Seasonal Dynamics of Algal Communities and Key Environmental Drivers in the Subpolar Front Zone off Eastern Korea
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Marine Environment
2.3. Algal Community Structure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
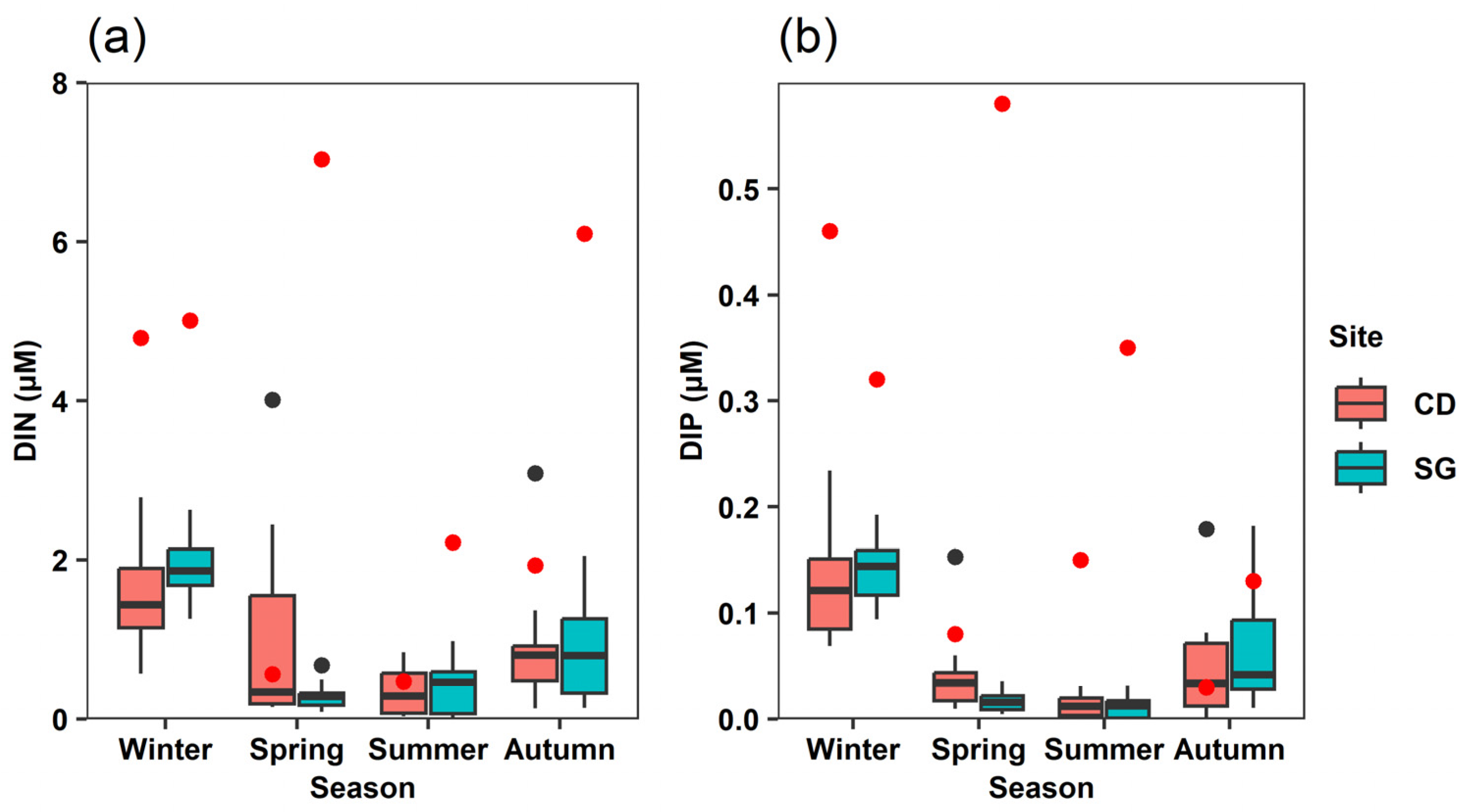
3.1. Seasonal Changes in Environmental Factors
3.2. Seasonal Changes in Biomass of Algal Communities
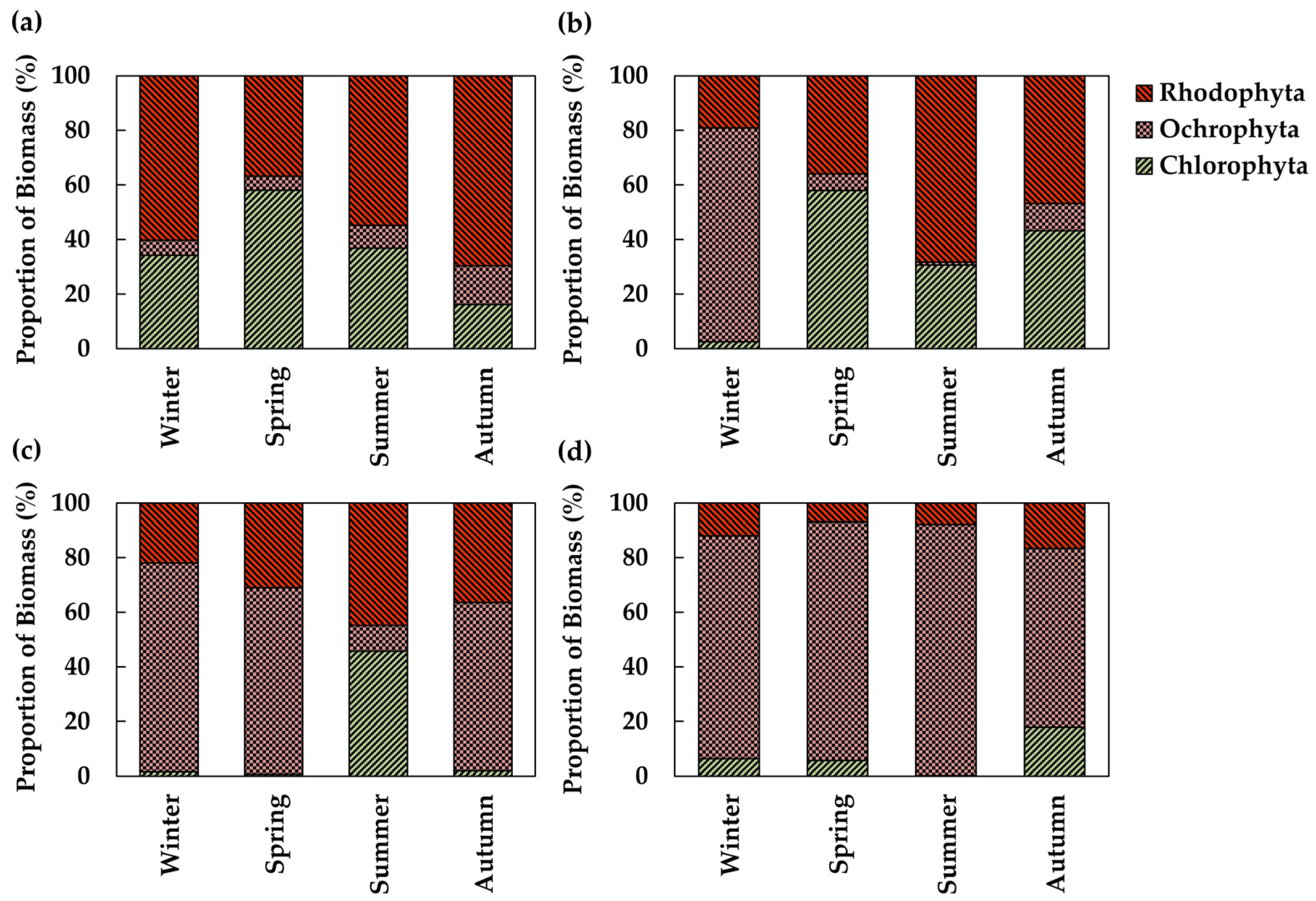
3.3. Taxonomic Composition of Algal Communities
3.4. Functional Group Composition of Algal Communities
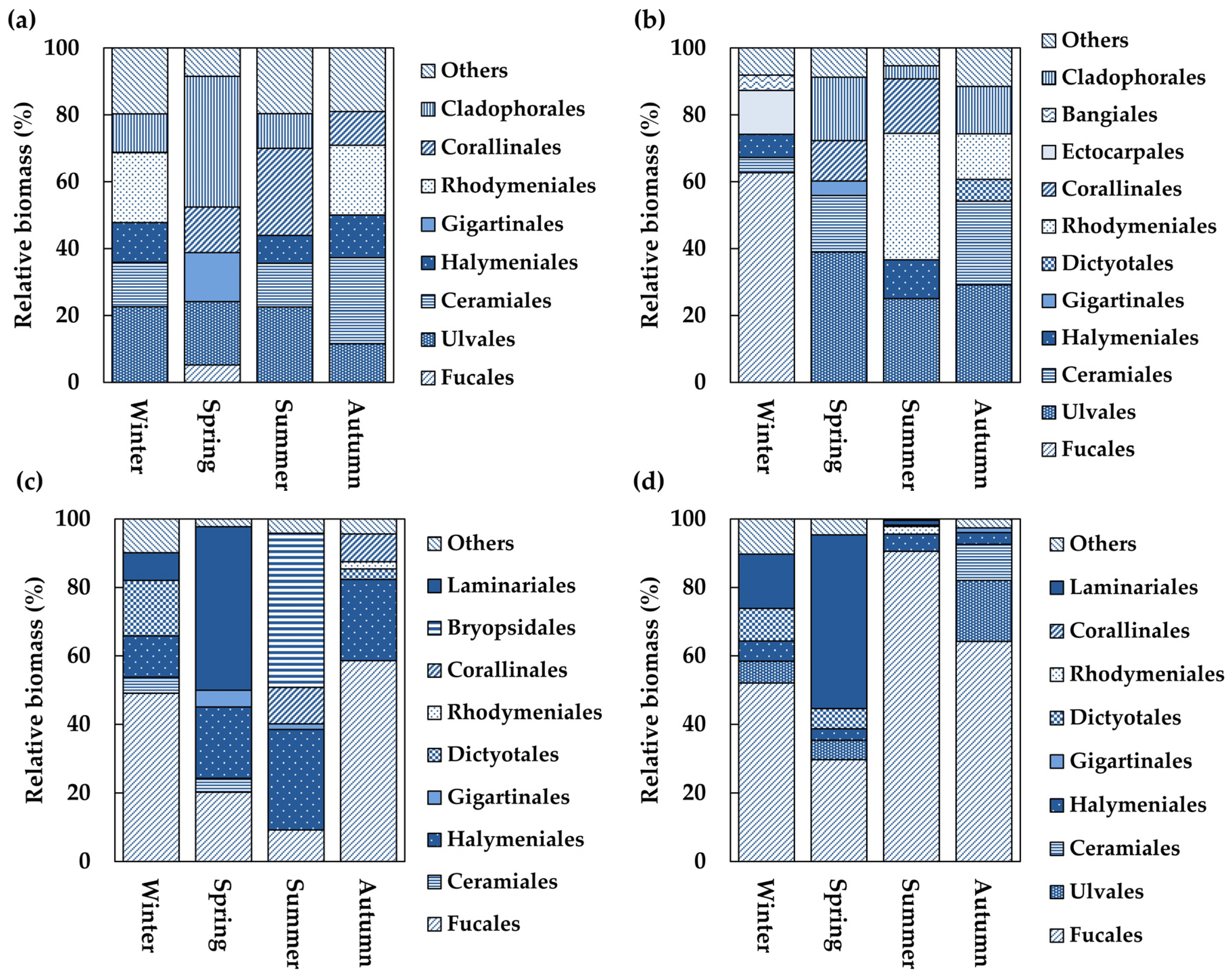
3.5. Order-Level Group Composition of Algal Communities
3.6. Seasonal Changes of Ecological Indices
3.7. Key Environmental Factors Influencing Algal Community Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPF | Subpolar front |
| SST | Sea surface temperature |
| ESG | Ecological status group |
| EEI-c | Ecological evaluation index |
| EQR | Ecological quality ratio |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PC | Principal component |
| DIN | Dissolved inorganic nitrogen |
| DIP | Dissolved inorganic phosphate |
| CD | Chodo |
| SG | Sageunjin |
| ECK | Eastern coast of Korea |
| KMA | Korea Meteorological Administration |
| KOEM | Korea Marine Environment Management |
References
- Lindstrom, S.C. The biogeography of seaweeds in Southeast Alaska. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.; Wesley, S.G. Diversity and distribution of seaweeds in the Kudankulam coastal waters, south-eastern coast of India. Biodivers. J. 2012, 3, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wernberg, T.; Filbee-Dexter, K. Missing the Marine Forest for the Trees. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 612, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.; Panayotidis, P.; Stamatis, N. An Insight to the Ecological Evaluation Index (EEI). Ecol. Indic. 2003, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.; Panayotidis, P.; Ugland, K.I. Ecological Evaluation Index Continuous Formula (EEI-c) Application: A Step Forward for Functional Groups, the Formula and Reference Condition Values. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2011, 12, 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernberg, T.; de Bettignies, T.; Joy, B.A.; Finnegan, P.M. Physiological Responses of Habitat-Forming Seaweeds to Increasing Temperatures. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, C.L. Water Motion, Marine Macroalgal Physiology, and Production. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpinen, S.; Jormalainen, V.; Honkanen, T. Effects of Nutrients, Herbivory, and Depth on the Macroalgal Community in the Rocky Sublittoral. Ecology 2007, 88, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burel, T.; Schaal, G.; Grall, J.; Le Duff, M.; Chapalain, G.; Schmitt, B.; Gemin, M.; Boucher, O.; Ar Gall, E. Small-Scale Effects of Hydrodynamics on the Structure of Intertidal Macroalgal Communities: A Novel Approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burel, T.; Grall, J.; Schaal, G.; Le Duff, M.; Ar Gall, E. Wave Height vs. Elevation Effect on Macroalgal Dominated Shores: An Intercommunity Study. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; Sand-Jensen, K. Salt Tolerance and Distribution of Estuarine Benthic Macroalgae in the Kattegat-Baltic Sea Area. Phycologia 2006, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Ito, Y.; Suenaga, Y. Construction of Climate Change-Adapted Seaweed Beds on the Japanese Coast. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hoek, C. World-Wide Latitudinal and Longitudinal Seaweed Distribution Patterns and Their Possible Causes, as Illustrated by the Distribution of Rhodophytan Genera. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1984, 38, 227–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeman, A.M. Relative Importance of Temperature and Other Factors in Determining Geographic Boundaries of Seaweeds: Experimental and Phenological Evidence. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1988, 42, 199–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüning, K. Environmental and Internal Control of Seasonal Growth in Seaweeds. Hydrobiologia 1993, 260–261, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerswell, A.P. Global Biodiversity Patterns of Benthic Marine Algae. Ecology 2006, 87, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.J. The Biogeography of Kelps (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae): A Global Analysis with New Insights from Recent Advances in Molecular Phylogenetics. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2010, 64, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkopoulou, E.; Serrão, E.A.; De Clerck, O.; Costello, M.J.; Araújo, M.B.; Duarte, C.M.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Assis, J. Global Biodiversity Patterns of Marine Forests of Brown Macroalgae. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeckis, R. A Survey of Worldwide Sea Surface Temperature Fronts Detected by Environmental Satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1978, 83, 4501–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, O.K. Spring Season Flow of the Tsushima Current and Its Separation from the Kuroshio: Satellite Evidence. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 9687–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokov, Y.N.; Kochergin, I.E.; Danchenkov, M.A.; Borozdinova, E.S.; Aubrey, D.G.; Belan, T.A.; Hong, G.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Karasev, E.V.; Kim, K.; et al. Executive Secretary “Pacific Oceanography Volume 1, Number 2” Registered with the Russian Ministry of Mass Media; Far Eastern Regional Hydrometeorological Research Institute (FERHRI): Vladivostok, Russia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.A.; Chung, J.Y.; Kim, K. Sea Surface Temperature Fronts in the East (Japan) Sea and Temporal Variations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.A.; Ullman, D.S.; Kim, K.; Yul Chung, J.; Kim, K.R. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Satellite-Observed Subpolar Front in the East/Japan Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.J.; Haidvogel, D.B.; Cho, Y.K. Interannual Variation of the Polar Front in the Japan/East Sea from Summertime Hydrography and Sea Level Data. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.J.; Depczynski, M.; Holmes, T.H.; Noble, M.M.; Radford, B.; Wernberg, T.; Wilson, S.K. Sea Temperature Shapes Seasonal Fluctuations in Seaweed Biomass within the Ningaloo Coral Reef Ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.D.G.; Anderson, K.M.; Demes, K.W.; Jorve, J.P.; Kordas, R.L.; Coyle, T.A.; Graham, M.H. EFfects of Climate Change on Global Seaweed Communities. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Wernberg, T. Rise of Turfs: A New Battlefront for Globally Declining Kelp Forests. Bioscience 2018, 68, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.K.; Boo, G.H.; Graf, L.; Yarish, C.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, J.K. Kelps in Korea: From Population Structure to Aquaculture to Potential Carbon Sequestration. Algae 2022, 37, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, C.H.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, H.G. Algal communities and useful seaweed distribution at Gangnung and it’s vicinity in east coast of Korea. Algae 2007, 22, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater and Analysis; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.-S.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-S. A Study on the Characteristics of Summer Water Temperature Fluctuations by Spectral Analysis in Coast of Korea in 2016. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2020, 26, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, C.J.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, G.H.; Klochkova, T.A. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 1, No. 1, Marine Green Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Boo, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Hwang, I.K.; Keum, Y.S.; Oak, J.H.; Cho, G.Y. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 2, No. 2, Marine Brown Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 6, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 8, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Boo, S.M. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 2, No. 1, Marine Brown Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Hwang, I.K. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 10, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, I.G. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 5, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, G.W. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 3, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, G.W.; Kang, P.J. Algal Flora of Korea. Vol. 4, No. 11, Marine Red Algae; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, M.A.; Gordon, D.P.; Orrell, T.M.; Bailly, N.; Bourgoin, T.; Brusca, R.C.; Cavalier-Smith, T.; Guiry, M.D.; Kirk, P.M. A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, F.; Sánchez, I.; Hawkins, S.J.; Jenkins, S.R. The Invasibility of Marine Algal Assemblages: Role of Functional Diversity and Identity. Ecology 2006, 87, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.J.; Reed, D.C.; Brzezinski, M.A. Community Structure and Productivity of Subtidal Turf and Foliose Algal Assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 388, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, S.D.; Foster, M.S.; Airoldi, L. What Are Algal Turfs? Towards a Better Description of Turfs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.; Dencheva, K.; Nakou, K.; Tsioli, S.; Papathanasiou, V.; Rosati, I. Benthic Macrophyte Metrics as Bioindicators of Water Quality: Towards Overcoming Typological Boundaries and Methodological Tradition in Mediterranean and Black Seas. Hydrobiologia 2014, 740, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, E.; Wilkinson, M.; Wood, P.; Scanlan, C. The Use of Macroalgal Species Richness and Composition on Intertidal Rocky Seashores in the Assessment of Ecological Quality under the European Water Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, A.Q.; Reis, R.P. Brazilian Macroalgae Assemblages Analyzed Using the Ecological Evaluation Index (EEI-c). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 182, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, F.M.; Neto, A.I.; Patarra, R.F.; Prestes, A.C.L.; Álvaro, N.V.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Wilkinson, M. Indices to Monitor Coastal Ecological Quality of Rocky Shores Based on Seaweed Communities: Simplification for Wide Geographical Use. Rev. Gestão Costeira Integr. 2013, 13, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information Theory in Ecology; Real Academia de Ciencias y Artes de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 1973; pp. 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. In CRAN: Contributed Packages; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj, S.; Case, B.S.; White, W.L. Effects of Location and Season on Seaweed Spectral Signatures. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 581852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, C.; Hofstra, N.; Ivens, W.; Löhr, A.; Strokal, M.; van Wijnen, J. The Links between Global Carbon, Water and Nutrient Cycles in an Urbanizing World—The Case of Coastal Eutrophication. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, T.C.; Newton, A. The Globalization of Cultural Eutrophication in the Coastal Ocean: Causes and Consequences. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, K.T.; Lim, J.