In Silico Discovery of a Novel Potential Allosteric PI3Kα Inhibitor Incorporating 3-(2-Chloro-5-fluorophenyl)isoindolin-1-one to Target Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
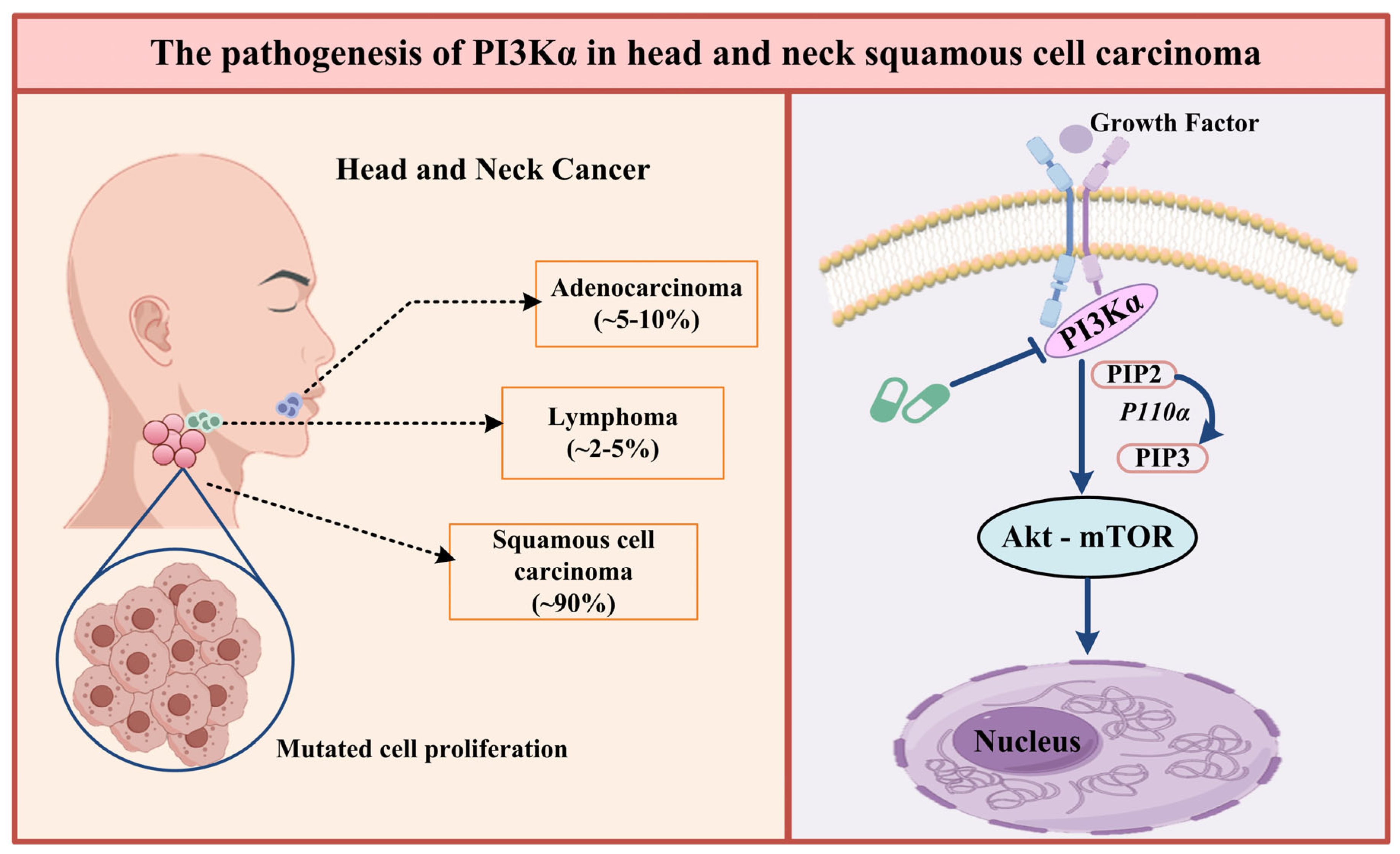
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
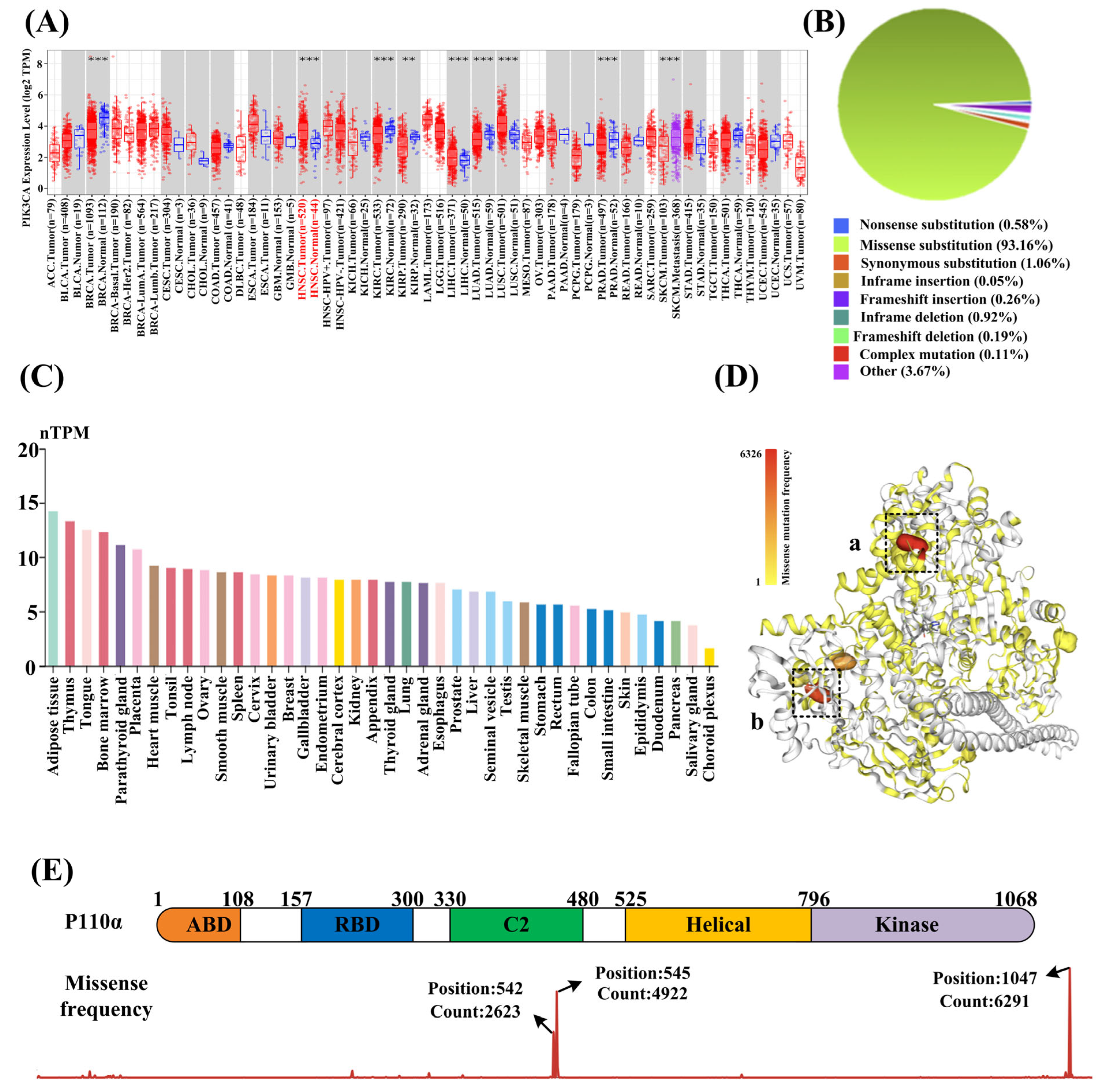
2.1. Correlation Analysis Between Genes and HNSCC
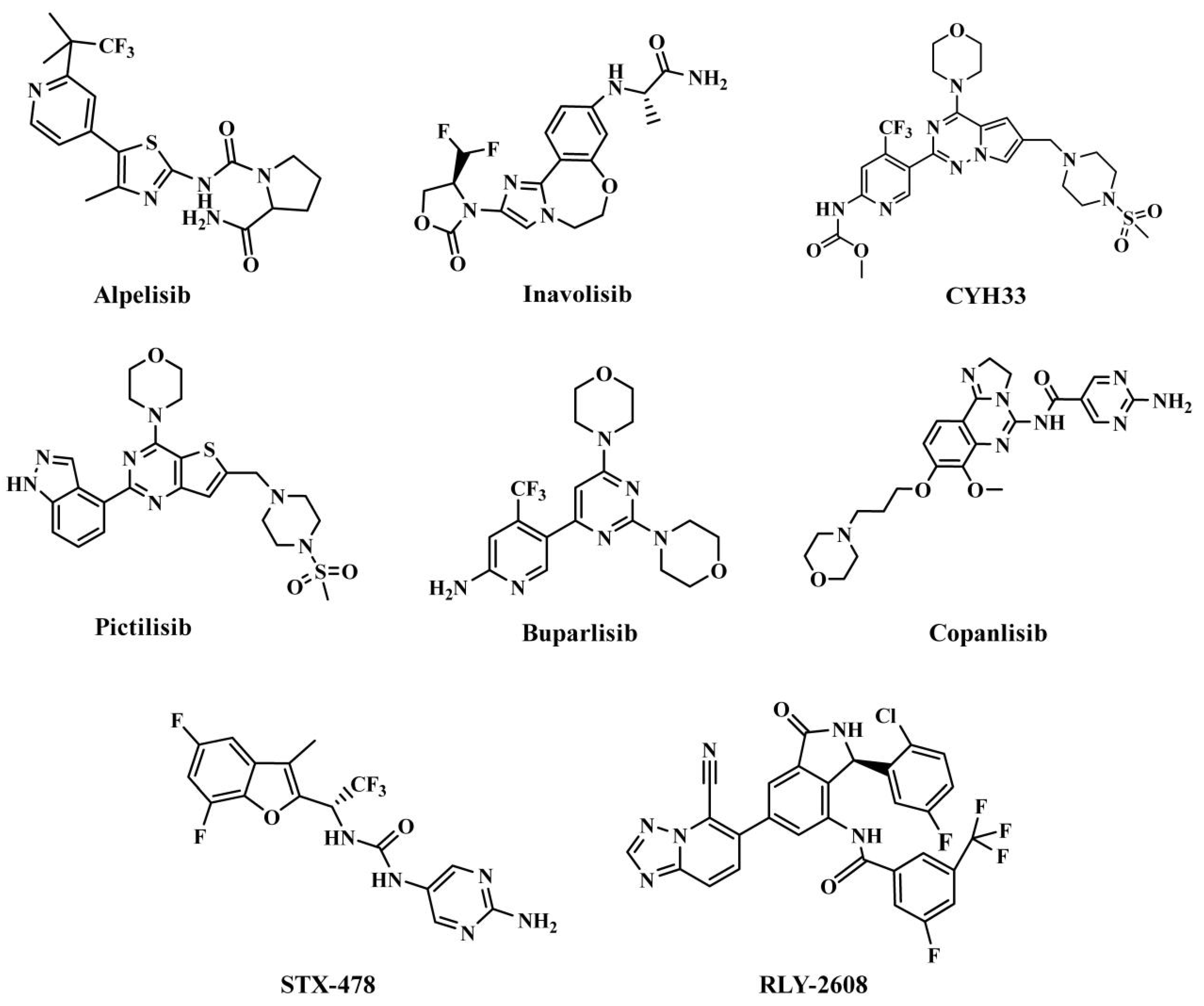
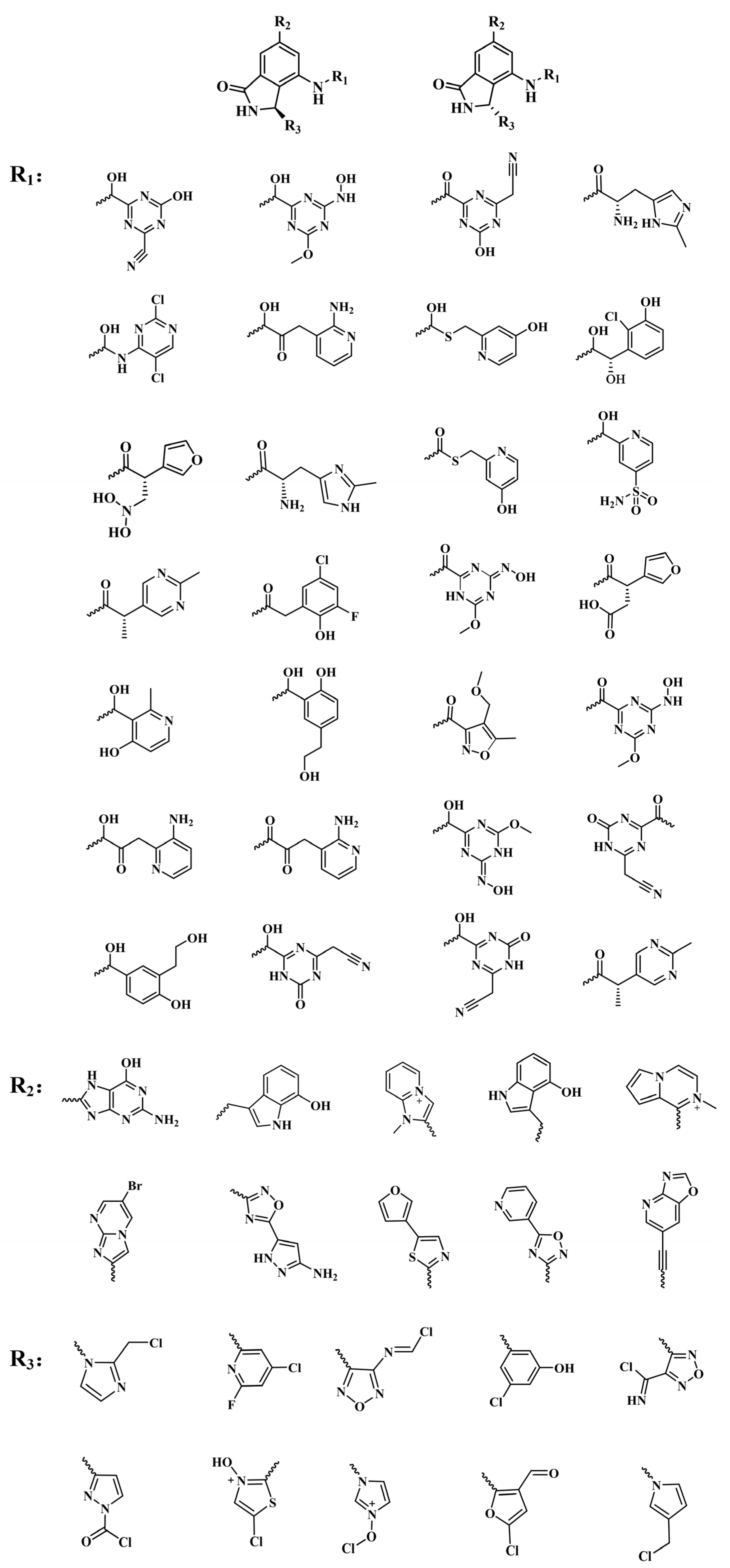
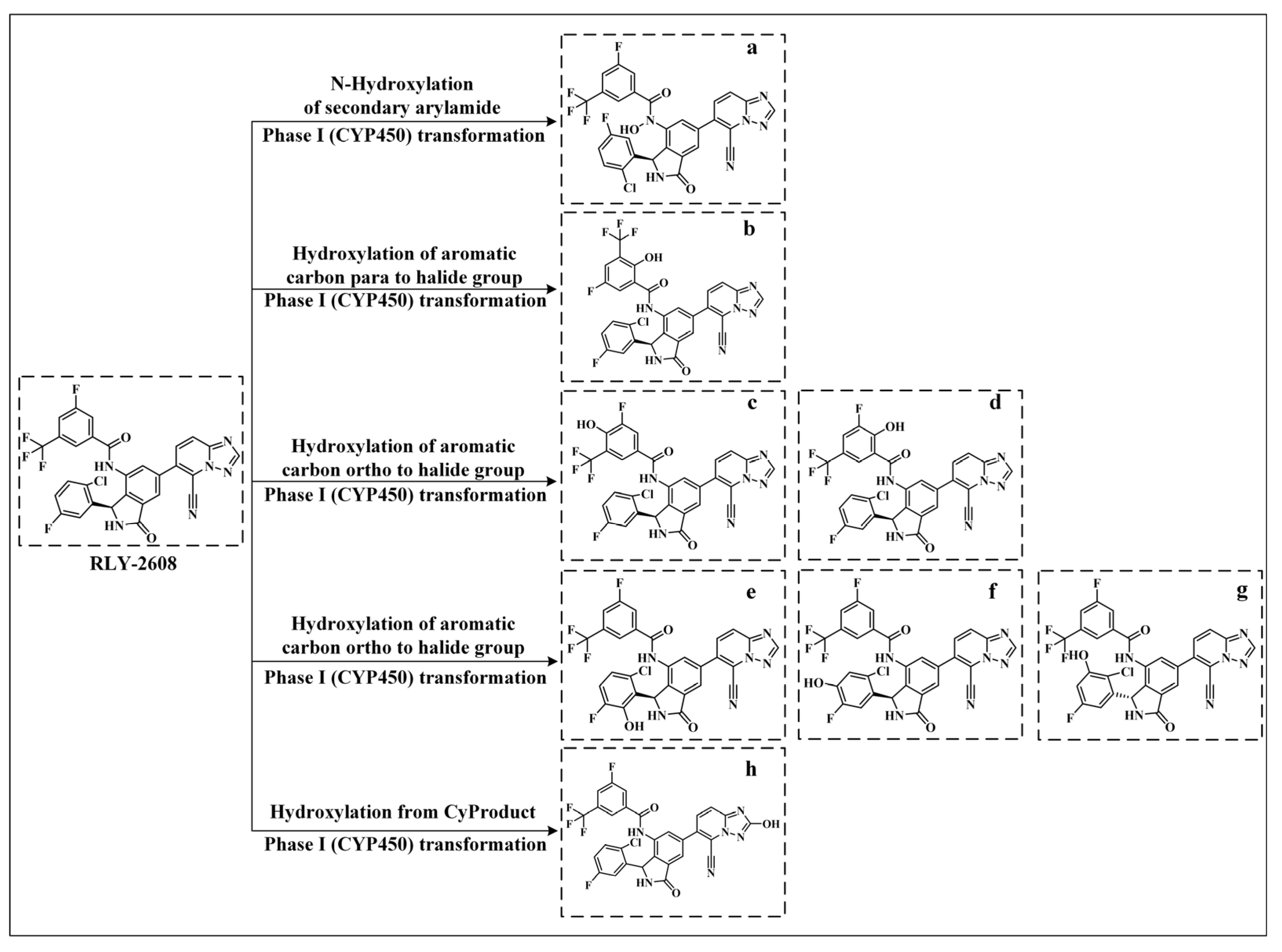
2.2. Scaffold Hopping of RLY-2608
2.3. In Silico Screening Employing Molecular Docking Techniques
2.4. Compounds’ Target Prediction
2.5. The Evaluation of Druggability
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.7. Analysis of Metabolic Pathways and Metabolites
3. Results
3.1. PIK3CA Is Highly Correlated with HNSCC
3.2. Scaffold Hopping of RLY-2608
3.3. In Silico Screening Employing Molecular Docking Techniques
3.4. The SuperPred Web Server Was Utilized to Predict Targets of the Top 9 Compounds
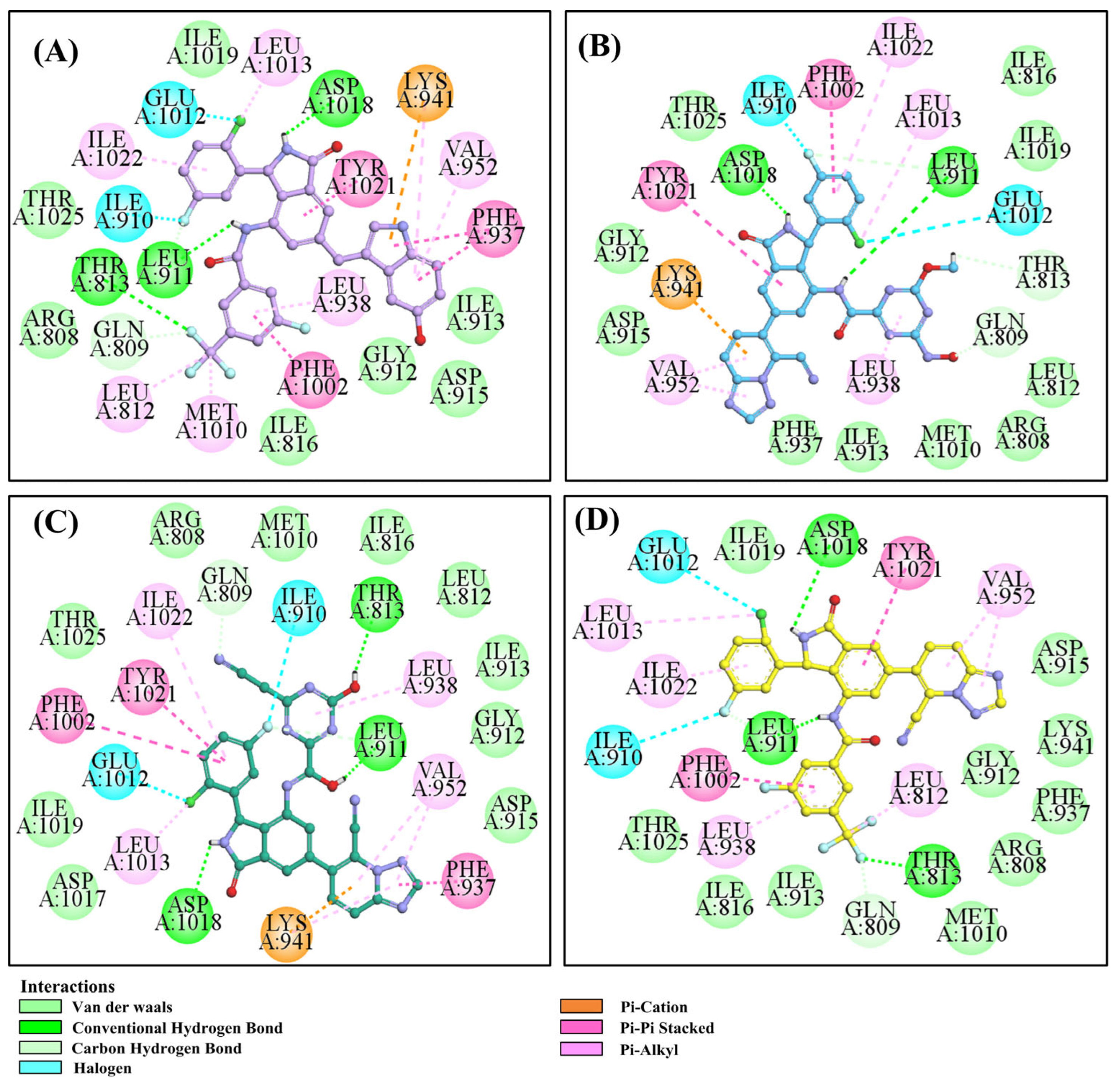
3.5. The Evaluation of Druggability
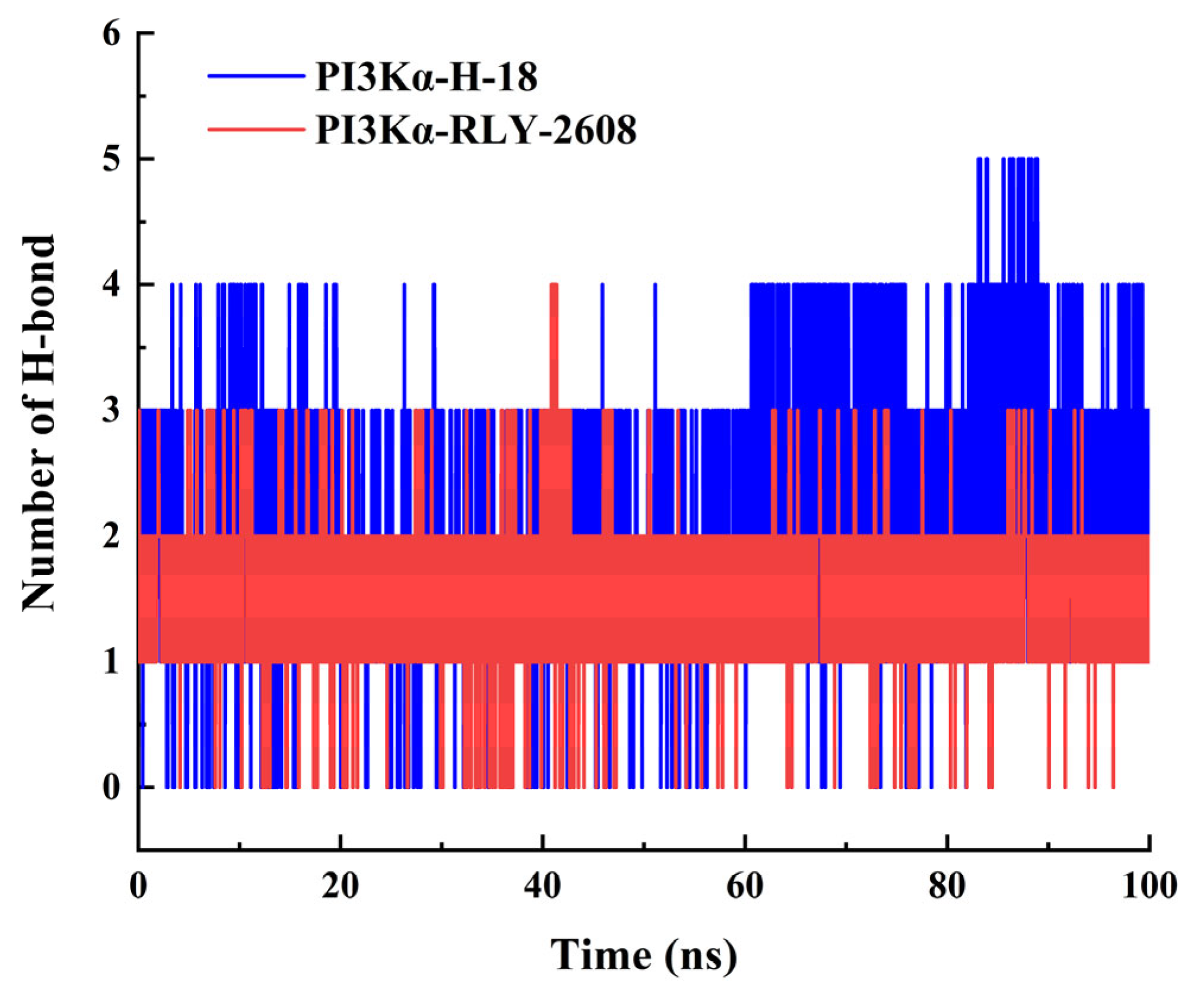
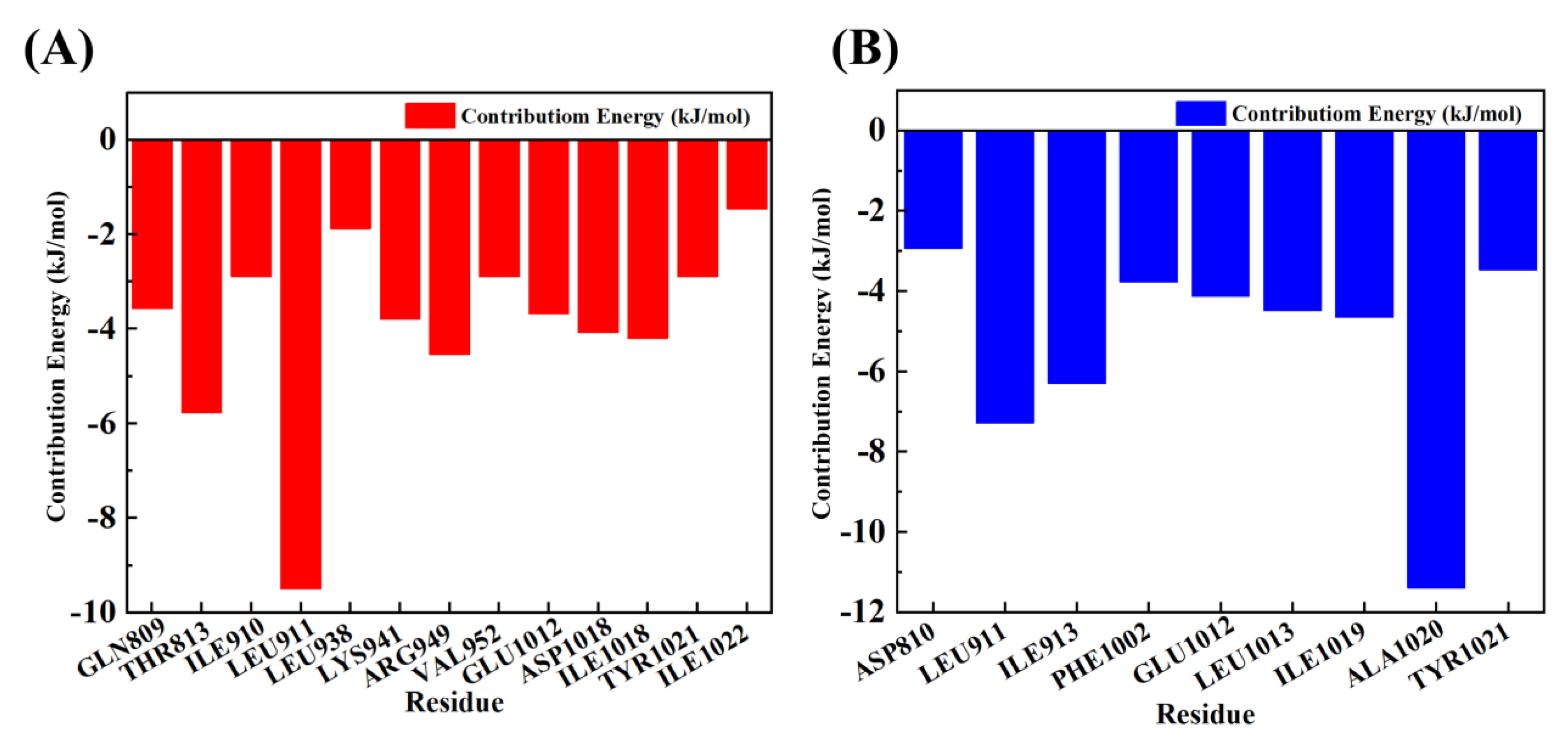
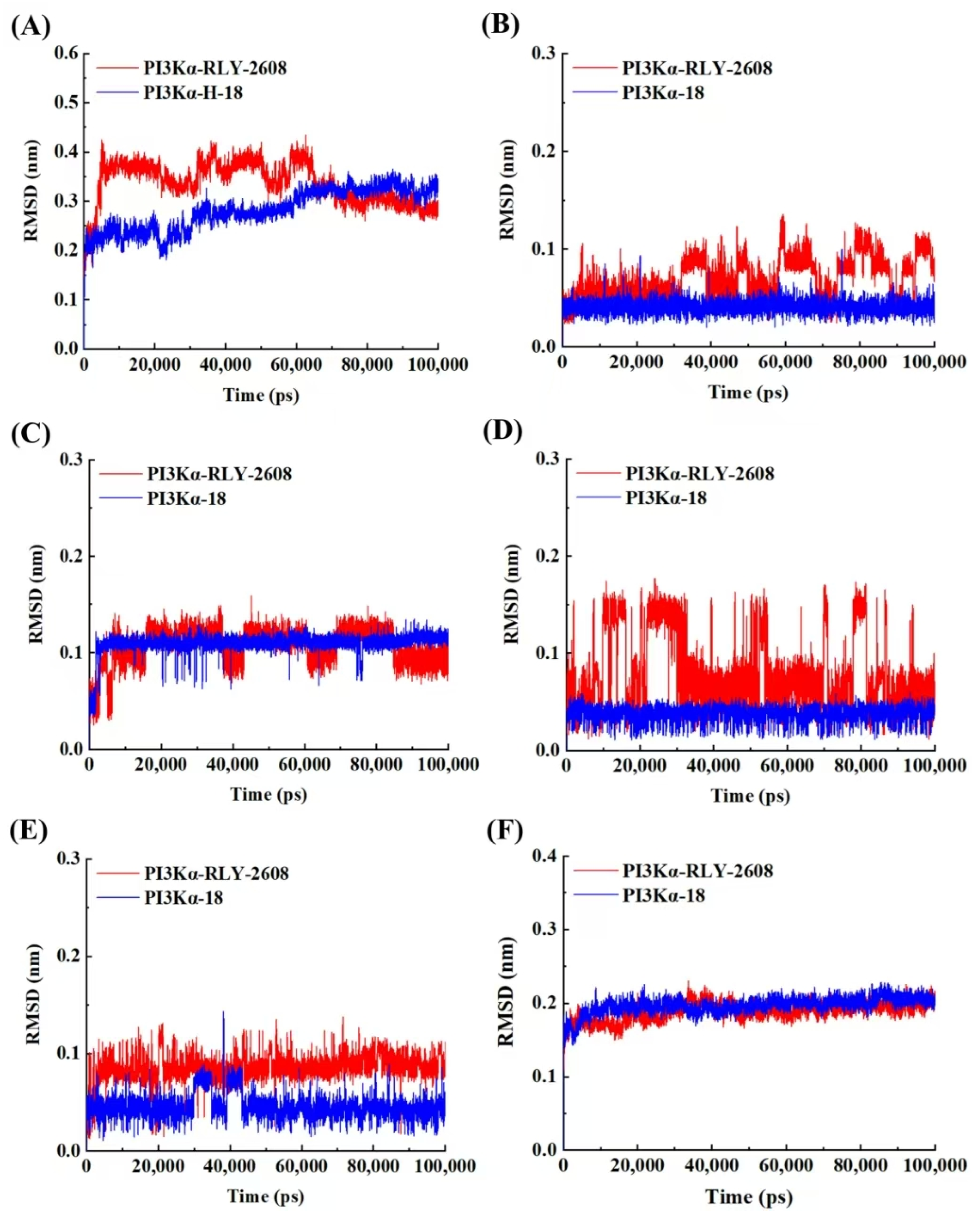
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of H-18/RLY-2608-PI3Kα System
3.7. Analysis of Metabolic Pathways and Metabolites of H-18 and RLY-2608
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saintigny, P. 77 Emerging strategies for head & neck cancer prevention. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 192, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiris, A.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Raben, D.; Ferris, R.L. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2008, 371, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, S.F.; Vu, L.; Spanos, W.C.; Pyeon, D. The key differences between human papillomavirus-positive and -negative head and neck cancers: Biological and clinical implications. Cancers 2021, 13, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodsinia, A.A.; Lego, J.A.M.T.; Garcia, R.L. Mutation-associated phenotypic heterogeneity in novel and canonical PIK3CA helical and kinase domain mutants. Cells 2020, 9, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higginson, J.A.; Breik, O.; Thompson, A.H.; Ashrafian, H.; Hardman, J.C.; Takats, Z.; Paleri, V.; Dhanda, J. Diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative margin assessment techniques in surgery for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2023, 142, 106419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejenaru, P.L.; Popescu, B.; Oancea, A.L.A.; Simion-Antonie, C.B.; Berteșteanu, G.S.; Condeescu-Cojocarița, M.; Cîrstea, A.I.; Oașă, I.D.; Schipor-Diaconu, T.E.; Popescu, D.; et al. Quality-of-Life Assessment after head and neck oncological surgery for advanced-stage tumours. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Vogt, P.K. Helical domain and kinase domain mutations in p110alpha of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase induce gain of function by different mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2652–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. Therapeutic implications of the genetic landscape of head and neck cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ye, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, S.; Xiao, M. Novel genetic alterations and their impact on target therapy response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, B.