The Stylohyoid Complex: An Update on Its Embryology, Comparative Anatomy and Human Variations
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Embryological Development of the Stylohyoid Complex
2.1. Early Segmentation of the Reichert’s Cartilage
2.2. Relationship with Surrounding Structures-Otic Capsule, Stapes and Nerves
2.3. Ossification and Persistency Processes
2.4. Associated Muscular, Fasciae and Connective Derivatives
2.5. Developmental and Evolutionary Implications
3. Comparative Anatomy of the Stylohyoid Complex
3.1. General Mammalian Pattern
3.2. Primates
3.3. Rodents and Lagomorphs
3.4. Carnivores
3.5. Ungulates
3.6. Proboscideans
3.7. Cetaceans
3.8. Xenarthrans and Fossil Glyptodonts
3.9. Functional Trends
- Ossified continuity (cetaceans, ungulates, many carnivores, elephants): supports powerful and specialized feeding or vocal functions (suction feeding, grazing, roaring, infrasonics).
- Reduction and ligamentous suspension (primates, rodents, lagomorphs, humans): enhances cranial mobility, facilitates hyoid descent, and in humans, underpins the evolution of speech.
4. Human Variations and Relationships with Neurovascular Structures
4.1. Length Variability
4.2. Angulation and Orientation
4.3. Morphological Variations
4.4. Ossification of the Stylohyoid Ligament
4.5. Relationship with Neurovascular Structures
5. Clinical Anatomy of the Stylohyoid Complex
- Jugular variant (Eagle jugular syndrome): Zamboni et al. [55] described compression of the IJV between the SP and the C1 transverse process, producing intracranial hypertension, papilledema, venous congestion, and even peri-mesencephalic hemorrhage [55]. Headache and orbital symptoms dominate, distinguishing it from the carotid subtype [56].
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCA | Common carotid artery |
| CCAD | Cervical carotid artery dissection |
| CN | Cranial nerve |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTA | CT angiography |
| ECA | External carotid artery |
| HB | Hyoid bone |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| IJV | Internal jugular vein |
| RC | Reichert’s cartilage |
| SHC | Stylohyoid complex |
| SHL | Stylohyoid ligament |
| SP | Styloid process |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Triantafyllou, G.; Piagkou, M. The Developing Human Sphenoid Bone: Linking Embryological Development to Adult Morphology. Biology 2025, 14, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Samolis, A.; Landfald, I.C.; Olewnik, Ł.; Cavalcante, J.C.; Piagkou, M. Comparative Anatomy of the Coracobrachialis Muscle: Insights into Human Typical and Variant Morphology. Biology 2025, 14, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Jin, Z.; Hayashi, S.