Non-Canonical Male Meiosis in a Marine Gastropod, Littorina saxatilis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
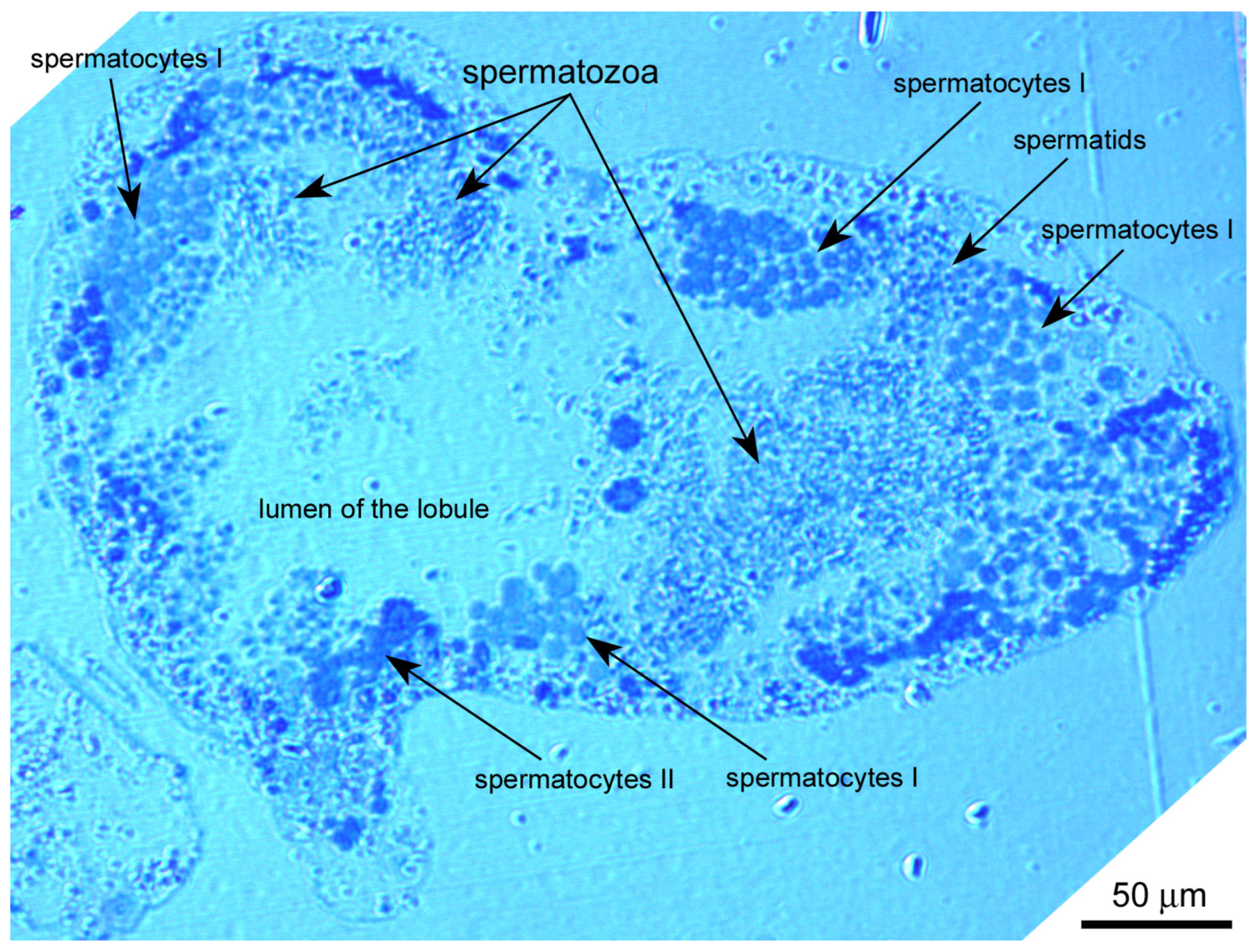
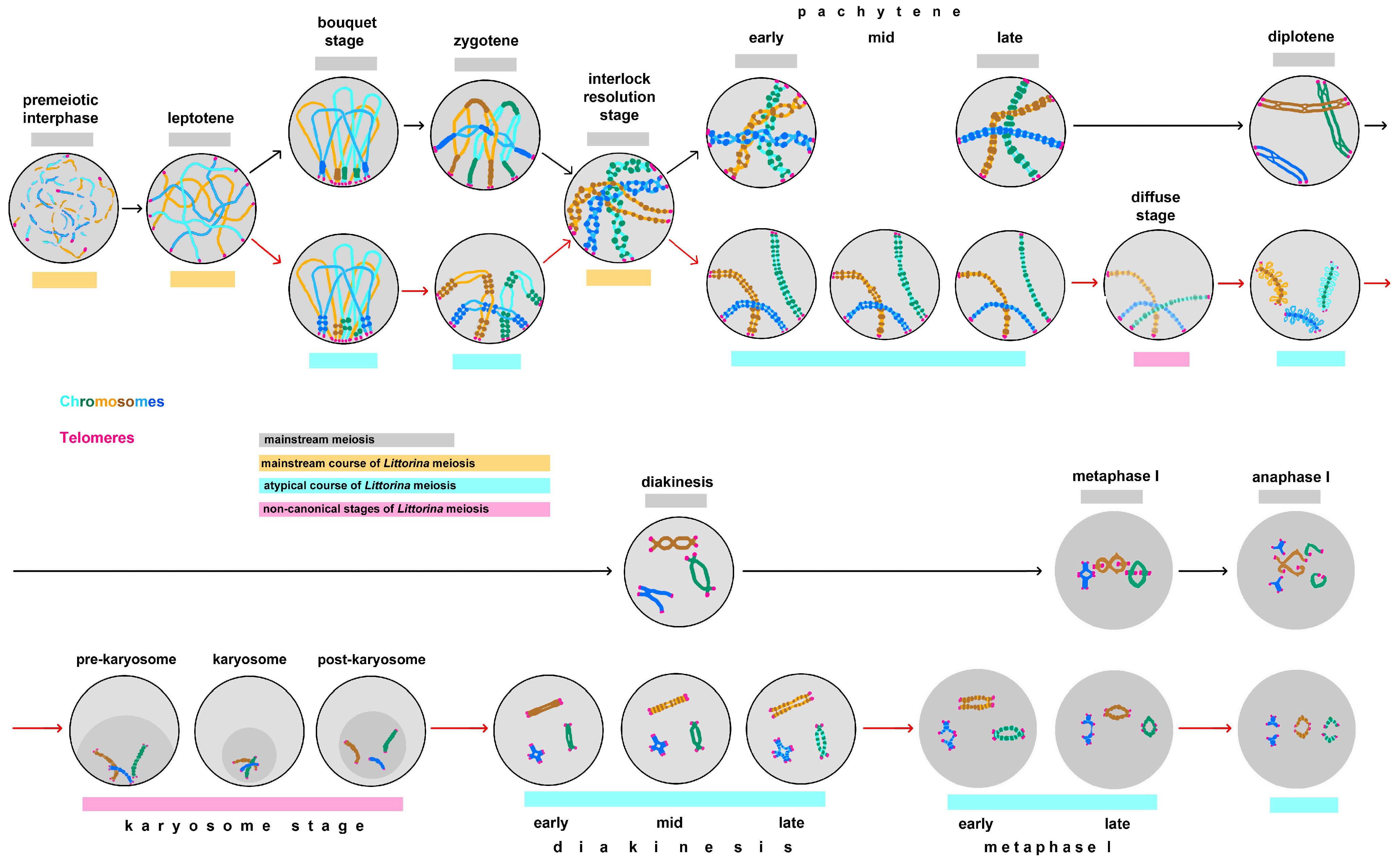
3.1. Sequential Stages of L. saxatilis Male Meiosis
3.1.1. Spermatogonia
3.1.2. Primary Spermatocytes
Leptotene, Zygotene and the Stage of Interlock Resolution
Pachytene
Diffuse Stage
Diplotene and Karyosome Stage
Diakinesis
Metaphase—Telophase I
3.1.3. Secondary Spermatocytes
3.2. Comparison of the Pachytene—Diplotene Period in Male and Female Meiosis of L. saxatilis
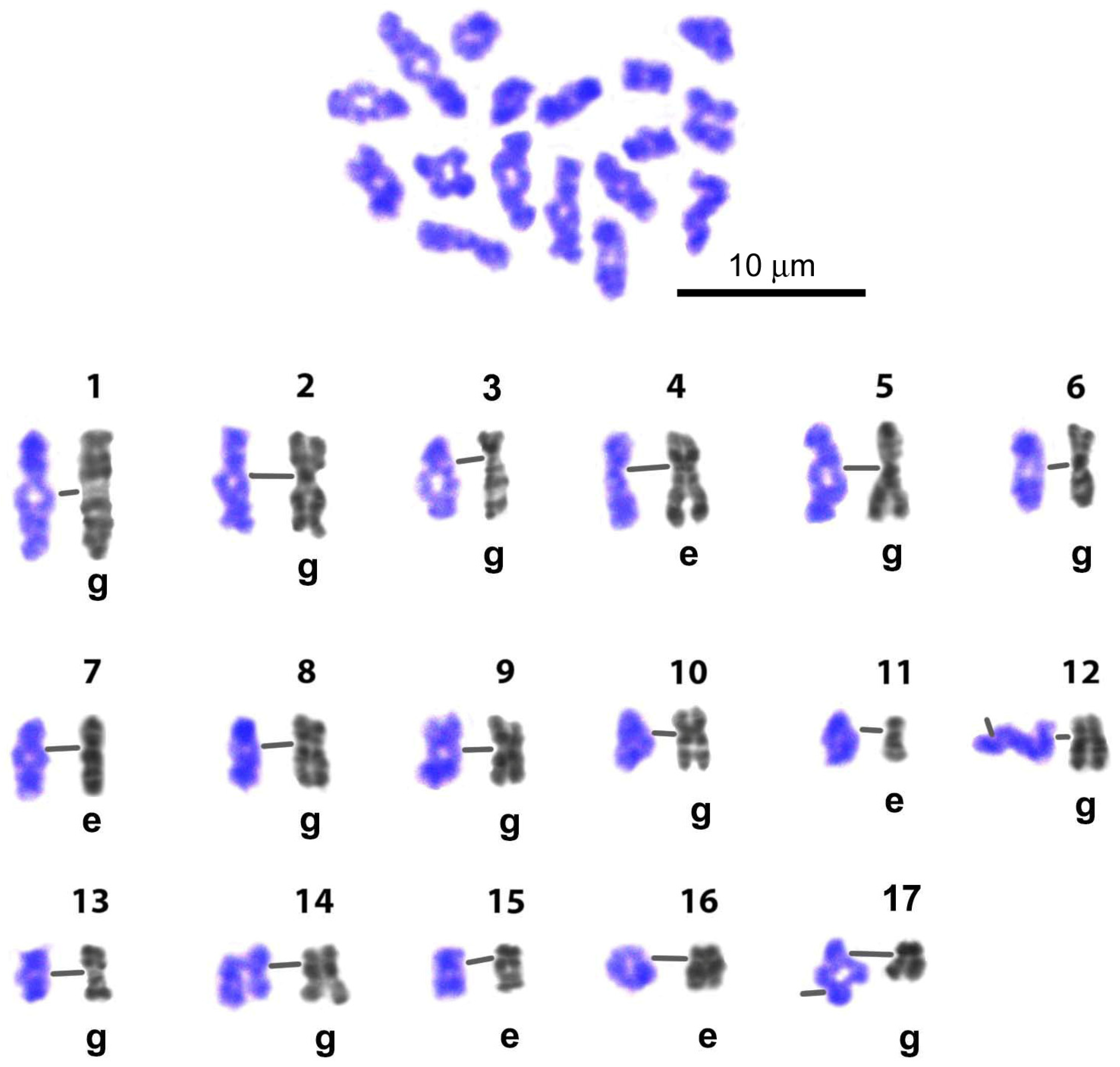
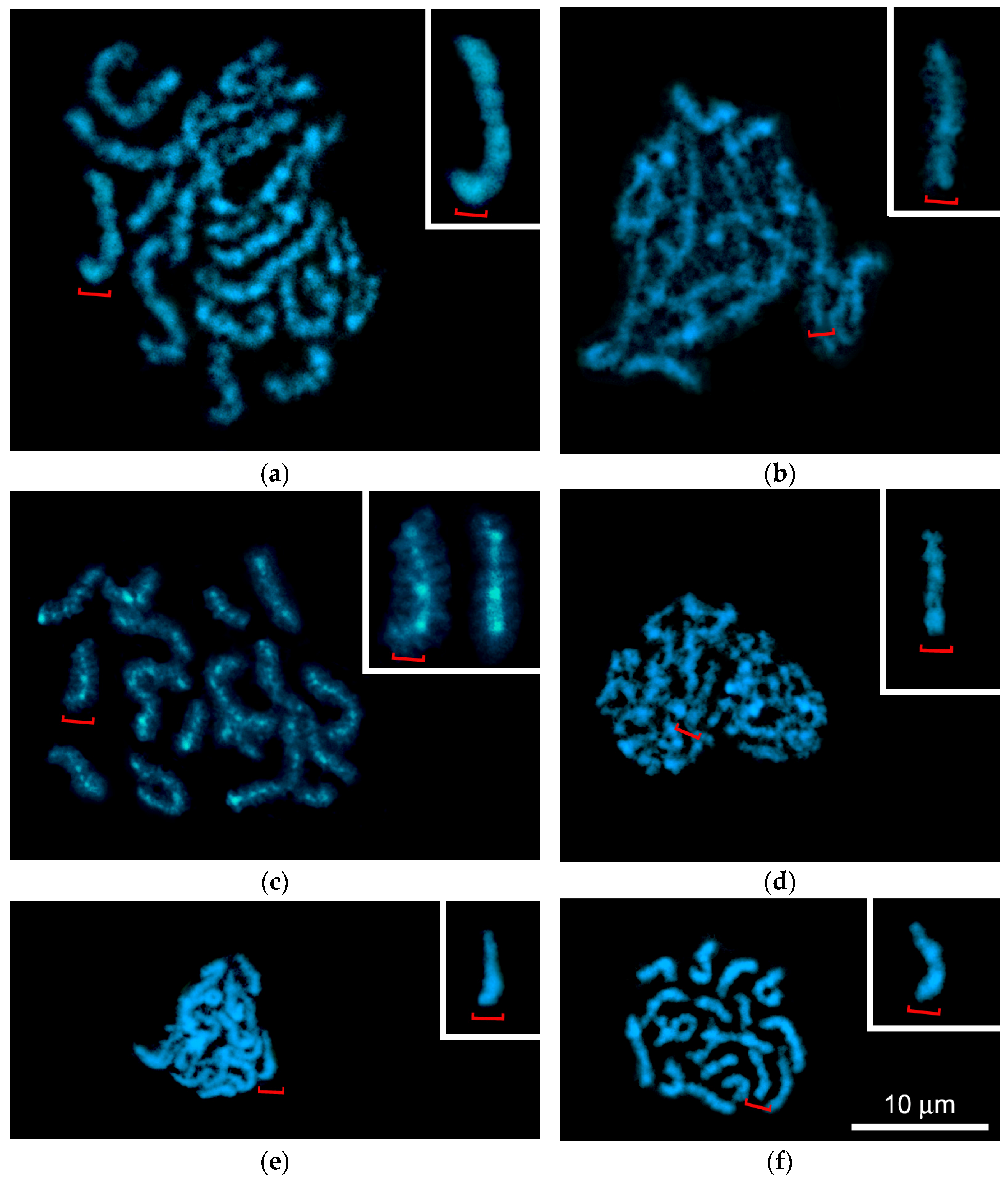
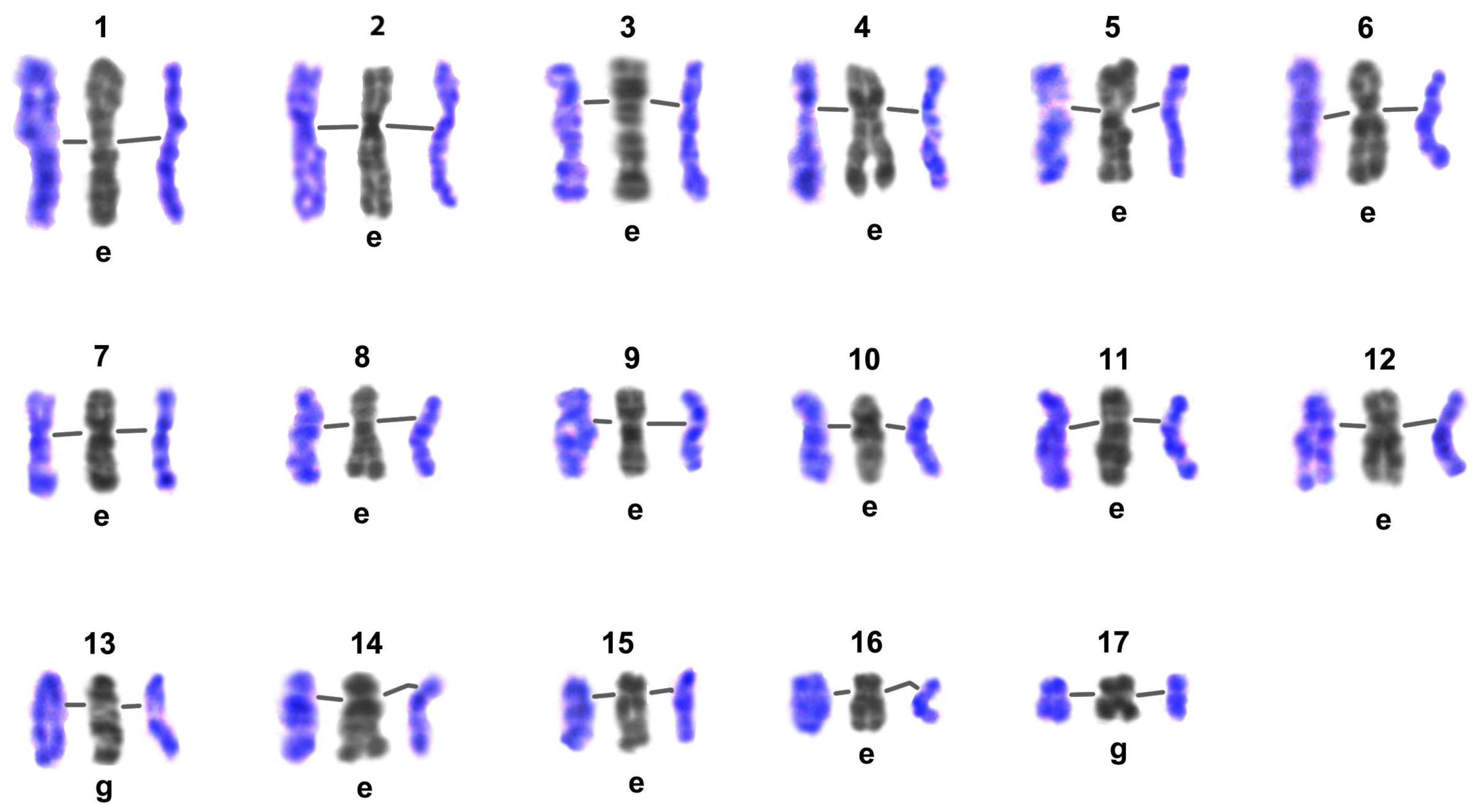
3.3. G-Banding and Chromomere/Interchromomere Patterns of Chromosomes During L. saxatilis Mitosis and Male Meiosis
3.3.1. The Image Bank
3.3.2. G-Banding Patterns of Individual Early and Late Pachytene Bivalents
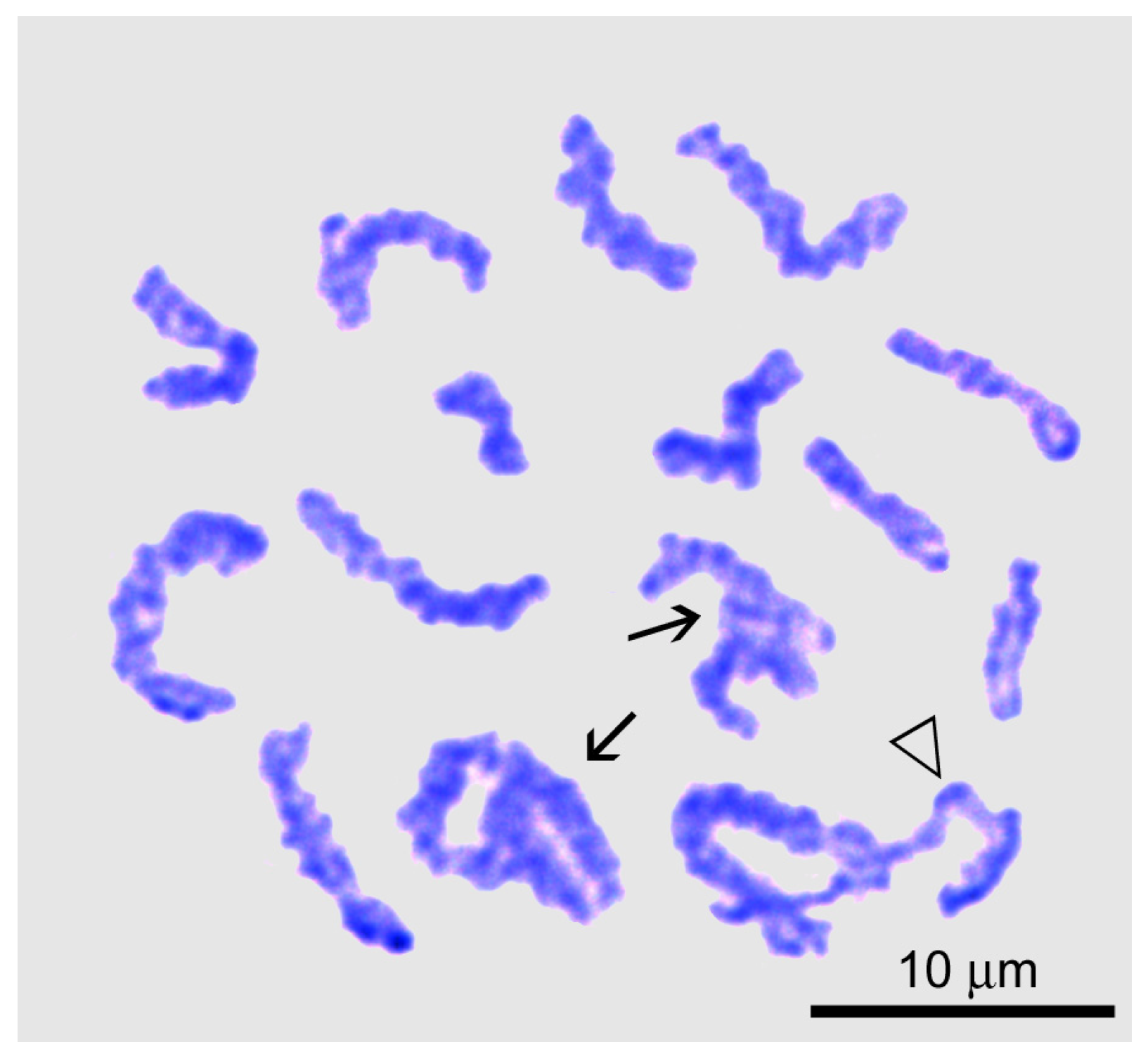
3.3.3. Delayed Expression of Chiasmata and Chromomeric Patterns of Individual Bivalents During Late Diakinesis—Metaphase I
4. Discussion
4.1. Karyotype of Littorina saxatilis and the Image Bank of Individual Chromosomes
4.2. Male Meiosis Is Non-Canonical in Littorina saxatilis
4.3. Two Ways of Bivalent Formation: Pairing and Synapsis of Homologous Chromosomes
4.4. Bouquet-Like Stages of Meiosis
4.5. Atypical Pachytene in Littorina saxatilis Male Meiosis
4.6. G-Banding Patterns of Individual Pachytene Bivalents and High-Resolution Mitotic Chromosomes
4.7. Non-Canonical and Atypical Diffuse Stage in L. saxatilis Male Meiosis
4.8. Atypical Diplotene in Male but Not Female Meiosis of Littorina saxatilis: The Karyosome Stage
4.9. Atypical Diakinesis in L. saxatilis Male Meosis: Inverse Order of Chromatin Compaction and Delayed Expression of Chiasmata
4.10. Atypical Features of Metaphase and Anaphase I in Littorina saxatilis Male Meiosis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNOR | Silver-staining for nucleolar organizer regions (NORs) |
| AHC | Alternative homolog conjunction |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DIC | Differential interference contrast |
| DSB | DNA double-strand break |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SC | Synaptonemal complex |
| SSC | Saline-sodium citrate |
References
