Transcriptome Analysis of the Pathogenic Mechanism of the Novel Pathogenic Fungus Bipolaris fujianensis in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Shoot Blight
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.2. Data Quality Control and Analysis
2.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Validation of DEGs by RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing Data Analysis
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
3.3. Functional Annotation and Go Analysis
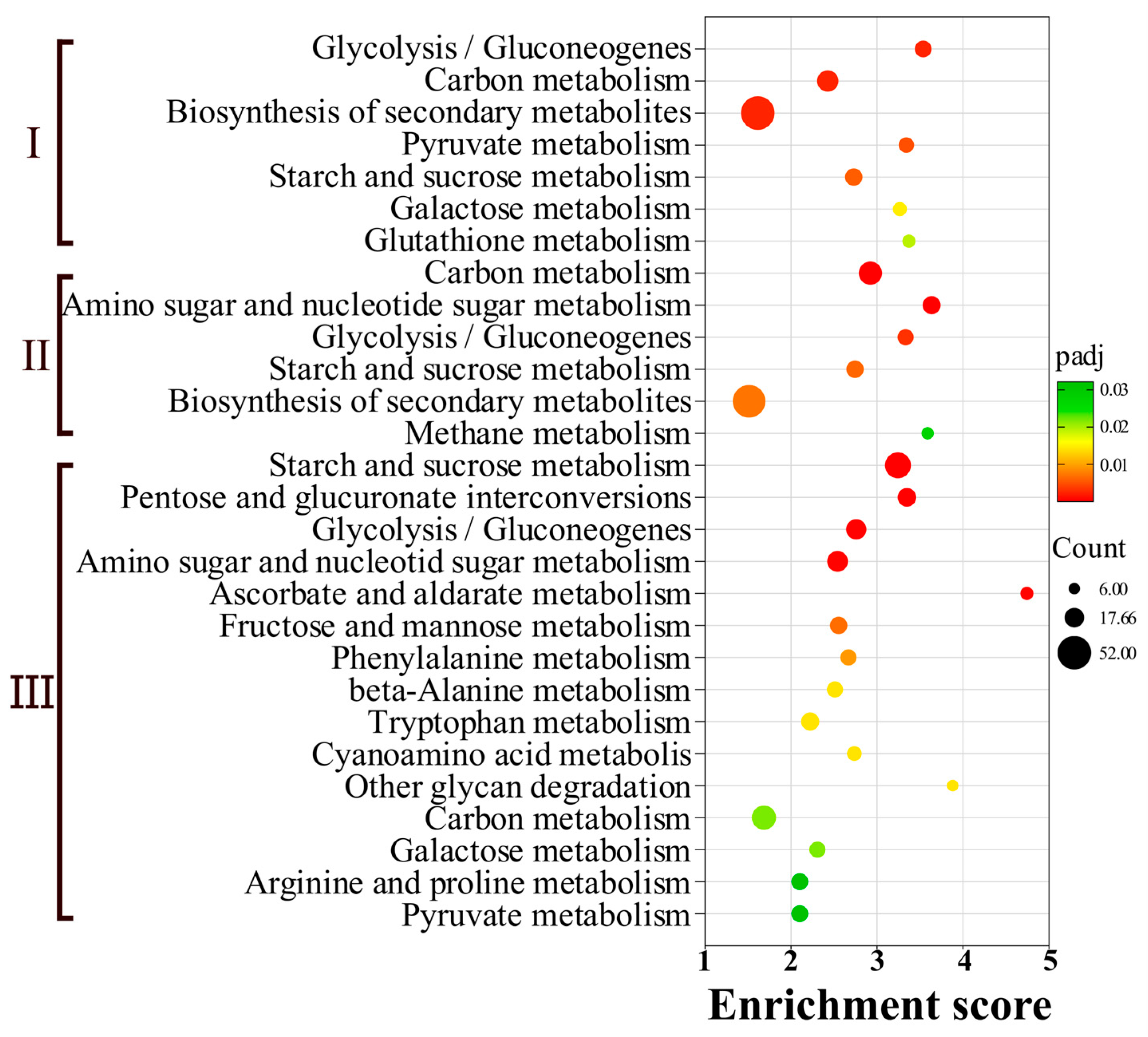
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3.5. Candidate Genes Associated with Pathogenesis
3.6. Expression Validation of Pathogenicity-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| GHs | Glycoside hydrolases |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| FPKM | Fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments |
| PDA | Potato dextrose agar |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| NCBI | National center for biotechnology information |
References
- Zheng, G.; Su, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, M.; Ju, W.; Zou, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.; Guo, J.; et al. Variations in fine root biomass, morphology, and vertical distribution in both trees and understory vegetation among Chinese fir plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 557, 121748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, X. Response of Functional Diversity of Soil Microbial Community to Forest Cutting and Regeneration Methodology in a Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests 2022, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.N.; Yang, J.Y.; Li, D.W.; Li, Y.; Bian, L.M.; Ye, J.R. Shoot Blight on Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) is Caused by Bipolaris oryzae. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, D.-W.; Cui, W.-L.; Huang, L. Seven new species of Alternaria (Pleosporales, Pleosporaceae) associated with Chinese fir, based on morphological and molecular evidence. MycoKeys 2024, 101, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kim, K.-T.; Yang, J.-Y.; Song, H.; Choi, G.; Jeon, J.; Cheong, K.; Ko, J.; Xu, H.; Lee, Y.-H. A High-Quality Draft Genome Sequence of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides sensu stricto SMCGl#C, a Causal Agent of Anthracnose on Cunninghamia lanceolata in China. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Ye, C.; Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; He, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, S. Leaching alleviates phenol-mediated root rot in Panax notoginseng by modifying the soil microbiota. Plant Soil 2021, 468, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, D.M.; Barreto, R.W. First report of leaf blight of Brachiaria brizantha in Brazil caused by Bipolaris cynodontis. