Organic Mulching Enhances Soil Health and Fungal Diversity to Promote Growth of Aralia continentalis Kitag: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Fertilization in Agroecosystems
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil and Plant Measurements
2.3.1. Soil Properties
2.3.2. Fungal Diversity Analysis
2.3.3. Plant Growth and Health Assessment
2.4. Integrated Metrics and Causal Insight
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics Under Different Treatments
3.1.1. Soil Physical Properties (pH, EC, Bulk Density, Porosity, Moisture)
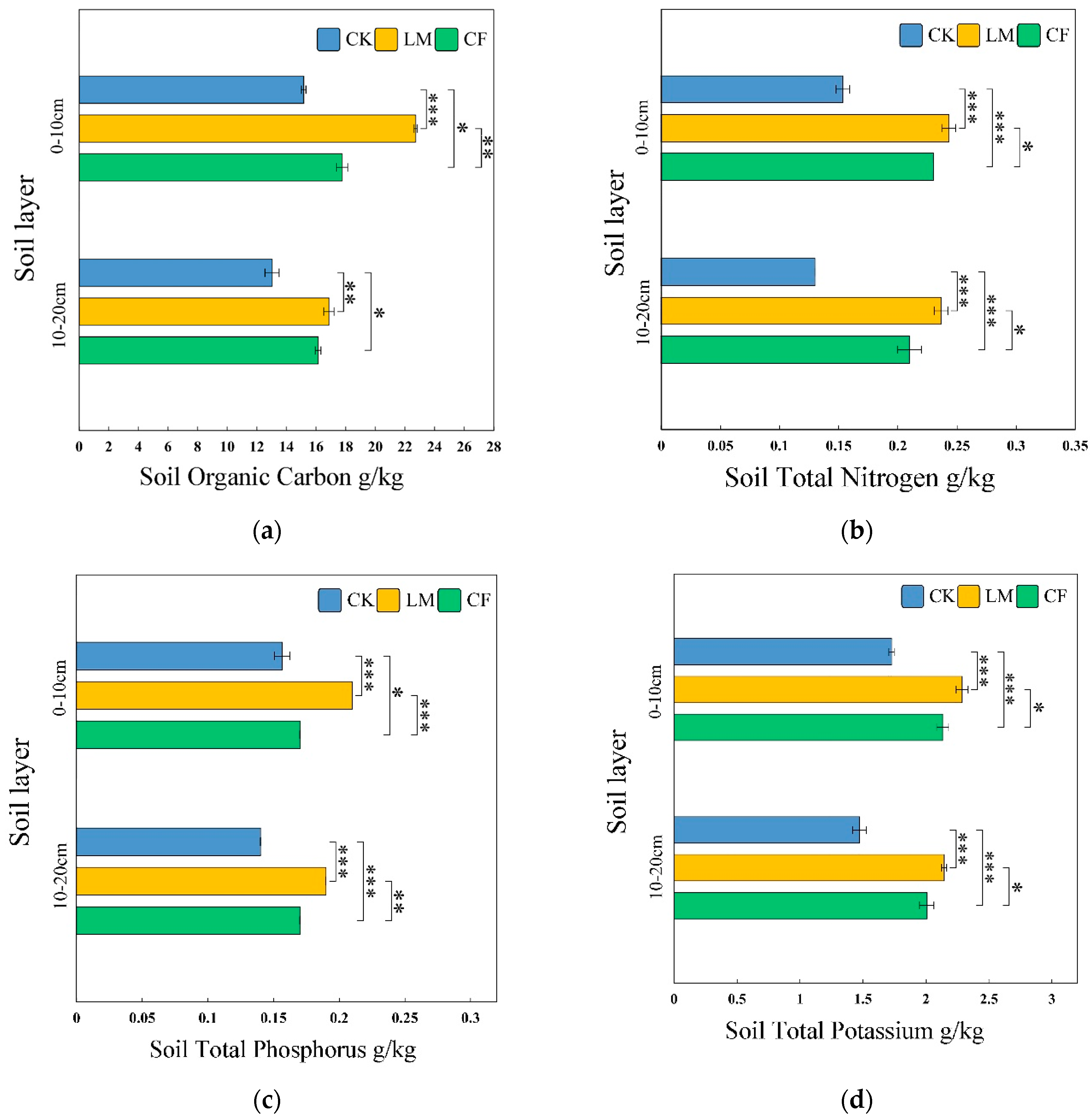
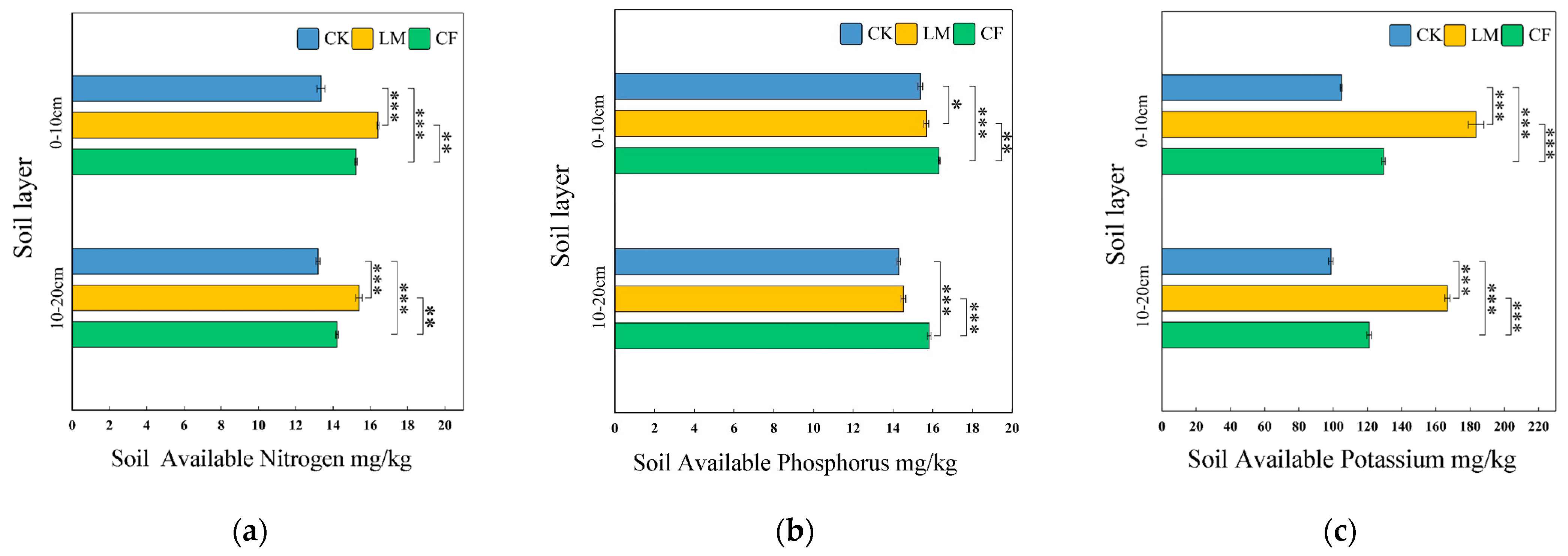
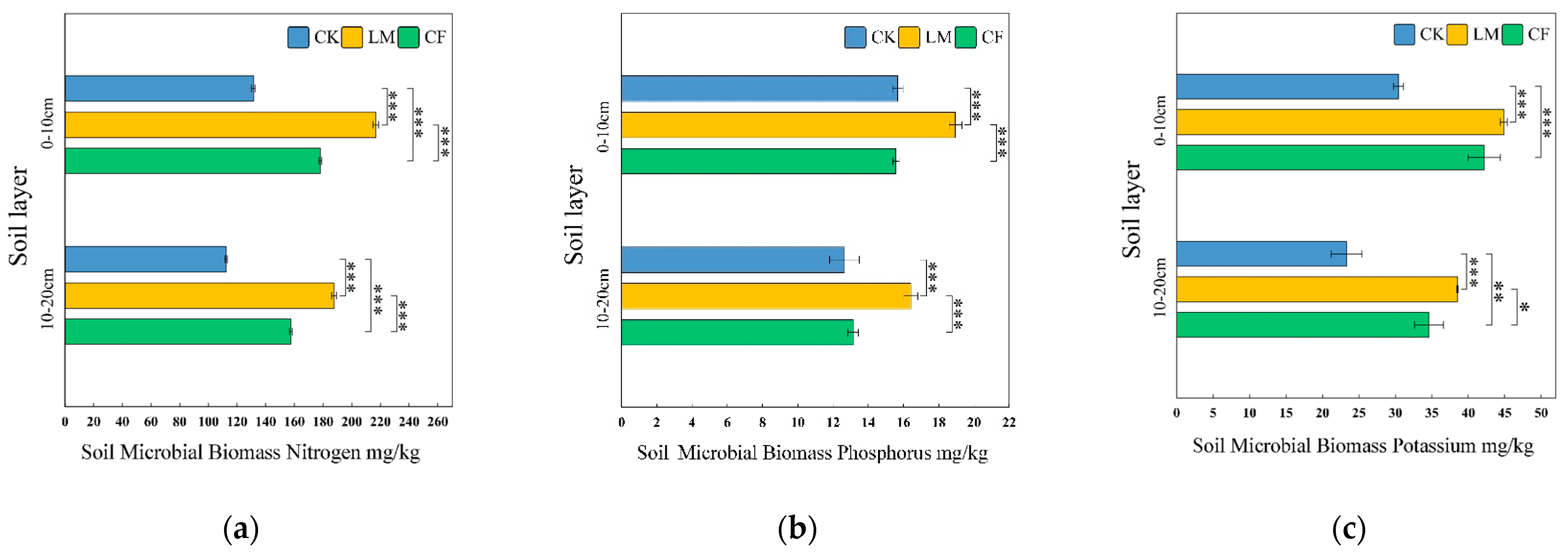
3.1.2. Soil Chemical and Nutrient Characteristics (SOC, TN, TP, TK, Available Nutrients, Microbial Biomass Nutrients)
Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
Soil Total Nitrogen (TN)
Soil Total Phosphorus (TP)
Available Potassium (AK)
Available Nitrogen (AN)
Available Phosphorus (AP)
Available Potassium (AK)
Soil Microbial Biomass Nitrogen (SMBN)
Soil Microbial Biomass Phosphorus (SMBP)
Soil Microbial Biomass Potassium (SMBK)
3.2. Soil Humus Composition and Transformation
3.2.1. Humus Carbon
3.2.2. Fulvic Acid Carbon
3.2.3. Humic Acid Carbon
3.2.4. HA/FA Ratio
3.3. Soil Microbial Characteristics Under Different Treatments
3.3.1. Soil Fungal Diversity Under Different Management Practices
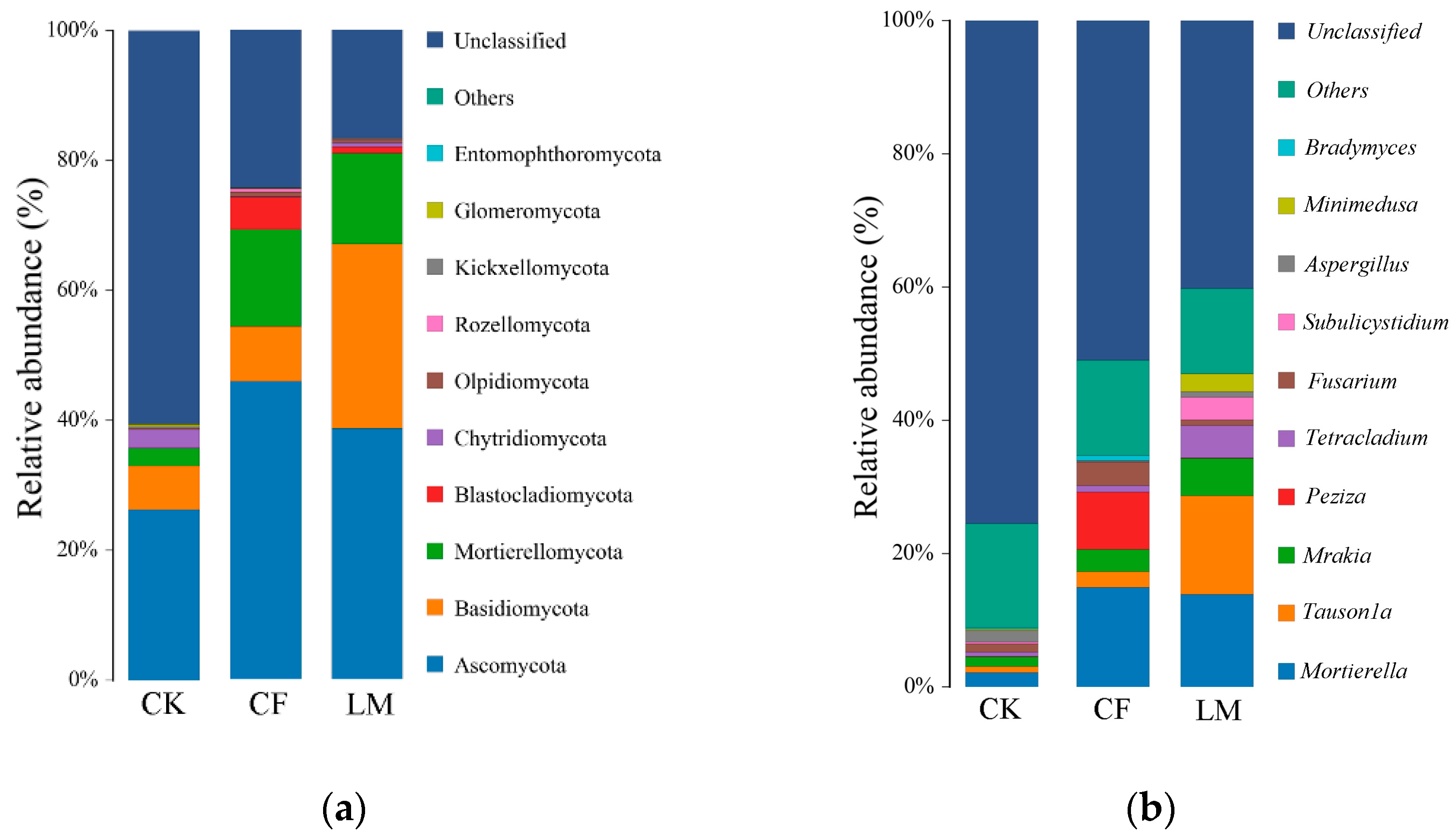
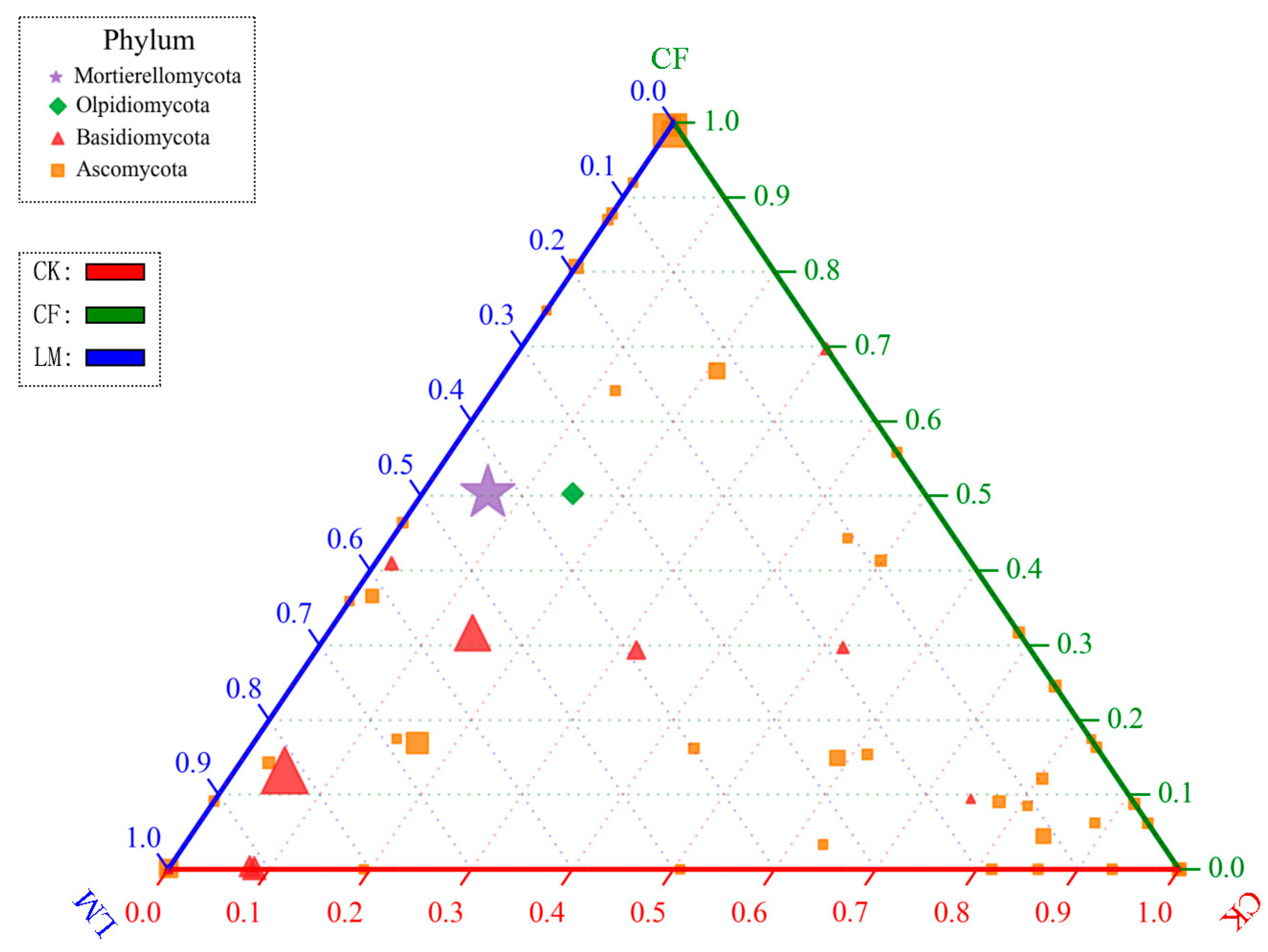
3.3.2. Community Composition at the Soil Phylum Level and Genus Level
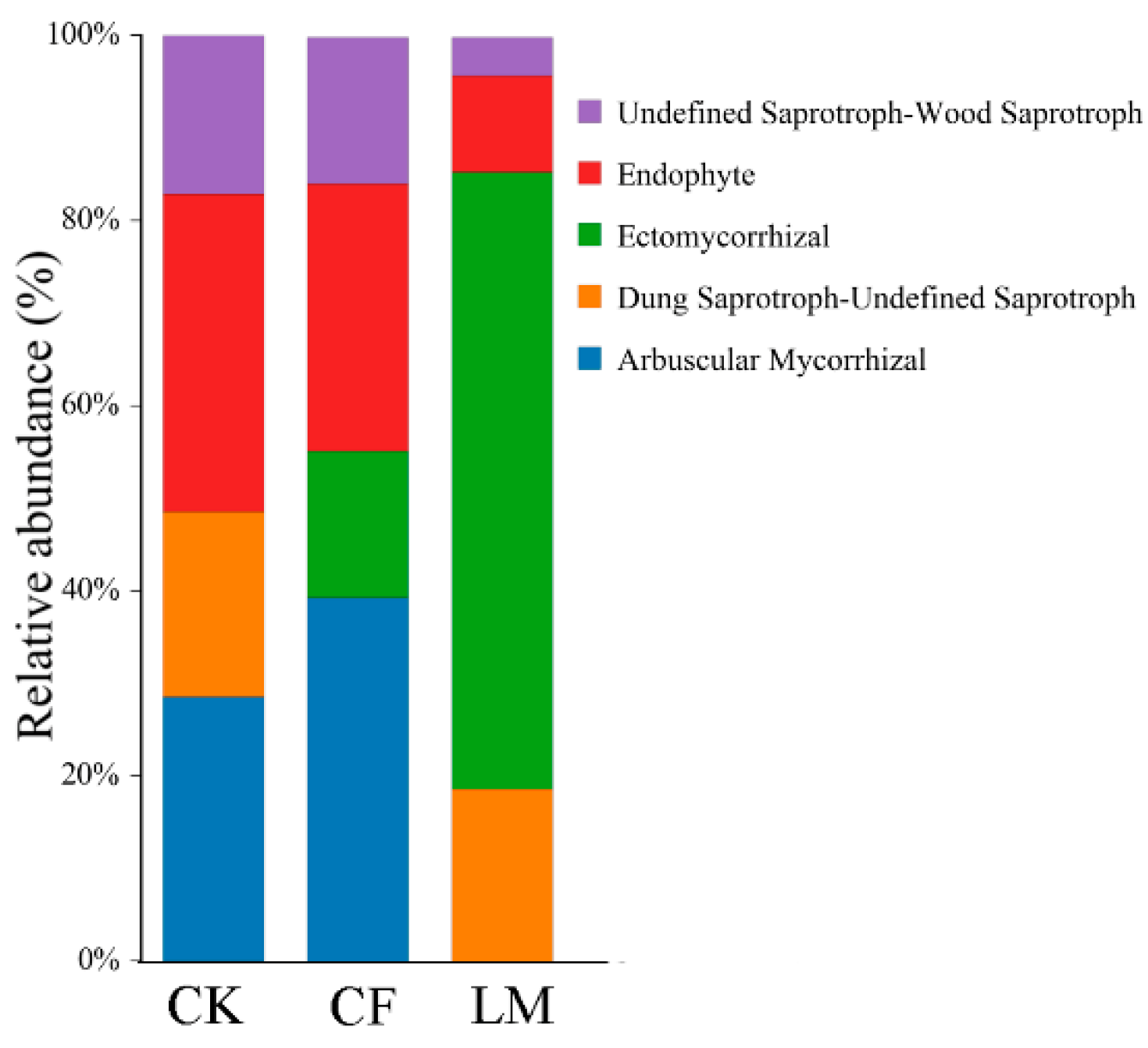
3.3.3. Functional Prediction of Fungal Communities
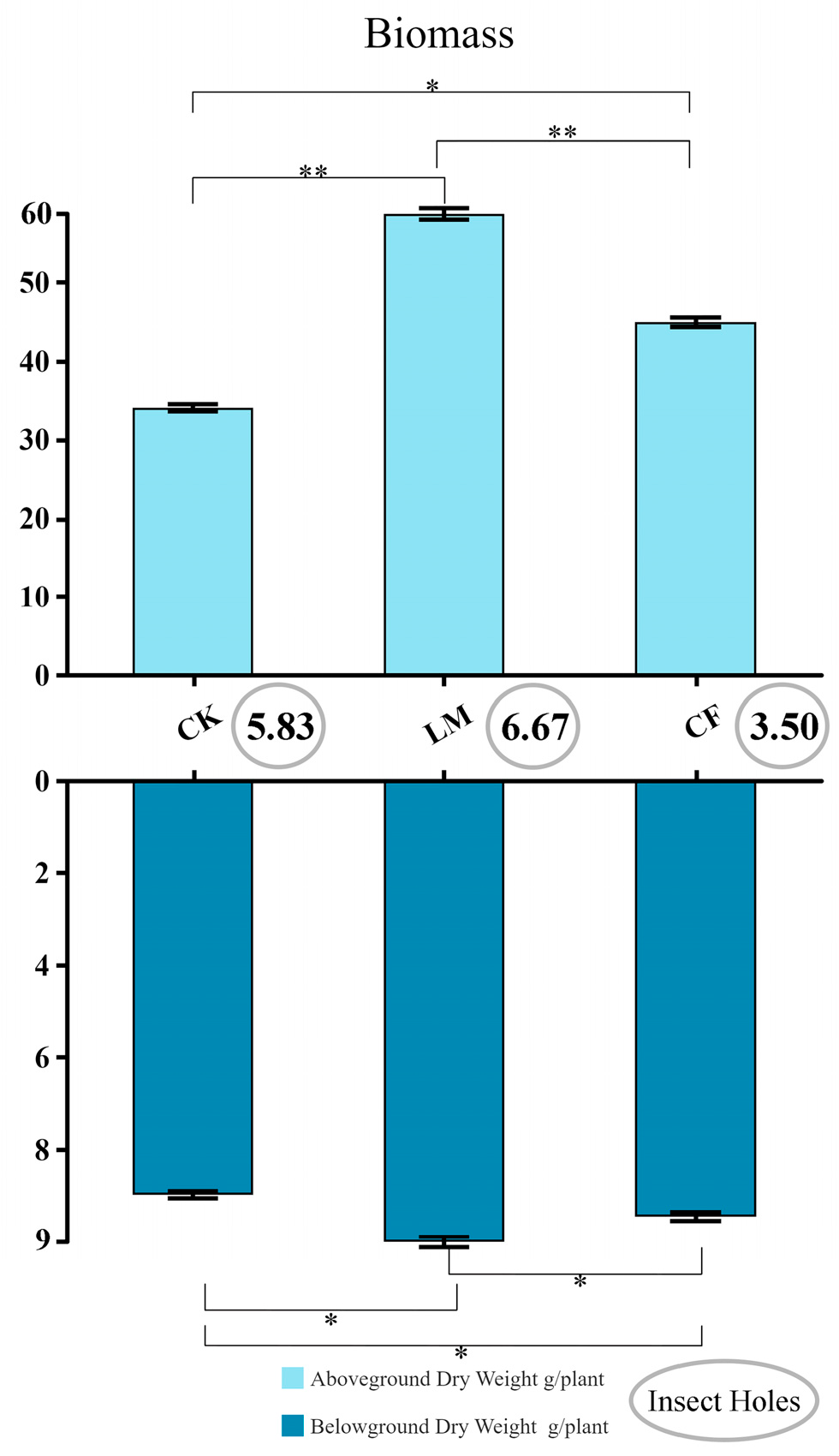
3.4. Effects of Different Treatments on Plant Biomass Accumulation
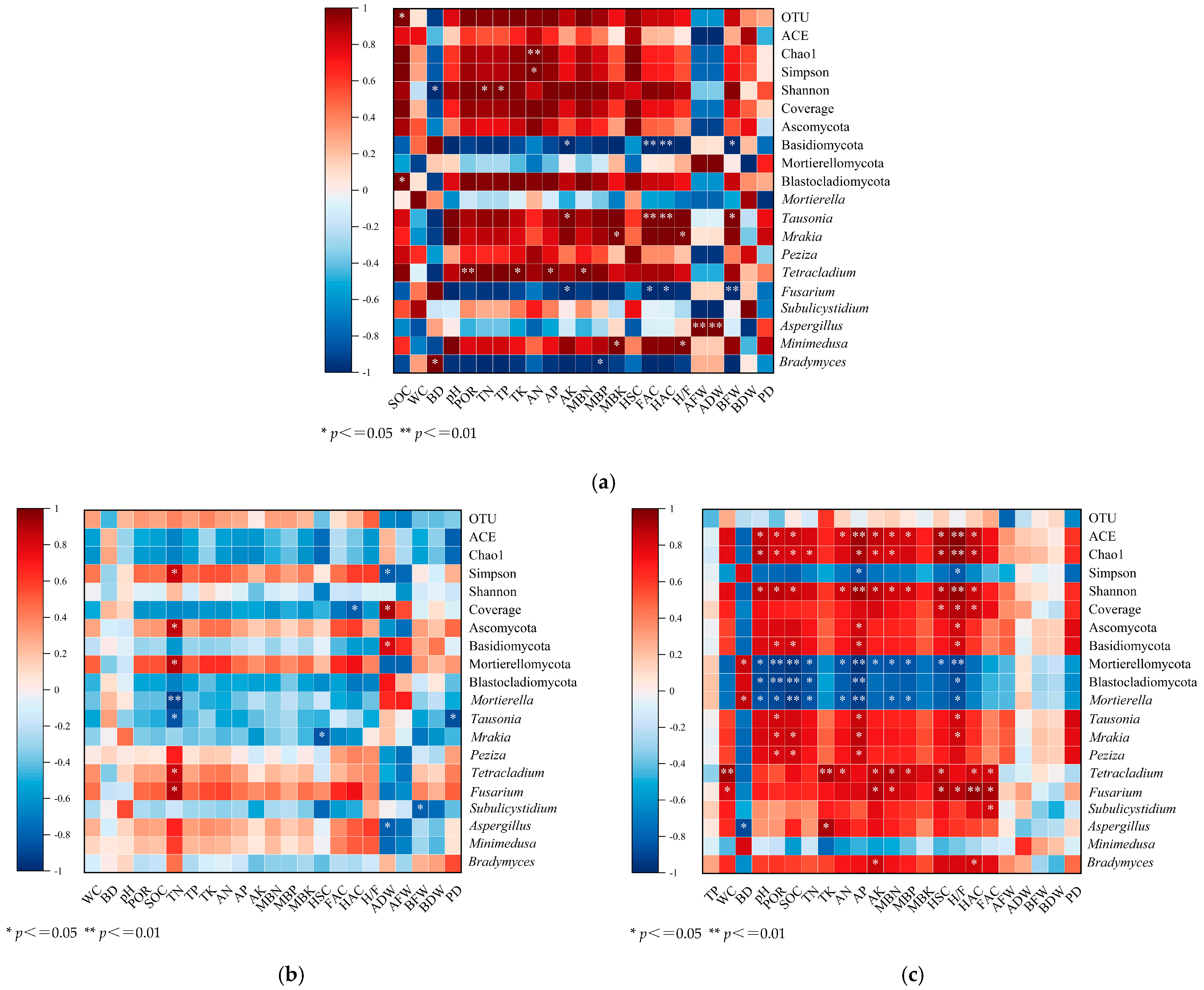
3.5. Relationships Among Soil Health, Microbial Diversity, and Plant Growth
3.5.1. CK Treatment
3.5.2. LM Treatment
3.5.3. CF Treatment
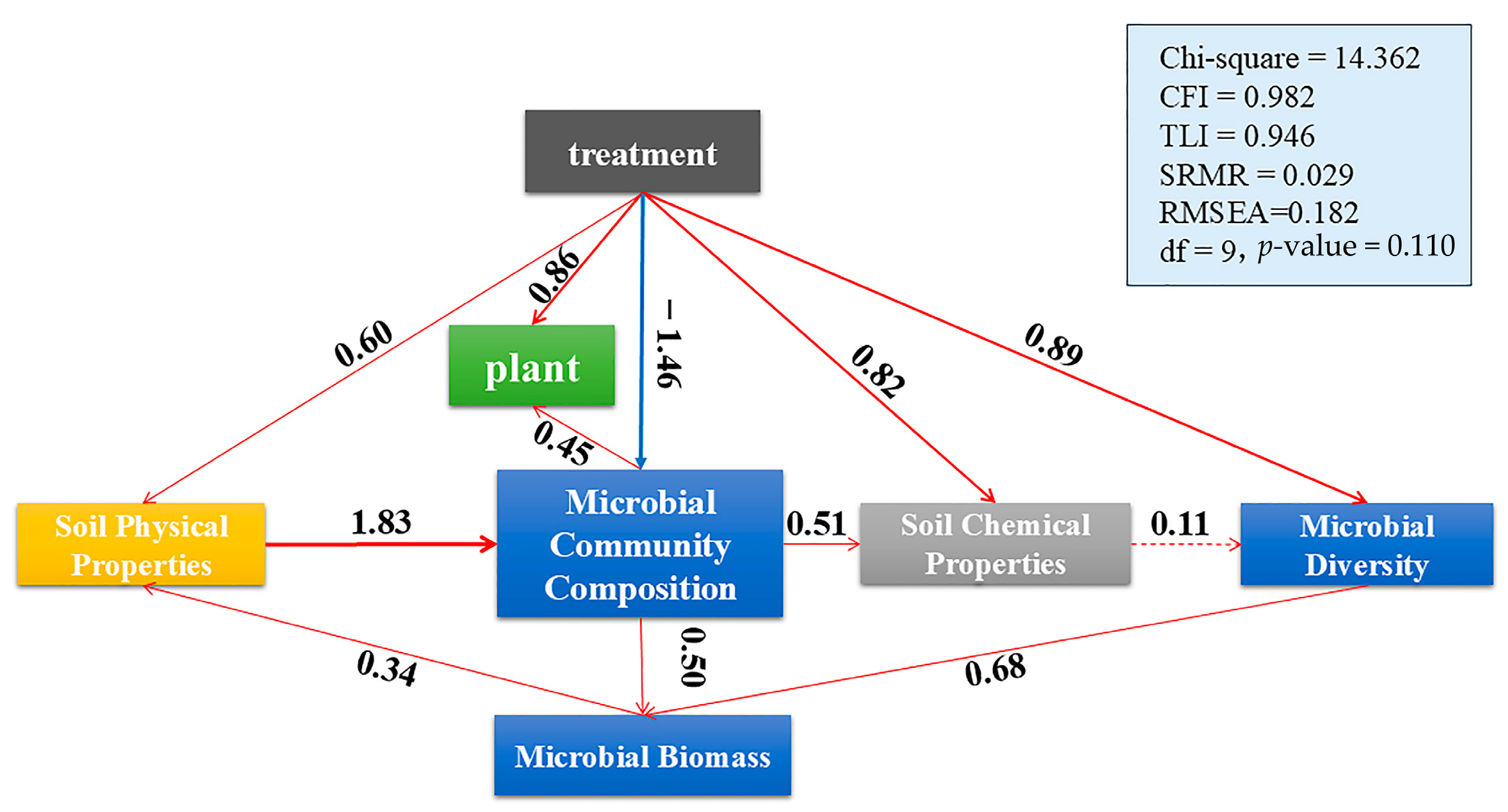
3.6. Structural Equation Modeling of Soil–Microbe–Plant Interactions Under Different Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durmuş, M.; Kızılkaya, R. The Effect of Tomato Waste Compost on Yield of Tomato and Some Biological Properties of Soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Qiao, Y.; Jin, N.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, G.; Hu, L.; Yu, J. Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Environment of Greenhouse Zucchini in Response to Different Planting and Breeding Waste Composts. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luskar, L.; Polanšek, J.; Hladnik, A.; Čeh, B. On-Farm Composting of Hop Plant Green Waste—Chemical and Biological Value of Compost. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, P.; Mishra, S.; Qiu, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z. Microbial agents obtained from tomato straw composting effectively promote tomato straw compost maturation and improve compost quality. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.; Sardar, F.; Khaliq, Z.; Nawaz, M.S.; Shehzad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Yasmin, S.; Hakim, S.; Mirza, B.S.; Mubeen, F. Tailored Bioactive Compost from Agri-Waste Improves the Growth and Yield of Chili Pepper and Tomato. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 787764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarefee, H.A.; Ishak, C.F.; Karam, D.S.; Othman, R. Efficiency of Rice Husk Biochar with Poultry Litter Co-Composts in Oxisols for Improving Soil Physico-Chemical Properties and Enhancing Maize Performance. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, N.; Tranchida-Lombardo, V.; Gabrielli, P.; Aguzzi, A.; Caputo, M.