Impact of Particle Size on the Aerobic Decomposition and Fertilizer Efficiency of Corn Cobs: A Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composting Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. Indicator Measurements
2.2.1. Physicochemical Indicators
2.2.2. Microbial Indicators
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physicochemical Indicators During the Composting Process
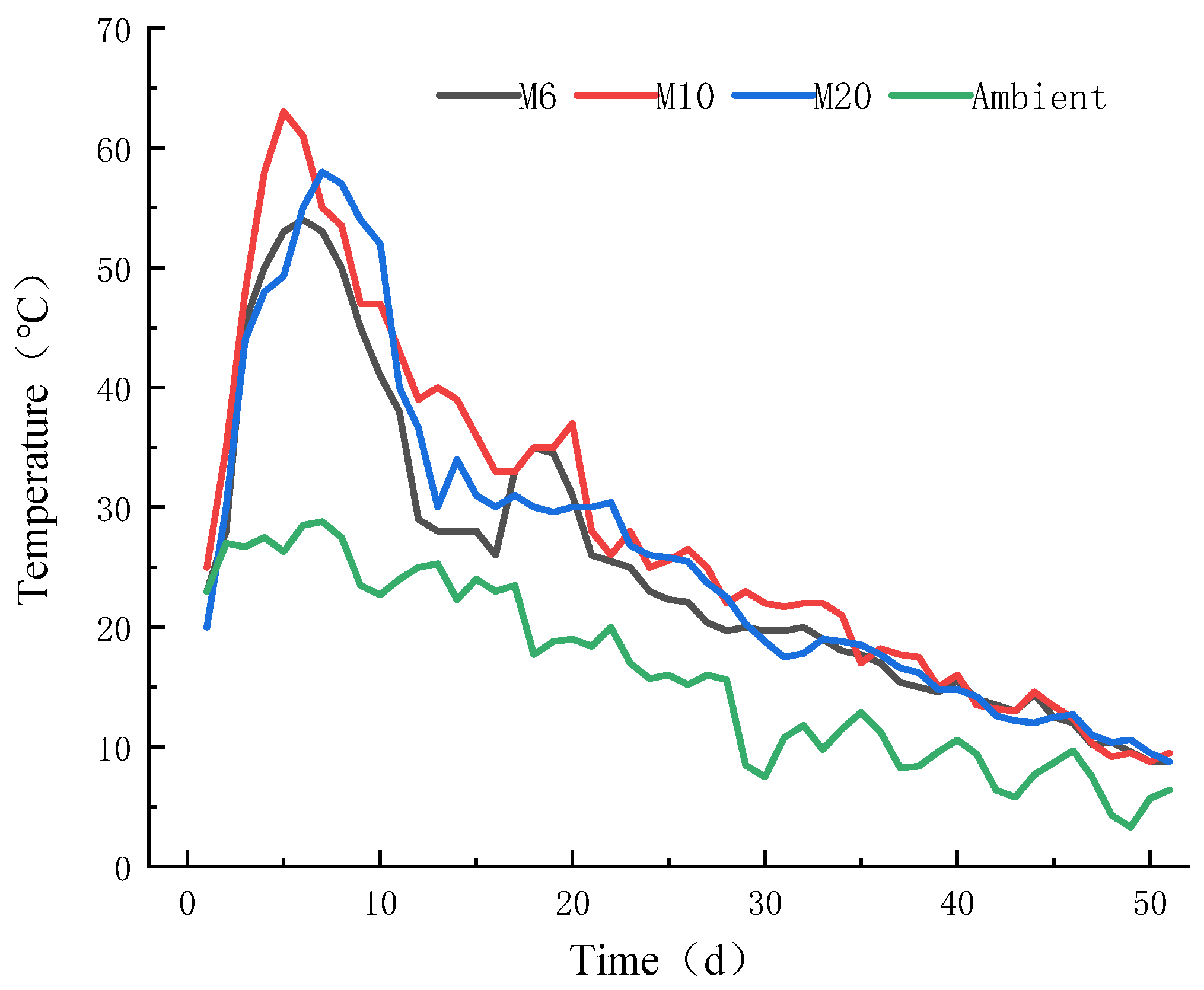
3.1.1. Temperature
3.1.2. pH Value, EC Value, and Organic Matter
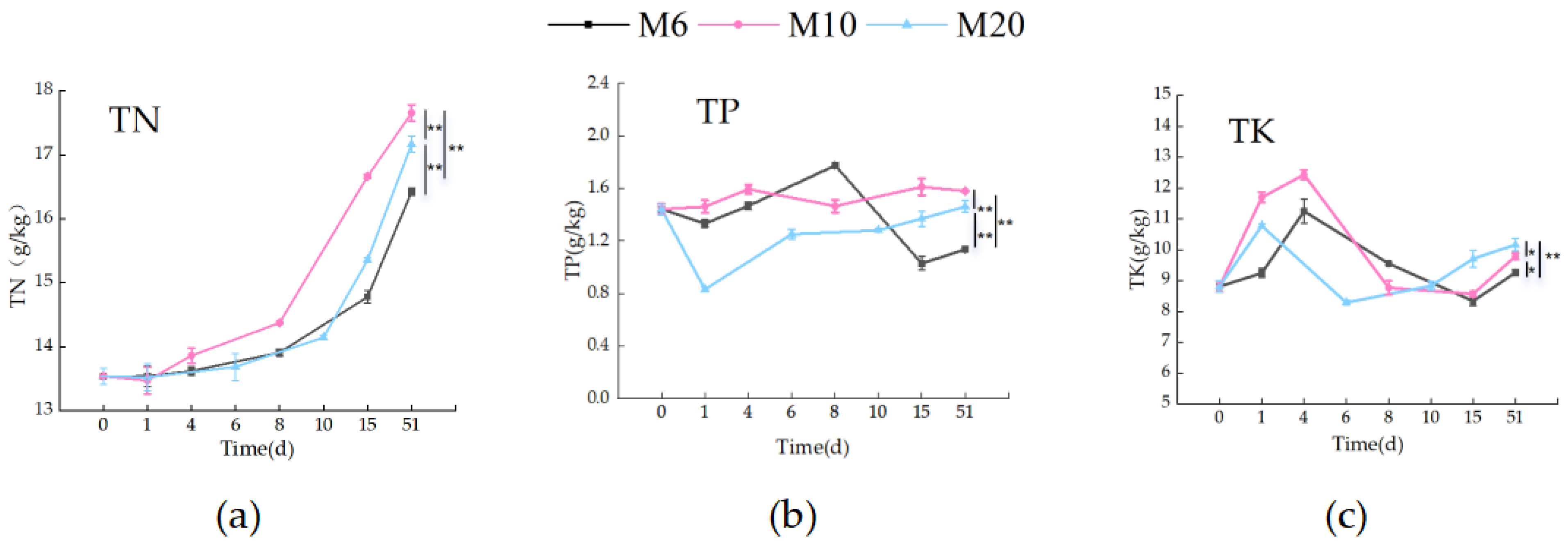
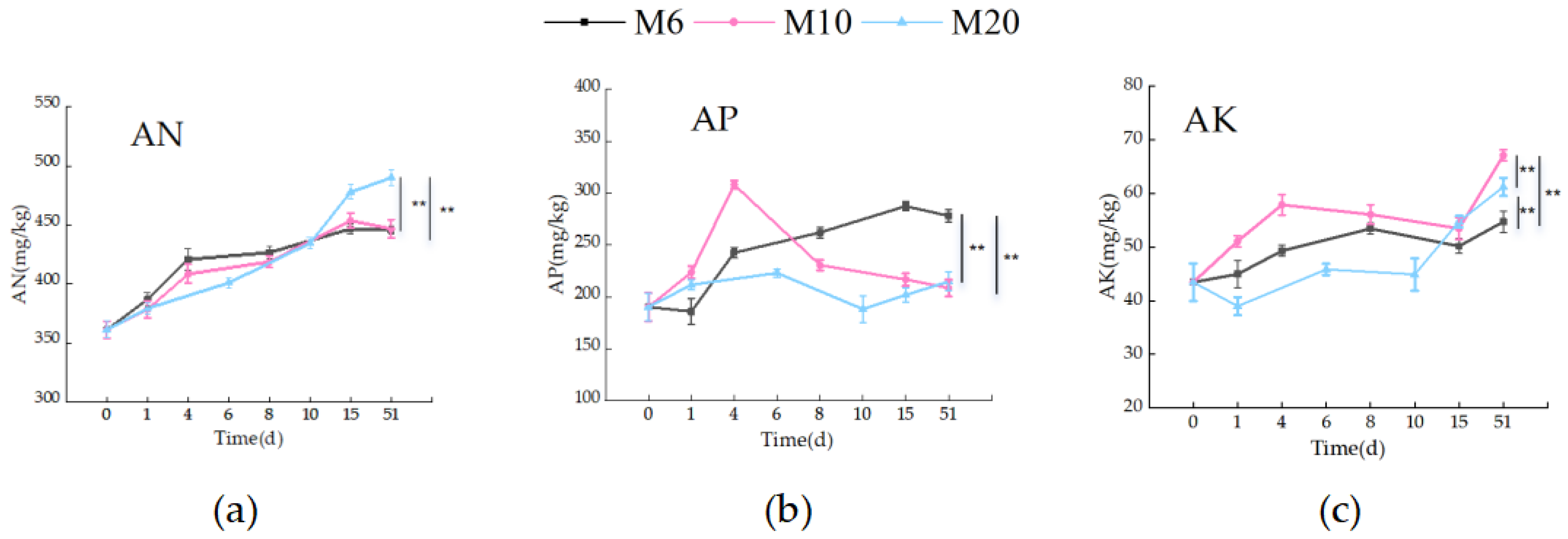
3.1.3. Nutrient Content During the Composting Process
3.2. Changes in Humic Substances Components During Composting
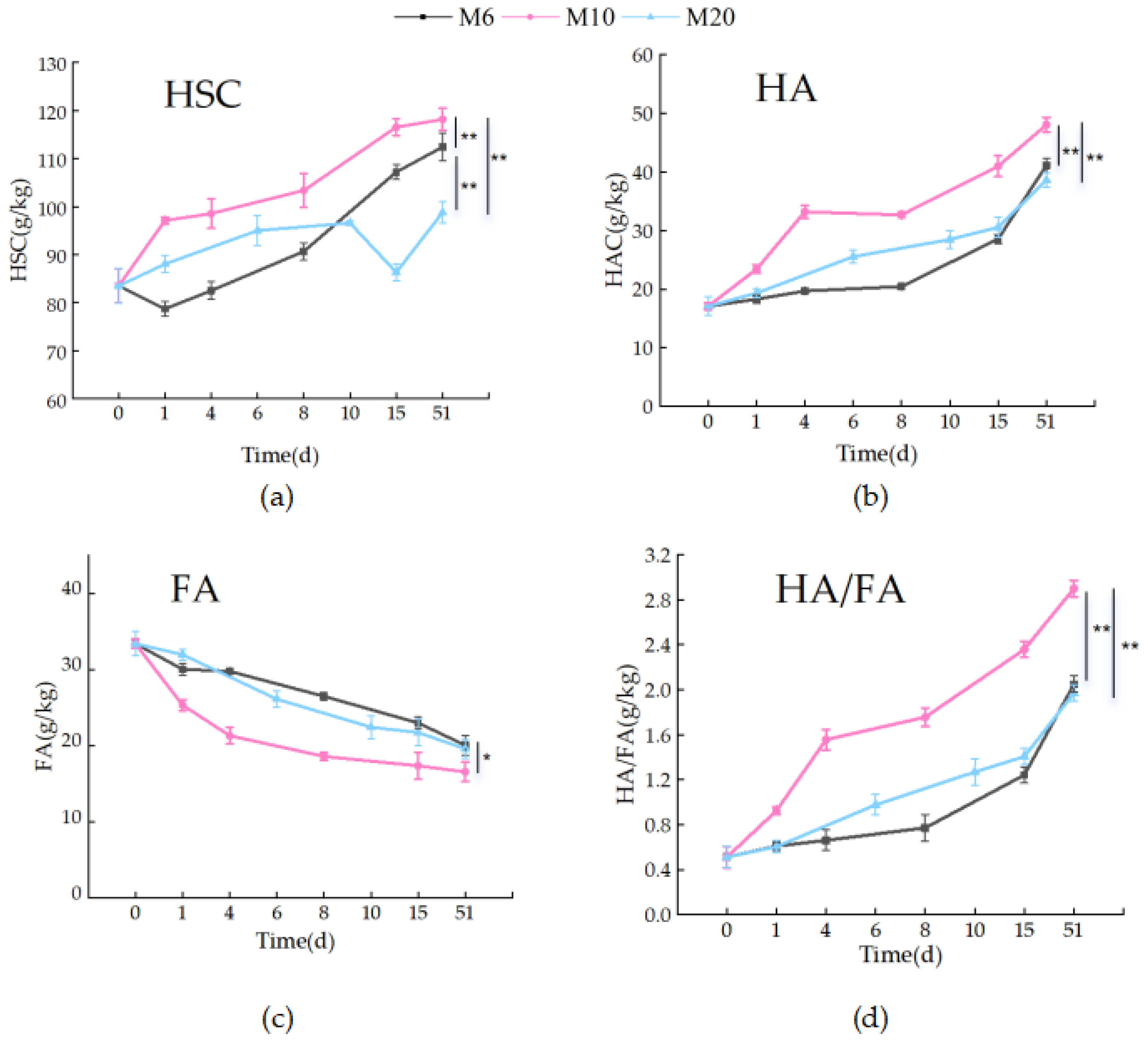
3.2.1. Humic Substance Carbon Transformations (HSC, HAC, FAC)
3.2.2. Evolution of Humification Degree and Compost Maturity (HA/FA)
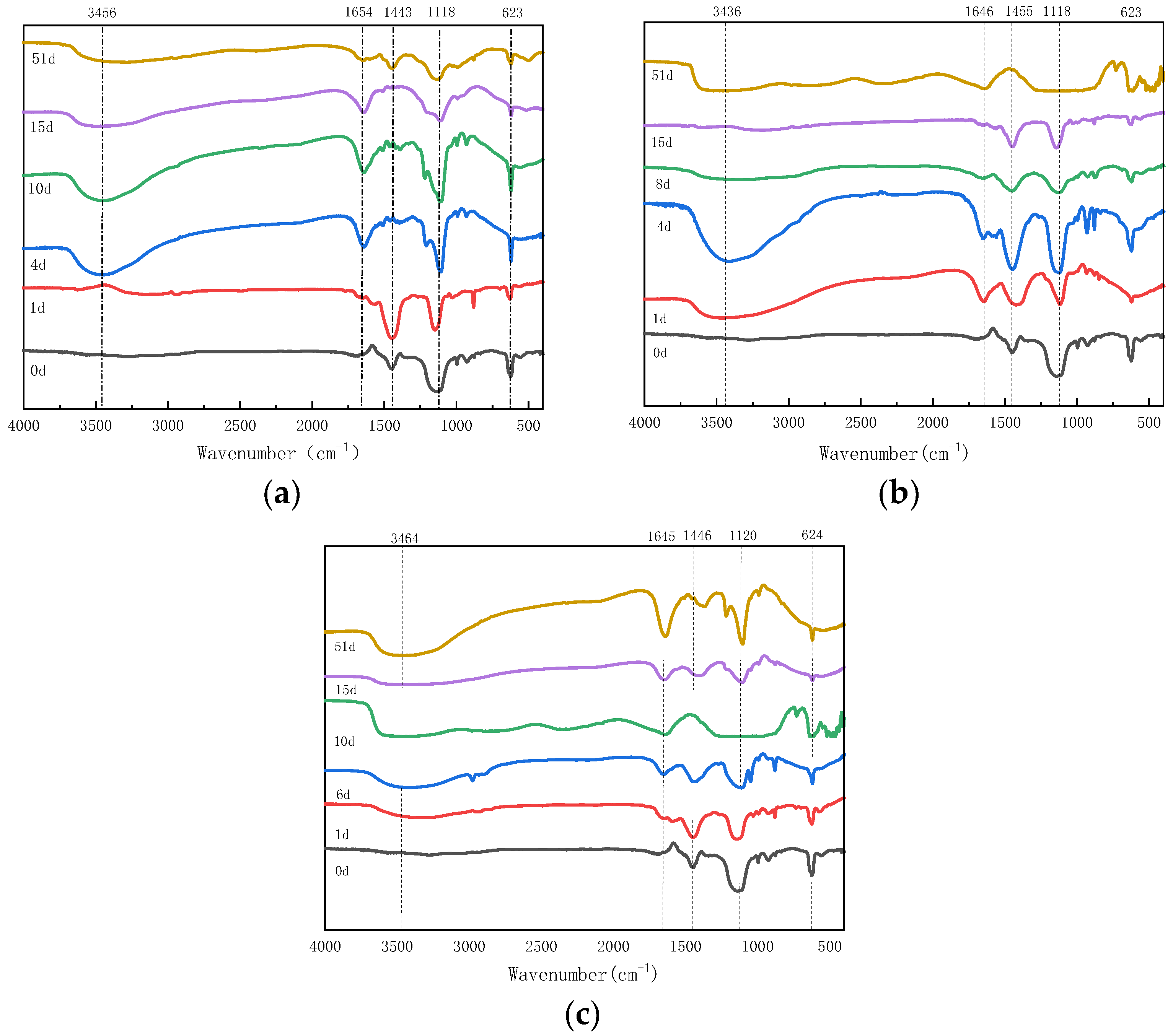
3.2.3. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Humic Acids During Composting
3.3. Assessment of Compost Quality: Phytotoxicity and Heavy Metal Safety
3.4. Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity During Composting
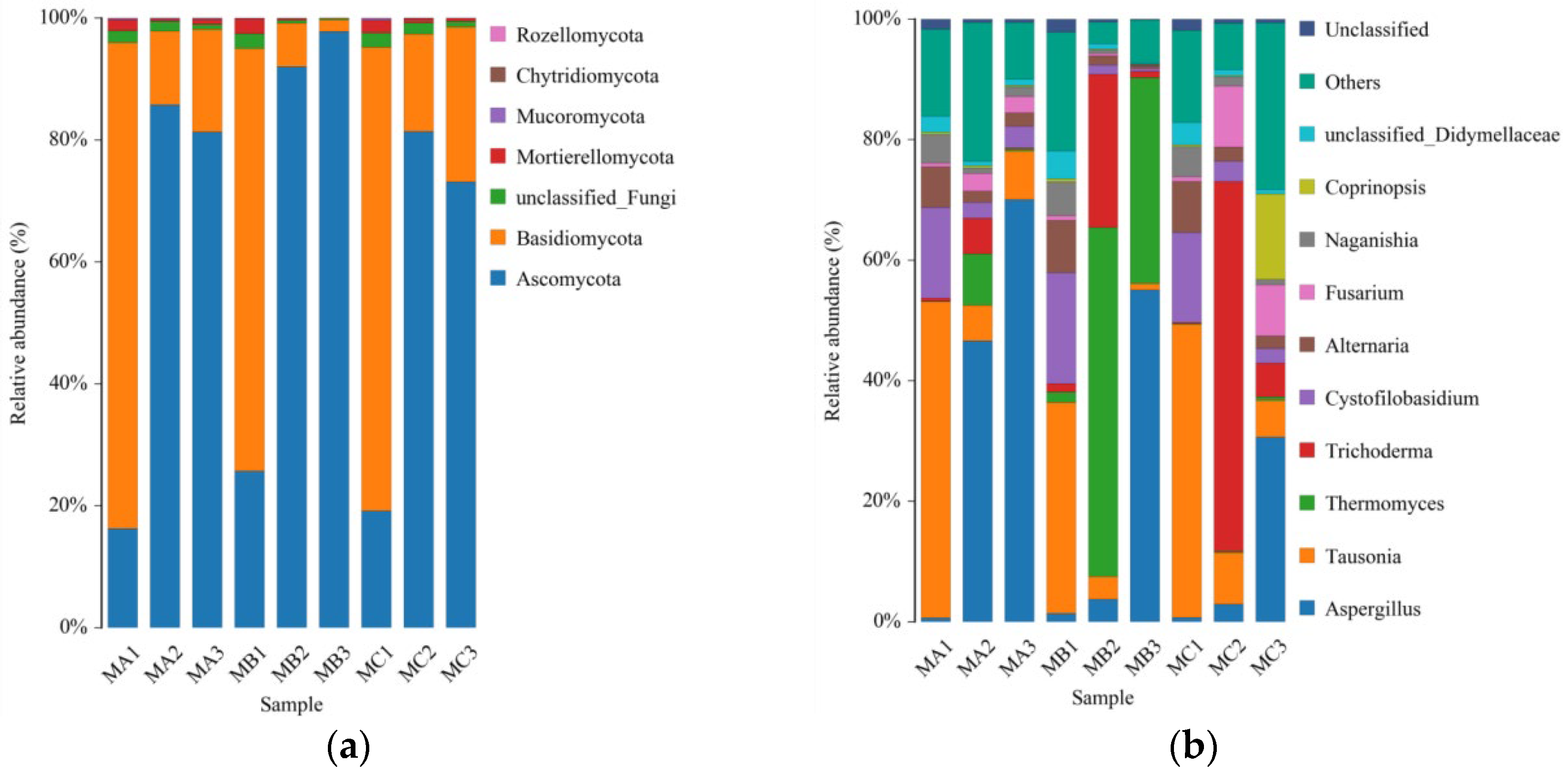
3.5. Dynamics of Fungal Community Structure and Diversity During Composting
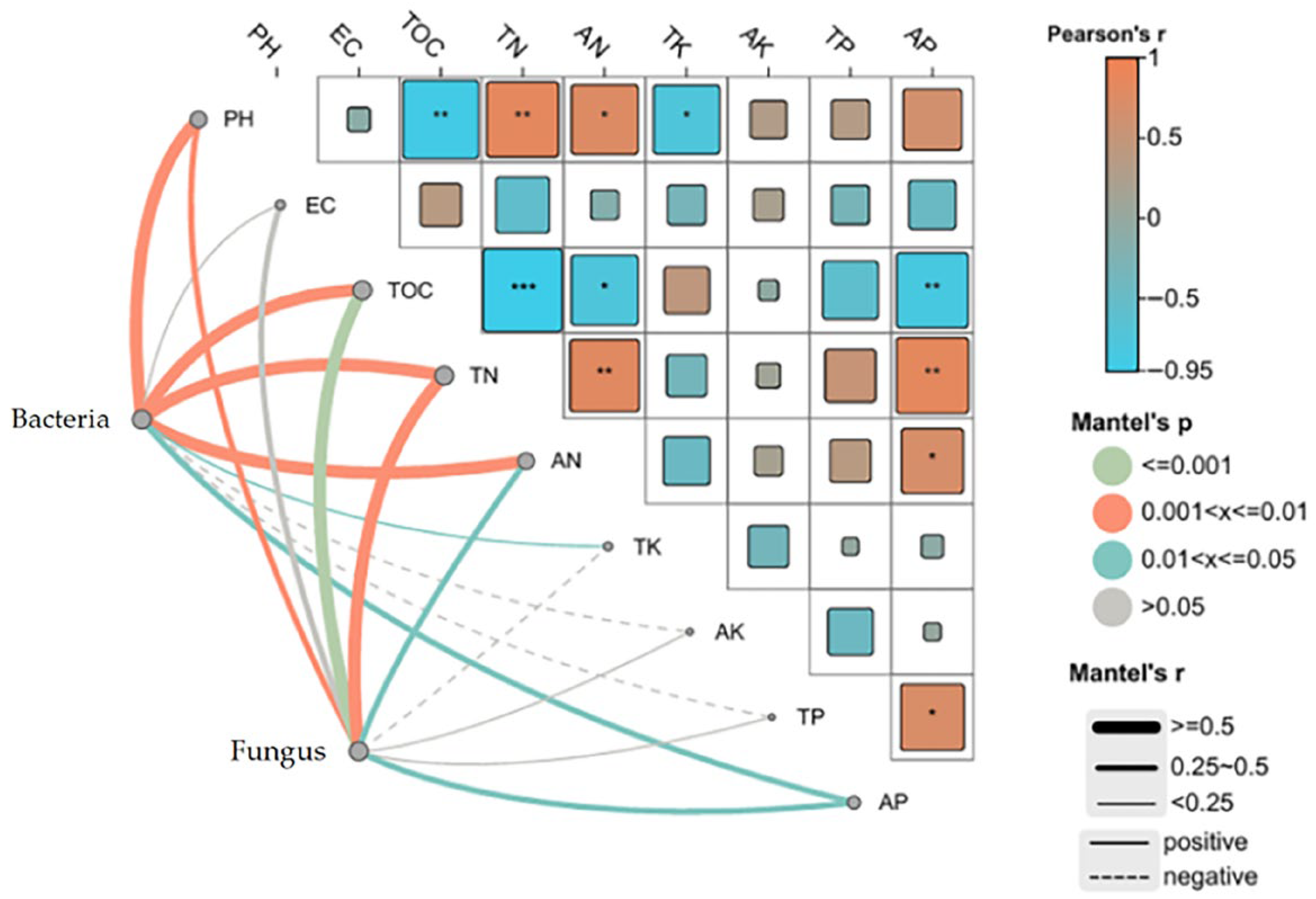
3.6. Correlation Between Microbial Community Structure and Nutrient Indicators
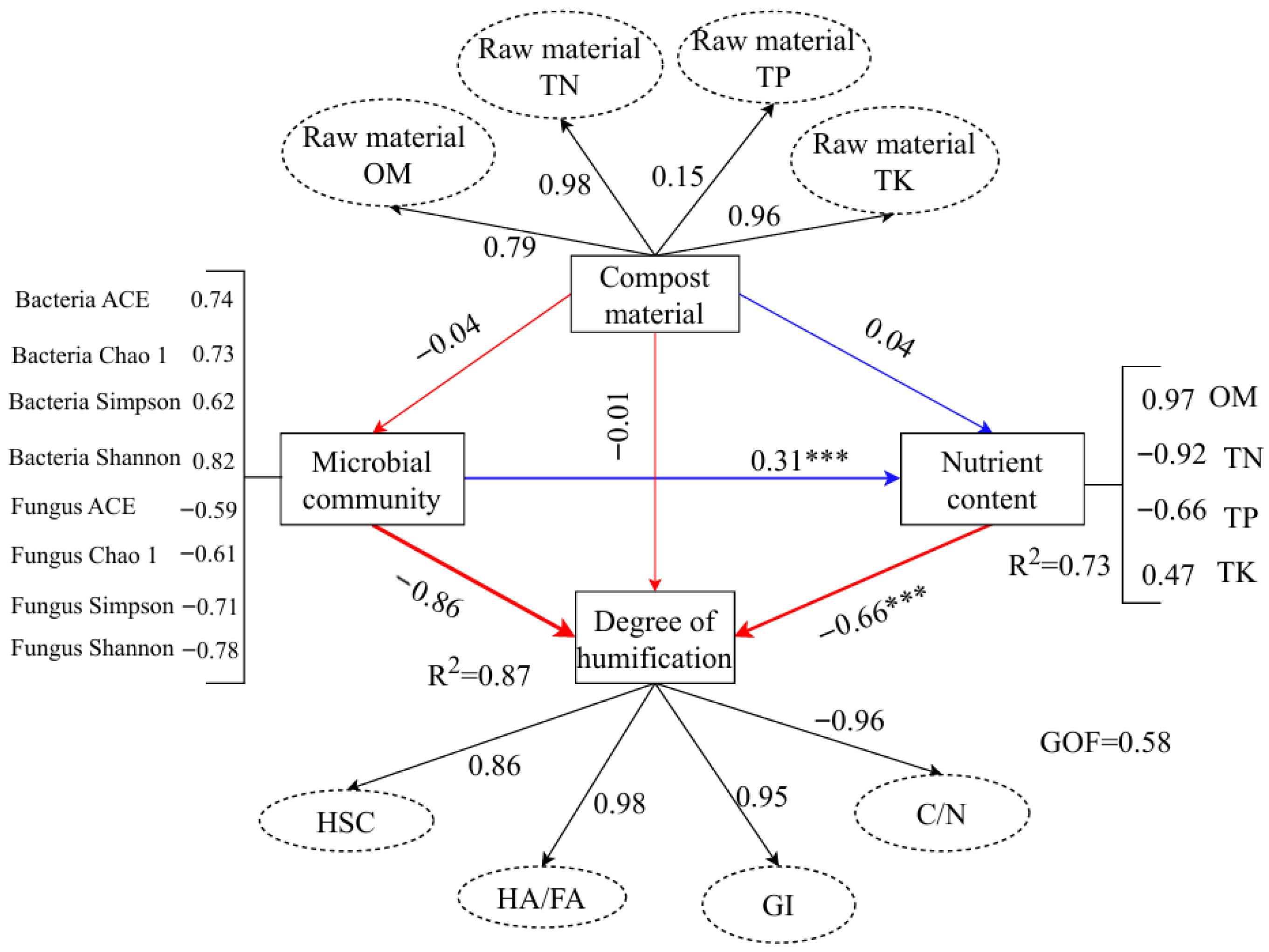
3.7. Structural Equation Model of the Degree of Humification During Composting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayilara, M.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O.; Odeyemi, O. Waste management through composting: Challenges and potentials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Soni, R.; Soni, S.K. From waste to wealth: Exploring modern composting innovations and compost valorization. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 20–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Liang, J.; Zhu, J. Production of hemicellulose sugars combined with the alkaline extraction lignin increased the hydro-depolymerization of cellulose from corn cob. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Bhadu, A.; Sharma, J.; Ali, O.; Neogi, S.; Gunri, S.K.; Roy, D. Effect of microbes in enhancing the composting process: A review. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2022, 34, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedeji, O.; Gitman, P.; Qu, J.; Webb, E. Understanding the impact of lignocellulosic biomass variability on the size reduction process: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2327–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, M.; Nandal, M.; Khosla, B. Microbes as vital additives for solid waste composting. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Paredes, A.; Valdés, G.; Araneda, N.; Valdebenito, E.; Hansen, F. Microbial community in the composting process and its positive impact on the soil biota in sustainable agriculture. Agronomy 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.L.; Wu, H.; Song, S.L.; Bai, H.Y.; Tang, M.J.; Xu, F.J.; Ma, Y.; Dai, C.C.; Jia, Y. Effects of multi-phase inoculation on the fungal community related with the improvement of medicinal herbal residues composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27998–28013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Kang, S.; Song, L.; et al. Assessment of Chinese Medicinal Herbal Wastes Compost Inoculated with Antagonistic Fungi: Nitrogen Retention and Microbial Community in Phytopathogenic Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruba, N.J.M.; Saeid, A. An insight into microbial inoculants for bioconversion of waste biomass into sustainable “bio-organic” fertilizers: A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y.; Lu, S.F.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, S.X. Effect of different microbial agents on corn stalk composting. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 4743–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Zhao, Z.H.; Han, D.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Yuan, X.T.; Ai, Y.J. Activation of Iron Tailings with Organic Acids: A Sustainable Approach for Soil Amelioration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.D.; Zhao, X.Y.; He, X.S.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, W.B.; Gao, R.T.; Zhang, H.; Li, D. Successions and diversity of humic-reducing microorganisms and their association with physical-chemical parameters during composting. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.Y.; Ji, M.H.; Chen, A.; Zhang, B.G.; Shi, J.P.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Sun, J.S. Evaluating the impact of rice husk on successions of bacterial and fungal communities during cow manure composting. J. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, G.Z.; Li, L.B.; Su, F.K.; Yang, J. Optimal Color Development Conditions and Spectrophotometric Wavelength for Determination of Total Phosphorus in Soil by Mo-Sb Anti Colorimetric Method. J. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 1992, 2, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.H.; Gong, H.R.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Miao, X.X.; Wang, J.M. Determination of Total Potassium in Plants by Microwave Digestion-Flame Photometry. J. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2019, 58, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Dodor, D.E.; Tabatabai, M.A. A simple alkaline hydrolysis method for estimating nitrogen mineralization potential of soils. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 27, 16–31. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, S.; Chand, R.G.; Gulshan, B.; Vijay, S. Comparison of Key Mineral Elements in Wild Edible Fruits of Ziziphus mauritiana and Z. nummularia Using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS) and Flame Photometer. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 20 (Suppl. S2), S987–S994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yi, T.; Li, Q.; Ju, H.; Wei, H. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by Suaeda salsa in the tidal flat of the liaohe estuary. Separations 2022, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, H.; Yue, D.; Huang, J. Is the traditional alkali extraction method valid in isolating chemically distinct humic acid? Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 6, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwatsuka, S.; Watanabe, A.; Itoh, K.; Arai, S. Comparision of Two Methods of Preparation of Humic and Fulvic Acids, IHSS Method and NAGOYA Method. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1992, 38, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Kong, Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.N.; Shen, Y.J.; Li, G.X.; Yuan, J. Superphosphate, Biochar, and a Microbial Inoculum Regulate Phytotoxicity and Humification During Chicken Manure Composting. J. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2022, 824, 153958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, M.; Liu, G.; Tang, H. Study on the diversity of epiphytic bacteria on corn and alfalfa using Illumina MiSeq/NovaSeq high-throughput sequencing system. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, Y.E.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Konng, X.; Zhou, W.; Yi, Y.; Qu, Y. Exploring the accuracy of amplicon—based internal transcribed spacer markers for a fungal community. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ju, T.; Lin, L.; Meng, F.; Han, S.; Meng, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, M.; Lan, T.; Jiang, J. Biodrying with the hot-air aeration system for kitchen food waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehusheia, S.L.K.; Roman, C.; Braissant, O.; Arnoldini, M.; Hierold, C. Enabling direct microcalorimetric measurement of metabolic activity and exothermic reactions onto microfluidic platforms via heat flux sensor integration. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, P.; Qu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zheng, J.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes. Biology 2025, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finore, I.; Feola, A.; Russo, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Donato, P.; Nicolaus, B.; Poli, A.; Romano, L. Thermophilic bacteria and their thermozymes in composting processes: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, P.N.; Gahukar, S.J.; Rathod, D.R.; Taynath, B.S.; Chavan, R.S.; Tupke, A.H.; Zadokar, A.R.; Raut, P.M.; Kharade, S.J. Utilization of flower waste for nutrient rich compost generation through decomposition. Ann. Phytomed. 2021, 10, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, C.N.; McLaughlin, R.A.; Johnson, A.; Miller, G.; Heitman, J. The effects of compost incorporation on soil physical properties in urban soils–A concise review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Cui, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; He, P.; Lv, F. Compost quality, earthworm activities and microbial communities in biochar-augmented vermicomposting of dewatered activated sludge: The role of biochar particle size. Biochar 2024, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Yadav, K.D. Effect of particle size on rotary drum composting of garden waste and their ranking using analytical hierarchy process. Res. Sq. 2021, preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, B.; Hu, S.; Shi, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, W. Effects of initial corncob particle size on the short-term composting for preparation of cultivation substrates for Pleurotus ostreatus. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Gunine, A.; Yangm, Y.; Peixoto, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zang, H.; Kuzyakov, Y. Diversified cropping systems benefit soil carbon and nitrogen stocks by increasing aggregate stability: Results of three fractionation methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Liu, F. Effects of biochar particle size and concomitant nitrogen fertilization on soil microbial community structure during the maize seedling stage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13095–13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltohamy, K.M.; Milham, P.J.; Gouda, M.; Blackburn, D.; Khan, S.; Liu, B.; Jin, J.; Ye, Y. Size and composition of colloidal phosphorus across agricultural soils amended with biochar, manure and biogas slurry. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, P.; YANG, N.; WANG, K.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of different tillage measures and organic manure application amount on soil phosphorus fractions in dry-land wheat fields. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Mili, C.; Biswas, P.R.; Saha, S.; Tayung, K. Application of lignocellulolytic fungal consortium for quality composting of spent mushroom substrate: Physicochemical parameters and maturity assessment of the end-products. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2025, 14, 101800. [Google Scholar]
- Sustr, M.; Soukup, A.; Tylova, E. Potassium in root growth and development. Plants 2019, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzyb, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. The significance of microbial transformation of nitrogen compounds in the light of integrated crop management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata Verma, S.; Marschner, P. Compost effects on microbial biomass and soil P pools as affected by particle size and soil properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lin, J.Y.; Sayre, J.M.; Schmidt, R.; Fonte, S.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Scow, K.M. Compost amendment maintains soil structure and carbon storage by increasing available carbon and microbial biomass in agricultural soil—A six-year field study. Geoderma 2022, 427, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, R.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S. Short term effects of biochar with different particle sizes on phosphorous availability and microbial communities. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 126862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głąb, T.; Żabiński, A.; Sadowska, U.; Gondek, K.; Kopeć, M.