Spatial Heterogeneity and Methodological Insights in Fish Community Assessment: A Case Study in Hulun Lake
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Assess methodological performance in characterizing fish assemblages, including comparisons of alpha and beta diversity metrics recovered by ASV- and OTU-based eDNA pipelines and their correlations with traditional survey data.
- (ii)
- Identify habitat-driven community clusters and quantify spatial variability in fish diversity using both eDNA and in-net data.
- (iii)
- Explore the relationship between fish community patterns and anthropogenic stressors to inform targeted conservation strategies. By bridging molecular and traditional monitoring approaches, this study aims to improve spatial conservation planning for the Hulun Lake ecosystem.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
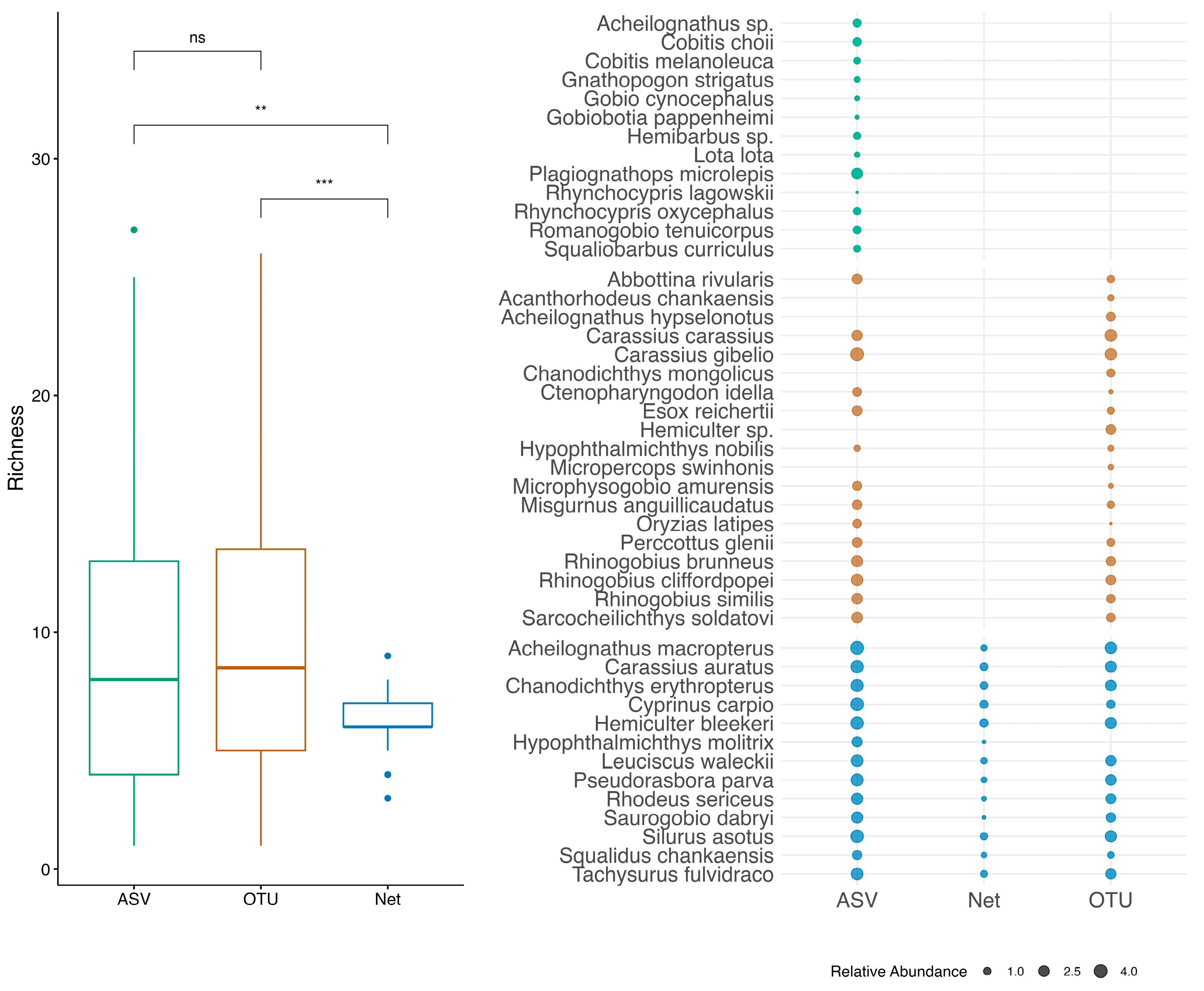
3.1. Alpha Diversity and Species Composition
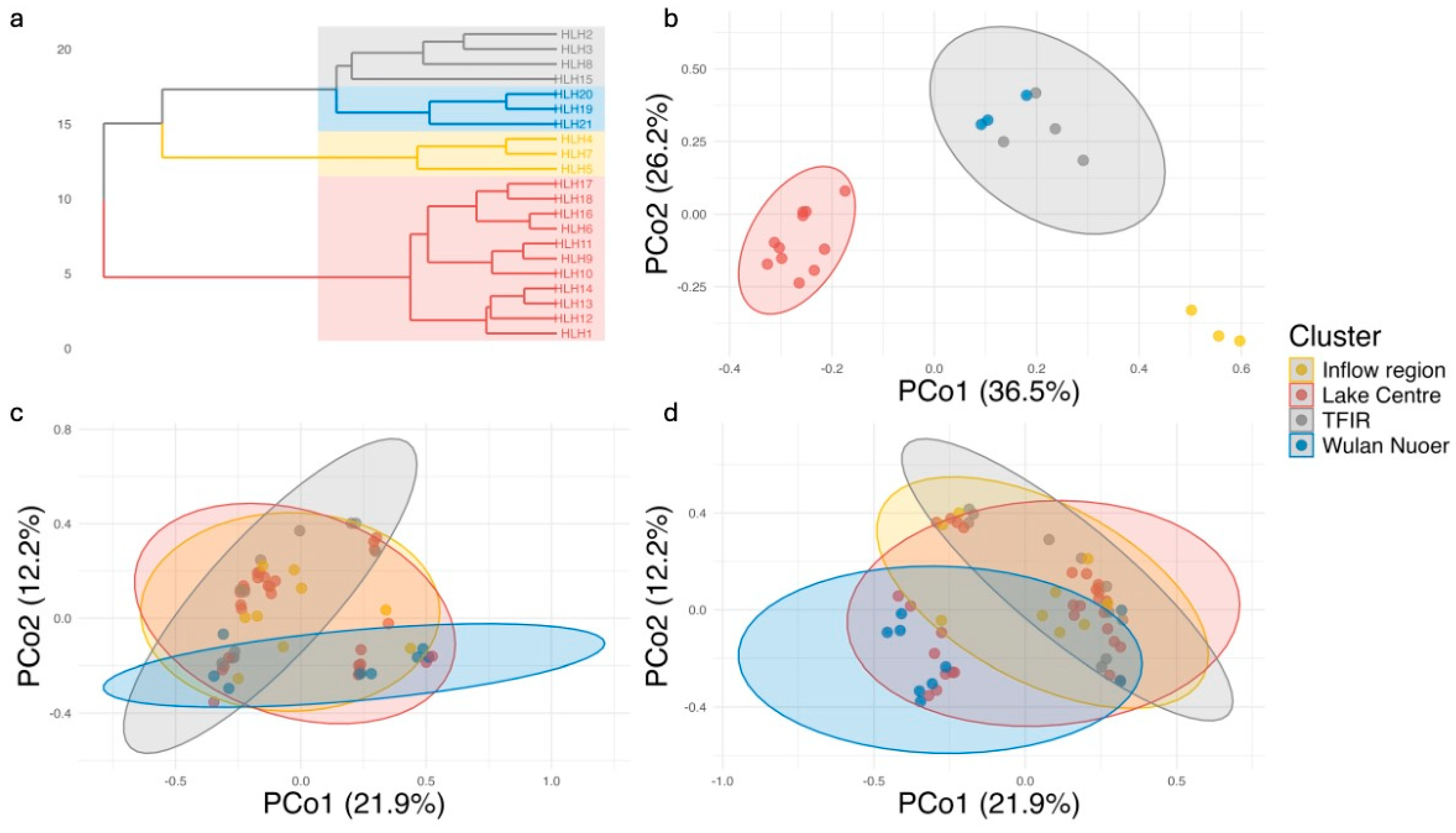
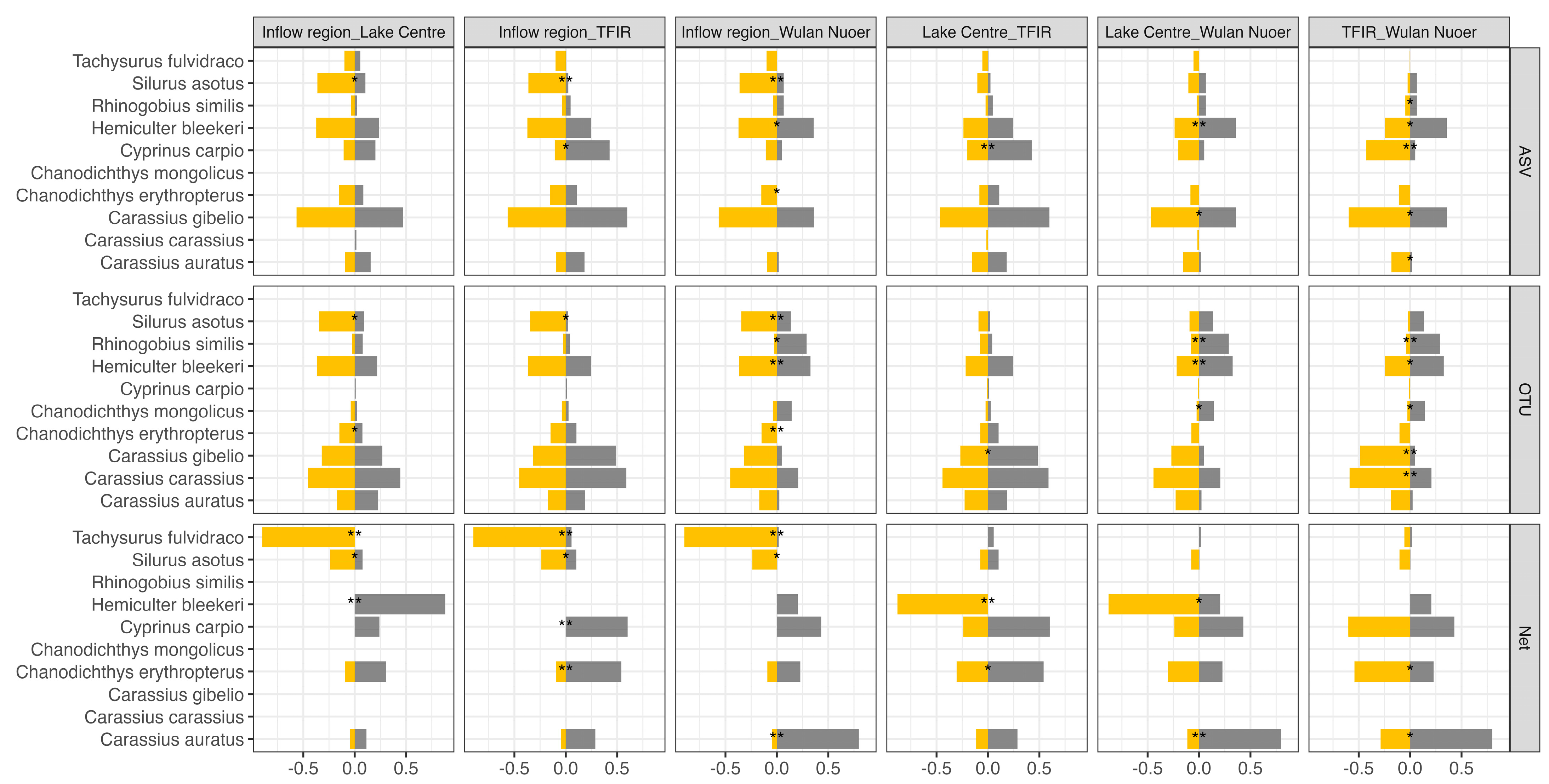
3.2. Beta Diversity and Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Consistency
4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity in Fish Communities
4.3. Conservation and Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Bini, L.M.; Cai, Y.; Heiskanen, S.; Hellsten, S.; Kortelainen, P.; Kotamäki, N.; Tolonen, K.T.; Vihervaara, P.; et al. Lakes in the era of global change: Moving beyond single-lake thinking in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging Threats and Persistent Conservation Challenges for Freshwater Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, B.; Wang, S.; Ni, S.Q. Leveraging Bayesian network to reveal the importance of water level in a shallow lake ecosystem: A study based on Paleo-diatom and fish community. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Dou, H.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Bacterial and fungal community structures in Hulun Lake are regulated by both stochastic processes and environmental factors. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03245-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA–An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.R.; Buxton, A.S.; Rees, H.C.; Bruce, K.; Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Read, D.S.; Watson, H.V.; Sayer, C.D.; Jones, E.P.; et al. Prospects and challenges of environmental DNA (eDNA) monitoring in freshwater ponds. Hydrobiologia 2019, 826, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Rocle, M.; Valentini, A.; Civade, R.; Jean, P.; Maire, A.; Roset, N.; Schabuss, M.; Zornig, H.; Dejean, T. Environmental DNA reveals quantitative patterns of fish biodiversity in large rivers despite its downstream transportation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Adolf, J.