Role of Cholecystokinin (cck) in Feeding Regulation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): Peptide Activation and Antagonist Inhibition
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish
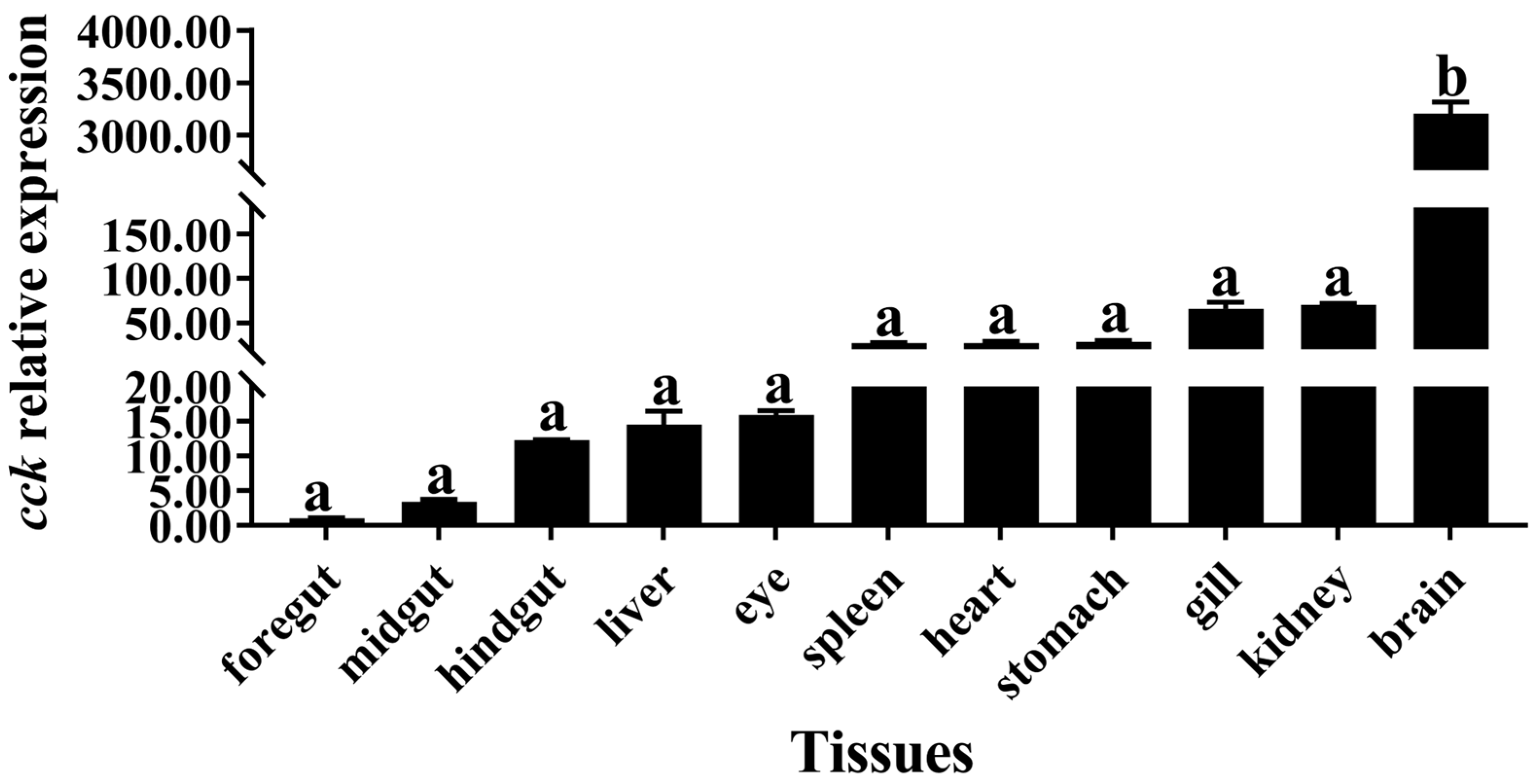
2.2. Expression Levels of the cck Gene in Different Tissues
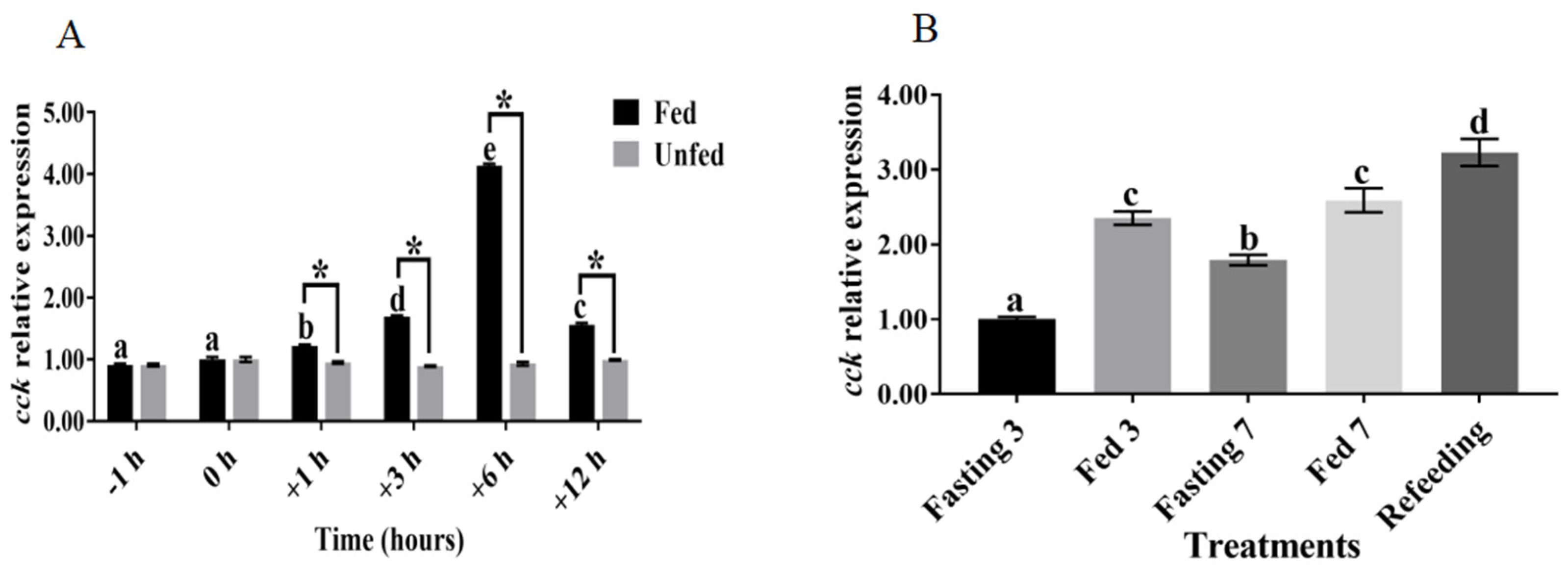
