Effect of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Pancreatic Islet Development
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of Diabetes and Mating Schedule
2.3. Tissue Collection and Histological Analyses
2.4. Quantification and Assessment of Fetal Islet Size
2.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Fetal Pancreatic Tissue
2.6. Evaluation of Pdx1 and Pax4 Expression by RT-qPCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
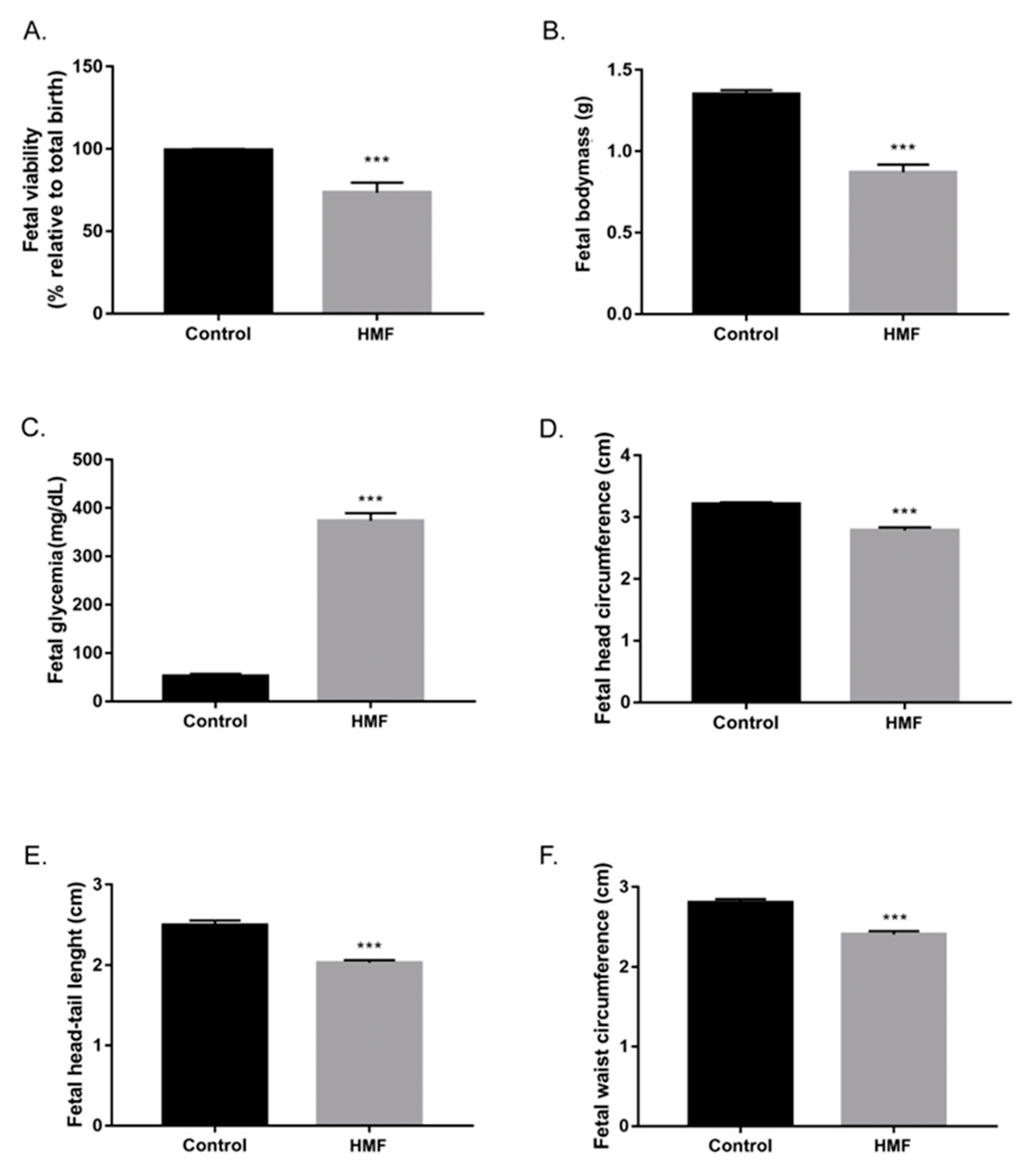
3.1. Maternal Hyperglycemia Induces Fetal Hyperglycemia and Decreases the Number of Viable Fetuses
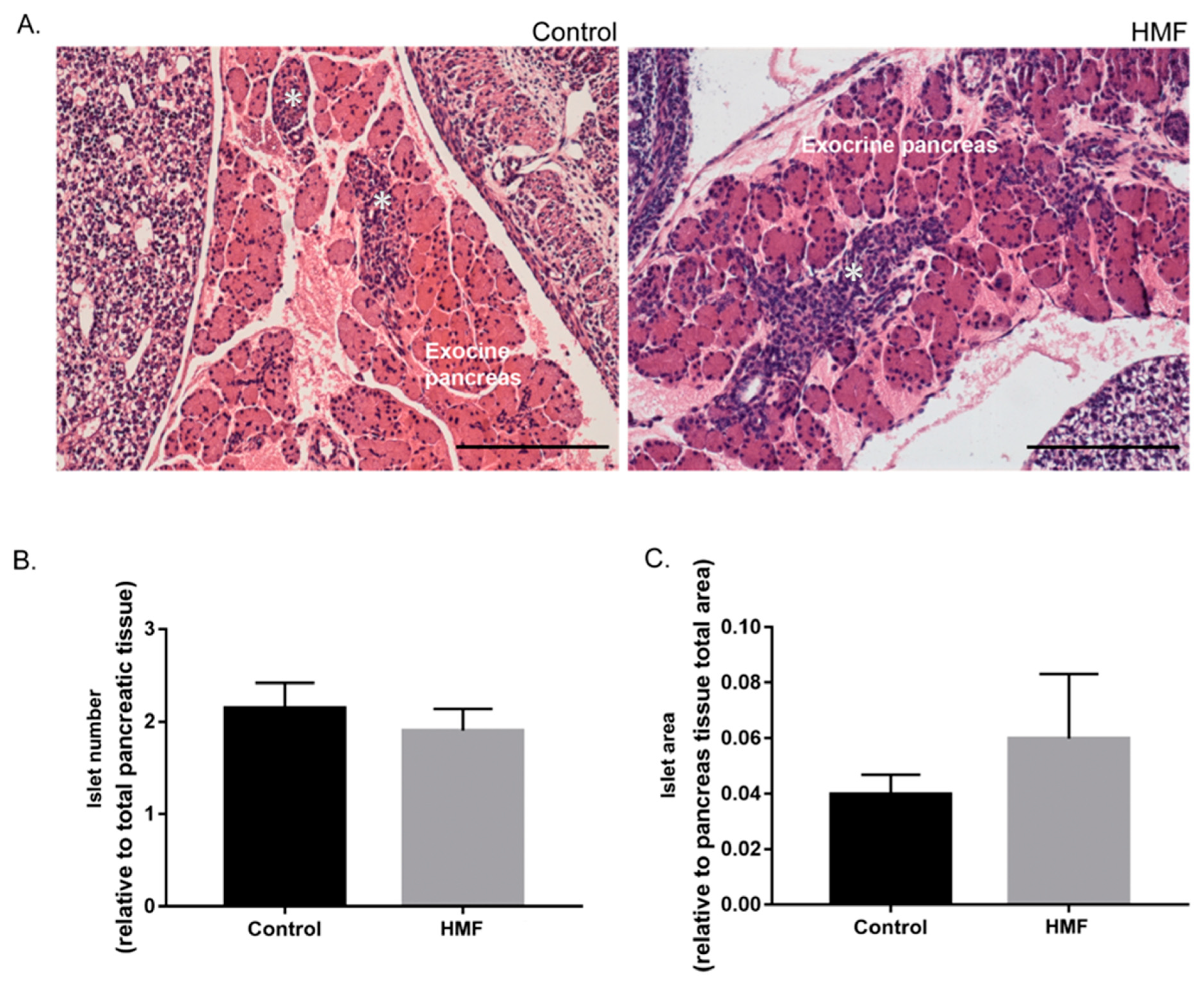
3.2. Maternal Hyperglycemia Promotes Modification in Size and Morphology of Fetal Pancreatic Islets
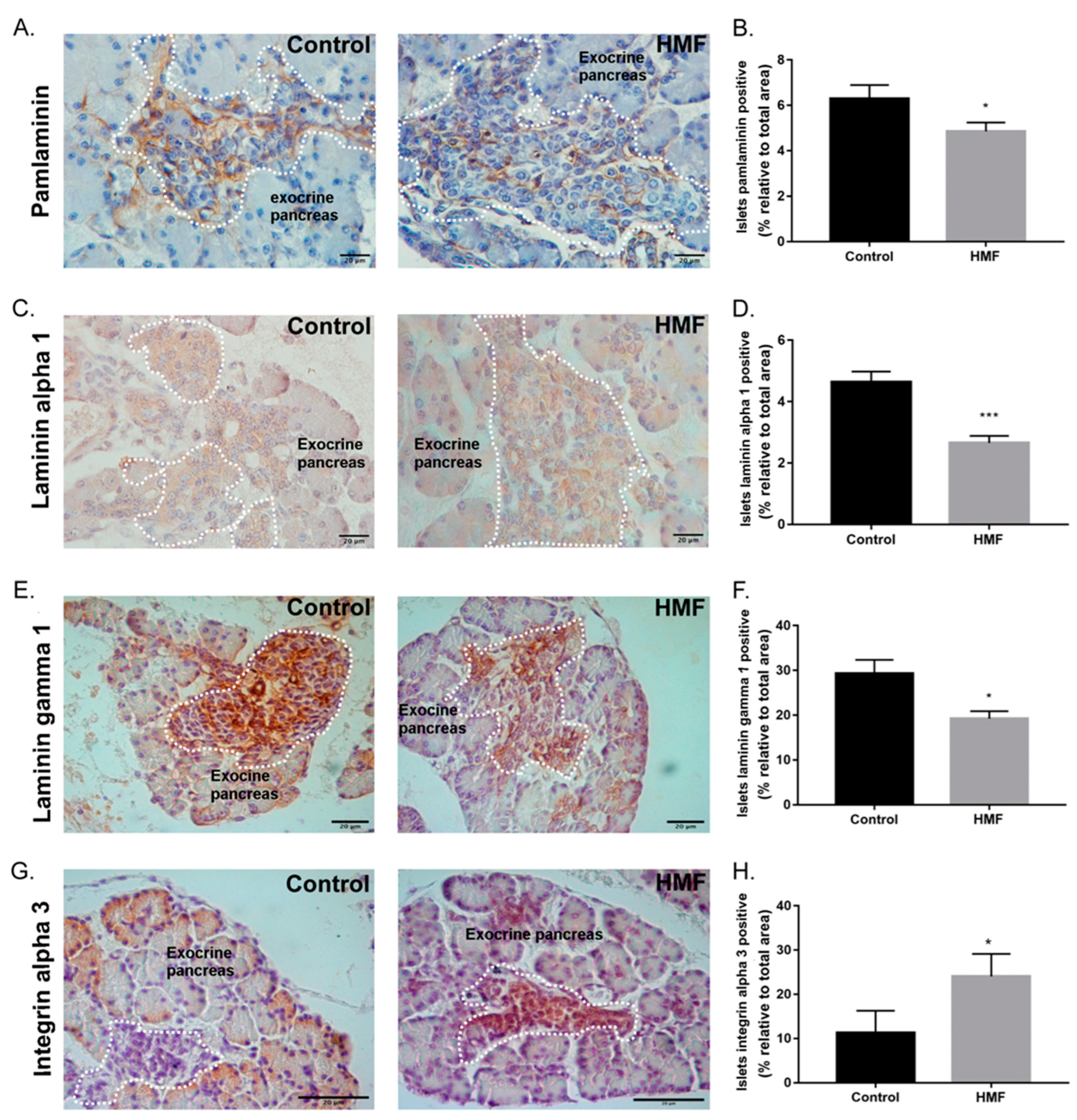
3.3. Maternal Hyperglycemia Decreases Pan-Laminin, Laminin Alpha 1 and Gamma 1 Chains and Increases Alpha 3 Integrin Deposition in the Fetal Pancreas
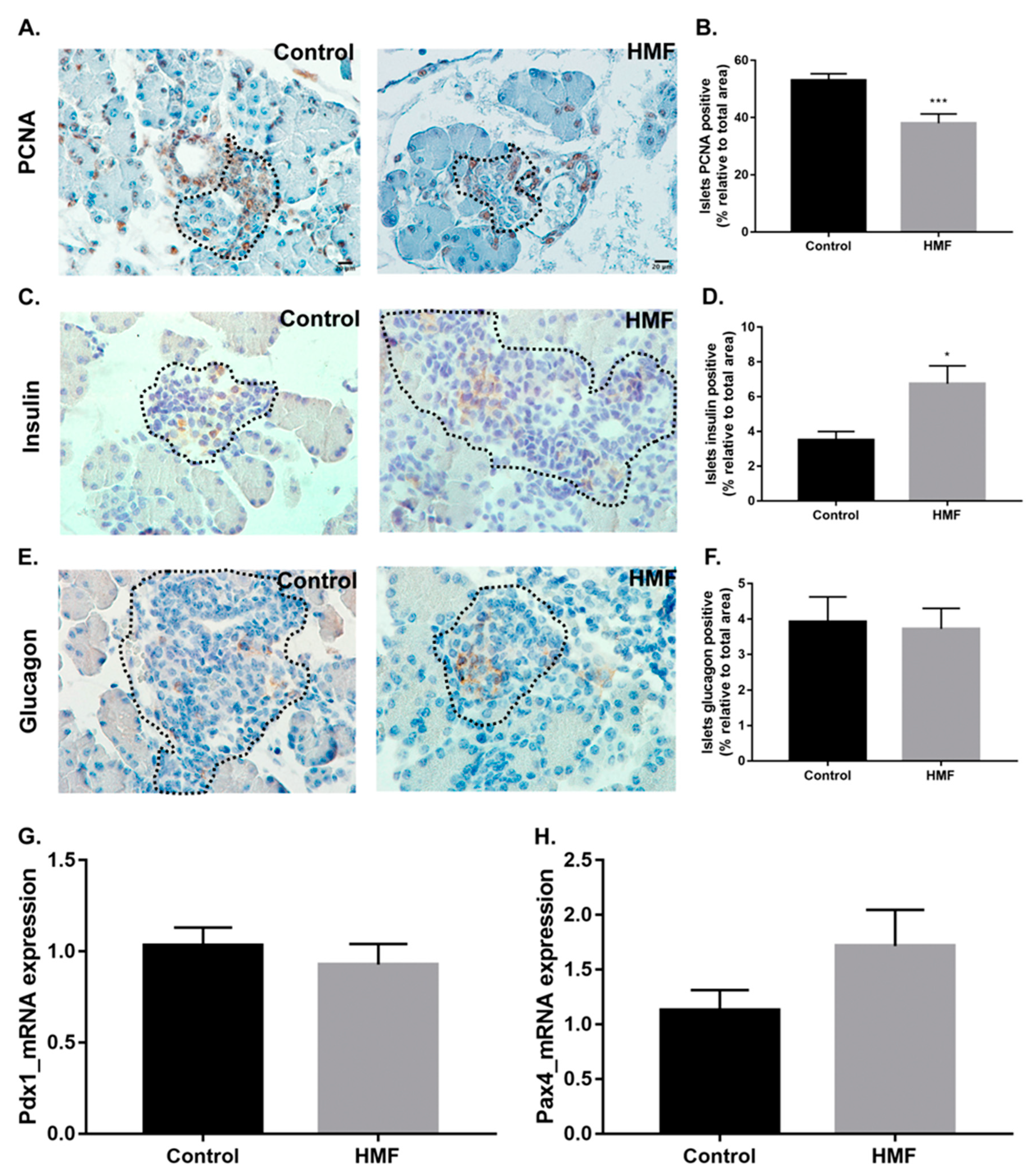
3.4. Maternal Hyperglycemia Affects the Proliferation of Fetal Pancreas Endocrine Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aerts, L.; Van Assche, F. Rat fetal endocrine pancreas in experimental diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 1977, 73, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervran, A.; Guillaume, M.; Jost, A. The endocrine pancreas of the fetus from diabetic pregnant rat. Diabetologia 1978, 15, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Chenier, I.; Tran, S.; Scotcher, M.; Chang, S.-Y.; Zhang, S.-L. Maternal diabetes programs hypertension and kidney injury in offspring. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, L.; Vercruysse, L.; Van Assche, F.A. The endocrine pancreas in virgin and pregnant offspring of diabetic pregnant rats. Diabetes Res. Clin. Practic. 1997, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J.P. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: The thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 42, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freinkel, N. Banting Lecture 1980: Of pregnancy and progeny. Diabetes 1980, 29, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauguier, D.; Bihoreau, M.