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Zaccardelli, M. Effect of Compost Tea in Horticulture. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliha, B.B.; Jeyasree, R.; Banupriya, P.; Indirani, R. Long Term Influence of Manure-Fertilizer Treatments on Soil Biological Health and Yield of Rice Crop. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2021, 9, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Effects of compost as a soil amendment on bacterial community diversity in saline–alkali soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1253415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.; Pascual, J.A.; López-García, Á.; Romo-Vaquero, M.; De Santiago, A.; Ros, M.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Alguacil, M.D.M. Effects of inorganic and compost tea fertilizers application on the taxonomic and functional microbial diversity of the purslane rhizosphere. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1159823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, R.; Armand, N. Effect of Ecophysiological Characteristics of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) in Response to Organic Fertilizers (compost and Vermicompost). Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 48, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadias, V.; Ioannou, Z.; Vavoulidou, E.; Paschalidis, C. Short Term Effects of Chemical Fertilizer, Compost and Zeolite on Yield of Lettuce, Nutrient Composition and Soil Properties. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Khan, A.; Shen, G.; Wei, D.; Wang, W. Effects of Straw Return on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities in a Cold-Region Alkaline Farmland. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, G.C. Taxonomic and functional diversity of rhizosphere microbiome recruited from compost synergistically determined by plant species and compost. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 798476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Din, A.R.J.; Cheng, K.K.; Sarmidi, M.R. Assessment of compost extract on yield and phytochemical contents of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa cv. chinensis) grown under different fertilizer strategies. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 2, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; Gou, Z.; Hou, Y.; Lai, Y. An Investigation into the Viability of Portable Proximal Sensor X-Ray Fluorescence Data for Assessing Heavy Metal Contamination in Urban Soils: A Case Study in Changchun, China. Toxics 2024, 12, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheberl, L.; Scharenbroch, B.C.; Werner, L.P.; Prater, J.R.; Fite, K.L. Evaluation of soil pH and soil moisture with different field sensors: Case study urban soil. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, B.; Dufey, J.E. The resistance of centennial soil charcoal to the “Walkley-Black” oxidation. Geoderma 2017, 303, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Hou, J.; Zhao, J.; Clarke, N.; Kempenaar, C.; Chen, X. Predicting Soil Organic Matter, Available Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus and Available Potassium in a Black Soil Using a Nearby Hyperspectral Sensor System. Sensors 2024, 24, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Weng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pei, J. Plant–Soil–Microbial Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry in Mongolian Pine-Planted Forests Under Different Environmental Conditions in Liaoning Province, China. Forests 2025, 16, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblaciones, M.J.; García-Latorre, C.; Velazquez, R.; Broadley, M.R. Effects of Selenate Application on Growth, Nutrient Bioaccumulation, and Bioactive Compounds in Broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica L.). Horticulturae 2024, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.J.; Huang, W.; Timokhin, V.I.; Hammel, K.E. Lignin lags, leads, or limits the decomposition of litter and soil organic carbon. Ecology 2020, 101, 03113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xing, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Xu, D. Canopy Gaps Control Litter Decomposition and Nutrient Release in Subtropical Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Chang, Y.; Hou, H.; Peng, P.; Xiang, W. Quantification of the sources of soluble organic N (SON) from new litter or indigenous soil in a typical subtropical forest. Authorea 2021, 12, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; de Vries, W.; Thomas, B.; Hao, X.; Shi, X. Impacts of long-term nitrogen fertilization on acid buffering rates and mechanisms of a slightly calcareous clay soil. Geoderma 2017, 11, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G. Effects of Straw Mulching Thickness on the Soil Health in a Temperate Organic Vineyard. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, M.; Duan, Y.; Wu, L. Phosphorus fertilizer input level regulates soil organic carbon physical fraction sequestration by influencing the microbial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 210, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yan, H.; Zhou, G.S.; Jiang, C.H.; Liu, P.; Yu, G.; Duan, J. A Insights into the mechanism of the effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on the quality of authentic Angelica sinensis under different soil microenvironments. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Singh, V.K.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Meena, A.L.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.P.; Panwar, A.S. Long-term impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon dynamics in a rice-wheat system. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1862–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Tang, D.W. Soil enzyme activities, soil physical properties, photosynthetic physical characteristics and water use of winter wheat after long-term straw mulch and organic fertilizer application. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1186376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, K.H.E.; Chenu, C.; Coucheney, E.; Herrmann, A.M.; Keller, T.; Kätterer, T.; Jarvis, N. Modelling dynamic interactions between soil structure and the storage and turnover of soil organic matter. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2020, 17, 5025–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, Z.; Dai, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, T. Soil organic carbon, carbon fractions, and microbial community under various organic amendments. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Teng, W.; Cheng, K.; Yang, F. Artificial humic acid regulates the impact of fungal community on soil macroaggregates formation. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Gao, C.; Pan, X.; Tang, D.W.; van der Ploeg, M. Effects of long-term super absorbent polymer and organic manure on soil structure and organic carbon distribution in different soil layers. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.G.; Choudoir, M.; Fierer, N.; Strickland, M.S. Volatile organic compounds from leaf litter decomposition alter soil microbial communities and carbon dynamics. Ecology 2020, 101, e03130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-F.