Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Babesia bigemina Isolates in Cattle from South Africa Based on BgRAP-1, BgAMA-1 and BgβTUB Genes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation
2.3. Primer Design
2.4. PCR and Nested PCR Assays
2.5. Validation of Primers
2.6. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Nested PCR Assays
3.2. Comparative Sequence Analyses
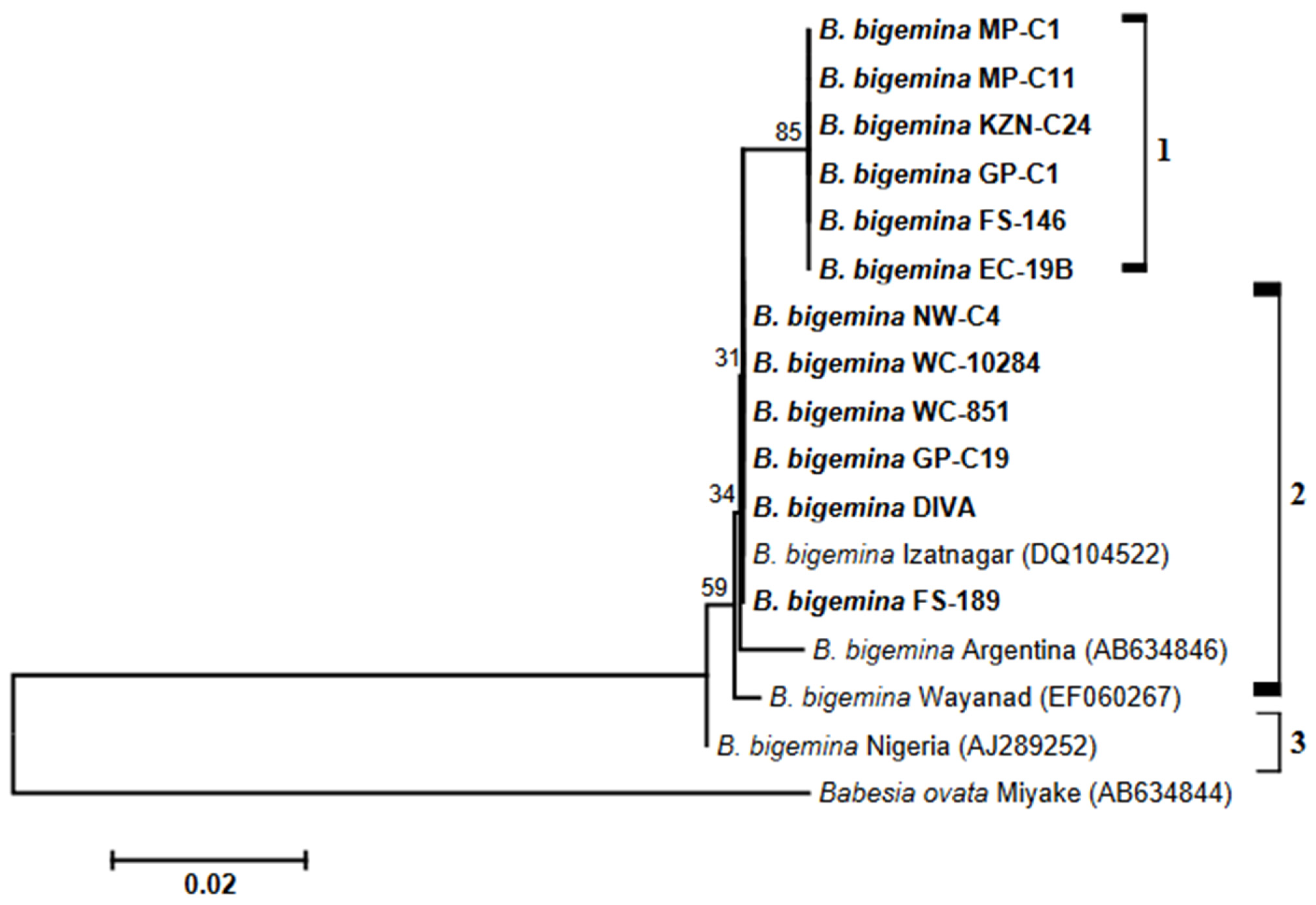
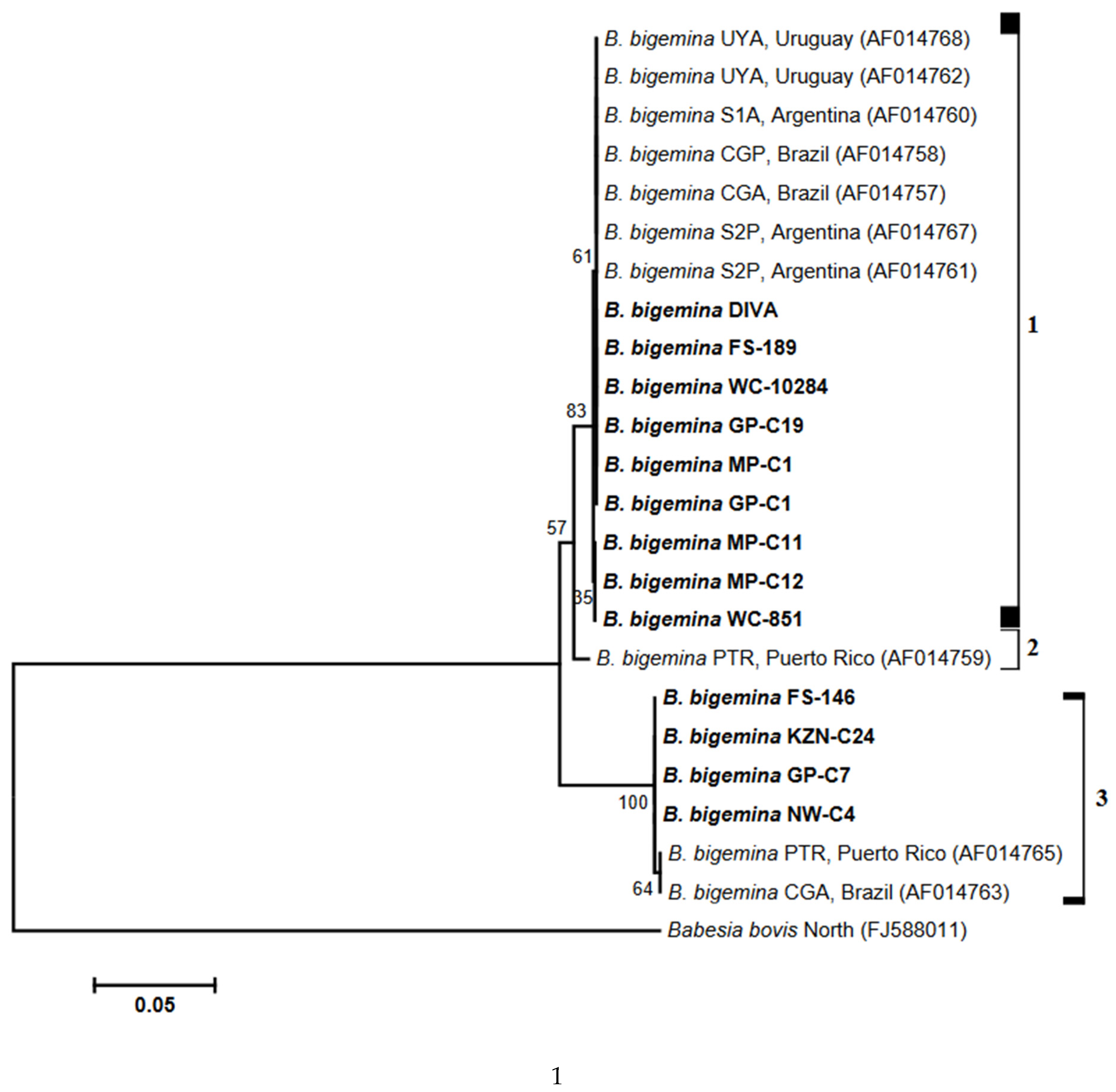
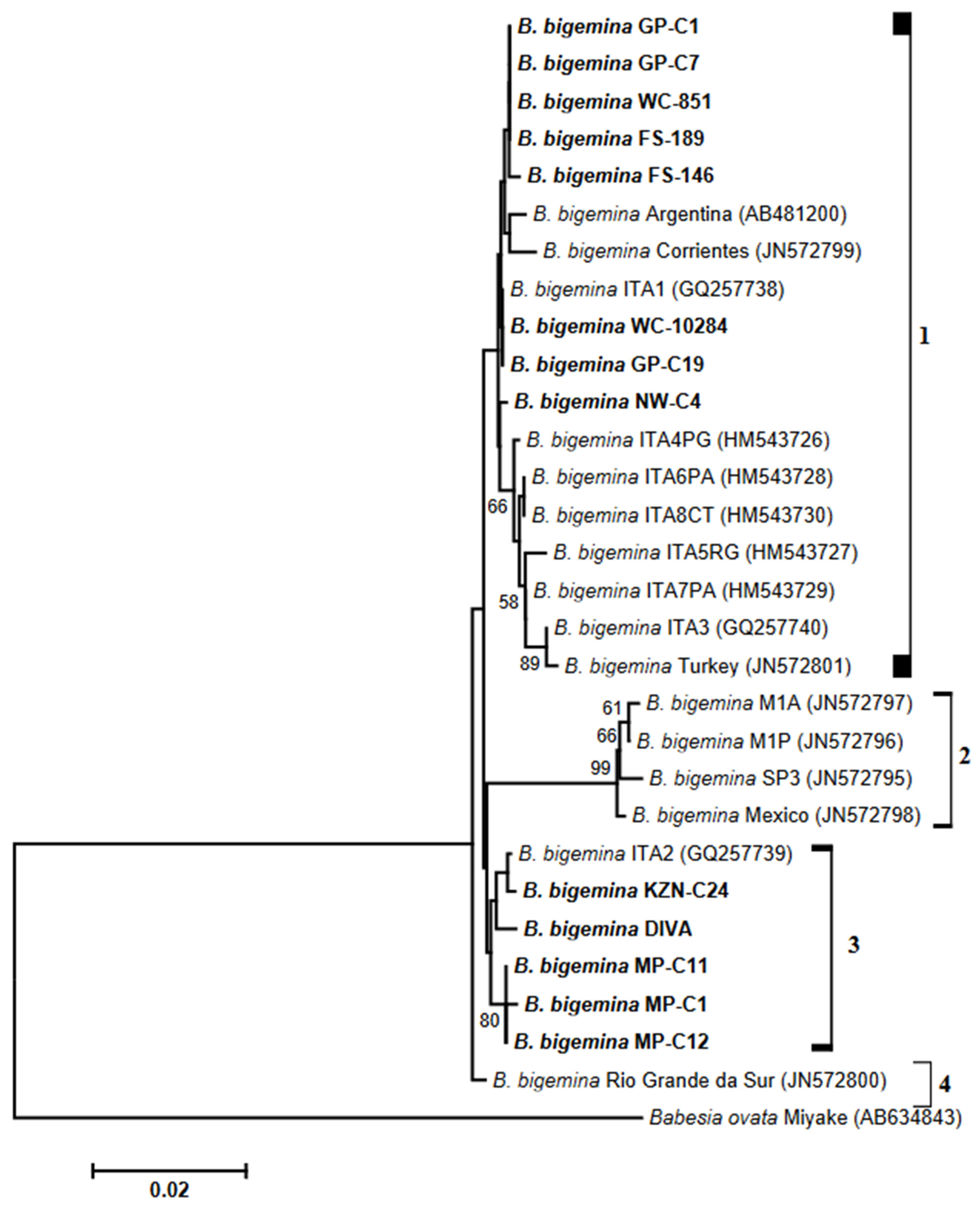
3.3. Analysis of Phylogenies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCosker, P.J. The global importance of babesiosis. In Babesiosis; Ristic, M., Kreier, J.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Norval, R.A. Tick infestations and tick-borne diseases in Zimbabwe Rhodesia. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1979, 50, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ristic, M. Babesiosis. In Diseases of Cattle in the Tropics; Ristic, M., MacIntyre, I., Eds.; Martinus Nijhof Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 443–468. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; de Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.C.; Norimine, J.; Goff, W.L.; Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Prospects for recombinant vaccines against Babesia bovis and related parasites. Parasitol. Immunol. 2006, 28, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, A.J.; Potgieter, F.T. Bovine babesiosis. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock; Coetzer, J.A.W., Thomson, G.R., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1994; pp. 278–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Terkawi, M.A.; Cruz-Flores, M.J.; Claveria, F.G.; Aboge, G.O.; Yamagishi, J.; Goo, Y.-K.; Cao, S.; Masatani, T.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Epidemiological survey of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infections of cattle in Philippines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 995–998. [Google Scholar]
- Riek, R.F. The life cycle of Babesia bigemina (Smith & Kilborne, 1893) in the tick vector Boophilus microplus (Canestrini). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1964, 15, 802–821. [Google Scholar]
- Jerzak, M.; Gandurski, A.; Tokaj, M.; Stachera, W.; Szuba, M.; Dybicz, M. Advances in Babesia vaccine development: An overview. Pathogens 2023, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeria, S.; Castella, J.; Ferrer, D.; Ortuno, A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Gutierrez, J.F. Bovine piroplasms in Minorca (Balearic Islands, Spain): A comparison of PCR-based and light microscopy detection. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessenger, R.; Schoeman, J.H. Serological responses of cattle to infection with Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis in southern Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1983, 50, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Passos, L.M.F.