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S. In vitro anticancer activity of PI3K alpha selective inhibitor BYL719 in head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majchrzak, A.; Witkowska, M.; Smolewski, P. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Current knowledge and clinical significance. Molecules 2014, 19, 14304–14315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Bie, Q.; Zhao, R.; Yan, Y.; Dong, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Tian, D.; Hao, Y.; et al. Arachidonic acid released by PIK3CA mutant tumor cells triggers malignant transformation of colonic epithelium by inducing chromatin remodeling. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Burke, J.E.; Madsen, R.R. Precision targeting of mutant PI3Kα in cancer by selective degradation. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Yang, K.; Ma, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Intact regulation of G1/S transition renders esophageal squamous cell carcinoma sensitive to PI3Kα inhibitors. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.A. Treatment strategies for advanced hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor 2-negative breast cancer: The role of treatment order. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 24, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endicott, S.J.; Ziemba, Z.J.; Beckmann, L.J.; Boynton, D.N.; Miller, R.A. Inhibition of class I PI3K enhances chaperone-mediated autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202001031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.; Appleman, L.J.; Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Beeram, M.; Rasco, D.W.; Weiss, G.J.; Sachdev, J.C.; Chadha, M.; Fulk, M.; et al. First-in-human phase I study of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946), an intravenous pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzampasi, D.M.; Papadourakis, M.; Burke, J.E.; Cournia, Z. Free energy landscape of the PI3Kα C-terminal activation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 3118–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkaris, A.; Pazolli, E.; Gunaydin, H.; Wang, Q.; Pierce, L.; Boezio, A.A.; Bulku, A.; DiPietro, L.; Fridrich, C.; Frost, A.; et al. Discovery and clinical proof-of-concept of RLY-2608, a first-in-class mutant-selective allosteric PI3Kα inhibitor that decouples antitumor activity from hyperinsulinemia. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckbinder, L.; St Jean, D.J., Jr.; Tieu, T.; Ladd, B.; Hilbert, B.; Wang, W.; Alltucker, J.T.; Manimala, S.; Kryukov, G.V.; Brooijmans, N.; et al. STX-478, a mutant-selective, allosteric PI3Kα inhibitor spares metabolic dysfunction and improves therapeutic response in PI3Kα-mutant xenografts. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2432–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, I.M.; Okines, A.F.C. Resistance to targeted inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in advanced oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanker, A.B.; Kaklamani, V.; Arteaga, C.L. Challenges for the clinical development of PI3K inhibitors: Strategies to improve their impact in solid tumors. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkaris, A.; Fece de la Cruz, F.; Martin, E.E.; Norden, B.L.; Chevalier, N.; Kehlmann, A.M.; Leshchiner, I.; Barnes, H.; Ehnstrom, S.; Stavridi, A.M.; et al. Allosteric PI3Kα inhibition overcomes on-target resistance to orthosteric inhibitors mediated by secondary PIK3CA mutations. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.; Gohlke, B.O.; Erehman, J.; Banerjee, P.; Rong, W.W.; Goede, A.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. SuperPred: Update on drug classification and target prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W26–W31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. In silico discovery of a novel PI3Kδ inhibitor incorporating 3,5,7-trihydroxychroman-4-one targeting diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostefai, N.; Cherif, F.Y.; Hosen, M.N.; Ouici, H.B.; Brahim, H.; Guendouzi, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Guendouzi, A.; Alharbi, H.M.; Jawi, M.; et al. Identification of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and stability analysis of THC@HP-β-CD inclusion complex: A comprehensive computational study. Talanta 2025, 286, 127370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roney, M.; Wong, K.K.V.; Uddin, M.N.; Rullah, K.; Septama, A.W.; Antika, L.D.; Mohd Aluwi, M.F.F. Design, synthesis, structural characterization, cytotoxicity and computational studies of Usnic acid derivative as potential anti-breast cancer agent against MCF7 and T47D cell lines. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2025, 115, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, T.; Riyed, T.H.; Ornob, A. Deep learning based predictive modeling to screen natural compounds against TNF-alpha for the potential management of rheumatoid arthritis: Virtual screening to comprehensive in silico investigation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Mahesh, Y.; Prabhu, D.; Sekar, K.; Sen, P. Identification