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.-X.; Zhang, W.-M.; Cheng, X.-Y.; Chen, W.-F. Effects of straw and biochar addition on soil nitrogen, carbon, and super rice yield in cold waterlogged paddy soils of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Shah, F.; Zhou, C. Combining rice straw biochar with leguminous cover crop as green manure and mineral fertilizer enhances soil microbial biomass and rice yield in South China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 778738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, I.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Huang, Y. Effects of different straw biochars on soil organic carbon, nitrogen, available phosphorus, and enzyme activity in paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Ma, X. Dynamics of Non-Structural Carbohydrates Release in Chinese Fir Topsoil and Canopy Litter at Different Altitudes. Plants 2023, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, T. Responses of soil organic and inorganic carbon to organic and phosphorus fertilization in a saline-alkaline paddy field. Geosci. Lett. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; DeBruyn, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Eash, N. Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: Implications for soil quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Levavasseur, F.; Houot, S. Substitution of mineral N fertilizers with organic wastes in two long-term field experiments: Dynamics and drivers of crop yields. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, S.; Luan, C.S.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.L.; Li, X.X.; Song, H. Partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer improves soil fertility and crop yields while mitigating N2O emissions in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresch, S.; Frey, D.; Le Bayon, R.C.; Zanetta, A.; Rasche, F.; Fliessbach, A.; Moretti, M. Litter decomposition driven by soil fauna, plant diversity and soil management in urban gardens. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Li, D.-C.; Huang, J.; Han, T.-F.; Ahmed, W.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.N.; Khan, Z.H.; Xu, Y.-M.; Li, Q.; et al. Dynamics of organic carbon and nitrogen in deep soil profile and crop yields under long-term fertilization in wheat-maize cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othieno, C.O. The effect of organic mulches on yields and phosphorus utilization by plants in acid soils. Plant Soil 1973, 38, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Garnier, J.; da Silveira Pontes, L.; de Faccio Carvalho, P.C.; Billen, G.; Simioni Assmann, T. Domestic Herbivores, the Crucial Trophic Level for Sustainable Agriculture: Avenues for Reconnecting Livestock to Cropping Systems. Agronomy 2023, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, J.R.; Singh, B.P.; Dougherty, W.J.; Fang, Y.; Badgery, W.; Hoyle, F.C.; Cowie, A.L. Impact of agricultural management practices on the nutrient supply potential of soil organic matter under long-term farming systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Mou, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Fertilization effects on soil organic matter chemistry. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Tian, R.; Zhang, R.; Chen, P.; Jing, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Li, Z. Millimeter-scale interactions of nitrogen and potassium on denitrification, anammox, and Feammox in soil fertilization zones. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 157, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Niu, X.; Chen, B.; Pu, S.; Ma, H.; Li, P.; Ma, X. Chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and diversity and yield of cotton. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1295722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, S.; He, X.; Liu, S.; Kong, X.; Dong, F. Differences of C sequestration in functional groups of soil humic acid under long term application of manure and chemical fertilizers in North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 176, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, D.N.; Nath, C.P.; Hazra, K.K.; Senthilkumar, M.; Singh, S.S.; Praharaj, C.S.; Kumar, N. Long-term impact of diversified crop rotations and nutrient management practices on soil microbial functions and soil enzymes activity. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbeault-Mayers, X.; Laliberté, E. Root phosphatase activity is coordinated with the root conservation gradient across a phosphorus gradient in a lowland tropical forest. New Phytol. 2024, 243, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cheng, H.; Peng, Y.; Sun, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Ning, Q. Relative role of soil nutrients vs. carbon availability on soil carbon mineralization in grassland receiving long-term N addition. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Han, X.; Yan, J.; Zou, W. Impact of combined organic amendments and chemical fertilizers on soil microbial limitations, soil quality, and soybean yield. Plant Soil 2025, 507, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, L. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Lou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Response of soil organic matter fractions and composition of microbial community to long-term organic and mineral fertilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Q.; Liu, M.; Wu, L. Changes in humus carbon fractions in paddy soil given different organic amendments and mineral fertilizers. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of long-term fertilization on humic redox mediators in multiple microbial redox reactions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębska, B.; Długosz, J.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A. The content and quality of soil carbon and nitrogen as well as enzymatic activity in soils with diverse texture following different land use and management practices. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liao, G.; Banerjee, S.; Gu, S.; Liang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, T. Long-term organic fertilization promotes the resilience of soil multifunctionality driven by bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Yang, R.; Jie, X.; Lian, T.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y. Organic management improved the multifunctionality in recolonization soil by increasing microbial diversity and function. Funct. Ecol. 2024, 38, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Plaza, C.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Trivedi, C.; Wang, J.; Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Litter and soil biodiversity jointly drive ecosystem functions. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, X.; Liao, H.