How Wastewater Addition Reshapes Peatland Vegetation via Linked Abiotic and Biotic Changes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
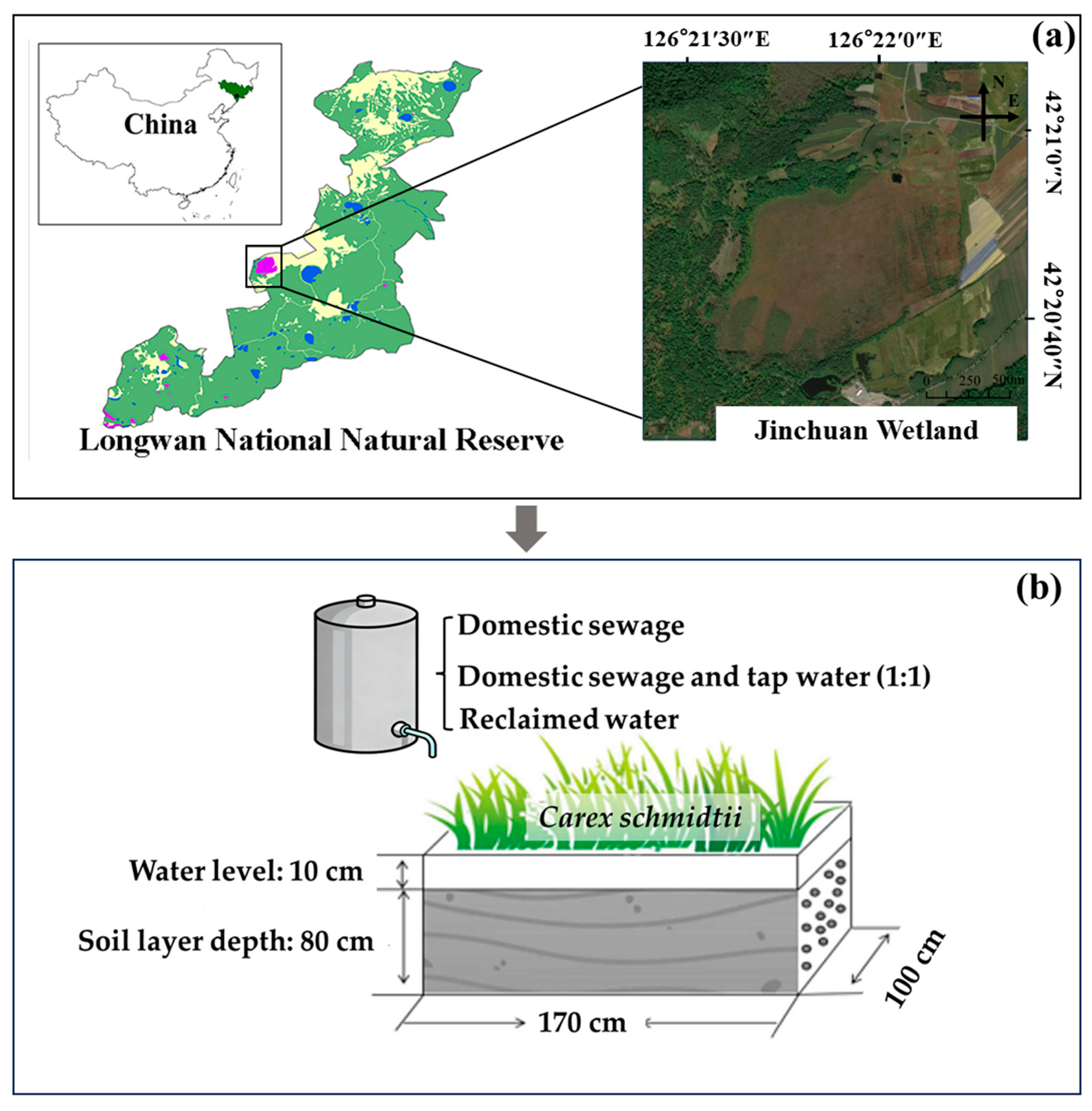
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Determination Indicators and Methods for Plants
2.4.1. Nutrients and Biomass in Aboveground Plant Parts
2.4.2. Plant Diversity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
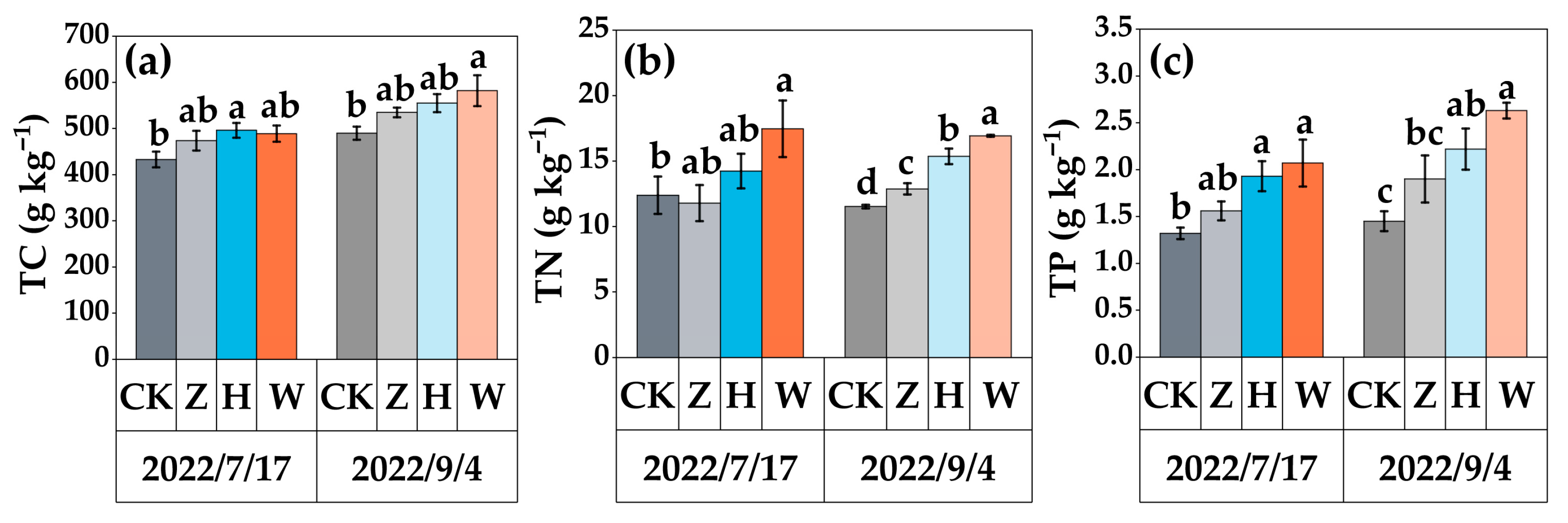
3.1. Soil Properties
3.2. Plant Nutrient Dynamics
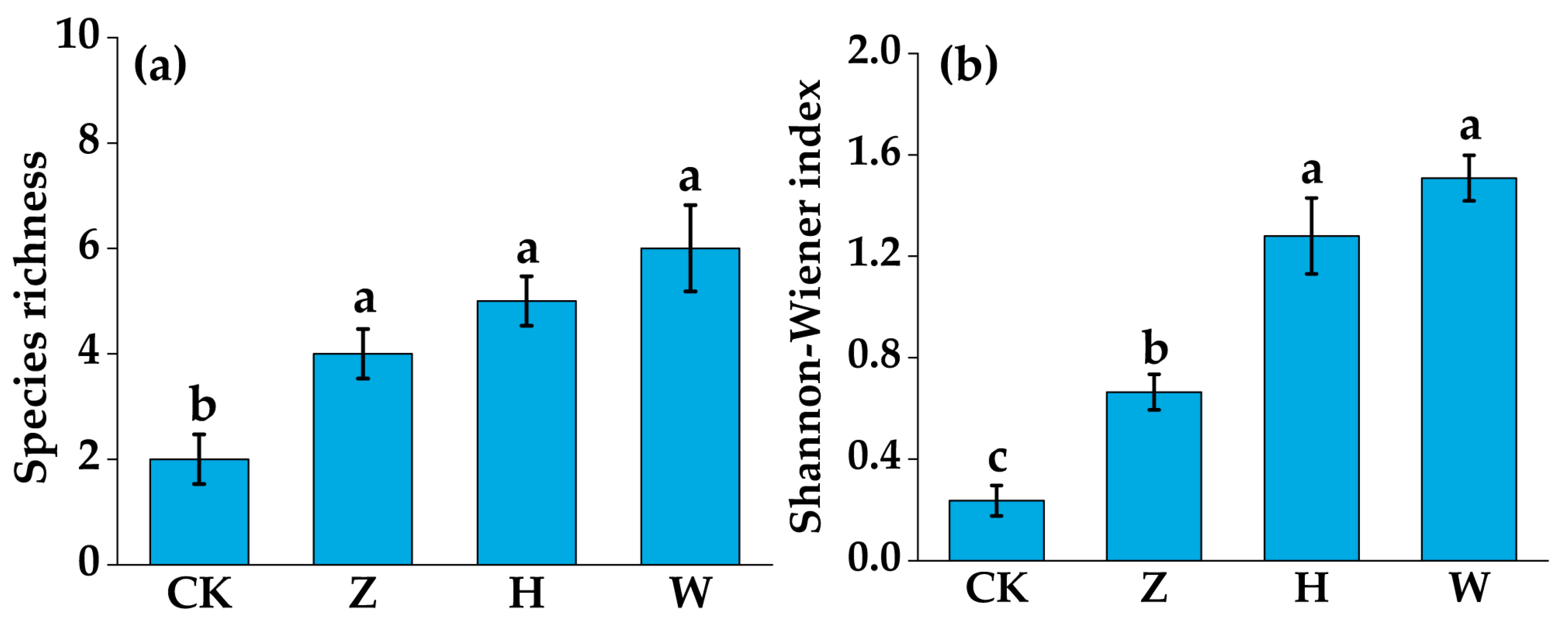
3.3. Changes in Plant Community Composition and Diversity Indices
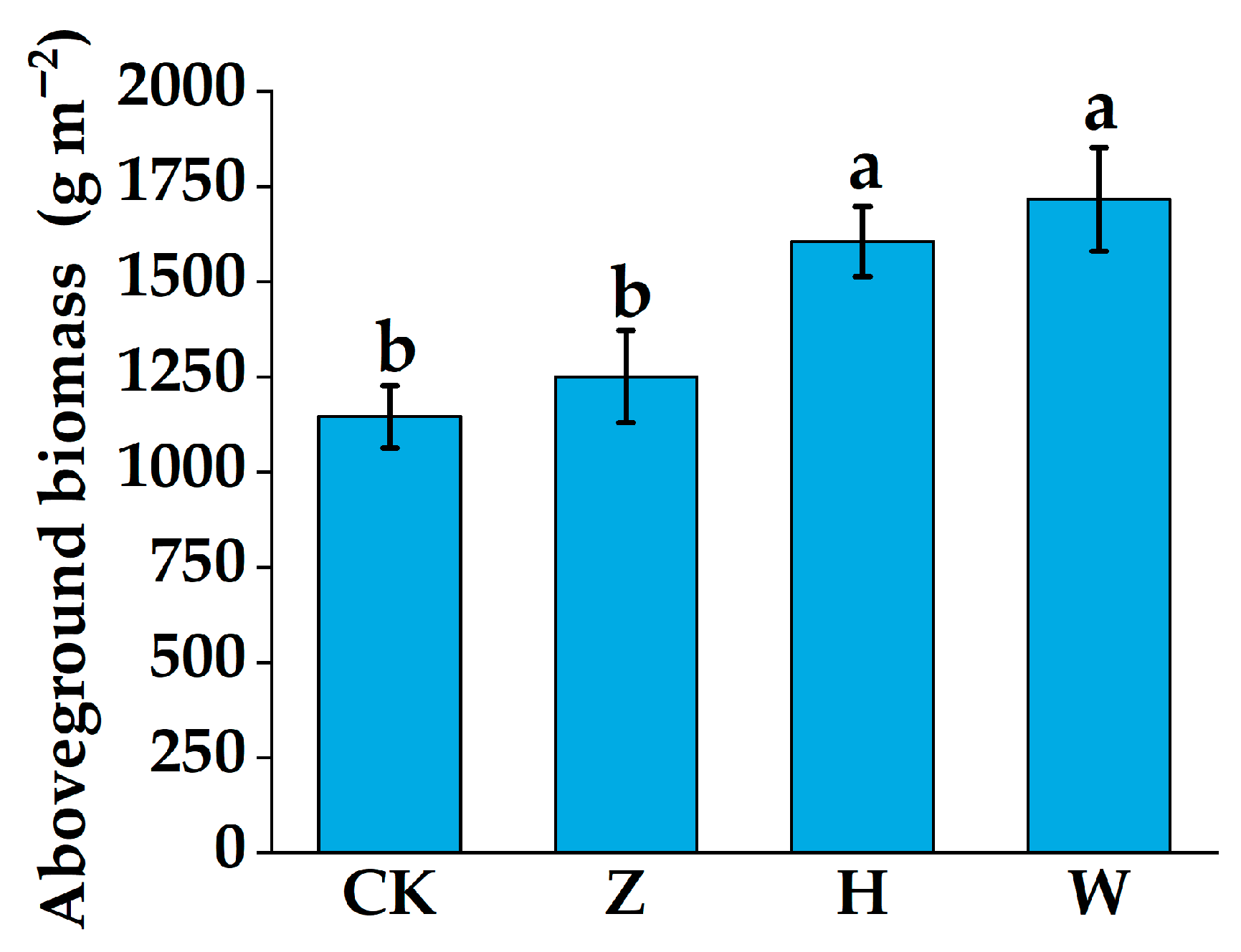
3.4. Variation Characteristics of Aboveground Plant Biomass
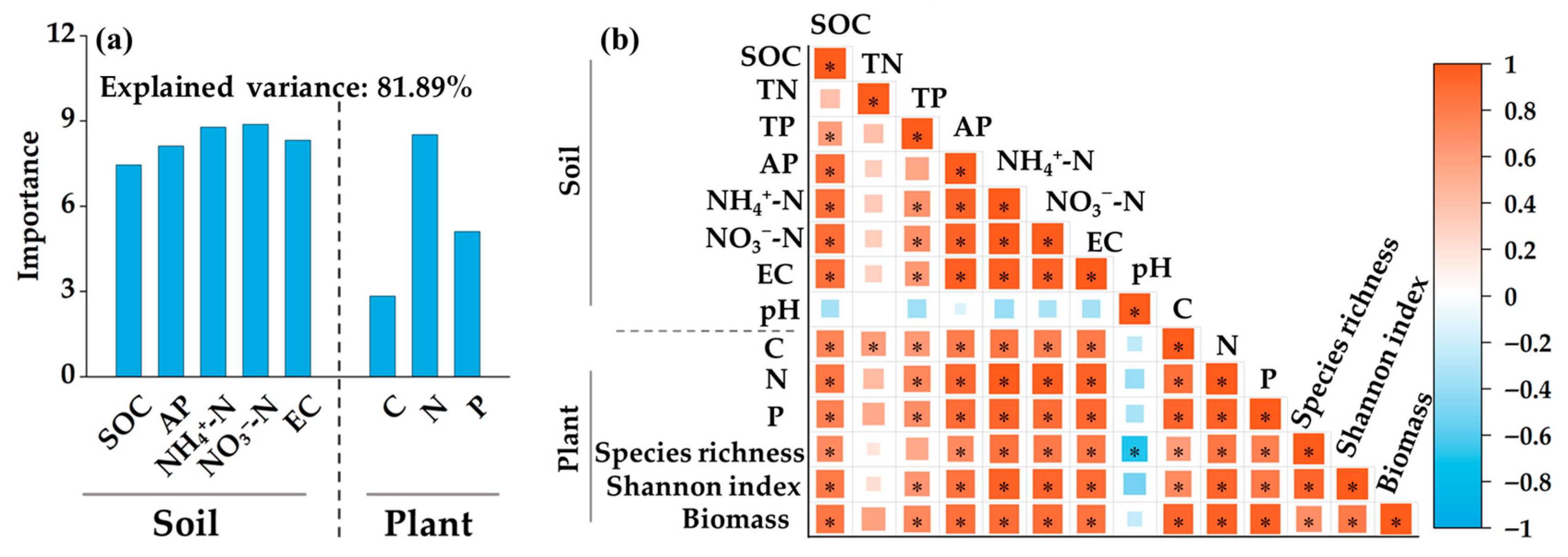
3.5. Effects of Soil Parameters and Plant Traits on Plant Diversity and Aboveground Biomass
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Domestic Sewage with Different Treatment Gradients on Plant Community Structure
4.2. Effects of Domestic Sewage with Different Treatment Gradients on Aboveground Plant Biomass
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, K.; Thompson, D.; Hopkinson, C.; Petrone, R.; Chasmer, L. Peatland-fire interactions: A review of wildland fire feedbacks and interactions in Canadian boreal peatlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, E. Northern peatlands: Role in the carbon cycle and probable responses to climatic warming. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.R.; Trofymow, J.A.; Siltanen, M.; Kozak, L.M. Litter decomposition and nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in peatlands and uplands over 12 years in central Canada. Oecologia 2008, 157, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AminiTabrizi, R.; Dontsova, K.; Grachet, N.G.; Tfaily, M.M. Elevated temperatures drive abiotic and biotic degradation of organic matter in a peat bog under oxic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuper, F.