Molecular Mechanism of Body Color Change in the Ecological Seedling Breeding Model of Apostichopus japonicus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
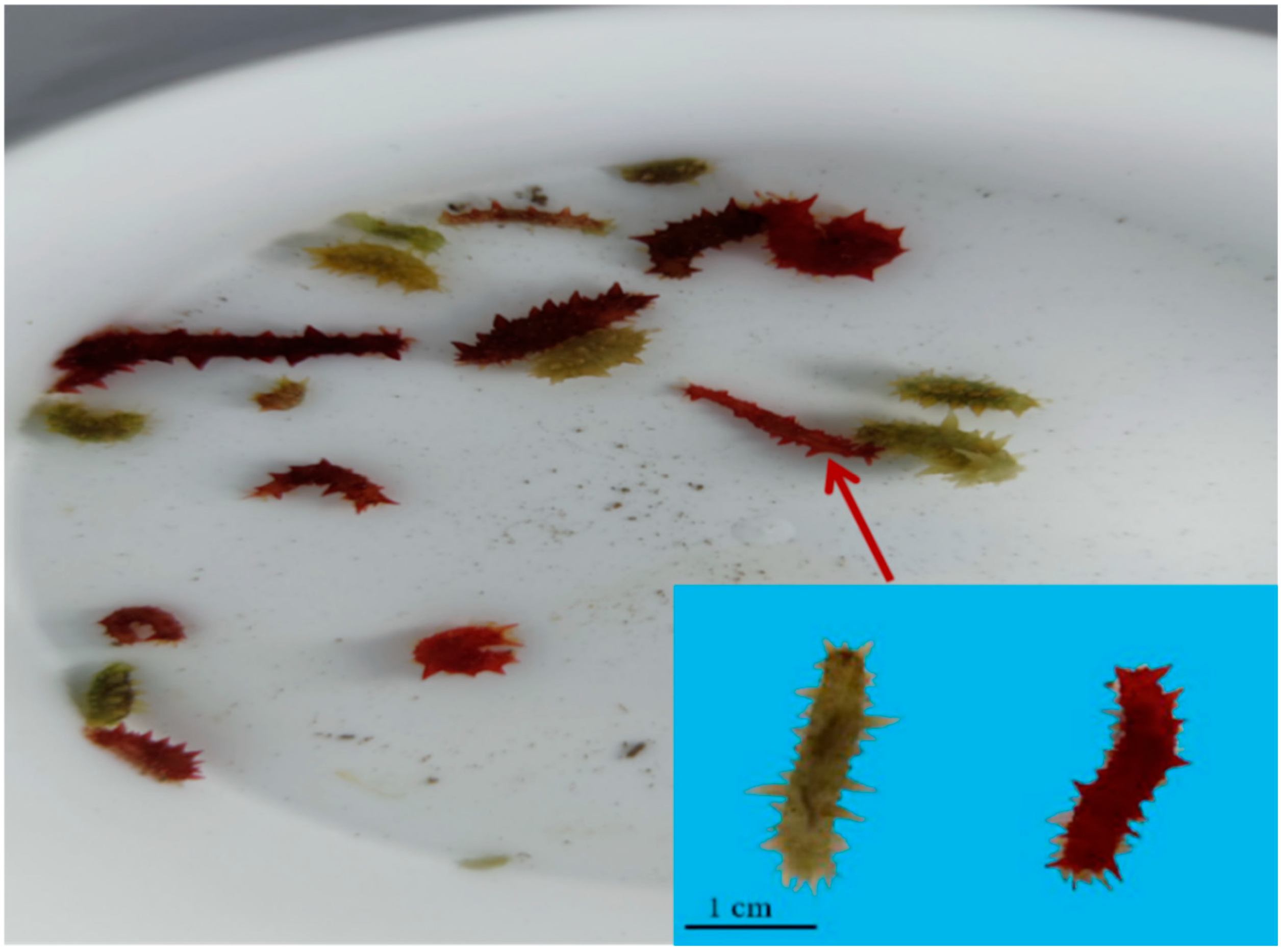
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Measurement of Body Length and Weight of Different Body Colors of Sea Cucumber
2.3. Determination of Astaxanthin, Keratoxanthin, Lutein and Β-Carotene in Different Body Colors of Stichopus japonicum
2.4. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Illumina Sequencing
2.5. Quality Control and Assembly of Transcriptome Data
2.6. Gene Function Annotation
2.7. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes, Enrichment Analysis and qRT-PCR Validation
2.8. Extraction and LC-MS/MS Analysis of Body Wall Metabolites in Different Body Colors of A. japonicus
2.9. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
2.10. Combined RNA-Seq and Metabolome Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Growth and the Pigment Content of the Body Wall of Red and Green A. japonicus
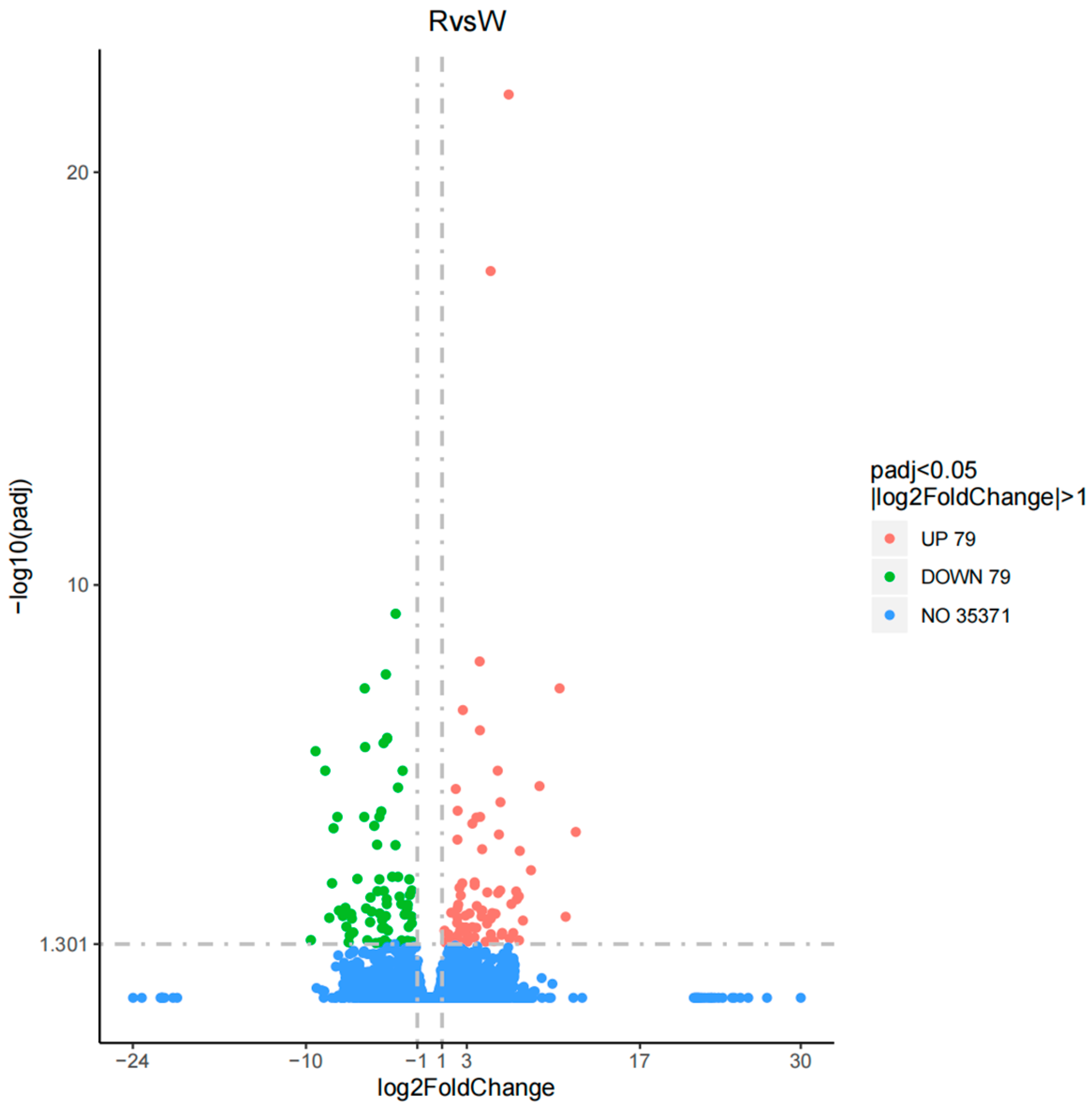
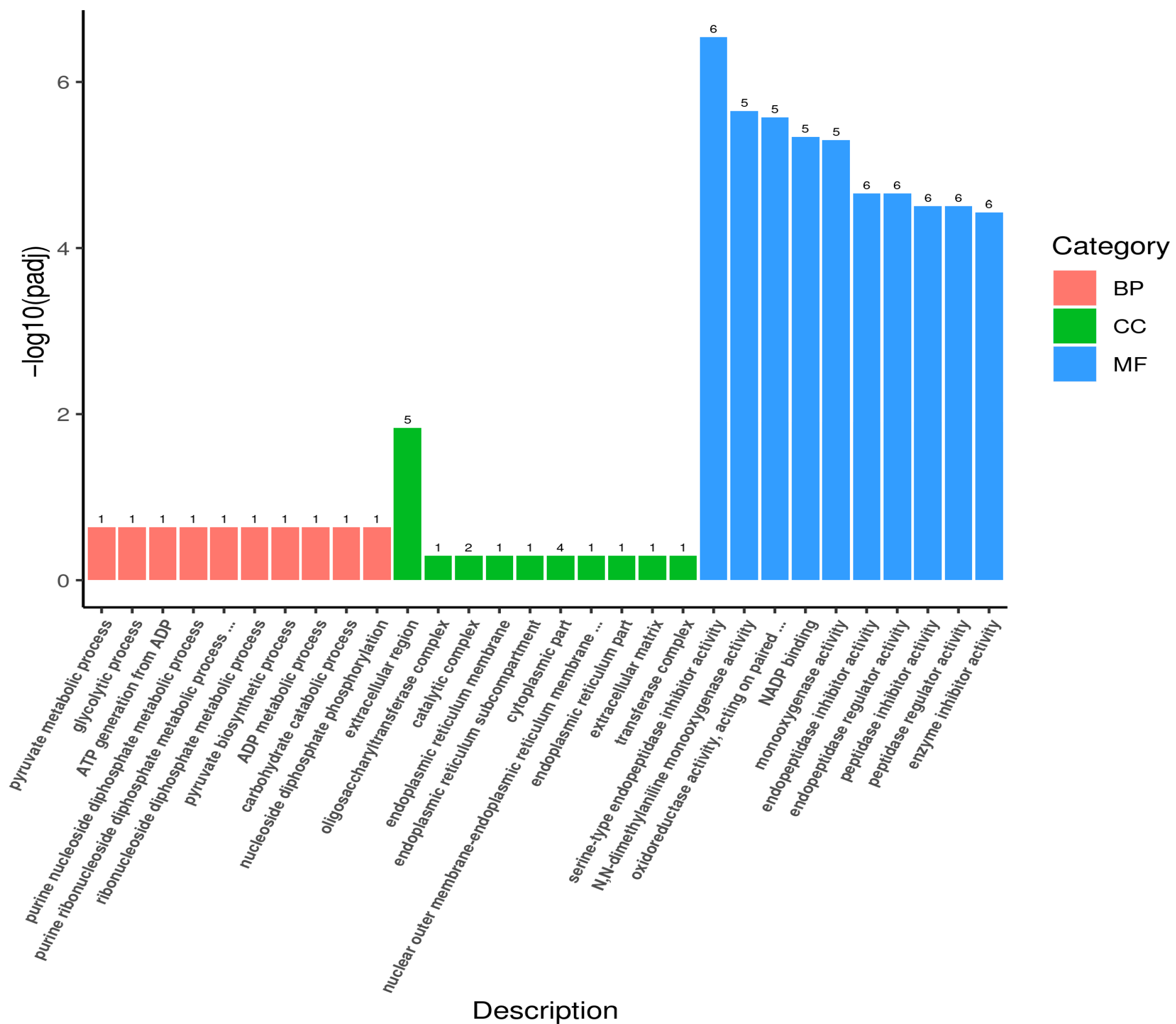
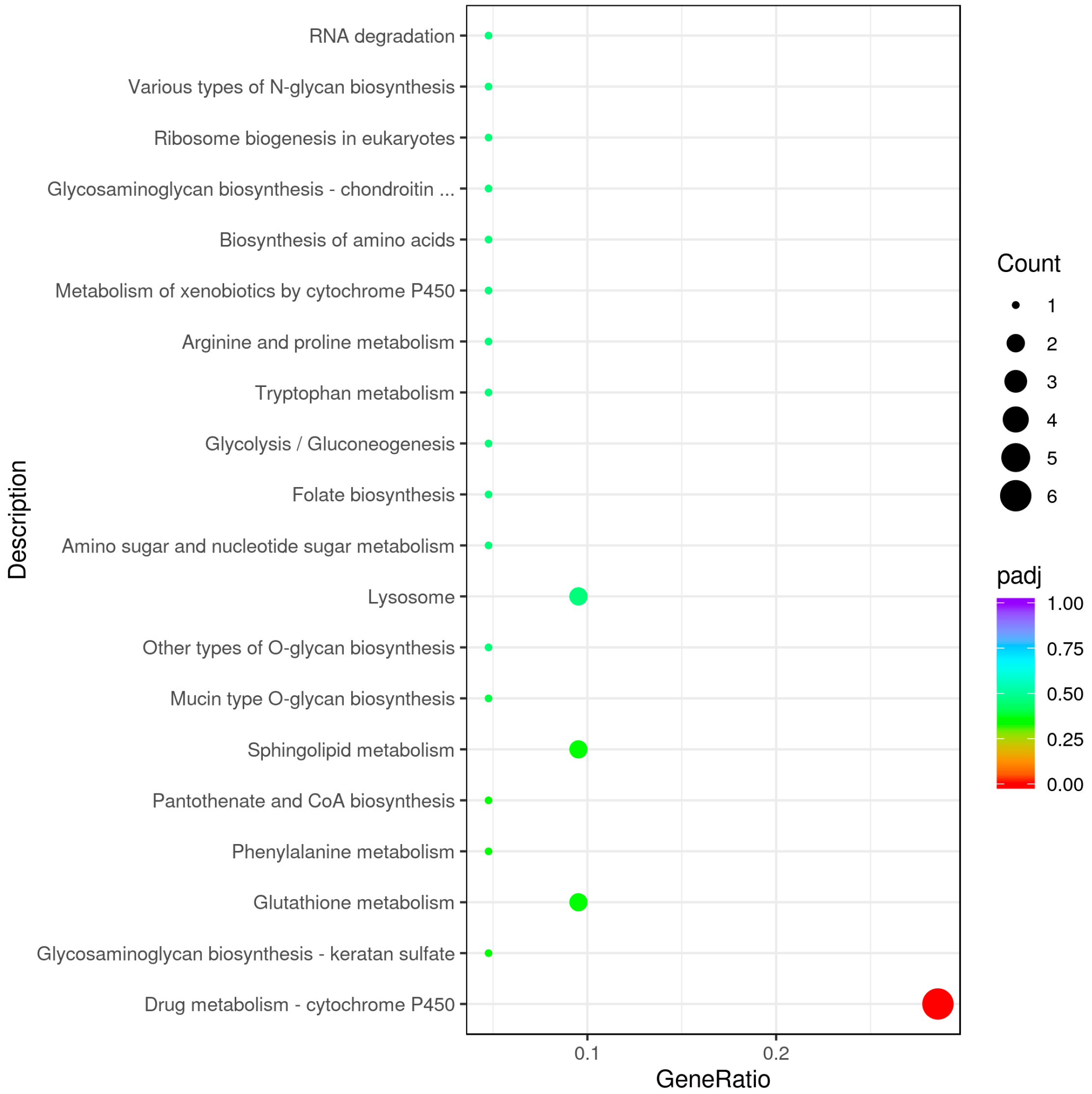
3.2. Analysis and Functional Annotation of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
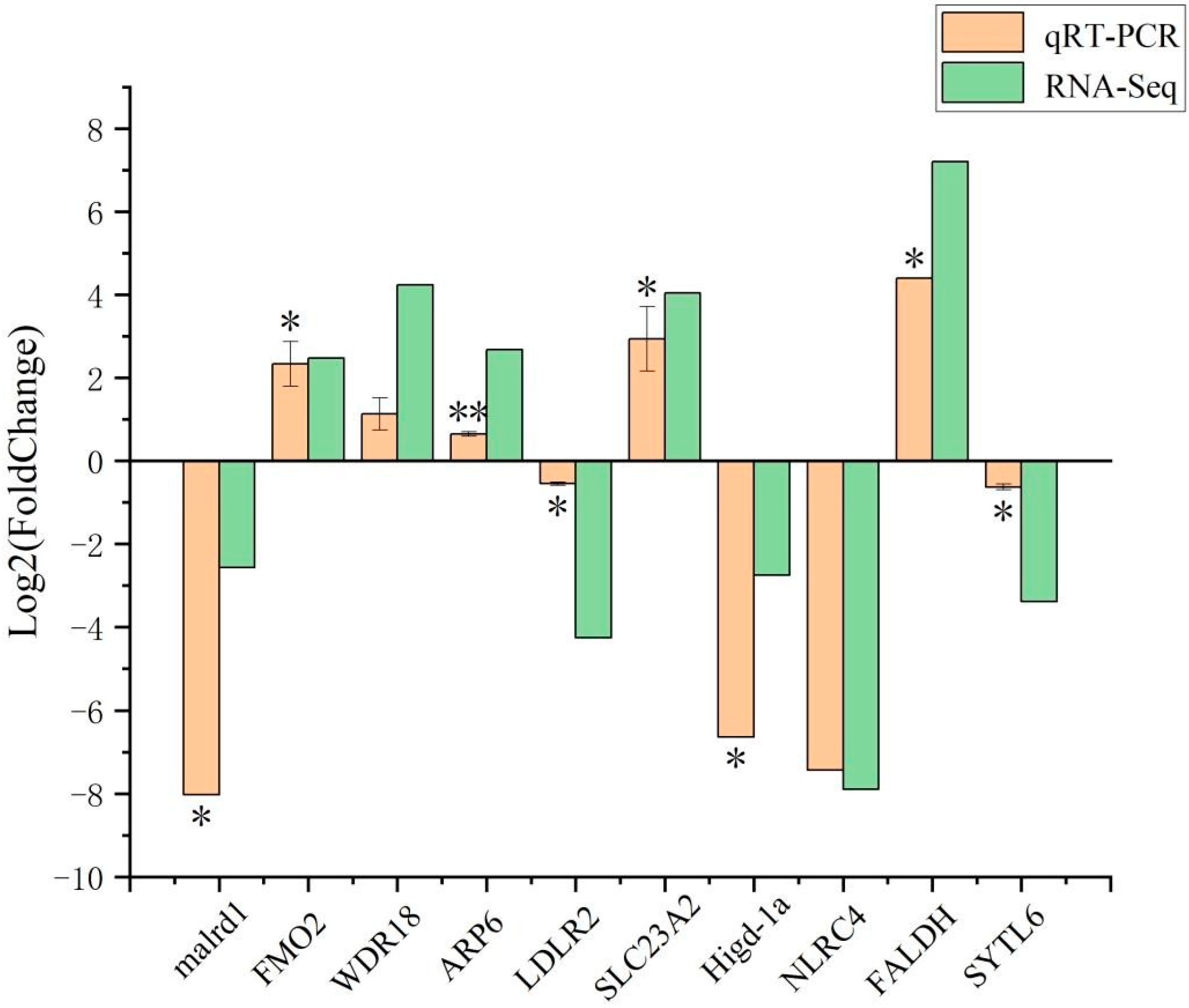
3.3. qRT-PCR Validation of DEGs
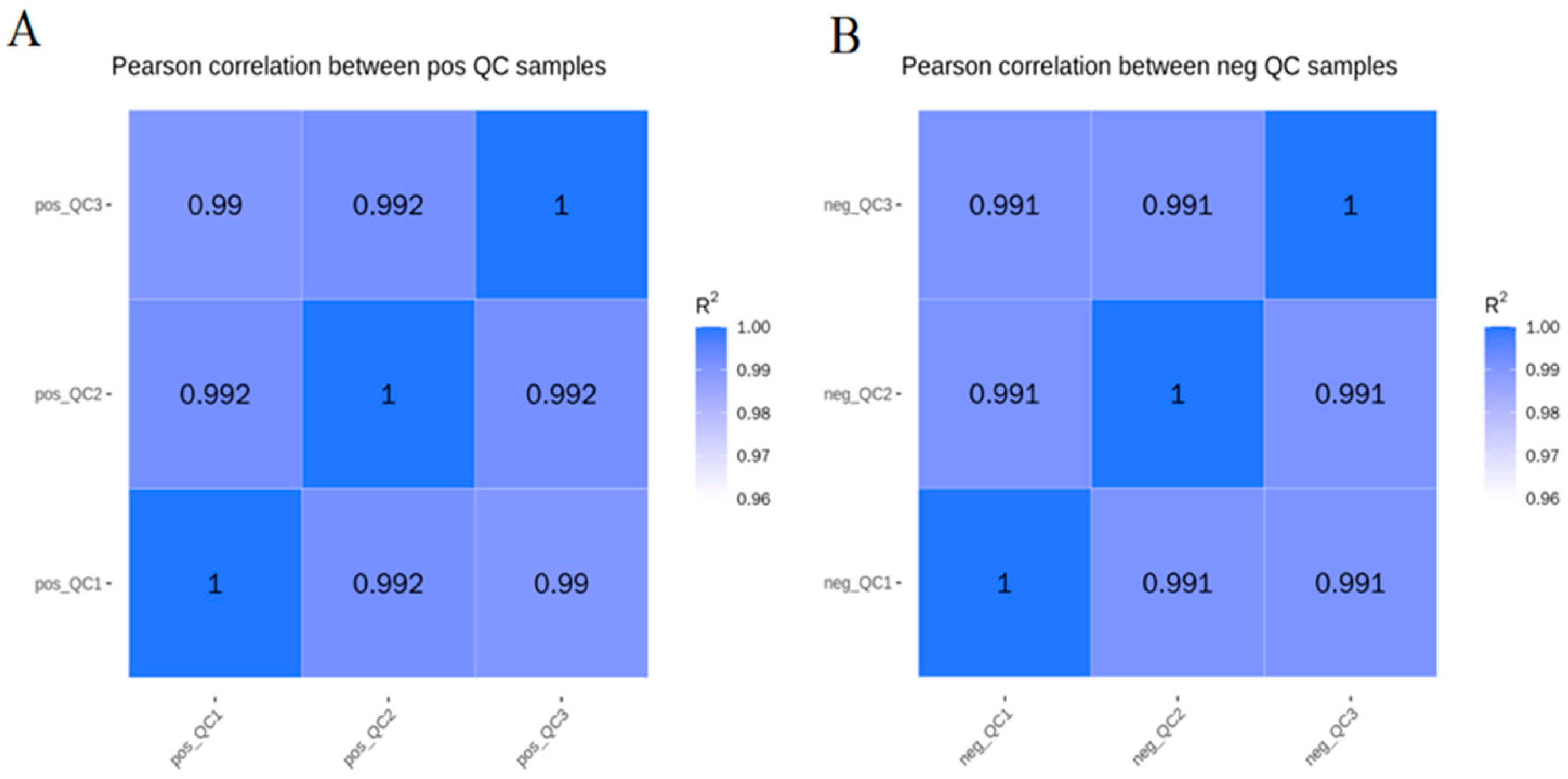
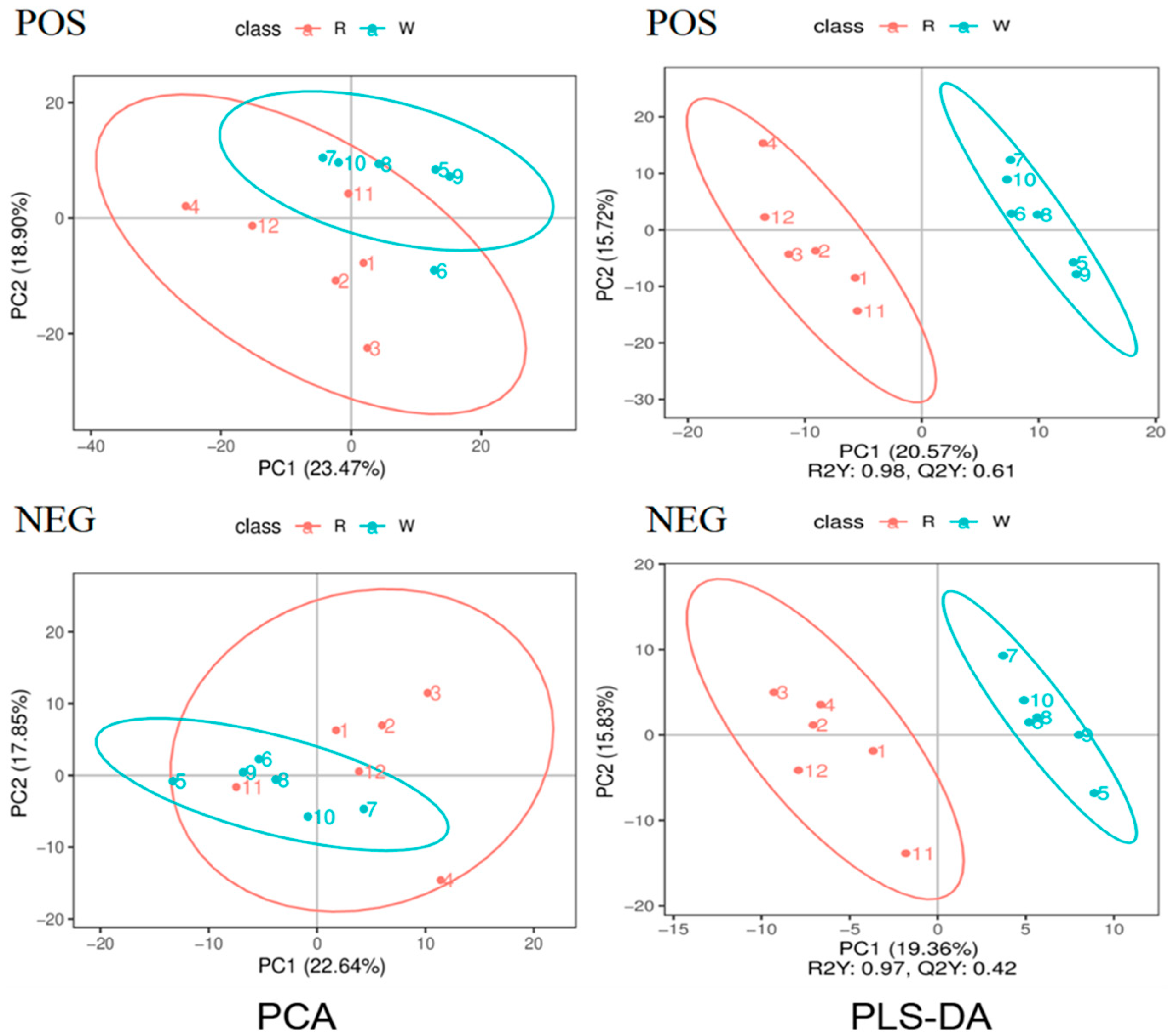
3.4. Principal Component Analysis and Pls-Da of Body Wall Metabolic Profiles of Red and Green A. japonicus
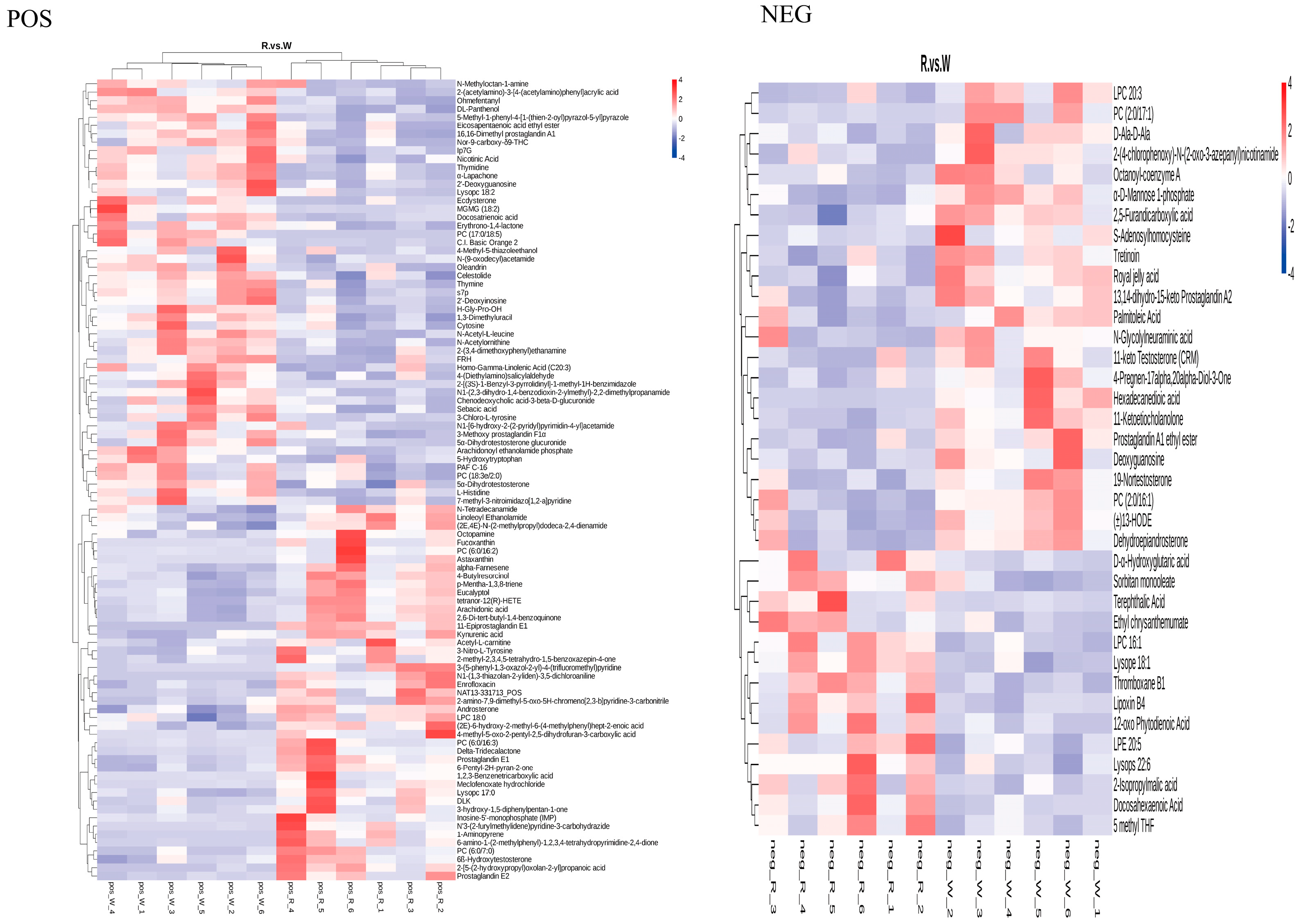
3.5. Identification of Metabolites in the Body Walls of Red and Green A. japonicus
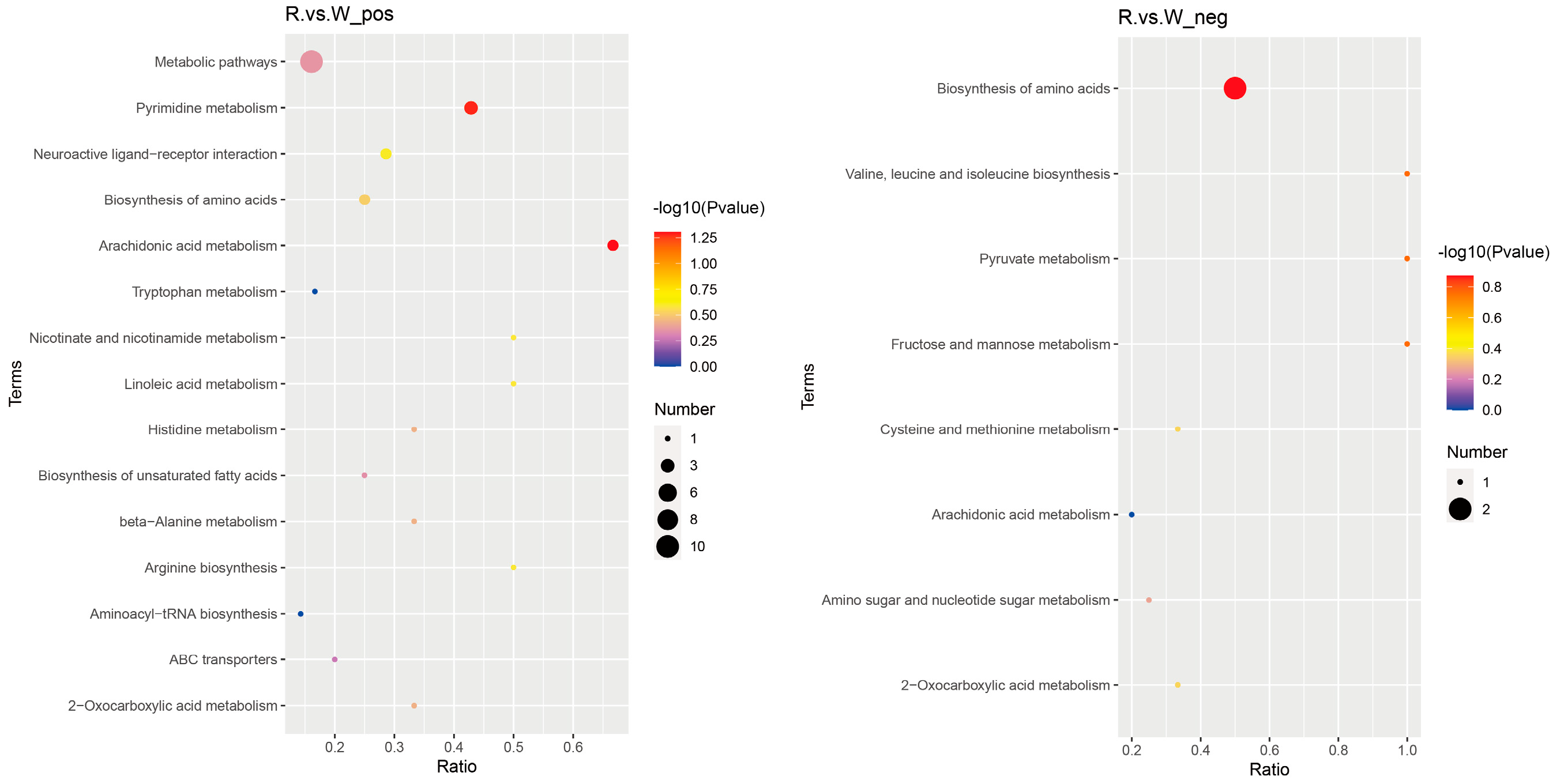
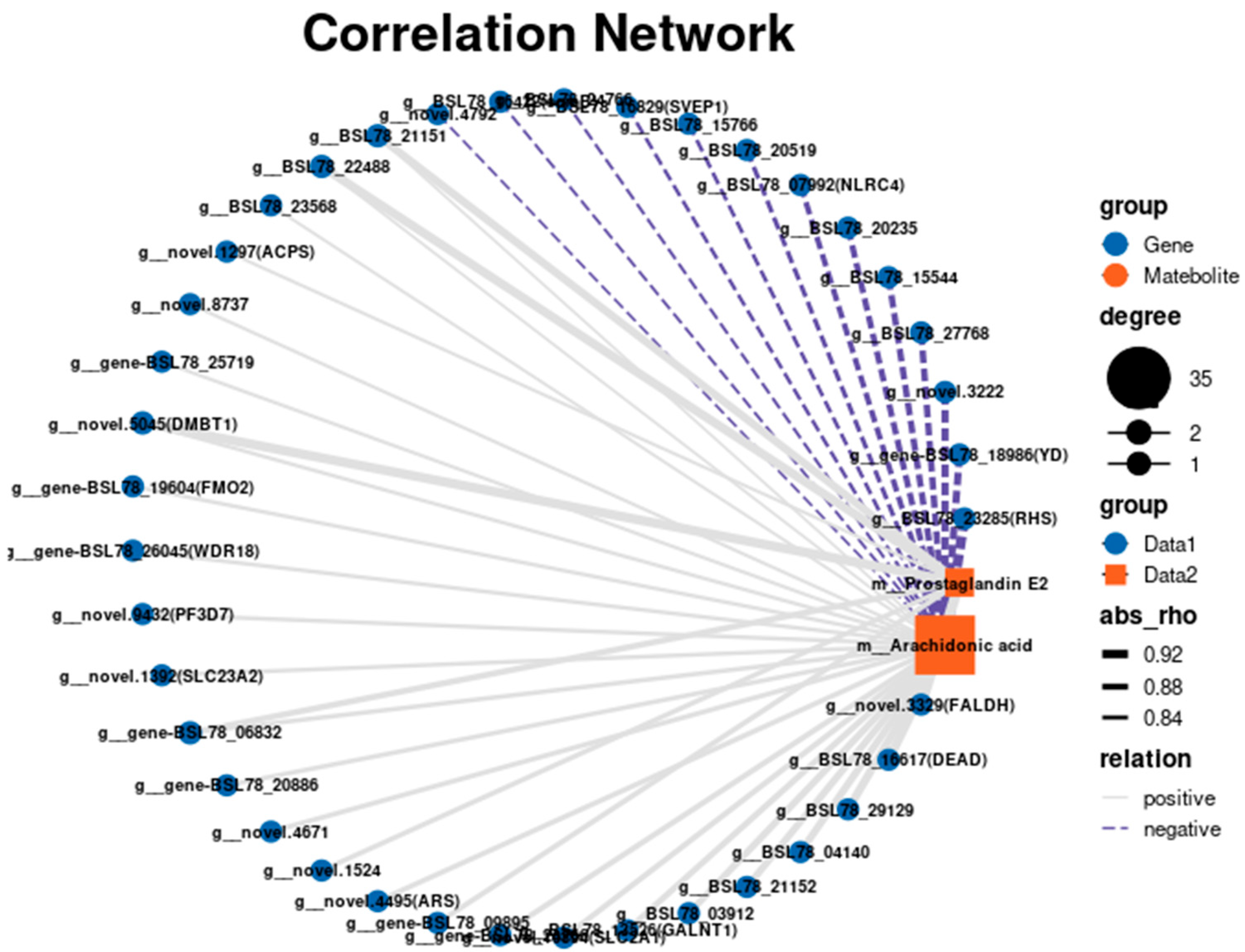