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Murakami, G.; Abe, S. Association between the Developing Sphenoid and Adult Morphology: A Study Using Sagittal Sections of the Skull Base from Human Embryos and Fetuses. J. Anat. 2021, 239, 1300–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jin, Z.-W.; Li, C.-A.; Yamamoto, M.; Murakami, G.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Hayashi, S. Orbital Roof Cartilage and Bone in Human Fetuses with Special Reference to Changing Territories among the Ala Minor of the Sphenoid, Frontal Bone, and Ethmoid. Anat. Cell Biol. 2025, 58, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S.; Anand, N.; Birch, R.; Collins, P.; Crossman, A.; Gleeson, M.; Jawaheer, G.; Smith, A.; Spratt, J.; Stringer, M.; et al. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lassalle, S.L.; Serrano Bernárdez, V.C.; Cifone, T.; Rimoldi, S.; Benitez, N.; Diaz, F.D.; Garay, V.; Bendersky, M. Compartmentalization of the Human Cephalic Parapharyngeal Space: A Scoping Review. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2025, 47, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoton, A.L. The Temporal Bone and Transtemporal Approaches. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, S211–S265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Inui, Y.; Katada, K. Temporal Bone Anatomy: Correlation of Multiplanar Reconstruction Sections and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Images. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2010, 28, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudose, R.C.; Triantafyllou, G.; Piagkou, M.; Rusu, M.C. Pneumatisation Patterns Surrounding the Internal Acoustic Meatus. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2025, 263, 152724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, M.C.; Rusu, M.I.; Vrapciu, A.D. The Posterior-Inferior Recess of the Sinus Tympani, an Anatomical Novelty. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2025, 257, 152336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsis, K.; Repousi, E.; Noussios, G.; Papathanasiou, E.; Apostolidis, S.; Piagkou, M. The Styloid Process in a Greek Population: An Anatomical Study with Clinical Implications. Anat. Sci. Int. 2015, 90, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. Elongated styloid processes: Report of Two Cases. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1937, 25, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.W. Elongated Styloid Process: Further Observations and a New Syndrome. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1948, 47, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, F.; Tillmann, B.; Christofides, C.; Richter, W.; Koebke, J. Curving and Looping of the Internal Carotid Artery in Relation to the Pharynx: Frequency, Embryology and Clinical Implications. J. Anat. 2000, 197, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Paschopoulos, I.; Duparc, F.; Tsakotos, G.; Tsiouris, C.; Olewnik, Ł.; Georgiev, G.; Zielinska, N.; Piagkou, M. The