Comparative Analysis of Microbial Communities in Each Developmental Stage of Dermacentor nuttalli in Two Regions in Inner Mongolia, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
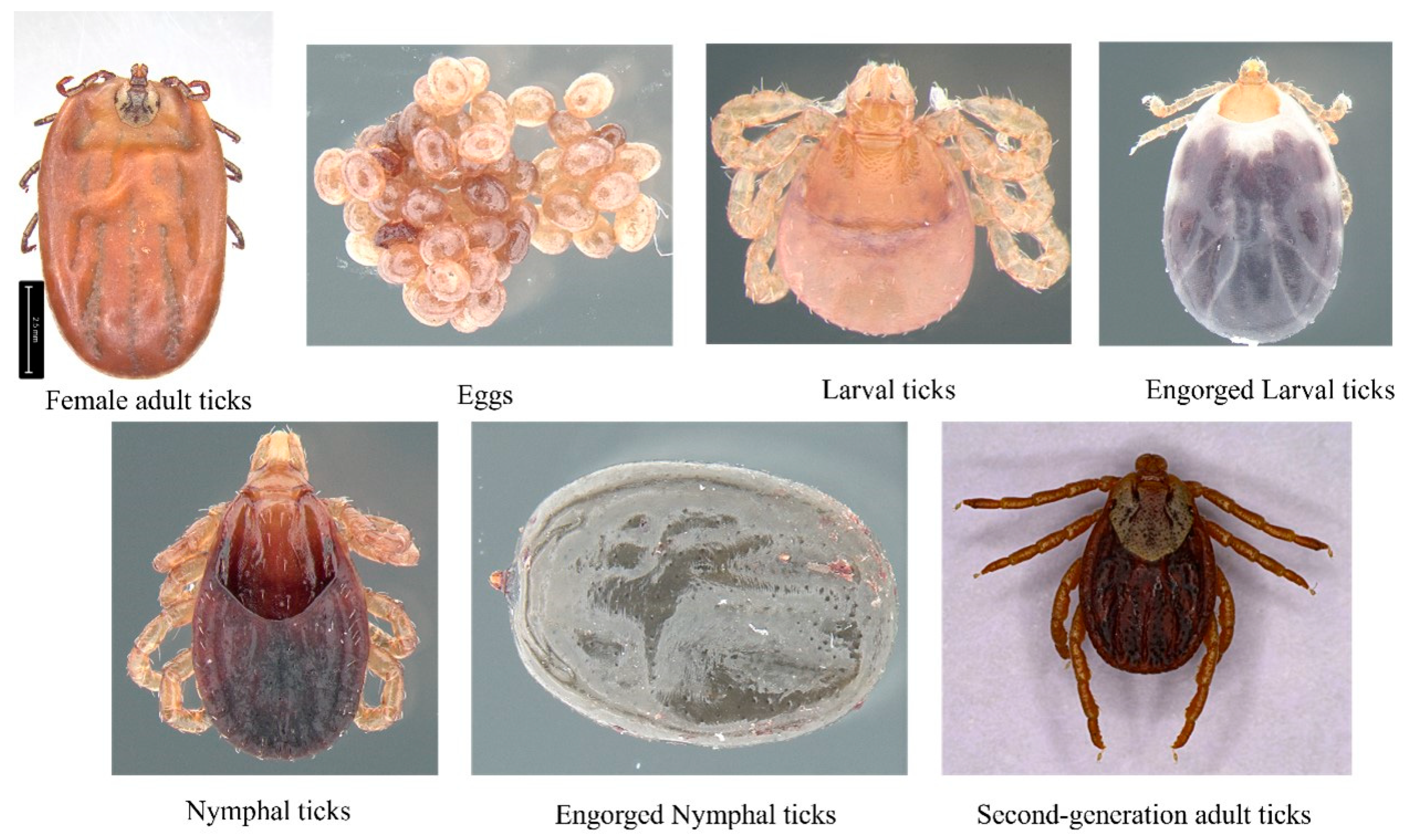
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA and RNA Extraction
2.3. Library Construction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Results of Illumina PE250
3.1.1. General Statistics
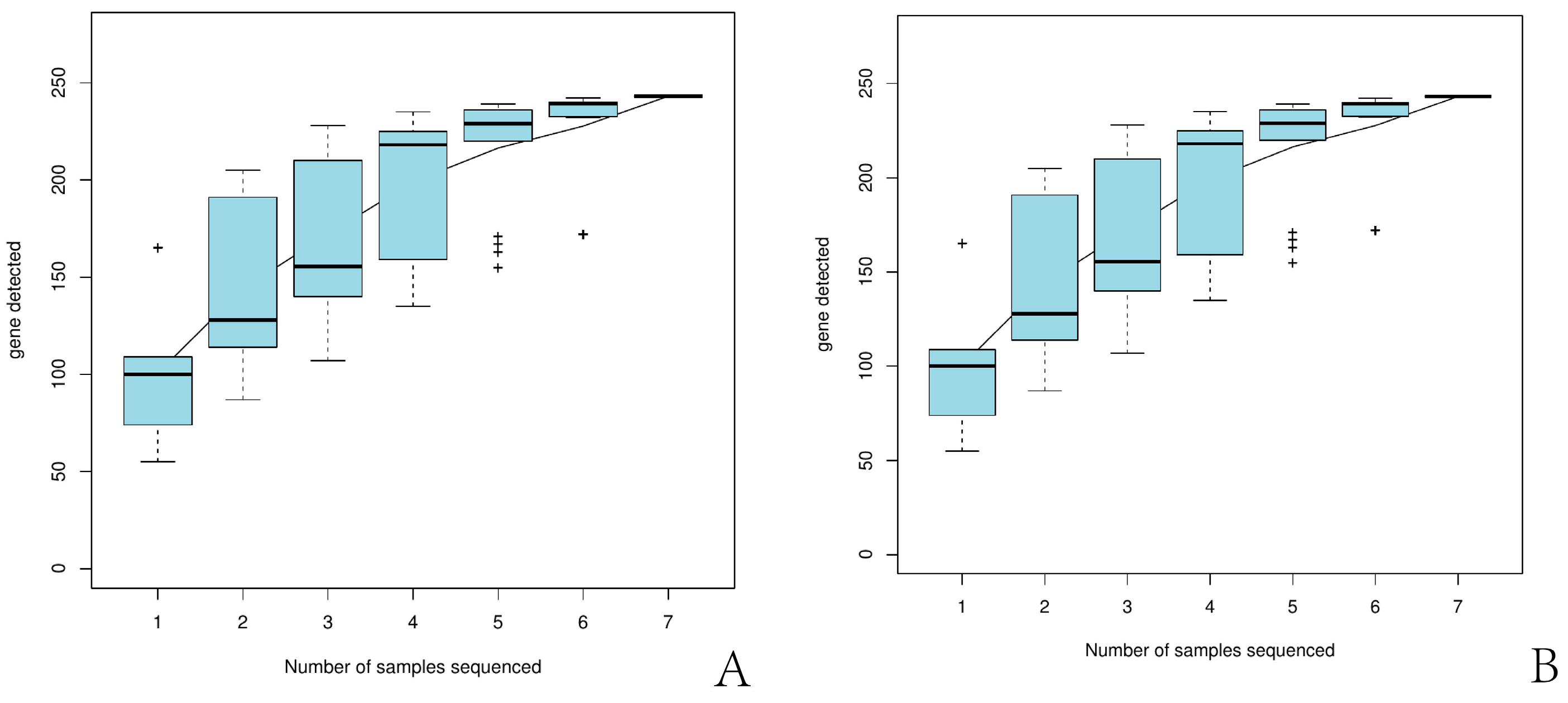
3.1.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis
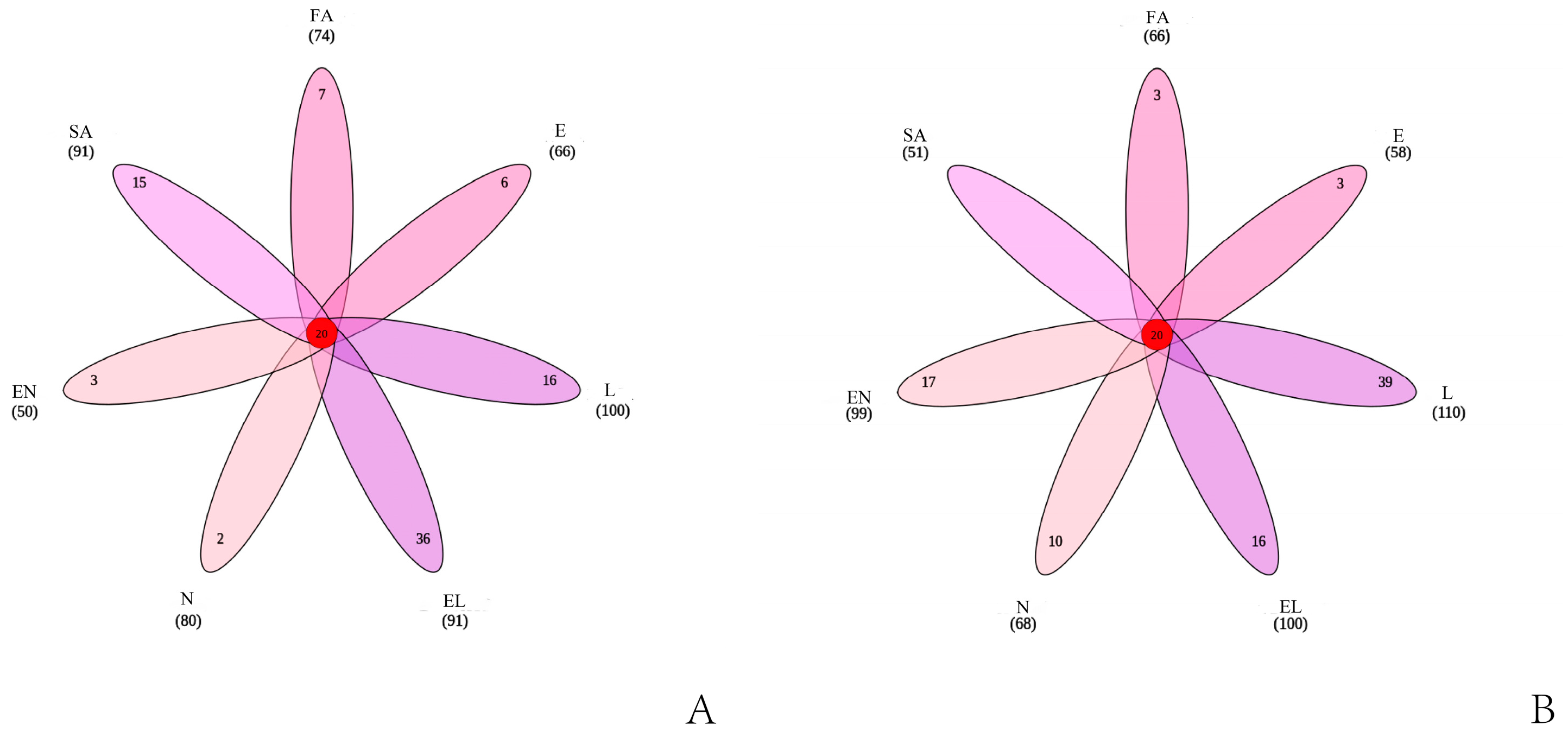
3.1.3. OTU Cluster Analysis
3.2. Microbial Population
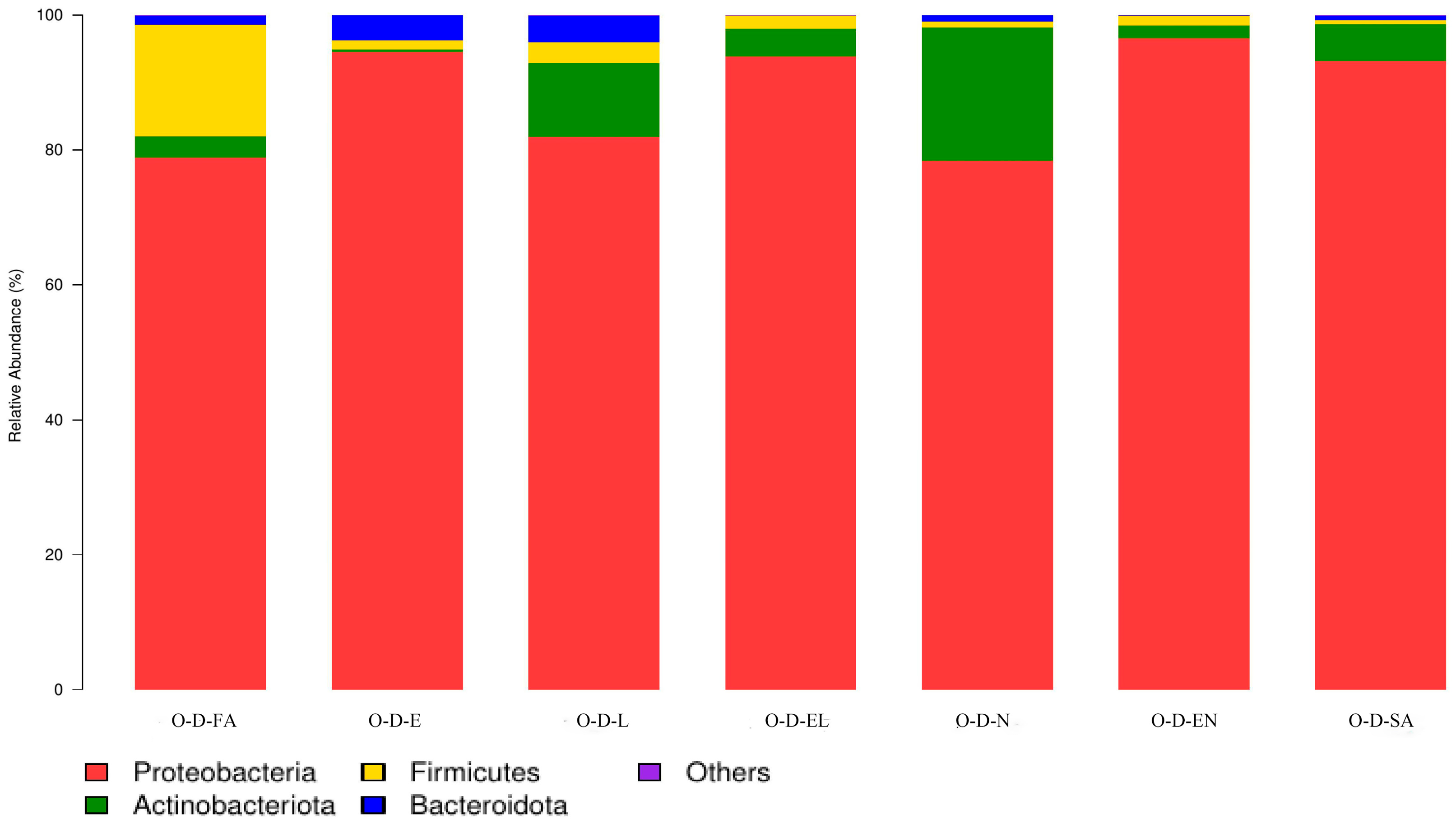
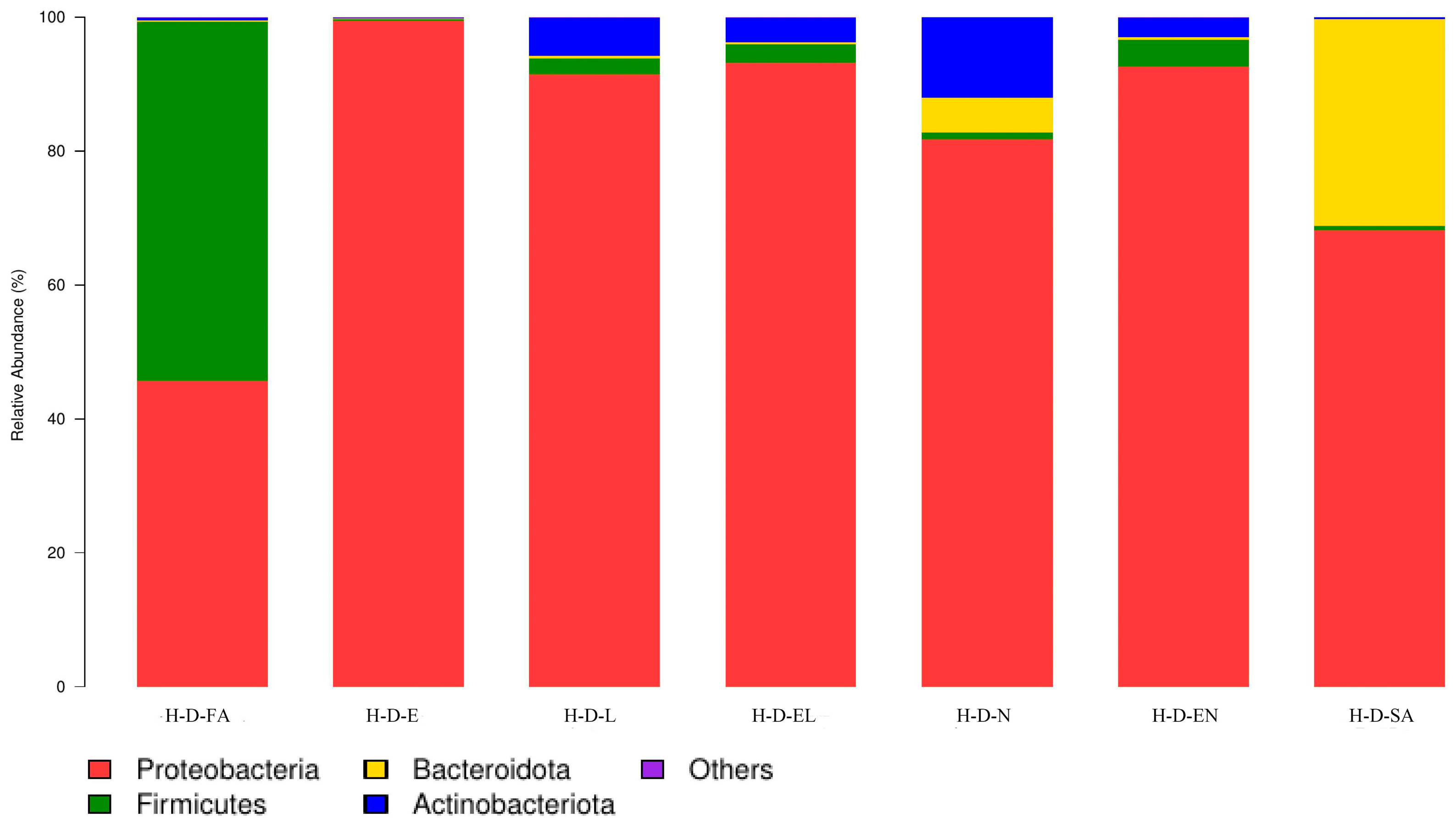
3.2.1. Microbial Community Composition at the Phylum Level
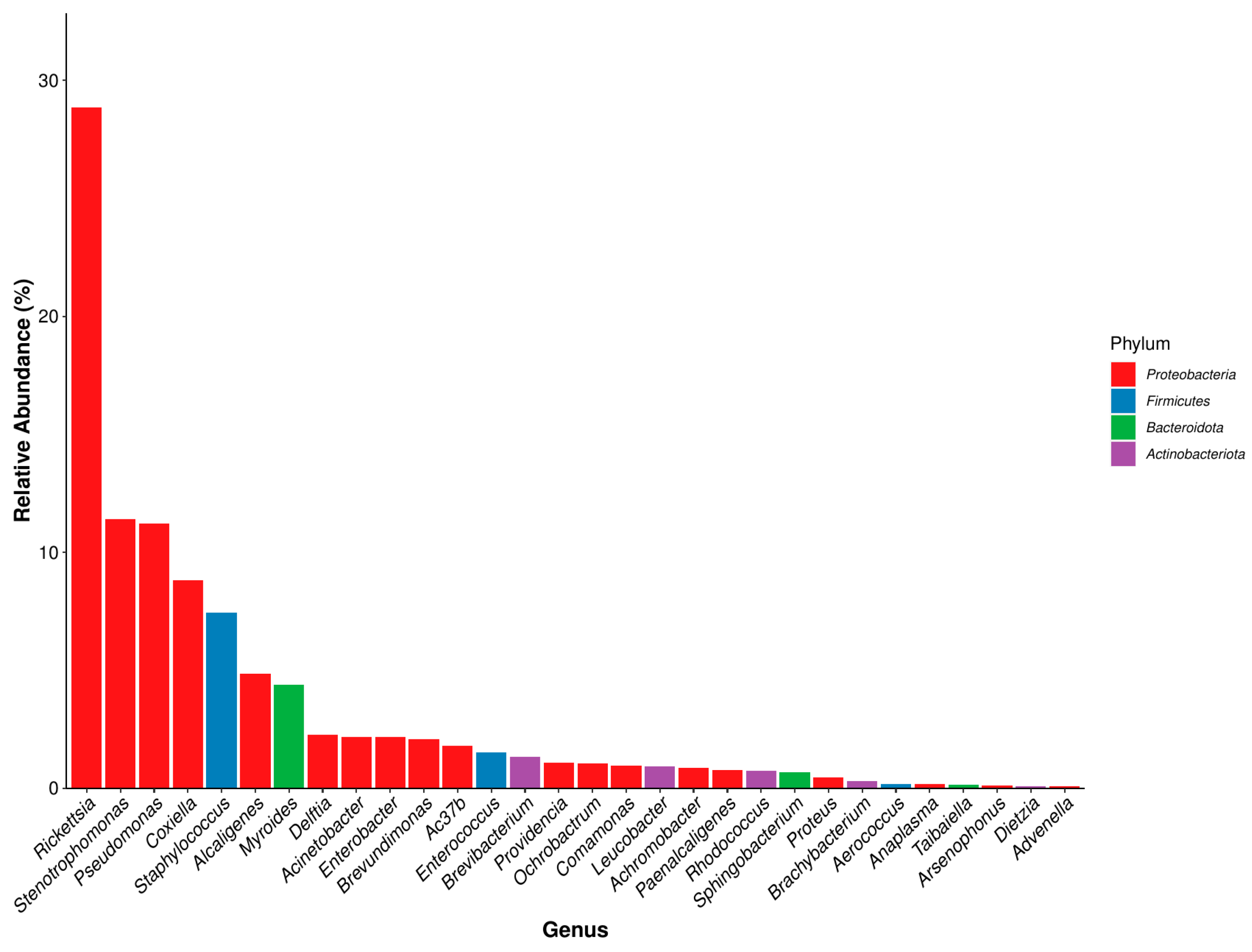
3.2.2. Microbial Community Composition at the Genus Level
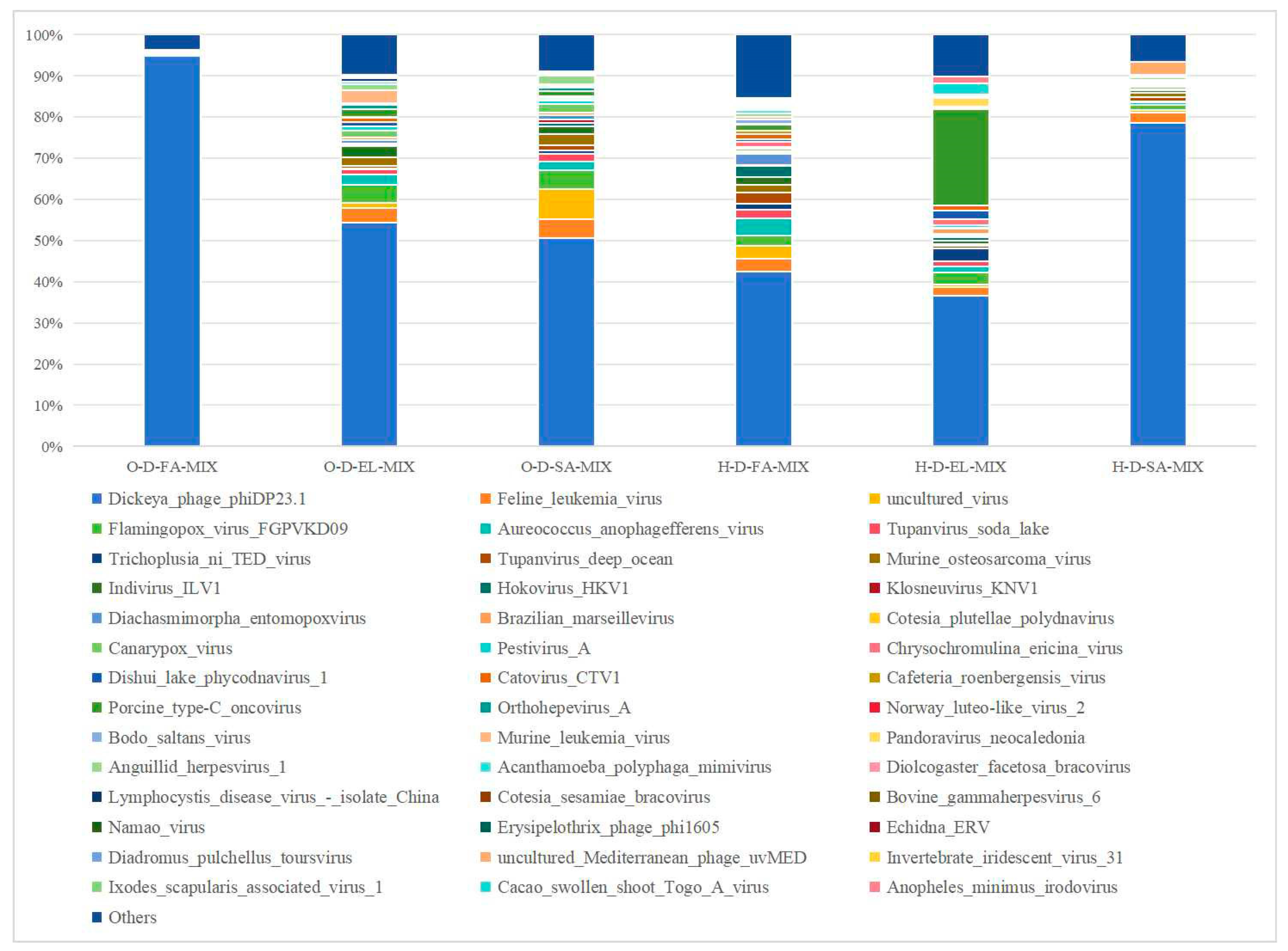
3.2.3. Microbial Community Composition at the Species Level
3.3. Illumina PE150 Sequencing Results
3.3.1. Species Classification Annotation Data
3.3.2. Species Composition at the Order Level
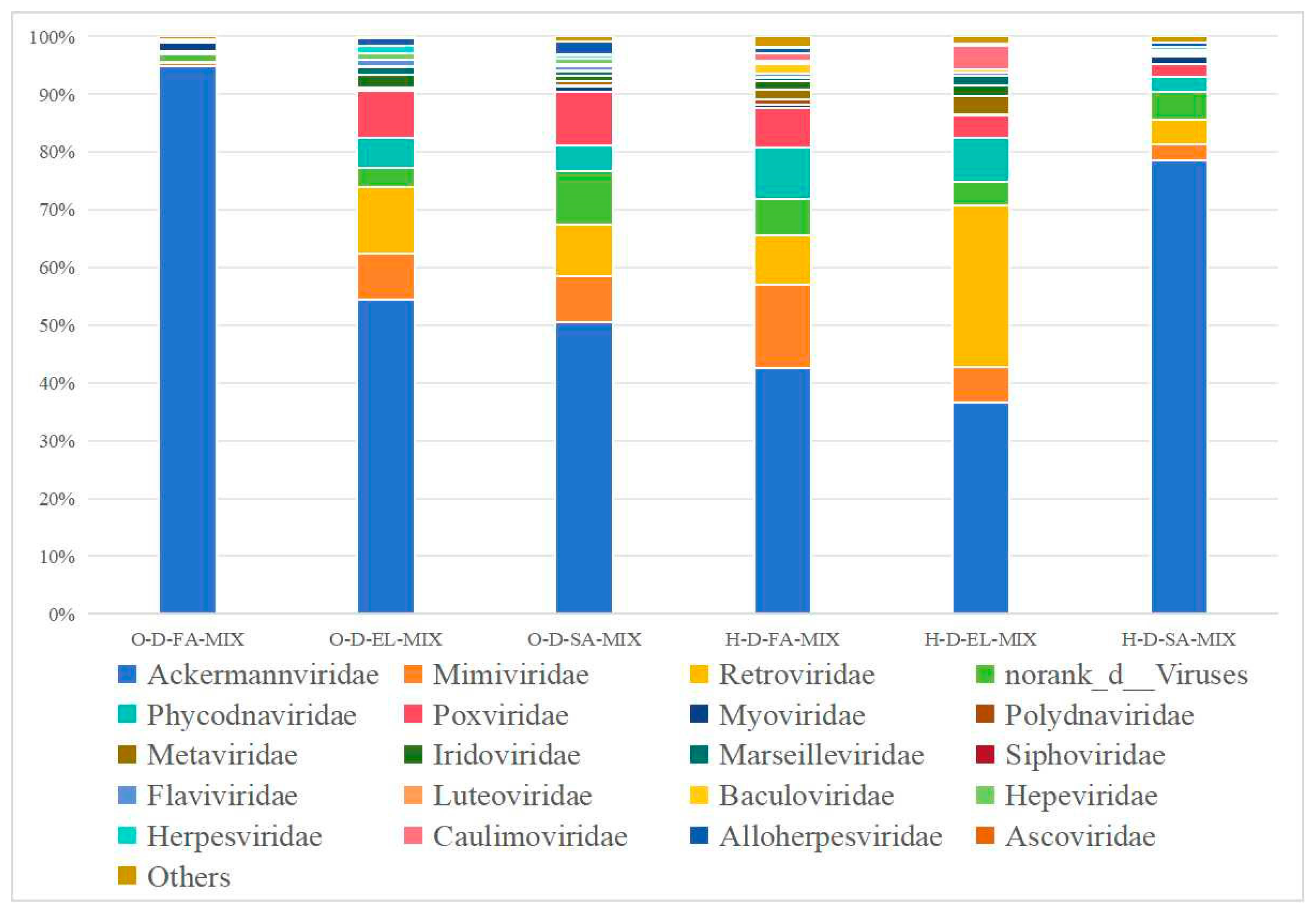
3.3.3. Species Composition at the Family Level
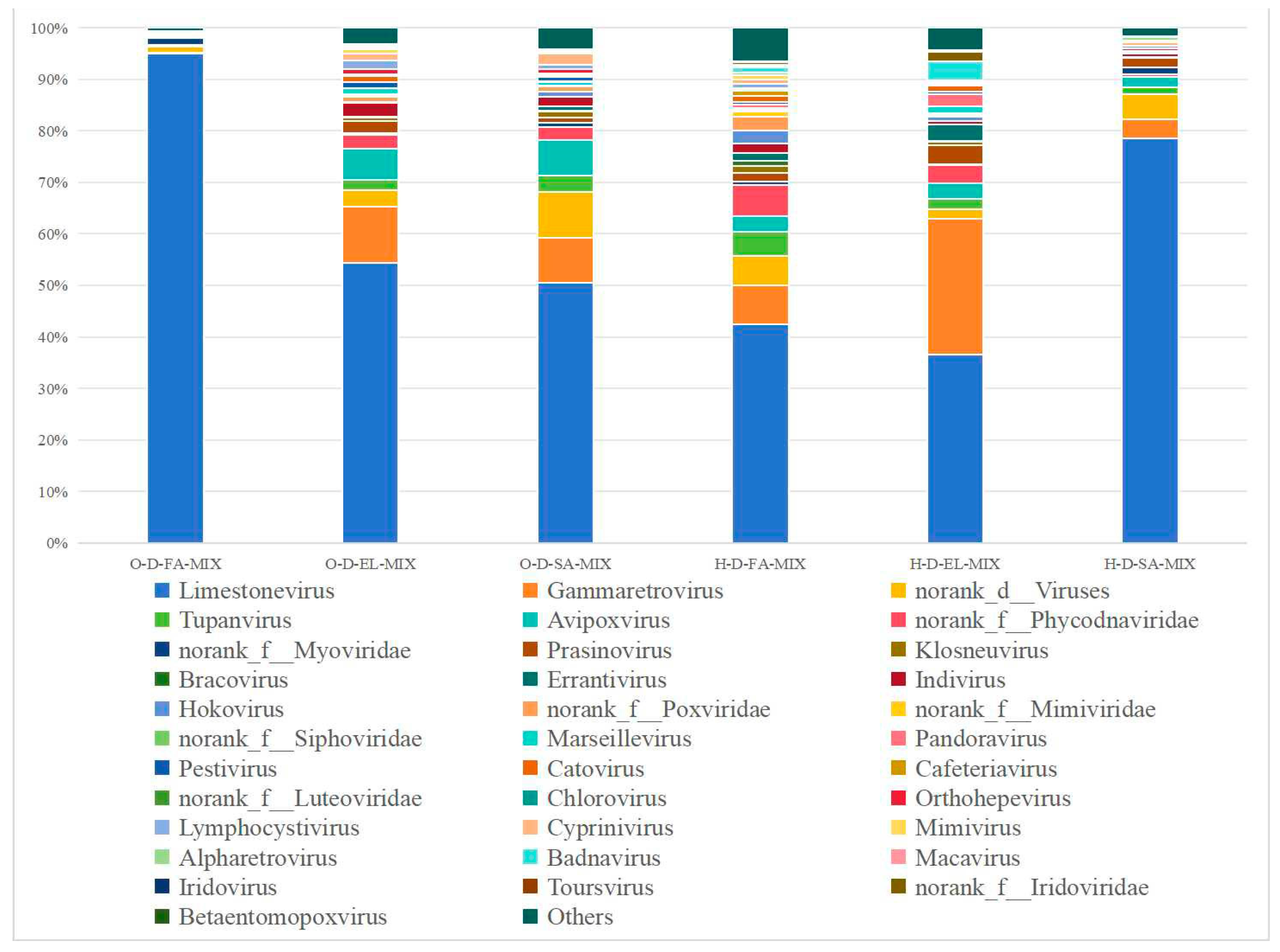
3.3.4. Species Composition at the Genus Level
3.3.5. Species Composition at the Species Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units. |
| ACE | abundance-based coverage estimator |
References
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Tick symbiosis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 62, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipe, D.T. Species concepts: What about ticks? Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Fan, Z.W.; Ji, Y.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, S.X.; Li, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Mapping ticks and tick-borne pathogens in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, J.Z. Ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea) in China: Geographical distribution, host diversity, and specificity. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 102, e21544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Cai, H.; Qi, D.; Zhang, S.; Fu, S.; Yu, J.; Si, X.; Cai, T.; Mao, R. Identification and genetic diversity analysis of Rickettsia in Dermacentor nuttalli within inner Mongolia, China. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; de la Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genomic insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, M.A.; Padilla, S.L.; Jamsransuren, D.; Koehler, J.W.; Delp, K.L.; Adiyadorj, D.; Baasandagwa, U.; Jigjav, B.; Olschner, S.P.; Minogue, T.D.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, Mongolia, 2013–2014. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2018, 24, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, Y.S.; Jiang, B.G.; Ye, R.Z.; Chang, Q.C.; Shao, H.Z.; Cui, X.M.; Xu, D.L.; Li, L.F.; Wei, W.; et al. Prevalence of multiple tick-borne pathogens in various tick vectors in Northeastern China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkhtaivan, B.; Narantsatsral, S.; Davaasuren, B.; Otgonsuren, D.; Amgalanbaatar, T.; Uuganbayar, E.; Zoljargal, M.; Myagmarsuren, P.; Suganuma, K.; Molefe, N.I.; et al. Molecular detection of Anaplasma ovis in small ruminants and ixodid ticks from Mongolia. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 69, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, S.; Ding, C.; Cao, M.; Kawabata, H.; Sato, K.; Ando, S.; Fujita, H.; Kawamori, F.; Su, H.; et al. Spotted fever group rickettsiae in inner Mongolia, China, 2015–2016. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2018, 24, 2105–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Fricken, M.E.; Qurollo, B.A.; Boldbaatar, B.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, R.R.; Lkhagvatseren, S.; Koehler, J.W.; Moore, T.C.; Nymadawa, P.; Anderson, B.D.; et al. Genetic diversity of anaplasma and ehrlichia bacteria found in dermacentor and ixodes ticks in Mongolia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Fricken, M.E.; Voorhees, M.A.; Koehler, J.W.; Asbun, C.; Lam, B.; Qurollo, B.; Hogan, K.M.; Baasandagva, U.; Jigjav, B.; Schoepp, R.J. Molecular characteristics of rickettsia in ticks collected along the Southern Border of Mongolia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lv, X.L.; Han, S.Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Song, M. First detection of Borrelia miyamotoi infections in ticks and humans from the northeast of Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Trop. 2021, 217, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, M.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Galon, E.M.; Guo, Q.; Rizk, M.A.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; et al. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens harbored by ticks collected from livestock in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.N.; Chen, C.F.; Yang, M.H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Hornok, S.; Makhatov, B.; Rizabek, K.; Wang, Y. Diversity of Rickettsia species in border regions of northwestern China. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Bai, X.; Hu, B.; Shi, N.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; et al. Molecular evidence of the spotted fever group Rickettsiae in ticks from Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 80, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.W.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, W.J.; Huang, H.L.; Yan, J. Distribution and molecular characterization of rickettsiae in ticks in Harbin area of Northeastern China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Lin, H.L.; Xu, X.F.; Ren, Q.Y.; Aizezi, M.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tan, Y.C.; et al. Coxiella burnetii is widespread in ticks (Ixodidae) in the Xinjiang areas of China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Yang, J.F.; Niu, Q.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Chen, Z.; Kan, W.; Hu, G.W.; Liu, G.Y.; Luo, J.X.; Yin, H. Molecular prevalence of spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks from Qinghai Province, northwestern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.D.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.N.; Liu, Q. Prevalence and Identification of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Genospecies in Ticks from Northeastern China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Huang, S.J.; Wang, Z.D.; Wei, F.; Feng, X.M.; Jiang, D.X.; Liu, Q. Isolation and genomic characterization of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in ticks from northeastern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 17339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Wang, Q.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Song, S.; Chen, C.; Tu, C.; Wureli, H.; Wang, Y. Detection of Babesia spp. Theileria spp. and Anaplasma ovis in Border Regions, northwestern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.D.; Dong, Z.H.; Xie, S.S.; Jiang, M.M.; Song, R.X.