-T.; Ktorza, A.; Berthault, M.-F.; Picon, L. Inheritance of diabetes mellitus as consequence of gestational hyperglycemia in rats. Diabetes 1990, 39, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holemans, K.; Aerts, L.; Van Assche, F.A. Evidence for an insulin resistance in the adult offspring of pregnant streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 1991, 34, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holemans, K.; Aerts, L.; Assche, F.A. Lifetime consequences of abnormal fetal pancreatic development. J. Physiol. 2003, 547, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, M. The history of insulin. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnop, M.; Welsh, N.; Jonas, J.-C.; Jörns, A.; Lenzen, S.; Eizirik, D.L. Mechanisms of pancreatic β-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 2005, 54, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhalima, K.; Devlieger, R.; Van Assché, A. Screening and management of gestational diabetes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 29, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaight, C.; Gross, J.; Horsch, A.; Puder, J.J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 31, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.; Gelardi, N.L.; Cha, C.-J. Maternal hyperglycemia in pregnant rats: Its effect on growth and carbohydrate metabolism in the offspring. Metabolism 1988, 37, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, I.F.; Clarke, C.A.; Howard, C.V.; McKendrick, O.; Pennycook, S.; Pharoah, P.O.; Platt, M.J.; Stanisstreet, M.; Van Velszen, D.; Walkinshaw, S. Outcomes of pregnancy in insulin dependent diabetic women: Results of a five year population cohort study. Br. Med. J. 1997, 315, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemicstry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, J.C.; Gautam, D.; Burks, D.J.; Gillette, J.; Schubert, M.; Orban, P.C.; Klein, R.; Krone, W.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Kahn, C.R. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Science 2000, 289, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhseed, M.; Musini, V.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Al-Harmi, J. Placental pathology in relation to the White’s classification of diabetes mellitus. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2002, 266, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M.; Aiello, L.P.; Cooper, M.E.; Vinik, A.I.; Nesto, R.W.; Boulton, A.J.M. Complications of diabetes mellitus. In Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 13a ed.; Melmed, S., Polonsky, K.S., Larsen, P.R., Kronenberg, H.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1484–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, M.; Cerami, A. The Pathobiology of Diabetic Complications: A Unifying Mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcakus, M.; Koklu, E.; Baykan, A.; Yikilmaz, A.; Coskun, A.; Gunes, T.; Kurtoglu, S.; Narin, N. Macrosomic newborns of diabetic mothers are associated with increased aortic intima-media thickness and lipid concentrations. Horm. Res. 2007, 67, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, L.J.; McCloskey, K.; Vuillermin, P.J.; Burgner, D.; Said, J.; Ponsonby, A.-L. Cardiovascular Disease Risk in the Offspring of Diabetic Women The Impact of the Intrauterine Environment. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 565160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.M.; Wahab, N.A. Extracellular Matrix Metabolism in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 14, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia-Santos, A.M.; Vicente, G.C.; Suzuki, A.; Pereira, A.D.; dos Anjos, J.S.; Lenzi-Almeida, K.C.; Boaventura, G.T. Maternal use of flaxseed oil during pregnancy and lactation prevents morphological alterations in pancreas of female offspring from rat dams with experimental diabetes. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 96, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.P.; Wang, A.; Sander, M. Pancreas Organogenesis: From Lineage Determination to Morphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, G.M.; Rubin, J.S.; Mally, M.I.; Otonkoski, T.; Hayek, A. Regulation of proliferation and differentiation of human fetal pancreatic islet cells by extracellular matrix, hepatocyte growth factor, and cell-cell contact. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.X.; Cram, D.S.; DeAizpurua, H.J.; Harrison, L.C. Laminin-1 promotes differentiation of fetal mouse pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes 1996, 48, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, M.; Li, J.; Fellows, G.F.; Rosenberg, L.; Goodyer, C.G.; Wang, R. Integrin α3, but not β1, regulates islet cell survival and function via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, R.R.; Salgado, R.M.; Raspantini, P.R.; Fortes, Z.B.; Zorn, T.M.T. Effects of long-term diabetes on the structure and cell proliferation of the myometrium in the early pregnancy of mice. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 91, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, R.; Salgado, R.; Covarrubias, A.; Bruni, F.; Lima, C.; Fortes, Z.; Zorn, T. Long-term type 1 diabetes impairs decidualization and extracellular matrix remodeling during early embryonic development in mice. Placenta 2013, 34, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, J.C.; Favaro, R.R.; Barrence, F.C.; Bevilacqua, E.; Fortes, Z.B.; Zorn, T.M. Distinct effects of short- and long-term type 1 diabetes to the placental extracellular matrix and fetal development in mice. Placenta 2017, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.G.; Noh, H.L.; Lee, S.K.; Chung, Y.S.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.M. Insulin and glucagon secretions, and morphological change of pancreatic islets in OLETF rats, a model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2002, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, D.; Armanet, M.; Morel, P.; Niclauss, N.; Sgroi, A.; Muller, Y.D.; Giovannoni, L.; Parnaud, G.; Berney, T. Unique arrangement of α- and β-cells in human islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pictet, R.L.; Clark, W.R.; Williams, R.H.; Rutter, W.J. An ultrastructural analysis of the developing embryonic pancreas. Dev. Biol. 1972, 29, 436–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.C.; Wright, C. Pancreas organogenesis From bud to plexus to gland. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 530–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Hebrok, M. Intercellular signals regulating pancreas development and function. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, J.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L.; Tabrizian, M. The effect of extracellular matrix components on the preservation of human islet function in vitro. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldager, K.R.D.; Karsdal, M.A. Chapter 29 Laminins. Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin: Structure, Function and Biomarkers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 163–196. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, K.D.; Barritt, L.; Miner, J.H.; Cosgrove, D. The laminins in the murine inner ear: Developmental transitions and expression in cochlear basement membranes. Hear. Res. 2001, 158, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarsio, J.F.; Reger, L.A.; Furcht, L.T. Molecular mechanisms in basement membrane complications of diabetes. Alterations in heparin, laminin, and type IV collagen association. Diabetes 1988, 37, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charonis, A.S.; Reger, L.A.; Dege, J.E.; Kouzi-Koliakos, K.; Furcht, L.T.; Wohlhueter, R.M.; Tsilibary, E.C. Laminin alterations after in vitro nonenzymatic glycosylation. Diabetes 1990, 39, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arous, C.; Wehrle-Haller, B. Role and impact of the extracellular matrix on integrin-mediated pancreatic β-cell functions. Biol. Cell 2017, 109, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iype, T.; Francis, J.; Garmey, J.C.; Schisler, J.C.; Nesher, R.; Weir, G.C.; Becker, T.C.; Newgard, C.B.; Griffen, S.C.; Mirmira, R.G. Mechanism of insulin Gene Regulation by the Pancreatic Transcription Factor Pdx-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16798–16807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; McKenna, B.; Li, C.; Reichert, M.; Nguyen, J.; Singh, T.; Yang, C.; Pannikar, A.; Doliba, N.; Zhang, T.; et al. Pdx1 maintains β cell identity and function by repressing an α cell program. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.B.; Ee, H.C.; Conners, J.R.; German, M.S. Paired-Homeodomain Transcription Factor PAX4 Acts as a Transcriptional Repressor in Early Pancreatic Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 19, 8272–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, T.; He, K.H.H.; Lupi, R.; Boehm, B.; Wojtusciszyn, A.; Sauter, N.; Donath, M.; Marchetti, P.; Maedler, K.; Gauthier, B.R. The diabetes-linked transcription factor Pax4 is expressed in human pancreatic islets and is activated by mitogens and GLP-1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, C.P.; Teixeira Paiva de Moraes, M.R.; Correia Barrence, F.A.; Balbino da Silva, C.S.; Smuckzec, B.; Ortis, F.; Zorn, T.M.T. Effect of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Pancreatic Islet Development. Biology 2025, 14, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060728
Dias CP, Teixeira Paiva de Moraes MR, Correia Barrence FA, Balbino da Silva CS, Smuckzec B, Ortis F, Zorn TMT. Effect of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Pancreatic Islet Development. Biology. 2025; 14(6):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060728
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Carina Pereira, Michel Raony Teixeira Paiva de Moraes, Fernanda Angela Correia Barrence, Camila Stephanie Balbino da Silva, Basilio Smuckzec, Fernanda Ortis, and Telma Maria Tenório Zorn. 2025. "Effect of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Pancreatic Islet Development" Biology 14, no. 6: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060728
APA StyleDias, C. P., Teixeira Paiva de Moraes, M. R., Correia Barrence, F. A., Balbino da Silva, C. S., Smuckzec, B., Ortis, F., & Zorn, T. M. T. (2025). Effect of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Pancreatic Islet Development. Biology, 14(6), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060728