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Dorrepaal, E.; Weedon, J.T.; van Hal, J.; van Logtestijn, R.S.P.; Aerts, R. A frozen feast: Thawing permafrost increases plant-available nitrogen in subarctic peatlands. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, M. Ecological ditch system for nutrient removal of rural domestic sewage in the hilly area of the central Sichuan Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.R.; Bubier, J.L. Plant and soil nitrogen in an ombrotrophic peatland, southern Canada. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangremond, E.M.; Simpson, L.T.; Osborne, T.Z.; Feller, I.C. Nitrogen enrichment accelerates mangrove range expansion in the temperate–tropical ecotone. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den, E.E.; van den Berg, L.J.L.; van der, W.B.; Fritz, C.; Sheppard, L.J.; Lamers, L.P.M. Effects of airborne ammonium and nitrate pollution strongly differ in peat bogs, but symbiotic nitrogen fixation remains unaffected. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, P.; van Dijk, N.; Gray, A.; Sutton, M.; Jones, M.; Leeson, S.; Dise, N.; Leith, I.; Sheppard, L. Response of a peat bog vegetation community to long-term experimental addition of nitrogen. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1167–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, R.K.; Vitt, D.H.; Vile, M.A.; Graham, J.A.; Hartsock, J.A.; Fillingim, H.; House, M.; Quinn, J.C.; Scott, K.D.; Petix, M.; et al. Experimental nitrogen addition alters structure and function of a boreal bog: Critical load and thresholds revealed. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89, e01371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juutinen, S.; Bubier, J.L.; Moore, T.R. Responses of vegetation and ecosystem CO2 exchange to 9 years of nutrient addition at Mer Bleue bog. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midolo, G.; Alkemade, R.; Schipper, A.M.; Benítez-López, A.; Perring, M.P.; De Vries, W. Impacts of nitrogen addition on plant species richness and abundance: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2019, 28, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Loreau, M.; Lü, X.; He, N.; Zhang, G.; Han, X. Nitrogen enrichment weakens ecosystem stability through decreased species asynchrony and population stability in a temperate grassland. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.J.; David, T.I.; Storkey, J. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Its impact on plant communities and consequences across trophic levels. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Bu, Z.J.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.Z.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, H.K.; Wang, S.Z. Effects of nitrogen deposition on peatland: A review. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Ryo, M.; Roy, J.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Plant and soil biodiversity have non-substitutable stabilising effects on biomass production. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, P.; Dai, L.; Ma, Z.; Liu, J. Climate vs. nutrient control: A global analysis of driving environmental factors of wetland plant biomass allocation strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Eisenhauer, N.; Roscher, C. Linking plant diversity–productivity relationships to plant functional traits of dominant species and changes in soil properties in 15-year-old experimental grasslands. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Song, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, X.; Gong, C.; Ma, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Du, Y. Long-term nitrogen addition alters peatland plant community structure and nutrient resorption efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.E.; Godwin, C.M.; Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature 2017, 549, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D. Biodiversity: Population versus ecosystem stability. Ecology 1996, 77, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Wang, G.; Jia, L.; Xing, W. Anthropogenic impacts in the Changbai Mountain region of NE China over the last 150 years: Geochemical records of peat and altitude effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7512–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qomariyah, S.; Utomo, B.; Wahyudi, A.H. Constructed wetlands with Cyperus alternifolius as a sustainable solution for household greywater treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1065, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jiang, H.; Bian, H.; He, C.; Gao, Y. Effects of hydrologic mediation and plantation of Carex schmidtii Meinsh on peatland restoration in China’s Changbai Mountain region. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 96, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrame, K.K.; Souza, A.M.; Coelho, M.R.; Winkler, T.C.; Souza, W.E.; Valderrama, P. Soil organic carbon determination using NIRS: Evaluation of dichromate oxidation and dry combustion analysis as reference methods in multivariate calibration. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yan, L.; Li, G.; Sadiq, M.; Rahim, N.; Wu, J.; Ma, W.; Xu, G.; Du, M. Effects of conservation tillage strategies on soil physicochemical indicators and N2O emission under spring wheat monocropping system conditions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wen, Y.; Tan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Shang, Q. Adsorption and leaching characteristics of ammonium and nitrate from paddy soil as affected by biochar amendment. Plant Soil. Environ. 2021, 67, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Wu, Y. Effects of different land use types on soil hydrological properties and soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in typical Karst Region. JEES 2023, 5, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; He, C.; Shi, Y.; Sheng, L. Effects and driving factors of domestic sewage from different sources on nitrous oxide emissions in a bog. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastin, E.F. Total nitrogen determination for plant material containing nitrate. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 85, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, S.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Xing, T.; Jin, Y.; Colinet, G.; Lu, C. Short-Term Effects of Incorporation Depth of Straw Combined with Manure During the Fallow Season on Maize Production, Water Efficiency, and Nutrient Utilization in Rainfed Regions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Jiang, H.; Sheng, L. Multi-environment factors dominate plant community structure and diversity in an ombrotrophic bog: The water level is the main regulating mechanism. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1032068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Huo, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, B. Effects of nitrogen addition and watering on soil seed bank germination in a semiarid grassland on the Loess Plateau of China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpens, J.; Berendse, F.; Klees, H. N deposition affects N availability in interstitial water, growth of Sphagnum and invasion of vascular plants in bog vegetation. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. High nitrogen: Phosphorus ratios reduce nutrient retention and second-year growth of wetland sedges. New Phytol. 2005, 166, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Yi, B.; Qin, K.; Bu, Z.J. Long-Term Nitrogen Addition Eliminates the Cooling Effect on Climate in a Temperate Peatland. Plants 2025, 14, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Shi, F.X.; Yang, G.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Mao, R. Effects of nutrient addition on plant community composition and aboveground biomass in a marshy meadow in the Sanjiang Plain. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 1440. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Iversen, C.M.; Bridgham, S.D.; Kellogg, L.E. Scaling plant nitrogen use and uptake efficiencies in response to nutrient addition in peatlands. Ecology 2010, 91, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, M.; Charef, A.; Azouzi, R.; Trifi, M.; Khiari, N. Impact of induced natural organic carbons on soil organic carbon (SOC), permeability and production of sandy and clay soils in Mediterranean semi-arid Eco-system. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2023, 54, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.G.; Toor, G.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Mechtensimer, S.; De, M.; Obreza, T.A. A review of the fate and transport of nitrogen, phosphorus, pathogens, and trace organic chemicals in septic systems. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 455–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holaday, A.S.; Schwilk, D.W.; Waring, E.F.; Guvvala, H.; Griffin, C.M.; Lewis, O.M. Plasticity of nitrogen allocation in the leaves of the invasive wetland grass, Phalaris arundinacea and co-occurring Carex species determines the photosynthetic sensitivity to nitrogen availability. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 177, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Bao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Christie, P.; Fangmeier, A.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen enrichment enhances the dominance of grasses over forbs in a temperate steppe ecosystem. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassen, R.; Buckling, A.; Bell, G.; Rainey, P.B. Diversity peaks at intermediate productivity in a laboratory microcosm. Nature 2000, 406, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiliko, N.; Moore, T.R.; Jeannotte, R.; Bubier, J.L. Nutrient input and carbon and microbial dynamics in