The Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Fish Pathogen Mycobacterium marinum Trigger a Core Set of Late Innate Immune Response Genes in Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture
2.2. Zebrafish Experiments Ethics Statement
2.3. Zebrafish Embryo Injections and Larvae Culturing
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. CFU Counting
2.6. RNA Isolation, MBL Assay and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Illumina RNAseq Analysis
2.9. Illumina Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term Survival of M. tuberculosis in Zebrafish Larvae
3.2. Transcriptional Profiling of Zebrafish Larvae Infected with M. tuberculosis
3.3. Effect of Increased Temperature on Transcriptome Profile of Zebrafish Larvae
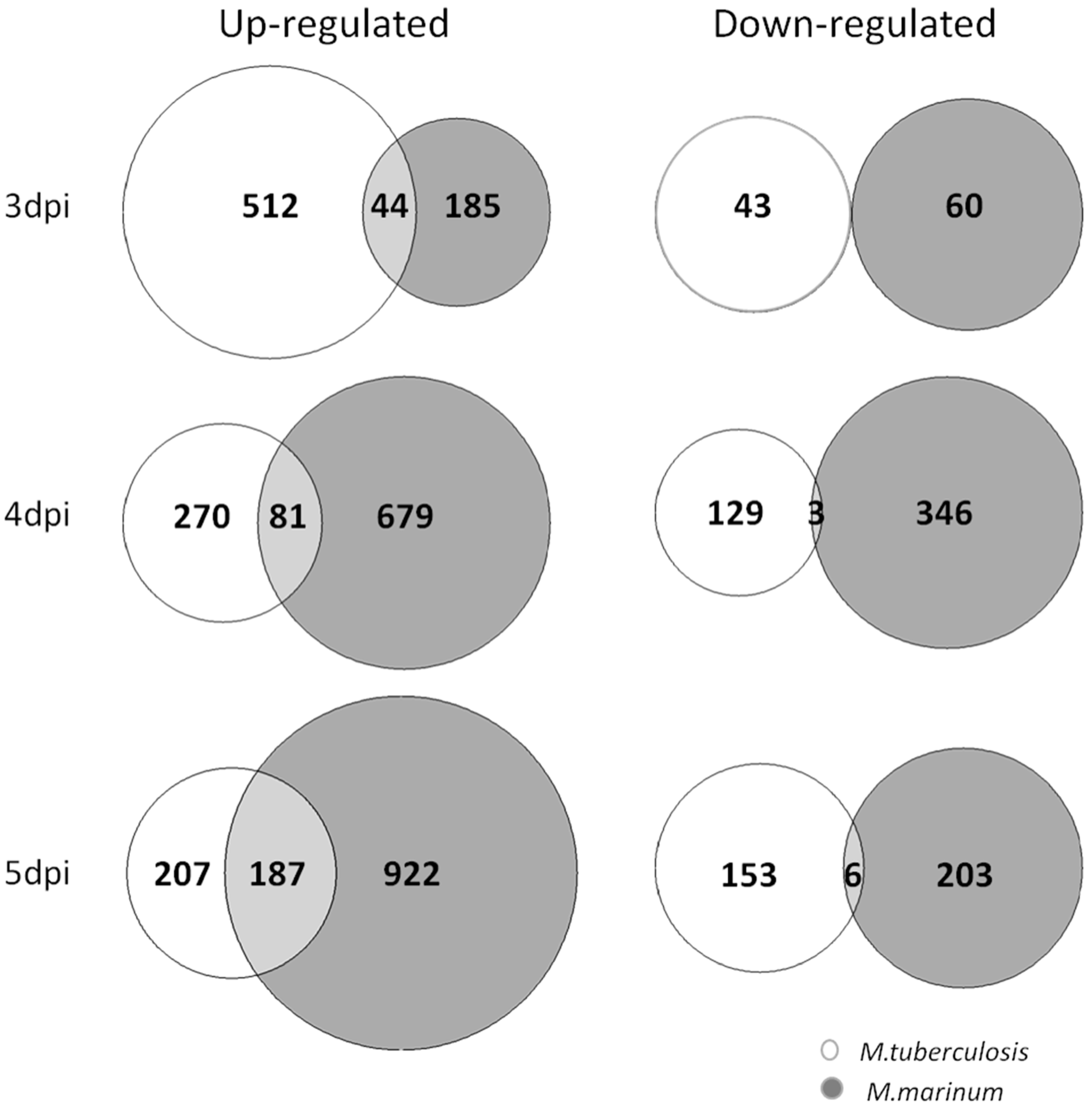
3.4. Comparison of Host Transcriptional Response between Zebrafish Larvae Infected with M. tuberculosis and Larvae Infected with M. marinum
3.5. Comparison of Transcriptome Data of Zebrafish Mtb Infection with Human Macrophage Mtb Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, P. Challenges & Solutions for Recent Advancements in Multi-Drugs Resistance Tuberculosis: A Review. Microbiol. Insights 2023, 16, 11786361231152438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, L.E.; Abendaño, N.; Juste, R.A.; Alonso-Hearn, M. Three-dimensional in vitro models of granuloma to study bacteria-host interactions, drug-susceptibility, and resuscitation of dormant Mycobacteria. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 623856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.L. Lessons from experimental Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, D.M.; Ramakrishnan, L. Comparative pathogenesis of Mycobacterium marinum and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.L.; Gideon, H.P.; Mattila, J.T.; Lin, P.L. Immunology studies in non-human primate models of tuberculosis. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, W.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Thacker, T.C.; Davis, W.C.; Sreevatsan, S.; Coussens, P.; Meade, K.G.; Hope, J.C.; Estes, D.M. Tuberculosis immunity: Opportunities from studies with cattle. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 768542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rhijn, I.; Godfroid, J.; Michel, A.; Rutten, V. Bovine tuberculosis as a model for human tuberculosis: Advantages over small animal models. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesciaroli, M.; Alvarez, J.; Boniotti, M.B.; Cagiola, M.; Di Marco, V.; Marianelli, C.; Pacciarini, M.; Pasquali, P. Tuberculosis in domestic animal species. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, S78–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, R. Experimental Models Used to Study Human Tuberculosis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, U.D.; Katoch, V.M. Animal models of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2005, 85, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerz, T.; Hall, C.J. The diverse roles of phagocytes during bacterial and fungal infections and sterile inflammation: Lessons from Zebrafish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.H.; Grange, J.M.; Noble, W.C.; Yates, M.D. Mycobacterium marinum infections in man. J. Hyg. 1985, 94, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonamonte, D. Aquarium-borne Mycobacterium marinum skin infection. Report of 15 cases and review of the literature. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, E.L.; Watt, C.J.; Walker, N.; Maher, D.; Williams, B.G.; Raviglione, M.C.; Dye, C. The growing burden of tuberculosis: Global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, L. The zebrafish guide to tuberculosis immunity and treatment. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2013, 78, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghan, E.; Schnurr, Y.Y.; Scott, G.R. Temperature during embryonic development has persistent effects on metabolic enzymes in the muscle of zebrafish. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The behaviour and ecology of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Olmeda, J.F.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Thermal biology of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Therm. Biol. 2011, 36, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; de Sonneville, J.; Stockhammer, O.W.; Savage, N.D.; Veneman, W.J.; Ottenhoff, T.H.; Dirks, R.P.; Meijer, A.H.; Spaink, H.P. A high-throughput screen for tuberculosis progression. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e16779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaink, H.P.; Cui, C.; Wiweger, M.I.; Jansen, H.J.; Veneman, W.J.; Marín-Juez, R.; de Sonneville, J.; Ordas, A.; Torraca, V.; Van der Ent, W.; et al. Robotic injection of zebrafish embryos for high-throughput screening in disease models. Methods 2013, 62, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.R.; Schnurr, M.E.; Yin, Y.; Johnston, I.A. Embryonic temperature produces persistent effects on the capacity for thermal acclimation in adult zebrafish. FASEB J. 2014, 26, 1072.5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneman, W.J.; De Sonneville, J.; Van der Kolk, K.J.; Ordas, A.; Al-Ars, Z.; Meijer, A.H.; Spaink, H.P. Analysis of RNAseq datasets from a comparative infectious disease zebrafish model using GeneTiles bioinformatics. Immunogenetics 2015, 67, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Ghanwat, S.; Matta, S.K.; Yadav, S.S.; Mehta, M.; Siddiqui, Z.; Singh, A.; Kumar, D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibits RAB7 recruitment to selectively modulate autophagy flux in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, H.; Koidis, A.; Stewart, L.D.; Grant, I.R. Optimization of the composition of a solid culture medium for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis using factorial design and response surface methodology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4252–4265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clay, H.; Davis, J.M.; Beery, D.; Huttenlocher, A.; Lyons, S.E.; Ramakrishnan, L. Dichotomous role of the macrophage in early Mycobacterium marinum infection of the zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeyborne, I.; McHugh, T.D.; Phillips, P.P.; Bannoo, S.; Bateson, A.; Carroll, N.; Perrin, F.M.; Ronacher, K.; Wright, L.; van Helden, P.D.; et al. Molecular bacterial load assay, a culture-free biomarker for rapid and accurate quantification of sputum Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillary load during treatment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Amilburu, V.; Jong-Raadsen, S.; Bakkers, J.; Spaink, H.P.; Marín-Juez, R. GLUT12 deficiency during early development results in heart failure and a diabetic phenotype in zebrafish. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 224, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.-Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, E.L.; Rougeot, J.; Racz, P.I.; Spaink, H.P.; Meijer, A.H. Transcriptomic approaches in the zebrafish model for tuberculosis-insights into host- and pathogen-specific determinants of the innate immune response. Adv. Genet. 2016, 95, 217–251. [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling, F.; Kostidis, S.; Spaink, H.P.; Haks, M.C.