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Gong, G. Etiology and Symptoms of Maize Leaf Spot Caused by Bipolaris spp. in Sichuan, China. Pathogens 2020, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songsomboon, K.; Crawford, R.; Crawford, J.; Hansen, J.; Cummings, J.; Mattson, N.; Bergstrom, G.; Viands, D. Recurrent phenotypic selection for resistance to diseases caused by Bipolaris oryzae in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 125, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, F.; Strobel, G.; Strange, R.N.; Siedow, J.N.; Van Duyne, G.D.; Clardy, J. Phytotoxins from the pathogenic fungi Drechslera maydis and Drechslera sorghicola. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 3081–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, T.K.; Chick, W.S.; Leung, P.C. The biology of ophiobolins. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Samaddar, K.R. Effects of Helminthosporium oryzae infection and ophiobolin on the cell membranes of host tissues. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1976, 8, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Rodriguez, L.M.; Chilton, W.S. 3-Anhydroophiobolin A and 3-Anhydro-6-epi-ophiobolin A, Phytotoxic Metabolites of the Johnson Grass Pathogen Bipolaris sorghicola. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, H.G.; Crumley, F.G.; Cox, R.H.; Springer, J.P.; Arrendale, R.F.; Cole, R.J.; Cole, P.D. Ophiobolins G and H: New fungal metabolites from a novel source, Aspergillus ustus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.; Lodge, T.; Evidente, A.; Kiss, R.; Townley, H. Ophiobolin A, a sesterpenoid fungal phytotoxin, displays different mechanisms of cell death in mammalian cells depending upon the cancer cell origin. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xue, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, C. Bipolaris fujianensis sp. nov., an Emerging Pathogen of Sapling Shoot Blight on Chinese Fir, and Its Sensitivity to Fungicides. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, L.; Lanver, D.; Schweizer, G.; Tanaka, S.; Liang, L.; Tollot, M.; Zuccaro, A.; Reissmann, S.; Kahmann, R. Fungal Effectors and Plant Susceptibility. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Nandineni, M.R. Genome sequencing and comparative genomics reveal a repertoire of putative pathogenicity genes in chilli anthracnose fungus Colletotrichum truncatum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noar, R.D.; Daub, M.E. Transcriptome sequencing of Mycosphaerella fijiensis during association with Musa acuminata reveals candidate pathogenicity genes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, N.; Meng, X.; Friedlander, G.; Reuveni, E.; Sukno, S.; Sherman, A.; Thon, M.; Fluhr, R.; Prusky, D. Global Aspects of pacC Regulation of Pathogenicity Genes in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides as Revealed by Transcriptome Analysis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, S.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, H.; Qiao, T.; Lin, T.; Zhu, T. Comparative Transcriptomics and Gene Knockout Reveal Virulence Factors of Neofusicoccum parvum in Walnut. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Bipolaris oryzae Strain TG12bL2 Genome Assembly. GCA_001675385.1. Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_001675385.1/ (accessed on 21 October 2025).