of potent anti-fibrinolytic compounds against plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator employing in silico approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 3204–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Mandelker, D.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Samuels, Y.; Velculescu, V.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Gabelli, S.B.; Amzel, L.M. The structure of a human p110alpha/p85alpha complex elucidates the effects of oncogenic PI3Kalpha mutations. Science 2007, 318, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochicho, D.; Esteves, S.; Rito, M.; Silva, F.; Martins, L.; Montalvão, P.; Cunha, M.; Magalhães, M.; Gil da Costa, R.M.; Felix, A. PIK3CA gene mutations in HNSCC: Systematic review and correlations with HPV status and patient survival. Cancers 2022, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Juric, D.; Loibl, S.; Campone, M.; Mayer, I.A.; Rubovszky, G.; Yamashita, T.; Kaufman, B.; Lu, Y.S.; et al. Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival results from SOLAR-1. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Wu, Y.; He, P.; Fan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zheng, H.; Luo, T. PI3K/AKT/mTOR-targeted therapy for breast cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juric, D.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J.; Janku, F.; Burris, H.A.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Middleton, M.R.; Berlin, J.; Schuler, M.; Gil-Martin, M.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α-selective inhibition with Alpelisib (BYL719) in PIK3CA-altered solid tumors: Results from the first-in-human study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| ID Number | Chemical Structure | Molecular Formula | -Cdocker Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-18 |  | C31H19ClF5N3O3 | 35.9705 |