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; Joosten, S.A. Analyzing the impact of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection on primary human macrophages by combined exploratory and targeted metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhan, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, G.; Ge, Z. Mmu-miR-25-3p promotes macrophage autophagy by targeting DUSP10 to reduce mycobacteria survival. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1120570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, T.E.; Wiesmüller, K.H.; Lucas, M.; Dobos, K.M.; Baxter, A.G.; Blumenthal, A. The N-terminal peptide moiety of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19 kDa lipoprotein harbors RP105-agonistic properties. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2018, 103, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.H.; Micaroni, M.; Puyskens, A.; Schultz, T.E.; Yeo, J.C.; Stanley, A.C.; Lucas, M.; Kurihara, J.; Dobos, K.M.; Stow, J.L.; et al. RP105 engages phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p110δ to facilitate the trafficking and secretion of cytokines in macrophages during mycobacterial infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3890–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.; Lee, J.; Ren, F.; Chen, M.; Kornfeld, H.; Remold, H.G. Mycobacterium tuberculosis blocks crosslinking of annexin-1 and apoptotic envelope formation on infected macrophages to maintain virulence. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J. Zebrafish—An emerging genetic model for the study of cytokines and hematopoiesis in the era of functional genomics. Int. J. Hematol. 2001, 73, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasanov, E.V.; Jędrychowska, J.; Kuźnicki, J.; Korzh, V. Evolutionary context can clarify gene names: Teleosts as a case study. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 43, 2000258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) or M. tuberculosis-DsRed (
) or M. tuberculosis-DsRed ( )H37Rv strains and raised at 34 °C along with control groups of PVP-injected (
)H37Rv strains and raised at 34 °C along with control groups of PVP-injected ( ) and uninjected (
) and uninjected ( ) embryos. The last viable larvae were collected at 9 dpf. Percent survival for each group is shown on the survival curve. The number of injected embryos was 1000, 1200, 2000 and 400 for the M. tuberculosis wild-type strain, M. tuberculosis-H37Rv DsRed strain, PVP-injected and uninjected embryos, respectively. Raw data is presented in Table S4.
) embryos. The last viable larvae were collected at 9 dpf. Percent survival for each group is shown on the survival curve. The number of injected embryos was 1000, 1200, 2000 and 400 for the M. tuberculosis wild-type strain, M. tuberculosis-H37Rv DsRed strain, PVP-injected and uninjected embryos, respectively. Raw data is presented in Table S4.
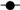 ) or M. tuberculosis-DsRed (
) or M. tuberculosis-DsRed ( )H37Rv strains and raised at 34 °C along with control groups of PVP-injected (
)H37Rv strains and raised at 34 °C along with control groups of PVP-injected ( ) and uninjected (
) and uninjected (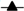 ) embryos. The last viable larvae were collected at 9 dpf. Percent survival for each group is shown on the survival curve. The number of injected embryos was 1000, 1200, 2000 and 400 for the M. tuberculosis wild-type strain, M. tuberculosis-H37Rv DsRed strain, PVP-injected and uninjected embryos, respectively. Raw data is presented in Table S4.