Superior Thyroid Artery Origin Pattern: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 46, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Vassiou, K.; Duparc, F.; Vlychou, M.; Paschopoulos, I.; Tsakotos, G.; Tudose, R.C.; Rusu, M.C.; Piagkou, M. The Lingual and Facial Arteries’ Common Origin: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and a Computed Tomography Angiography Study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 46, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karangeli, N.; Triantafyllou, G.; Duparc, F.; Vassiou, K.; Vlychou, M.; Tsakotos, G.; Piagkou, M. Retrostyloid and Retromandibular Courses of the External Carotid Artery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 47, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, C.C.; Vrapciu, A.D.; Jianu, A.M.; Hostiuc, S.; Rusu, M.C. The Retromandibular Loop of the External Carotid Artery. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2024, 253, 152226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Verdugo-López, S.; Abe, H.; Murakami, G. The Origin of the Variations of the Hyoid Apparatus in Human. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Mérida-Velasco, J.R.; Verdugo-López, S.; Sánchez-Montesinos, I.; Mérida-Velasco, J.A. Morphogenesis of the Second Pharyngeal Arch Cartilage (Reichert’s Cartilage) in Human Embryos. J. Anat. 2006, 208, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anson, B.J.; Bast, T.H.; Richany, S.F. The Development of the Second Branchial Arch (Reichert’s Cartilage), Facial Canal and Associated Structures in Man. Q. Bull. Northwest. Univ. Med. Sch. 1956, 30, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.H.; Honkura, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hayashi, S.; Kitamura, K.; Murakami, G.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F. Topohistology of the Cranial Nerves IX–XII at the Cranial Base and Upper Parapharyngeal Space: A Histological Study Using Human Fetuses. Anat. Rec. 2025, 308, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-A.; Jin, Z.-W.; Honkura, Y.; Hirano-Kawamoto, A.; Murakami, G.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Katori, Y. Branched Ends of Reichert’s Cartilage in the Ear: A Histological Study Using Human near-Term Fetuses. Anat. Cell Biol. 2025, 58, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérida-Velasco, J.R.; Rodríguez-Vazquez, J.F.; De La Cuadra Blanco, C.; Sánchez-Montesinos, I.; Mérida-Velasco, J.A. Origin of the Styloglossus Muscle in the Human Fetus. J. Anat. 2006, 208, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katori, Y.; Kawase, T.; Ho Cho, K.; Abe, H.