| H-72 | 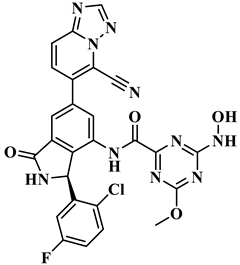 | C26H16ClFN10O4 | 35.5813 |
| H-872 |  | C27H14ClFN10O3 | 35.4137 |
| H-222 |  | C27H15ClF5N7O3 | 34.0786 |
| H-702 | 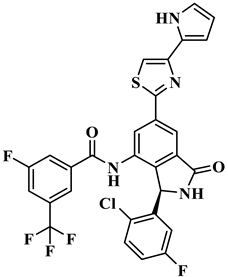 | C29H16ClF5N4O2S | 32.8416 |
| H-139 | 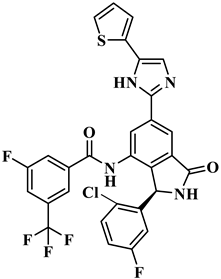 | C29H16ClF5N4O2S | 32.0775 |
| H-176 | 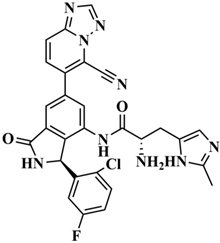 | C28H21ClFN9O2 | 30.5798 |
| H-742 |  | C26H12ClF4N9O3 | 30.4041 |
| H-392 |  | C29H14ClF4N5O4 | 27.8655 |
| RLY-2608 |  | C29H14ClF5N6O2 | 21.4709 |
| Target Name | Probability | Model Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| H-18 | 80.72% | 94.33% |
| H-72 | 78.09% | 97.47% |
| H-872 | 61.53% | 94.33% |
| H-222 | 64.53% | 94.33% |
| H-702 | 57.49% | 94.33% |
| H-139 | 65.56% | 94.33% |
| H-176 | 91.76% | 94.33% |
| H-742 | 69.89% | 94.33% |
| H-392 | 88.32% | 94.33% |
| RLY-2608 | 60.31% | 97.47% |
| H-18 | H-72 | H-872 | H-222 | H-702 | H-139 | H-176 | H-742 | H-392 | RLY-2608 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD50 (mg/kg) | 2000 | 300 | 300 | 1250 | 300 | 110 | 1120 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| H-18 | RLY-2608 | |
|---|---|---|
| Clplasma 1 (mL/min/kg) | 0.863 | 1.049 |
| T1/2 2 (h) | 1.438 | 1.697 |
| Bioavailability score 3 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| Log Kp 4 (cm/s) | −5.27 | −6.10 |
| VDss 5 (L/kg) | 3.608 | 1.792 |
| Synthetic accessibility | 4.22 | 4.27 |
| H-18 | RLY-2608 | |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiotoxicity | Inact81% | Inact90% |
| Mutagenicity | Inact66% | Inact58% |
