TWIK Complex Expression in Prostate Cancer: Insights into the Biological and Therapeutic Significances of Potassium Ion Channels in Clinical Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PCa Cohorts
2.2. Study Approach
2.3. Data Retrieval and Processing
2.4. Gene Expression Signature Generation
2.5. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. PPI and Cox Regression Analyses Confirm the TWIK Subfamily as a Gene Network
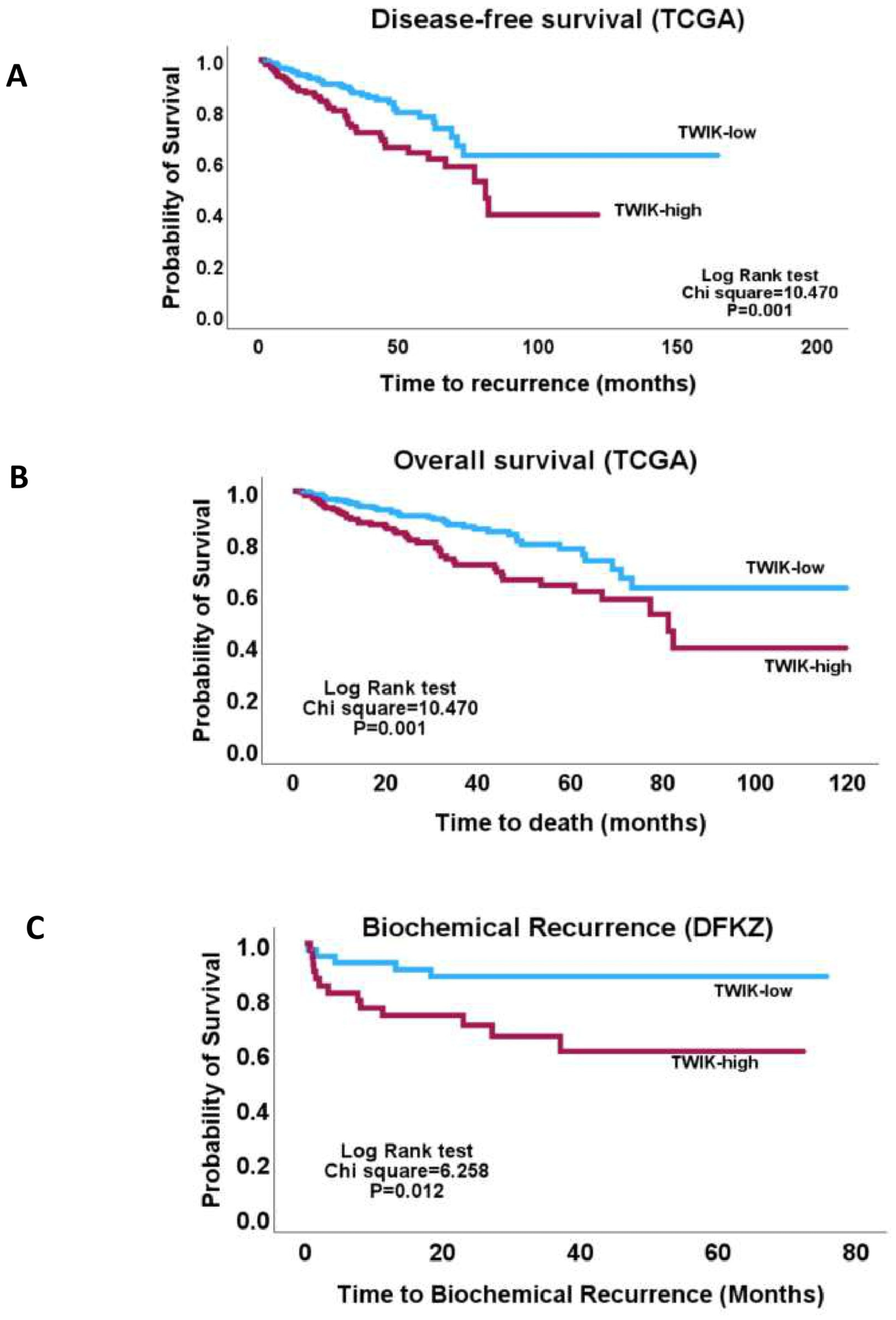
3.2. TWIK Signature Exhibits Associations with Clinicopathological and Molecular Features
3.3. TWIK Expression Signature Displays Differential Oncogenic Signalling Pathway Enrichment
3.4. TWIK Complex Expression Displays Differential Metabolic Pathway Enrichment
3.5. Differential Drug Set Enrichment Characterises TWIK Complex Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TWIK | Two P-domain in a weakly inward rectifying K+ |
| KCNK | K subfamily of the two-pore domain potassium channels |
| ISUP | International Society of Urological Pathology |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| DFKZ | Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum |
| MSKCC | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulac, I.; Roudier, M.P.; Haffner, M.C. Molecular Pathology of Prostate Cancer. Clin. Lab. Med. 2024, 44, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, S.; Takata, R.; Obara, W. Molecular Mechanisms of Prostate Cancer Development in the Precision Medicine Era: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chao, H.; Xu, F.; Deng, H.; Deng, L.; Song, Z.; Zeng, T. Identification of a Prognostic Biomarker Predicting Biochemical Recurrence and Construction of a Novel Nomogram for Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lv, D.; Eftekhar, M.; Khan, A.; Cai, C.; Zhao, Z.; Gu, D.; Liu, Y. A New Risk Stratification System of Prostate Cancer to Identify High-Risk Biochemical Recurrence Patients. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2572–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Oh, H.; Lee, J.A.; Kim, E.J. Prostate Cancer Risk Prediction Based on Clinical Factors and Prostate-Specific Antigen. BMC Urol. 2023, 23, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, A.M.; Kweldam, C.F.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H. Prognostic Histopathological and Molecular Markers on Prostate Cancer Needle-Biopsies: A Review. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 341324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfahed, A.; Ebili, H.O.; Almoammar, N.E.; Alasiri, G.; AlKhamees, O.A.; Aldali, J.A.; Al Othaim, A.; Hakami, Z.H.; Abdulwahed, A.M.; Waggiallah, H.A. Prognostic Values of Gene Copy Number Alterations in Prostate Cancer. Genes 2023, 14, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, S.M.; Vourganti, S. Predictors of Pathologically Aggressive Prostate Cancer and Surgical Management. AME Med. J. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfahed, A.; Ebili, H.O.; Waggiallah, H.A. Chromosome-Specific Segment Size Alterations Are Determinants of Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Ion Channels in Cancer: Are Cancer Hallmarks Oncochannelopathies? Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 559–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.C.; Leanza, L.; Gentile, S.; Sauter, D.R. News and Views on Ion Channels in Cancer: Is Cancer a Channelopathy? Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1258933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Adinolfi, E.; Roger, S. Editorial: Ion Channel Signalling in Cancer: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 711593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capatina, A.L.; Lagos, D.; Brackenbury, W.J. Targeting Ion Channels for Cancer Treatment: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 183, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushiro-Lopes, D.; Hegel, A.D.; Russo, A.; Senyuk, V.; Liotta, M.; Beeson, G.C.; Beeson, C.C.; Burdette, J.; Potkul, R.K.; Gentile, S. Repurposing Kir6/SUR2 Channel Activator Minoxidil to Arrests Growth of Gynecologic Cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, T.K.; Brückner, L.; Chawla, S.; Brackenbury, W.J. Inhibitory Effect of Eslicarbazepine Acetate and S-Licarbazepine on Nav1.5 Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 555047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeules, M.; Scarpitta, A.; Abad, C.; Gondé, H.; Hardet, R.; Pinto-Espinoza, C.; Eichhoff, A.M.; Schäfer, W.; Haag, F.; Koch-Nolte, F.; et al. Evaluation of P2X7 Receptor Function in Tumor Contexts Using rAAV Vector and Nanobodies (AAVnano). Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, F.; Krüwel, T.; Shi, X.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Kontermann, R.; Chames, P.; Alves, F.; Pardo, L.A. A Novel Anti-Kv10.1 Nanobody Fused to Single-Chain TRAIL Enhances Apoptosis Induction in Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Bateman, A.; O’Kelly, I. Altered Expression of Two-Pore Domain Potassium (K2P) Channels in Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-Y.; Qin, C.-J.; Lv, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-P.; Zou, Y.-C.; Guo, S.-T.; Shi, Q. Homeostasis Regulation by Potassium Channel Subfamily K Member 3 (KCNK3) in Various Fishes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 816861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewdney, B.; Miranda, P.J.; Kuchibhotla, M.; Palanisamy, R.; Richworth, C.; Milligan, C.J.; Ng, Z.Y.; Ursich, L.; Petrou, S.; Fletcher, E.V.; et al. Ion Channel Modulator DPI-201-106 Significantly Enhances Antitumor Activity of DNA Damage Response Inhibitors in Glioblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2024, 6, vdae187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Cheng, W. The Modulation of Ion Channels in Cancer Chemo-Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 945896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kischel, P.; Girault, A.; Rodat-Despoix, L.; Chamlali, M.; Radoslavova, S.; Abou Daya, H.; Lefebvre, T.; Foulon, A.; Rybarczyk, P.; Hague, F.; et al. Ion Channels: New Actors Playing in Chemotherapeutic Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belpomme, D.; Gauthier, S.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Facchini, T.; Goudier, M.J.; Krakowski, I.; Netter-Pinon, G.; Frenay, M.; Gousset, C.; Marié, F.N.; et al. Verapamil Increases the Survival of Patients with Anthracycline-Resistant Metastatic Breast Carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Wall, B.A.; Chen, S. The Current Management of Brain Metastasis in Melanoma: A Focus on Riluzole. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, J.M.; Silk, A.W.; Lee, J.H.; Dudek, L.; Jeong, B.S.; Li, J.; Schenkel, J.M.; Sadimin, E.; Kane, M.; Lin, H.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Riluzole, an Antagonist of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 (GRM1) Signaling, in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciangeli, S.; Chatelain, F.C.; Bichet, D.; Lesage, F. The Family of K2P Channels: Salient Structural and Functional Properties. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2587–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-C.; Xiong, Z.-Y.; Huang, P.-Z.; Liao, Y.-J.; Li, Q.-X.; Yao, Z.-C.; Liao, Y.-D.; Xu, S.-L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.-L.; et al. KCNK Levels Are Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Aging 2019, 11, 8169–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzmann, D.; Derand, R.; Jungbauer, S.; Bandulik, S.; Sterner, C.; Schweda, F.; El Wakil, A.; Lalli, E.; Guy, N.; Mengual, R.; et al. Invalidation of TASK1 Potassium Channels Disrupts Adrenal Gland Zonation and Mineralocorticoid Homeostasis. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.A.; Hu, C.; Guagliardo, N.A.; Sen, N.; Chen, X.; Talley, E.M.; Carey, R.M.; Bayliss, D.A.; Barrett, P.Q. TASK Channel Deletion in Mice Causes Primary Hyperaldosteronism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, I.; Zanzouri, M.; Honoré, E.; Duprat, F.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; Lazdunski, M.; Patel, A.J. K+-Dependent Cerebellar Granule Neuron Apoptosis: Role of Task Leak K+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32068–32076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; See, L.H.; Koch, C.M.; Yen, C.; Tong, J.J.; Spiegel, L.; Nguyen, K.C.; Servoss, A.; et al. Genomic Amplification and Oncogenic Properties of the KCNK9 Potassium Channel Gene. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Cavanaugh, E.J.; Kim, I.; Carroll, J.L. Heteromeric TASK-1/TASK-3 Is the Major Oxygen-Sensitive Background K+ Channel in Rat Carotid Body Glomus Cells. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2963–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckler, K.J.; Williams, B.A.; Honoré, E. An Oxygen-, Acid- and Anaesthetic-Sensitive TASK-Like Background Potassium Channel in Rat Arterial Chemoreceptor Cells. J. Physiol. 2000, 525, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestreau, C.; Heitzmann, D.; Thomas, J.; Dubreuil, V.; Bandulik, S.; Reichold, M.; Bendahhou, S.; Pierson, P.; Sterner, C.; Peyronnet-Roux, J.; et al. Task2 Potassium Channels Set Central Respiratory CO2 and O2 Sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, S.; Ruck, T.; Fernández-Orth, J.; Meuth, S.G. TREK-King the Blood-Brain-Barrier. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, S.; Ruck, T.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Herrmann, A.M.; Moha ou Maati, H.; Bobak, N.; Göbel, K.; Langhauser, F.; Stegner, D.; Ehling, P.; et al. Endothelial TWIK-Related Potassium Channel-1 (TREK1) Regulates Immune-Cell Trafficking Into the CNS. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, E.E.; Crossland, R.F.; Phillips, S.C.; Marrelli, S.P.; Reddy, A.K.; Taffet, G.E.; Hartley, C.J.; Bryan, R.M., Jr. Disruption of K2P6.1 Produces Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension in Mice. Hypertension 2011, 58, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, L.M.; Lloyd, E.E.; Reynolds, J.O.; Lawrence, W.S.; Reynolds, C.; Wehrens, X.H.; Bryan, R.M. TWIK-2 Channel Deficiency Leads to Pulmonary Hypertension Through a Rho-Kinase-Mediated Process. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Kadir, L.; Stacey, M.; Barrett-Jolley, R. Emerging Roles of the Membrane Potential: Action Beyond the Action Potential. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Lin, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Y. KCNK3 Inhibits Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Activation of AMPK-TXNIP Pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tang, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, F.; Mo, Y.; Jiang, X.; Deng, X.; Peng, M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, M.; et al. Potassium Channel Protein KCNK6 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 616784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, R.; Valenzuela, C.; Concha, G.; Brown, N.; Zúñiga, L. TASK-3 Downregulation Triggers Cellular Senescence and Growth Inhibition in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikutović-Molina, R.; Herrada, A.A.; González, W.; Brown, N.; Zúñiga, L. TASK-3 Gene Knockdown Dampens Invasion and Migration and Promotes Apoptosis in KATO III and MKN-45 Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala, W.D.; Foscolo, M.R.; Kunda, P.E.; Cavicchia, J.C.; Acosta, C.G. Changes in the Expression of the Potassium Channels TASK1, TASK3 and TRESK in a Rat Model of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Relation to Malignancy. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 100, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abriel, H.; Rougier, J.-S.; Jalife, J. Ion Channel Macromolecular Complexes in Cardiomyocytes: Roles in Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1971–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Fakler, B.; Kaczmarek, L.K.; Isom, L.L. More Than a Pore: Ion Channel Signaling Complexes. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15159–15169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the CBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, l1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebili, H.O.; Omenai, S.A.; Ezenkwa, U.S.; Ale, A.O.; Akintola, P.A.; Adetona, A.E.; Akunwata, C.U.; Mashor, M.I.; Nwanji, I.D.; Iyapo, O.; et al. Molecular and Clinicopathological Correlates of Wild-Type KRAS Expression in Prostate Cancer. Ann. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhauser, C.; Favero, F.; Risch, T.; Simon, R.; Feuerbach, L.; Assenov, Y.; Heckmann, D.; Sidiropoulos, N.; Waszak, S.M.; Hübschmann, D.