- Zickler, D.; Kleckner, N. Meiotic chromosomes: Integrating structure and function. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1999, 33, 603–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickler, D.; Kleckner, N. Recombination, pairing, and synapsis of homologs during meiosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, Y.F. Variation and evolution of meiosis. Rus. J. Genet. 2003, 39, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egel, R. Meiotic crossing-over and disjunction: Overt and hidden layers of description and control. In Recombination and Meiosis. Genome Dynamics and Stability; Egel, R., Lankenau, D.-H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Scherthan, H. A bouquet makes ends meet. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Golubovskaya, I.; Cande, W.Z. A bouquet of chromosomes. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickler, D.; Kleckner, N. A few of our favorite things: Pairing, the bouquet, crossover interference and evolution of meiosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 54, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascom-Slack, C.A.; Ross, L.O.; Dawson, D.S. Chiasmata, crossovers, and meiotic chromosome segregation. Adv. Genet. 1997, 35, 253–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultén, M.A. On the origin of crossover interference: A chromosome oscillatory movement (COM) model. Mol. Cytogenet. 2011, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satomura, K.; Osada, N.; Endo, T. Achiasmy and sex chromosome evolution. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 13, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.W. How meiotic cells deal with non-exchange chromosomes. Bioessays 1994, 16, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loidl, J. Conservation and variability of meiosis across the eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.W. Meiosis in Bombyx mori females. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1977, 277, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wettstein, D.; Rasmussen, S.W.; Holm, P.B. The synaptonemal complex in genetic segregation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1984, 18, 331–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, B.R.R.; Noronha, R.C.R.; da Costa, M.J.R.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C. Meiosis in the scorpion Tityus silvestris: New insights into achiasmatic chromosomes. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio040352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callan, H.G. Lampbrush Chromosomes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gaginskaya, E.; Kulikova, T.; Krasikova, A. Avian lampbrush chromosomes: A powerful tool for exploration of genome expression. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 124, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, J.G.; Wu, Z.; Murphy, C.; Gao, H. Structure in the amphibian germinal vesicle. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 296, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, A.; Kulikova, T. Identification of genomic loci responsible for the formation of nuclear domains using lampbrush chromosomes. Noncoding RNA 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.T. Lampbrush chromosomes and associated bodies: New insights into principles of nuclear structure and function. Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotina, A.; Dedukh, D.; Krasikova, A. Amphibian and avian karyotype evolution: Insights from lampbrush chromosome studies. Genes 2017, 8, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogolyubov, D. Karyosphere (karyosome): A peculiar structure of the oocyte nucleus. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 337, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzova, M.N.; Parfenov, V.N. Karyosphere in oogenesis and intranuclear morphogenesis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1993, 144, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakes, D.C.; Wu, J.; Sadler, P.L.; LaPrade, K.; Moore, L.L.; Noritake, A.; Chu, D.S. Spermatogenesis-specific features of the meiotic program in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, S.M.; Anderson, L.K. A model for chromosome structure during the mitotic and meiotic cell cycles. Chromosome Res. 2001, 9, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-G.; Yang, W.-H.; Qi, Y.-C.; Li, M.-X.; Wang, J.-H.; Sun, X.-M.; Wang, X.-S.; Qi, L.-W. Development of male gametophyte of Larix leptolepis Gord. with emphasis on diffuse stage of meiosis. Plant Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, I.; Darrier, B.; Arrieta, M.; Mittmann, S.U.; Ramsay, L.; Sourdille, P.; Waugh, R. Observation of extensive chromosome axis remodeling during the “diffuse-phase” of meiosis in large genome cereals. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbäck, B.; André, C.; Galindo, J.; Johannesson, K.; Johansson, T.; Panova, M.; Tunlid, A.; Butlin, R. The Littorina sequence database (LSD)—An online resource for genomic data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, H.E.; Faria, R.; Johannesson, K.; Larsson, T.; Panova, M.; Westram, A.M.; Butlin, R.K. Genomic architecture of parallel ecological divergence: Beyond a single environmental contrast. Sci Adv. 2019, 5, eaav9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.P.; Sotelo, G.; Galindo, J.; Chaube, P.; Costa, D.; Afonso, S.; Panova, M.; Nowick, K.; Butlin, R.; Hollander, J.; et al. Transcriptomic resources for evolutionary studies in flat periwinkles and related species. Sci Data 2020, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltseva, A.L.; Varfolomeeva, M.A.; Lobov, A.A.; Tikanova, P.; Panova, M.; Mikhailova, N.A.; Granovitch, A.I. Proteomic similarity of the littorinid snails in the evolutionary context. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, A.A.; Maltseva, A.L.; Mikhailova, N.A.; Granovitch, A.I. The molecular mechanisms of gametic incompatibility in invertebrates. Acta Naturae 2019, 11, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, G.; Duvetorp, M.; Costa, D.; Panova, M.; Johannesson, K.; Faria, R. Phylogeographic history of flat periwinkles, Littorina fabalis and L. obtusata. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demin, S.I.; Stefanova, V.N.; Granovitch, A.I.; Mikhailova, N.A. Spermatogenesis and lobular cyst type of testes organization in marine gastropod Littorina saxatilis (Olivi 1792). Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 376, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, A.I.; Stefanova, V.N.; Podgornaya, O.I.; Demin, S.I. Karyotype features of trematode Himasthla elongata. Mol. Cytogenet. 2016, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Black, D.A. Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: A 1-step method. Exp. Dermatol. 1980, 36, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demin, S.Y.; Berdieva, M.A.; Podlipaeva, Y.I.; Goodkov, A.V. Karyotypic instability of endoprophase and mitotic cells of Amoeba sp. strain Cont from the “proteus-type” group (Amoebozoa, Euamoebida, Amoebidae). Eur. J. Protistol. 2020, 74, 125691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodyuchenko, T.; Gagiskaya, E.; Krasikova, A. Non-canonical Cajal bodies form in the nucleus of late stage avian oocytes lacking functional nucleolus. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 138, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, G.K.; Fang, C.; Olson, M.A.; Falque, M.; Martin, O.C.; Pawlowski, W.P. Recombination patterns in maize reveal limits to crossover homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15982–15987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demin, S.I.; Bogolyubov, D.S.; Granovitch, A.I.; Mikhailova, N.A. New data on spermatogenic cyst formation and cellular composition of the testis in a marine gastropod, Littorina saxatilis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.R.; Carlton, P.M.; Golubovskaya, I.N.; Cande, W.Z. Interlock formation and coiling of meiotic chromosome axes during synapsis. Genetics 2009, 183, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickler, D.; Espagne, E. Sordaria, a model system to uncover links between meiotic pairing and recombination. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 54, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.; Schubert, V.; Osman, K.; Darbyshire, A.; Sanchez-Moran, E.; Franklin, F.C.H. TOPII and chromosome movement help remove interlocks between entangled chromosomes during meiosis. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4070–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, Y.P.; Nguyen, A.D.; Draper, B.W.; Burgess, S.M. The telomere bouquet is a hub where meiotic double-strand breaks, synapsis, and stable homolog juxtaposition are coordinated in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.J.; Marshall, W.F.; Fung, J.C. Modeling cell biological features of meiotic chromosome pairing to study interlock resolution. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, K. Chromosome number in two phenotypically distinct populations of Littorina saxatilis Olivi, and in the specimens of the Littorina obtusata (L.) species-complex. J. Mollus. Stud. 1983, 49, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birstein, V.J.; Mikhailova, N.A. On the karyology of trematodes of the genus Microphallus and their intermediate gastropod host, Littorina saxatilis. II. Karyological study of Littorina saxatilis (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia). Genetica 1990, 80, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolán-Alvarez, E.; Buño, I.; Gonsalvez, J. Sex is determined by sex chromosomes in Littorina saxatilis (Olivi) (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia). Hereditas 1996, 124, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Souto, D.; Alonso-Rubido, S.; Costa, D.; Eirín-López, J.M.; Rolán-Álvarez, E.; Faria, R.; Galindo, J.; Pasantes, J.J. Karyotype characterization of nine periwinkle species (Gastropoda, Littorinidae). Genes 2018, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westram, A.M.; Rafajlović, M.; Chaube, P.; Faria, R.; Larsson, T.; Panova, M.; Ravinet, M.; Blomberg, A.; Mehlig, B.; Johannesson, K.; et al. Clines on the seashore: The genomic architecture underlying rapid divergence in the face of gene flow. Evol. Lett. 2018, 2, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovich, A.I.; Mikhailova, N.A.; Znamenskaya, O.; Petrova, Y.A. Species complex of mollusks of the genus Littorina (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia) from the Eastern Murman coast. Zool. Zhurnal 2004, 83, 1305–1316, (In Russian, English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailova, N.A.; Gracheva, Y.A.; Backeljau, T.; Granovitch, A.I. A