Use of Bacillus pretiosus and Pseudomonas agronomica for the Synthesis of a Valorized Water Waste Treatment Plant Waste as a Biofertilizer Intended for Quercus pyrenaica L. Fertigation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Experimental Design: Irrigation Matrices (Chemical Treatment) and Biological Treatment (PGPB Strains)
2.3. Preparation of Bacterial Suspensions and Biofertilizers
2.3.1. Preparation of Bacterial Suspensions
2.3.2. Preparation of Biofertilizers and Addition of PGPBs to WWTP Fertilizer: Fertilizer Formation
2.3.3. Plant Growth Conditions and Irrigation Regime
2.3.4. Harvesting, Total Biomass Measurement, and Nutritional Analysis
2.4. Extraction of Soil Microbial Communities
2.5. Cenoantibiogram
2.6. Study of the Functional Diversity of the Microbial Community
2.7. Statistical Analysis
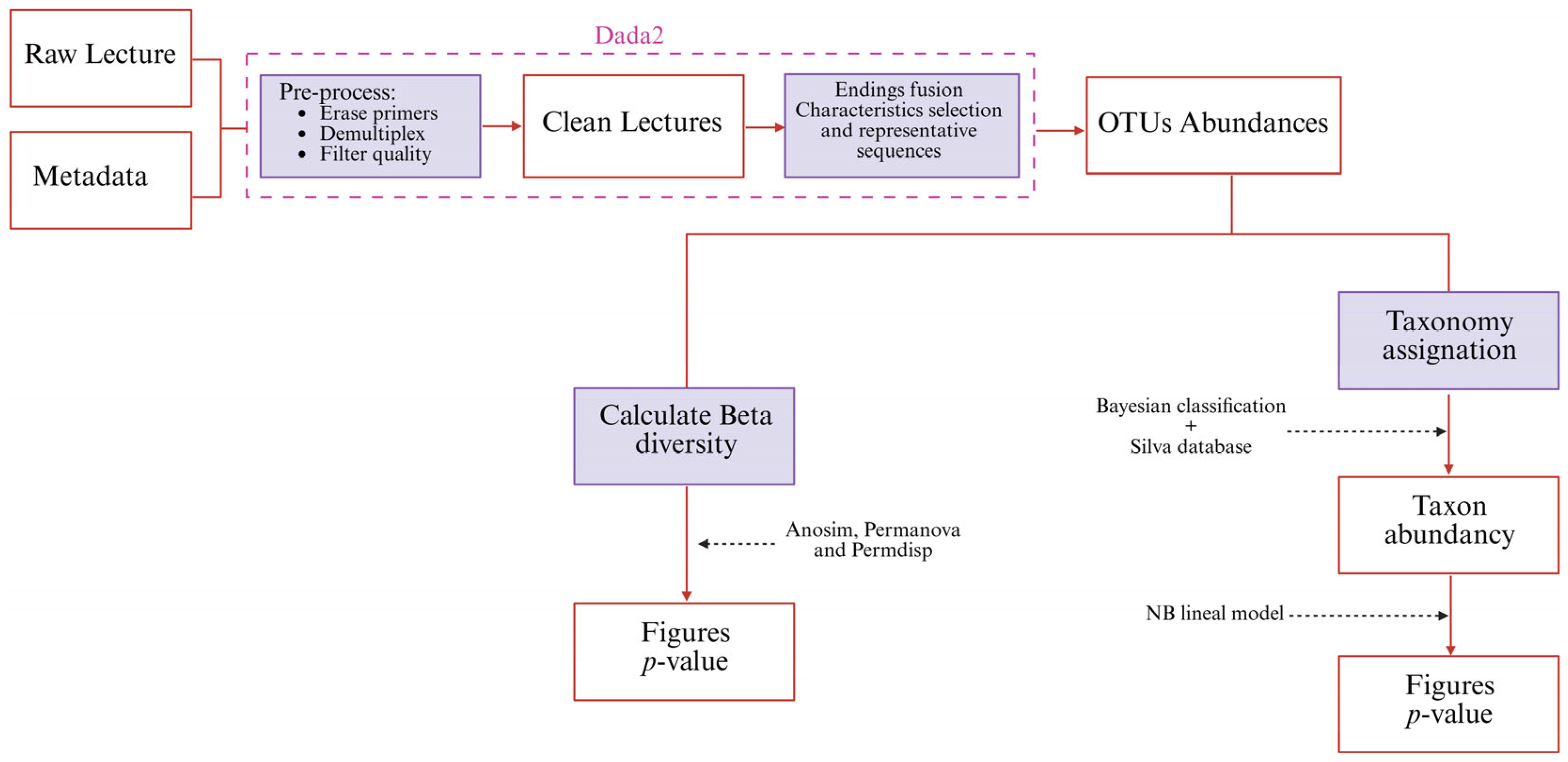
2.8. Metagenomics
Bioinformatics Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
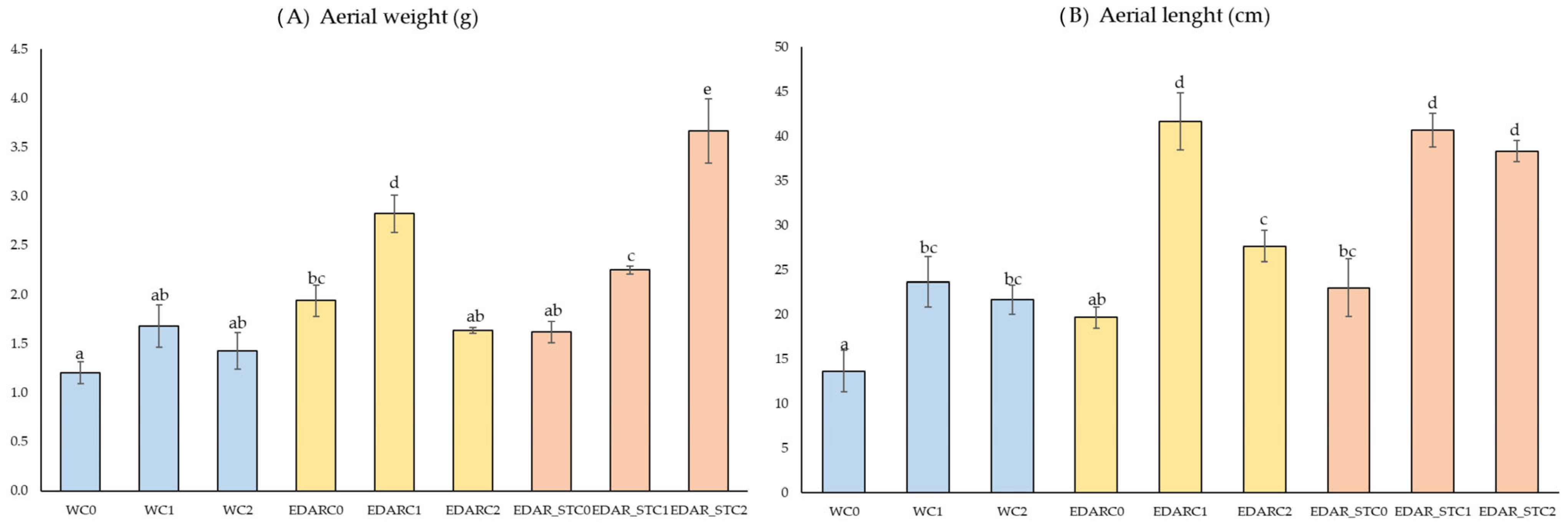
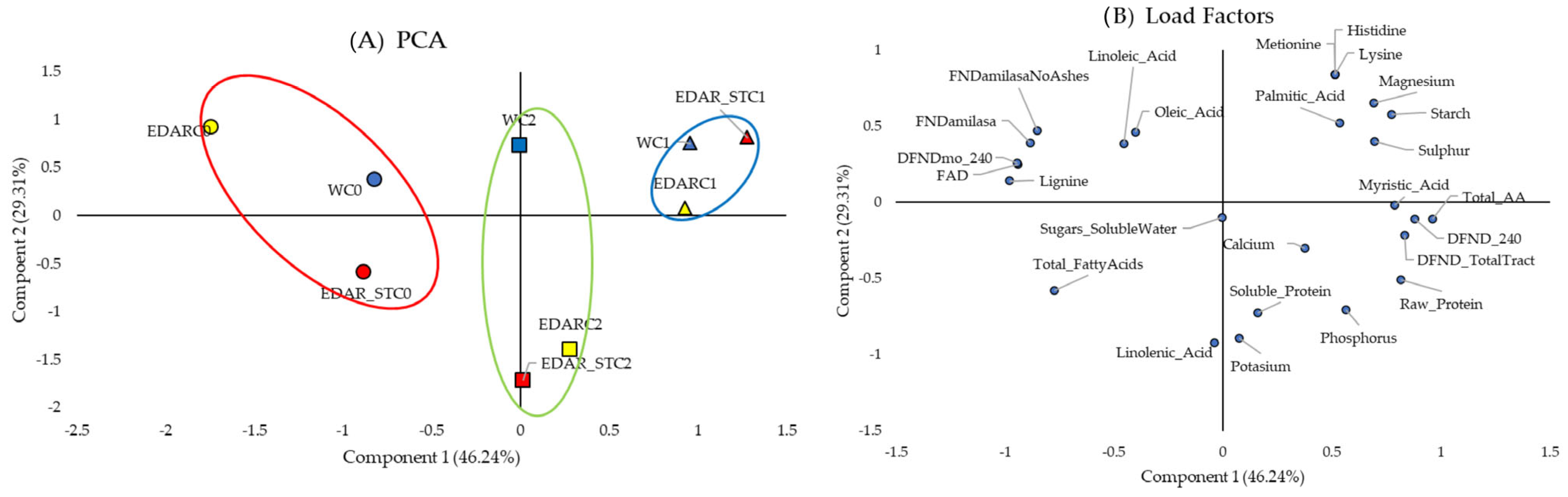
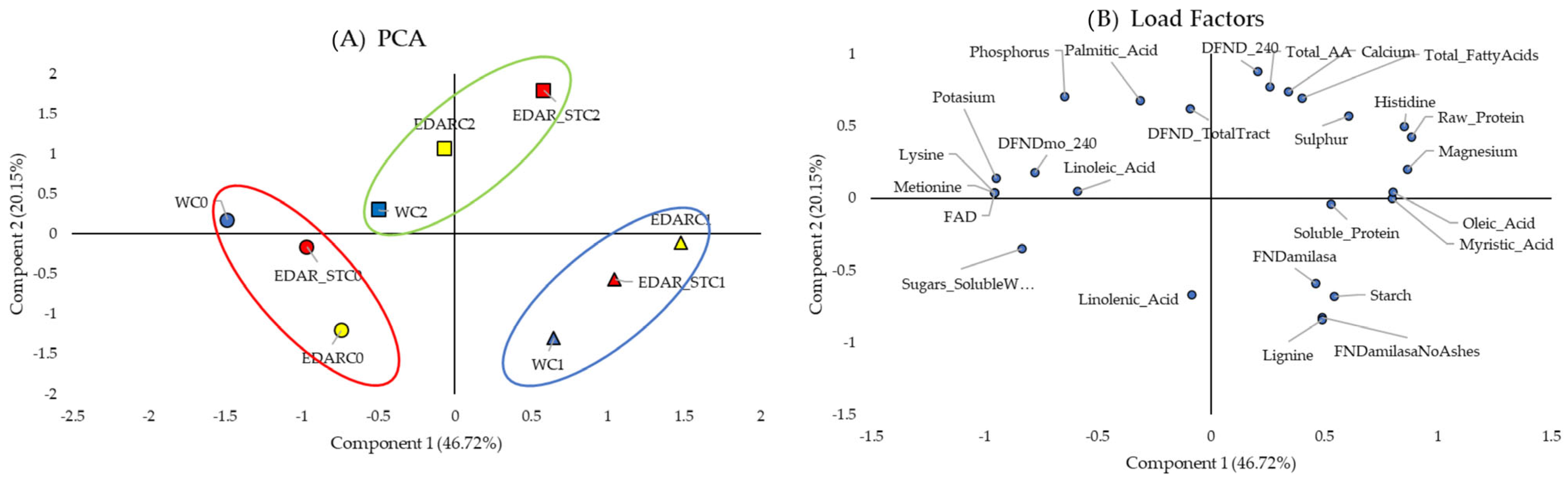
3.1. Biometrics
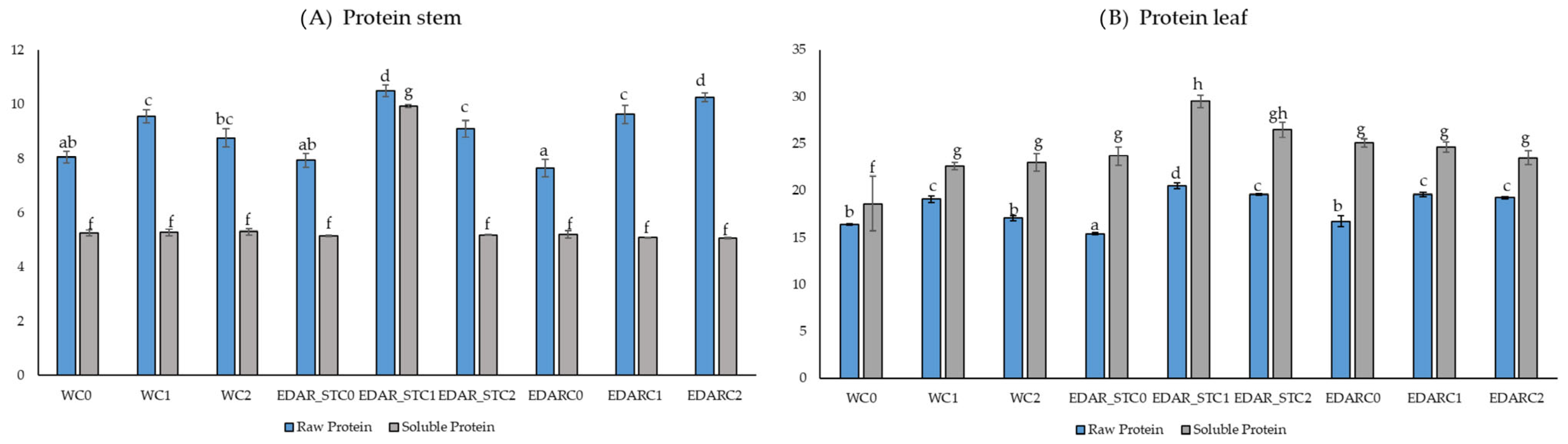
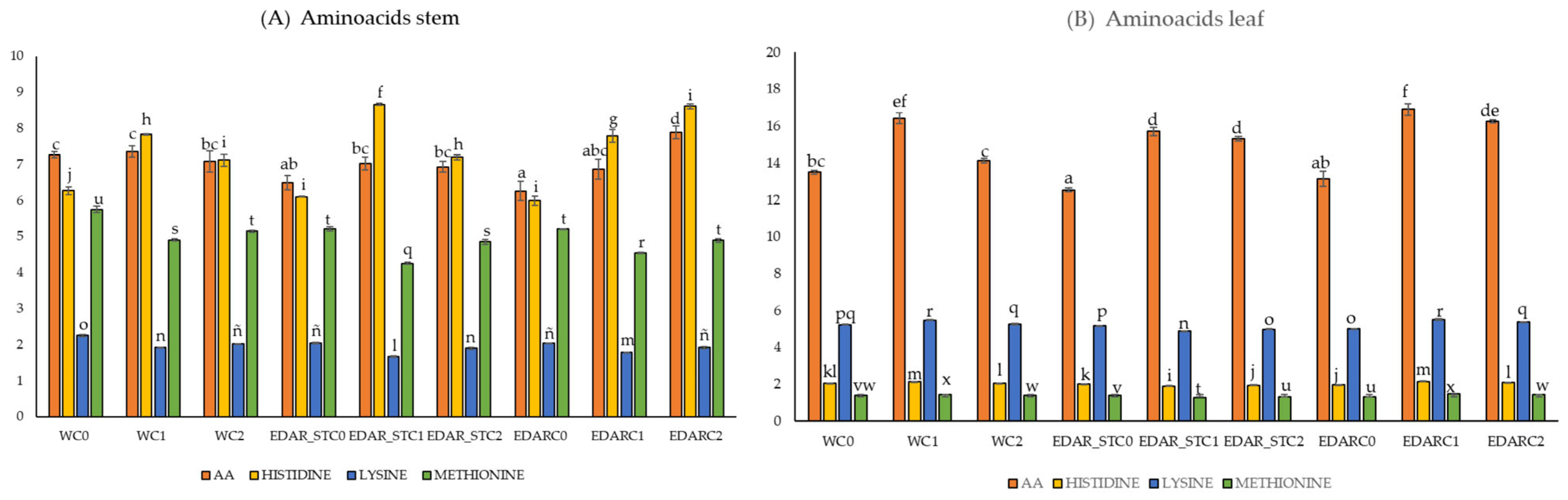
3.2. Nutritional Analysis
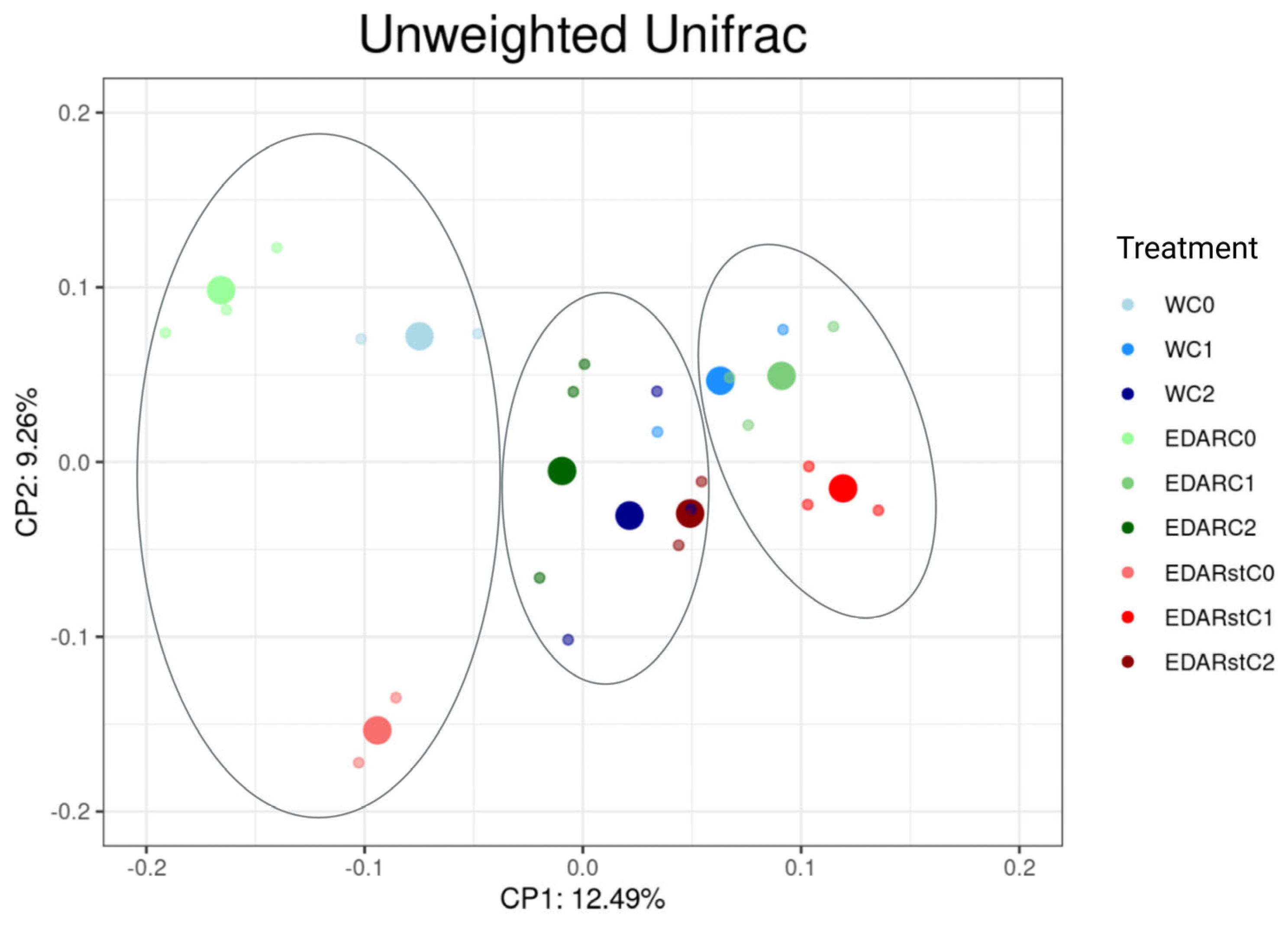
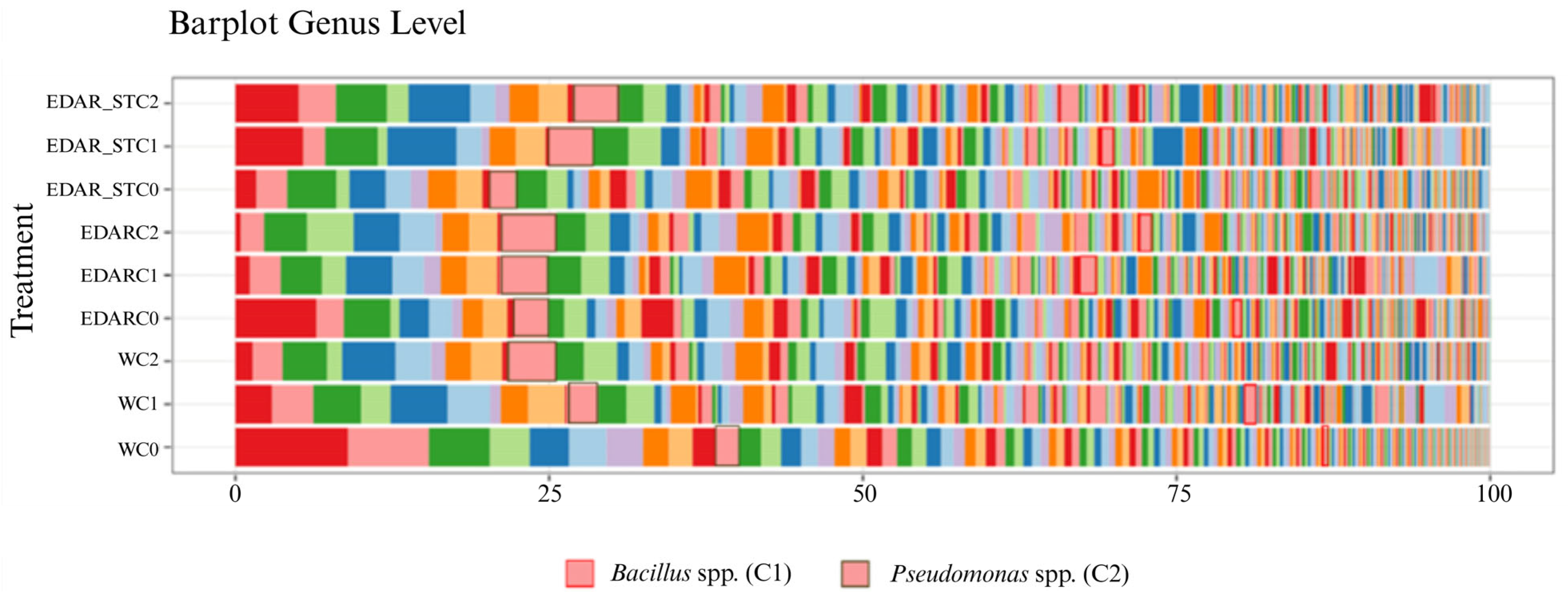
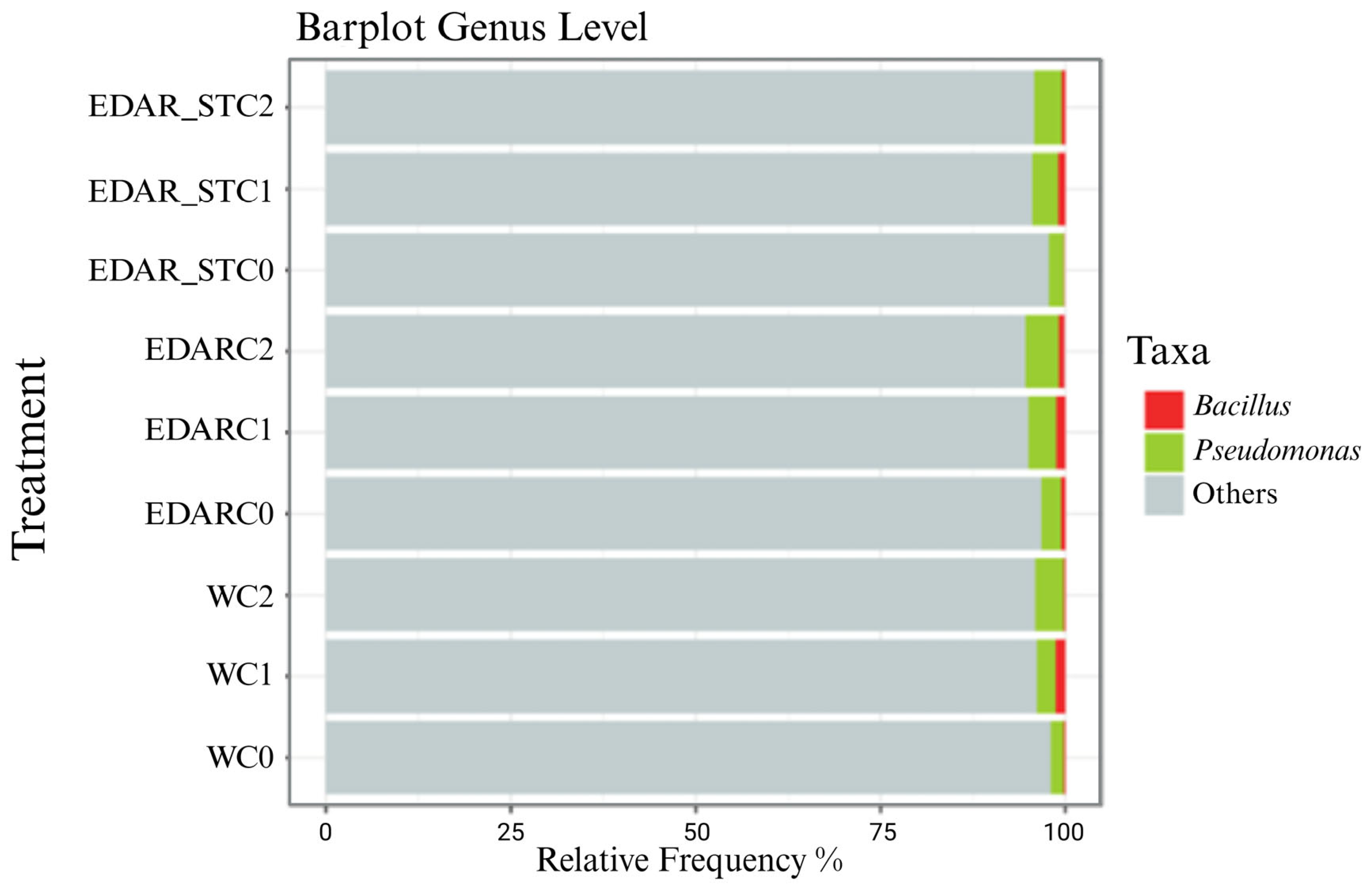
Relative Abundances at the Gender Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perez-Luque, A.J.; Benito, B.M.; Bonet-Garcia, F.J.; Zamora, R. Ecological Diversity within Rear-Edge: A Case Study from Mediterranean Quercus Pyrenaica Willd. Forests 2020, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Carrera, S.; Escudero, A.; Fernández-Fuentes, A.; Martínez-Ortega, M.; Mediavilla, S. Variations in Acorn Characteristics Between Two Mediterranean Quercus Species and Their Hybrids Through Contrasting Environmental Gradients in Spain. Plants 2025, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Triana, N.; Solakis, A.; Casimiro-Soriguer, F.; Choe, H.; Navarro, T.; Pérez-Latorre, A.V.; Thorne, J.H. The High Climate Vulnerability of Western Mediterranean Forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 164983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.M.; Gillett, N.P.; Simpson, I.R.; Athanasiadis, P.J.; Baehr, J.; Bethke, I.; Bilge, T.A.; Bonnet, R.; Boucher, O.; Findell, K.L. Attribution of Multi-Annual to Decadal Changes in the Climate System: The Large Ensemble Single Forcing Model Intercomparison Project (LESFMIP). Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 955414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutika, L.-S.; Matondo, R.; Mabiala-Ngoma, A.; Tchichelle, V.S.; Toto, M.; Madzoumbou, J.-C.; Akana, J.A.; Gomat, H.Y.; Mankessi, F.; Mbou, A.T. Sustaining Forest Plantations for the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyaningsih, A.P.; Deanova, A.K.; Pristiawati, C.M.; Ulumuddin, Y.I.; Kusumaningrum, L.; Setyawan, A.D. Causes and Impacts of Anthropogenic Activities on Mangrove Deforestation and Degradation in Indonesia. Int. J. Bonorowo Wetl. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyere-Boateng, R.; Marek, M.V. Analysis of the Social-Ecological Causes of Deforestation and Forest Degradation in Ghana: Application of the DPSIR Framework. Forests 2021, 12, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, A.F.; Harden, J.; Georgiou, K.; Hemes, K.S.; Malhotra, A.; Nolan, C.J.; Jackson, R.B. Fire Effects on the Persistence of Soil Organic Matter and Long-Term Carbon Storage. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the Unknown: Disentangling the Complexities of the Soil Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, C.; Rojas, C. Early Responses of Soil Health Indicators to Organic Amendments and Plant Establishment at a Fire-Affected Sclerophyllous Forest. Agro Sur 2020, 48, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos, D.; Alberdi, A.; Morriën, E.; van der Putten, W.H.; Rodríguez-Uña, A.; Montoya, D. The Long-Term Restoration of Ecosystem Complexity. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, A.; Chattaraj, S.; Mitra, D.; Ganguly, A.; Kumar, R.; Gaur, A.; Mohapatra, P.K.D.; Santos-Villalobos, S.d.l.; Rani, A.; Thatoi, H. Advances in Microbial Based Bio-Inoculum for Amelioration of Soil Health and Sustainable Crop Production. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 7, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Akhdar, I.; Shabana, M.M.; El-Khateeb, N.M.; Elhawat, N.; Alshaal, T. Sustainable Wheat Cultivation in Sandy Soils: Impact of Organic and Biofertilizer Use on Soil Health and Crop Yield. Plants 2024, 13, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashoka, P.; Singh, V.; Bhargavi, R.; Pujitha, N.; Anusha, T.; Bindu, T.P.L.H. The Role of Biofertilizers in Soil Health Improvement and Sustainable Farming: A Comprehensive Review. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2025, 25, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.E.F.; Saetta, R.; Raimondo, R.; Costa, J.M.; Ferreira, J.V.; Brás, I. Forest Waste Composting—Operational Management, Environmental Impacts, and Application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradelo, R.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Cancelo-González, J.; Basanta, R.; Pena, M.; Díaz-Fierros, F.; Barral, M. Effect of a Compost Mulch on Seed Germination and Plant Growth in a Burnt Forest Soil from NW Spain. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussein, M.; Ali, M.; Abbas, M.H.; Bassouny, M.A. Composting Animal and Plant Residues for Improving the Characteristics of a Clayey Soil and Enhancing the Productivity of Wheat Plant Grown Thereon. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 62, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, C. Effects of Biochar Carried Microbial Agent on Compost Quality, Greenhouse Gas Emission and Bacterial Community during Sheep Manure Composting. Biochar 2023, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguero, B.G.; Renaud, F.G.; Van Zanten, B.; Cohen-Shacham, E.; Beck, M.W.; Di Sabatino, S.; Jongman, B. Nature-Based Solutions for Natural Hazards and Climate Change. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouzi, M.M.A.; Allouzi, S.M.A.; Keng, Z.X.; Supramaniam, C.V.; Singh, A.; Chong, S. Liquid Biofertilizers as a Sustainable Solution for Agriculture. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitter, E.K.; Tosi, M.; Obregón, D.; Dunfield, K.E.; Germida, J.J. Rethinking Crop Nutrition in Times of Modern Microbiology: Innovative Biofertilizer Technologies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 606815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Gupta, A.; Nandi, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sarkar, S.; Ray, K.; Tripathi, S.; Ravisankar, N.; Chatterjee, G. Exploring the Microbial Community Dynamics of Jeevamrit Reveals the Multifaceted Roles of the Bacillus and Pseudomonas Genera in Nutrient Availability and Plant Growth Promotion in India’s Zero Budget Natural Farming. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, W.; Yadav, R.; Li, K. Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria in Agriculture: Two Sides of a Coin. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youseif, S.H.; El-Megeed, F.H.A.; Soliman, M.S.; Ageez, A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Ali, S.A.; El-Kholy, A.A. Nodules-Associated Klebsiella Oxytoca Complex: Genomic Insights into Plant Growth Promotion and Health Risk Assessment. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-S.; Huang, X.-R.; Neilson, R.; Yang, X.-R. Effects of Biofertilizer on Soil Microbial Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Reguero, D.; Robas-Mora, M.; Fernández-Pastrana, V.M.; Probanza-Lobo, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, P.A. Reduced Antibiotic Resistance in the Rhizosphere of Lupinus Albus in Mercury-Contaminated Soil Mediated by the Addition of PGPB. Biology 2023, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robas Mora, M.; Fernández Pastrana, V.M.; Oliva, L.L.G.; Lobo, A.P.; Jiménez Gómez, P.A. Plant Growth Promotion of the Forage Plant Lupinus albus var. Orden Dorado Using Pseudomonas agronomica sp. nov. and Bacillus pretiosus sp. nov. Added over a Valorized Agricultural Biowaste. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1046201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Reguero, D.; Robas-Mora, M.; Alonso, M.R.; Fernández-Pastrana, V.M.; Lobo, A.P.; Gómez, P.A.J. Induction of Phytoextraction, Phytoprotection and Growth Promotion Activities in Lupinus Albus under Mercury Abiotic Stress Conditions by Peribacillus frigoritolerans subsp., Mercuritolerans subsp. nov. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Carlin, M.; Cano, R.d.J. Holobiome Harmony: Linking Environmental Sustainability, Agriculture, and Human Health for a Thriving Planet and One Health. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Dimopoulos, G. Microbial Biopesticides: A One Health Perspective on Benefits and Risks. One Health 2024, 20, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carril, P.; Ghorbani, M.; Azarnejad, N.; Anselmi, S.; Renzi, M.; Loppi, S. Promoting Early Growth in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by Co-Application of Biochar and Beneficial Bacteria. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, A.B.; Fernandez, M.; Paulucci, N.S.; Dardanelli, M.S. Long-Life Inoculant: Bradyrhizobium Stored in Biodegradable Beads for Four Years Shows Optimal Cell Vitality, Interacts with Peanut Roots, and Promotes Early Growth. Plants 2024, 13, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papin, M.; Philippot, L.; Breuil, M.; Bru, D.; Dreux-Zigha, A.; Mounier, A.; Le Roux, X.; Rouard, N.; Spor, A. Survival of a Microbial Inoculant in Soil after Recurrent Inoculations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, T.; Alonso-Sáez, L.; Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil, L.; Aylagas, E.; Bohan, D.A.; Bouchez, A.; Chariton, A.; Creer, S.; Frühe, L.; Keck, F. Ecosystems Monitoring Powered by Environmental Genomics: A Review of Current Strategies with an Implementation Roadmap. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 2937–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Huang, S.; Gonzalez, A.; McGrath, I.; McDonald, D.; Haiminen, N.; Armstrong, G.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Yu, J.; Kuczynski, J. Phylogeny-Aware Analysis of Metagenome Community Ecology Based on Matched Reference Genomes While Bypassing Taxonomy. mSystems 2022, 7, e0016722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, A.G.-V.; Probanza, A.; Mañero, F.G.; Ramos, B.; García, J.L. Functional Diversity of Rhizosphere Microorganisms from Different Genotypes of Arabidopsis Thaliana. Community Ecol. 2009, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.L. Analytical Approaches to the Characterization of Samples of Microbial Communities Using Patterns of Potential C Source Utilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel Test in the Face of Heterogeneous Dispersions: What Null Hypothesis Are You Testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A Comprehensive Online Resource for Quality Checked and Aligned Ribosomal RNA Sequence Data Compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 1-4757-3121-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lasa, A.V.; Fernández-González, A.J.; Villadas, P.J.; Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; Fernández-López, M. Bacterial Inoculation of Quercus Pyrenaica Trees Alters Co-occurrence Patterns but Not the Composition of the Rhizosphere Bacteriome in Wild Conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, V.; Amicucci, A.; Landi, L.; Castelli, I.; Romanazzi, G.; Peroni, C.; Ranocchi, B.; Zambonelli, A.; Neri, D. Effect of Bacteria Inoculation on Colonization of Roots by Tuber Melanosporum and Growth of Quercus Ilex Seedlings. Plants 2024, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Kuramae, E.E. Insight into Farming Native Microbiome by Bioinoculant in Soil-Plant System. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 285, 127776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreslassie, S.; Jida, M.; Puente, M.L.; Covacevich, F.; Belay, Z. Inoculation of Native Arbuscular Mycorrhizae and Bacillus Subtilis Can Improve Growth in Vegetable Crops. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 2024, 9226715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiu, L. Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) against Insects and Other Agricultural Pests. Agronomy 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakar, N.P.; Munis, M.F.H.; Chaudhary, H.J. Synergistic Inoculation of Diazotrophic Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp. in Mitigating Salt-Drought Stress in Cicer arietinum L. via Phytohormonal Modulation and Antioxidant Pathways. Plant Soil 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinskienė, J.; Tamošiūnė, I.; Andriūnaitė, E.; Gelvonauskienė, D.; Rugienius, R.; Hakim, M.F.; Stanys, V.; Buzaitė, O.; Baniulis, D. Inoculum of Endophytic Bacillus spp. Stimulates Growth of Ex Vitro Acclimatised Apple Plantlets. Plants 2025, 14, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-T.; Bao, Y.-Q.; Feng, B.-Y.; Xu, L.-R.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Wang, E.-X.; Chen, Y.-P. Impact of a Potent Strain of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB), Bacillus subtilis S1 on Bacterial Community Composition, Enzymatic Activity, and Nitrogen Content in Cucumber Rhizosphere Soils. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, A.; Padda, K.P.; Chanway, C.P. In Vitro and in Vivo Analyses of Plant-Growth-Promoting Potential of Bacteria Naturally Associated with Spruce Trees Growing on Nutrient-Poor Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 149, 103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, W.; Kondo, S.; Iguchi, R.; Mahmood, A.; Kataoka, R. Agricultural Utilization of Unused Resources: Liquid Food Waste Material as a New Source of Plant Growth-Promoting Microbes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, H.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X. Alkaline Thermal Hydrolysis of Sewage Sludge to Produce High-Quality Liquid Fertilizer Rich in Nitrogen-Containing Plant-Growth-Promoting Nutrients and Biostimulants. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdon, K.; Fortin, J.; Dessureault-Rompré, J.; Caron, J. Agricultural Peatlands Conservation: How Does the Addition of Plant Biomass and Copper Affect Soil Fertility? Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlidag, H.; Esitken, A.; Turan, M.; Sahin, F. Effects of Root Inoculation of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Yield, Growth and Nutrient Element Contents of Leaves of Apple. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 114, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajšman, M.; Šantavec, I.; Kolmanič, A.; Kocjan Ačko, D. Bacterial Seed Inoculation and Row Spacing Affect the Nutritional Composition and Agronomic Performance of Soybean. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2019, 13, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesamäki, J.S.; Rigaud, C.; Litmanen, J.J.; Nissinen, R.; Taube, R.; Taipale, S.J. Recycled by Leaf Inhabitants: Terrestrial Bacteria Drive the Mineralization of Organic Matter in Lake Water. Ecosphere 2024, 15, e4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, J.; Peng, X.; Fu, Q.