- Jiang, H.; Cao, Q.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Pectate Lyase Genes Abundantly Expressed During the Infection Regulate Morphological Development of Colletotrichum camelliae and CcPEL16 Is Required for Full Virulence to Tea Plants. mSphere 2023, 8, e0067722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Starr, T.L.; Glass, N.L. Plant Cell Wall–Degrading Enzymes and Their Secretion in Plant-Pathogenic Fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlak, T.A.; Kombrink, A.; Shinya, T.; Ryder, L.S.; Otomo, I.; Saitoh, H.; Terauchi, R.; Nishizawa, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; et al. Effector-Mediated Suppression of Chitin-Triggered Immunity by Magnaporthe oryzae Is Necessary for Rice Blast Disease. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cruz, A.; Amrine, K.C.H.; Blanco-Ulate, B.; Lawrence, D.P.; Travadon, R.; Rolshausen, P.E.; Baumgartner, K.; Cantu, D. Distinctive expansion of gene families associated with plant cell wall degradation, secondary metabolism, and nutrient uptake in the genomes of grapevine trunk pathogens. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, V.; Vélëz, H.; Tzelepis, G. The Role of Glycoside Hydrolases in Phytopathogenic Fungi and Oomycetes Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.C.; Taylor, W.A.; Wang, J.H.; Tipton, C.L. Role of calmodulin inhibition in the mode of action of ophiobolin a. Plant Physiol 1985, 77, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodolfo, C.; Rocco, M.; Cattaneo, L.; Tartaglia, M.; Sassi, M.; Aducci, P.; Scaloni, A.; Camoni, L.; Marra, M. Ophiobolin A Induces Autophagy and Activates the Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis in Human Melanoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Schoonbeek, H.