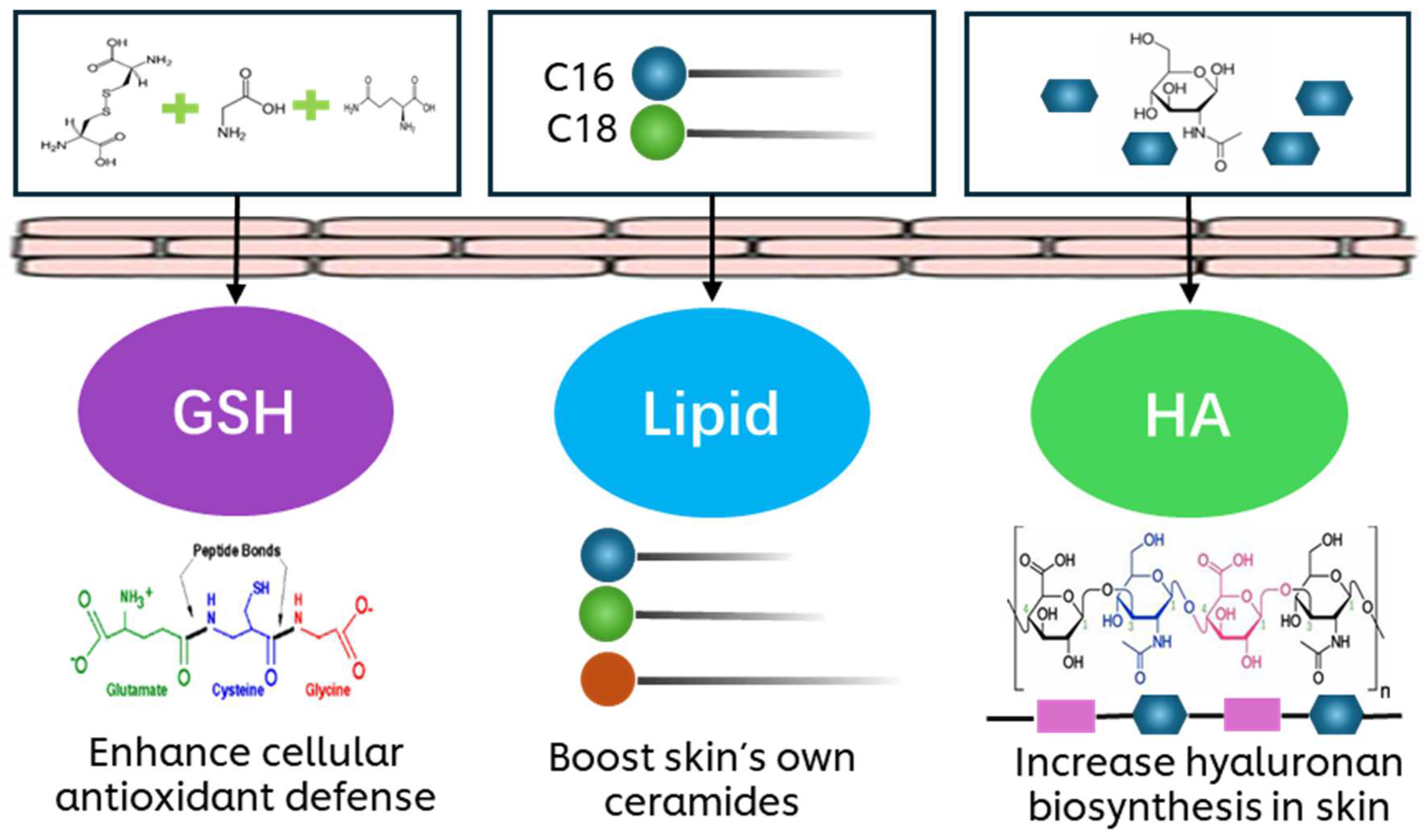
A Triple-Precursor Blend as a Topical Solution to Protect the Skin Against Environmental Damage
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UVB-Challenged Human Keratinocytes
2.2. Oxidative Stress-Challenged Human Keratinocytes
2.3. Transcriptomic Profiling of Blue Light-Challenged Human Keratinocytes Using RNA Sequencing
2.4. Application of the LSE Model and Histological Analysis
2.5. Application of the pLSE Model and Measurement of L* and Melanin Content
2.6. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
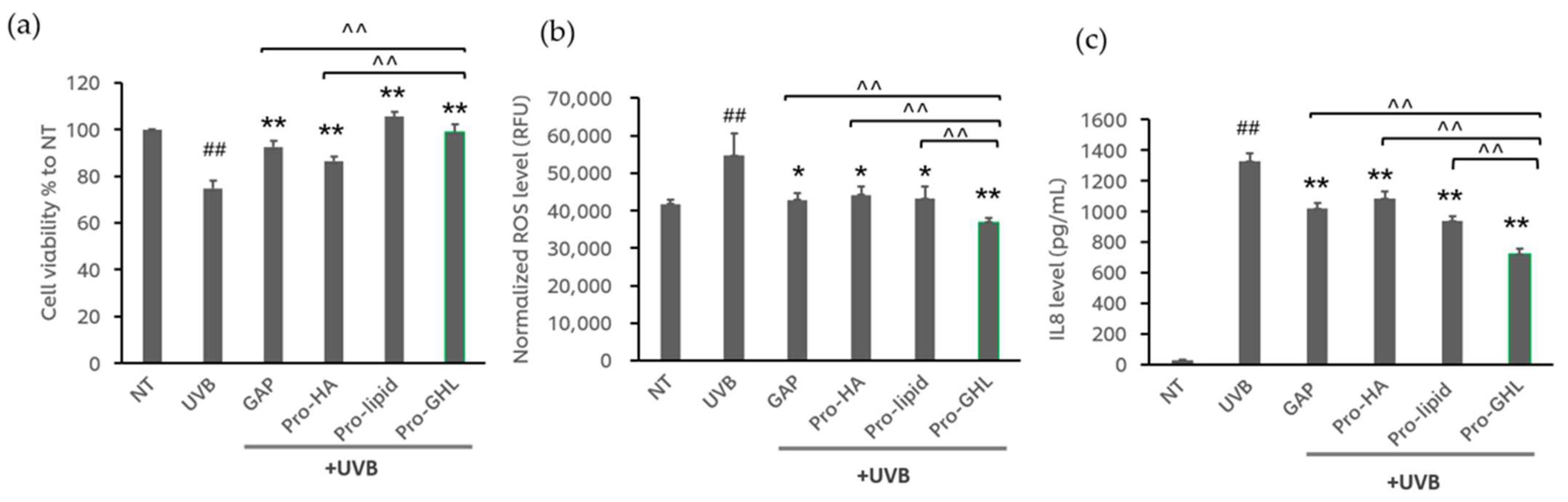
3.1. The Effects of GAPs, Pro-HA, Pro-Lipid and Pro-GHL in UVB-Exposed Keratinocytes
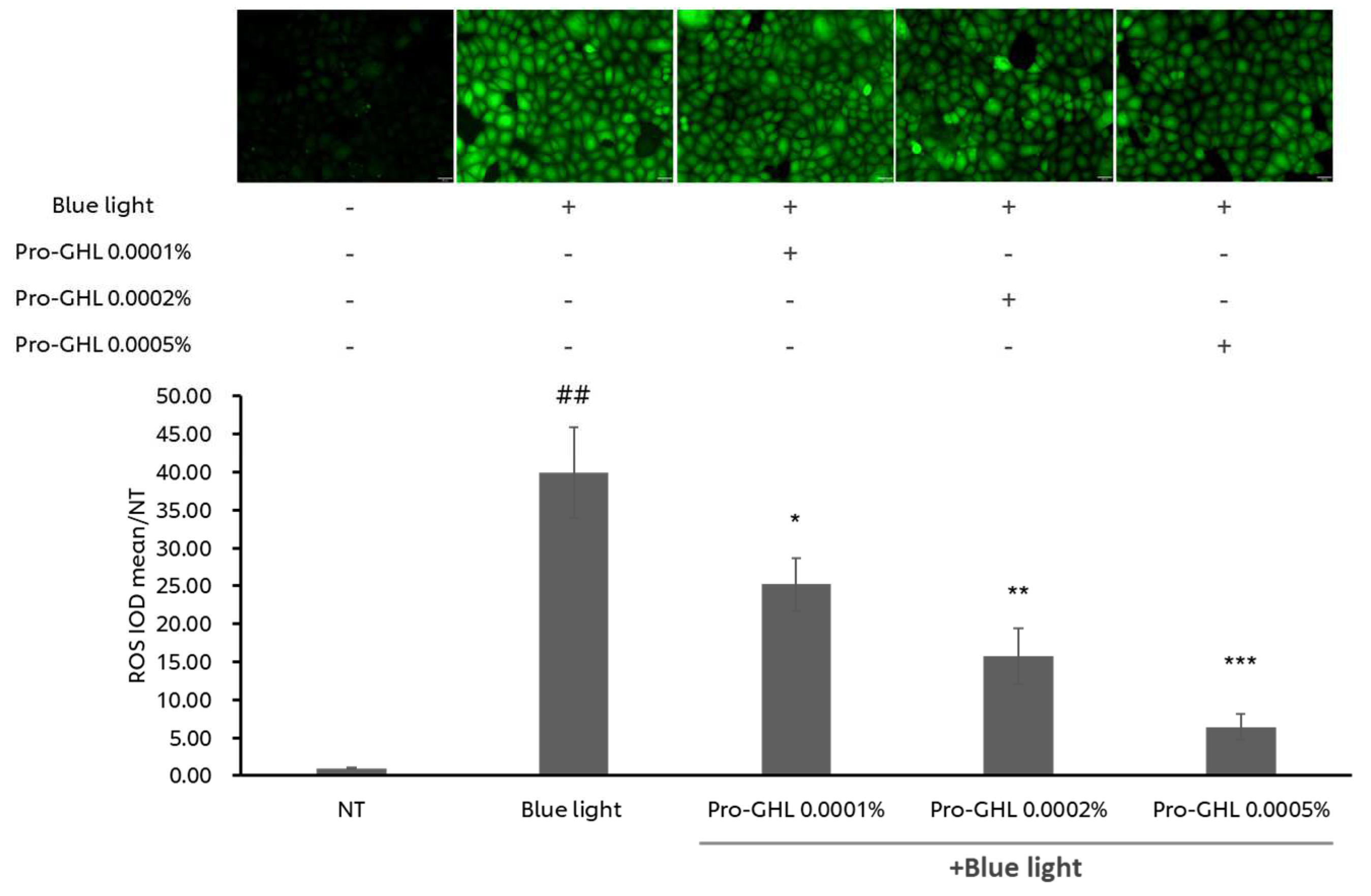
3.2. Dose–Response Effect of Pro-GHL on Blue Light-Exposed Keratinocytes
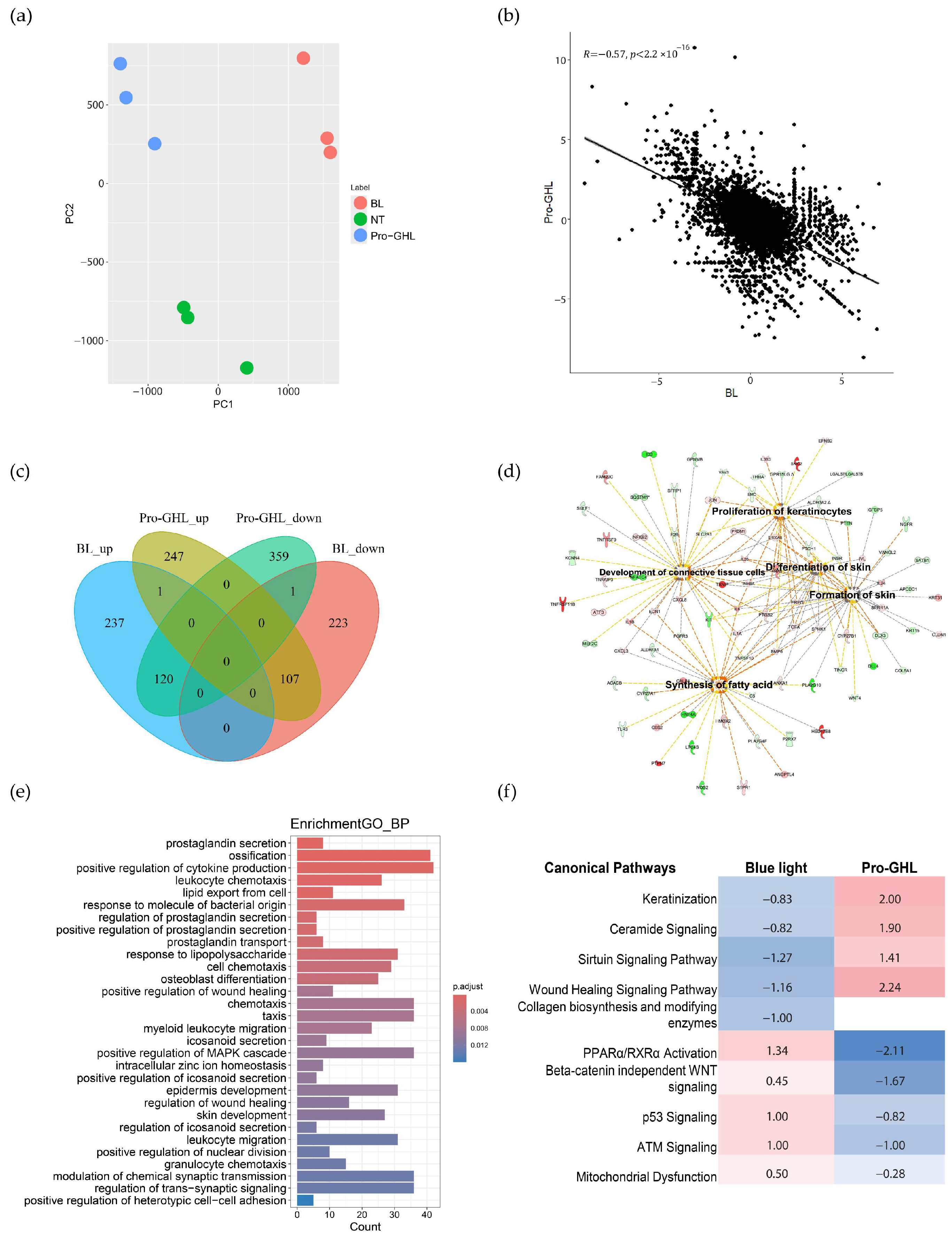
3.3. Transcriptomic Analysis of Pro-GHL in Blue Light-Challenged Keratinocytes
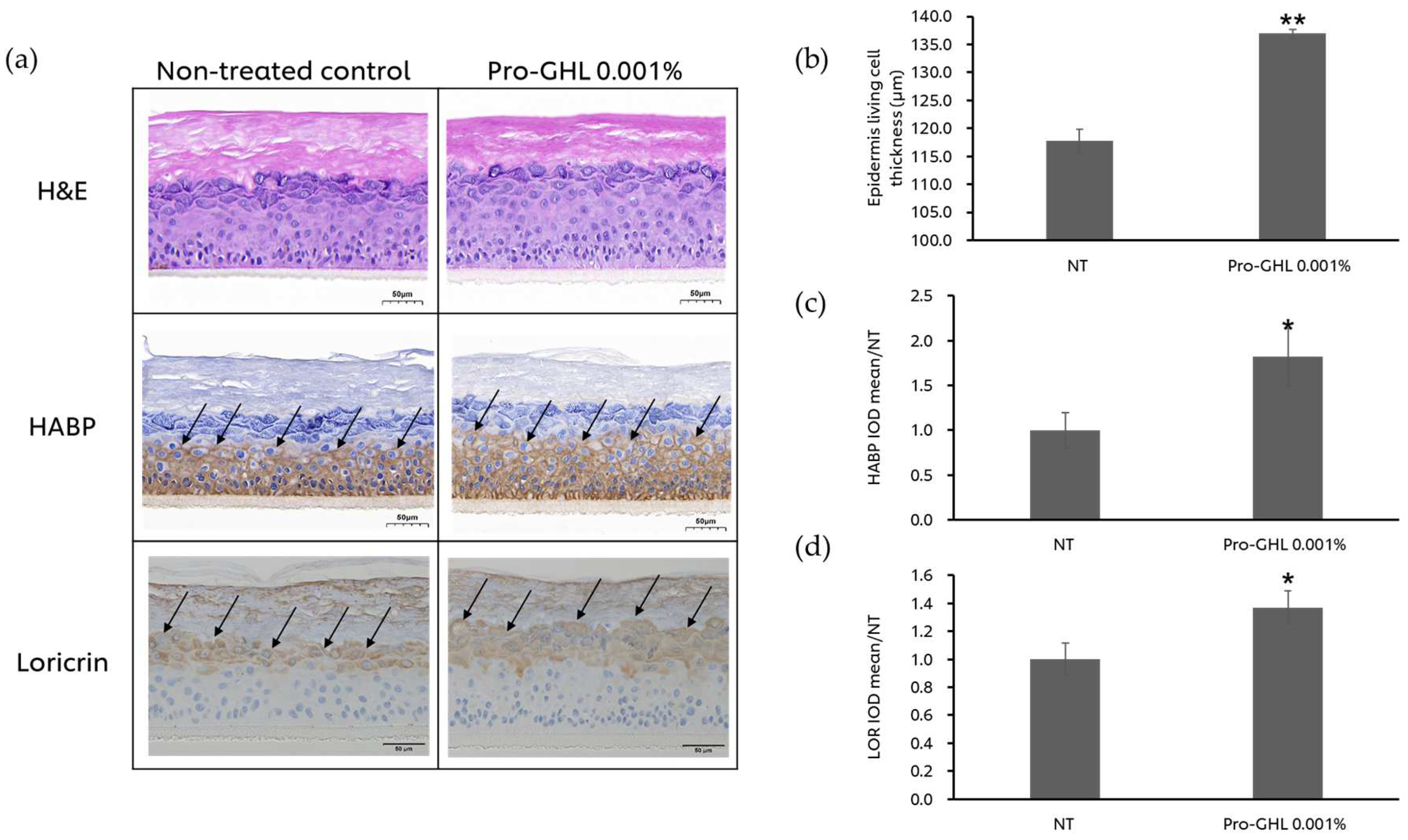
3.4. The Effects of Pro-GHL on the 3D Skin Equivalent Model
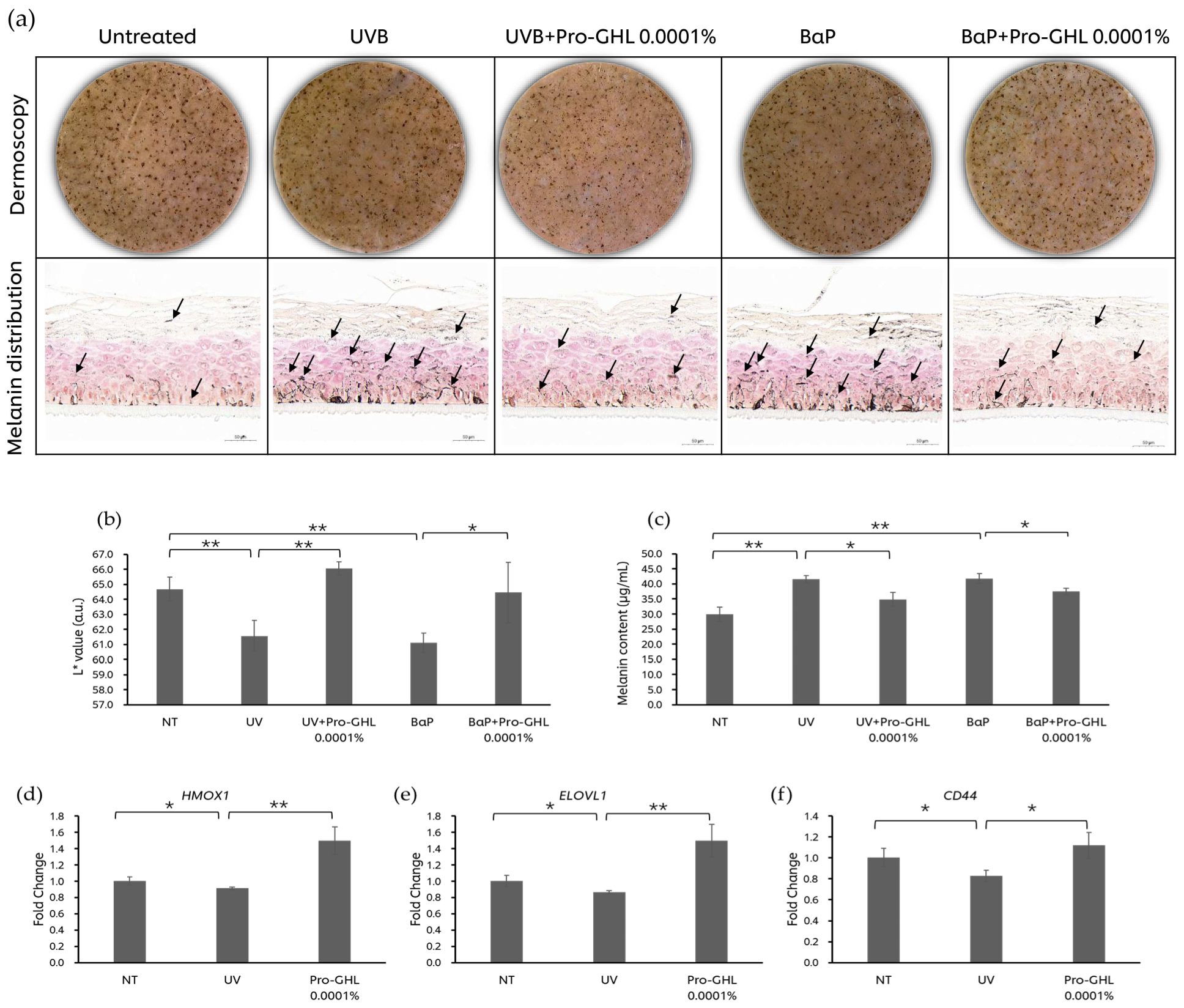
3.5. The Effects of Pro-GHL on the UV- and Pollutant-Challenged Pigmented 3D Skin Equivalent Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velarde, M.C. Epidermal Barrier Protects against Age-Associated Systemic Inflammation. J. Invest Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1206–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Vale, D.L.; Steffen, V.S.; Vicentini, F.T.M.C.; Vignoli, J.A.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Casagrande, R. Trans-Chalcone Added in Topical Formulation Inhibits Skin Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Model of Ultraviolet B Radiation Skin Damage in Hairless Mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 171, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.C.; Piao, M.J.