3.6. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of the Body Walls of Red and Green A. japonicus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ru, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Development strategies for the sea cucumber industry in China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D. A review of sea cucumber aquaculture, ranching, and stock enhancement in China. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Omont, A.; Spanopoulos-Zarco, M.; Pacheco-Vega, J.M.; Peña-Rodríguez, A. Evolving challenges and innovations in sea cucumber aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurdjevič, I.; Kreft, M.E.; Sušnik Bajec, S. Comparison of pigment cell ultrastructure and organisation in the dermis of marble trout and brown trout, and first description of erythrophore ultrastructure in salmonids. J. Anat. 2015, 227, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Miao, T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Comparison of pigment composition and melanin content among white, light-green, dark-green, and purple morphs of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Zhao, C. Resistance to temperature change, handling stress, and disease in small sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in different color morphs. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, S. Effect of light intensity on the growth and energy allocation of greenand red variants of Apostichopus japonicas Selenka. J. Ocean Univ. China: Nat. Sci. Ed. 2013, 43, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, J.; Park, J.; Lee, H.-G.; Kern, E.M.; Cheon, S.; Jin, S.; Park, J.-K.; Cho, S.-J.; Park, C. Comparative transcriptome analysis of three color variants of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Mar. Genom. 2016, 28, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, M.; Kijima, A. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation on the color variation of the Japanese sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Aquac. Sci. 2002, 50, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Wan, Z.; Li, X.; Miao, T.