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, J.; Tang, L. Dynamics of Organic Matter and Bacterial Community during the Composting Process of Food Waste Rich in Oil with the Amendment of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 506, 145456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, I.d.C.M.; da Silva, A.V.R.; Boleta, E.H.M.; Pellegrinetti, T.A.; Zagatto, L.F.G.; Zagatto, S.d.S.S.; de Chaves, M.G.; Mendes, R.; Patreze, C.M.; Tsai, S.M. The Interplay between the Inoculation of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria and the Rhizosphere Microbiome and Their Impact on Plant Phenotype. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 283, 127706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Feng, C.; Liu, F.; Li, J. Biodiversity Conservation in China: A Review of Recent Studies and Practices. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, Y.M.; Peri, P.L.; Lencinas, M.V.; Lizarraga, L.; Martínez Pastur, G. Multi-Taxon Biodiversity Assessment of Southern Patagonia: Supporting Conservation Strategies at Different Landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, A.J.; Baetens, J.M.; De Baets, B. Ecological Diversity: Measuring the Unmeasurable. Mathematics 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Su, L. Effects of Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Microbial Communities, CO2 Emissions, and Organic Carbon Content in Soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Qin, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, M.; Ren, X.; Yu, W.; Ji, K. Analysis on Metabolic Functions of Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Pinus Massoniana Provenances with Different Carbon Storage by Biolog Eco Microplates. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1365111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ge, Z.; Poudel, D.R. Application and Optimization of Biolog EcoPlates in Functional Diversity Studies of Soil Microbial Communities; EDP Sciences: Xiamen, China, 2015; Volume 22, p. 04015. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, A.; de Souza, R.; Passaglia, L.M. Ecological Role of Bacterial Inoculants and Their Potential Impact on Soil Microbial Diversity. Plant Soil 2016, 400, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, I.; Fahsi, N.; Hijri, M.; Sobeh, M. Antibiotic Resistance in Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives to Mitigate Potential Gene Invasion Risks. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Huang, W.; Zeng, M. The Diversity, Functional Regulation Mechanisms, and Future Research Directions of Rice Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities. Resour. Data J. 2025, 4, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, M.M.; Karathia, H.; Pujolassos, M.; Troisi, J.; Valitutti, F.; Subramanian, P.; Camhi, S.; Kenyon, V.; Colucci, A.; Serena, G.