Caco2/HT-29 In Vitro Cell Co-Culture: Barrier Integrity, Permeability, and Tight Junctions’ Composition During Progressive Passages of Parental Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
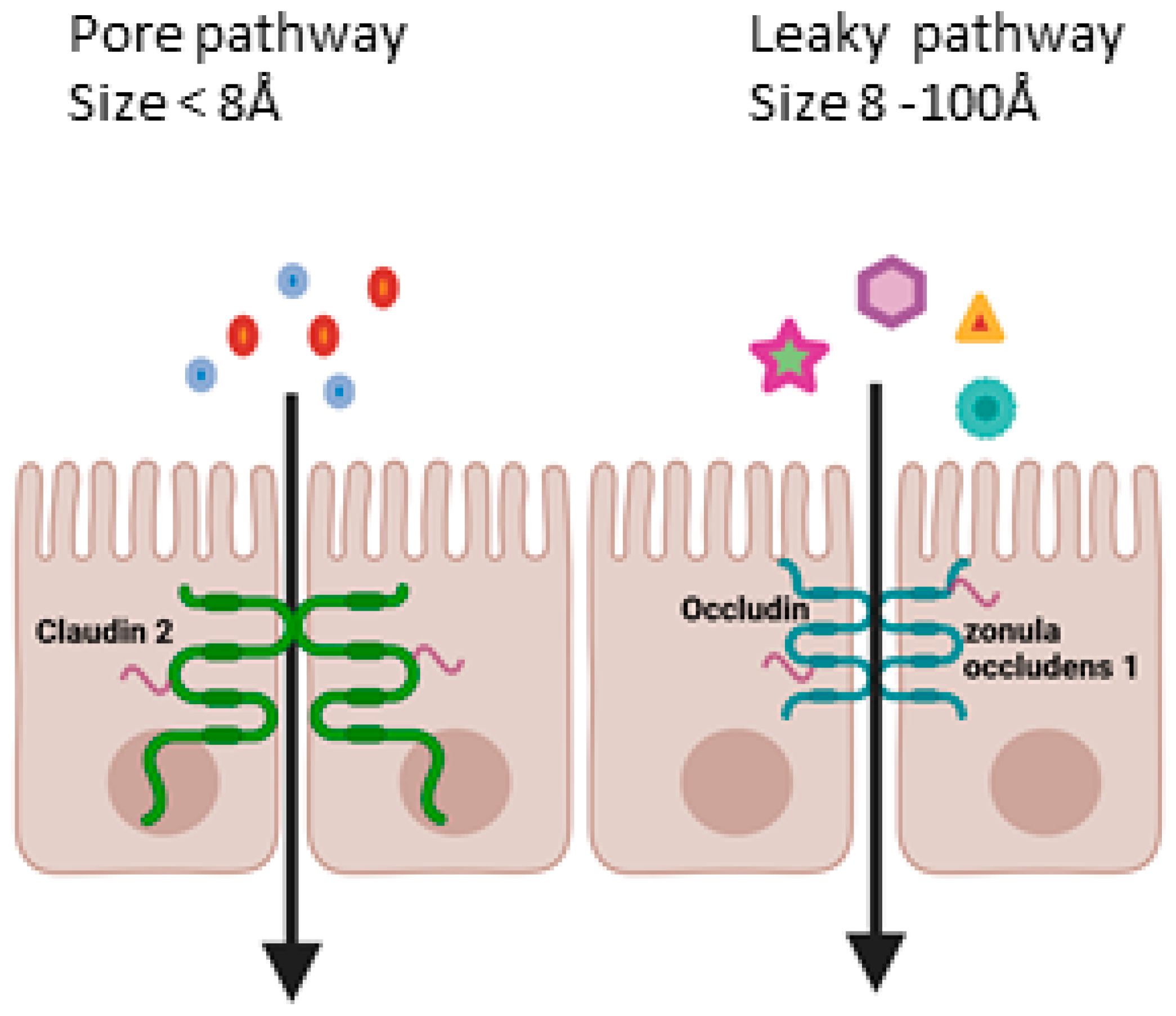
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Functional Properties of IEB: Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) Measurement and Intestinal Paracellular Permeability Assay
2.3. Morphological Properties of IEB: Immunofluorescence and Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
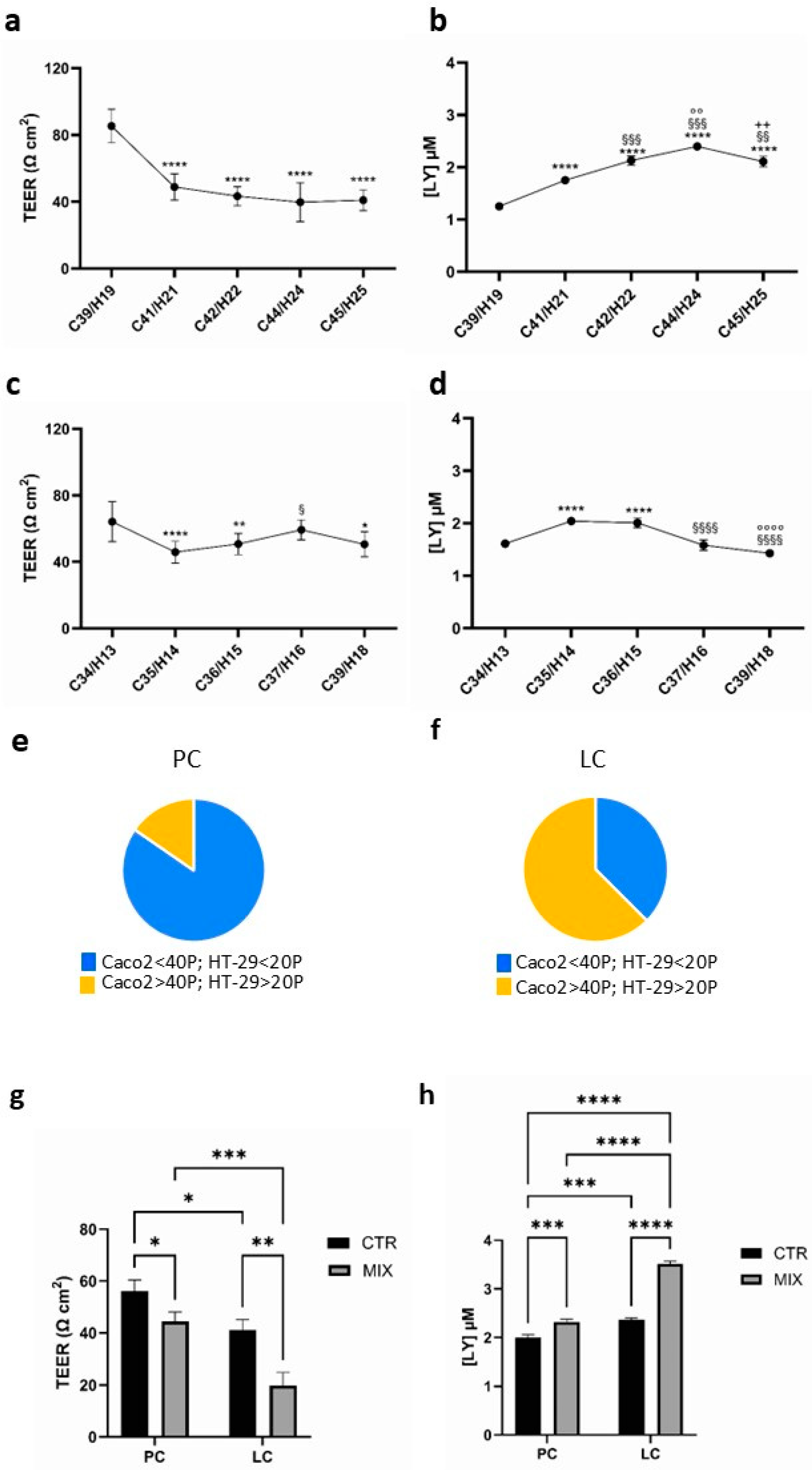
3.1. Functional Properties of Caco2/HT-29 70/30 Co-Culture in Basal Condition and After Pro-Inflammation Cytokine Treatment with the Increasing Passage Number of the Parental Cells
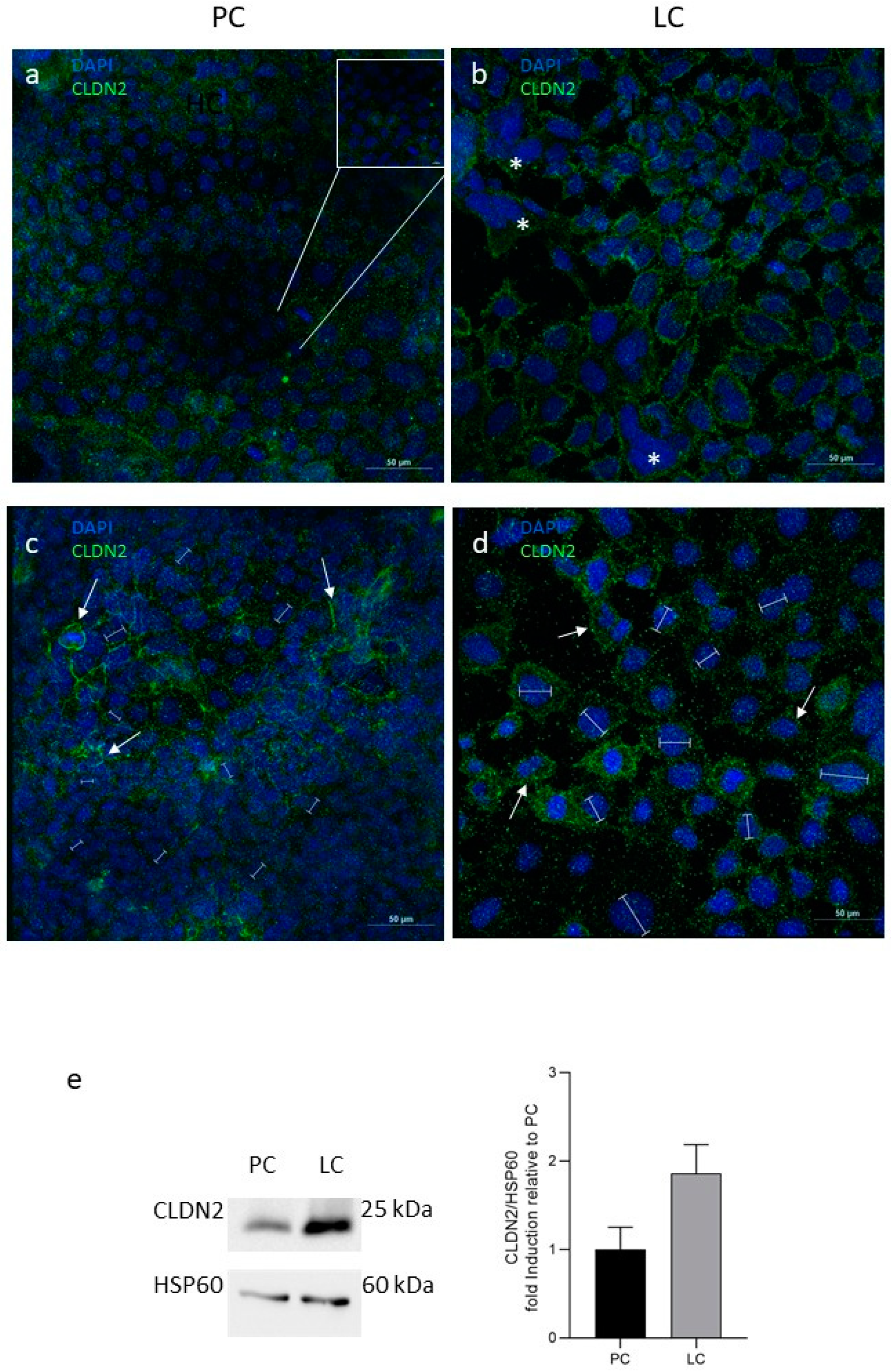
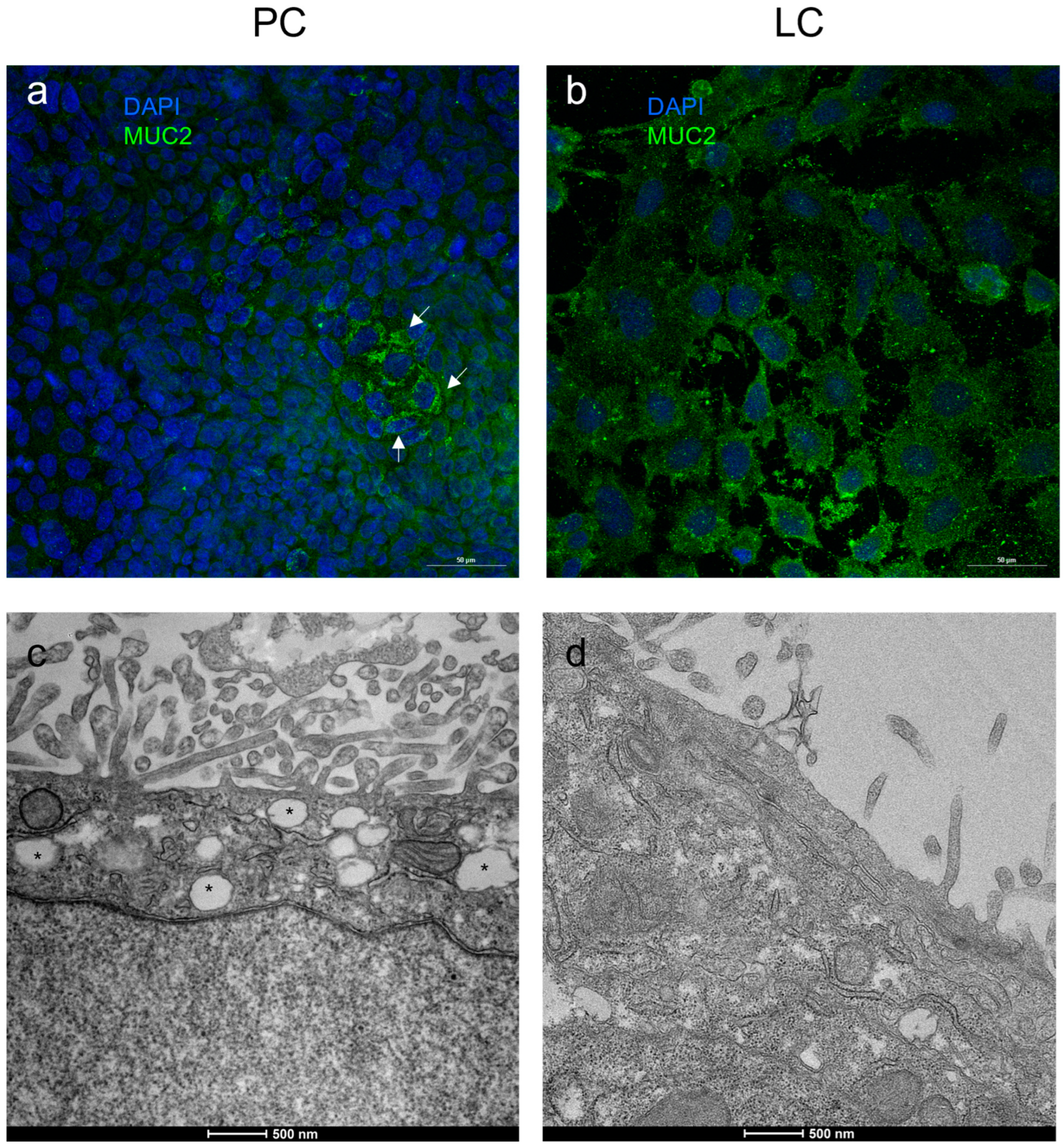
3.2. Molecular Composition of IEB: Tight Junctions and MUC-2 Analysis
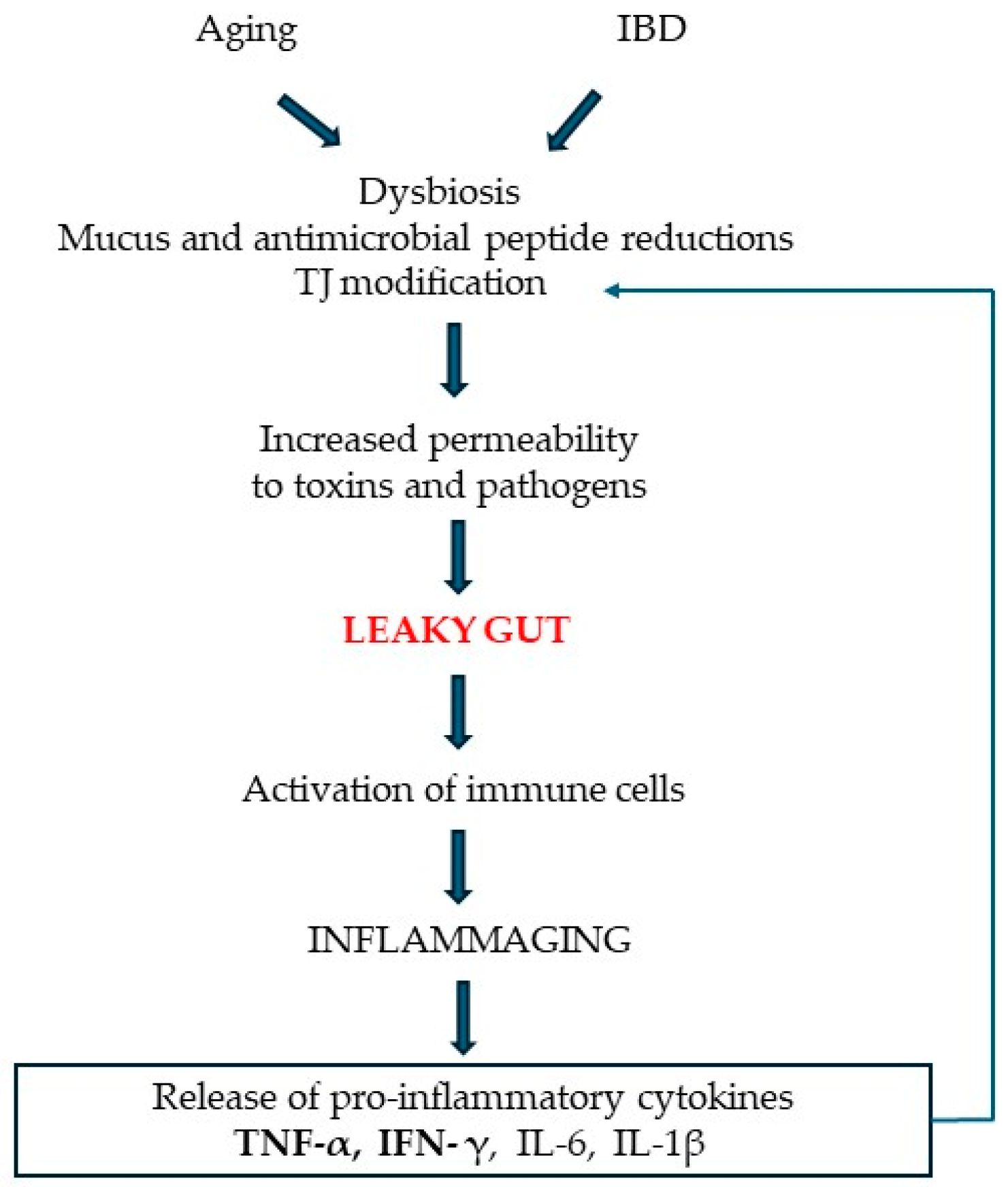
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CLN2 | Claudin 2 |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IBS | Irritable Bowel Syndrome |
| IEB | Intestinal Epithelial Barrier |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| LC | Leaky co-cultures with TEER values < 50 Ωcm2 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LY | Lucifer Yellow |
| MLCK | Myosin Light Chain Kinase |
| MUC-2 | Mucin 2 |
| NGS | Normal Goat Serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PC | Physiological co-cultures with TEER values > 50 Ωcm2 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| TEER | Transepithelial Electrical Resistance |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TJs | Tight Junctions |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| ZO | Zonula Occluden |
References