-j.; De Waard Maarten, A. Bcmfs1, a Novel Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter from Botrytis cinerea, Provides Tolerance towards the Natural Toxic Compounds Camptothecin and Cercosporin and towards Fungicides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4996–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyne, L.; Van Poucke, C.; Di Mavungu, D.J.; Zainudin, N.A.I.M.; Vanhaecke, L.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Turgeon, B.G.; De Saeger, S.; Höfte, M. Comparative chemical screening and genetic analysis reveal tentoxin as a new virulence factor in Cochliobolus miyabeanus, the causal agent of brown spot disease on rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohparvar, R.; Mehrabi, R.; Van Nistelrooy, J.G.M.; Zwiers, L.-H.; De Waard, M.A. The drug transporter MgMfs1 can modulate sensitivity of field strains of the fungal wheat pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola to the strobilurin fungicide trifloxystrobin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Bui, D.C.; Lee, Y.; Nam, H.; Jung, S.; Fang, M.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, T.; Kim, H.; Choi, G.J.; et al. Functional characterization of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in the cereal head blight fungus Fusarium graminearum. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Kong, Z.Q.; Gui, Y.J.; Li, N.Y.; Bao, Y.M.; Dai, X.F. Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Situ, J.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, P.; Jiang, Z.; Kong, G. A Cytochrome B5-Like Heme/Steroid Binding Domain Protein, PlCB5L1, Regulates Mycelial Growth, Pathogenicity and Oxidative Stress Tolerance in Peronophythora litchii. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 783438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.; Jiaru, D.; Ruqing, F.; Wenqiang, Z.; Yifang, W.; Meixin, Y.; Chang, C. SsCyp86 modulates Sporisorium scitamineum mating/filamentation and pathogenicity through regulating fatty acid metabolism. Virulence 2024, 15, 2395833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
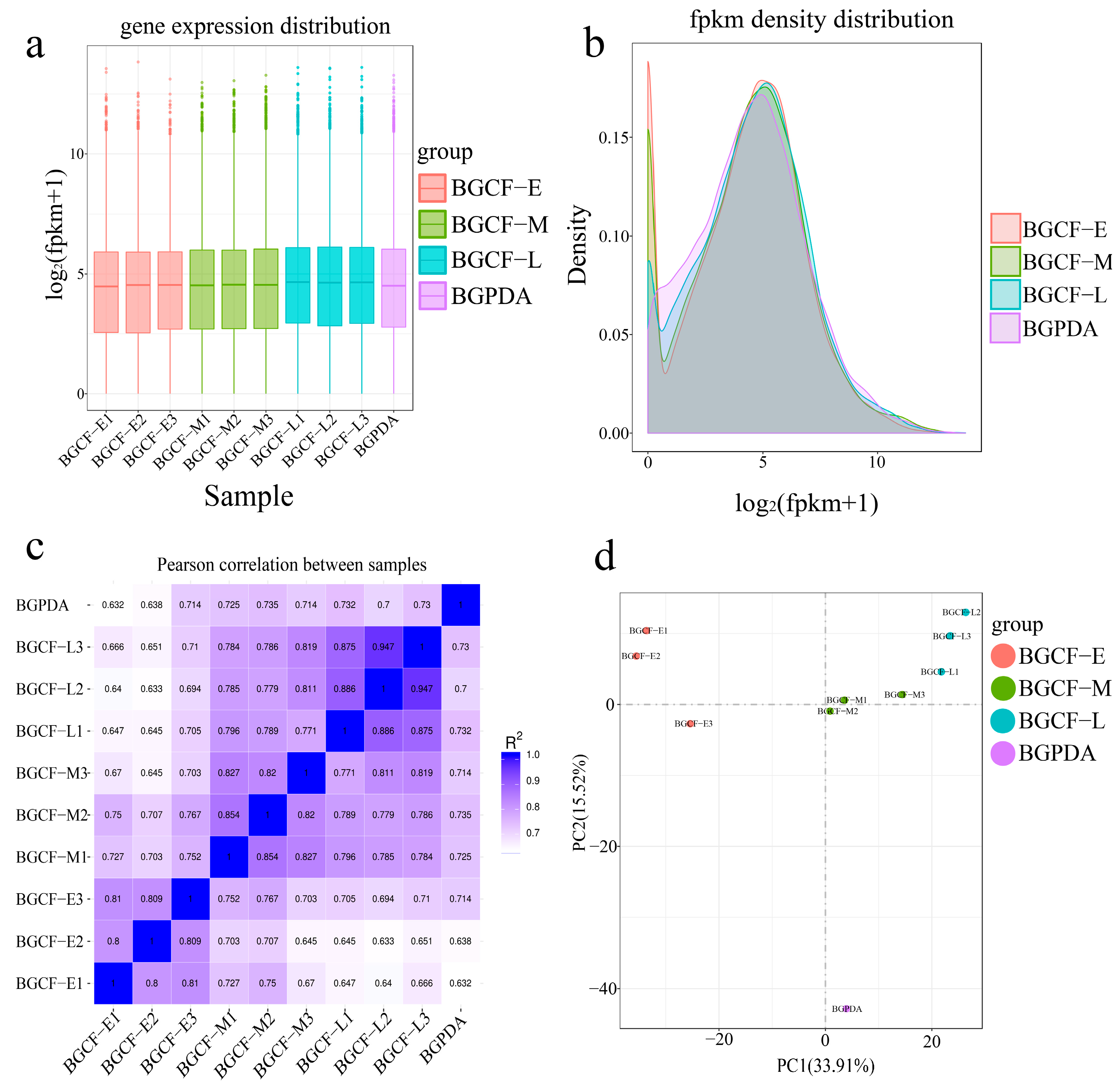
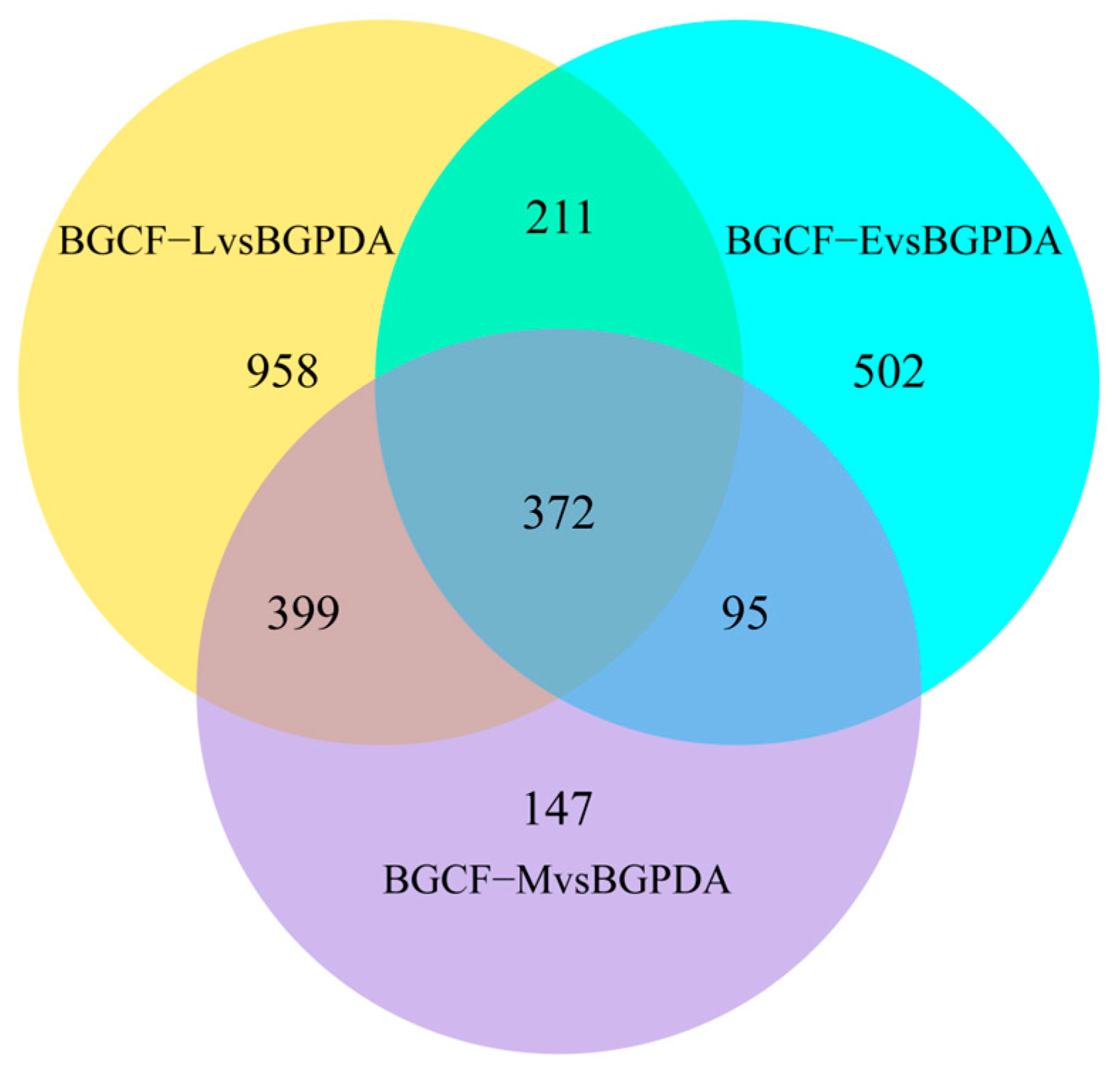
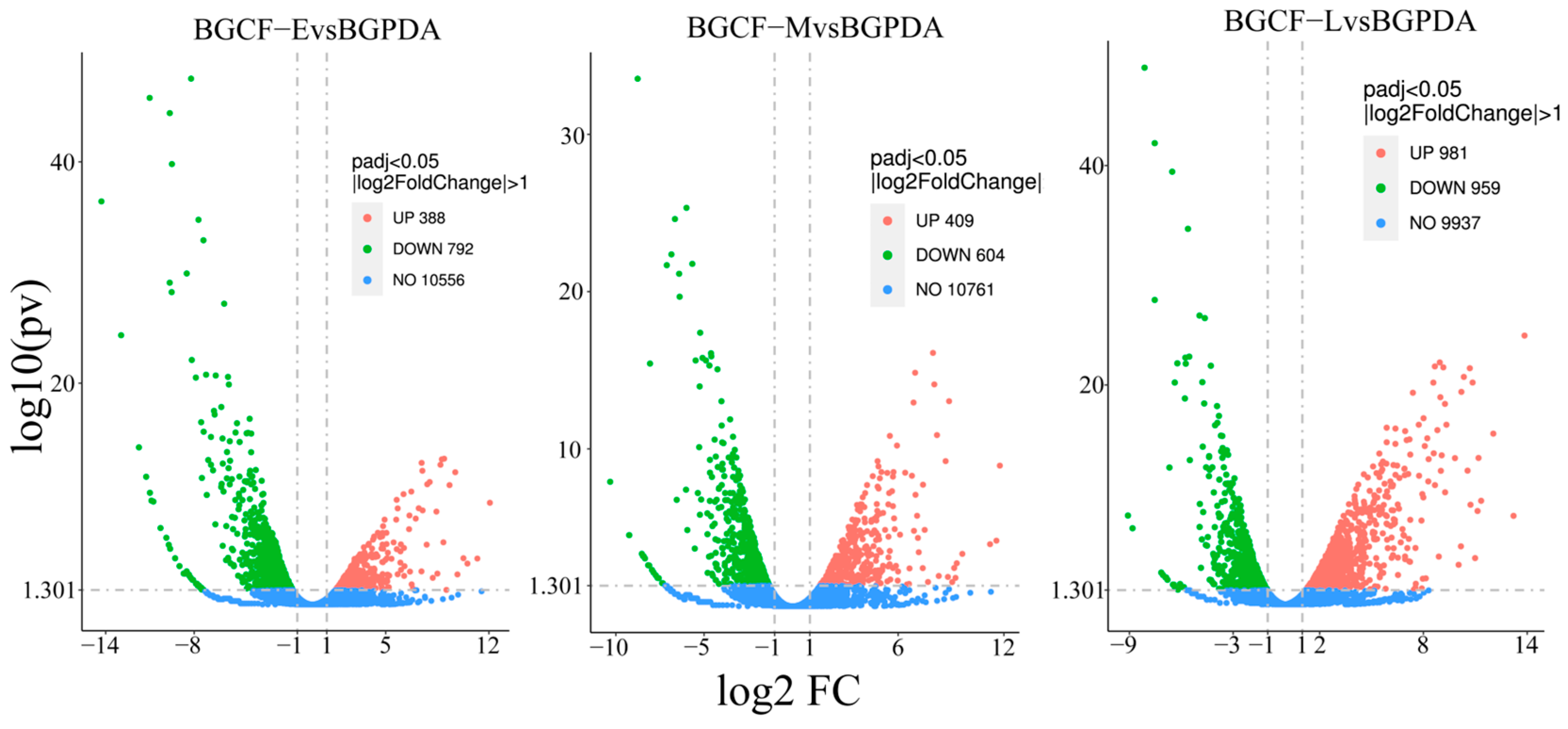
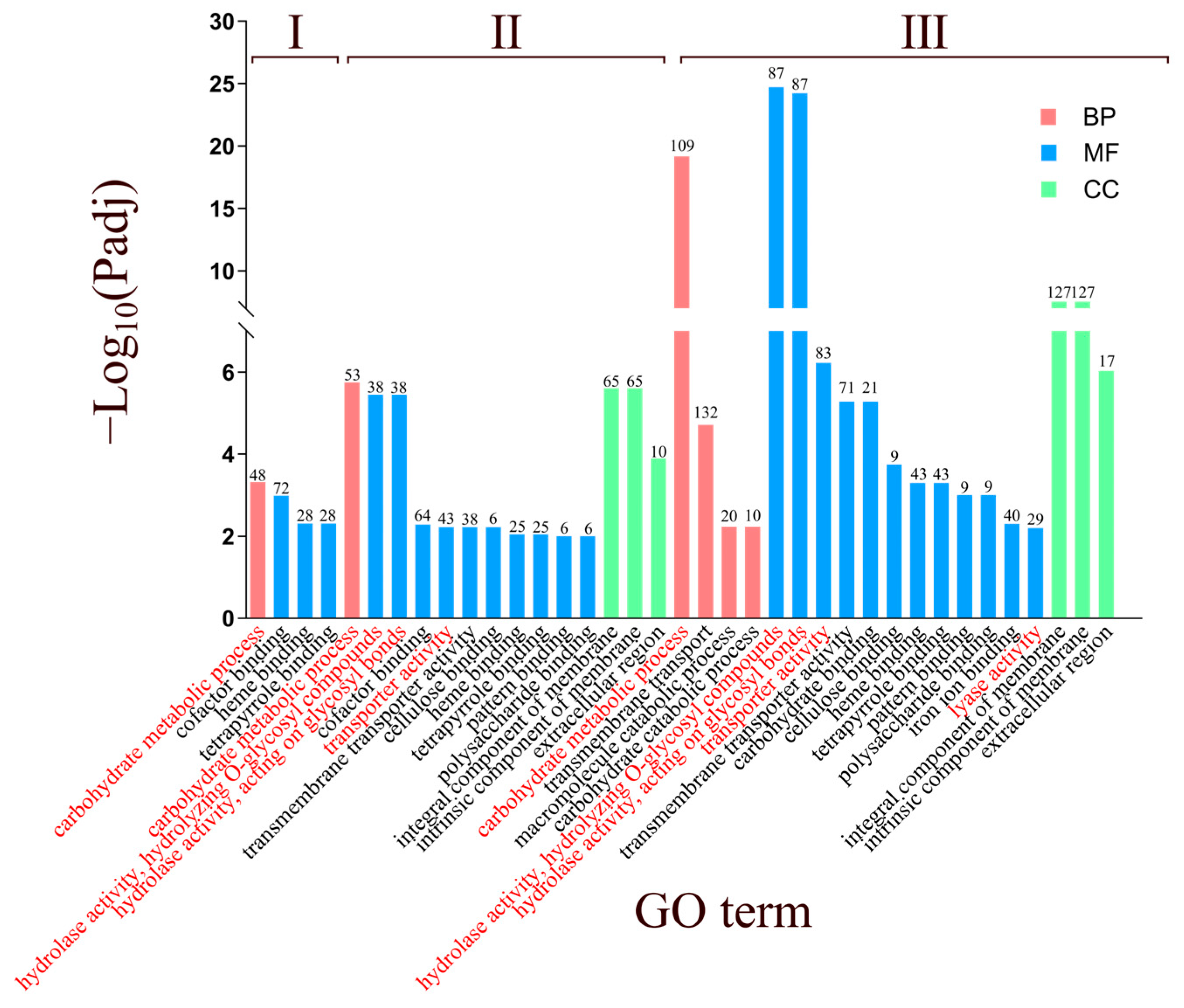

| Genes ID | Description | Primer Sequence 5′-3′ (F; R) |
|---|---|---|
| 19117903 | Cytochrome P450 | CCATCCTCCAATTCTCGCTCCT |
| GCAACTTCCTCGCCCTGTAGA | ||
| 19117919 | MFS-type transporter | TGGCTCCGTCATCCTCCTCT |
| GTTGTGGGCGTTGTGTGGTAG | ||
| 19116538 | Glycoside hydrolase family 3 protein | GGAGAAGATGCTGGCGAGAACC |
| CGCTTGATGGCTTCGAGAGGAG | ||
| 19119884 | LysM domain-containing protein | GTTGCCGACTCCATCACCATTG |
| GCCGCACAAGACGACGAATAC | ||
| 19124682 | Glycoside hydrolase-61 | CGGCACTGGCGACATCATCT |
| TAGGAAGCAGCGTAGGTGAGGA | ||
| 19119147 | ABC transporter | TCTGCGGCGGAATCATCACTT |
| TGCGAAGAAGACACCGTTGAGT | ||
| 19119514 | Ophiobolin F synthase | ACTACTGGTGCTCGGCTTGC |
| GCGAAGGCTCATCATCACTGGA | ||
| Reference gene | Actin | TATGGGCCAAAAGGACTCA |
| CACGCAGCTCGTTGTAGAAG |
| Sample | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | Unique Map | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC pct (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGPDA | BGPDA | 43773234 | 6.57 G | 38,260,232 (87.41%) | 97.67 | 93.65 | 53.36 |
| BGCF-E | E1 | 41553844 | 6.23 G | 19,533,51 (4.7%) | 97.84 | 93.54 | 44.64 |
| E2 | 42628686 | 6.39 G | 99,231,4 (2.33%) | 97.84 | 93.52 | 44.25 | |
