Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Rats by Influencing Intestinal Flora and Activating Nrf2 Pathway
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
2.2. Behavioral Measurement
2.3. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Markers and CORT
2.4. Histological and Ultrastructural Observations, and AB-PAS Staining
2.5. TUNEL Assays
2.6. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.7. The RT-PCR Analysis
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Molecular Docking
2.10. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of CGA on Alleviating Stress in Rats
3.2. The Effects of CGA on the Structure of the Intestinal Tract
3.3. The Effects of CGA in Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis
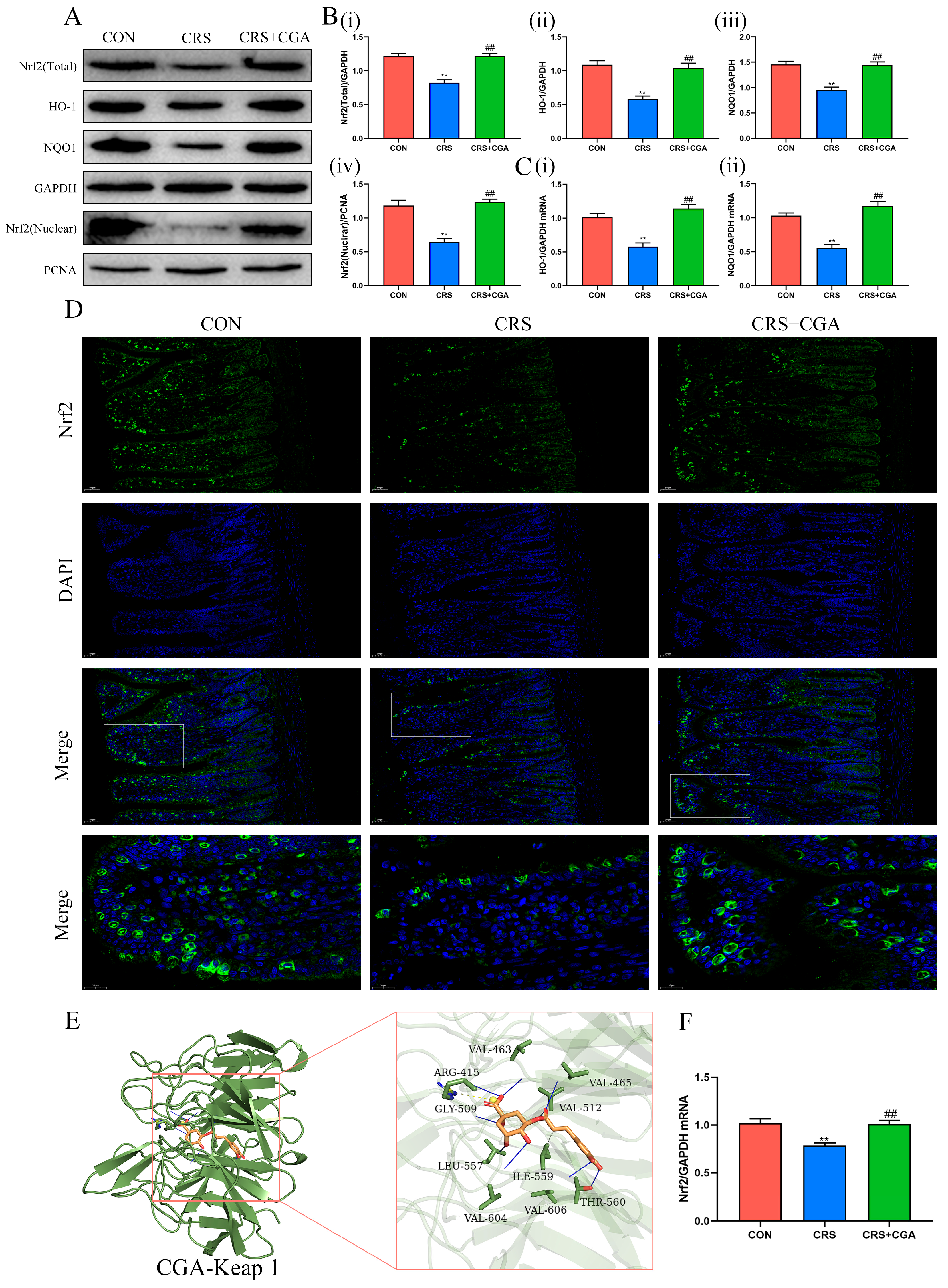
3.4. The Effects of CGA on the Nrf2 Pathway in the Ileum
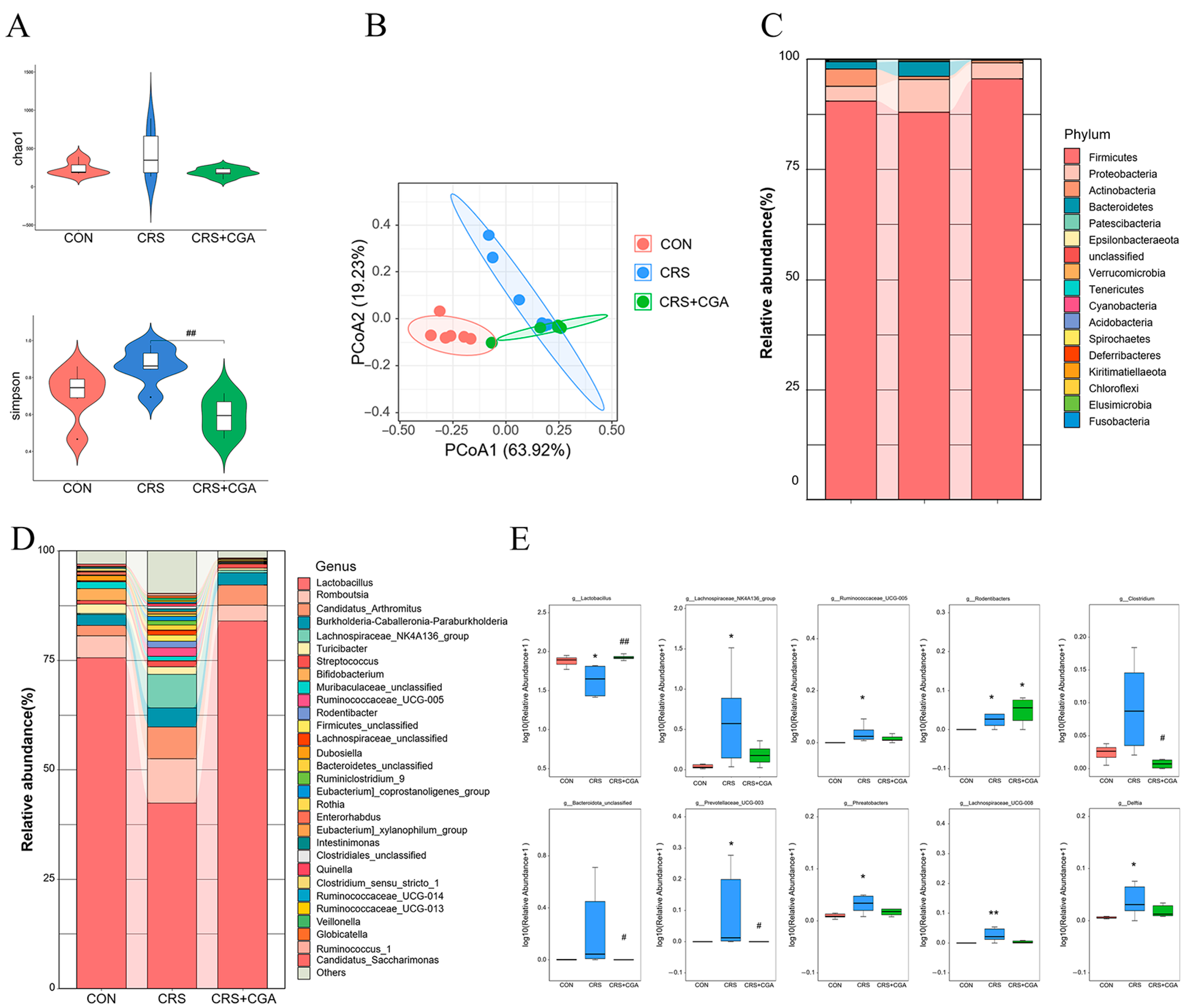
3.5. The Effect of CGA on the Bacterial Flora in the Rat Ileum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AB-PAS | Alcian Blue-Periodic Acid Schiff |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| Bax | BCL2-Associated X Protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| CGA | Chlorogenic Acid |
| CORT | Corticosterone |
| CRS | Chronic Restraint Stress |
| Cyt C | Cytochrome C |
| CCL4 | Carbon Tetrachloride |
| GC | Glucocorticoid |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IBS | Irritable Bowel Syndrome |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MPTP | Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 |
| OFT | Open Field Test |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinates Analysis |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RT-PCR | Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SEM | Standard Error of Mean |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TJ | Tight Junction |
| T-SOD | Total Superoxide Dismutase |
| WB | Western Blot |
| ZO-1 | Zonula Occludens-1 |
References
- Weimers, P.; Munkholm, P. The Natural History of IBD: Lessons Learned. Curr Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, J.; Munkholm, P. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovani, D.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Lytras, T.; Bonovas, S. Environmental Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, S. Chronic stress can inflame the gut—Now scientists know why. Nature 2023, 618, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.X.; Wang, C.C.; Chin, Y.X.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, S.H.; Xue, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Tang, Q.J. DHA-phospholipids (DHA-PL) and EPA-phospholipids (EPA-PL) prevent intestinal dysfunction induced by chronic stress. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.M.; Blank, N.; Alvarez, Y.; Thum, K.; Lundgren, P.; Litichevskiy, L.; Sleeman, M.; Bahnsen, K.; Kim, J.; Kardo, S.; et al. The enteric nervous system relays psychological stress to intestinal inflammation. Cell 2023, 186, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Saigo, N.; Nagasaki, Y. Direct evidence for the involvement of intestinal reactive oxygen species in the progress of depression via the gut-brain axis. Biomaterials 2023, 295, 122053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviello, G.; Knaus, U.G. ROS in gastrointestinal inflammation: Rescue Or Sabotage? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 174, 1704–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Guo, C.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, P.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Guo, X.N.; Cao, S.X.; Dong, Y.Y.; et al. Hypothalamus-habenula potentiation encodes chronic stress experience and drives depression onset. Neuron 2022, 110, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Yang, T.Y.; Zhao, S.P.; Sun, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Fan, H.G. Effect of Chlorogenic Acid via Upregulating Resolvin D1 Inhibiting the NF-ΚB Pathway on Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Liver Inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10532–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cong, W.; Zhang, K.; Jia, Y.; Wu, L. Chronic Heat Stress Affects Bile Acid Profile and Gut Microbiota in Broilers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singla, R.K.; Pandey, A.K. Chlorogenic Acid: A Dietary Phenolic Acid with Promising Pharmacotherapeutic Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 3905–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošović, J.; Marković, S.; Dimitrić Marković, J.M.; Mojović, M.; Milenković, D. Antioxidative mechanisms in chlorogenic acid. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Zhou, L.L.; Shu, X.G.; Sun, X.H.; Mi, S.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Yin, Y.L. Chlorogenic acid ameliorates endotoxin-induced liver injury by promoting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tian, L.; Lv, H.; Pang, Z.; Li, D.; Yao, Z.; Wang, S. Chlorogenic acid prevents acute myocardial infarction in rats by reducing inflammatory damage and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, W.; Zeng, T.; Wu, W.; Lu, L. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Chen, D.W.; Yu, B.; Luo, Y.H.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.B.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.Q.; Huang, Z.Q.; Yan, H.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Intestinal Mucosa Disruption in Weaned Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 806253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.H.; Zhong, Y.C.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Xie, J.; Peng, X.G.; Luo, J.; Xu, W. Chlorogenic Acid Ameliorates Post-Infectious Irritable Bowel Syndrome by Regulating Extracellular Vesicles of Gut Microbes. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Yu, B.; Chen, D.W.; Zheng, P.; Luo, Y.H.; Huang, Z.Q.; Luo, J.Q.; Mao, X.B.; Yu, J.; He, J. Changes of porcine gut microbiota in response to dietary chlorogenic acid supplementation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2019, 103, 8157–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.Y.; Song, M.Y.; Wang, C.R.; Yao, Y.J.; Fan, H.G. Glucocorticoid-Driven NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Hippocampal Microglia Mediates Chronic Stress-Induced Depressive-Like Behaviors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Yang, T.