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Tabor, S.; Stanek-Tarkowska, S. Fertilization effects of compost produced from maize, sewage sludge and biochar on soil water retention and chemical properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Potassium-solubilizing microorganisms: Mechanism and their role in potassium solubilization and uptake. In Potassium Solubilizing Microorganisms for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 203–219. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.S.A.; Colen, F.; Sampaio, R.A.; Azevedo, A.M.; Basílio, J.J.N.; Cota, C.G.; Fernandes, L.A.; Rural, C.; Brasil, S. Biochar from Caryocar brasiliense as a soil conditioner for common bean plants. Ciência Rural. 2022, 52, e2000871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Bejger, R.; Debaene, G.; Smreczak, B. Characterization of soil organic matter individual fractions (fulvic acids, humic acids, and humins) by spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques in agricultural soils. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Graham, A.J.; Kolli, J.; Lynd, N.A.; Keitz, B.K.; Chemistry, N. Aerobic radical polymerization mediated by microbial metabolism. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Ban, T.; Ma, C. Preparation of Agricultural Jiaosu from vegetable waste: Multi-dimensional effects of microbial inoculants on the properties of Agricultural Jiaosu and fertilizer efficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1576663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rahim, A.; Mohamed, M.G.; Abdelrhman, A.A.; Rekaby, S.A.; Thabit, F.N. Compost combined with peanut shells biochar: Enhanced formation and structural characteristics of soil humic acids and yield of wheat crop in a clay loam soil. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 65, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Jien, S.H. Using fluorescence spectroscopy to assess compost maturity degree during composting. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gowthaman, S.; Nakashima, K.; Kawasaki, S. Influence of humic acid on microbial induced carbonate precipitation for organic soil improvement. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 15230–15240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, A.S.; Dunne, J.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F. Soil organic matter carbon chemistry signatures, hydrophobicity and humification index following land use change in temperate peat soils. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Lu, M.; Xiang, H.; Ding, D.; Niu, S.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Huang, Z. Insights into nitrogen metabolism and humification process in aerobic composting facilitated by microbial inoculation. Environ. Res. 2025, 269, 120894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Jawhari, F.Z.; Urbonavičius, J.; Merzouki, M. Assessment of Textile Waste Circularity through Composting Using the Seed Germination Index as Indicator for a Sustainable Management. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 16, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutasknit, A.; Anli, M.; Lahlali, R.; Meddich, A. Effect of Organic Waste and Inorganic Additives on Organic Matter Transformation and Mineral Availability in Composting Green Waste. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 93, 2227–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 525-2021; Chinese Organic Fertilizer Standard. National Standards of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Kulikowska, D. High temperature composting supresses humification: Process rate and humic substances content. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 233, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Tian, P.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Jiang, S.; Deng, H. Uptake and volatilization of gaseous elemental mercury by paddy rice. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2017, 38, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, P.; Liang, B. Exploring dynamics and associations of dominant lignocellulose degraders in tomato stalk composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ji, M.; Xie, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J. Exploring the microbial dynamics of organic matter degradation and humification during co-composting of cow manure and bedding material waste. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Ghanney, P. Influence of aeration method on gaseous emissions and the losses of the carbon and nitrogen during cow manure composting. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, D.; Wang, F.; Wei, Z.; Mao, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Biodegradation of humic acids by Streptomyces rochei to promote the growth and yield of corn. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 286, 127826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Gao, P.; Lai, K.; Yan, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, X.; Lyu, C.; Kang, C.; Guo, L. Mechanistic insights from metagenomics into the early-stage quality improvement of licorice under partial replacement of chemical by organic fertilizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1613771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, F.; Gao, Z.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum combined with Phanerochaete chrysosporium on lignin degradation and humification during chicken manure and rice husk composting. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1515931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, W.; Song, L.; Guo, Z.; Bian, Z.; Han, Y.; Cai, H.; Yang, P.; Meng, K. The potential of Trichoderma asperellum for degrading wheat straw and its key genes in lignocellulose degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1550495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, K.; Ren, Z.; Wu, J. Regulation of nitrogen transformation and microbial community by inoculation during livestock manure composting. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohórquez-Sandoval, L.J.; Hernandez-Lara, A.; Gómez-Morte, J.A.; Cuartero, J.; García-Molano, J.; Pascual, A.; Ros, M. The potential bioavailability of phosphorus and the microbial community involved in agro-industrial composts as organic amendments or growing media. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 386, 125762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo GongWen, L.G.W.; Ling Ning, L.N.; Nannipieri, P.; Chen, H.; Raza, W.