) embryos. The last viable larvae were collected at 9 dpf. Percent survival for each group is shown on the survival curve. The number of injected embryos was 1000, 1200, 2000 and 400 for the M. tuberculosis wild-type strain, M. tuberculosis-H37Rv DsRed strain, PVP-injected and uninjected embryos, respectively. Raw data is presented in Table S4.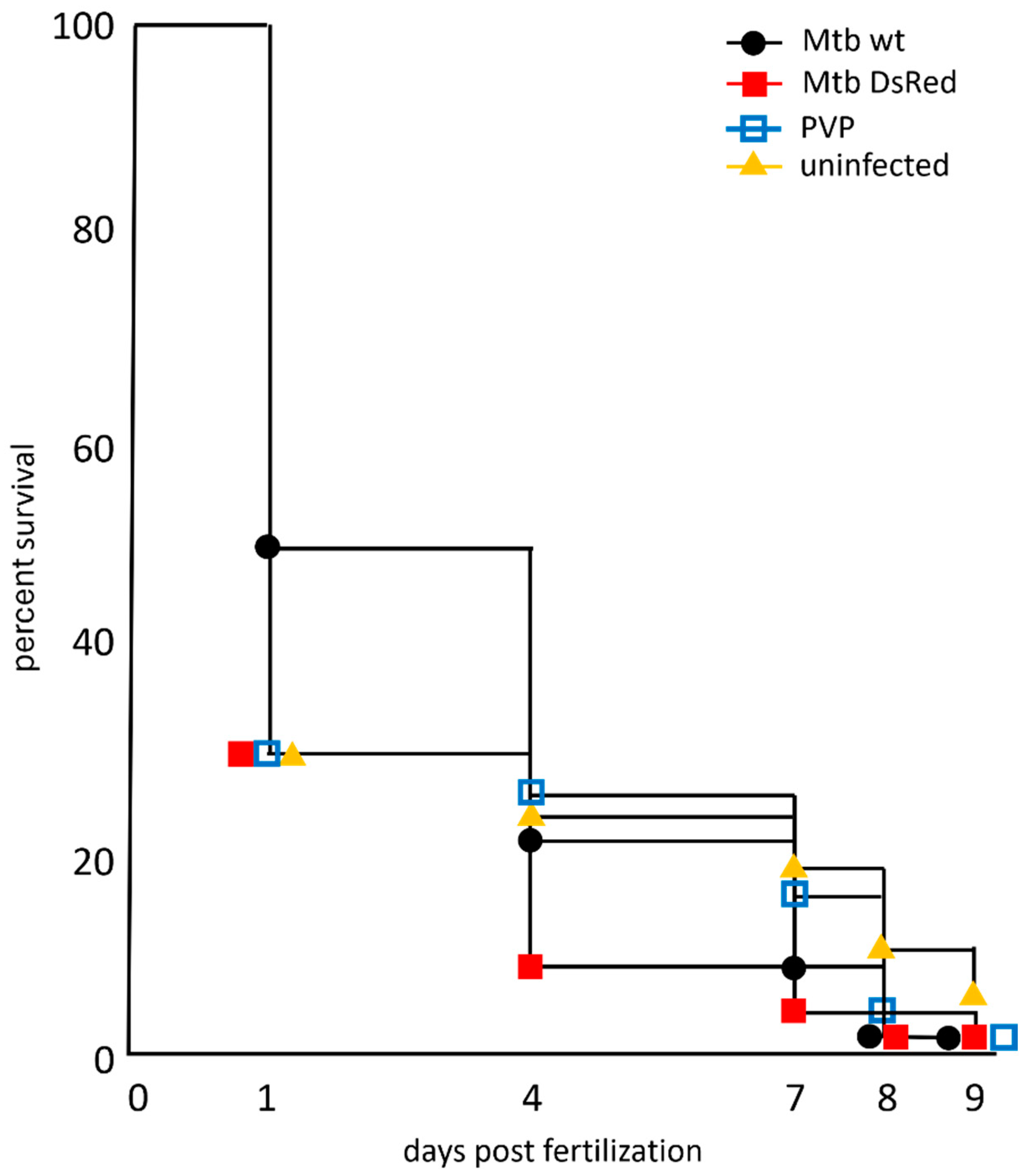
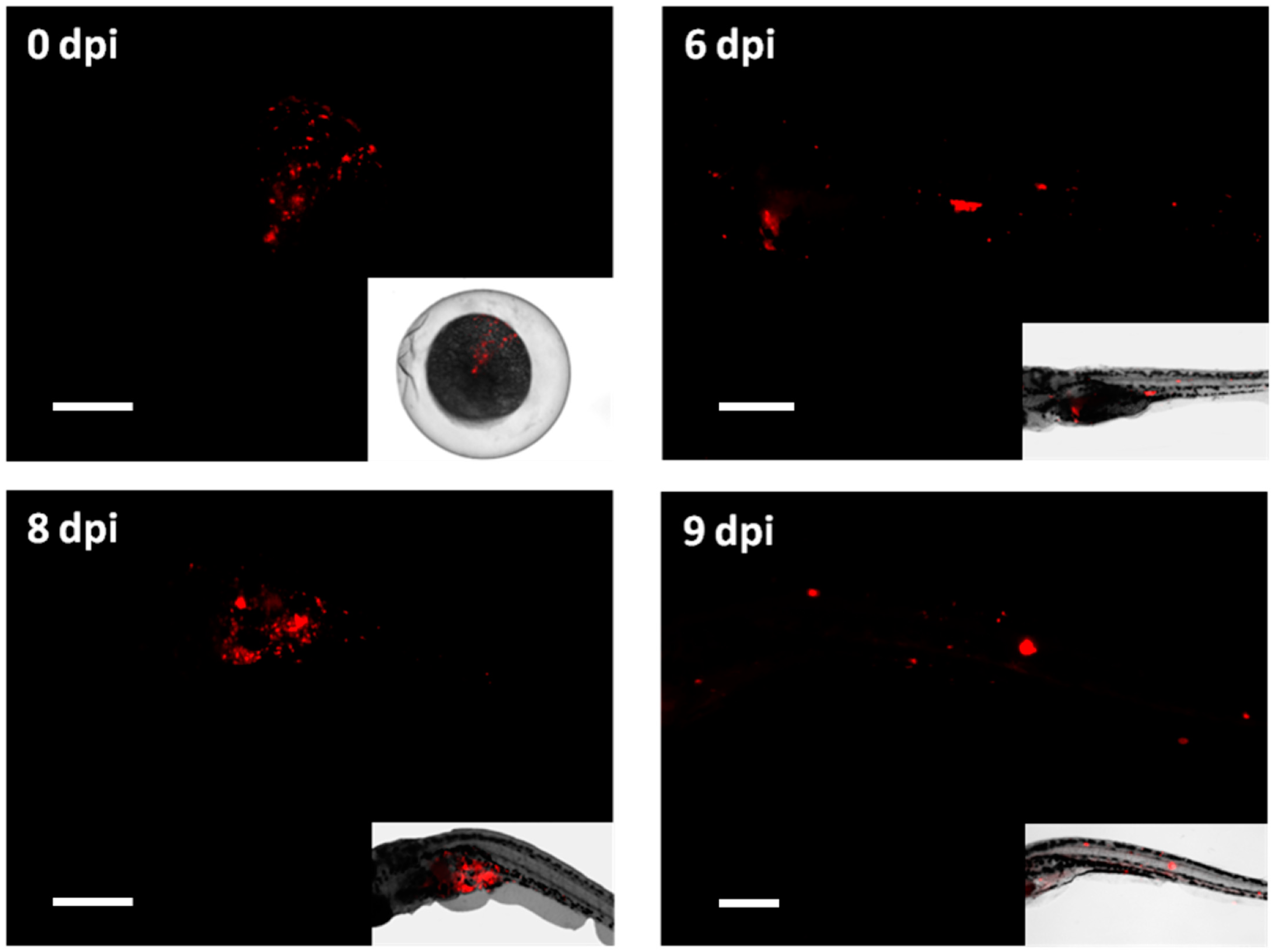


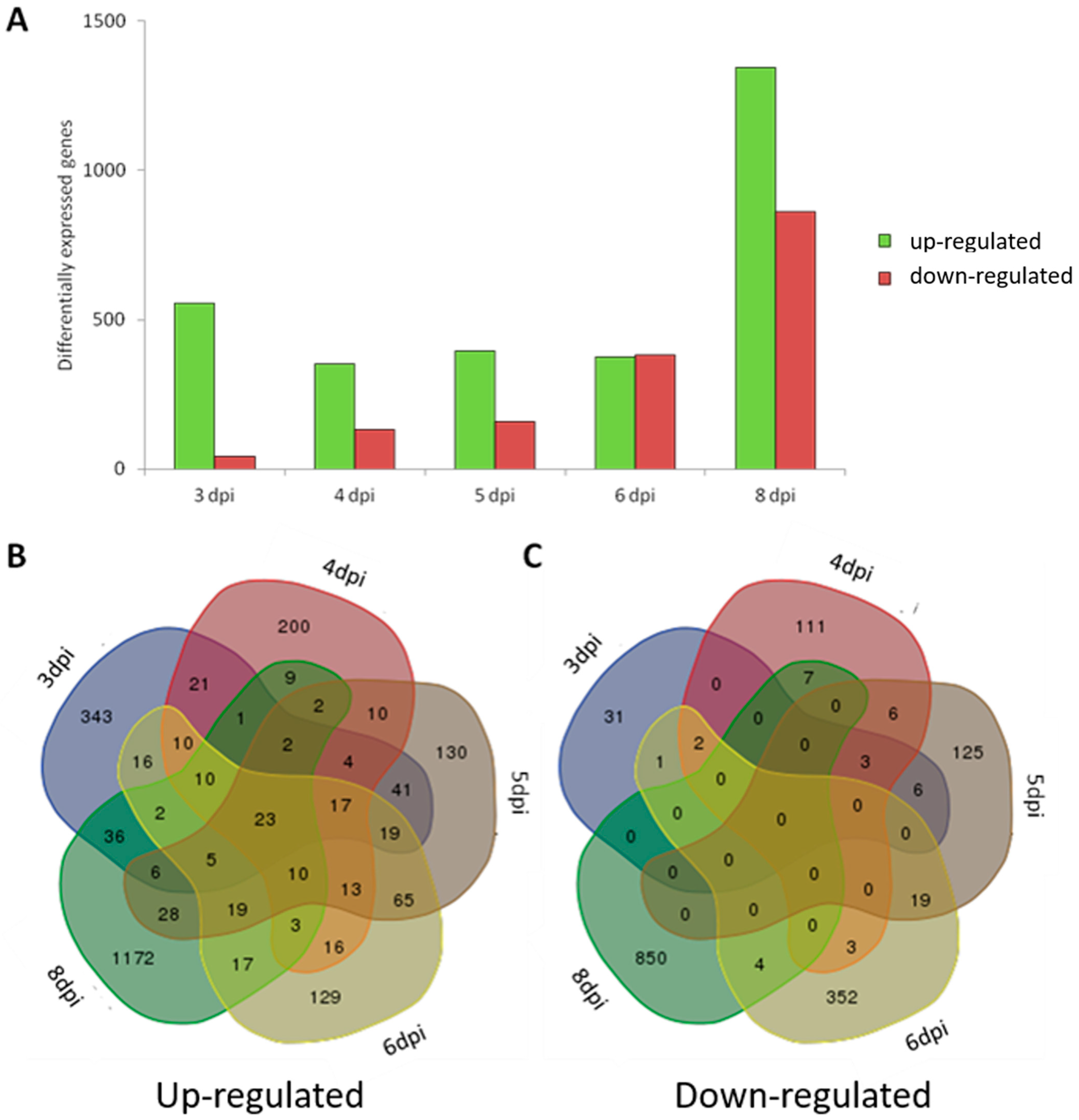
| Mycobacterium Species | M. tuberculosis | M. marinum |
|---|---|---|
| natural hosts | humans, cattle | fish, amphibians, zoonosis |
| infection route | lung | skin |
| optimum temperature | 38 °C | 32 °C |
| minimum doubling time | 18 h | 4 h |
| biosafety level | 3 | 2 |
| genome size | 4.41 Mb | 6.64 Mb |
| gene number | 4008 | 5503 |
| Gene Code | Gene Name | Gene Description | Mm 3 dpi | Mm 4 dpi | Mm 5 dpi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSDARG00000101479 | BX908782.3 | three-finger protein 5 (LOC100003647) | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000093712 | CABZ01021530.1 | Interferon-inducible protein Gig1-like (teleost-specific) | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000086654 | cbln11 | cerebellin 11 | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000026417 | ccr12b.2 | chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 12b2 | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000051912 | hpx | hemopexin | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000069844 | irg1 | immunoresponsive 1 homolog (aconitate decarboxylase) | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000003523 | itln3 | intelectin 3 (bacterial arabinogalactan receptor) | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000090889 | lect2 | leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000012395 | mmp13a | matrix metallopeptidase 13a | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000042816 | mmp9 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000045999 | saa | serum amyloid A | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000086337 | si:dkey-102g19.3 | urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor-like | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000095798 | si:dkey-119g10.3 | non-protein coding | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000090352 | si:dkey-97i18.5 | non-protein coding | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000007769 | sult5a1 | sulfotransferase family 5A, member 1 | √ | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000045561 | dram1 | DNA-damage regulated autophagy modulator 1 | - | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000026049 | mxf | myxovirus (influenza virus) resistance F | - | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000095909 | si:ch211-253b18.3 | non-protein coding | - | √ | √ |
| ENSDARG00000086947 | si:ch211-147m6.1 | olfactomedin-4-like | √ | - | - |
| ENSDARG00000104399 | CABZ01064972.2 | Uncharacterized protein | - | - | √ |
| ENSDARG00000033587 | CABZ01088134.1 | trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial-like | - | - | √ |
| ENSDARG00000089362 | grn1 | granulin 1 | - | - | √ |
| ENSDARG00000069944 | p2ry13 | purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 13 | - | - | - |
| Gene Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Up-Regulated | ||
| ENSDARG00000067672 | card9 | caspase recruitment domain family, member 9 |
| ENSDARG00000090873 | ccl34a.4 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 34a, duplicate 4 |
| ENSDARG00000026417 | ccr12b.2 | chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 12b, tandem duplicate 2 |
| ENSDARG00000055278 | cfb | complement factor B |
| ENSDARG00000051912 | hpx (1 of many) | hemopexin |
| ENSDARG00000053131 | irak3 | interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 |
| ENSDARG00000069844 | irg1 | immunoresponsive 1 homolog (mouse) |
| ENSDARG00000003523 | itln3 | intelectin 3 |
| ENSDARG00000090889 | lect2 (1 of many) | leukocyte cell derived chemotaxin 2 |
| ENSDARG00000012395 | mmp13a | matrix metallopeptidase 13a |
| ENSDARG00000042816 | mmp9 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 |