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q. Ureolytic microbial community is modulated by fertilization regimes and particle-size fractions in a Black soil of Northeastern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Zhu, D.; Lindhardt, J.H.; Lin, S.M.; Ke, X.; Cui, L. Long-term fertilization history alters effects of microplastics on soil properties, microbial communities, and functions in diverse farmland ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, B.; Borkotoki, B.; Narzari, R.; Kataki, R.; Gogoi, N. Organic amendments: Effect on carbon mineralization and crop productivity in acidic soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, R.P. Effects of Different Cover Crops and Amendments on Soil and Crop Properties in Organic Vegetable Production. Agronomy 2024, 14, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Man, J.; Romero, F.; Bergmann, J.; Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Mycorrhization enhances plant growth and stabilizes biomass allocation under drought. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronson, E.; Enders, L. Root microbes can improve plant tolerance to insect damage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecology 2025, 106, e4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, P.; Bommarco, R.; Strengbom, J.; Viketoft, M. Above-and belowground insect herbivores mediate the impact of nitrogen eutrophication on the soil food web in a grassland ecosystem. Oikos 2018, 127, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchenko, M.; Saar, S.; Lepik, A. Intraspecific genetic diversity modulates plant–soil feedback and nutrient cycling. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Xue, P.; Yang, H.; Mörchen, R.; Wang, J. Soil Fertility and Maize Residue Quality All Effect the Exogenous Carbon Sequestration Only in the Short Term in Macroaggregates, but Not in Microaggregates. Agronomy 2025, 15, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.F.; Luperini, B.C.O.; Barcelos, J.P.d.Q.; Putti, F.F.; Mooney, S.J.; Calonego, J.C. Mechanical Chiseling Versus Root Bio-Tillage on Soil Physical Quality and Soybean Yield in a Long-Term No-Till System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, F.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, B. Fungal alpha diversity influences stochasticity of bacterial and fungal community assemblies in soil aggregates in an apple orchard. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 162, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikryukov, V.; Dulya, O.; Zizka, A.; Bahram, M.; Hagh-Doust, N.; Anslan, S.; Tedersoo, L. Connecting the multiple dimensions of global soil fungal diversity. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Boland, G.; Zhou, T. Concurrent selection for microbial suppression of Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium head blight and deoxynivalenol in wheat. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, E.; Hanaka, A. Mortierella Species as the Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi Present in the Agricultural Soils. Agriculture 2021, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.W.; Lu, L.X.; Shi, H.M.; Ye, J.R. Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the growth and soil microbial community of Carya illinoinensis. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Eberl, L.; Hartmann, A. The rhizosphere as a reservoir for opportunistic human pathogenic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 7, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Qiu, C.; Ding, Y.; Gu, H.; Ding, Z. Organic mulching positively regulates the soil microbial communities and ecosystem functions in tea plantation. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caboň, M.; Galvánek, D.; Detheridge, A.P.; Griffith, G.W.; Maráková, S.; Adamčík, S. Mulching has negative impact on fungal and plant diversity in Slovak oligotrophic grasslands. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 52, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ye, Y.; Liao, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, D.; Guan, Q. Organic mulching alters the composition, but not the diversity, of rhizosphere bacterial and fungal communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinhut, T.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Degradation and transformation of humic substances by saprotrophic fungi: Processes and mechanisms. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2007, 21, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, H.; McLean, M.A. Decomposition rate of organic substrates in relation to the species diversity of soil saprophytic fungi. Oecologia 2004, 139, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Han, F.; Che, Y. Changes in soil microbial biomass and functional diversity with a nitrogen gradient in soil columns. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 64, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ge, T.; Zhou, P.; Liu, S.; Roberts, P.; Zhu, H.; Wu, J. Soil microbial biomass and bacterial and fungal community structures responses to long-term fertilization in paddy soils. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Su, Y.; Qu, H.; Han, L.; He, X.; Guo, J.; Huang, G. Effects of micro-positive pressure environment on nitrogen conservation and humification enhancement during functional membrane-covered aerobic composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiao, M.; Zhan, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z. Humification and fungal community succession during pig manure composting: Membrane covering and mature compost addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bruggen, A.H.; Sharma, K.; Kaku, E.; Karfopoulos, S.; Zelenev, V.V.; Blok, W.J. Soil health indicators and Fusarium wilt suppression in organically and conventionally managed greenhouse soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 92–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Deng, L.; Chachar, M.; Tu, P. Symbiotic synergy: How Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi enhance nutrient uptake, stress tolerance, and soil health through molecular mechanisms and hormonal regulation. IMA Fungus 2025, 16, e144989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Cai, H. Soil Enzyme Activities Affect SOC and TN in Aggregate Fractions in Sodic-Alkali Soils, Northeast of China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Hu, H.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Q.; Sun, K.; Feng, Y.; Ning, T. Shifts in microbial community and carbon sequestration in farmland soil under long-term conservation tillage and straw returning. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 136, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Heck, R.H.; Glazer, C.T.; Loo, M.K.; Zayas, J.R.; Krenz, A.; Deenik, J.L. Measuring the immeasurable: A structural equation modeling approach to assessing soil health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardol, P.; Souza, L.; Classen, A.T. Resource availability mediates the importance of priority effects in plant community assembly and ecosystem function. Oikos 2013, 122, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Wang, J.; Sainju, U.M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Khan, A. Cover cropping enhances soil microbial biomass and affects microbial community structure: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 381, 114696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgolozeli, S.; Nciizah, A.D.; Wakindiki, I.I.; Dhavu, K.; Mudau, F.N.; Onwona-Agyeman, S. Agri-Mat Mulching Improves Aggregate Stability and Soil Pore Formation on Smallholder Farms in Sub-Saharan Africa. Food Energy Secur. 