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Influence of Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors on Developing Gut Microbiota in Infants at Risk of Celiac Disease. Microbiome 2020, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X. The Multi-Omics Study on the Dynamics of Soil Microbial Communities and Nitrogen Cycling Optimization under Organic Fertilizer Application and Water Regulation. Adv. Resour. Res. 2025, 5, 946–970. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa-Asuar, L.; Escalante, A.E.; Falcón, L.I.; Bonilla-Rosso, G.; Ramírez-Barahona, S.; Eguiarte, L.E.; Souza, V. Comparación de Tres Métodos Moleculares Para El Análisis de Procariontes Ambientales En El Mar Del Canal de Yucatán, México. Hidrobiológica 2014, 24, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Laudadio, I.; Fulci, V.; Palone, F.; Stronati, L.; Cucchiara, S.; Carissimi, C. Quantitative Assessment of Shotgun Metagenomics and 16S rDNA Amplicon Sequencing in the Study of Human Gut Microbiome. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2018, 22, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, S.; Maurya, P. Comparison of Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Soils Managed with Organic and Chemical Fertilization Strategies Using Amplicon Sequencing of 16 s and ITS Regions. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1444903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babalola, O.O.; Osuji, I.E.; Akanmu, A.O. Amplicon-Based Metagenomic Survey of Microbes Associated with the Organic and Inorganic Rhizosphere Soil of Glycine max L. BMC Genom. Data 2025, 26, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tang, X. Prospecting the Plant Growth–Promoting Activities of Endophytic Bacteria Franconibacter sp. YSD YN2 Isolated from Cyperus esculentus L. var. Sativus leaves. Ann. Microbiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawxhurst, C.J.; Micciulla, J.L.; Bridges, C.M.; Shor, M.; Gage, D.J.; Shor, L.M. Soil Protists Can Actively Redistribute Beneficial Bacteria along Medicago Truncatula Roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0181922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramae, E.E.; Derksen, S.; Schlemper, T.R.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Costa, O.Y.; da Silveira, A.P. Sorghum Growth Promotion by Paraburkholderia Tropica and Herbaspirillum Frisingense: Putative Mechanisms Revealed by Genomics and Metagenomics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Code | Identification (WGS) | Origin Insulation | IAA (µg·mL−1) | ACCd (p/a) | Siderophores (p/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAICEU11 | Bacillus pretiosus | Medicago sativa | 5.61 ± 0.03 | − | + |
| SAICEU22 | Pseudomonas agronomica | Bulk soil | 5.85 ± 0.09 | + | + |
| Parameters | Methods | Results | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physico-chemical characteristics | Conductivity at 20 °C | A-F-PE-0015 Electrometry | 1454 | µS/cm |
| Conductivity at 25 °C | A-F-PE-0015 Electrometry | 1612 | µS/cm | |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD5) | A-F-PE-0002 Manometric Method | 3200 | mg O2/L | |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand | A-F-PE-0003 Digestion–Colorimetry | 6720 | mg O2/L | |
