AgileMultiIdeogram: Rapid Identification and Visualization of Autozygous Regions Using Illumina Short-Read Sequencing Data
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data
2.2. Exome Sequencing and Variant Detection
2.3. Identification of Autozygous Regions with Exome Data Using PLINK, H3M2, SavvyHomozygosity, SavvyVCFHomozygosity, AUDACITY, AutozygosityMapper and AutoMAP
2.4. Microarray SNP Genotype Data Production
3. Results
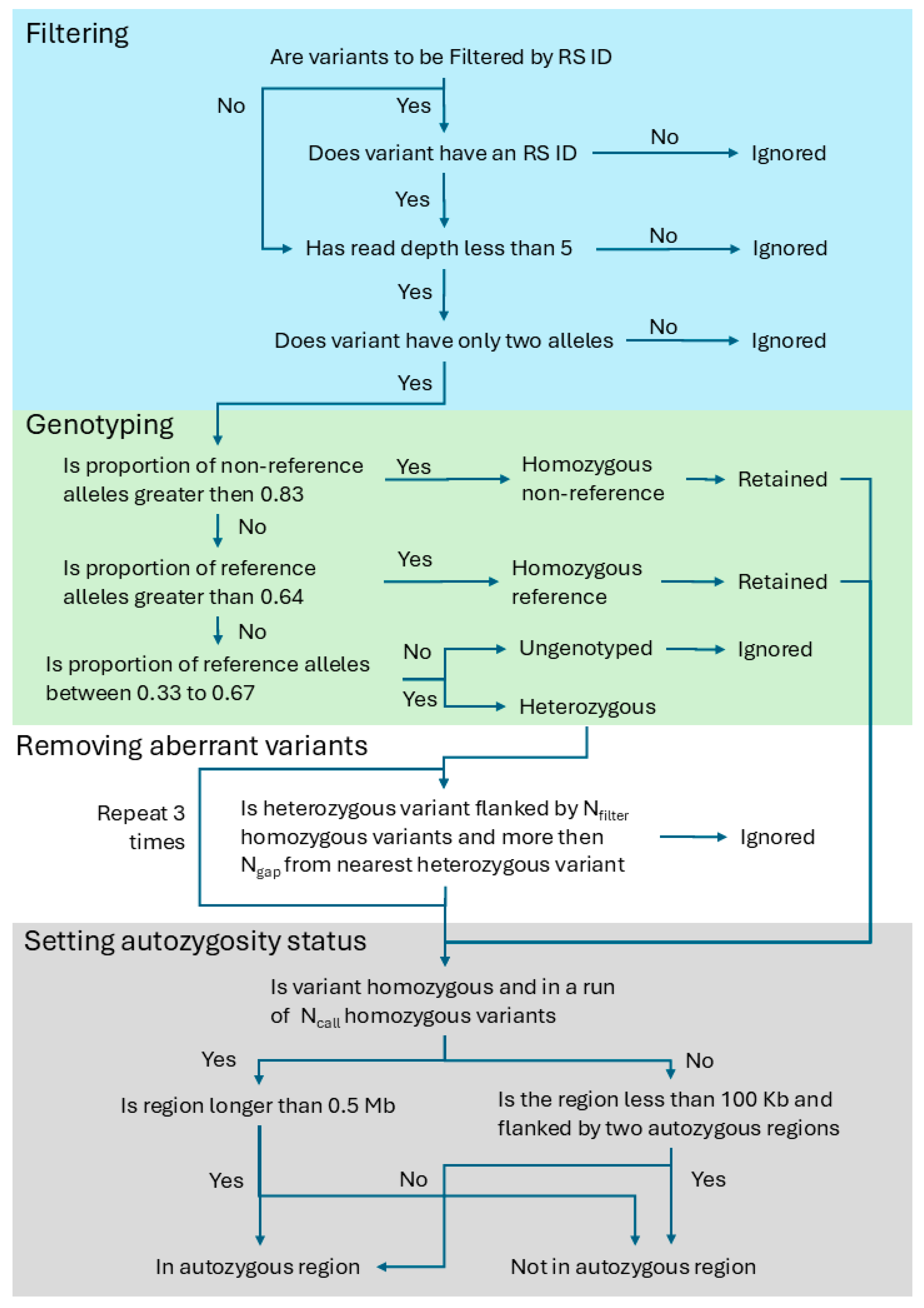
3.1. The Algorithm to Detect Autozygous Regions
3.2. Parameter Optimization by Simulated Evolution
3.3. Comparison of AgileMultiIdeogram, H3M2, AutoMAP, PLINK, AutozygosityMapper, SavvyHomozygosity and SavvyVCFHomozygosity
3.4. Implementation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
References
- Forman, J.; Taruscio, D.; Llera, V.A.; Barrera, L.A.; Coté, T.R.; Edfjäll, C.; Gavhed, D.; Haffner, M.E.; Nishimura, Y.; Posada, M.; et al. The need for worldwide policy and action plans for rare diseases. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKusick, V.A. Mendelian Inheritance in Man and its online version, OMIM. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Botstein, D. Homozygosity mapping: A way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science 1987, 236, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, C.G.; Cox, J.; Springell, K.; Hampshire, D.J.; Mohamed, M.D.; McKibbin, M.; Stern, R.; Raymond, F.L.; Sandford, R.; Sharif, S.M.; et al. Quantification of homozygosity in consanguineous individuals with autosomal recessive disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, I.M.; Bhaskar, S.; O’Sullivan, J.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; Shamseldin, H.E.; Markham, A.F.; Bonthron, D.T.; Black, G.; Alkuraya, F.S. Autozygosity mapping with exome sequence data. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, A.; Tattini, L.; Palombo, F.; Benelli, M.; Gialluisi, A.; Giusti, B.; Abbate, R.; Seri, M.; Gensini, G.F.; Romeo, G.; et al. H3M2: Detection of runs of homozygosity from whole-exome sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2852–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A toolset for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinodoz, M.; Peter, V.G.; Bedoni, N.; Bertrand, B.R.; Cisarova, K.; Salmaninejad, A.; Sepahi, N.; Rodrigues, R.; Piran, M.; Mojarrad, M.; et al. AutoMap is a high performance homozygosity mapping tool using next-generation sequencing data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, A.; Giangregorio, T.; Semeraro, R.; Carangelo, G.; Palombo, F.; Romeo, G.; Seri, M.; Pippuccid, T. AUDACITY: A comprehensive approach for the detection and classification of Runs of Homozygosity in medical and population genomics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeling, M.N. SavvySuite. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/rdemolgen/SavvySuite (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Steinhaus, R.; Boschann, F.; Vogel, M.; Fischer-Zirnsak, B.; Seelow, D. AutozygosityMapper: Identification of disease-mutations in consanguineous families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W83–W89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Min Kang, H.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Gabor, M.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The Variant Call Format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, S.; Lowy-Gallego, E.; Perry, E.; Flicek, P. The International Genome Sample Resource (IGSR) collection of open human genomic variation resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, I.M.; Flintoff, K.J.; Taylor, G.R.; Markham, A.F.; Bonthron, D.T. Interactive visual analysis of SNP data for rapid autozygosity mapping in consanguineous families. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Asrag, M.E.; Sergouniotis, P.I.; McKibbin, M.; Plagnol, V.; Sheridan, E.; Waseem, N.; Abdelhamed, Z.; McKeefry, D.; Van Schil, K.; Poulter, J.A.; et al. Biallelic mutations in the autophagy regulator DRAM2 cause retinal dystrophy with early macular involvement. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 96, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, A.; Al Saegh, A.; Al-Mamari, W.; El-Asrag, M.E.; Ivorra, J.L.; Cardno, A.G.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Clapcote, S.J.; Ali, M. Homozygous single base deletion in TUSC3 causes intellectual disability with developmental delay in an Omani family. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 170, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirevula, S.; Alhebbi, H.; Alqahtani, A.; Algoufi, T.; Alsaif, H.S.; Ibrahim, N.; Abdulwahab, F.; Barr, M.; Alzaidan, H.; Almehaideb, A.; et al. Identification of novel loci for pediatric cholestatic liver disease defined by KIF12, PPM1F, USP53, LSR, and WDR83OS pathogenic variants. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monies, D.; Vågbø, C.B.; Al-Owain, M.; Alhomaidi, S.; Alkuraya, F.S. Recessive truncating mutations in ALKBH8 cause intellectual disability and severe impairment of wobble uridine modification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpidorou, M.; Best, S.; Poulter, J.A.; Hartill, V.; Hobson, E.; Sheridan, E.; Johnson, C.A. Novel loss-of-function mutation in HERC2 is associated with severe developmental delay and paediatric lethality. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpidorou, M.; Poulter, J.A.; Szymanska, K.; Baron, W.; Junger, K.; Boldt, K.; Ueffing, M.; Green, L.; Livingston, J.H.; Sheridan, E.G.; et al. Missense mutation of MAL causes a rare leukodystrophy similar to Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajlan, H.; Raducanu, V.S.; Lopez de Los Santos, Y.; Tehseen, M.; Alruwaili, H.; Al-Mazrou, A.; Mohammad, R.; Al-Alwan, M.; De Biasio, A.; Merzaban, J.S.; et al. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency from a Homozygous DNA Ligase 1 Mutant with Reduced Catalytic Activity but Increased Ligation Fidelity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 44, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlHargan, A.; AlMuhaizea, M.A.; Almass, R.; Alwadei, A.H.; Daghestani, M.; Arold, S.T.; Kaya, N. SHQ1-associated neurodevelopmental disorder: Report of the first homozygous variant in unrelated patients and review of the literature. Hum Genome Var. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Range of Tested Values | Minimum Change in Value | Final Optimized Value for All Subsequent Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 0–19 | 1 | 5 |
| NAA | 0.56–0.95 | 0.01 | 0.64 |
| NBB | 0.05–0.34 | 0.01 | 0.17 |
| Nhet | 0.05–0.34 | 0.01 | 0.17 |
| Xfilter | 75–574 | 1 | 386 |
| Xminimum | 0.01–0.50 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| Xcall | 300–1499 | 1 | 575 |
| Method | True Positives | False Positives | True Negatives | False Negatives | TPR | TNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agile- MultiIdeogram | 22,821 | 9214 | 315,182 | 725 | 0.9692 | 0.9716 |
| PLINK (VCF) | 9279 | 2202 | 322,194 | 14,267 | 0.3941 | 0.9932 |
| AutoMAP | 22,301 | 9612 | 314,784 | 1245 | 0.9471 | 0.9704 |
| H3M2 | 22,158 | 21,094 | 303,302 | 1388 | 0.9411 | 0.9350 |
| Savvy- Homozygosity | 22,820 | 21,026 | 303,370 | 726 | 0.9692 | 0.9352 |
| Savvy- VCFHomozgosity | 22,680 | 8572 | 315,824 | 866 | 0.9632 | 0.9736 |
| AUDACITY | 20,231 | 4673 | 319,723 | 3315 | 0.8592 | 0.9856 |
| Autozygosity- Mapper | 22,470 | 13,261 | 311,135 | 1076 | 0.9543 | 0.9591 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watson, C.M.; Lascelles, C.; Raynor, M.; Elpidorou, M.; Hany, U.; Crinnion, L.; Johnson, C.A.; Sheridan, E.; Markham, A.F.; Poulter, J.A.; et al. AgileMultiIdeogram: Rapid Identification and Visualization of Autozygous Regions Using Illumina Short-Read Sequencing Data. Biology 2025, 14, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060666
Watson CM, Lascelles C, Raynor M, Elpidorou M, Hany U, Crinnion L, Johnson CA, Sheridan E, Markham AF, Poulter JA, et al. AgileMultiIdeogram: Rapid Identification and Visualization of Autozygous Regions Using Illumina Short-Read Sequencing Data. Biology. 2025; 14(6):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060666
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatson, Christopher M., Carolina Lascelles, Morag Raynor, Marilena Elpidorou, Ummey Hany, Laura Crinnion, Colin A. Johnson, Eamonn Sheridan, Alexander F. Markham, James A. Poulter, and et al. 2025. "AgileMultiIdeogram: Rapid Identification and Visualization of Autozygous Regions Using Illumina Short-Read Sequencing Data" Biology 14, no. 6: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060666
APA StyleWatson, C. M., Lascelles, C., Raynor, M., Elpidorou, M., Hany, U., Crinnion, L., Johnson, C. A., Sheridan, E., Markham, A. F., Poulter, J. A., Bonthron, D. T., & Carr, I. M. (2025). AgileMultiIdeogram: Rapid Identification and Visualization of Autozygous Regions Using Illumina Short-Read Sequencing Data. Biology, 14(6), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060666