2025, 14, e70036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Qadir, A.A.; Alserae, H.; Raza, A.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W. Organic amendment-mediated reclamation and build-up of soil microbial diversity in salt-affected soils: Fostering soil biota for shaping rhizosphere to enhance soil health and crop productivity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 109889–109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Layer (cm) | Test Treatment | pH | Moisture Content (%) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | CK | 6.91 ± 0.09 a | 11.49 ± 1.12 c | 1.56 ± 0.04 a | 33.72 ± 1.50 c |
| LM | 5.93 ± 0.10 c | 36.06 ± 0.26 a | 1.07 ± 0.02 c | 58.71 ± 0.29 a | |
| CF | 6.31 ± 0.02 b | 29.03 ± 0.38 b | 1.33 ± 0.03 b | 41.17 ± 0.27 b | |
| 10–20 | CK | 6.68 ± 0.15 a | 10.23 ± 0.62 c | 1.76 ± 0.03 a | 30.84 ± 0.30 c |
| LM | 5.94 ± 0.05 c | 31.11 ± 0.44 a | 1.16 ± 0.05 c | 46.84 ± 0.47 a | |
| CF | 6.17 ± 0.08 b | 26.20 ± 0.58 b | 1.40 ± 0.02 b | 39.69 ± 0.72 b |
| Soil Layer (cm) | Test Treatment | Humus Carbon g/kg | Fulvic Acid Carbon g/kg | Humic Acid Carbo g/kg | Humic Acid/ Fulvic Acid Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | CK | 7.14 ± 0.06 c | 3.31 ± 0.19 a | 1.51 ± 0.13 c | 0.46 ± 0.02 c |
| LM | 10.53 ± 0.68 a | 3. 10 ± 0.17 a | 6.36 ± 0.22 a | 2.06 ± 0.05 a | |
| CF | 8.04 ± 0.24 b | 2.26 ± 0.14 b | 4.32 ± 0.34 b | 1.91 ± 0.04 b | |
| 10–20 | CK | 6.68 ± 0.31 c | 2.73 ± 0.15 a | 1.19 ± 0.11 c | 0.43 ± 0.02 c |
| LM | 9.51 ± 0.44 a | 2.82 ± 0.11 a | 5.68 ± 0.36 a | 2.01 ± 0.02 a | |
| CF | 7.06 ± 0.07 b | 2.08 ± 0.04 b | 3.63 ± 0.11 b | 1.74 ± 0.04 b |
| Treatment | OTU | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 228 ± 5.2 b | 242.19 ± 8.5 b | 243.95 ± 7.8 b | 0.07 ± 0.004 b | 3.93 ± 0.05 b | 0.9961 |
| CF | 430 ± 0.7 a | 444.16 ± 12.9 a | 447.03 ± 9.3 a | 0.03 ± 0.002 a | 4.38 ± 0.07 a | 0.9990 |
| LM | 428 ± 9.3 a | 436.99 ± 10.2 a | 442.29 ± 10.0 a | 0.03 ± 0.003 a | 4.40 ± 0.06 a | 0.9994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Xing, Y.; Guo, X.; Qu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G. Organic Mulching Enhances Soil Health and Fungal Diversity to Promote Growth of Aralia continentalis Kitag: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Fertilization in Agroecosystems. Biology 2025, 14, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111624
Liu Q, Zheng J, Xing Y, Guo X, Qu Y, Dong Z, Yu W, Zhang G. Organic Mulching Enhances Soil Health and Fungal Diversity to Promote Growth of Aralia continentalis Kitag: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Fertilization in Agroecosystems. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qian, Junyan Zheng, Yuhe Xing, Xingchi Guo, Ying Qu, Zhiyu Dong, Wei Yu, and Guoyu Zhang. 2025. "Organic Mulching Enhances Soil Health and Fungal Diversity to Promote Growth of Aralia continentalis Kitag: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Fertilization in Agroecosystems" Biology 14, no. 11: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111624
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zheng, J., Xing, Y., Guo, X., Qu, Y., Dong, Z., Yu, W., & Zhang, G. (2025). Organic Mulching Enhances Soil Health and Fungal Diversity to Promote Growth of Aralia continentalis Kitag: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Fertilization in Agroecosystems. Biology, 14(11), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111624