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.F.; Murakami, G.; Fujimiya, M. Suprahyoid Neck Fascial Configuration, Especially in the Posterior Compartment of the Parapharyngeal Space: A Histological Study Using Late-stage Human Fetuses. Clin. Anat. 2013, 26, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisdal, A.; Trainor, P.A. Development and Evolution of the Pharyngeal Apparatus. WIREs Dev. Biol. 2014, 3, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.; Izumi, M.; Gotoh, K. Comparative Anatomy of the Hyoid Apparatus of Carnivores. Mammal Study 2009, 34, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilloowala, R.A. Comparative Anatomical Study of the Hyoid Apparatus in Selected Primates. Am. J. Anat. 1975, 142, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, J.M. The Hyoid Apparatus of Neotoma. J. Mammal. 1942, 23, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anapol, F. Morphological and Videofluorographic Study of the Hyoid Apparatus and Its Function in the Rabbit (Oryctolagus Cuniculus). J. Morphol. 1988, 195, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissengruber, G.E.; Forstenpointner, G.; Peters, G.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Fitch, W.T. Hyoid Apparatus and Pharynx in the Lion (Panthera Leo), Jaguar (Panthera Onca), Tiger (Panthera Tigris), Cheetah (Acinonyx Jubatus) and Domestic Cat (Felis Silvestris f. Catus). J. Anat. 2002, 201, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, D.; Eldridge, E.I.; Elminowski, E.E.; Dickinson, E.; Hartstone-Rose, A. The Howl of Rancho La Brea: Comparative Anatomy of Modern and Fossil Canid Hyoid Bones. J. Morphol. 2020, 281, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, B.; Egerbacher, M.; Kneissl, S.M. Correlated Imaging of the Equine Hyoid Apparatus Using CT, Micro-CT, and Histology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 652563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshani, J.; Marchant, G. Hyoid Apparatus: A Little Known Complex of Bones and Its “Contribution” to Proboscidean Evolution. In The World of Elephants; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 668–675. [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg, J.S.; Laitman, J.T. Anatomy of the Hyoid Apparatus in Odontoceti (Toothed Whales): Specializations of Their Skeleton and Musculature Compared with Those of Terrestrial Mammals. Anat. Rec. 1994, 240, 598–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.M.; Toledo, N.; De Iuliis, G.; Bargo, M.S.; Vizcaíno, S.F. Morphology and Function of the Hyoid Apparatus of Fossil Xenarthrans (Mammalia). J. Morphol. 2010, 271, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano, M.; Scillato-Yané, G.J.; Soibelzon, E.; Soibelzon, L.H.; Bonini, R.; Rodriguez, S.G. Hyoid Apparatus of Panochthus Sp. (Xenarthra; Glyptodontidae) from the Late Pleistocene of the Pampean Region (Argentina). Comparative Description and Muscle Reconstruction. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Palaontol. Abh. 2018, 288, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Tschernitschek, H.; Hippen, H.; Schneider, B.; Borchers, L. Elongated Styloid Process: When Is It Really Elongated? Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2004, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsour, P.A.; Young, W.G. Variability of the Styloid Process and Stylohyoid Ligament in Panoramic Radiographs. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1986, 61, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafne, E.C.; Hollinshead, W.H. Roentgenographic Observations on the Stylohyoid Chain. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1962, 15, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Paschopoulos, I.; Duparc, F.; Tsakotos, G.; Papadopoulos-Manolarakis, P.; Piagkou, M. The Anatomy of the Stylohyoid Chain: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, F.; Motoc, A.G.M.; Didilescu, A.C.; Rusu, M.C. A 3D Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study of the Styloid Process of the Temporal Bone. Folia Morphol. 2013, 72, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onbas, O.; Kantarci, M.; Murat Karasen, R.; Durur, I.; Cinar Basekim, C.; Alper, F.; Okur, A. Angulation, Length, and Morphology of the Styloid Process of the Temporal Bone Analyzed by Multidetector Computed Tomography. Acta Radiol. 2005, 46, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal Ramadan, S.; Gökharman, D.; Koşar, P.; Kacar, M.; Koşar, U. The Stylohyoid Chain: CT Imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 75, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raser, J.M.; Mullen, M.T.; Kasner, S.E.; Cucchiara, B.L.; Messé, S.R. Cervical Carotid Artery Dissection Is Associated with Styloid Process Length. Neurology 2011, 77, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, J.M.; Pereira, D.; Rodrigues, M.G.; Beato-Coelho, J.; Lopes, M.; Cunha, A.; Figueiredo, S.; Mendes-Pinto, M.; Ferreira, C.; Sargento-Freitas, J.; et al. Anatomical Characteristics of the Styloid Process in Internal Carotid Artery Dissection: Case–Control Study. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, D.; Azakri, S.; Arquizan, C.; Swinnen, B.; Labauge, P.; Thijs, V. Styloid and Hyoid Bone Proximity Is a Risk Factor for Cervical Carotid Artery Dissection. Stroke 2013, 44, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Botis, G.; Vassiou, K.; Vlychou, M.; Tsakotos, G.; Kalamatianos, T.; Matsopoulos, G.; Piagkou, M. Τhe Styloid Process Length and the Stylohyoid Chain Ossification Affect Its Relationship with the Carotid Arteries. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2025, 257, 152342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllou, G.; Papadopoulos-Manolarakis, P.; Vassiou, K.; Vlychou, M.; Karangeli, N.; Papanagiotou, P.; Tsakotos, G.; Piagkou, M. The Impact of the Styloid Process Angulation on the Carotid Arteries. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2025, 258, 152378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calotă, R.N.; Rusu, M.C.; Vrapciu, A.D. The External Carotid Artery and the Styloid Process. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piagkou, M.N.; Anagnostopoulou, S.; Kouladouros, K.; Piagkos, G. Eagle’s Syndrome: A Review of the Literature. Clin. Anat. 2009, 22, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohée-Traoré, A.; Boucher, S. Ossification of Stylohyoid Complex in Eagle Syndrome. Radiology 2023, 306, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, D.J.; Asteraki, S.; Spetzler, R.F. Eagle’s Syndrome: Embryology, Anatomy, and Clinical Management. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ravin, E.; Frost, A.S.; Mady, L.J.; Newman, J.G. Transcervical Styloidectomy for Eagle Syndrome. Head Neck 2022, 44, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, P.; Scerrati, A.; Menegatti, E.; Galeotti, R.; Lapparelli, M.; Traina, L.; Tessari, M.; Ciorba, A.; De Bonis, P.; Pelucchi, S. The Eagle Jugular Syndrome. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincă, V.; Ionescu, P.; Tudose, R.C.; Munteanu, M.; Vrapciu, A.D.; Rusu, M.C. Anatomical Reasons for an Impaired Internal Jugular Flow. Medicina 2025, 61, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.C.; Kamath, M.P.; Reddy, K.J.M.; Raju, K.; Agarwal, S. Elongated Styloid Process (Eagle’s Syndrome): A Clinical Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, R.; Caranti, A.; Meccariello, G.; Stringa, L.M.; Bianchini, C.; Ciorba, A.; Pelucchi, S.; Vicini, C. Transoral Robotic Styloidectomy for Eagle Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2024, 49, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, A.; Brizzi, V.; Majoufre, C.; Nicot, R.; Schlund, M. Eagle Syndrome and Vascular Complications—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2025, 54, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Grønlund, E.W.; Albrechtsen, S.S.; Kondziella, D. Neurological Phenotypes and Treatment Outcomes in Eagle Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y. Anatomical Characteristics of the Styloid Process in Cerebral Infarction Related to Carotid Artery Dissection: A Case-Control Study. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1573667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, B.S.; de Bakker, H.M.; Soerdjbalie-Maikoe, V.; Dikkers, F.G. Variants of the Hyoid-Larynx Complex, with Implications for Forensic Science and Consequence for the Diagnosis of Eagle’s Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadav, D.; Kanchan, T.; Shekhawat, R.S.; Meshram, V.; Tak, M. Elongated Styloid Process: An Incidental Autopsy Finding of Clinical and Medico-Legal Significance. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2022, 87, 102334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
