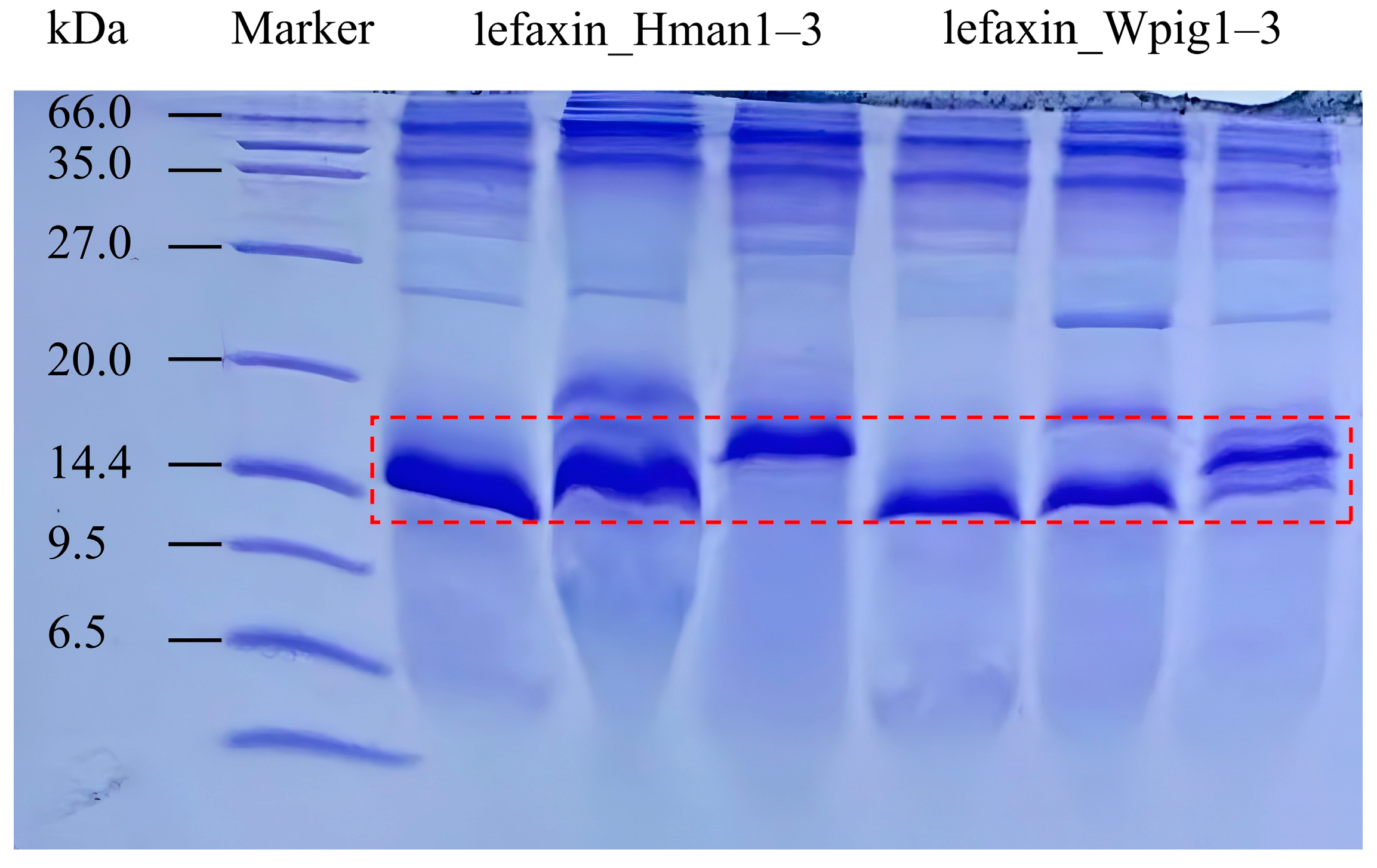
| Gene | Sequence Length | Coding Sequence | Protein Sequence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS | HN | WD | VS | HN | WD | ||
| lefaxin_Hman1 | 363 | 4 | 5 | 0.00529 | 0 | 1 | 0.00000 |
| lefaxin_Hman2 | 363 | 3 | 5 | 0.00397 | 1 | 2 | 0.00826 |
| lefaxin_Hman3 | 378 | 7 | 10 | 0.00655 | 2 | 3 | 0.01058 |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 | 363 | 3 | 5 | 0.00397 | 1 | 2 | 0.00826 |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 | 363 | 2 | 3 | 0.00367 | 1 | 2 | 0.00826 |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 | 378 | 1 | 2 | 0.00265 | 0 | 1 | 0.00000 |
| Total | 2208 | 20 | 30 | — | 5 | 11 | — |
| Gene | Branch Model | Branch-Site Model | Bayesian Empirical Bayesian Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foreground ω | Site Class, Proportion, Foreground ω | Positive Sites (Probability. ω > 1) | |
| lefaxin_Hman1 | 0.02863 | 0, 0.95156, 0.04615 1, 0.04844, 1.00000 2a, 0.00000, 1.00000 2b, 0.00000, 1.00000 | 41 T, 0.569 |
| lefaxin_Hman2 | 0.01793 | 0, 0.03077, 0.04615 1, 0.00157, 1.00000 2a, 0.92080, 1.00000 2b, 0.04687, 1.00000 | — |
| lefaxin_Hman3 | 0.08985 | 0, 0.86746, 0.03985 1, 0.04522, 1.00000 2a, 0.08299, 1.00000 2b, 0.00433, 1.00000 | 80 H, 0.557 81 A, 0.590 |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 | 0.12575 | 0, 0.88938, 0.04210 1, 0.04605, 1.00000 2a, 0.06139, 1.00000 2b, 0.00318, 1.00000 | 27 N, 0.518 30 K, 0.551 61 E, 0.507 |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 | 0.08171 | 0, 0.94221, 0.04591 1, 0.04738, 1.00000 2a, 0.00991, 1.00000 2b, 0.00050, 1.00000 | 87 K, 0.666 |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 | 0.0592 | 0, 0.95156, 0.04615 1, 0.04844, 1.00000 2a, 0.00000, 1.00000 2b, 0.00000, 1.00000 | 48 T, 0.504 |
| Gene | TPM (Mean ± SD) | Mann–Whitney U Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. manillensis | W. pigra | Z | p | |
| lefaxin1 | 5394.3 ± 2064.9 a | 5729.7 ± 2729.1 b | −0.402 | 0.688 |
| lefaxin2 | 4540.1 ± 3822.4 a | 23,205.8 ± 10,273.6 a | −6.803 | <0.001 |
| lefaxin3 | 78.6 ± 42.9 b | 105.9 ± 28.1 c | −3.289 | <0.001 |
| total | 10,013.0 ± 5930.2 | 29,041.4 ± 13,030.8 | −3.814 | <0.001 |
| Protein | Sequence Length | Molecular Weight (Da) | pI | II | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lefaxin_Hman1 | 120 | 13,856.54 | 5.64 | 29.55 | 76.33 | −0.524 |
| lefaxin_Hman2 | 120 | 13,772.50 | 5.69 | 27.27 | 69.08 | −0.588 |
| lefaxin_Hman3 | 125 | 14,800.67 | 5.75 | 34.55 | 80.32 | −0.626 |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 | 120 | 13,904.55 | 5.77 | 34.05 | 73.08 | −0.600 |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 | 120 | 13,858.55 | 5.69 | 27.79 | 68.25 | −0.631 |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 | 125 | 14,947.90 | 5.72 | 38.34 | 78.00 | −0.658 |
| Protein | Interacting Residue Pairs Between Factor Xa and Each Lefaxin | ZDOCK Scores |