| E3 | 40086040 | 6.01 G | 26,738,55 (6.67%) | 97.76 | 93.36 | 44.81 | |
| BGCF-M | M1 | 44515990 | 6.68 G | 36,054,76 (7.97%) | 97.76 | 93.36 | 45.01 |
| M2 | 42124290 | 6.32 G | 11,495,698 (27.58%) | 97.81 | 93.49 | 45.22 | |
| M3 | 43925140 | 6.59 G | 77,371,51 (18.71%) | 98.03 | 94.08 | 44.86 | |
| BGCF-L | L1 | 45264002 | 6.79 G | 24,171,85 (5.43%) | 97.79 | 93.47 | 45.65 |
| L2 | 41676764 | 6.25 G | 21,130,60 (5.02%) | 97.78 | 93.56 | 48.55 | |
| L3 | 41358898 | 6.2 G | 26,293,76 (5.99%) | 97.89 | 93.78 | 47.57 |
| Gene ID | Description | E-log2FC | M-log2FC | L-log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall Degrading Enzymes | ||||
| 19122268 | glycoside hydrolase family 18 protein | 7.50 | 6.99 | 5.92 |
| 19126100 | glycoside hydrolase family 62 protein | 4.82 | 5.53 | 8.60 |
| 19124354 | glycoside hydrolase family 10 protein | 3.08 | 5.39 | 6.24 |
| 19126327 | glycoside hydrolase family 18 protein | 4.78 | 5.15 | 5.32 |
| 19118171 | glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein | 2.77 | 4.84 | 3.25 |
| 19119168 | glycoside hydrolase family 10 protein | 3.14 | 4.56 | 3.13 |
| 19125825 | glycoside hydrolase family 71 protein | 4.44 | 4.48 | 1.88 |
| 19121668 | glycoside hydrolase family 18 protein | 5.99 | 4.17 | 5.07 |
| 19126538 | glycoside hydrolase family 3 protein | 2.39 | 4.12 | 4.35 |
| 19120137 | glycoside hydrolase family 15 protein | 2.51 | 1.88 | 2.95 |
| 19126692 | glycoside hydrolase family 31 protein | 2.26 | 1.85 | 1.83 |
| 19125121 | glycoside hydrolase family 20 protein | 2.25 | 1.80 | 2.24 |
| 19122960 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase D | 3.96 | 4.45 | 5.16 |
| 19124682 | Cellulase-61a | 3.11 | 5.94 | 5.11 |