an ombrotrophic bog. Geomicrobiol. J. 2006, 23, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsonneault, A.J.; Moore, T.R.; Roulet, N.T. Effects of long-term fertilization on peat stoichiometry and associated microbial enzyme activity in an ombrotrophic bog. Biogeochemistry 2016, 129, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Sheng, Z.; Xu, X.; Duan, L. Response of aboveground biomass and diversity to nitrogen addition–a five-year experiment in semi-arid grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautier, Y.; Niklaus, P.A.; Hector, A. Competition for light causes plant biodiversity loss after eutrophication. Science 2009, 324, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Yan, E.R.; Chang, S.X.; Cheng, J.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Community-weighted mean of leaf traits and divergence of wood traits predict aboveground biomass in secondary subtropical forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B.; Tilman, D.; Isbell, F.; Mueller, K.; Hobbie, S.E.; Flynn, D.F.; Eisenhauer, N. Impacts of biodiversity loss escalate through time as redundancy fades. Science 2012, 336, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Wright, J.P.; Cadotte, M.W.; Carroll, I.T.; Hector, A.; Srivastava, D.S.; Loreau, M.; Weis, J.J. Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18123–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prommer, J.; Walker, T.W.; Wanek, W.; Braun, J.; Zezula, D.; Hu, Y.; Hofhansl, F.; Richter, A. Increased microbial growth, biomass, and turnover drive soil organic carbon accumulation at higher plant diversity. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavitt, J.B.; Kryczka, A.K.; Huber, M.E.; Pipes, G.T.; Rodriguez, A.M. Inferring methane production by decomposing tree, shrub, and grass leaf litter in bog and rich fen peatlands. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Renella, G.; Wirth, S.; Islam, R. Secondary salinity effects on soil microbial biomass. Biol. Fert. Soils 2010, 46, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.W.; Klaminder, J.