|---|---|---|
| lefaxin_Hman1 | G2-G216, N107-G218, M1-D189 | 881.685 |
| lefaxin_Hman2 | S70-Q192, S70-R143, S68-G218, S68-G216, L120-Q61, K66-K96, K66-Y99 | 1028.977 |
| lefaxin_Hman3 | R41-G218, D45-K96 | 669.794 |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 | E103-K96, E103-Y99, G2-G216, K110-R222 | 932.989 |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 | M1-G218, M1-D189, M1-A190, T112-N107, T112-R222 | 1123.996 |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 | G114-S173, M1-S195, H3-Y99, I5-K96, N2-D102, R4-I175 | 955.779 |
| Treat | ACT | CR | PF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 228.3 ± 14.7 | 23.6 ± 1.9 | 2.5 ± 0.4 |
| lefaxin_Hman1 (13.7 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Hman2 (30.4 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Hman3 (24.2 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 (25.4 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 (28.1 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 (22.6 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Hman1 (8.0 mg/mL) | 371.7 ± 35.5 | 16.6 ± 2.4 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| lefaxin_Hman2 (8.0 mg/mL) | 453.7 ± 93.1 | 13.0 ± 1.7 | 1.3 ± 0.5 |
| lefaxin_Hman3 (8.0 mg/mL) | 863.7 ± 344.2 | 4.2 ± 2.2 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 (8.0 mg/mL) | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| lefaxin_Wpig1 (2.0 mg/mL) | 547.3 ± 80.7 | 6.4 ± 2.4 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| lefaxin_Wpig2 (8.0 mg/mL) | 539.0 ± 46.8 | 8.0 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| lefaxin_Wpig3 (8.0 mg/mL) | 690.3 ± 124.6 | 6.6 ± 2.1 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, T.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, M.; Yin, J.; Ai, R.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lin, G. Comparative Study of Lefaxin Family in Two Asian Leeches: Hirudinaria manillensis and Whitmania pigra. Biology 2025, 14, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080918
Ye T, Zhao F, Xiao M, Yin J, Ai R, Tang L, Liu Z, Huang Z, Lin G. Comparative Study of Lefaxin Family in Two Asian Leeches: Hirudinaria manillensis and Whitmania pigra. Biology. 2025; 14(8):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080918
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Tianyu, Fang Zhao, Mingkang Xiao, Jingjing Yin, Rui Ai, Lizhou Tang, Zichao Liu, Zuhao Huang, and Gonghua Lin. 2025. "Comparative Study of Lefaxin Family in Two Asian Leeches: Hirudinaria manillensis and Whitmania pigra" Biology 14, no. 8: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080918
APA StyleYe, T., Zhao, F., Xiao, M., Yin, J., Ai, R., Tang, L., Liu, Z., Huang, Z., & Lin, G. (2025). Comparative Study of Lefaxin Family in Two Asian Leeches: Hirudinaria manillensis and Whitmania pigra. Biology, 14(8), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080918