| 19125385 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase D | 2.98 | 2.28 | 1.64 |
| 19122221 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase D | 2.84 | 4.49 | 8.98 |
| 19129443 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase D | 2.81 | 6.88 | 5.47 |
| 19127491 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase D | 2.39 | 3.60 | 1.49 |
| 19122124 | Cutinase transcription factor 1 beta | 2.73 | 3.19 | 3.60 |
| 19127443 | polysaccharide lyase family 1 protein | 2.15 | 2.92 | 1.63 |
| Gene ID | Description | E-log2FC | M-log2FC | L-log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes Related to Proteases | ||||
| 19124929 | Proteinase R | 3.56 | 2.72 | 2.16 |
| 19125779 | Putative aspergillopepsin A-like aspartic endopeptidase | 5.05 | 3.19 | 2.35 |
| Genes Related to Toxins Production | ||||
| 19119514 | Ophiobolin F | −1.51 | −2.93 | 1.90 |
| Genes Related to Detoxification of Toxic Compounds | ||||
| 19126575 | Probable sterigmatocystin biosynthesis P450 monooxygenase stcF | 6.84 | 7.12 | 13.85 |
| 19117903 | Probable sterigmatocystin biosynthesis P450 monooxygenase stcF | 4.18 | 6.78 | 10.34 |
| 19128488 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase paxP | 3.12 | 3.83 | 3.67 |
| 19128498 | Ent-kaurene oxidase | 2.59 | 2.79 | 2.79 |
| 19117888 | Dehydrogenase patE | 7.42 | 6.65 | 6.89 |
| 19122885 | Cellobiose dehydrogenase | 3.69 | 4.90 | 3.40 |
| 19124701 | Dehydrogenase patE | 3.61 | 2.71 | 1.90 |
| Genes Related to Transport of Toxic Compounds | ||||
| 19119582 | Glucose/galactose transporter | 4.10 | 4.32 | 2.61 |
| 19124715 | ABC transporter CDR4 | 3.47 | 4.20 | 6.60 |
| 19128823 | Probable glucose transporter rco-3 | 3.46 | 3.71 | 2.02 |
| 19117919 | MFS-type transporter C1271.10c | 2.53 | 2.40 | 3.54 |