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Dunton, K.J.; Hinks, G.; VanMorter, S.M. Trawl and eDNA assessment of marine fish diversity, seasonality, and relative abundance in coastal New Jersey, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Collins, R.A.; Baillie, C.; Rainbird, S.; Brittain, R.; Griffiths, A.M.; Sims, D.W.; Mariani, S.; Genner, M.J. Environmental DNA captures elasmobranch diversity in a temperate marine ecosystem. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.C.; Fraser, D.J.; Derry, A.M. Meta-analysis supports further refinement of eDNA for monitoring aquatic species-specific abundance in nature. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact Sequence Variants Should Replace Operational Taxonomic Units in Marker-Gene Data Analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, S.I.; Martiny, J.B.H. Broadscale ecological patterns are robust to use of exact sequence variants versus operational taxonomic units. mSphere 2018, 3, 00148-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antich, A.; Palacín, C.; Cebrian, E.; Golo, R.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Turon, X. Marine biomonitoring with eDNA: Can metabarcoding of water samples cut it as a tool for surveying benthic communities? Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Lin, J.Y.; Xu, Y.; Cao, T.; Feng, J.; Peng, Z. Investigating the fish diversity in Erhai Lake based on environmental DNA metabarcoding. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2020, 5, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, F.; Mercier, C.; Bonin, A.; Le Bras, Y.; Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E. obitools: A unix-inspired software package for DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, P.; Kozlov, A.M.; Czech, L.; Morel, B.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. EPA-ng: Massively parallel evolutionary placement of genetic sequences. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (Version 4.3.0). R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2025. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Laporte, M.; Reny-Nolin, E.; Chouinard, V.; Hernandez, C.; Normandeau, E.; Bougas, B.; Côté, C.; Behmel, S.; Bernatchez, L. Proper environmental DNA metabarcoding data transformation reveals temporal stability of fish communities in a dendritic river system. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Arbizu, P. Pairwise Adonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis. R Package Version 0.4. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Farrington, H.L.; Edwards, C.E.; Bartron, M.; Lance, R.F. Phylogeography and population genetics of introduced Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and Bighead Carp (H. nobilis) in North America. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 2789–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Xu, J.W.; Yang, Q.L.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Chapman, D.C.; Lu, G. A comparison of complete mitochondrial genomes of silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis: Implications for their taxonomic relationship and phylogeny. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 1787–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Cao, Y.; Luo, J.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, H.; Jeppesen, E. How does fish functional diversity respond to environmental changes in two large shallow lakes? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Shibukawa, K.; Senou, H.; Chen, I.S. Redescription of Rhinogobius similis Gill 1859 (Gobiidae: Gobionellinae), the type species of the genus Rhinogobius Gill 1859, with designation of the neotype. Ichthyol. Res. 2016, 63, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; McCauley, M.; Villéger, S.; Jackson, C.R. Ranking the biases: The choice of OTUs vs. ASVs in 16S rRNA amplicon data analysis has stronger effects on diversity measures than rarefaction and OTU identity threshold. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasolo, A.; Deb, S.; Stevanato, P.; Concheri, G.; Squartini, A. ASV vs. OTUs clustering: Effects on alpha, beta, and gamma diversities in microbiome metabarcoding studies. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Mächler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänfling, B.; Lawson Handley, L.; Read, D.S.; Hahn, C.; Li, J.; Nichols, P.; Blackman, R.C.; Oliver, A.; Winfield, I.J. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of lake fish communities reflects long-term data from established survey methods. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3101–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, M.; Zhu, L.; Bernatzhez, L.; Li, S. Evolution and genetics of bighead and silver carps: Native population conservation versus invasive species control. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.; Tharwat, E.K.; Cleenwerck, I.; Monsieurs, P.; Van Houdt, R.; Vandamme, P.; El-Hadidi, M.; Mysara, M. The unresolved struggle of 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing: A benchmarking analysis of clustering and denoising methods. Environ. Microbiome 2025, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Leese, F. Validation and development of COI metabarcoding primers for freshwater macroinvertebrate bioassessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zinger, L.; Bonin, A.; Alsos, I.G.; Bálint, M.; Bik, H.; Boyer, F.; Chariton, A.A.; Creer, S.; Coissac, E.; Deagle, B.E.; et al. DNA metabarcoding—Need for robust experimental designs to draw sound ecological conclusions. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Schneyder, I.; Matchado, M.S.; Reitmeier, S.; Sommer, A.; Sewald, Z.; Baumbach, J.; List, M.; Neuhaus, K. Primer, pipelines, parameters: Issues in 16S rRNA gene sequencing. mSphere 2021, 6, 01202-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.P.; Port, J.A.; Yamahara, K.M.; Crowder, L.B. Using environmental DNA to census marine fishes in a large mesocosm. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson Handley, L. How will the ‘molecular revolution’ contribute to biological recording? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 115, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, M.E.; Hebert, P.D.N. Uses and Misuses of Environmental DNA in Biodiversity Science and Conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.Z.; Cao, W.X. Coexistence of Two Closely Related Cyprinid Fishes (Hemiculter bleekeri and Hemiculter leucisculus) in the Upper Yangtze River, China. Diversity 2020, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funao, T.; Nishida, T.; Kurashige, Y.; Sawada, H. Different suitability of improved irrigation channels as reproductive sites for Cyprininae and Silurus asotus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; de los Ángeles González-Sagrario, M. Habitat complexity in shallow lakes and ponds: Importance, threats, and potential for restoration. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 3737–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.A.; Blabolil, P. Comparison of Bioinformatic Pipelines for eDNA Metabarcoding Data Analysis of Fish Populations. Fishes 2025, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Invasive species and habitat degradation in Iberian streams: An analysis of their role in freshwater fish diversity loss. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 892–900. [Google Scholar]