potential species-specific molecular marker suggests interspecific hybridization between sibling species Littorina arcana and L. saxatilis (Mollusca, Caenogastropoda) in natural populations. Genetica 2009, 137, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.; Nibau, C.; Wnetrzak, J.; Jenkins, G. High resolution analysis of meiotic chromosome structure and behaviour in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, M.J.; Pawlowski, W.P. Live imaging of rapid chromosome movements in meiotic prophase I in maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20989–20994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Jin, G.L.; Zhao, S.H.; Yu, M.; Xiong, T.A.; Peng, Z.Z.; Li, K. Preparation and analysis of spermatocyte meiotic pachytene bivalents of pigs for gene mapping. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, E.T.; de Carvalho, C.R. Chromomere mapping in maize pachytenes. Caryologia 2003, 56, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, E.T.; Carvalho, C.R.; Clarindo, W.R. Modified protocol for obtaining isolated and high-resolution pachytene chromosomes. Nucleus 2011, 54, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmido, N.; Iwata, A.; Kato, S.; Wako, T.; Fukui, K. Development of a quantitative pachytene chromosome map and its unification with somatic chromosome and linkage maps of rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, K.-W.; Lin, C.-Y.; Peng, S.-F.; Cheng, Y.-M. Characterization of four B-chromosome-specific RAPDs and the development of SCAR markers on the maize B-chromosome. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2015, 290, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, E.; De Muyt, A.; Soyer, J.L.; Budin, K.; Legras, M.; Piolot, T.; Debuchy, R.; Kleckner, N.; Zickler, D.; Espagne, E. Building bridges to move recombination complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12400–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Liu, C.; Dernburg, A.F. How and why chromosomes interact with the cytoskeleton during meiosis. Genes 2022, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, M.; Pascual, Á.; Anton, E.; Blanco, J.; Sarrate, Z. The courtship choreography of homologous chromosomes: Timing and mechanisms of DSB-independent pairing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1191156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytlis, A.; Levy, K.; Elkouby, Y.M. The many faces of the bouquet centrosome MTOC in meiosis and germ cell development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2023, 81, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rog, O.; Dernburg, A.F. Chromosome pairing and synapsis during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, D.J.; Rog, O.; Carlton, P.M.; Dernburg, A.F. Dynein-dependent processive chromosome motions promote homologous pairing in C. elegans meiosis. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Conrad, M.N.; Dresser, M.E. Meiotic chromosome pairing is promoted by telomere-led chromosome movements independent of bouquet formation. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajan, S.; Mohideen, F.; Tzur, Y.B.; Ferrandiz, N.; Crawley, O.; Montoya, A.; Faull, P.; Snijders, A.P.; Cutillas, P.R.; Jambhekar, A.; et al. The MAP kinase pathway coordinates crossover designation with disassembly of synaptonemal complex proteins during meiosis. Elife 2016, 5, e12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, G.M.; Fang, J.S. Complete autosomal chromomere maps of human early and mid/late pachytene spermatocytes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1982, 34, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Fang, J.S.; Jagiello, G. Complete chromomere map of mid/late pachytene human oocytes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1983, 35, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Fang, J.S.; Jagiello, G. A pachytene map of the mouse spermatocyte. Chromosoma 1981, 82, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhanwar, S.C.; Chaganti, R.S. Pachytene chromomere maps of Chinese hamster autosomes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1981, 31, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.S.; Jagiello, G.M. The chromomere map of the pachytene spermatocyte of the Turkish hamster (Mesocricetus brandti). Genome 1991, 34, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasterska, I.; Ramel, C. A comparative study of male meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster and D. virilis. Genetica 1990, 81, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samejima, K.; Booth, D.G.; Ogawa, H.; Paulson, J.R.; Xie, L.; Watson, C.A.; Platani, M.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Earnshaw, W.C. Functional analysis after rapid degradation of condensins and 3D-EM reveals chromatin volume is uncoupled from chromosome architecture in mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs210187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piergentili, R. Evolutionary conservation of lampbrush-like loops in drosophilids. BMC Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, S.; Lake, C.M.; Morais-de-Sá, E.; Sunkel, C.E.; Hawley, R.S. Synaptonemal complex-dependent centromeric clustering and the initiation of synapsis in Drosophila oocytes. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, M.W. The spermatogenesis of the myriapods. II. On the chromatin in the spermatocytes of Scolopendra heros. Biol. Bull. 1903, 5, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.S.; Jagiello, G.M. An analysis of the chromomere map and chiasmata characteristics of human diplotene spermatocytes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1988, 47, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Láscarez-Lagunas, L.I.; Martinez-Garcia, M.; Colaiácovo, M.P. Loss, gain, and retention: Mechanisms driving late prophase I chromosome remodeling for accurate meiotic chromosome segregation. Genes 2022, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakiya, M.; Nishi, E.; Kawai, S.; Yamada, K.; Katsumata, K.; Hirayasu, A.; Itabashi, Y.; Yamamoto, A. Chiasmata and the kinetochore component Dam1 are crucial for elimination of erroneous chromosome attachments and centromere oscillation at meiosis I. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.E.; He, Q.; McKee, B.D. How noncrossover homologs are conjoined and segregated in Drosophila male meiosis I: Stable but reversible homolog linkers require a novel Separase target protein. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, A.A.; Danilov, L.G.; Masharskiy, A.E.; Predeus, A.V.; Mikhailova, N.A.; Granovitch, A.I.; Maltseva, A.L. Data on RNA-seq analysis of the oviducts of five closely related species genus Littorina (Mollusca, Caenogastropoda): L. saxatilis, L. arcana, L. compressa, L. obtusata, L. fabalis. Data Brief 2022, 42, 108122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demin, S.I.; Mikhailova, N.A.; Granovitch, A.I.; Bogolyubov, D.S. Non-Canonical Male Meiosis in a Marine Gastropod, Littorina saxatilis. Biology 2025, 14, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111572
Demin SI, Mikhailova NA, Granovitch AI, Bogolyubov DS. Non-Canonical Male Meiosis in a Marine Gastropod, Littorina saxatilis. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111572
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemin, Sergei Iu., Natalia A. Mikhailova, Andrei I. Granovitch, and Dmitry S. Bogolyubov. 2025. "Non-Canonical Male Meiosis in a Marine Gastropod, Littorina saxatilis" Biology 14, no. 11: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111572
APA StyleDemin, S. I., Mikhailova, N. A., Granovitch, A. I., & Bogolyubov, D. S. (2025). Non-Canonical Male Meiosis in a Marine Gastropod, Littorina saxatilis. Biology, 14(11), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111572






