Starvation Influences the Microbiota in the Stomach of the Corallivorous Crown-of-Thorns Starfish
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
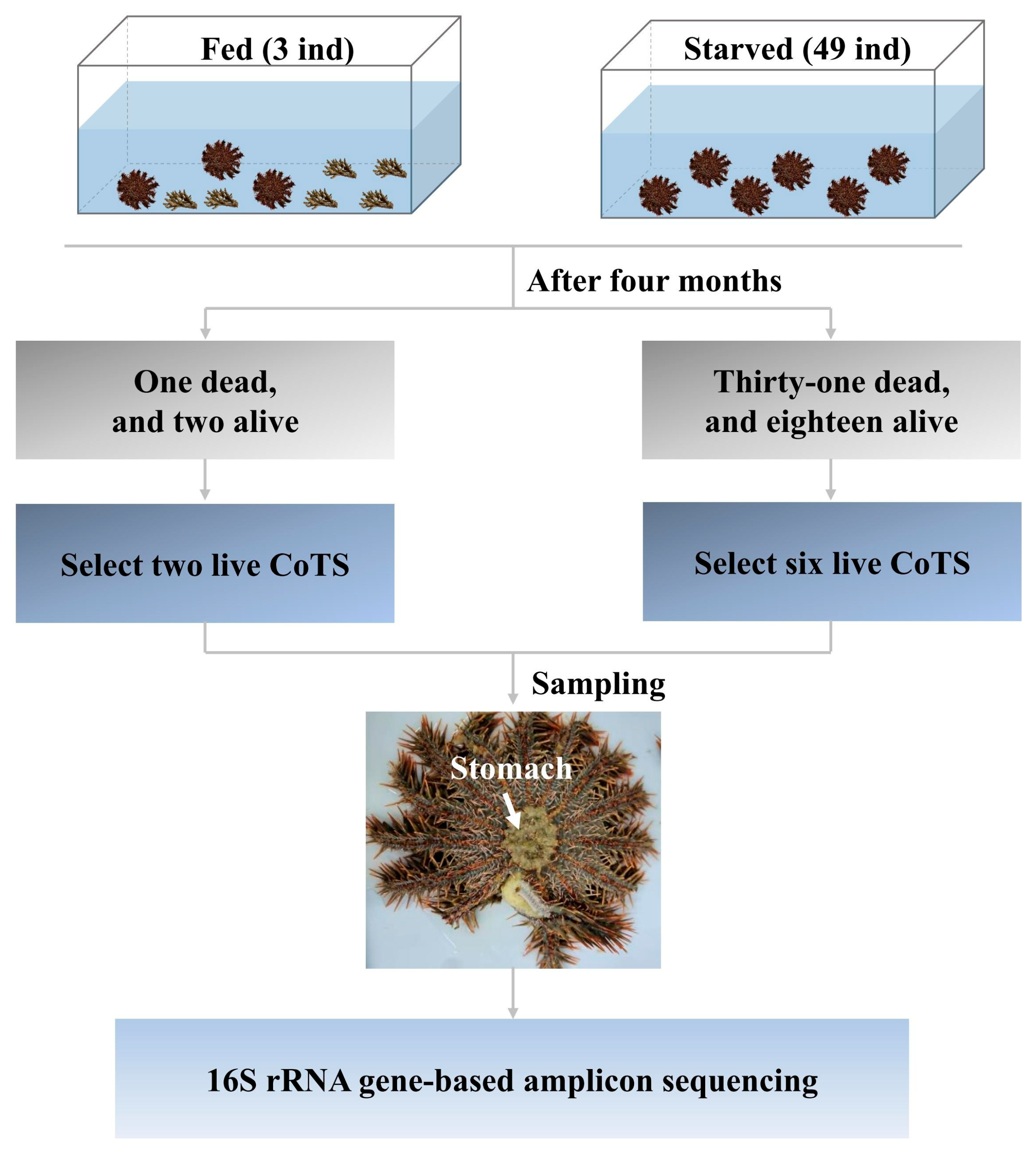
2.1. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 16S rRNA Gene Composition
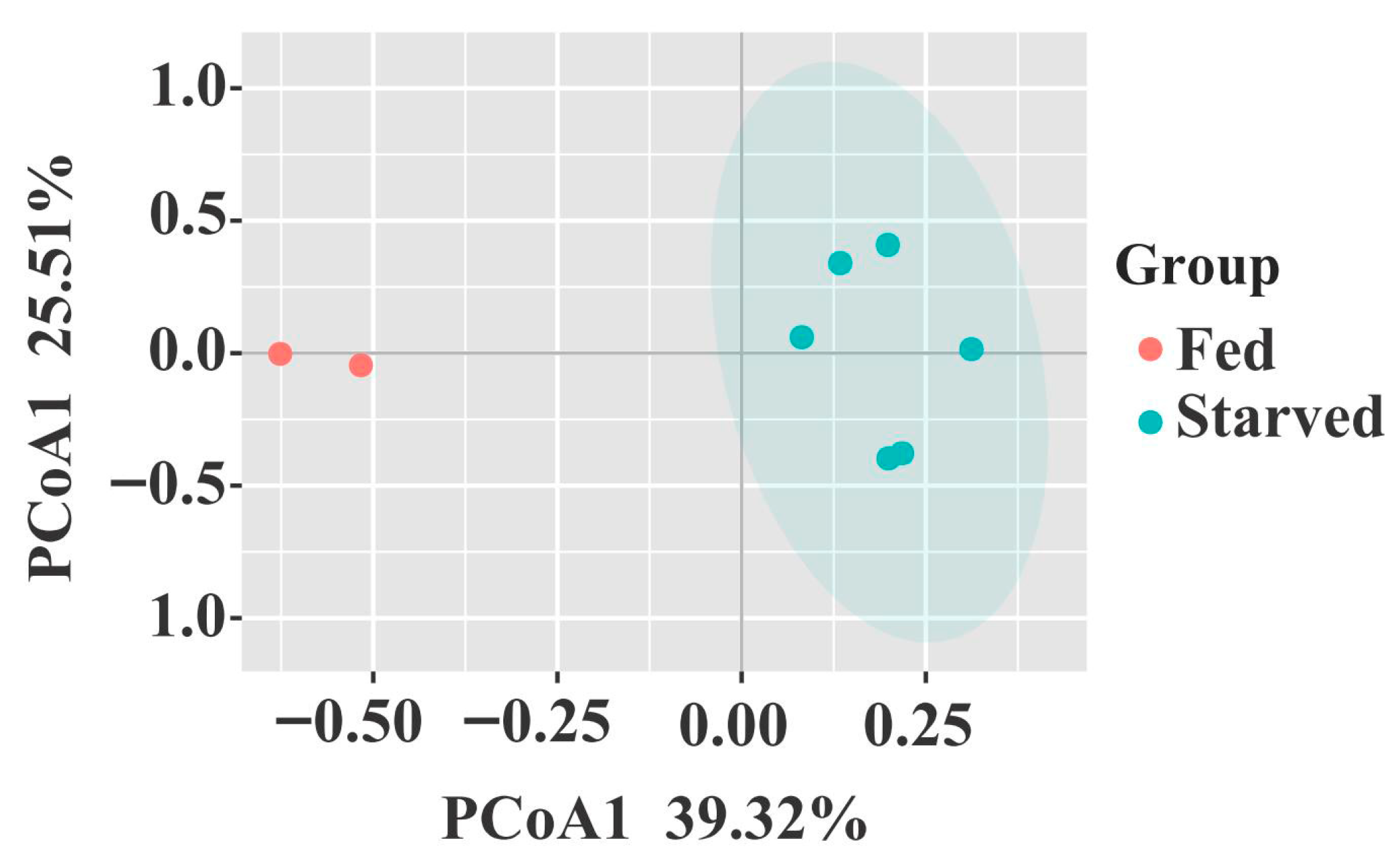
3.2. Variation Stomach Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure in CoTS
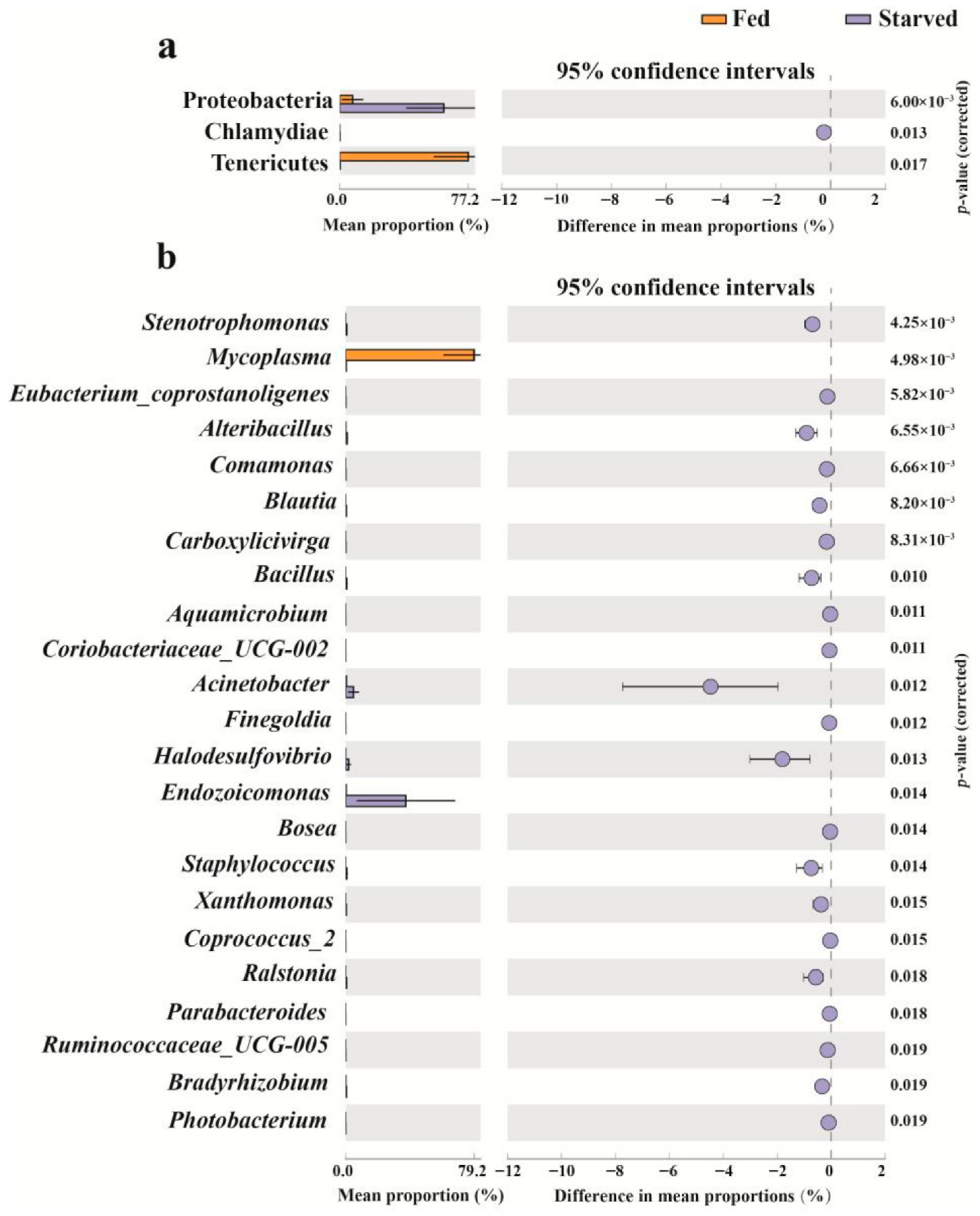
3.3. Changes in Stomach Bacterial Composition in CoTS Under Starvation Conditions
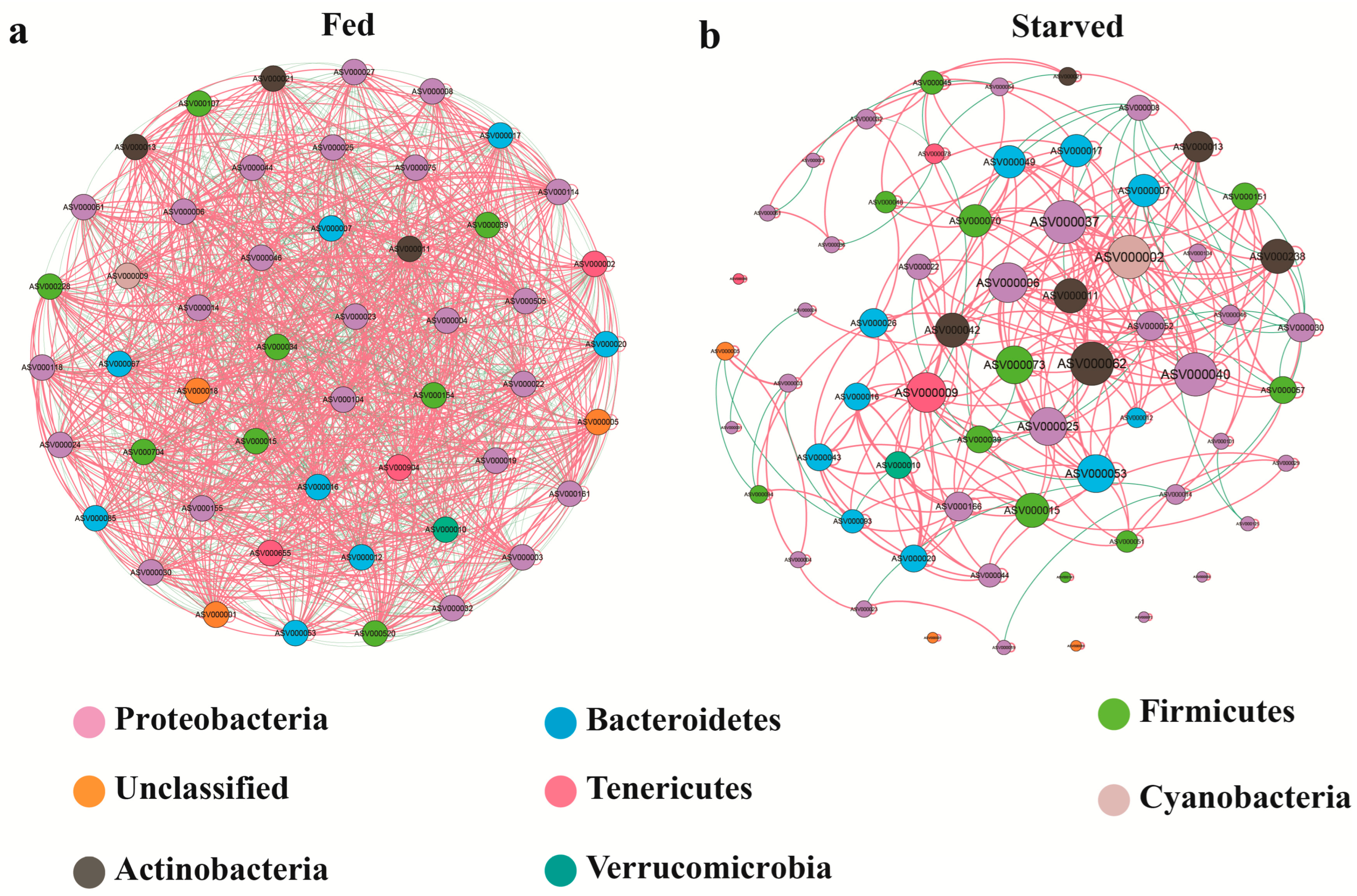
3.4. Network
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity in the CoTS Stomach
4.2. Changes in the Key Bacteria in CoTS Stomach Under Starvation
4.3. Interaction Relationships Between Bacterial Communities by Co-Occurrence Network in the CoTS Stomach
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliff, C.I.; Silva, I.R. Coral reefs as the first line of defense: Shoreline protection in face of climate change. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 127, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, F.; Folke, C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackall, L.L.; Wilson, B.; Van Oppen Madeleine, J.H. Coral-the world’s most diverse symbiotic ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5330–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E.; Sweatman, H.; Puotinen, M. The 27-year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17995–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, K.S.; Huan, N.H.; Thanh, N.H.; Britaye, T.A. Extensive coral reef decline in Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam: Acanthaster planci outbreak: The final event in a sequence of chronic disturbances. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Be´Raud, M.; Anker, A.; Chancerelle, Y.; Mills, S.C. Acanthaster planci outbreak: Decline in coral health, coral size structure modification and consequences for obligate decapod assemblages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaker, D.J.; Mos, B.; Lin, H.A.; Lawson, C.; Budden, C.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Byrne, M. Diet flexibility and growth of the early herbivorous juvenile crown-of-thorns sea star, implications for its boom-bust population dynamics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaker, D.J.; Mos, B.; Lawson, C.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Budden, C.; Byrne, M. Coral defences: The perilous transition of juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish to corallivory. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 665, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, W.K.; Ho, M.J.; Kuo, C.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Jeng, M.S.; Chen, C.A. Crown-of-thorns starfish outbreak at Taiping Island (Itu Aba), Spratlys, South China Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2022, 98, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.; Caballes, C.; Wilmes, J.; Matthews, S.; Mellin, C.; Sweatman, H.; Nadler, L.; Brodie, J.; Thompson, C.; Hoey, J.; et al. Thirty years of research on Crown-of-Thorns Starfish (1986–2016): Scientific advances and emerging opportunities. Diversity 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponari, L.; Montalbetti, E.; Galli, P.; Strona, G.; Seveso, D.; Dehnet, I.; Montano, S. Monitoring and assessing a 2-year outbreak of the corallivorous seastar Acanthaster planci in Ari Atoll, Republic of Maldives. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Ho, M.J.; Heng, W.K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Jiang, G.C.; Jeng, M.S.; Chen, C.L.A. What is for dessert? Crown-of-thorns starfish feeds on non-scleractinian anthozoans at Taiping Island (Itu Aba), Spratlys, South China Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2022, 52, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Okaji, K.; Higa, Y.; Yamakawa, E.; Mitarai, S. Spatial and temporal population dynamics of the crown-of-thorns starfish, Acanthaster planci, over a 24-year period along the central west coast of Okinawa Island, Japan. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.J. The acanthaster phenomenon. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1986, 24, 379–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, C.; Lucas, J.S. Acanthaster Planci: Major Management Problems of Coral Reefs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; 257p. [Google Scholar]
- Zann, L.; Brodie, J.; Berryman, C.; Naqasima, M. Recruitment, ecology, growth and behavior of juvenile Acanthaster planci (L.) (Echinodermata:Asteroidea). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 41, 561–575. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, S.D.; Cowan, Z.L.; Boada, J.; Flukes, E.B.; Pratchett, M.S. Homing behaviour by destructive crown-of-thorns starfish is triggered by local availability of coral prey. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigl, R.; Laforsch, C. The Influence of water currents on movement patterns on sand in the Crown-of-Thorns Seastar (Acanthaster cf. solaris). Diversity 2016, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Gao, Q.; Luo, P.; Hu, J.X.; Zheng, F.Y.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Fu, L.; Chen, C. Physiological and transcriptomic responses to starvation in the corallivorous crown-of-thorn starfish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1021377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.J.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xiao, C.X.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.Y.; Li, J.L.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.G.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P.; Walker, C.W. Comparative study of the uptake of dissolved amino acids in sympatric brittle stars with and without endosymbiotic bacteria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 101, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, M.S.; Wieland, A.; Ploug, H.; Kragelund, C.; Nielsen, P.H. Distribution, identity and activity of symbiotic bacteria in anoxic aggregates from the hindgut of the sea urchinechinocardium cordatum. Ophelia 2003, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, M.S. Abundance and biomass of the gut-living microorganisms (bacteria, protozoa and fungi) in the irregular sea urchin Echinocardium cordatum (Spatangoida: Echinodermata). Mar. Biol. 1999, 133, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Yuasa, H.; Kajitani, R.; Gotoh, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Yoshimura, D.; Toyoda, A.; Tang, S.L.; Higashimura, Y.; Swarman, H.; et al. A ubiquitous subcuticular bacterial symbiont of a coral predator, the crown-of-thorns starfish, in the Indo-Pacific. Microbiome 