Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Regional and Temporal Dynamics of Gene Expression in the Mouse Brain Across Development and Aging
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Model
2.2. FFPE Tissue Block Preparation
2.3. FFPE Visium Spatial Transcriptomics Library Preparation
2.4. Analysis of FFPE Visium Spatial Transcriptomics Data
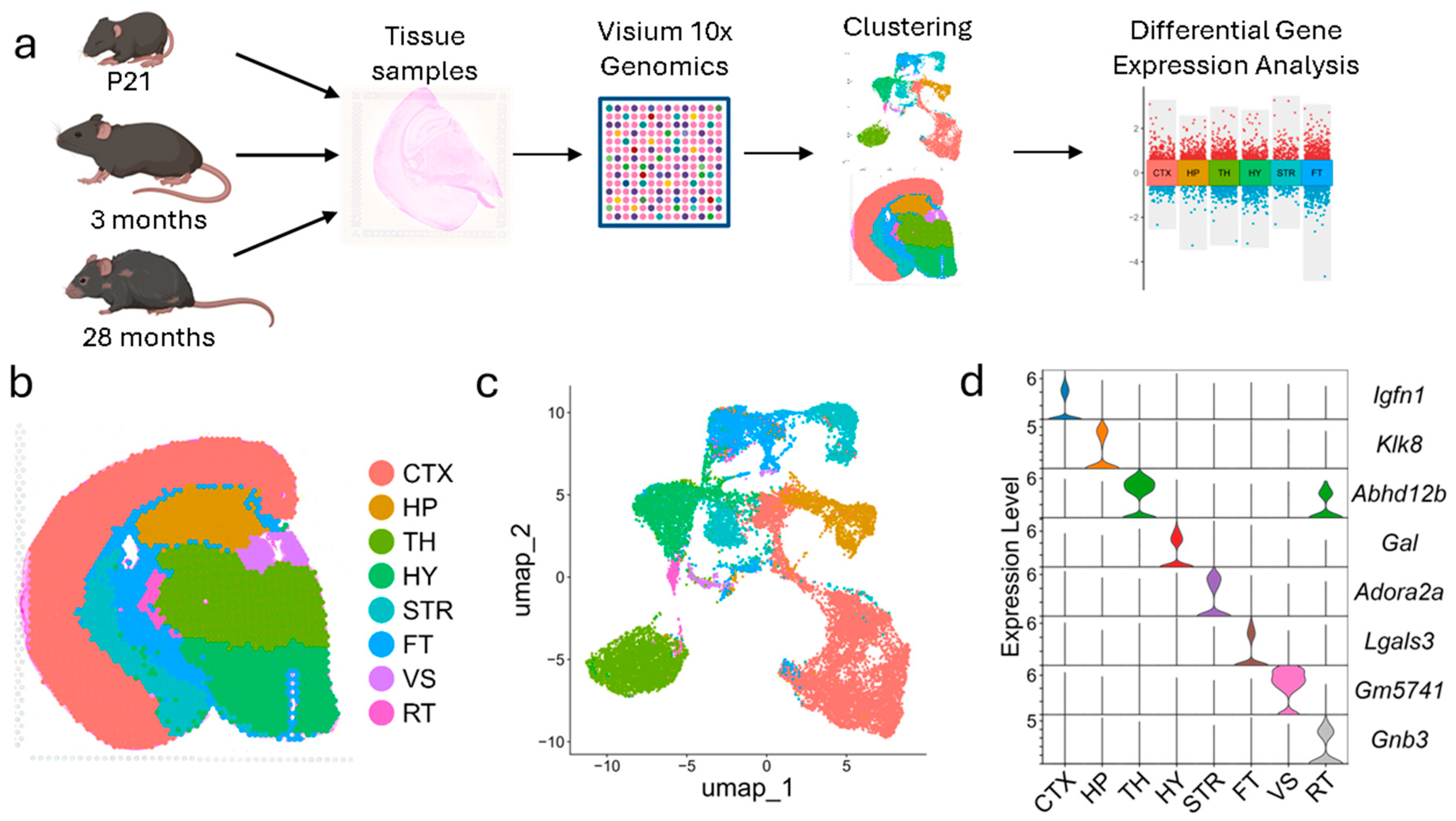
3. Results
3.1. FFPE Visium Spatial Transcriptomics Recaptures the Major Brain Regions
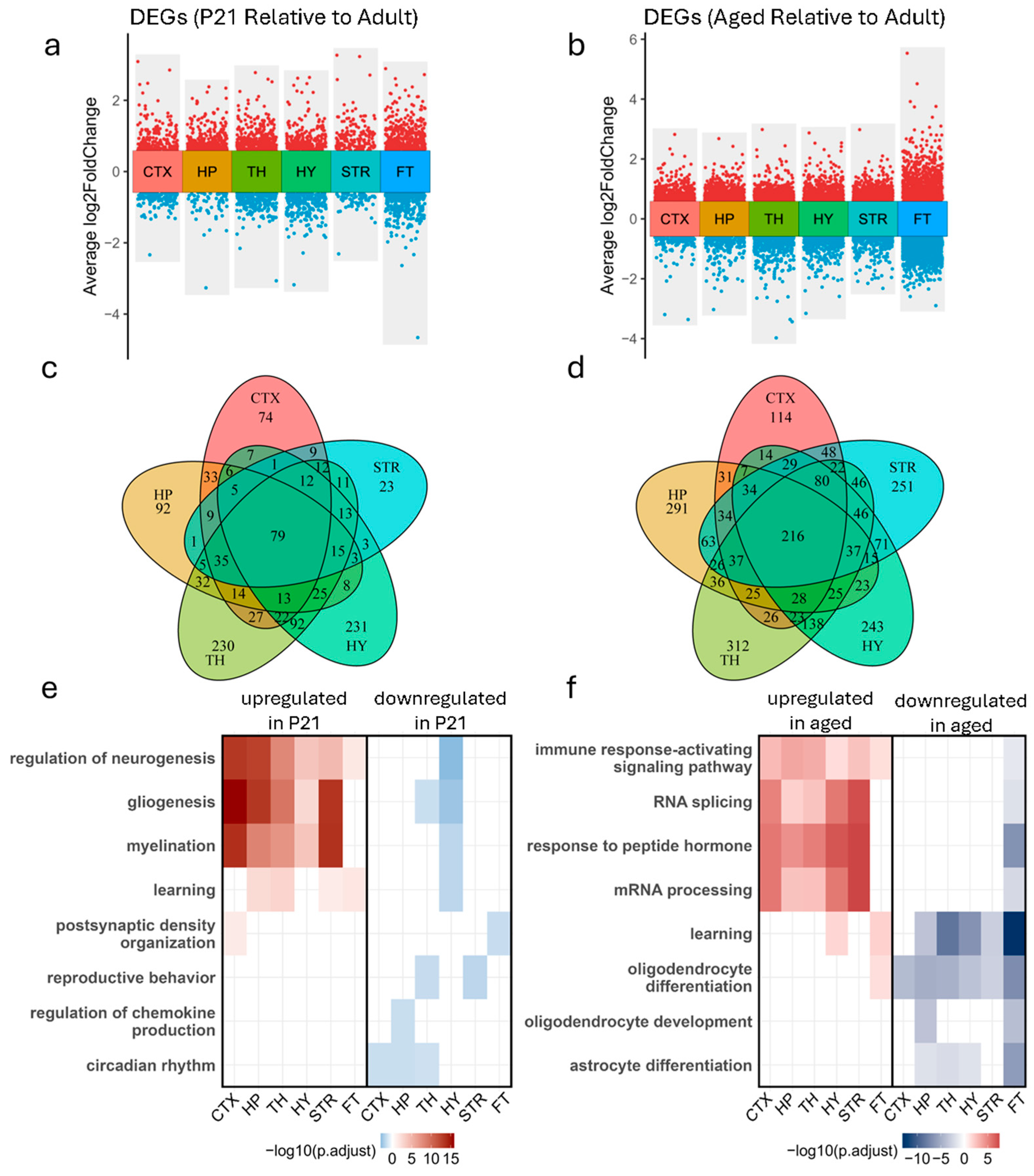
3.2. Brain Region-Specific Gene Expression Changes Across Developmental Stages
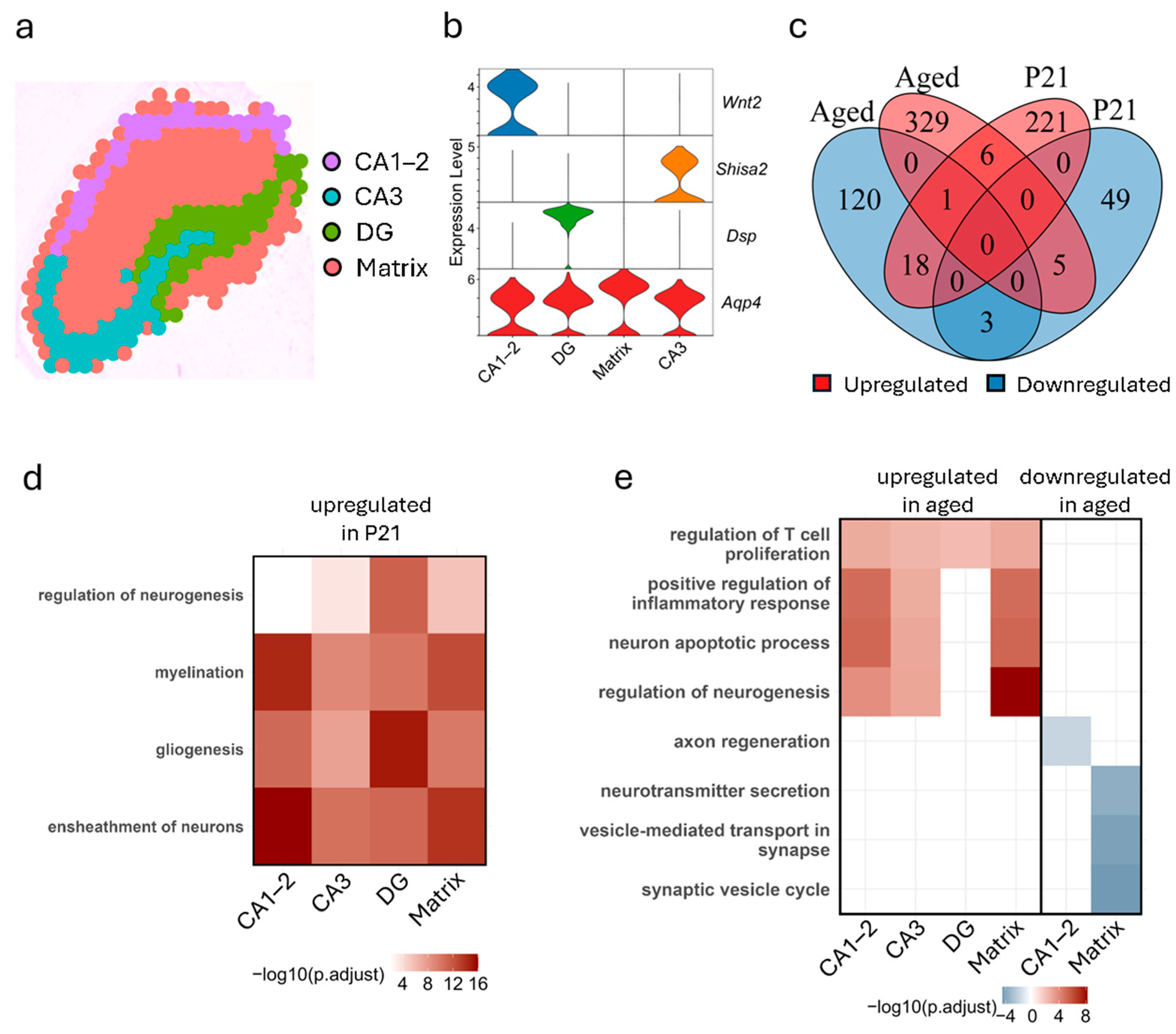
3.3. Hippocampus Exhibits Subregion-Specific Transcriptomic Changes Across Development and Aging
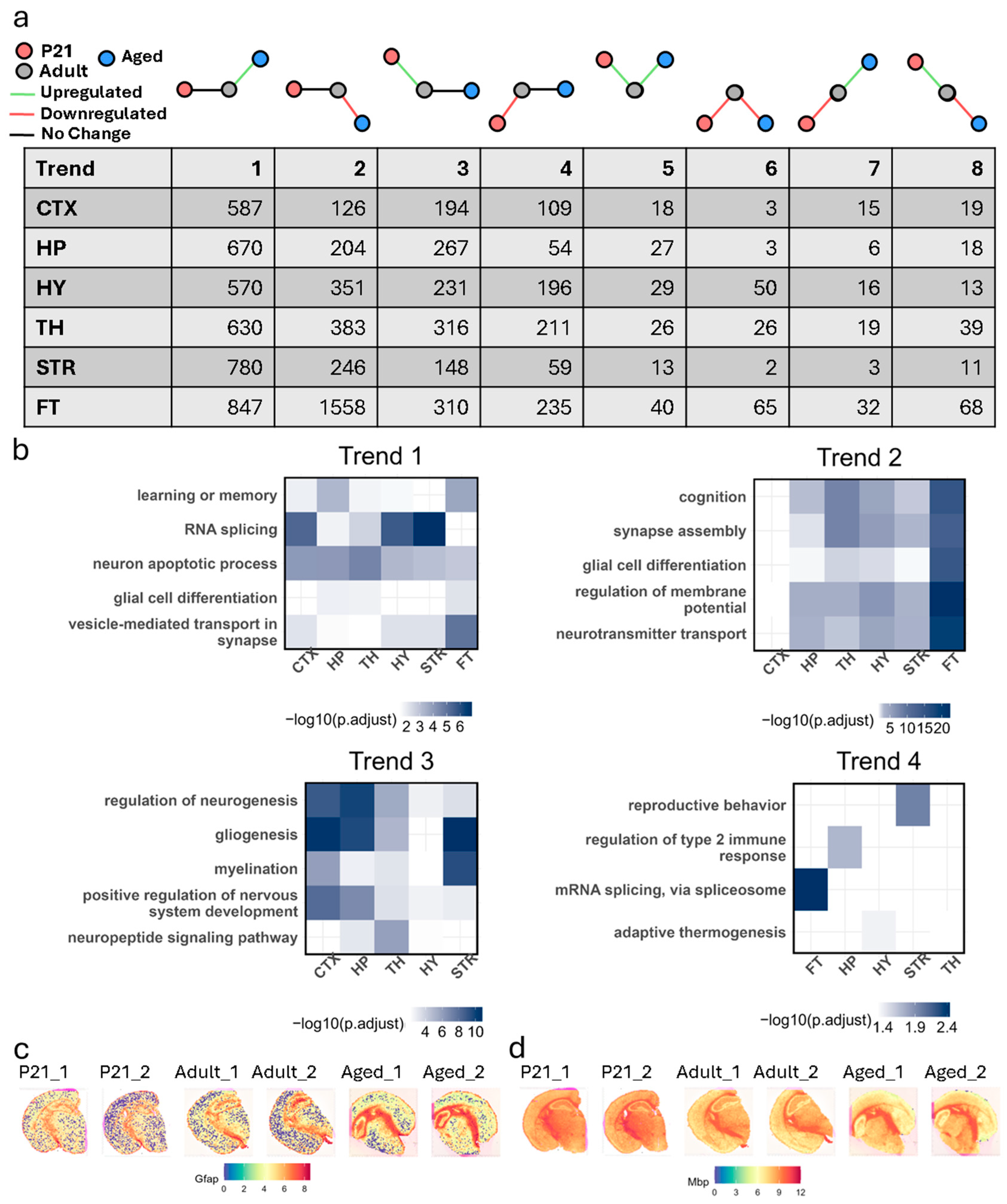
3.4. Differential Gene Expression Trends Across Life Stages
3.4.1. Trend 1: Upregulated in Only Aged Samples
3.4.2. Trend 2: Downregulated in Only Aged Samples
3.4.3. Trend 3: Upregulated in Only P21 Samples
3.4.4. Trend 4: Downregulated in Only P21 Samples
3.4.5. Trend 5: Upregulated in Both Comparisons (Up/Up)
3.4.6. Trend 6: Downregulated in Both Comparisons (Down/Down)
3.4.7. Trend 7: Downregulated in P21 but Upregulated in Aged Samples (Down/Up)
3.4.8. Trend 8: Upregulated in P21 but Downregulated in Aged Samples (Up/Down)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulis, K.; Tabury, K.; Benotmane, M.A.; Polanska, J. Transcriptomic Profile of Mouse Brain Ageing in Early Developmental Stages. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, S.; Toda, T. Epigenetic aging in adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2023, 33, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensch, T.K. Critical period plasticity in local cortical circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milbocker, K.A.; Campbell, T.S.; Collins, N.; Kim, S.; Smith, I.F.; Roth, T.L.; Klintsova, A.Y. Glia-Driven Brain Circuit Refinement Is Altered by Early-Life Adversity: Behavioral Outcomes. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 786234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakafuku, M.; Del Aguila, A. Developmental dynamics of neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the postnatal mammalian brain in health and disease: Historical and future perspectives. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2020, 9, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sale, A.; Berardi, N.; Maffei, L. Environment and brain plasticity: Towards an endogenous pharmacotherapy. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 189–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, H.S.; Wang, X.; Dumont, A.S.; Liu, Q. Cellular senescence, DNA damage, and neuroinflammation in the aging brain. Trends Neurosci. 2024, 47, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T.V. Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Adaptive and Pathological Modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Avila, J.C.; Siqueira, L.D.; Mazeraud, A.; Azevedo, E.P.; Foguel, D.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Sharshar, T.; Chretien, F.; Bozza, F.A. Age-related cognitive impairment is associated with long-term neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in a mouse model of episodic systemic inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Schurman, S.H.; Bektas, A.; Kaileh, M.; Roy, R.; Wilson, D.M., 3rd; Sen, R.; Ferrucci, L. Aging and Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2024, 14, a041197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.M.; Berg, D.A.; Lee, S.; Garcia-Epelboim, A.S.; Adusumilli, V.S.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Differential Timing and Coordination of Neurogenesis and Astrogenesis in Developing Mouse Hippocampal Subregions. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, J.O.; Rezaie, P.; Gabbott, P.L.; Stewart, M.G. Impact of age-related neuroglial cell responses on hippocampal deterioration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geigenmuller, J.N.; Tari, A.R.; Wisloff, U.; Walker, T.L. The relationship between adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 7369–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, L.E.; Hartley, J.; Showmaker, K.C.; Challagundla, L.; Vandewege, M.W.; Martin, B.E.; Blair, E.; Bollavarapu, R.; Antonyraj, R.B.; Hilton, K.; et al. Molecular profiling of the hippocampus of children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1968–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S. Whole brain alignment of spatial transcriptomics between humans and mice with BrainAlign. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.Y.; Tian, L.; Su, J.H.; Radovan, M.T.; Tourdias, T.; Tran, T.T.; Trelle, A.N.; Mormino, E.; Wagner, A.D.; Rutt, B.K. Thalamic nuclei atrophy at high and heterogenous rates during cognitively unimpaired human aging. Neuroimage 2022, 262, 119584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, P.L.; Salmen, F.; Vickovic, S.; Lundmark, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Magnusson, J.; Giacomello, S.; Asp, M.; Westholm, J.O.; Huss, M.; et al. Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science 2016, 353, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.D.; Zhou, O.Y.; Hauptschein, M.; Rappoport, N.; Xu, L.; Navarro Negredo, P.; Liu, L.; Rando, T.A.; Zou, J.; Brunet, A. Spatial transcriptomic clocks reveal cell proximity effects in brain ageing. Nature 2025, 638, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tu, T.; Xie, M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Z. Spatially resolved transcriptome of the aging mouse brain. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Stuart, T.; Kowalski, M.H.; Choudhary, S.; Hoffman, P.; Hartman, A.; Srivastava, A.; Molla, G.; Madad, S.; Fernandez-Granda, C.; et al. Dictionary learning for integrative, multimodal and scalable single-cell analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K. cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions, R package version 2.1.8.1; 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cluster/index.html (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Lee, G.Y.; Ham, S.; Sohn, J.; Kwon, H.C.; Lee, S.V. Meta-analysis of the transcriptome identifies aberrant RNA processing as common feature of aging in multiple species. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.H.; Kluever, V.; Barth, E.; Krautwurst, S.; Furlan, M.; Pelizzola, M.; Marz, M.; Fornasiero, E.F. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis reveals altered mRNA splicing and post-transcriptional changes in the aged mouse brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 2865–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Jimenez, E.P.; Flor-Garcia, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rabano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Avila, J.; Llorens-Martin, M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nyul-Toth, A.; DelFavero, J.; Balasubramanian, P.; Tarantini, S.; Faakye, J.; Gulej, R.; Ahire, C.; Ungvari, A.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; et al. Spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals inflammatory foci defined by senescent cells in the white matter, hippocampi and cortical grey matter in the aged mouse brain. Geroscience 2022, 44, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Navarro, J.F.; Jurek, A.; Martin, A.; Lundeberg, J.; Meletis, K. Molecular atlas of the adult mouse brain. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Xiao, M. A Review of the Application of Spatial Transcriptomics in Neuroscience. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2024, 16, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, O.; Foltz, A.G.; Atkins, M.; Kedir, B.; Moran-Losada, P.; Guldner, I.H.; Munson, C.; Kern, F.; Palovics, R.; Lu, N.; et al. Atlas of the aging mouse brain reveals white matter as vulnerable foci. Cell 2023, 186, 4117–4133 e4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.E.; Blosser, T.R.; Sullivan, Z.A.; Dulac, C.; Zhuang, X. Molecular and spatial signatures of mouse brain aging at single-cell resolution. Cell 2023, 186, 194–208 e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.A.; Wever, D.D.; McNamara, N.B.; Bourik, M.; Smolders, J.; Hamann, J.; Huitinga, I. Inflammatory microglia correlate with impaired oligodendrocyte maturation in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1522381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivellini, C.; Porrello, E.; Dina, G.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Vezzoli, A.; Bacigaluppi, M.; Gullotta, G.S.; Chaabane, L.; Leocani, L.; Marenna, S.; et al. JAB1 deletion in oligodendrocytes causes senescence-induced inflammation and neurodegeneration in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e145071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A.; Amit, I. The Physiology, Pathology, and Potential Therapeutic Applications of the TREM2 Signaling Pathway. Cell 2020, 181, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zveik, O.; Rechtman, A.; Ganz, T.