| 19125740 | Inorganic phosphate transporter 1–2 | 2.51 | 3.52 | 2.40 |
| 19118321 | ABC transporter G family member 11 | 2.32 | 2.23 | 2.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, B.; Yang, P.; Luo, R.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shang, M.; Xu, W.; Huang, Z.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q. Transcriptome Analysis of the Pathogenic Mechanism of the Novel Pathogenic Fungus Bipolaris fujianensis in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Shoot Blight. Biology 2025, 14, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111488
Lin B, Yang P, Luo R, Lu Y, Li Z, Shang M, Xu W, Huang Z, Liang G, Zhang Q. Transcriptome Analysis of the Pathogenic Mechanism of the Novel Pathogenic Fungus Bipolaris fujianensis in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Shoot Blight. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111488
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Bin, Peiwen Yang, Ruifeng Luo, Ying Lu, Zhe Li, Menglan Shang, Wangdong Xu, Zihui Huang, Guanghong Liang, and Qinghua Zhang. 2025. "Transcriptome Analysis of the Pathogenic Mechanism of the Novel Pathogenic Fungus Bipolaris fujianensis in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Shoot Blight" Biology 14, no. 11: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111488
APA StyleLin, B., Yang, P., Luo, R., Lu, Y., Li, Z., Shang, M., Xu, W., Huang, Z., Liang, G., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Transcriptome Analysis of the Pathogenic Mechanism of the Novel Pathogenic Fungus Bipolaris fujianensis in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Shoot Blight. Biology, 14(11), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111488