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Y.; Yang, H. Growth, histology, ultrastructure and expression of MITF and astacin in the pigmentation stages of green, white and purple morphs of the sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanna, T.; Maneeruttanarungroj, C. Identification of major carotenoids from green alga Tetraspora sp. CU2551: Partial purification and characterization of lutein, canthaxanthin, neochrome, and β-carotene. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gao, P.; Quan, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Analysis of the gene transcription patterns and DNA methylation characteristics of triploid sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Ding, B.; Gao, C.; Hao, P.; Jin, X.; Chang, Y. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses provide insights into the growth and development advantages of triploid Apostichopus japonicus. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Park, J.W.; Lu, Z.-x.; Lin, L.; Henry, M.D.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhou, Q.; Xing, Y. rMATS: Robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5593–E5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, Y.; Wang, E.T.; Airoldi, E.M.; Burge, C.B. Analysis and design of RNA sequencing experiments for identifying isoform regulation. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ruan, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Han, L.; Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Papillae growth and molecular responses in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) exposed to light spectra. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2025, 56, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocho, A.; Chen, B.; Ladanyi, M.; Pan, Q. Validation of the 2-DeltaDeltaCt calculation as an alternate method of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. Part B 2006, 15, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Ding, S.; Chang, Y. Metabolomic changes and polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis during gonadal growth and development in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 32, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Ding, S.; Chang, Y. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses identify critical genes in eicosapentaenoic acid biosynthesis and metabolism in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: Applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Che, Z.; Xu, W.; Jiao, Y.; Xiong, H. The Advancement of the Physiological Functions and Extraction Technology of β-Carotene. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 1, 71–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, B. Pigment evaluation and artificial regulation of fish body color. Feed Ind. 2008, 29, 58–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- You, X.; Liao, Y.; Sun, S. Developments in the use of prepared feeds in sea urchin aquaculture. Mar. Sci. 2003, 8, 24–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kotake-Nara, E.; Asai, A.; Nagao, A. Neoxanthin and fucoxanthin induce apoptosis in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 220, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Leng, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, X. Effect of Haematococcus pluvialis on growth, body color andantioxidation capacity of discus fish Symphysodon haraldi. Freshw. Fish. 2016, 46, 92–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cashman, J.R.; Zhang, J. Human flavin-containing monooxygenases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 46, 65–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calestani, C.; Rast, J.P.; Davidson, E.H. Isolation of pigment cell specific genes in the sea urchin embryo by differential macroarray screening. Development 2003, 130, 4587–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xing, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Su, F.; Cui, W.; Jiang, C. Transcriptome analysis of purple and green Apostichopus japonicus reared under different breeding environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1334761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nocker, S.; Ludwig, P. The WD-repeat protein superfamily in Arabidopsis: Conservation and divergence in structure and function. BMC Genom. 