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Brown, C.G.D. Immunochemical characterization of in vitro culture-derived antigens of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 76, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrimal, Y.; Goff, W.L.; Jasmer, D.P. Detection of Babesia bovis carrier cattle by using polymerase chain reaction amplification of parasite DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction based assay for the detection of Babesia bigemina, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale DNA in bovine blood. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 50, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smeenk, I.; Kelly, P.J.; Wray, K.; Musuka, G.; Trees, A.J.; Jongejan, F. Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina DNA detected in cattle and ticks from Zimbabwe by polymerase chain reaction. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2000, 71, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.G.; Oliveira, M.C.S.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Amarante, A.F.T. PCR-based detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in their natural host Boophilus microplus and cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, F.D.; Bendele, K.G.; Davey, R.B.; George, J.E. Detection of Babesia bigemina infection in strains of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from outbreaks in south Texas. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, T.; Altangerel, K.; Battsetseg, B.; Battur, B.; Aboulaila, M.; Munkhjargal, T.; Yoshinari, T.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Genetic detection of Babesia bigemina from Mongolian cattle using apical membrane antigen-1 gene-based PCR assay. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Alhasan, H.; Huyen, N.X.; Sabagh, A.; Awier, K.; Cao, S.; Goo, Y.K.; Aboge, G.; Yokoyama, N.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Molecular and serological prevalence of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle from central region of Syria. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Mtshali, M.S.; Mtshali, P.S. Molecular diagnosis and phylogenetic analysis of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis hemoparasites from cattle in South Africa. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Giglioti, R.; Filho, A.E.V.; Domingos, A.G.; da Silva, S.S.; Cunha, R.C.; Ibelli, A.M.G.; Okino, C.H.; de Sena Oliveira, M.C. Detection and quantification of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina using different target genes. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 168, 105122. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Aboge, G.O.; Terkawi, M.A.; Yu, L.; Kamyingkird, K.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Goo, Y.-K.; Yamagishi, J.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Molecular detection and identification of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle in northern Thailand. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, L.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Soldati-Favre, D. Subversion of host cellular functions by the apicomplexan parasites. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 607–631. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, C.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Hines, S.A.; Hotzel, I.; McElwain, T.F. Organization, transcription and expression of rhoptry associated protein genes in the Babesia bigemina rap-1 locus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 127, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumouni, P.F.A.; Aboge, G.O.; Terkawi, M.A.; Masatani, T.; Cao, S.; Kamyingkird, K.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of Babesia bovis, Babesia bigemina, Theileria species and Anaplasma marginale isolated from cattle in Kenya. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torina, A.; Agnone, A.; Sireci, G.; Mosqueda, J.J.; Blanda, V.; Albanese, I.; La Farina, M.; Cerrone, A.; Cusumano, F.; Caracappa, S. Characterization of the apical membrane antigen-1 in Italian strains of Babesia bigemina. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2010, 57, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciò, S.; Cammà, C.; Onuma, M.; Severini, C. The β-tubulin gene of Babesia and Theileria parasites is an informative marker for species discrimination. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamoto, A.; Tsuji, M.; Wei, Q.; Cho, S.H.; Shin, E.H.; Kim, T.S.; Leonova, G.N.; Hagiwara, K.; Asakawa, M.; Kariwa, H.; et al. Epizootiologic survey for Babesia microti among small wild mammals in northeastern Eurasia and a geographic diversity in the beta-tubulin gene sequences. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Thekisoe, O.M.M.; Katsande, C.; Latif, A.A.; Mans, B.J.; Matthee, O.; Mkize, N.; Mabogoane, N.; Marais, F.; Yokoyama, N.; et al. Serological survey of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle in South Africa. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, A.; Jorgensen, W. Molecular approaches to detect and study the organisms causing bovine tick borne diseases: Babesiosis and anaplasmosis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 292–302. [Google Scholar]
- Madruga, C.R.; Leal, C.R.B.; Ferreira, A.M.T.; Araújo, F.R.; Bonato, A.L.V.; Kessler, R.H.; Schenk, M.A.M.; Soares, C.O. Genetic and antigenic analysis of Babesia bigemina isolates from five geographical regions of Brazil. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2002, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazan, C.; Tipacamu, G.A.; Rodriguez, S.; Mosqueda, J.; Perez de Leon, A. Immunological control of ticks and tick-borne diseases that impact cattle health and production. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2018, 23, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Buening, G.M. In vitro inhibition of multiplication of Babesia bigemina by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, T.; Tagawa, M.; Yoshinari, T.; Ybañez, A.P.; Igarashi, I.; Ikehara, Y.; Hata, H.; Kondo, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Inokuma, H.; et al. PCR detection of Babesia ovata from cattle reared in Japan and clinical significance of coinfection