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoj, L.; Levy, N.; Baillie, B.K.; Clode, P.L.; Strohmaler, R.C.; Siboni, N.; Webster, N.S.; Uthick, S.; Bournea, D.G. Crown-of-thorns sea star, Acanthaster cf. solaris, have tissue characteristic microbiomes with potential roles in health and reproduction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00181-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Water, J.A.J.M.; Melkonian, R.; Junca, H.; Voolstra, C.R.; Reynaud, S.; Allemand, D.; Christine, F.P. Spirochaetes dominate the microbial community associated with the red coral Corallium rubrum on a broad geographic scale. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, W.; Sprungala, S.; Watson, S.A.; Miller, D.J.; Bourn, D.G. The microbiome of the octocoral Lobophytum pauciflorum: Minor differences between sexes and resilience to short-term stress. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, T.J.; Wolfe, K.; Lopez, K.; Gall, M.; Janies, D.A.; Byrne, M.; Reitzel, A.M. Diet-induced shifts in the crown-of-thorns (Acanthaster sp.) larval microbiome. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Saito, H.; Tame, A.; Hirai, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sunata, T.; Aida, M.; Muto, H.; Sawayama, S.; Takaki, Y. Microbiota in the coelomic fluid of two common coastal starfish species and characterization of an abundant Helicobacter-related taxon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Takai, K. Deep-sea vent chemoautotrophs: Diversity, biochemistry and ecological significance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaker, D.J.; Byrne, M. Crown of thorns starfish life-history traits contribute to outbreaks, a continuing concern for coral reefs. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2022, 6, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2020, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.F.; Sapp, J.; Tauber, A.I. A symbiotic view of life: We have never been individuals. Q. Rev. Biol. 2012, 87, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Role of microorganisms in the evolution of animals and plants: The hologenome theory of evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Amaya, J.; Passement, C.A.; Dearing, M.D.; McCue, M.D. Unique and shared responses of the gut microbiota to prolonged fasting: A comparative study across five classes of vertebrate hosts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Li, J.; Ao, M.; Mclaughlin, R.W.; Fan, F.; Wang, D.; Zheng, J. The intestinal microbiota of a Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus): Possible relationships with starvation raised by macro-plastic ingestion. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Xiong, F.; Hao, Y.T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.G.; Wang, G.T. Starvation influences the microbiota assembly and expression of immunity-related genes in the intestine of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 2018, 489, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Ni, M.; Liu, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Gu, Z.M.; Yuan, J.L. Starvation alters gut microbiome and mitigates off-flavors in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Folia Microbiol. 2023, 68, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Guo, H.Y.