2003, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cui, Y.; Yao, Y.; An, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Wu, K. Genome-wide identification of WD40 transcription factors and their regulation of the MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) complex related to anthocyanin synthesis in Qingke (Hordeum vulgare L. var. nudum Hook. f.). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kalinin, V.I. Cucumariosides F1 and F2, two new triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix and their LC-ESI MS/MS identification in the starfish Patiria pectinifera, a predator of the sea cucumber. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, N.; Goulter, K.C.; Wilson, K.J.; Hall, M.R.; Degnan, B.M. Esterified astaxanthin levels in lobster epithelia correlate with shell colour intensity: Potential role in crustacean shell colour formation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 141, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandaranayake, W.M.; Rocher, A.D. Role of secondary metabolites and pigments in the epidermal tissues, ripe ovaries, viscera, gut contents and diet of the sea cucumber Holothuria atra. Mar. Biol. 1999, 133, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeczuga, B. Some carotenoids in the jelly-fish Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa: Discomedusae). Mar. Biol. 1970, 5, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerpak, R.t.; Czeczuga, B. Studies of the pigments in the shrimp Crangon crangon (Crustacea: Malacostraca). Mar. Biol. 1969, 3, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreon, M.S.; Ceolín, M.; Heras, H. Astaxanthin binding and structural stability of the apple snail carotenoprotein ovorubin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 460, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, G.; Davies, S. Tissue astaxanthin and canthaxanthin distribution in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 143, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, J. Astaxanthin isomers: Selective distribution and isomerization in aquatic animals. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Che, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Hou, P. Research progress on digestion, absorption and health efficacy of astaxanthin ester. Food Mach. 2025, 40, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ingle de la Mora, G.; Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L.; Ponce-Palafox, J.T.; Barriga-Soca, I.d.A.; Vernon-Carter, J.E. Comparison of red chilli (Capsicum annuum) oleoresin and astaxanthin on rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss) fillet pigmentation. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville-Smith, R.; Cheng, Y.W.; Thomson, A.W. Factors affecting colour change in ‘white’western rock lobsters, Panulirus cygnus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 291, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, A.; Hu, C. The development of retinoic acid metabolism and common digestive tract tumors. Electron. J. Metab. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 5, 430–435. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sangeetha, R.K.; Bhaskar, N.; Baskaran, V. Comparative effects of beta-carotene and fucoxanthin on retinol deficiency induced oxidative stress in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 331, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, B.; Lei, X.; Li, A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Progress on physicochemical and biological properties, preparationtechniques and physiological activities of fucoxanthin. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2015, 34, 81–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Maoka, T. Recent progress in structural studies of carotenoids in animals and plants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, R.C.; Kelly, M.S.; Suckling, C.C.; Young, A.J. Carotenoids in the gonad and gut of the edible sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Román, L.; Rivero-Ramírez, F.; Caballero, M.J.; Pascual, C.; Robaina, L.