- Fu, R.; Jiang, X.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H. Junctional Complexes in Epithelial Cells: Sentinels for Extracellular Insults and Intracellular Homeostasis. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 7314–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, S.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, P. Role of Barrier Integrity and Dysfunctions in Maintaining the Healthy Gut and Their Health Outcomes. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 715611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of Tight Junctions and Principles of Molecular Composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M. Molecular Basis of the Core Structure of Tight Junctions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balda, M.S.; Matter, K. Tight Junctions. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R1135–R1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight Junction Structure and Function Revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Van Itallie, C.M. Physiology and Function of the Tight Junction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Pelaseyed, T.; Svensson, F.; Johansson, M.E.V. Study of Mucin Turnover in the Small Intestine by In Vivo Labeling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; He, C.; Xia, Y.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Mao, F. Intestinal Mucus Barrier: A Potential Therapeutic Target for IBD. Autoimmun. Rev. 2025, 24, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, G.; Day, A.S.; Kang, B.; Kang, Y.; Park, H.; Choe, B.-H. The Role and Function of Mucins and Its Relationship to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Med. 2022, 1, 848344. [Google Scholar]
- Aleman, R.S.; Moncada, M.; Aryana, K.J. Leaky Gut and the Ingredients That Help Treat It: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Shin, J.; Shim, E.; Ohtani, N.; Jeon, O.H. The Connection Between Aging, Cellular Senescence and Gut Microbiome Alterations: A Comprehensive Review. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Pongkorpsakol, P.; Xiong, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Relief Effects of Icariin on Inflammation-Induced Decrease of Tight Junctions in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 903762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.Y.; Söderholm, J.D. Importance of Disrupted Intestinal Barrier in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.L.; Bertelli, E.; Rentini, S.; Regoli, M.; Briars, G.; Marini, M.; Watson, A.J.M.; Nicoletti, C. Age-Associated Modifications of Intestinal Permeability and Innate Immunity in Human Small Intestine. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.H.; Martínez, E.; Barrias, C.C.; Sarmento, B. Development of an Improved 3D in Vitro Intestinal Model to Perform Permeability Studies of Paracellular Compounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 524018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A.R.; Esch, M.B.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L.; Hickman, J.J. TEER Measurement Techniques for In Vitro Barrier Model Systems. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P. Epithelial Transport of Drugs in Cell Culture. I: A Model for Studying the Passive Diffusion of Drugs over Intestinal Absorbtive (Caco-2) Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 1990, 79, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, A.; Bottani, M.; De Luca, P.; Cornaghi, L.; Arnaboldi, F.; Maggioni, M.; Fiorilli, A.; Donetti, E. Morphofunctional Properties of a Differentiated Caco2/HT-29 Co-Culture as an In Vitro Model of Human Intestinal Epithelium. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendinelli, P.; De Noni, I.; Cattaneo, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M.; Piazzalunga, F.; Donetti, E.; Ferraretto, A. Surface Layer Proteins from Lactobacillus helveticus ATCC® 15009TM Affect the Gut Barrier Morphology and Function. Tissue Barriers 2024, 12, 2289838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonwiriyakit, A.; Pathomthongtaweechai, N.; Steinhagen, P.R.; Chantawichitwong, P.; Satianrapapong, W.; Pongkorpsakol, P. Tight Junctions: From Molecules to Gastrointestinal Diseases. Tissue Barriers 2023, 11, 2077620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A Novel Integral Membrane Protein Localizing at Tight Junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, A.; Gravaghi, C.; Donetti, E.; Cosentino, S.; Donida, B.M.; Bedoni, M.; Lombardi, G.; Fiorilli, A.; Tettamanti, G. New Methodological Approach to Induce a Differentiation Phenotype in Caco-2 Cells Prior to Post-Confluence Stage. Anticancer. Res. 2007, 27, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar]
- Gravaghi, C.; Del Favero, E.; Cantu’, L.; Donetti, E.; Bedoni, M.; Fiorilli, A.; Tettamanti, G.; Ferraretto, A. Casein Phosphopeptide Promotion of Calcium Uptake in HT-29 Cells–Relationship between Biological Activity and Supramolecular Structure. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 4999–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, J.C.; Cho, J.; Bolling, B.W. Aronia Berry Inhibits Disruption of Caco-2 Intestinal Barrier Function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 688, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, D.G.; Cook, H.; Ortori, C.; Barrett, D.; Lund, J.N.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Palmitoylethanolamide and Cannabidiol Prevent Inflammation-Induced Hyperpermeability of the Human Gut In Vitro and In Vivo—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putt, K.K.; Pei, R.; White, H.M.; Bolling, B.W. Yogurt Inhibits Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Caco-2 Cells by Increasing Tight Junctions. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.E.; Sheean, P.M.; Gleason, P.M.; Bruemmer, B.; Boushey, C. Publishing Nutrition Research: A Review of Multivariate Techniques—Part 2: Analysis of Variance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luettig, J.; Rosenthal, R.; Barmeyer, C.; Schulzke, J. Claudin-2 as a Mediator of Leaky Gut Barrier during Intestinal Inflammation. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e977176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.-J.; Shi, L.-L.; Ren, Y.-R.; Yao, C.-Y.; Lu, Y.-M.; Chen, Y. Polysaccharide ORP-1 Isolated from Oudemansiella Raphanipes Ameliorates Age-Associated Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Caco-2 Cells Monolayer. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.; Nagpal, R.; Wang, B.; Jain, S.; Razazan, A.; Mishra, S.P.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kavanagh, K.; et al. A Human-Origin Probiotic Cocktail Ameliorates Aging-Related Leaky Gut and Inflammation via Modulating the Microbiota/Taurine/Tight Junction Axis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, 132055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus, M.; Ibragimow, I.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H. Caco-2 Cell Line Standardization with Pharmaceutical Requirements and In Vitro Model Suitability for Permeability Assays. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Uosef, A.; Subuddhi, A.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Piprek, R.P.; Ghobrial, R.M. Giant Multinucleated Cells in Aging and Senescence—An Abridgement. Biology 2022, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, I.; Kissel, T. Do Cell Culture Conditions Influence the Carrier-Mediated Transport of Peptides in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 19, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuytsel, T.; Tack, J.; Farre, R. The Role of Intestinal Permeability in Gastrointestinal Disorders and Current Methods of Evaluation. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 717925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammarchi, I.; Santacroce, G.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Hayes, B.; Crotty, R.; O’Driscoll, E.; Majumder, S.; Kaczmarczyk, W.; Maeda, Y.; McCarthy, J.; et al. Epithelial Neutrophil Localization and Tight Junction Claudin-2 Expression Are Innovative Outcome Predictors in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; You, Y.; Cha, S.; Kim, T.R.; Sohn, M.; Park, J. Multi-Species Probiotic Strain Mixture Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function by Regulating Inflammation and Tight Junctions in Lipopolysaccharides Stimulated Caco-2 Cells. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, M.; Furuse, M.; Sasaki, H.; Schulzke, J.R.-D.; Fromm, M.; Takano, H.; Noda, T.; Tsukita, S. Complex Phenotype of Mice Lacking Occludin, a Component of Tight Junction Strands. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 4131–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Fogg, V.C.; Margolis, B. Tight Junctions and Cell Polarity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 207–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo, N.; Sanger, G. Age-Related decline in Goblet Cell Numbers and Mucin Content of the Human Colon: Implications for Lower Bowel Functions in the Elderly. Exp. Mol. Path 2024, 139, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiando, A.M.; Shen, L.; Graham, W.V.; Weber, C.R.; Schwarz, B.T.; Austin, J.R.; Raleigh, D.R.; Guan, Y.; Watson, A.J.M.; Montrose, M.H.; et al. Caveolin-1–Dependent Occludin Endocytosis Is Required for TNF-Induced Tight Junction Regulation in Vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 200902153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms Regulating Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Its Pathological Implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharl, M.; Paul, G.; Barrett, K.E.; McCole, D.F. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Mediates the Interferon-γ-Induced Decrease in Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27952–27963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikari, A.; Sato, T.; Watanabe, R.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sugatani, Y. Increase in Claudin-2 Expression by an EGFR/MEK/ERK/c-Fos Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 cells. BBA 2012, 1823, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Boivin, M.; Ma, T. Mechanism of Cytokine Modulation of Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R.; Buschmann, M.M.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Sailer, A.; Shen, L. The Role of Molecular Remodeling in Differential Regulation of Tight Junction Permeability. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CLDN2 | OCCLUDIN | MUC-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Block of nonspecific binding sites | 30’ at RT in NGS 1:10 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 | 30’ at RT in NGS 1:10 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 | 30’ at RT in NGS 1:10 and BSA 5% in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 |
| Primary antibody | Mouse anti-human claudin 2 (Invitrogen, Monza (MB), Italy, #32-5600) 1:100 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 for 4 h at RT | Rabbit anti-human occludin (Invitrogen, Monza (MB), Italy, #MA3-012) 1:100 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 overnight at 4 °C | Mouse anti-human MUC-2 Merck Italy (Milan, Italy, #1412598) 1:10 in 3% BSA/PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4 for 1 h at 37 °C |
| Secondary antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) dilution 1:200 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4, 1 h at RT in the dark | Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) dilution 1:200 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4, 1 h at RT in the dark | Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) dilution 1:200 in PBS 0.1 M pH 7.4, 1 h at RT in the dark |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donetti, E.; Bendinelli, P.; Correnti, M.; Gammella, E.; Recalcati, S.; Ferraretto, A. Caco2/HT-29 In Vitro Cell Co-Culture: Barrier Integrity, Permeability, and Tight Junctions’ Composition During Progressive Passages of Parental Cells. Biology 2025, 14, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030267
Donetti E, Bendinelli P, Correnti M, Gammella E, Recalcati S, Ferraretto A. Caco2/HT-29 In Vitro Cell Co-Culture: Barrier Integrity, Permeability, and Tight Junctions’ Composition During Progressive Passages of Parental Cells. Biology. 2025; 14(3):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030267
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonetti, Elena, Paola Bendinelli, Margherita Correnti, Elena Gammella, Stefania Recalcati, and Anita Ferraretto. 2025. "Caco2/HT-29 In Vitro Cell Co-Culture: Barrier Integrity, Permeability, and Tight Junctions’ Composition During Progressive Passages of Parental Cells" Biology 14, no. 3: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030267
APA StyleDonetti, E., Bendinelli, P., Correnti, M., Gammella, E., Recalcati, S., & Ferraretto, A. (2025). Caco2/HT-29 In Vitro Cell Co-Culture: Barrier Integrity, Permeability, and Tight Junctions’ Composition During Progressive Passages of Parental Cells. Biology, 14(3), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030267