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Kim, I.N. Hypoxia in Korean Coastal Waters: A Case Study of the Natural Jinhae Bay and Artificial Shihwa Bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.A.; Imberger, J. Modeling the Impact of Natural and Anthropogenic Nutrient Sources on Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Shallow Coastal Domain, Western Australia. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2014, 14, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.-Y.; Shim, J.H.; Shim, J.-M. Temporal Variations of Sea Water Environment and Nutrients in the East Coast of Korea in 2013~2017: Sokcho, Jukbyeon and Gampo Coastal Areas. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2019, 25, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, G.; Kwon, H.K.; Han, I.S. Long-Term Changes in the Concentrations of Nutrients in the Marginal Seas (Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and East/Japan Sea) Neighboring the Korean Peninsula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Kurashima, A.; Maegawa, M. Temperature Requirements for the Growth and Maturation of the Gametophytes of Undaria Pinnatifida and U. Undarioides (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae). Phycol. Res. 2003, 51, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Kurashima, A.; Maegawa, M. Temperature Requirements for the Growth of Young Sporophytes of Undaria Pinnatifida and Undaria Undarioides (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae). Phycol. Res. 2003, 51, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Bulleri, F.; Acunto, S.; Cinelli, F. Scales of variation in the effects of limpets on rocky shores in the northwest Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 209, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisak, M.D. MARINE BIOLOGY Nitrogen Limitation of Codium Fragile Ssp. Tomentosoides as Determined by Tissue Analysis. Mar. Biol. 1979, 50, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, J.H. NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On a Technique for Measurement of Turbulent Shear Stress in the Presence of Surface Waves. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 15, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.; Dubois, S.; Erga, Z.; Guillemain, D.; de Ville d’Avray, L.T.; Arvanitidis, C.; Cinar, M.; Sartoretto, S.; Zuberer, F.; Chenuil, A.; et al. CIGESMED’s protocol and network (Coralligenous based Indicators to evaluate and monitor the “Good Environmental Status” of Mediterranean coastal waters). In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium Monitoring of Mediterranean Coastal Areas: Problems and Measurement Techniques, Livorno, Italy, 17–19 June 2014; pp. 828–843. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, C.; Gall, E.A.; Levavasseur, G.; Deslandes, E. Effects of Short-Term Variations of Salinity and Temperature on the Photosynthetic Response of the Red Alga Grateloupia Doryphora from Brittany (France); Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Harlin, M.M.; Villalard-Bohnsack, M. Seasonal Dynamics and Recruitment Strategies of the Invasive Seaweed Grateloupia Doryphora (Halymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in Narragansett Bay and Rhode Island Sound, Rhode Island, USA. Phycologia 2001, 40, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalard-Bohnsack, M.; Harlin, M.M. The Appearance of Grateloupia Doryphora (Halymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) on the Northeast Coast of North America. Phycologia 1997, 36, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárbara, I.; Cremades, J. “Grateloupia lanceola” versus “Grateloupia turuturu”(Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) en la Península Ibérica. An. Jard. Bot. Madr. 2004, 61, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, G.W.; Withall, R.D. Collections of the Invasive Species Grateloupia Turuturu (Halymeniales, Rhodophyta) from Tasmania, Australia. Phycologia 2006, 45, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Archino, R.; Nelson, W.A.; Zuccarello, G.C. Invasive Marine Red Alga Introduced to New Zealand Waters: First Record of Grateloupia Turuturu (Halymeniaceae, Rhodophyta). N. Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2007, 41, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentinus, I. Comparisons of Nutrient Uptake Rates for Baltic Macroalgae with Different Thallus Morphologies. Mar. Biol. 1984, 80, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita’ Boston, R.M. The role of nitrogen status in regulating transient ammonium uptake and nitrogen storage by macroalgae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 92, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wre, E.; De, E. The Phenology of Three Species of Sargassum (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta) in Hawaii. Phycologia 1976, 15, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccourt, R.M. Seasonal Palterns of Abundance, Distributions, and Phenology in Relation to Growth Strategies of Three Sargassum Species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 14, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonbeck, M.; Norton, T.A. Factors Controlling the Upper Limits of Fucoid Algae on The Shore. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1978, 31, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connan, S.; Goulard, F.; Stiger, V.; Deslandes, E.; Gall, E.A. Interspecific and Temporal Variation in Phlorotannin Levels in an Assemblage of Brown Algae. Bot. Mar. 2004, 47, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, E.A.; Le Duff, M. Development of a Quality Index to Evaluate the Structure of Macroalgal Communities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 139, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Endo, H.; Agatsuma, Y. Combined Effects of Seawater Temperature and Nutrient Condition on Growth and Survival of Juvenile Sporophytes of the Kelp Undaria Pinnatifida (Laminariales; Phaeophyta) Cultivated in Northern Honshu, Japan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.H.; Dunstan, W.M. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science 1971, 171, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobban, C.S.; Harrison, P.J. Seaweed Ecology and Physiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; ISBN 0521408970. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, M.J.; Smith, S.V. C:N:P Ratios of Benthic Marine Plants. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M. Nutrient Concentration of Aquatic Plants: Patterns across Species. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Functional Group | Thallus Size | Growth Form |
|---|---|---|
| Canopy species | >1 m | Erect |
| Subcanopy species | 0.05–1 m | Erect |
| Turf species | <5 cm | Erect or prostrate |
| Encrusting species | Not erect | Covering the substratum |
| Site | Season | Richness | Diversity | EEI-c (0–10) 1 | EQR (0–1) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intertidal zone | SG | Winter | 19 | 2.03 | 1.76 | 0.53 |
| Spring | 15 | 1.85 | 3.84 | 0.18 | ||
| Summer | 11 | 1.57 | 4.27 | 0.36 | ||
| Autumn | 30 | 2.73 | 2.95 | 0.81 | ||
| CD | Winter | 23 | 2.16 | 7.99 | 0.76 | |
| Spring | 18 | 1.93 | 2.23 | 0.49 | ||
| Summer | 15 | 1.81 | 2.12 | 0.55 | ||
| Autumn | 21 | 2.12 | 1.59 | 0.59 | ||
| Subtidal zone | SG | Winter | 30 | 2.69 | 7.61 | 0.80 |
| Spring | 24 | 2.20 | 8.53 | 0.72 | ||
| Summer | 18 | 1.99 | 2.34 | 0.75 | ||
| Autumn | 28 | 2.29 | 7.47 | 0.88 | ||
| CD | Winter | 26 | 2.25 | 6.62 | 0.76 | |
| Spring | 26 | 2.26 | 8.92 | 0.76 | ||
| Summer | 14 | 1.74 | 10.00 | 0.55 | ||
| Autumn | 23 | 2.20 | 6.50 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.I.; Rho, H.S.; Park, J.M.; Kim, B.-S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, C.I. Seasonal Dynamics of Algal Communities and Key Environmental Drivers in the Subpolar Front Zone off Eastern Korea. Biology 2025, 14, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070738
Han PI, Rho HS, Park JM, Kim B-S, Park JW, Kim D, Lee DY, Lee CI. Seasonal Dynamics of Algal Communities and Key Environmental Drivers in the Subpolar Front Zone off Eastern Korea. Biology. 2025; 14(7):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Pyo Il, Hyun Soo Rho, Joo Myun Park, Beom-Sik Kim, Jong Won Park, Dongyoung Kim, Dong Young Lee, and Chung Il Lee. 2025. "Seasonal Dynamics of Algal Communities and Key Environmental Drivers in the Subpolar Front Zone off Eastern Korea" Biology 14, no. 7: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070738
APA StyleHan, P. I., Rho, H. S., Park, J. M., Kim, B.-S., Park, J. W., Kim, D., Lee, D. Y., & Lee, C. I. (2025). Seasonal Dynamics of Algal Communities and Key Environmental Drivers in the Subpolar Front Zone off Eastern Korea. Biology, 14(7), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070738