| Decanted chemical oxygen demand | A-F-PE-0003 Digestion–Colorimetry | 4220 | mg/L | |
| Nitrites | A-F-PE-0010 Digestion | <0.05 | mg/L | |
| Kjeldhal Nitrogen | A-F-PE-0007 Kjeldhal | 296.7 | mg/L | |
| pH | A-F-PE-0010 Electrometry | 6.5 | U. pH. | |
| Suspended solids | A-F-PE-0006 Gravimetry | 3228 | mg/L | |
| Toxicity | PIT-F/0012 Bioluminescence assay with Vibrio fisheri | 14 | U.T. | |
| Majority cations | Potassium | A-D-PE-0025-ICP-OES | 60.2 | mg/L |
| Anions | Nitrates | A-BV-PE-0001 HPLC–Conductivity | <2.5 | mg/L |
| Orthophosphates | Ca-R-PE-0011 Spectrometry | 74.32 | mg PO4/L | |
| Sulphates | A-BV-PE-0001 HPLC–Conductivity | 89.0 | mg/L | |
| Sulphites | A-F-PE-0040 Volumetry | 4.5 | mg/L | |
| WC0 | WC1 | WC2 | EDAR_STC0 | EDAR_STC1 | EDAR_STC2 | EDARC0 | EDARC1 | EDARC2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H’ 144 h | 4.86 ± 0.04 | 4.13 ± 0.06 | 4.88 ± 0.04 | 4.59 ± 0.02 | 4.68 ± 0.02 | 4.47 ± 0.01 | 4.90 ± 0.03 | 4.72 ± 0.13 | 4.92 ± 0.03 |
| Metric | Sample |
|---|---|
| Number of samples | 27 |
| Number of Features | 10,910 |
| Total frequency | 633,769 |
| Metric | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Minimum frequency | 1772 |
| First quartile | 19,134 |
| Median Frequency | 22,096 |
| Third quartile | 27,321 |
| Maximum Frequency | 54,530 |
| Medium Frequency | 23,472.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penalba-Iglesias, D.; Robas-Mora, M.; González-Reguero, D.; Fernández-Pastrana, V.M.; Probanza, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, P.A. Use of Bacillus pretiosus and Pseudomonas agronomica for the Synthesis of a Valorized Water Waste Treatment Plant Waste as a Biofertilizer Intended for Quercus pyrenaica L. Fertigation. Biology 2025, 14, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070902
Penalba-Iglesias D, Robas-Mora M, González-Reguero D, Fernández-Pastrana VM, Probanza A, Jiménez-Gómez PA. Use of Bacillus pretiosus and Pseudomonas agronomica for the Synthesis of a Valorized Water Waste Treatment Plant Waste as a Biofertilizer Intended for Quercus pyrenaica L. Fertigation. Biology. 2025; 14(7):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070902
Chicago/Turabian StylePenalba-Iglesias, Diana, Marina Robas-Mora, Daniel González-Reguero, Vanesa M. Fernández-Pastrana, Agustín Probanza, and Pedro A. Jiménez-Gómez. 2025. "Use of Bacillus pretiosus and Pseudomonas agronomica for the Synthesis of a Valorized Water Waste Treatment Plant Waste as a Biofertilizer Intended for Quercus pyrenaica L. Fertigation" Biology 14, no. 7: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070902
APA StylePenalba-Iglesias, D., Robas-Mora, M., González-Reguero, D., Fernández-Pastrana, V. M., Probanza, A., & Jiménez-Gómez, P. A. (2025). Use of Bacillus pretiosus and Pseudomonas agronomica for the Synthesis of a Valorized Water Waste Treatment Plant Waste as a Biofertilizer Intended for Quercus pyrenaica L. Fertigation. Biology, 14(7), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070902