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.P.; Sun, N.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Fan, H.G. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Duodenal Ferroptosis via the Inhibition of the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4353–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Luo, L.; Zhu, Z.-D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, Z.-L.; Ma, Q.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Blocking the miR-21-Regulated TGF-β1/Smad7 Signaling Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandarkar, N.S.; Brown, L.; Panchal, S.K. Chlorogenic acid attenuates high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-induced cardiovascular, liver, and metabolic changes in rats. Nutr. Res. 2019, 62, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.G.; Fei, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, Z. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Colon Mucosal Damage Induced by a High-Fat Diet via Gut Microflora Adjustment to Increase Short-Chain Fatty Acid Accumulation in Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 3456542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Excessive Apoptosis in Ulcerative Colitis: Crosstalk Between Apoptosis, ROS, ER Stress, and Intestinal Homeostasis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, K.; Whitehead, L.W.; Heddleston, J.M.; Li, L.; Padman, B.S.; Oorschot, V.; Geoghegan, N.D.; Chappaz, S.; Davidson, S.; Chin, H.S.; et al. BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science 2018, 359, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; Xia, F.F.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.C.; Li, X.C.; Henzl, M.T.; Beamer, L.J.; Hannink, M. Structure of the Keap1: Nrf2 interface provides mechanistic insight into Nrf2 signaling. Embo J. 2006, 25, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousins, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP 1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaroque, C.; Chervy, M.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Social overcrowding impacts gut microbiota, promoting stress, inflammation, and dysglycemia. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 2000275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.D.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, S.; Cai, C.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, G.M.; Cao, G.Q.; Li, B.G.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of the Ileum Microbiota Composition in Piglets at Different Growth Stages. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 765691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, T.; Vobonl, M.; Schierová, D.; Valter, E.; Splichalová, I.; Dobe, J.; Brezina, J.; Dobesová, M.; Aidarova, A.; Jakubec, M.; et al. IL-17-driven induction of Paneth cell antimicrobial functions protects the host from microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in the ileum. Mucosal Immunol. 