with Theileria orientalis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2111–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L.; Dominguez, M.; Mesplet, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Ferreri, L.; Asenzo, G.; Wilkowsky, S.; Farber, M.; Echaide, I.; et al. Search for Babesia bovis vaccine candidates. Parassitologia 2007, 1, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, A.; Bock, R.E. Vaccination against bovine babesiosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 916, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, S.J.; Brayton, K.A.; Molloy, J.B.; Bock, R.E.; Lew, A.E.; McElwain, T.F. Merozoite surface antigen 2 proteins of Babesia bovis vaccine breakthrough isolates contain a unique hypervariable region composed of degenerate repeats. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7180–7189. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Studies on the isolation and preservation a single species of bovine haematocytozoon: The finding and isolation of Babesia ovata in China. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 1990, 16, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, T.; Ishihara, T. Babesia ovata sp. n. isolated from cattle in Japan. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1980, 20, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, M.D. Pure isolation and identification of Babesia ovata by morphological characteristics and complement fixation test in Korea. Korean J. Vet. Res. 1987, 27, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Asada, M.; Battsetseg, B.; Huang, X.; Lan, D.T.B.; Inpankaew, T.; Ybanez, A.; Alhassan, A.; Thekisoe, O.M.M.; et al. A PCR based survey of Babesia ovata in cattle from various Asian, African and South American countries. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.C.; McElwain, T.F.; Ruef, B.J.; Suarez, C.E.; Shkap, V.; Chitko-McKown, C.G.; Tuo, W.; Rice-Ficht, A.C.; Palmer, G.H. Babesia bovis rhoptry-associated protein 1 is immunodominant for T helper cells of immune cattle and contains T-cell epitopes conserved among geographically distant B. bovis strains. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3341–3350. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, M.E. Rhoptry organelles of apicomplexan parasites. Parasitol. Today 1992, 8, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, C.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Hötzel, I.; McElwain, T.F. Structure, sequence, and transcriptional analysis of the Babesia bovis rap-1 multigene locus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998, 93, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Remarque, E.J.; Faber, B.W.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Thomas, A.W. Apical membrane antigen 1: A malaria vaccine candidate in review. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 24, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, N.; Okamura, M.; Igarashi, I. Erythrocyte invasion by Babesia parasites: Current advances in the elucidation of the molecular interactions between the protozoan ligands and host receptors in the invasion stage. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hötzel, I.; Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F.; Palmer, G.H. Genetic variation in the dimorphic regions of rap-1 genes and rap-1 loci of Babesia bigemina. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1997, 90, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, S.D.; Boothroyd, J.C. The α- and β-tubulins of Toxoplasma gondii are encoded by single-copy genes containing multiple introns. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1988, 26, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delves, C.J.; Ridley, R.G.; Goman, M.; Holloway, S.P.; Hyde, J.E.; Scaife, J.G. Cloning of β-tubulins gene from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Microbiol. 1989, 3, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar]

| Target Gene | Assay | Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Annealing | Product Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpeI-AvaI | PCR | BiIA | CATCTAATTTCTCTCCATACCCCTCC | 55 °C | 278 bp | [14] |
| BiIB | CCTCGGCTTCAACTCTGATGCCAAAG | [14] | ||||
| nPCR | BiIAN | CGCAAGCCCAGCACGCCCCGGTGC | 59 °C | 170 bp | [14] | |
| BiIBN | CCGACCTGGATAGGCTGTGTGATG | [14] | ||||
| BgRAP-1 | PCR | BigRAP1 | GTTATGTCAGCAGAGGTGGTTGGA | 70.5 °C | 564 bp | This study |
| BigRAP2 | ACCGAACAGGCGAGTTGTGAA | This study | ||||
| nPCR | BigRAP3 | GAGGTTGTCAATGCTGAAATGGAAGC | 71.5 °C | 472 bp | This study | |
| BigRAP4 | ACTTAGCCGCCGTAAAGTCAACG | This study | ||||
| BgAMA-1 | PCR | BigAmaF | CGTATGCCCACAGGAAAATGC | 62 °C | 1046 bp | This study |
| BigAmaR | GTTTTCATGTTGAGAGCGGTGG | This study | ||||
| nPCR | BigAmaFN | CGGACTTCCTCGAACCGAT | 66 °C | 765 bp | This study | |
| BigAmaRN | CGTAGTTCGCCCAGTTCATACC | This study | ||||
| BgβTUB | PCR | BtBigA | CTCTGACGAGCATGGAATCG | 48.5 °C | 408 bp | This study |
| BtBigB | CTTTGGCCCAGTTGTTACCAG | This study | ||||
| nPCR | BtBigAN | CATGGCAGCCTGAAGCTTTG | 67 °C | 302 bp | This study | |
| BtBigBN | CGAAATTGTCGGGCCTGAAG | This study |
| Sample ID | Place of Origin | Collection Date | Source | Nested PCR Assay Results 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpeI-AvaI | BgRAP-1 | BgAMA-1 | BgβTUB | ||||
| K0500-10 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| KZN-C24 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| KZN-C25 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | – | + | – | + |
| KZN-C31 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| KZN-C50 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | – |
| KZN-C58 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| KZN-C60 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| ARUSHA | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| COCO2 | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| DIVA | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| NATALIE | KwaZulu-Natal | May 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| MP-C1 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| MP-C2 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| MP-C8 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | – |
| MP-C11 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| MP-C12 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | – |
| MP-C18 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | – | – | + | – |
| MP-C19 | Mpumalanga | June 2011 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| WC-723 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| WC-851 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| WC-10272 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| WC-10284 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| WC-11134 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| WC-BC8 | Western Cape | July 2012 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| FS-80 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| FS-156 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| FS-146 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| FS-189 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| FS-284 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| FS-289 | Free State | July 2005 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| GP-C1 | Gauteng | December 2009 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| GP-C2 | Gauteng | May 2010 | Bovine | – | + | – | – |
| GP-C3 | Gauteng | May 2010 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| GP-C7 | Gauteng | March 2010 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | + |
| GP-C9 | Gauteng | May 2010 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| GP-C19 | Gauteng | May 2010 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| EC-28A | Eastern Cape | May 2009 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| EC-37A | Eastern Cape | May 2009 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| EC-9B | Eastern Cape | May 2009 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| EC-19B | Eastern Cape | May 2009 | Bovine | + | + | – | ++ |
| NW-C2 | Northwest | March 2011 | Bovine | + | + | + | + |
| NW-C4 | Northwest | March 2011 | Bovine | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| NW-C7 | Northwest | June 2012 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| NW-C10 | Northwest | June 2012 | Bovine | + | + | – | – |
| NW-C17 | Northwest | June 2012 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| NC-1 | Northern Cape | August 2012 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| NC-8 | Northern Cape | August 2012 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| NC-20 | Northern Cape | August 2012 | Bovine | + | – | – | – |
| NC-24 | Northern Cape | August 2012 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| NC-41 | Northern Cape | August 2012 | Bovine | – | – | – | – |
| Sequences 1 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB481200 | 01 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.3 | 99.1 | 99.5 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.6 |
| GQ257738 | 02 | 100 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 100 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 100 | |