- Habit, E.; Piedra, P.; Ruzzante, D.E.; Walde, S.J.; Belk, M.C.; Cussac, V.E.; Gonzalez, J.; Colin, N. Changes in the distribution of native fishes in response to introduced species and other anthropogenic effects. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Strickler, K.M.; Pilliod, D.S. Moving environmental DNA methods from concept to practice for monitoring aquatic macroorganisms. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 183, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E. How to limit false positives in environmental DNA and metabarcoding? Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 16, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Gleeson, D.M.; Lintermans, M.; Hardy, C.M.; Beitzel, M.; Gilligan, D.M.; Furlan, E.M. Monitoring riverine fish communities through eDNA metabarcoding: Determining optimal sampling strategies along an altitudinal and biodiversity gradient. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2018, 2, e30457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Frøslev, T.G.; Paupério, J.; Thalinger, B.; Klymus, K.; Helbing, C.C.; Villacorta-Rath, C.; Silliman, K.; Thompson, L.R.; Jungbluth, S.P.; et al. A Metadata Checklist and Data Formatting Guidelines to Make eDNA FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable). Environ. DNA 2025, 7, e70100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Passive eDNA sampling facilitates biodiversity monitoring and rare species detection. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerde, C.L. Can we manage fisheries with the inherent uncertainty from eDNA? J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Df | SS | r2 | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net | |||||
| Model | 3 | 3.5841 | 0.70293 | 13.409 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 17 | 1.5147 | 0.29707 | ||
| Total | 20 | 5.0988 | 1 | ||
| OTU | |||||
| Model | 3 | 2.3209 | 0.12514 | 2.6224 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 55 | 16.2255 | 0.87486 | ||
| Total | 58 | 18.5464 | 1 | ||
| ASV | |||||
| Model | 3 | 1.9136 | 0.10572 | 2.0885 | 0.005 |
| Residual | 53 | 16.1878 | 0.89428 | ||
| Total | 56 | 18.1014 | 1 |
| Pairs | SS | F | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net | ||||