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Acosta, F.; Montero, D. Supplementation of arachidonic acid rich oil in European sea bass juveniles (Dicentrarchus labrax) diets: Effects on leucocytes and plasma fatty acid profiles, selected immune parameters and circulating prostaglandins levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissio, P.G.; Darias, M.J.; Di Yorio, M.P.; Pérez Sirkin, D.I.; Delgadin, T.H. Fish skin pigmentation in aquaculture: The influence of rearing conditions and its neuroendocrine regulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 301, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, J.; Bell, G.; McEvoy, L.; Tocher, D.; Estevez, A. Recent developments in the essential fatty acid nutrition of fish. Aquaculture 1999, 177, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, I.; Steenfeldt, S.J.; Hansen, B.W. Influence of dietary arachidonic acid combined with light intensity and tank colour on pigmentation of common sole (Solea solea L.) larvae. Aquaculture 2010, 308, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene ID | Forward Primers (5′-3′) | Reverse Primers (3′-5′) |
|---|---|---|
| malrd1 | TCACGAGACCAGGTACAGATGTTC | GAAGGAAGGAAACCATACGCTCAG |
| FMO 2 | GACTGCCTCCCCGCTCTCC | TCGCAGCACGGTAGTATAACACATC |
| WDR18 | ACATAGCGGAGCGTCAATAGGTAC | TGAAGGTTGAGTGAGGTCAAGTTCC |
| ARP6 | TGTATAGCCTAAGCAACGAAGAGTC | CCGCACAGTACCTACAGTAATCAC |
| LDLR2 | CGCACAGAATACAGACAGGTTAATG | TTATCTCCTACCGCTCCTCTTCC |
| SLC23A2 | GCAGCGAATACTACGGAGGTTG | GTCCCGATGAGTCCAGTGAAAC |
| Higd-1a | CATGCTGGCACACTTGTATTGAG | CTATTACGACTACGAGGCTCTTGG |
| NLRC4 | AGGGCGATTAAGTGTTTCTTCTCTC | GACGGACGAGCAACTACGAATG |
| FALDH | CTCCGCTCGCCATACATACATTC | CATTAAGACCCTCTCCCGCATAAAC |
| SYTL6 | TTAGGCAAGTGGTGATGGTGAAC | GTGAGCAGACAACTGTGATGAATG |
| CYTB | TGACAGGACCGCTACGAAAGAGG | AAAGTTTTCTTGGGGCCGGAAGG |