| ENSDARG00000033735 | ncf1 | neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 |
| ENSDARG00000045999 | saa | serum amyloid A |
| ENSDARG00000053836 | si:ch211-284o19.8 | si:ch211-284o19.8 |
| ENSDARG00000086337 | si:dkey-102g19.3 | si:dkey-102g19.3 |
| ENSDARG00000095798 | si:dkey-119g10.3 | si:dkey-119g10.3 |
| ENSDARG00000097909 | si:dkey-195m11.11 | si:dkey-195m11.11 |
| ENSDARG00000090352 | si:dkey-97i18.5 | si:dkey-97i18.5 |
| ENSDARG00000055252 | snap23.2 | synaptosomal-associated protein 23.2 |
| ENSDARG00000007769 | sult5a1 | sulfotransferase family 5A, member 1 |
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish (Mtb3,4,5,6,8-2379 Genes) | Human Macrophages (MF1 and 2) | Ensembl Gene ID | Gene Name | Description | |
| 4 hr (11 Genes) | 24 hr (161 Genes) | ||||
| x (Mtb3) | x | ENSDARG00000002917 | gls2b | glutaminase 2b (liver, mitochondrial) | |
| x (Mtb3) | x | ENSDARG00000093750 | cd180 | CD180 molecule | |
| x (Mtb5) | x | ENSDARG00000036106 | rgs18 | regulator of G-protein signaling 18 | |
| x (Mtb5) | x | ENSDARG00000101050 | tmc8 | transmembrane channel-like 8 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000009978 | icn | ictacalcin | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000013335 | anxa6 | annexin A6 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000087554 | cdk1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000098946 | pald1a | phosphatase domain containing, paladin 1a | |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||||
| Zebrafish (Mtb3,4,5,6,8-1520 Genes) | Human Macrophages (MF1 and 2) | Ensembl Gene ID | Gene Name | Description | |
| 4 hr (149 Genes) | 24 hr (438 Genes) | ||||
| x (Mtb6) | x | ENSDARG00000062947 | amn | amnion associated transmembrane protein | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000030722 | xirp1 | xin actin binding repeat containing 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000037196 | arid5B | AT-rich interaction domain 5B | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000056929 | kdm6bb | lysine (K)-specific demethylase 6B, b | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000070538 | hey1 | hes-related family bHLH transcription factor with YRPW motif 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000105261 | nfkb1 | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 | |