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Early-Onset Prostate Cancer Identifies Molecular Risk Markers and Clinical Trajectories. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 996–1011.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein–Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaufrère, A.; Caruso, S.; Calderaro, J.; Poté, N.; Bijot, J.-C.; Couchy, G.; Cauchy, F.; Vilgrain, V.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Paradis, V. Gene Expression Signature as a Surrogate Marker of Microvascular Invasion on Routine Hepatocellular Carcinoma Biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, R.; Leimanis, M.L.; Newbury, P.A.; Liu, K.; Xing, J.; Nedveck, D.; Kort, E.J.; Prokop, J.W.; Zhou, G.; Bachmann, A.S.; et al. Gene Expression Signatures Identify Paediatric Patients with Multiple Organ Dysfunction Who Require Advanced Life Support in the Intensive Care Unit. EBioMedicine 2020, 62, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfahed, A. Cell Migration–Proliferation Dichotomy in Cancer: Biological Fact or Experimental Artefact? Biology 2024, 13, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, G.F. A Two-Step Approach for Transforming Continuous Variables to Normal: Implications and Recommendations for IS Research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2011, 28, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Kocabaş, P.; Wang, H.; Cholley, P.-E.; Cook, D.; Nilsson, A.; Anton, M.; Ferreira, R.; Domenzain, I.; Billa, V.; et al. An Atlas of Human Metabolism. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaz1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.; Shin, J.; Kim, J.; Ryall, K.A.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.; Jeon, M.; Kang, J.; Tan, A.C. DSigDB: Drug Signatures Database for Gene Set Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3069–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithner, K.; Hirschmugl, B.; Li, Y.; Tang, B.; Papp, R.; Nagaraj, C.; Stacher, E.; Stiegler, P.; Lindenmann, J.; Olschewski, A.; et al. TASK-1 Regulates Apoptosis and Proliferation in a Subset of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, A.; Gui, D.Y.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Targeting Metabolism for Cancer Therapy. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soave, C.L.; Guerin, T.; Liu, J.; Dou, Q.P. Targeting the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System for Cancer Treatment: Discovering Novel Inhibitors from Nature and Drug Repurposing. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, D.; Catara, G. Targeting the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System and Recent Advances in Cancer Therapy. Cells 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ge, S.; Singh, R.; Basu, S.; Shatzer, K.; Zen, M.; Liu, J.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; et al. Glucuronidation: Driving Factors and Their Impact on Glucuronide Disposition. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination Therapy in Combating Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfahed, A. TWIK Complex Expression in Prostate Cancer: Insights into the Biological and Therapeutic Significances of Potassium Ion Channels in Clinical Cancer. Biology 2025, 14, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050569
Alfahed A. TWIK Complex Expression in Prostate Cancer: Insights into the Biological and Therapeutic Significances of Potassium Ion Channels in Clinical Cancer. Biology. 2025; 14(5):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050569
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfahed, Abdulaziz. 2025. "TWIK Complex Expression in Prostate Cancer: Insights into the Biological and Therapeutic Significances of Potassium Ion Channels in Clinical Cancer" Biology 14, no. 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050569
APA StyleAlfahed, A. (2025). TWIK Complex Expression in Prostate Cancer: Insights into the Biological and Therapeutic Significances of Potassium Ion Channels in Clinical Cancer. Biology, 14(5), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050569