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q. Long-term fertilisation regimes affect the composition of the alkaline phosphomonoesterase encoding microbial community of a vertisol and its derivative soil fractions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Duan, W.; Qiao, C.; Shen, Q.; Li, R. Microbial community composition turnover and function in the mesophilic phase predetermine chicken manure composting efficiency. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yujia, S.H.I.; Haixia, Z.; Linfa, F.; Yue, D.; Ran, X. Mineralization and humification of chicken manure and composted kitchen waste in soils based on an in situ litter-bag experiment: Impacts of organic inputs and microbial community. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 602. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kuthiala, T.; Thakur, K.; Thatai, K.; Singh, G.; Kumar, P.; Arya, S. Kitchen waste: Sustainable bioconversion to value-added product and economic challenges. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuglova, O.; Klimenko, A. Application of humic substances in agricultural industry. Agronomy 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulia, M. Sustainable utilization of humic substances and organic waste in green agriculture. Agriculture 2024, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, G.; Li, X. Effect of organic material ratio on change of humus and nutrient content in compost. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2021, 50, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, V.K.H.; Truong, H.B.; Hong, S.; Li, X.; Hur, J. Biotic and abiotic catalysts for enhanced humification in composting: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Chang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, T.; Ding, G.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Insight into the dynamic microbial community and core bacteria in composting from different sources by advanced bioinformatics methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8956–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cong, H.; Feng, S.; Sun, F. Relative contribution of fungal communities to carbon loss and humification process in algal sludge aerobic composting. Water 2024, 16, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

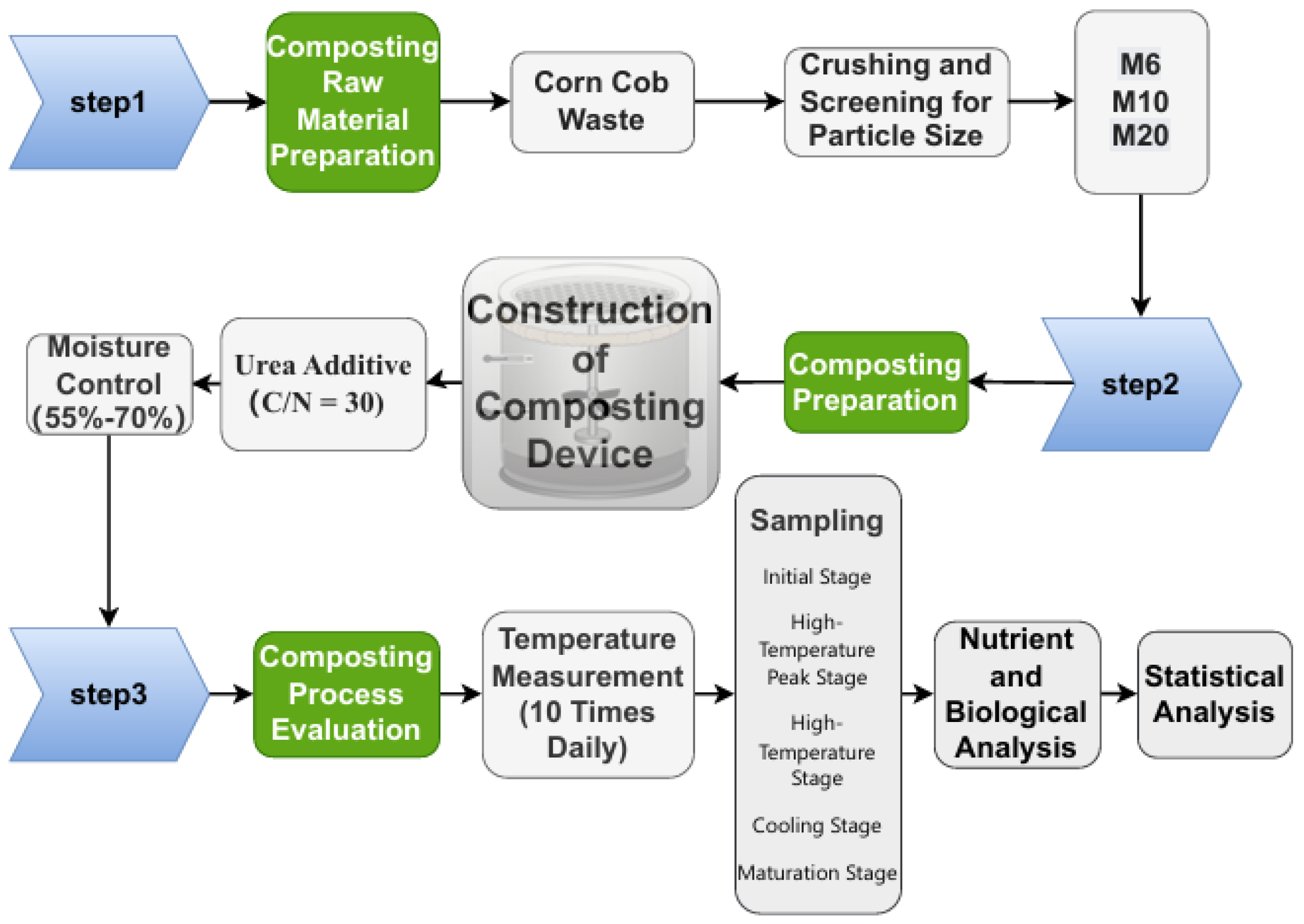


| Sample Collection | M6 | M10 | M20 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Stage | 1d (9.24) | 1d (9.24) | 1d (9.24) |
| Peak Thermophilic Stage | 4d (9.27) | 4d (9.28) | 6d (9.30) |
| Thermophilic Stage | 8d (10.1) | 8d (10.1) | 10d (10.4) |
| Cooling Stage | 15d (10.8) | 15d (10.8) | 15d (10.9) |
| Curing Stage | 51d (11.13) | 51d (11.13) | 51d (11.13) |
| Samples | Germination Index (%) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | As (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 91.52 b | 16.2 ± 2.3 a | 1.9 ± 0.4 a | 41.7 ± 4.5 a | 4.1 ± 0.6 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 ab |
| M10 | 93.63 a | 9.4 ± 1.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.2 b | 28.3 ± 3.8 b | 1.9 ± 0.2 b | 0.3 ± 0.08 b |