| x (Mtb5) | x | ENSDARG00000102729 | samd9 | sterile alpha motif domain containing 9 | |
| x (Mtb5) | x | ENSDARG00000016733 | psat1 | phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000005526 | igfn1.1 | immunoglobulin-like and fibronectin type III domain containing 1, tandem duplicate 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000011257 | enpp2 | ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000018773 | hivep2 (1 of many) | human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000020581 | otofb | otoferlin b | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000040523 | smpd2a | sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 2a, neutral membrane (neutral sphingomyelinase) | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000042055 * | fam129aa | family with sequence similarity 129, member Aa | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000045802 | hapln3 | hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 3 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000057317 | nexn | nexilin (F actin binding protein) | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000059090 | sstr2 (1 of many) | somatostatin receptor 2 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000061070 | chst3a | carbohydrate (chondroitin 6) sulfotransferase 3a | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000063475 | abcg1 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000075263 | ankrd1a | ankyrin repeat domain 1a (cardiac muscle) | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000088137 | adrg2 (1 of many) | adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G2 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000088937 | adrg2 (1 of many) | adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G2 | |
| x (Mtb8) | x | ENSDARG00000100518 | Uncharacterized | ||
| x (Mtb8) | x | x | ENSDARG00000007080 * | rhcgl1 | Rh family, C glycoprotein, like 1 |