| Cytotoxicity | Inact69% | Inact78% |
| Energy | H-18 | RLY-2608 |
|---|---|---|
| Van der Waals Energy (kJ/mol) | −251.206 | −180.671 |
| Electrostatic energy (kJ/mol) | −55.374 | −187.826 |
| Polar solvation energy (kJ/mol) | 197.626 | 310.695 |
| Nonpolar solvation energy (kJ/mol) | −27.680 | −23.788 |
| Total binding energy (kJ/mol) | −136.634 | −81.590 |
| T∆S (kJ/mol) | 24.935 | 16.499 |
| Total binding free energy (kJ/mol) | −111.699 | −65.091 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, W.; Cheng, X. In Silico Discovery of a Novel Potential Allosteric PI3Kα Inhibitor Incorporating 3-(2-Chloro-5-fluorophenyl)isoindolin-1-one to Target Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology 2025, 14, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070896
Jia W, Cheng X. In Silico Discovery of a Novel Potential Allosteric PI3Kα Inhibitor Incorporating 3-(2-Chloro-5-fluorophenyl)isoindolin-1-one to Target Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology. 2025; 14(7):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070896
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Wenqing, and Xianchao Cheng. 2025. "In Silico Discovery of a Novel Potential Allosteric PI3Kα Inhibitor Incorporating 3-(2-Chloro-5-fluorophenyl)isoindolin-1-one to Target Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biology 14, no. 7: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070896
APA StyleJia, W., & Cheng, X. (2025). In Silico Discovery of a Novel Potential Allosteric PI3Kα Inhibitor Incorporating 3-(2-Chloro-5-fluorophenyl)isoindolin-1-one to Target Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology, 14(7), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070896