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, K.C.; et al. A tentative tamdy orthonairovirus related to febrile illness in Northwestern China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narankhajid, M.; Yeruult, C.; Gurbadam, A.; Battsetseg, J.; Aberle, S.W.; Bayartogtokh, B.; Joachim, A.; Duscher, G.G. Some aspects on tick species in Mongolia and their potential role in the transmission of equine piroplasms, Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi L. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 355766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Duan, X.M.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Kou, C.; Liu, D.; et al. A novel tickborne phlebovirus, closely related to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus and Heartland virus, is a potential pathogen. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Hong, M.; Cui, M.Y.; Gui, Z.; Ma, S.; Wu, L.; Xing, L.; Mu, L.; Yu, J.; Fu, S.; et al. Microbial diversity of ticks and a novel typhus group Rickettsia species (Rickettsiales bacterium Ac37b) in Inner Mongolia, China. Parasite 2023, 30, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Song, F.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ci, Y.; Cheng, X.; Nie, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Epidemiological and Molecular Study on Tick-Borne Pathogens in Argun Port Area Near the Chinese–Russian Border. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.; Kwak, D.; Nyamsuren, O.; Guugandaa, N.; Seo, M.G. Tick-borne pathogens in Mongolian ticks: The high prevalence of Rickettsia raoultii and its public health implications. Acta Trop. 2024, 260, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Geriletu. A novel arthropod host of brucellosis in the arid steppe ecosystem. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 566253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodilov, I.; Belova, O.; Burenkova, L.; Korotkov, Y.; Romanova, L.; Morozova, L.; Kudriavtsev, V.; Gmyl, L.; Belyaletdinova, I.; Chumakov, A.; et al. Ixodid ticks and tick-borne encephalitis virus prevalence in the South Asian part of Russia (Republic of Tuva). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Litov, A.G.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Makenov, M.T.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Aibulatov, S.V.; Bazarova, G.K.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; et al. Geographical and tick-dependent distribution of flavi-like Alongshan and Yanggou Tick viruses in Russia. Viruses 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.; Myalkhaa, M.; Krücken, J.; Battsetseg, G.; Batsukh, Z.; Baumann, M.P.O.; Clausen, P.; Nijhof, A. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in bovine blood and ticks from Khentii, Mongolia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67 (Suppl. S2), 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Lu, Q.; Xu, G.; Luo, Y.; Ni, X.; Zhou, E.M. Molecular detection of spotted fever group rickettsiae in hard ticks, northern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, M.H.; Jiang, M.M.; Yan, B.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, W.; Wang, B.; Hornok, S.; Wang, Y. Rickettsia raoultii and Rickettsia sibirica in ticks from the long-tailed ground squirrel near the China-Kazakhstan border. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 77, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, T.C.; Pulscher, L.A.; Caddell, L.; von Fricken, M.E.; Anderson, B.D.; Gonchigoo, B.; Gray, G.C.; Gonchigoo, B. Evidence for transovarial transmission of tick-borne rickettsiae circulating in Northern Mongolia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Lu, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Ou, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Identification of tickborne pathogens by metagenomic next-generation sequencing in Dermacentor nuttalli and Ixodes persulcatus in Inner Mongolia, China. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkov, V.G.; Dolgova, A.S.; Safonova, M.V.; Samoilov, A.E.; Belova, O.A.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Matsvay, A.D.; Speranskaya, A.S.; Khafizov, K.; Karganova, G.G. Isolation and characterization of Wad Medani virus obtained in the tuva Republic of Russia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Ding, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; He, B.; Tu, C. Virome analysis of tick-borne viruses in Heilongjiang Province, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Ji, Y.X.; Sun, S.R.; Yue, X.H.; Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Moming, A.; Song, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, R.F.; et al. Bacterial microbiota in unfed ticks (Dermacentor nuttalli) from Xinjiang detected through 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing and culturomics. Zoonoses 2021, 12, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Matulis, G.A.; Sakolvaree, J.; Boldbaatar, B.; Cleary, N.; Takhampunya, R.; Poole-Smith, B.K.; Lilak, A.A.; Altantogtokh, D.; Tsogbadrakh, N.; Chanarat, N.; et al. Applying next generation sequencing to detect tick-pathogens in Dermacentor nuttalli, Ixodes persulcatus, and Hyalomma asiaticum collected from Mongolia. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, R.; Gao, A.; Jiang, N.; Sang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Feng, X. Deciphering the microbial communities in ticks of Inner Mongolia: Ecological determinants and pathogen profiles. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Cui, M.Y.; Xing, L.L.; Gao, R.J.; Mu, L.; Hong, M.; Guo, Q.Q.; Ren, H.; Yu, J.F.; Si, X.Y.; et al. Metatranscriptomic analysis reveals the diversity of RNA viruses in ticks in Inner Mongolia, China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Cui, M.Y.; Gui, Z.; Guo, Q.Q.; Ren, H.; Ma, S.F.; Mu, L.; Yu, J.F.; Fu, S.Y.; Qi, D.D. First detection of Candidatus Rickettsia tarasevichiae in Hyalomma marginatum ticks. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.M.; Yang, B.; Han, W.X.; Zhao, W.H.; Chai, H.L.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhan, Y.J.; Wang, L.F.; Xing, Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of microbial communities in different growth stages of Dermacentor nuttalli. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1021426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.Y.; Cheng, T.Y. Determination of the microbial community features of Haemaphysalis flava in different developmental stages by high-throughput sequencing. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Ma, Y.M.; Tian, H.O.; Yang, B.; Han, W.X.; Zhao, W.H.; Chai, H.L.; Zhang, Z.S.; Wang, L.F.; Chen, L.; et al. First determination of DNA virus and some additional bacteria from Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) in Tibet, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 988136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhu, W.Y.; Mao, S.Y. Comparative studies of the composition of bacterial microbiota associated with the ruminal content, ruminal epithelium and in the faeces of lactating dairy cows. Microb Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Vijayan, R.; Al-Deeb, M.A. Microbial communities associated with the camel tick, Hyalomma dromedarii: 16S rRNA gene-based analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, R.; Tagliafierro, T.; Sameroff, S.; Cucura, D.M.; Oleynik, A.; Che, X.; Jain, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Microbiome analysis of Ixodes scapularis ticks from New York and Connecticut. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurfield, N.; Grewal, S.; Cua, L.S.; Torres, P.J.; Kelley, S.T. Endosymbiont interference and microbial diversity of the Pacific coast tick, Dermacentor occidentalis, in San Diego County, California. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, S.; Yi, M.; Kim, M.; Yun, S.; Choi, J.H.; Yoon, M.; Yong, T.-S.; Lee, B.; Noh, K.T.; et al. Comparative microbiome analysis of Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks at the Korea Combat Training Center in 2022. Entomol. Res. 2023, 53, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyedem, H.; Lekired, A.; Mhadhbi, M.; Dhibi, M.; Romdhane, R.; Chaari, S.; Rekik, M.; Ouzari, H.I.; Hajji, T.; Darghouth, M.A.; et al. First insights into the microbiome of Tunisian Hyalomma ticks gained through next-generation sequencing with a special focus on H. scupense. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budachetri, K.; Browning, R.E.; Adamson, S.W.; Dowd, S.E.; Chao, C.C.; Ching, W.M.; Karim, S. An insight into the microbiome of the Amblyomma maculatum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budachetri, K.; Gaillard, D.; Williams, J.; Mukherjee, N.; Karim, S. A snapshot of the microbiome of Amblyomma tuberculatum ticks infesting the gopher tortoise, an endangered species. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lao, Y.; Liu, S.; Ai, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Kang, M.; Li, j.; Sun, Y. The diurnal salivary glands transcriptome of Dermacentor nuttalli from the first four days of blood feeding. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkerhoff, R.J.; Clark, C.; Ocasio, K.; Gauthier, D.T.; Hynes, W.L. Factors affecting the microbiome of Ixodes scapularis and Amblyomma americanum. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duron, O.; Morel, O.; Noël, V.; Buysse, M.; Binetruy, F.; Lancelot, R.; Loire, E.; Ménard, C.; Bouchez, O.; Vavre, F.; et al. Tick-Bacteria Mutualism Depends on B Vitamin Synthesis Pathways. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1896–1902.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu-Chuang, A.; Hodžić, A.; Mateos-Hernández, L.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Obregon, D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Current debates and advances in tick microbiome research. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2021, 1, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeghaire, S.; Argudín, M.A.; Feßler, A.T.; Hauschild, T.; Schwarz, S.; Butaye, P. The ecological importance of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group as a reservoir for resistance and virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.C.; Chu, Y.L.; Buysse, M.; Binetruy, F.; Lancelot, R.; Loire, E.; Ménard, C.; Bouchez, O.; Vavre, F.; et al. Skin infectome of patients with a tick bite history. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1113992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, J.; You, Y.; Tan, J.; Shen, H. Distribution characteristics of Staphylococcus spp. in different phases of periprosthetic joint infection: A review. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, S.I.; Binetruy, F.; Hernández-Jarguín, A.M.; Duron, O. The Tick Microbiome: Why Non-pathogenic Microorganisms Matter in Tick Biology and Pathogen Transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Ferreira, E.; Vizzoni, V.F.; Balsemão-Pires, E.; Moerbeck, L.; Gazeta, G.S.; Piesman, J.; Voloch, C.M.; Soares, C.A.G. Coxiella symbionts are widespread into hard ticks. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4691–4699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.M.; Li, N.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Qiu, Z.X.; Li, Y.; Li, L.W.; Liu, J.Z. Endosymbiont CLS-HI plays a role in reproduction and development of Haemaphysalis longicornis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 73, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Jasinskas, A.; Barbour, A.G. Antibiotic treatment of the tick vector Amblyomma americanum reduced reproductive fitness. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.Y.; Liu, G.H. PCR denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis as a useful method to identify of intestinal bacteria flora in Haemaphysalis flava ticks. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, K.R.; Macedo, A.J.; Nicastro, G.G.; Baldini, R.L.; Termignoni, C. Egg wax from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, R.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Hynes, W.L. Control of bacterial infections in the hard tick Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae): Evidence for the existence of antimicrobial proteins in tick hemolymph. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessard, C. Classics in infectious diseases. On the blue and green coloration that appears on bandages. By Carle Gessard (1850–1925). Rev. Infect. Dis. 1984, 6, S775–S776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartíková, P.; Holíková, V.; Kazimírová, M.; Štibrániová, I. Tick-borne viruses. Acta Virol. 2017, 61, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Fikrig, E. Tick microbiome: The force within. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, S.; Bartolini, S.; Morandi, F.; Cuteri, V.; Preziuso, S. Genotyping of Pestivirus A (Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus 1) detected in faeces and in other specimens of domestic and wild ruminants at the wildlife-livestock interface. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 235, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterhans, E.; Jungi, T.W.; Schweizer, M. BVDV and innate immunity. Biologicals 2003, 31, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. Elife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xie, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Human Tacheng Tick Virus 2 Infection, China, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.J. African swine fever: An unprecedented disaster and challenge to China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Pan, J.; Zhang, G. African swine fever virus in Asia: Its rapid spread and potential threat to unaffected countries. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golnar, A.J.; Martin, E.; Wormington, J.D.; Kading, R.C.; Teel, P.D.; Hamer, S.A.; Hamer, G.L. Reviewing the Potential Vectors and Hosts of African Swine Fever Virus Transmission in the United States. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Bei, J.L.; Jin, X.F.; Dou, W.H.; Ji, H.S.; Duan, Y.J.; Yang, X.J.; Gao, S.; et al. DNA segments of African Swine Fever Virus detected for the first time in hard ticks from sheep and bovines. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.I.; Bouhsira, E.; De Regge, N.; Fite, J.; Etoré, F.; Garigliany, M.; Jori, F.; Lempereur, L.; Le Potier, M.; Quillery, E.; et al. Putative Role of Arthropod Vectors in African Swine Fever Virus Transmission in Relation to Their Bio-Ecological Properties. Viruses 2020, 12, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Cheng, T.Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, F. Identification of intestinal bacterial flora in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks by conventional methods and PCR-DGGE analysis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 66, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams-Newkirk, A.J.; Rowe, L.A.; Mixson-Hayden, T.R.; Dasch, G.A. Characterization of the bacterial communities of life stages of free living lone star ticks (Amblyomma americanum). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, K.; Klyachko, O.; Grindle, N.; Civitello, D.; Oleske, D.; Fuqua, C. Microbial communities and interactions in the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4371–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swei, A.; Kwan, J.Y. Tick microbiome and pathogen acquisition altered by host blood meal. ISME J. 2017, 11, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heise, S.R.; Elshahed, M.S.; Little, S.E. Bacterial diversity in Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) with a focus on members of the genus Rickettsia. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Yang, Z.N.; Lu, B.; Ma, X.F.; Zhang, C.X.; Xu, H.J. The composition and transmission of microbiome in hard tick, Ixodes persulcatus, during blood meal. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, G.; Cagnacci, F.; Wittekindt, N.E.; Zhao, F.; Qi, J.; Tomsho, L.P.; Drautz, D.I.; Rizzoli, A.; Schuster, S.C. Metagenomic profile of the bacterial communities associated with Ixodes ricinus ticks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Region | Sample | Sequences | Bases (bp) | Average Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordos | O-D-EN | 41,334 | 17,437,036 | 421.86 |
| O-D-EL | 255,821 | 107,654,007 | 420.82 | |
| O-D-SA | 62,405 | 26,458,024 | 423.97 | |
| O-D-E | 33,565 | 14,034,524 | 418.13 | |
| O-D-N | 59,702 | 25,172,642 | 421.64 | |
| O-D-FA | 36,789 | 15,430,339 | 419.43 | |
| O-D-L | 73,069 | 30,818,614 | 421.77 | |
| Hinggan League | H-D-EN | 30,495 | 12,936,993 | 424.23 |
| H-D-EL | 28,435 | 11,635,803 | 409.21 | |
| H-D-SA | 131,101 | 55,929,480 | 426.61 | |
| H-D-E | 60,090 | 24,652,783 | 410.26 | |
| H-D-N | 80,153 | 33,865,155 | 422.51 | |
| H-D-FA | 68,050 | 28,708,458 | 421.87 | |
| H-D-L | 36,736 | 15,595,860 | 424.54 |
| Region | Sample ID | Reads | 0.97 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU | Ace | Chao | Coverage | Shannon | Simpson | |||
| Ordos | O-D-FA | 27,346 | 74 | 94 | 81 | 0.999525 | 2.46 | 0.1424 |
| O-D-E | 30,080 | 68 | 84 | 83 | 0.999501 | 1.28 | 0.3973 | |
| O-D-L | 57,407 | 109 | 113 | 113 | 0.999843 | 2.58 | 0.1732 | |
| O-D-EL | 245,845 | 165 | 171 | 169 | 0.999943 | 1.17 | 0.467 | |
| O-D-N | 52,228 | 89 | 102 | 101 | 0.999713 | 1.96 | 0.2667 | |
| O-D-EN | 37,595 | 55 | 61 | 59 | 0.999787 | 1.61 | 0.3281 | |
| O-D-SA | 53,541 | 100 | 107 | 103 | 0.999813 | 2.19 | 0.1792 | |
| Hinggan League | H-D-FA | 60,335 | 75 | 81 | 81 | 0.999834 | 1.77 | 0.2695 |
| H-D-E | 55,182 | 68 | 77 | 75 | 0.999783 | 0.88 | 0.6072 | |