2023, 16, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Wu, H.; Cao, X.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; Fan, W.; Liu, B.; Song, S. Lactobacillus johnsonii 3-1 and Lactobacillus crispatus 7-4 promote the growth performance and ileum development and participate in lipid metabolism of broilers. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12535–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Baz, A.M.; Khodir, A.E.; El-Sokkary, M.M.A.; Shata, A. The protective effect of Lactobacillus versus 5-aminosalicylic acid in ulcerative colitis model by modulation of gut microbiota and Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | No. | Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Claudin3 | NM_031700.2 | Forward: GACAAAGACACCTCGCCCTT Reverse: TGCCCACTATGAGCCTTCTG |
| Occludin | NM_031329.2 | Forward: GATTGAGCCCGAGTGGAAAGG Reverse: CAGCATGAAGGACTTCCCAG |
| ZO-1 | NM_001106266.1 | Forward: CCACCTCGCACGTATCACAAGC Reverse: GCAATGACACTCCTTCGTCTCTG |
| NQO1 | XM-017595908.1 | Forward: CAGCGGCTCCATGTACT Reverse: GACCTGGAAGCCACAGAAG |
| HO-1 | NM-0125802 | Forward: ATCGTGCTCGCATGAAC Reverse: CAGCTCCTCAAACAGCTCAA |
| Nrf2 | NM_031789.3 | Forward: AAGTTGCCGCTCAGAACTGT Reverse: TTGCCATCTCTGGTCTGCTG |
| GAPDH | NM_017008.4 | Forward: AGTGCCAGCCTCGTCTCATA Reverse: GATGGTGATGGGTTTCCCGT |
| Chemical Composition | Target | Docking Position | Molecule Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGA | Keap 1 | VAL-463, VAL-465, VAL-512, VAL-604, VAL-606, ARG-415, GLY-509, LEU-557, ILE-559, THR-560 | −9.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Tan, H.; Cheng, X.; Yang, T.; Ding, X.; Ji, Y.; Yang, H.; Sha, J.; Feng, G.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Rats by Influencing Intestinal Flora and Activating Nrf2 Pathway. Biology 2025, 14, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111483
Jiao W, Tan H, Cheng X, Yang T, Ding X, Ji Y, Yang H, Sha J, Feng G, Zhao Y, et al. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Rats by Influencing Intestinal Flora and Activating Nrf2 Pathway. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111483
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Wenjing, Haoyang Tan, Xin Cheng, Tianyuan Yang, Xuanpan Ding, Yaxin Ji, Haotian Yang, Jichen Sha, Guofeng Feng, Yuan Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Rats by Influencing Intestinal Flora and Activating Nrf2 Pathway" Biology 14, no. 11: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111483
APA StyleJiao, W., Tan, H., Cheng, X., Yang, T., Ding, X., Ji, Y., Yang, H., Sha, J., Feng, G., Zhao, Y., & Fan, H. (2025). Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Ileal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Rats by Influencing Intestinal Flora and Activating Nrf2 Pathway. Biology, 14(11), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111483