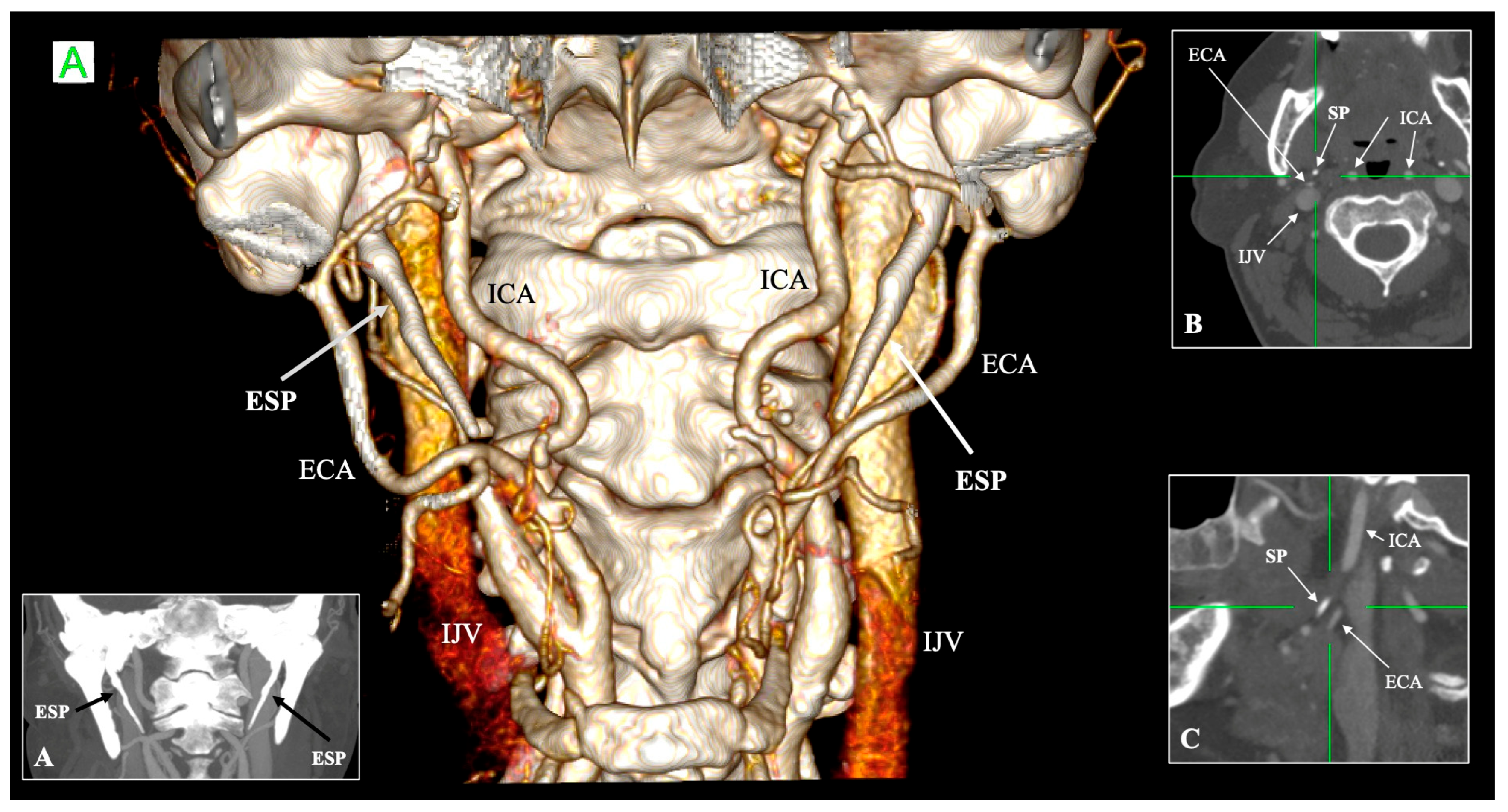
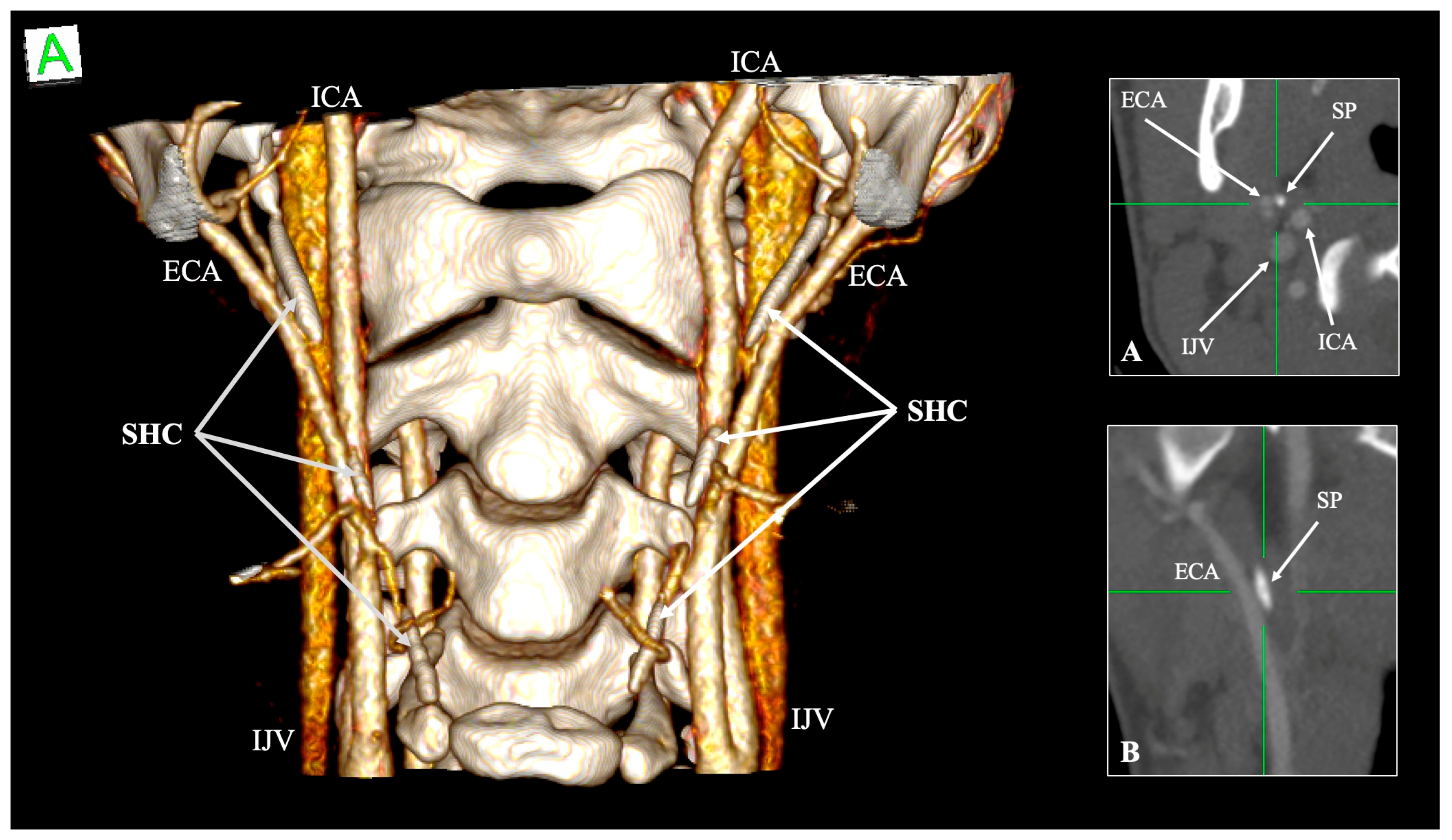
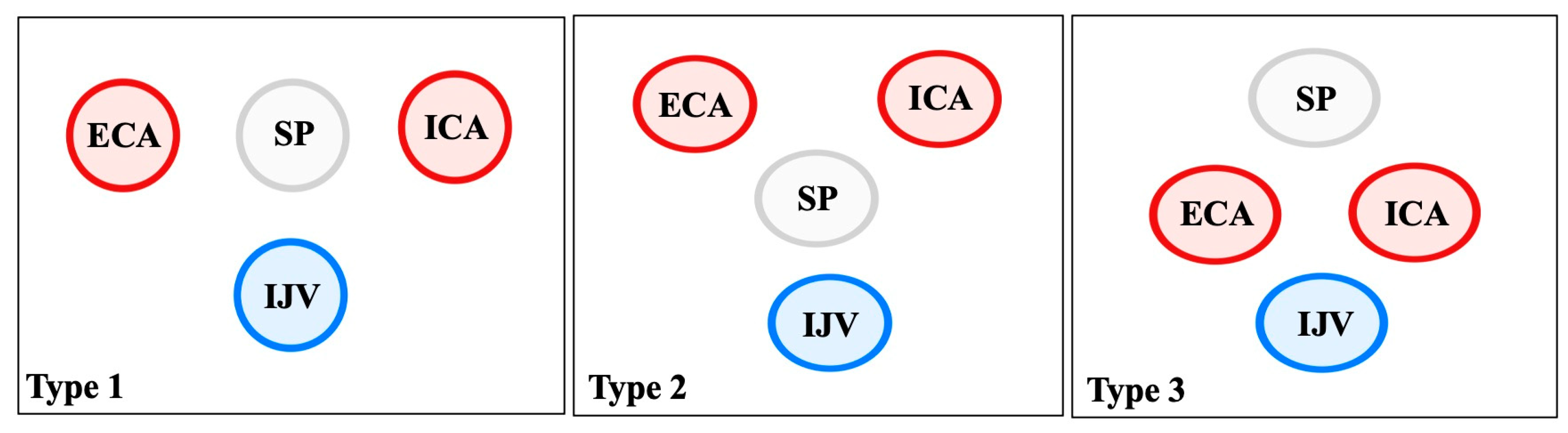
| Developmental Stage | Key Features of RC | Relationships with Adjacent Structures | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carnegie stage 17 (6 weeks) | RC appears as a mesenchymal condensation in the 2nd pharyngeal arch | Lies between the pharynx and the FN | Rodríguez-Vázquez et al. [19] |
| Carnegie stage 18 (6–7 weeks) | Cranial segment begins chondrogenesis → future SP- caudal segment remains precartilaginous → future LH of the HB | Close to otic capsule, ECA, CN IX–X | Rodríguez-Vázquez et al. [20] |
| 7–8 weeks | A mesenchymal bridge transiently connects cranial (styloid) and caudal (hyoid) segments | ICA and IJV separate RC from CN IX–XII | Rodríguez-Vázquez et al. [19]; Cho et al. [22] |
| ~10 weeks | Regression of mesenchymal bridge → no continuous cartilage | The FN runs laterally to the styloid segment | Cho et al. [22] |
| 19–34 weeks (fetal series) | The styloid segment forms part of the tympanic wall before being replaced by the membrane bone | The vertical portion of the FC is shaped | Anson et al. [21] |
| 25–40 weeks (near term) | The cranial part shows branched/T-shaped morphology, projecting toward the tympanic cavity and the FC | Fusion with petrosal & tympanic bones influences styloid root morphology | Li et al. [23] |
| Cranial segment undergoes endochondral ossification → SP; Caudal segment also undergoes endochondral ossification →LH of the HB | Muscles (styloglossus, stylohyoid, stylopharyngeus) originate from the RC; the styloid fascia divides the parapharyngeal space | Mérida-Velasco et al. [24]; Katori et al. [25] |
| Taxon/Group | Main SHC Elements | Distinctive Features | Functional Adaptations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammals (general) | Tympanohyal, stylohyal, epihyal, ceratohyal, basihyal, thyrohyal | Conserved suspensory + basal portions | Tongue and laryngeal support | Takada et al. [27]; Weissengruber et al. [31] |
| Primates | Reduced SP; variable hyoid ossicles | SP is distinct in baboons, rudimentary in macaques, and absent in small primates | Variation linked to vocalization and craniofacial size | Hilloowala [28] |
| Rodents/Lagomorphs | Ligamentous suspension of the HB | Tympanohyal fuses to the mastoid; stylohyal slender rod | Stable base for chewing and swallowing; mobility of the tongue | Sprague [29]; Anapol [30] |
| Carnivores (Felids, Canids, Ursids, Mustelids) | Ossified stylohyal, variable epihyal | Roaring cats: epihyal ligamentous; small cats: epihyal ossified | Roaring vs purring mechanisms; laryngeal descent | Weissengruber et al. [31]; Takada et al. [27] |