| H-D-L | 32,873 | 123 | 139 | 132 | 0.999331 | 1.81 | 0.2977 | |
| H-D-EL | 25,539 | 100 | 109 | 107 | 0.999452 | 1.52 | 0.4618 | |
| H-D-N | 66,081 | 84 | 94 | 95 | 0.999818 | 2.81 | 0.0814 | |
| H-D-EN | 21,434 | 99 | 108 | 106 | 0.999347 | 2.38 | 0.1461 | |
| H-D-SA | 113,346 | 71 | 79 | 76 | 0.999912 | 1.99 | 0.1888 | |
| Region | Sample | Proteobacteria (%) | Actinobacteria (%) | Firmicutes (%) | Bacteroidetes (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordos | O-D-FA | 78.81 | 3.19 | 16.55 | 1.42 | 0.03 |
| O-D-E | 94.56 | 0.35 | 1.32 | 3.76 | — | |
| O-D-L | 81.91 | 11.00 | 3.04 | 4.04 | — | |
| O-D-EL | 93.86 | 4.11 | 1.98 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| O-D-N | 78.32 | 19.85 | 0.90 | 0.94 | — | |
| O-D-EN | 96.49 | 1.99 | 1.47 | 0.05 | — | |
| O-D-SA | 93.13 | 5.49 | 0.61 | 0.76 | 0.01 | |
| Total proportion | 88.16 | 6.57 | 3.69 | 1.57 | 0.01 | |
| Hinggan League | H-D-FA | 45.64 | 53.70 | 0.21 | 0.44 | — |
| H-D-E | 99.43 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.18 | — | |
| H-D-L | 91.42 | 2.39 | 0.37 | 5.71 | 0.11 | |
| H-D-EL | 93.17 | 2.78 | 0.33 | 3.62 | 0.11 | |
| H-D-N | 81.74 | 1.07 | 5.13 | 12.06 | — | |
| H-D-EN | 92.57 | 4.10 | 0.31 | 2.98 | 0.04 | |
| H-D-SA | 68.17 | 0.68 | 30.82 | 0.33 | — | |
| Total proportion | 81.73 | 9.29 | 5.32 | 3.62 | 0.04 |
| Region | Sample | Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordos | O-D-FA-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 4 | 24 | 48 | 77 |
| O-D-EL-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 5 | 22 | 49 | 75 | |
| O-D-SA-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 4 | 18 | 47 | 91 | |
| Total | - | - | - | 4 | 26 | 61 | 126 | |
| Hinggan League | H-D-FA-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 5 | 18 | 35 | 61 |
| H-D-EL-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 5 | 20 | 42 | 66 | |
| H-D-SA-MIX | norank | norank | norank | 6 | 28 | 49 | 129 | |
| Total | - | - | - | 6 | 28 | 49 | 135 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Dong, X.-N.; Cui, H.; Sun, L.-Y.; Mu, R.; Nie, M.; Kang, J.-M.; Bu, N.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Qi, Z.-H.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Communities in Each Developmental Stage of Dermacentor nuttalli in Two Regions in Inner Mongolia, China. Biology 2025, 14, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060613
Zhao L, Dong X-N, Cui H, Sun L-Y, Mu R, Nie M, Kang J-M, Bu N, Zhang Y-S, Qi Z-H, et al. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Communities in Each Developmental Stage of Dermacentor nuttalli in Two Regions in Inner Mongolia, China. Biology. 2025; 14(6):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060613
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Xiao-Nan Dong, Hao Cui, Lian-Yang Sun, Ren Mu, Ming Nie, Jia-Mei Kang, Nan Bu, Yi-Shuai Zhang, Ze-Hao Qi, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Microbial Communities in Each Developmental Stage of Dermacentor nuttalli in Two Regions in Inner Mongolia, China" Biology 14, no. 6: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060613
APA StyleZhao, L., Dong, X.-N., Cui, H., Sun, L.-Y., Mu, R., Nie, M., Kang, J.-M., Bu, N., Zhang, Y.-S., Qi, Z.-H., Li, Z.-X., Zhang, Z.-L., Zhang, X.-Y., Ding, Y.-L., Wang, R., Wang, Y., & Liu, Y.-H. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Microbial Communities in Each Developmental Stage of Dermacentor nuttalli in Two Regions in Inner Mongolia, China. Biology, 14(6), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060613