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, J.W. Phloroglucinol Protects Human Keratinocytes from Ultraviolet B Radiation by Attenuating Oxidative Stress. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2012, 28, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrząb, A.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Markowska, A.; Wroński, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Cannabidiol Contributes to the Decreased Lipid Peroxidation of Keratinocytes of Rat Skin Exposed to UV Radiation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6647222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Hashizume, E.; Chan, G.P.; Kamimura, A. Skin-Whitening and Skin-Condition-Improving Effects of Topical Oxidized Glutathione: A Double-Blind and Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial in Healthy Women. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Mi, T.; Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Xiao, X.; Lee, J.; Guelakis, M.; Gu, X. Glutathione Amino Acid Precursors Protect Skin from UVB-Induced Damage and Improve Skin Tone. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38 (Suppl. S3), 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Mi, T.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Huang, N.; Gao, P.; Lee, J.; Guelakis, M.; Gu, X. Topical Glutathione Amino Acid Precursors Protect Skin against Environmental and Oxidative Stress. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38 (Suppl. S3), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.-M. The Skin: An Indispensable Barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Lamellar Bodies: The Key to Cutaneous Barrier Function. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijaljica, D.; Townley, J.P.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. The Heterogeneity and Complexity of Skin Surface Lipids in Human Skin Health and Disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 2024, 93, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammi, R.; Ripellino, J.A.; Margolis, R.U.; Tammi, M. Localization of Epidermal Hyaluronic Acid Using the Hyaluronate Binding Region of Cartilage Proteoglycan as a Specific Probe. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1988, 90, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, C.; de Rouvroit, C.L.; Poumay, Y. Epidermal Hyaluronan in Barrier Alteration-Related Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draelos, Z.D.; Diaz, I.; Namkoong, J.; Wu, J.; Boyd, T. Efficacy Evaluation of a Topical Hyaluronic Acid Serum in Facial Photoaging. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tanaka, T.; Mitlitski, V.; Heeter, J.; Balazs, E.A.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Protective Effect of Hyaluronate on Oxidative DNA Damage in WI-38 and A549 Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wilde, S.; Dash, A.; Johnson, A.; Mackey, K.; Okumura, C.Y.M.; LaRock, C.N. Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species by the Hyaluronic Acid Capsule of Group A Streptococcus. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0025823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hillpot, E.; Lin, Y.S.; Zakusilo, F.T.; Lu, J.Y.; Ablaeva, J.; Biashad, S.A.; et al. Evolution of High-Molecular-Mass Hyaluronic Acid Is Associated with Subterranean Lifestyle. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lierova, A.; Kasparova, J.; Filipova, A.; Cizkova, J.; Pekarova, L.; Korecka, L.; Mannova, N.; Bilkova, Z.; Sinkorova, Z. Hyaluronic Acid: Known for Almost a Century, but Still in Vogue. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.; Maibach, H.I. Hyaluronan in Skin: Aspects of Aging and Its Pharmacologic Modulation. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E.; Kaykın, M.; Şahin Bektay, H.; Güngör, S. Recent Advances on Topical Application of Ceramides to Restore Barrier Function of Skin. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Flach, C.R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Mao, G.; Pappas, A.; Mack, M.C.; Walters, R.M.; Southall, M.D. Topically Applied Ceramide Accumulates in Skin Glyphs. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Seino, S.; Kurihara, H.; Kage, M.; Tokudome, Y. 2-KDa Hyaluronan Ameliorates Human Facial Wrinkles through Increased Dermal Collagen Density Related to Promotion of Collagen Remodeling. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juncan, A.M.; Moisă, D.G.; Santini, A.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.-L.; Vonica-Țincu, A.L.; Loghin, F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoughrabie, S.; Cau, L.; Cavagnero, K.; O’Neill, A.M.; Li, F.; Roso-Mares, A.; Mainzer, C.; Closs, B.; Kolar, M.J.; Williams, K.J.; et al. Commensal Cutibacterium Acnes Induce Epidermal Lipid Synthesis Important for Skin Barrier Function. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nip, J.; Ilarslan, H.; Villa, A.; Mihalov, D.; Arcella, S.; Bajor, J. 33967 Nourishing Fatty Acid Moisturizers Provide Superior Barrier Benefits in Ex Vivo Skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, AB186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nip, J.; Ilarslan, H.; Villa, A.; Mihalov, D.; Misra, M.; Samaras, S.D.; Feng, L.; Arcella, S.; Bajor, J.; Mayes, A.E. Topically Applied, Fatty Acid-containing Formulations Provide Superior Barrier Benefits in an Ex Vivo Tape-stripped Skin Model. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2024, 46, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarova, G.; Lathrop, W.F.; Mayes, A.E.; Hawkins, S.; Dobkowski, B.; Dasgupta, B.R.; Bajor, J.S. In Vivo Elongation of Topically Applied Fatty Acids From a Range of Different Topical Skincare Formulations. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2023, 74, 188–199. [Google Scholar]
- Witting, M.; Boreham, A.; Brodwolf, R.; Vávrová, K.; Alexiev, U.; Friess, W.; Hedtrich, S. Interactions of Hyaluronic Acid with the Skin and Implications for the Dermal Delivery of Biomacromolecules. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayo, T.; Sakai, S.; Inoue, S. Synergistic Effect of N-Acetylglucosamine and Retinoids on Hyaluronan Production in Human Keratinocytes. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 17, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-X.; Zhang, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, T. Exogenous N-Acetylglucosamine Increases Hyaluronan Production in Cultured Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2009, 301, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Picardo, M. Antioxidant Activity, Lipid Peroxidation and Skin Diseases. What’s New. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2003, 17, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, R.; Lesiak, A. Mitigating Glycation and Oxidative Stress in Aesthetic Medicine: Hyaluronic Acid and Trehalose Synergy for Anti-AGEs Action in Skin Aging Treatment. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2701–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M. Epidermal Lipids, Barrier Function and Desquamation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 44s–49s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeichner, J.; Bussmann, T.; Weise, J.M.; Maass, E.; Krüger, A.; Schade, A.-K.; Lain, E.; Mariwalla, K.; Kirchner, F.; Draelos, Z.D. Evaluation of Antioxidants’ Ability to Enhance Hyaluronic-Acid Based Topical Moisturizers. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lúcio, M.; Giannino, N.; Barreira, S.; Catita, J.; Gonçalves, H.; Ribeiro, A.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, I.; Pinho, H.; Cerqueira, F.; et al. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Enriched Hydrogels for Skin Topical Administration of Quercetin and Omega-3 Fatty Acid. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Park, D.-R.; Kim, Y.-W.; Nam, T.-S.; Jang, K.Y.; Chung, H.T.; Kim, U.-H. The Essential Role of Ca2+ Signals in UVB–Induced IL-1β Secretion in Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H.; Izutsu, Y.; Yahagi, S.; Okano, Y. Reactive Oxygen Species in HaCaT Keratinocytes After UVB Irradiation Are Triggered by Intracellular Ca2+ Levels. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, E.; Kim, D.H.; Chung, H.Y. Protease-Activated Receptor 2 Induces ROS-Mediated Inflammation through Akt-Mediated NF-ΚB and FoxO6 Modulation during Skin Photoaging. Redox Biol. 2021, 44, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildesheim, J.; Awwad, R.T.; Fornace, A.J. P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitor Protects the Epidermis against the Acute Damaging Effects of Ultraviolet Irradiation by Blocking Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Kono, T.; Sauder, D.N.; McKenzie, R.C. IL-8 Gene Expression and Production in Human Keratinocytes and Their Modulation by UVB. J. Invest Dermatol. 1993, 101, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri Rudan, M.; Watt, F.M. Mammalian Epidermis: A Compendium of Lipid Functionality. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 804824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Ota, Y.; Akazawa, Y.; Sayo, T.; Hanai, U.; Imagawa, K.; Sasaki, M.; Takahashi, Y. Accelerated Human Epidermal Turnover Driven by Increased Hyaluronan Production. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 101, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Motte, C.A.; Drazba, J.A. Viewing Hyaluronan. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.M.; Lee, B.; Kim, D.H.; Chung, H.Y. FoxO6 Inhibits Melanogenesis Partly by Elevating Intracellular Antioxidant Capacity. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Moro, O.; Tagami, H.; Kishimoto, J. Gene Expression Profiling Analysis of Solar Lentigo in Relation to Immunohistochemical Characteristics. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, C.; Bourreau, E.; Warrick, E.; Bastien, P.; Nouveau, S.; Bernerd, F. A Chronic Pro-Inflammatory Environment Contributes to the Physiopathology of Actinic Lentigines. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ge, J.; Mi, T.; Cui, X.; Tu, F.; Gu, X.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L. Landscape Dynamic Network Biomarker Analysis Reveals the Tipping Point of Transcriptome Reprogramming to Prevent Skin Photodamage. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 13, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic Acid: A Key Molecule in Skin Aging. Dermatoendocrinology 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Li, M.; Xu, A.; Zhuo, F. Recent Applications and Molecular Mechanisms of Hyaluronic Acid in Skin Aging and Wound Healing. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2024, 23, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, G. The Skin’s “surprise” Power: It Has Its Very Own Immune System. Nature 2024, 637, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Subramanian, R.; Sinsawat, A.; Gu, X. A Triple-Precursor Blend as a Topical Solution to Protect the Skin Against Environmental Damage. Biology 2025, 14, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030266
Gao P, Xiao X, Zhou Z, Zhang H, Subramanian R, Sinsawat A, Gu X. A Triple-Precursor Blend as a Topical Solution to Protect the Skin Against Environmental Damage. Biology. 2025; 14(3):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030266
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ping, Xue Xiao, Zhuang Zhou, Hong Zhang, Raghupathi Subramanian, Anuchai Sinsawat, and Xuelan Gu. 2025. "A Triple-Precursor Blend as a Topical Solution to Protect the Skin Against Environmental Damage" Biology 14, no. 3: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030266
APA StyleGao, P., Xiao, X., Zhou, Z., Zhang, H., Subramanian, R., Sinsawat, A., & Gu, X. (2025). A Triple-Precursor Blend as a Topical Solution to Protect the Skin Against Environmental Damage. Biology, 14(3), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030266