| GQ257739 | 03 | 100 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 99.9 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | ||
| GQ257740 | 04 | 100 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.9 | 98.9 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 98.8 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | |||
| HM543726 | 05 | 100 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.7 | ||||
| HM543727 | 06 | 100 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 98.8 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | |||||
| JN572799 | 07 | 100 | 99.1 | 98.7 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | ||||||
| JN572800 | 08 | 100 | 98.5 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | |||||||
| JN572801 | 09 | 100 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 98.8 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.1 | ||||||||
| KZN-C24 * | 10 | 100 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.2 | |||||||||
| MP-C1 * | 11 | 100 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.3 | ||||||||||
| MP-C11 * | 12 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | |||||||||||
| MP-C12 * | 13 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.5 | ||||||||||||
| DIVA * | 14 | 100 | 99.5 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 99.2 | 99.3 | |||||||||||||
| NW-C4 * | 15 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.9 | ||||||||||||||
| FS-146 * | 16 | 100 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.7 | |||||||||||||||
| FS-189 * | 17 | 100 | 100 | 99.9 | 100 | 100 | 99.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| WC-851 * | 18 | 100 | 99.9 | 100 | 100 | 99.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| WC-10284 * | 19 | 100 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||
| GP-C1 * | 20 | 100 | 100 | 99.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GP-C7 * | 21 | 100 | 99.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GP-C19 * | 22 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mtshali, P.S.; Mtshali, M.S. Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Babesia bigemina Isolates in Cattle from South Africa Based on BgRAP-1, BgAMA-1 and BgβTUB Genes. Biology 2025, 14, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040355
Mtshali PS, Mtshali MS. Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Babesia bigemina Isolates in Cattle from South Africa Based on BgRAP-1, BgAMA-1 and BgβTUB Genes. Biology. 2025; 14(4):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMtshali, Phillip Senzo, and Moses Sibusiso Mtshali. 2025. "Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Babesia bigemina Isolates in Cattle from South Africa Based on BgRAP-1, BgAMA-1 and BgβTUB Genes" Biology 14, no. 4: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040355
APA StyleMtshali, P. S., & Mtshali, M. S. (2025). Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Babesia bigemina Isolates in Cattle from South Africa Based on BgRAP-1, BgAMA-1 and BgβTUB Genes. Biology, 14(4), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040355