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A. The interplay of inflammation and remyelination: Rethinking MS treatment with a focus on oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.M.A.; Watson, A.E.S.; Bibi, S.; Dittmann, N.L.; Goodkey, K.; Sharafodinzadeh, P.; Galleguillos, D.; Nakhaei-Nejad, M.; Kosaraju, J.; Steinberg, N.; et al. Fractalkine enhances oligodendrocyte regeneration and remyelination in a demyelination mouse model. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 18, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conacher, B.; Moore, A.; Yin, L.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Mao, Q.; Xie, H. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Regional and Temporal Dynamics of Gene Expression in the Mouse Brain Across Development and Aging. Biology 2025, 14, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060717
Conacher B, Moore A, Yin L, Lin Y, Xu X, Mao Q, Xie H. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Regional and Temporal Dynamics of Gene Expression in the Mouse Brain Across Development and Aging. Biology. 2025; 14(6):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060717
Chicago/Turabian StyleConacher, Benjamin, Amanda Moore, Liduo Yin, Yu Lin, Xiguang Xu, Qinwen Mao, and Hehuang Xie. 2025. "Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Regional and Temporal Dynamics of Gene Expression in the Mouse Brain Across Development and Aging" Biology 14, no. 6: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060717
APA StyleConacher, B., Moore, A., Yin, L., Lin, Y., Xu, X., Mao, Q., & Xie, H. (2025). Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Regional and Temporal Dynamics of Gene Expression in the Mouse Brain Across Development and Aging. Biology, 14(6), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060717