| x (Mtb8) | x | x | ENSDARG00000013168 | jag1b | jagged 1b |
| x (Mtb8) | x | x | ENSDARG00000039232 | dusp8 (1 of many) | dual specificity phosphatase 8 |
| x (Mtb8) | x | x | ENSDARG00000089871 | si:ch211-203c7.2 | si:ch211-203c7.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dirks, R.P.; Ordas, A.; Jong-Raadsen, S.; Brittijn, S.A.; Haks, M.C.; Henkel, C.V.; Oravcova, K.; Racz, P.I.; Tuinhof-Koelma, N.; Korzeniowska nee Wiweger, M.I.; et al. The Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Fish Pathogen Mycobacterium marinum Trigger a Core Set of Late Innate Immune Response Genes in Zebrafish Larvae. Biology 2024, 13, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090688
Dirks RP, Ordas A, Jong-Raadsen S, Brittijn SA, Haks MC, Henkel CV, Oravcova K, Racz PI, Tuinhof-Koelma N, Korzeniowska nee Wiweger MI, et al. The Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Fish Pathogen Mycobacterium marinum Trigger a Core Set of Late Innate Immune Response Genes in Zebrafish Larvae. Biology. 2024; 13(9):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090688
Chicago/Turabian StyleDirks, Ron P., Anita Ordas, Susanne Jong-Raadsen, Sebastiaan A. Brittijn, Mariëlle C. Haks, Christiaan V. Henkel, Katarina Oravcova, Peter I. Racz, Nynke Tuinhof-Koelma, Malgorzata I. Korzeniowska nee Wiweger, and et al. 2024. "The Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Fish Pathogen Mycobacterium marinum Trigger a Core Set of Late Innate Immune Response Genes in Zebrafish Larvae" Biology 13, no. 9: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090688
APA StyleDirks, R. P., Ordas, A., Jong-Raadsen, S., Brittijn, S. A., Haks, M. C., Henkel, C. V., Oravcova, K., Racz, P. I., Tuinhof-Koelma, N., Korzeniowska nee Wiweger, M. I., Gillespie, S. H., Meijer, A. H., Ottenhoff, T. H. M., Jansen, H. J., & Spaink, H. P. (2024). The Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Fish Pathogen Mycobacterium marinum Trigger a Core Set of Late Innate Immune Response Genes in Zebrafish Larvae. Biology, 13(9), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090688









