Environmental Effects on the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in the Northern South China Sea
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Methods
- (1)
- Factor analysis
- (2)
- Generalized Additive Models
- (3)
- Model testing
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Environmental Factors
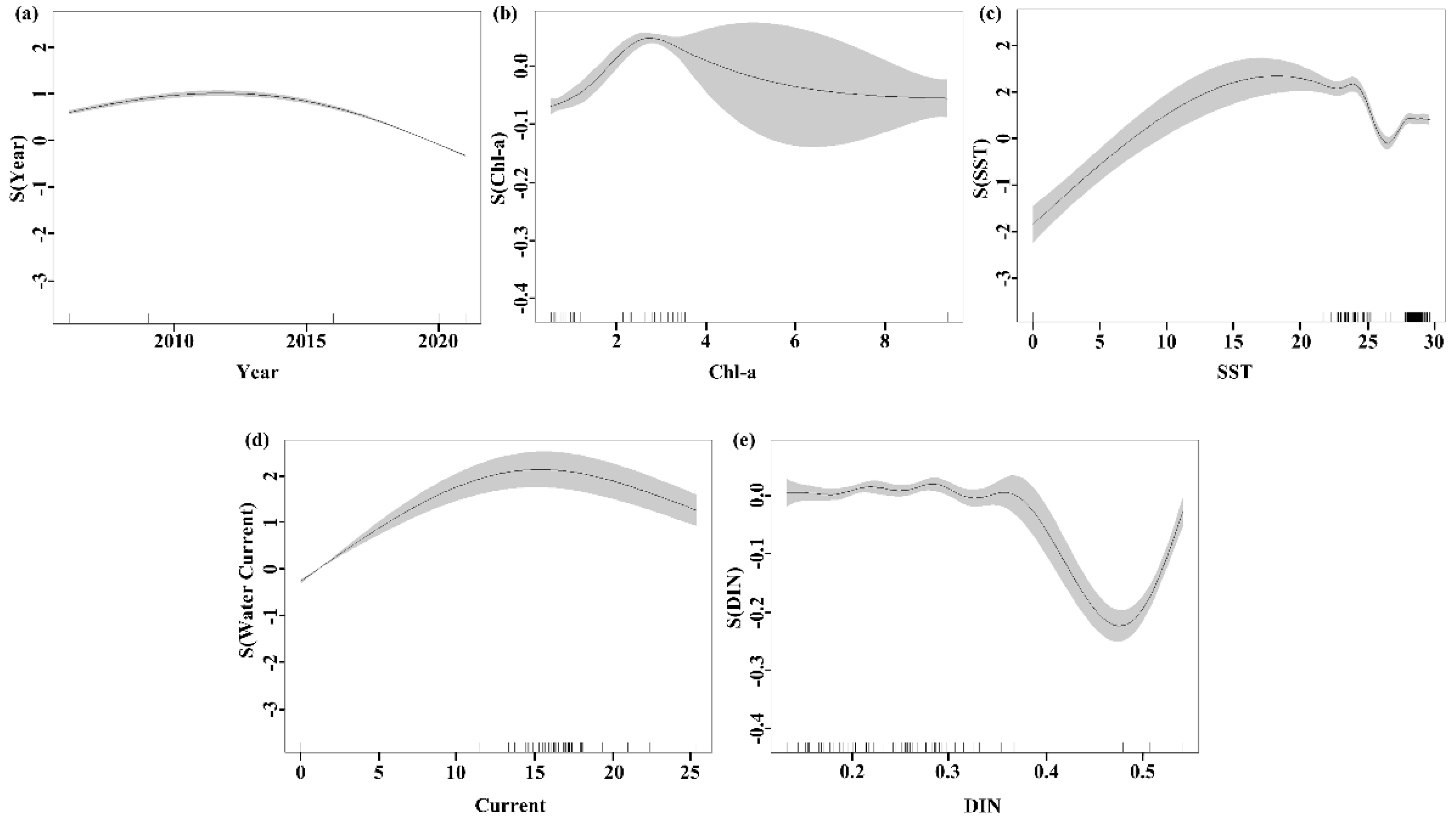
3.2. GAM Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Affecting MECC of Marine Ranching
4.2. Temporal Effects on the MECC of Marine Ranching
4.3. Environmental Effects on the MECC
4.4. Limitations and Implications of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variables (D) |
| Natural shoreline (D1) |
| Beach retention rate (D2) |
| Island area (D3) |
| Vegetation coverage (D4) |
| Biomass (D5) |
| Biodiversity index (D6) |
| Open aquaculture area (D7) |
| Artificial reef area (D8) |
| Dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentration (D9) |
| Reactive phosphate concentration (D10) |
| Temperature (D11) |
| Salinity (D12) |
| Depth (D13) |
| Current velocity (D14) |
| Species of fish eggs and larvae (D15) |
| Benthic biomass (D16) |
| Benthic biodiversity index (D17) |
| Zooplankton biomass (D18) |
| Zooplankton biodiversity index (D19) |
| Phytoplankton density (D20) |
| Phytoplankton biodiversity index (D21) |
| Nekton density (D22) |
| Nekton diversity index (D23) |
| Chl-a (D24) |
References
- Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Lozano-Montes, H.M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Zhang, X.; Tian, T.; Wu, Z. Estimating Ecological Carrying Capacity for Stock Enhancement in Marine Ranching Ecosystems of Northern China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 936028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, W.-S. Emergy Ecological Footprint Method Considering Uncertainty and its Application in Evaluating Marine Ranching Resources and Environmental Carrying Capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130363–130376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Zhang, C.I. Evaluation of the Effect of Marine Ranching Activities on the Tongyeong Marine Ecosystem. Ocean Sci. J. 2018, 53, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, G.; Wei, W. China’s coastal seawater environment caused by urbanization based on the seawater environmental Kuznets curve. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 213, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, D.; Tian, B.; Yuan, X.; Bo, S.; Ma, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Keesing, J.K. A solution for restoration of critical wetlands and waterbird habitats in coastal deltaic systems. J. Env. Manag. 2022, 302, 113996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Chen, P.; Yuan, H.; Feng, X.; Yu, J.; Shu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z. Evaluation on Carrying Capacity of Fishery Resources in Coastal Waters of Dapeng Peninsula, Shenzhen. South China Fish. Sci. 2019, 15, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.T.; Tran, D.L.T. Assessing Marine Environmental Carrying Capacity in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Areas-Models and Related Databases. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156043–156059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Pouso, S.; Galparsoro, I.; Manca, E.; Vasquez, M.; Lu, W.; Yang, L.; Uriarte, A. Applying the China’s Marine Resource-Environment Carrying Capacity and Spatial Development Suitability Approach to the Bay of Biscay (North-East Atlantic). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 972448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, K.; Liang, S.; Zhang, P.; Lin, G.; Wang, X. An Integrated Method for the Control Factor Identification of Resources and Environmental Carrying Capacity in Coastal Zones: A Case Study in Qingdao, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 142, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, H. Evaluation and Obstacle Factors of Marine Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity in Beibu Gulf Urban Agglomeration. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1196196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Du, Y.-W. Evaluation of Resources and Environmental Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in China: An Integrated Life Cycle Assessment-Emergy Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Luo, Q. Discussion Evaluation Index System and Method for Marine Environmental Capacity. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Yucel-Gier, G.; Eronat, C.; Sayin, E. The Impact of Marine Aquaculture on the Environment; the Importance of Site Selection and Carrying Capacity. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liao, B.; Xu, Y.; Sun, M.; Geng, P.; Chen, Z. Comparative Effects of Distorted Fishery Data on Assessment Results of Two Non-equilibrium Surplus Production Models. J. Fish. China 2018, 42, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Li, B.; Quan, X. Construction and Application of DPPD Model for Evaluating Marine Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119655–119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yu, J.; Chen, P.; Feng, X. Ecosystem Health Assessment of the Egong Bay Fisheries Area in Shenzhen. J. South. Agric. 2016, 47, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. A Comprehensive Evaluation Model of Regional Atmospheric Environment Carrying Capacity: Model Development and A Case Study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, T. Index System of Urban Resource and Environment Carrying Capacity Based on Ecological Civilization. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 68, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, X.; Gao, X.; Chang, K. Evaluation of Water Ecological Carrying Capacity Based on WBM Evaluation Model. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeman, A.J.; Elsawah, S.; Wang, H.-H.; Hamilton, S.H.; Melsen, L.; Grimm, V. Towards normalizing good practice across the whole modeling cycle: Its instrumentation and future research topics. Socio-Environ. Syst. Model. 