| Groups | Weight (g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 15 d | 30 d | 45 d | |
| R | 0.175 ± 0.03 | 0.247 ± 0.04 | 0.343 ± 0.05 | 0.78 ± 0.06 ab |
| W | 0.173 ± 0.02 | 0.201 ± 0.07 | 0.251 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.04 b |
| Groups | body length (cm) | |||
| R | 1.550 ± 0.11 | 1.723 ± 0.14 | 2.524 ± 0.15 a | 3.152 ± 0.11 a |
| W | 1.521 ± 0.10 | 1.604 ± 0.13 | 1.963 ± 0.23 b | 2.848 ± 0.17 b |
| Serial Number | Sample Name | Astaxanthin (mg/kg) | Lutein(mg/kg) | Canaxanthin (mg/kg) | β-Carotene (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R | 2.111 ab | 0.447 a | 0.554 a | 2.379 ab |
| 2 | W | 0.217 b | 0.057 b | 0.038 b | 0.066 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Hao, P.; Xiao, H.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Molecular Mechanism of Body Color Change in the Ecological Seedling Breeding Model of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology 2025, 14, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070873
Han L, Hao P, Xiao H, Li W, Fan Y, Tian W, Tian Y, Wang L, Chang Y, Ding J. Molecular Mechanism of Body Color Change in the Ecological Seedling Breeding Model of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology. 2025; 14(7):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070873
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lingshu, Pengfei Hao, Haoran Xiao, Weiyan Li, Yichen Fan, Wanrong Tian, Ye Tian, Luo Wang, Yaqing Chang, and Jun Ding. 2025. "Molecular Mechanism of Body Color Change in the Ecological Seedling Breeding Model of Apostichopus japonicus" Biology 14, no. 7: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070873
APA StyleHan, L., Hao, P., Xiao, H., Li, W., Fan, Y., Tian, W., Tian, Y., Wang, L., Chang, Y., & Ding, J. (2025). Molecular Mechanism of Body Color Change in the Ecological Seedling Breeding Model of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology, 14(7), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070873