| M20 | 88.54 c | 21.3 ± 3.0 c | 2.5 ± 0.4 c | 59.4 ± 5.5 c | 5.8 ± 0.9 c | 1.1 ± 0.2 a |
| Samples | ACE Index | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA1 | 400.87 ± 8.35 Ba | 400.37 ± 8.52 Ba | 0.91 ± 0.07 Ba | 5.10 ± 0.16 Ca |
| MA2 | 387.83 ± 10.35 Ba | 388.33 ± 10.84 Ba | 0.91 ± 0.05 Ba | 5.71 ± 0.23 Bb |
| MA3 | 455.22 ± 7.65 Ab | 455.36 ± 11.84 Ab | 0.99 ± 0.03 Aa | 7.86 ± 0.32 Aa |
| MB1 | 390.02 ± 10.77 Ca | 392.17 ± 12.86 Ca | 0.80 ± 0.05 Bb | 3.87 ± 0.18 Cb |
| MB2 | 492.16 ± 13.7 Bc | 493.75 ± 9.86 Bc | 0.93 ± 0.06 Aa | 5.53 ± 0.35 Bb |
| MB3 | 926.76 ± 12.52 Aa | 926.75 ± 12.16 Ab | 0.98 ± 0.06 A | 7.61 ± 0.49 Aa |
| MC1 | 306.20 ± 11.52 Cb | 307.0 ± 8.65 Cb | 0.89 ± 0.05 Aa | 4.20 ± 0.23 Cb |
| MC2 | 414.29 ± 11.32 Bb | 414.5 ± 9.53 Ba | 0.98 ± 0.07 Aa | 7.00 ± 0.14 Ba |
| MC3 | 914.21 ± 12.52 Aa | 914.66 ± 13.54 Aa | 0.98 ± 0.08 Aa | 7.88 ± 0.26 Aa |
| Samples | ACE Index | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA1 | 400.87 ± 8.35 Ba | 400.37 ± 8.52 Ba | 0.91 ± 0.07 Ba | 5.10 ± 0.16 Ca |
| MA2 | 387.83 ± 10.35 Ba | 388.33 ± 10.84 Ba | 0.91 ± 0.05 Ba | 5.71 ± 0.23 Bb |
| MA3 | 455.22 ± 7.65 Ab | 455.36 ± 11.84 Ab | 0.99 ± 0.03 Aa | 7.86 ± 0.32 Aa |
| MB1 | 390.02 ± 10.77 Ca | 392.17 ± 12.86 Ca | 0.80 ± 0.05 Bb | 3.87 ± 0.18 Cb |
| MB2 | 492.16 ± 13.7 Bc | 493.75 ± 9.86 Bc | 0.93 ± 0.06 Aa | 5.53 ± 0.35 Bb |
| MB3 | 926.76 ± 12.52 Aa | 926.75 ± 12.16 Ab | 0.98 ± 0.06 A | 7.61 ± 0.49 Aa |
| MC1 | 306.20 ± 11.52 Cb | 307.0 ± 8.65 Cb | 0.89 ± 0.05 Aa | 4.20 ± 0.23 Cb |
| MC2 | 414.29 ± 11.32 Bb | 414.5 ± 9.53 Ba | 0.98 ± 0.07 Aa | 7.00 ± 0.14 Ba |
| MC3 | 914.21 ± 12.52 Aa | 914.66 ± 13.54 Aa | 0.98 ± 0.08 Aa | 7.88 ± 0.26 Aa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Wu, P.; Guo, X.; Qu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xing, Y.; Dong, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X. Impact of Particle Size on the Aerobic Decomposition and Fertilizer Efficiency of Corn Cobs: A Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Approach. Biology 2025, 14, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111610
Liu Q, Wu P, Guo X, Qu Y, Zheng J, Xing Y, Dong Z, Yu W, Zhang G, Zhang X. Impact of Particle Size on the Aerobic Decomposition and Fertilizer Efficiency of Corn Cobs: A Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Approach. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qian, Pengbing Wu, Xingchi Guo, Ying Qu, Junyan Zheng, Yuhe Xing, Zhiyu Dong, Wei Yu, Guoyu Zhang, and Xu Zhang. 2025. "Impact of Particle Size on the Aerobic Decomposition and Fertilizer Efficiency of Corn Cobs: A Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Approach" Biology 14, no. 11: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111610
APA StyleLiu, Q., Wu, P., Guo, X., Qu, Y., Zheng, J., Xing, Y., Dong, Z., Yu, W., Zhang, G., & Zhang, X. (2025). Impact of Particle Size on the Aerobic Decomposition and Fertilizer Efficiency of Corn Cobs: A Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Approach. Biology, 14(11), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111610