2024, 6, 18755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, N.; Jackman, S. Beyond Linearity by Default: Generalized Additive Models. Am. J. Political Sci. 1998, 42, 596–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yao, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, P. The Role of Environmental Factors on the Fishery Catch of the Squid Uroteuthis chinensis in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Towards the Comprehensive Water Quality Control in Lake Taihu: Correlating Chlorphyll A and Water Quality Parameters with Generalized Additive Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhi, M.; Zhang, Y. Combined Generalized Additive Model and Random Forest to Evaluate the Influence of Environmental Factors on Phytoplankton Biomass in A Large Eutrophic Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108082–108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB17378-2007; Marine Monitoring. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, SAC: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB12763.6-2007; Oceanographic Survey-Marine Biological Survey. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, SAC: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chu, J. Extraction of Remotely Sensed Information of Island Intertidal Zone and Wetland: Taking the Dongsha Island as an Example. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2005, 23, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Yang, W. Evaluation of the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Wailingding Marine Ranching in Zhuhai, China by High-Resolution Remote Sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1354407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, H. Study on Factor Analysis and Selection of Common Landscape Metrics. For. Res. 2009, 22, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Yu, X. Multivariate Statistical Analysis; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Fast Stable Restricted Maximum Likelihood and Marginal Likelihood Estimation of Semiparametric Generalized Linear Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2010, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirkle, K.W.; Nolan, B.T.; Jones, R.R.; Weyer, P.J.; Ward, M.H.; Wheeler, D.C. Assessing the Relationship Between Groundwater Nitrate and Animal Feeding Operations in Lowa (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Edwards, T.C.; Hastie, T.J. Generalized Linear and Generalized Additive Models in Studies of Species Distributions: Setting the Scene. Ecol. Model. 2002, 157, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J. Assessment of Marine Ecological Carrying Capacity in Liaoning Province Based on the Ecosystem Health. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.S. The Diversity–Stability Debate. Nature 2000, 405, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.; Allen, C.R.; Holling, C.S. Ecological Resilience, Biodiversity, and Scale. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte-Luna, P.; Brook, B.W.; Zetina-Rejón, M.J.; Cruz-Escalona, V.H. The Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2004, 13, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Ma, C.-A.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. Macrobenthic Diversity in Protected, Disturbed, and Newly Formed Intertidal Wetlands of A Subtropical Estuary in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y. Assessment on Wetland Ecosystem Health in Daguhe Estuary. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, D.S.; Vellend, M. Biodiversity-Ecosystem Function Research: Is It Relevant to Conservation? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2005, 36, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, G.I.; Robert, K.H. A Framework for Strategic Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Gao, K. Ecological Security Evaluation of Marine Ranching with AHP-Entropy-Based TOPSIS: A Case Study of Yantai, China. Mar. Policy 2020, 122, 104223–104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hang, H.; Zhang, X. Research on Marine Resource and Rnvironment Carrying Capacity Based on Marine Ecosystem Services—A Case Study of Daya Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, G.; Shuo, Z. The Environmental Function and Fish Gather Effect of Atificial Reefs. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2002, 17, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.S.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; dos Santos, L.N.; Zalmon, I.R. Could Artificial Reefs Increase Access to Estuarine Fishery Resources? Insights from A Long-Term Assessment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraer, S.; Carey, D.; Coolen, J.; Hutchison, Z.; Kerckhof, F.; Rumes, B.; Vanaverbeke, J. Offshore Wind Farm Artificial Reefs Affect Ecosystem Structure and Functioning: A Synthesis. Oceanography 2020, 33, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, A.; Li, H.; Zhou, W.; Jiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Yue, W. Estimation of Ecological Carrying Capacity of Small-Scale Fish in Marine Ranch of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 61, 102901–102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Tan, Y.; Ke, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J. Seasonal Variations of Chlorophyll-A and Primary Production and their Influencing Factors in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2017, 36, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Huang, B.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, X. On the Spatial and Temporal Variations of Primary Production in the South China Sea. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q. Remote Sensing of Environmental Effects on the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis in the Xisha-Zhongsha Waters. Master’s Thesis, Shang Hai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Culver, M.E.; Smith, W.O. Effects of Environmental Variation on Sinking Rates of Marine Phytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1989, 25, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, F.; Buonocore, E.; Franzese, P.P.; Scardi, M. Global Assessment of Marine Phytoplankton Primary Production: Integrating Machine Learning and Environmental Accounting Models. Ecol. Model. 2021, 451, 109578–109588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Mao, J. Relationship Between the Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis Resource and Environmental Factors in the Xisha-Zhongsha Waters in Spring. Haiyang Xuebao 2017, 39, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, F.A.; Gasalla, M.A. On the Relationship Between Squid and the Environment: Artisanal jigging for Loligo plei at São Sebastião Island (24°S), Southeastern Brazil. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nanami, A.; Sato, T.; Kawabata, Y.; Okuyama, J. Spawning Aggregation of White-Streaked Grouper Epinephelus ongus: Spatial Distribution and Annual Variation in the Fish Density within A Spawning Ground. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, A.A.; Keller, D.; Bailey, E.J.; Goforth, R.R. Predictors of Bigheaded Carp Drifting Egg Density and Spawning Activity in an Invaded, Free-Flowing River. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, M.; Jeyid, M.A.; Vantrepotte, V.; Dessailly, D.; Amara, R. Environmental Effects on the Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Abundance and Distribution of Sardina Pilchardus and Sardinella off the Mauritanian Coast (North-West Africa). Fish. Oceanogr. 2016, 26, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of Temperature, Salinity and PH on Hatch and Larval Activity of Epinephelus Coioides. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2006, 25, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, W.; Gui, F.; Zeng, X.; Xu, K.; Zhao, S. Study of Suitable Habitats for Sepiella Maindroni in Zhoushan Sea Areas Based on MaxEnt Model. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Guan, X.; King, P.; Zhou, Z. Ecological Functions of Microbial Communities in Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon Polyculture Ponds. Fish. Sci. 2023, 42, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Ocean Color Elements in Response to Tropical Cyclone: A Case Study of Typhoon Mangkhut (2018) Past over the Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.M.; Mingels, B.; Tandon, A. The Impact of Lateral Advection on SST and SSS in the Northern Bay of Bengal during 2015. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2020, 172, 104653–104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, C. Fish Assemblage Structure and Fauna Discrimination in the Coastal Waters of Southern Yellow Sea. J. Fish. China 2017, 41, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H. Development of the Tourism Resources of the Wanshan Islands. Trop. Geogr. 2000, 20, 134–138+143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Dai, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, P. Seasonal Variation of Fishery Resources in Wailingding Marine Ranchingand Adjacent Waters. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. Influence of Artificial Fish Reef on Fishery Resources and Oceanic Ecological Environment and Research on Correlation Technique. J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 25, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Zhang, S.; Jia, X. Effect on Fishery Resources Multiplication of Artificial Reefs. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2009, 8, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, S. Research Advances on Physical Stability and Ecological Effects of Artificial Reef. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Yoon, H.-S.; Na, W.-B. Efficiency, Tranquillity and Stability Indices to Evaluate Performance in the Artificial Reef Wake Region. Ocean Eng. 2016, 122, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Cornwell, W.K.; Lowry, M.B.; Suthers, I.M. Modelling the Distribution of Fish Around An Artificial Reef. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Niu, L.; Wei, T.; Fu, L.; Yang, Q. Nutrient Dynamics in Pearl River Estuary and Their Eutrophication Evaluation. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2020, 40, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Cen, J.Y.; Ou, L.J.; Lv, S.H. Distribution Characteristics of COD, DO and Nutrients in Pearl River Estuary and its Eutrophication Assessment in Summer and Autumn. J. Jinan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Med. Ed.) 2014, 35, 221–227. [Google Scholar]