| Lake Centre vs. Inflow region | 1.7931209 | 28.711902 | 0.7052459 | 0.004 |
| Lake Centre vs. TFIR | 1.2167088 | 13.669433 | 0.5125506 | 0.002 |
| Lake Centre vs. Wulan Nuoer | 1.0026934 | 16.700379 | 0.5818871 | 0.004 |
| Inflow region vs. TFIR | 1.1072019 | 6.970397 | 0.5823029 | 0.032 |
| Inflow region vs. Wulan Nuoer | 1.1911925 | 13.325187 | 0.7691223 | 0.1 |
| TFIR vs. Wulan Nuoer | 0.4251528 | 2.777786 | 0.3571435 | 0.034 |
| OTU | ||||
| Lake Centre vs. Inflow region | 0.5677432 | 1.899191 | 0.0488234 | 0.025 |
| Lake Centre vs. TFIR | 0.5837242 | 2.030721 | 0.0494927 | 0.036 |
| Lake Centre vs. Wulan Nuoer | 1.0187869 | 2.99325 | 0.07484388 | 0.003 |
| Inflow region vs. TFIR | 0.4398811 | 2.179936 | 0.10802492 | 0.055 |
| Inflow region vs. Wulan Nuoer | 0.9516775 | 3.036197 | 0.15949598 | 0.004 |
| TFIR vs. Wulan Nuoer | 1.2599592 | 4.391153 | 0.19611108 | 0.001 |
| ASV | ||||
| Lake Centre vs. Inflow region | 0.5756267 | 1.834298 | 0.04848242 | 0.036 |
| Lake Centre vs. TFIR | 0.6427387 | 2.133024 | 0.05314884 | 0.02 |
| Lake Centre vs. Wulan Nuoer | 0.6415883 | 1.82848 | 0.04964853 | 0.045 |
| Inflow region vs. TFIR | 0.5698036 | 2.625317 | 0.12728614 | 0.019 |
| Inflow region vs. Wulan Nuoer | 0.5852228 | 1.853017 | 0.10995163 | 0.077 |
| TFIR vs. Wulan Nuoer | 0.8637256 | 3.00242 | 0.15010283 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, S.; Sun, B. Spatial Heterogeneity and Methodological Insights in Fish Community Assessment: A Case Study in Hulun Lake. Biology 2025, 14, 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121678
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Pan Y, Ma Z, Han X, Zhou Z, Tian S, Sun B. Spatial Heterogeneity and Methodological Insights in Fish Community Assessment: A Case Study in Hulun Lake. Biology. 2025; 14(12):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121678
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zifang, Yuetong Zhang, Yanan Pan, Zhousunxi Ma, Xin Han, Ziqi Zhou, Shuang Tian, and Bingjiao Sun. 2025. "Spatial Heterogeneity and Methodological Insights in Fish Community Assessment: A Case Study in Hulun Lake" Biology 14, no. 12: 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121678
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhang, Y., Pan, Y., Ma, Z., Han, X., Zhou, Z., Tian, S., & Sun, B. (2025). Spatial Heterogeneity and Methodological Insights in Fish Community Assessment: A Case Study in Hulun Lake. Biology, 14(12), 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121678