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K.H.; Egnell, G.; Laudon, H.; Högberg, P. A meta-analysis of the effects of nitrogen additions on base cations: Implications for plants, soils, and streams. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

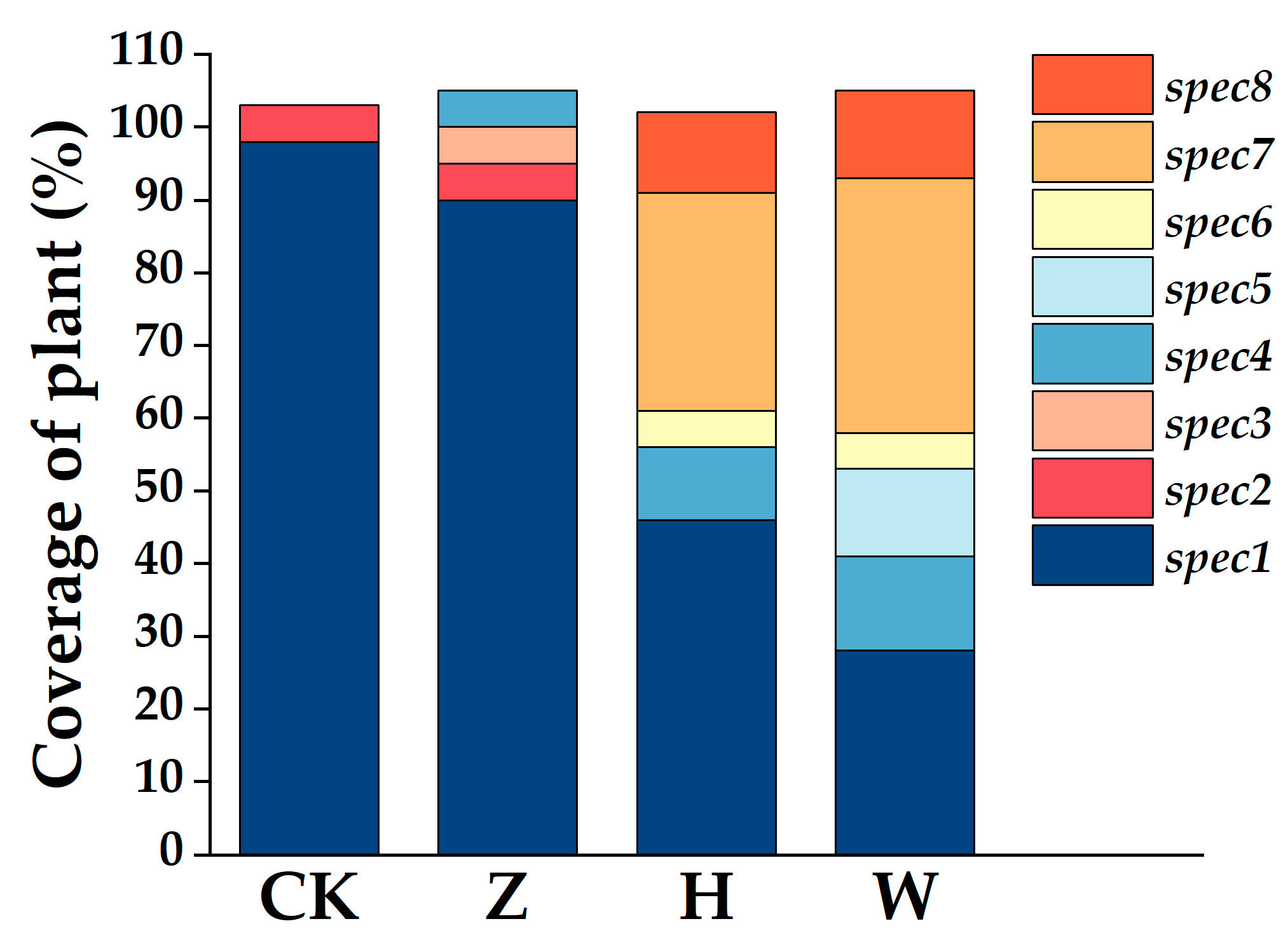
| SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | pH | EC (μs cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 520.56 ± 20.43 | 15.41 ± 1.85 | 1.31 ± 0.29 | 5.83 ± 0.02 | 62.6 ± 1.63 |
| COD (mg L−1) | TN (mg L−1) | NH4+-N (mg L−1) | TP (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.75 ± 0.56 | 0.76 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| COD (mg L−1) | TN (mg L−1) | NH4+-N (mg L−1) | TP (mg L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic sewage | ≤350 | ≤40 | ≤30 | ≤5 |
| Domestic sewage and tap water (1:1) | ≤175 | ≤20 | ≤15 | ≤2.5 |
| Reclaimed water | ≤50 | ≤15 | ≤5 | ≤0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Sheng, L.; He, C.; Jiang, H. How Wastewater Addition Reshapes Peatland Vegetation via Linked Abiotic and Biotic Changes. Biology 2025, 14, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111611
Li Y, Wang X, Sheng L, He C, Jiang H. How Wastewater Addition Reshapes Peatland Vegetation via Linked Abiotic and Biotic Changes. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yue, Xue Wang, Lianxi Sheng, Chunguang He, and Haibo Jiang. 2025. "How Wastewater Addition Reshapes Peatland Vegetation via Linked Abiotic and Biotic Changes" Biology 14, no. 11: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111611
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, X., Sheng, L., He, C., & Jiang, H. (2025). How Wastewater Addition Reshapes Peatland Vegetation via Linked Abiotic and Biotic Changes. Biology, 14(11), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111611