| Ungulates | Massive stylohyal + variable epihyal | Horses: temporohyoid synchondrosis; ruminants: synovial joint; pigs: epihyal replaced by ligament | Supports grazing mechanics and airway stability | Hartl et al. [33] |
| Proboscideans (Elephants) | Stylohyal Y-shaped; epihyal/ceratohyal absent | Fusion with basihyal-thyrohyal unit; deep neck stabilization | Supports trunk–tongue coordination and infrasonic calls | Shoshani and Marchang [34] |
| Cetaceans | Fully ossified, flattened hyoid | Enlarged and tilted apparatus | Anchor for suction feeding, echolocation sound production | Reidenberg and Laitman [35] |
| Xenarthrans/Fossil Glyptodonts | Fusion into sigmohyal and V-bone | Glyptodonts: rigid fusion; sloths: elongated, gracile elements | Dietary specialization and tongue mobility | Pérez et al. [36]; Zamorano et al. [37] |
| Structure | Typical Relationship with SP/SHC | Variant/Altered Relationship | Clinical Significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal carotid artery (ICA) | Medial to SP, ascends branchless to the skull base | Tortuosity, kinking, coiling; reduced ICA–SP distance; direct bony contact | Risk of dissection, ischemic stroke, and hemorrhage during pharyngeal surgery | Paulsen et al. [14]; Renard et al. [47]; Raser et al. [45]; Amorim et al. [46] |
| External carotid artery (ECA) | Anterolateral to SP; gives facial and pharyngeal branches | Retro-styloid course (~9–12%) | Altered surgical corridor; potential compression or irritation | Karangeli et al. [17]; Calotă et al. [50] |
| Internal jugular vein (IJV) | Posterolateral to SP within the carotid sheath | Compression between SP and C1 transverse process (“jugular nutcracker”) | Intracranial hypertension, venous congestion, hemorrhage | Triantafyllou et al. [48] |
| Facial nerve (CN VII) | Emerges from stylomastoid foramen, lateral to SP base | Variant styloid root morphology alters proximity | Risk of neuropathic pain, nerve traction post-tonsillectomy | Cho et al. [22]; Li et al. [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piagkou, M.; Triantafyllou, G. The Stylohyoid Complex: An Update on Its Embryology, Comparative Anatomy and Human Variations. Biology 2025, 14, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111500
Piagkou M, Triantafyllou G. The Stylohyoid Complex: An Update on Its Embryology, Comparative Anatomy and Human Variations. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111500
Chicago/Turabian StylePiagkou, Maria, and George Triantafyllou. 2025. "The Stylohyoid Complex: An Update on Its Embryology, Comparative Anatomy and Human Variations" Biology 14, no. 11: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111500
APA StylePiagkou, M., & Triantafyllou, G. (2025). The Stylohyoid Complex: An Update on Its Embryology, Comparative Anatomy and Human Variations. Biology, 14(11), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111500