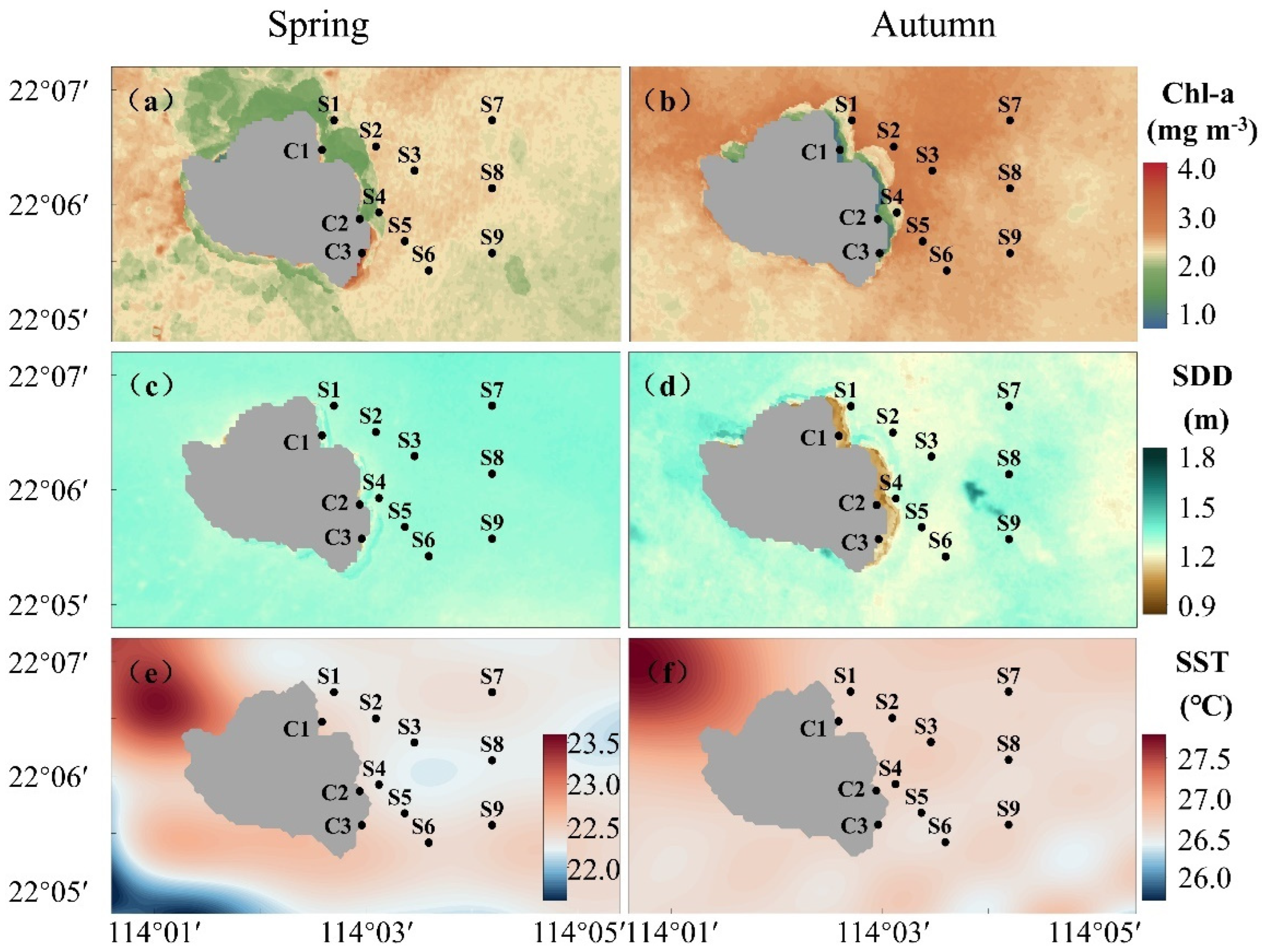
| Number | Data Name | Date | Data Source | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chl-a | January 2019~October 2022. | HY-1C | 50 m |
| 2 | SDD | January 2019~October 2022. | HY-1C | 50 m |
| 3 | SST | January 2019~October 2022. | HY-1C | 1 km |
| 4 | Water Current | 2006 2009 2016 2020 2021 | Global Ocean Physical Reanalysis Product of the Copernicus Marine Environment Management Service | 0.083° × 0.083° |
| 5 | Intertidal area | 10 November 2006. | Landsat-5 TM | 30 m |
| 6 | Intertidal area | 23 August 2009. | Landsat-5 TM | 30 m |
| 7 | Intertidal area | 27 March 2016. | BJ-2 | 0.8 m |
| 8 | Intertidal area | 22 July 2020. | GF-1 | 2 m |
| 9 | Intertidal area | 28 November 2021. | BJ-3 | 0.5 m |
| Model Factors | Residual Deviance | AIC | GCV | Accumulation of Deviance Explained (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| log(MECC)~NULL | 44.51 | 0.00 | −367.72 | 0.0225 | 0.00 |
| log(MECC)~s(year) | 130.92 | 0.66 | −783.25 | 0.0077 | 66.20 |
| log(MECC)~s(Year) + s(DIN) | 132.26 | 0.66 | −784.50 | 0.0077 | 66.80 |
| log(MECC)~s(Year) + s(DIN) + s(SST) | 150.49 | 0.70 | −829.00 | 0.0068 | 71.20 |
| log(MECC)~s(Year) + s(DIN)+s(SST) + s(Chl-a) | 477.83 | 0.90 | −1258.97 | 0.0023 | 91.80 |
| log(MECC)~s(Year) + s(DIN) + s(SST)+s(Chl-a) + s(Water Current) | 878.663 | 0.95 | −1492.57 | 0.0012 | 95.40 |
| Variables | d.f. | Contribution (%) | Pr (F) | Pr (Chrisq) | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1.999 | 66.20 | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 3.00 |
| Chl-a | 8.995 | 20.60 | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 3.66 |
| SST | 8.867 | 4.40 | 6.166 × 10−10 *** | 1.705 × 10−10 *** | 3.38 |
| Water Current | 2.000 | 3.60 | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 2.2 × 10−16 *** | 2.31 |
| DIN | 3.110 | 0.60 | 0.0930 | 0.0911 | 1.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, P. Environmental Effects on the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in the Northern South China Sea. Biology 2025, 14, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040419
Wang Z, Yao L, Yu J, Chen Y, Feng X, Chen P. Environmental Effects on the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in the Northern South China Sea. Biology. 2025; 14(4):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040419
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ziwen, Lijun Yao, Jing Yu, Yuxiang Chen, Xue Feng, and Pimao Chen. 2025. "Environmental Effects on the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in the Northern South China Sea" Biology 14, no. 4: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040419
APA StyleWang, Z., Yao, L., Yu, J., Chen, Y., Feng, X., & Chen, P. (2025). Environmental Effects on the Ecological Carrying Capacity of Marine Ranching in the Northern South China Sea. Biology, 14(4), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040419