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.W.; Guo, L.; Jiang, S.G.; Zhang, D.C. Starvation and refeeding influence the growth, biochemical index, intestinal microbiota, and transcriptomic profiles of golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 998190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.G.; Wirth, S.; Hao, Y.T.; Wang, W.W.; Zou, H.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. Diversity and activity of cellulolytic bacteria, isolated from the gut contents of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) (Valenciennes) fed on Sudan grass (Sorghum sudanense) or artificial feedstuffs. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F. Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasiri, A.K.S.; Brunvold, L.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Korsnes, K.; Bergh, Q.; Kiron, V. Changes in the intestinal microbiota of wild Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. upon captive rearing. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.J.; Yan, Q.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Zhang, T.L. Factors influencing the grass carp gut microbiome and its effect on metabolism. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, J.J.; Guruge, J.L.; Charbonneau, M.; Subramanian, S.; Seedorf, H.; Goodman, A.L.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Heath, A.C.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013, 341, 1237439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semova, I.; Carten, J.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Mackey, L.C.; Knight, R.; Farber, S.A.; Rawls, J.F. Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Costello, E.K.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Stombaugh, J.; Knights, D.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Fierer, N.; et al. Moving pictures of the human microbiome. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkessel, M.; Delavaine, L. Diversity in starvation survival strategies and outcomes among heterotrophic Proteobacteria. Microb. Physiol. 2021, 31, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingro, A.; Köstlbacher, S.; Horn, M. Chlamydiae in the Environment. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, J.; Tandon, K.; Collingro, A.; Meene, A.V.D.; Damjanovic, K.; Gotze, C.R.; Stephenson, S.; Philip, G.K.; Horn, M.; Cantin, N.E.; et al. Colocalization and potential interactions of Endozoicomonas and chlamydiae in microbial aggregates of the coral Pocillopora acuta. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 0773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, O.O.; Yang, J.; Bougouffa, S.; Wang, Y.; Batang, Z.; Tian, R.; Suwailem, A.A.; Qian, P.Y. Spatial and species variations in bacterial communities associated with corals from the Red Sea as revealed by pyrosequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7173–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.S.; Wang, L.; Zhen, H.; Guo, C.; Liu, A.Z.; Xia, X.L.; Pei, H.L.; Dong, C.K.; Ding, J. Nanoplastics affect the growth of sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) and damage gut health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.E.; Rack, F.R.; Zook, R.; Williams, M.J.M.; Higham, M.L.; Broe, M.; Kaufmann, R.S.; Daly, M. Microbiome composition and diversity of the ice-dwelling sea anemone, Edwardsiella andrillae. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.A.; Stone, R.P.; Mclaughlin, M.R.; Kellogg, C.A. Microbial consortia of gorgonian corals from the Aleutian islands. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neulinger, S.C.; Jarnegren, J.; Ludvigsen, M.; Lochte, K.; Dullo, W.C. Phenotype-specific bacterial communities in the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia) and their implications for the coral’s nutrition, health, and distribution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7272–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Neulinger, S.C.; Pinnow, N.; Kunzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Schmitz, R.A. Composition of bacterial communities associated with Aurelia aurita changes with compartment, life stage, and population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6038–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Huang, Y.M. A comparison of the prokaryotic communities associated with seven seaweed species, sediment, and seawater from the Penghu archipelago, Taiwan. Mar. Biol. Res. 2021, 16, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Swierts, T.; Coelho, F.; Polonia, A.R.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Ferreira, M.R.S.; Putchakarn, S.; Carvalheiro, L.; Ent, E.V.D.; Ueng, J.P.; et al. The sponge microbiome within the greater coral reef microbial metacommunity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuij, T.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Putchakarn, S.; Pires, A.C.C.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Voogd, N.J.D. Exploring prokaryotic communities in the guts and mucus of nudibranchs, and their similarity to sediment and seawater microbiomes. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, D.F.; Patin, N.V.; Hanora, A.; Aboseidah, A.; Desoky, S.; Desoky, S.G.; Stewart, F.J.; Lopanik, N.B. The natural product biosynthetic potential of Red Sea nudibranch microbiomes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, H.S.; Zellmer, A.J.; Goffredi, S.K. The specific and exclusive microbiome of the deep-sea bone-eating snail, Rubyspira osteovora. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fiw250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraune, S.; Zimmer, M. Host-specificity of environmentally transmitted Mycoplasma-like isopod symbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, C.L.; Labrie, M.; Jarett, J.K.; Lesser, M.P. Transcriptional activity of the giant barrel sponge, Xestospongia muta Holobiont: Molecular evidence for metabolic interchange. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katharios, P.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Fehr, A.; Mateos, J.M.; Qi, W.H.; Richter, D.; Nufer, L.; Ruetten, M.; Soto, M.G.; Ziegler, U.; et al. Environmental marine pathogen isolation using mesocosm culture of sharpsnout seabream: Striking genomic and morphological features of novel Endozoicomonas sp. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, N.L.; Juniper, K. Free-living bacterial communities associated with tubeworm (Ridgeia piscesae) aggregations in contrasting diffuse flow hydrothermal vent habitats at the Main Endeavour Field, Juan de Fuca Ridge. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishaw, L.J.; Flores-Torres, J.; Lax, S.; Gemayel, K.; Leigh, B.; Melillo, D.; Mueller, M.G.; Natale, L.; Zucchetti, I.; Santis, R.D.; et al. The gut of geographically disparate Ciona intestinalis harbors a core microbiota. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, K.M.; Moss, A.G.; Chadwick, N.E.; Liles, M.R. Bacterial associates of two Caribbean coral species reveal species-specific distribution and geographic variability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6438–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.; Duperron, S.; Birkeland, N.K.; Hovland, M. Intracellular Oceanospirillales bacteria inhabit gills of Acesta bivalves. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 74, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, M.; Yokota, A. Endozoicomonas elysicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a gamma-proteobacterium isolated from the sea slug Elysia ornata. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neave, M.J.; Apprill, A.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Voolstra, C.R. Diversity and function of prevalent symbiotic marine bacteria in the genus Endozoicomonas. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8315–8324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, K.M.; Bourne, D.G.; Humphrey, C.; Botte, E.S.; Laffy, P.; Zaneveld, J.; Uthicke, S.; Fabricius, K.E.; Webster, N.S. Natural volcanic CO2 seeps reveal future trajectories for host-microbial associations in corals and sponges. ISME J. 2015, 9, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, M.; Adachi, K.; Katsuta, A.; Shizuri, Y.; Yamasato, K. Endozoicomonas numazuensis sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from marine sponges, and emended description of the genus Endozoicomonas Kurahashi and Yokota 2007. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, H.; Haltli, B.; Duque, C.; Kerr, R. Bacterial communities of the gorgonian octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, D.G.; Dennis, P.G.; Uthicke, S.; Soo, R.M.; Tyson, G.W.; Webster, N. Coral reef invertebrate microbiomes correlate with the presence of photosymbionts. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Shu, J.; Xue, H.; Guo, K.; Zhou, X. Soil-derived bacteria endow Camellia weevil with more ability to resist plant chemical defense. Microbiome 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, D.Y.; Bryukhanov, A.L.; Nyanikova, G.G.; Zelenskaya, M.S.; Tsarovtseva, I.M.; Izatulina, A.R. The corrosive activity of microorganisms isolated from fouling of structural materials in the coastal zone of the Barents Sea. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2023, 59, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Tang, L.; Yang, S.H.; Tandon, K.; Lu, C.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Shih, C.J.; Tang, S.L. Potential syntrophic relationship between coral-associated Prosthecochloris and its companion sulfate-reducing bacterium unveiled by genomic analysis. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ai, C.; Ou, H.; Song, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.F. The Intestinal Microbiota Involves in the Deterioration of Live Sea Cucumber During Storage. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2023, 32, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.Q.; Jiang, C.Y.; Shang, S.; Wang, S.C.; Zhu, K.Y.; Dong, X.P.; Zhou, D.Y.; Jiang, P.F. Insight into the relationship between metabolite dynamic changes and microorganisms of sea urchin (S. intermedius) gonads during storage. Food Chem. 2023, 18, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, D.C.A.; Leão, P.; Garrido, A.G.; Lins, U.; Santos, H.F.; Pires, D.O.; Castro, C.B.; Elsas, J.D.V.; Zilberberg, C.; Rosado, A.S.; et al. Broadcast spawning coral mussismilia hispida can vertically transfer its associated bacterial core. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, T.D.; Krause, L.; Bridge, T.; Torda, G.; Raina, J.B.; Zakrzewski, M.; Gates, R.D.; Gamino, J.L.P.; Spalding, H.L.; Smith, C.; et al. The coral core microbiome identifies rare bacterial taxa as ubiquitous endosymbionts. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.M.; Judd, C.; Kuske, C.R.; Smith, C. Analysis of stomach and gut microbiomes of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from coastal Louisiana, USA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhao, P.; Hou, L.; Adyari, B.; Xu, E.G.; Huang, Q.S.; Hu, A. Network analysis reveals significant joint effects of microplastics and tetracycline on the gut than the gill microbiome of marine medaka. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, R.M.; Deng, Y.; Dersjant-Li, Y.; Petit, J.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Schrama, J.W.; Kokou, F. Exogenous enzymes and probiotics alter digestion kinetics, volatile fatty acid content and microbial interactions in the gut of Nile tilapia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratzke, C.; Barrere, J.; Gore, J. Strength of species interactions determines biodiversity and stability in microbial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerger, A.N.; Dillon, D.T.; Schmidt, J.; Yang, T.; Zubcevic, J.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Bisesi, J.H.J. Gastrointestinal dysbiosis following diethylhexyl phthalate exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Altered microbial diversity, functionality, and network connectivity. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Shrimp disease progression increases the gut bacterial network complexity and abundances of keystone taxa. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Xue, J.; Hu, Y.; Wen, C.; Hu, B.; Jian, S.; Liang, L.; Yang, G. Disturbance in the homeostasis of intestinal microbiota by a high-fat diet in the rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Aquaculture 2019, 502, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debofsky, A.; Xie, Y.; Challis, J.K.; Jian, N.; Brinkmann, M.; Jones, P.D.; Giesy, J.P. Responses of juvenile fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) gut microbiome to a chronic dietary exposure of benzo[a]pyrene. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Peng, M.; Tian, X.; Dong, S. Molecular ecological network analysis reveals the effects of probiotics and florfenicol on intestinal microbiota homeostasis: An example of sea cucumber. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Walder, F.; Büchi, L.; Meyer, M.; Held, A.Y.; Gattinger, A.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; Heijden, M.G.A.V.D. Agricultural intensification reduces microbial network complexity and the abundance of keystone taxa in roots. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolini, M.; Barabási, A.L. Predicting perturbation patterns from the topology of biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6375–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Singh, B.K.; He, J.Z.; Han, Y.L.; Li, P.P.; Wan, L.H.; Meng, G.Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Wu, C.F.; et al. Plant developmental stage drives the differentiation in ecological role of the maize microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.V.; Lord, A.; Betzel, R.; Zakrzewski, M.; Simms, L.A.; Zalesky, A.; Smith, G.R.; Cocchi, L. Co-existence of network architectures supporting the human gut microbiome. iScience 2019, 22, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.S.; Greenfield, D.L.; Lindenberg, A.M.; Weinberger, D.R.; Moore, S.W.; Bullmore, E.T. Efficient physical embedding of topologically complex information processing networks in brains and computer circuits. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolero, M.A.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Bassett, D.S.; Esposito, M.D. A mechanistic model of connector hubs, modularity and cognition. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltheart, M. Modularity and cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 1999, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clune, J.; Mouret, J.B.; Lipson, H. The evolutionary origins of modularity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashtan, N.; Alon, U. Spontaneous evolution of modularity and network motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13773–13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Fed | Starved | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Richness | 189.50 ± 24.75 | 511.33 ± 226.85 | 0.071 |
| Shannon_index | 1.25 ± 1.25 | 3.46 ± 1.06 | 0.071 |
| Pielou | 0.24 ± 0.23 | 0.56 ± 0.18 | 0.143 |
| Gini_simpson_index | 0.40 ± 0.42 | 0.83 ± 0.15 | 0.143 |
| Group | Permanova | Anosim | MRPP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | r | p | δ | p | |
| Fed vs. starved | 0.382 | 0.042 | 0.865 | 0.038 | 0.793 | 0.046 |
| Network Metrics | Fed | Starved |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 50 | 64 |
| Edges | 1275 | 308 |
| Positive edge | 675 (52.94%) | 265 (86.04%) |
| Negative edge | 600 (47.06%) | 43 (13.96%) |
| Average degree | 51 | 9.625 |
| Avg. weighted degree | 4 | 7.015 |
| Network diameter | 1 | 8 |
| Graph density | 1.041 | 0.153 |
| Modularity | 0 | 0.559 |
| Connected components | 1 | 7 |
| Avg. clustering coefficient | 0.989 | 0.647 |
| Avg. path length | 1 | 2.878 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Lai, F.; Yang, L.; Dai, L.; Su, N.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, F.; Chen, C. Starvation Influences the Microbiota in the Stomach of the Corallivorous Crown-of-Thorns Starfish. Biology 2025, 14, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081102
Zhang Y, Lai F, Yang L, Dai L, Su N, Hu J, Chen H, Gao Q, Zheng F, Chen C. Starvation Influences the Microbiota in the Stomach of the Corallivorous Crown-of-Thorns Starfish. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081102
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Fuxiang Lai, Litong Yang, Liling Dai, Nan Su, Jianxing Hu, Huizhen Chen, Qian Gao, Fanyu Zheng, and Chang Chen. 2025. "Starvation Influences the Microbiota in the Stomach of the Corallivorous Crown-of-Thorns Starfish" Biology 14, no. 8: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081102
APA StyleZhang, Y., Lai, F., Yang, L., Dai, L., Su, N., Hu, J., Chen, H., Gao, Q., Zheng, F., & Chen, C. (2025). Starvation Influences the Microbiota in the Stomach of the Corallivorous Crown-of-Thorns Starfish. Biology, 14(8), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081102