2.3. Changes in cck Gene Expression before and after Feeding
2.4. Study of cck Gene Expression after Short-Term Fasting
2.5. Treatment with CCK Peptide and CCK Peptide + Receptor Antagonists
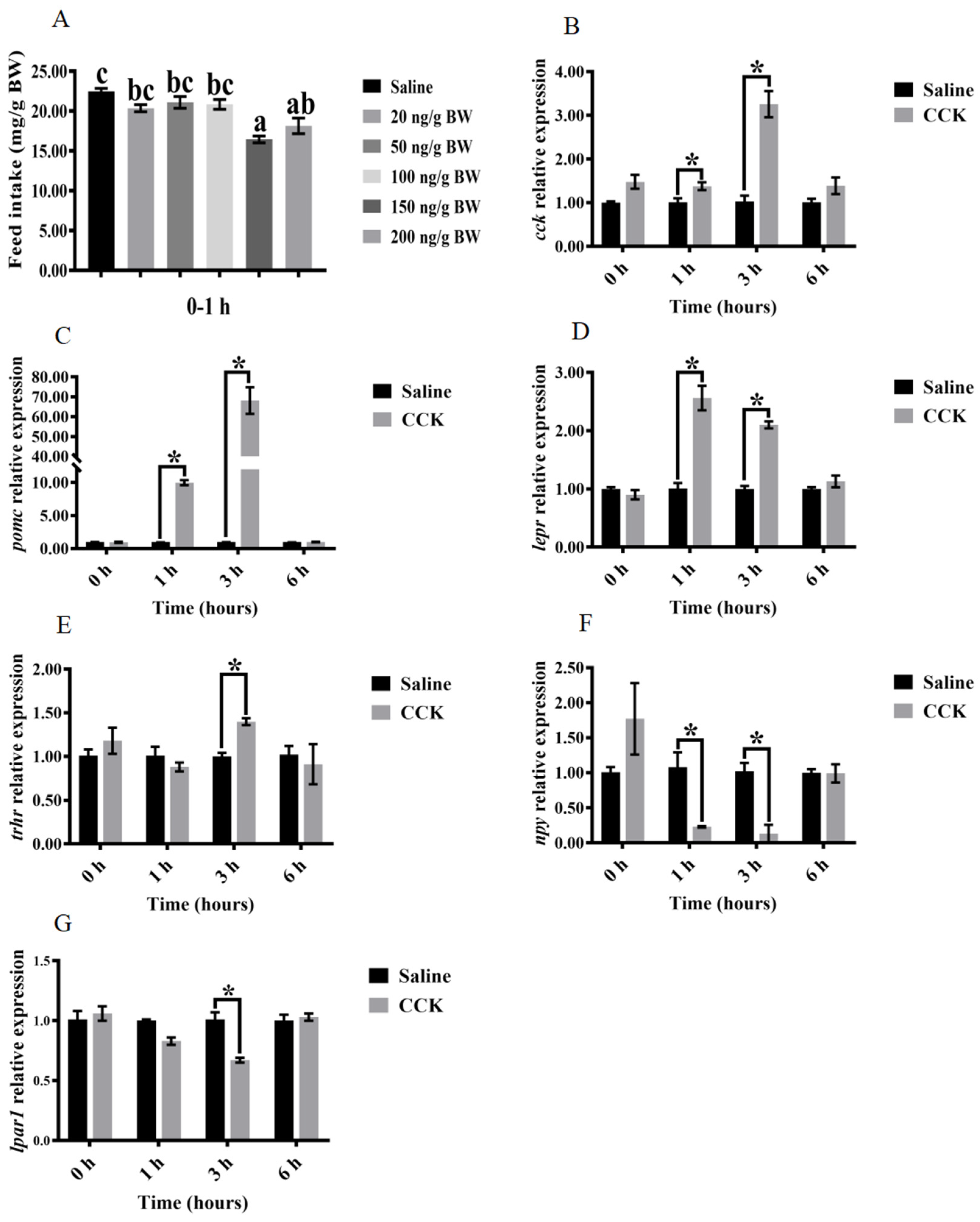
2.6. Expression of Feeding Genes in Brain and Intestine after CCK Peptide Injection
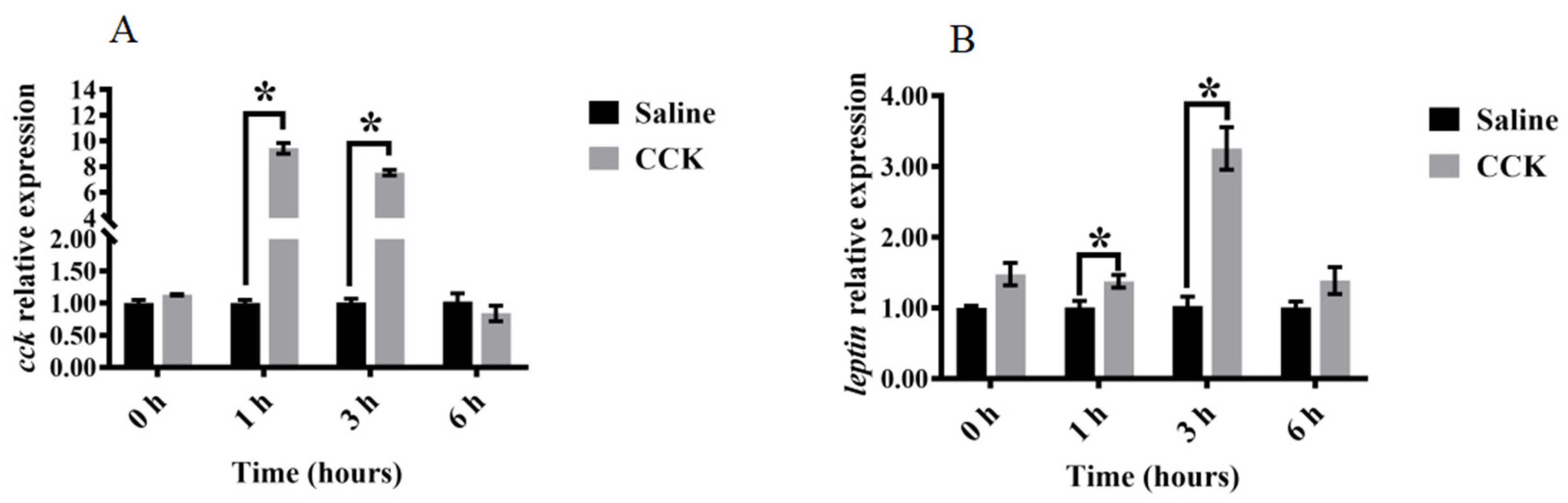
2.7. Expression of Feeding Genes in Brain and Intestine after Treatment with CCK Peptide and Receptor Antagonists
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative Fluorescence (qPCR) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression of cck Gene in Different Tissues
3.2. Relationship between cck Gene Expression and Feeding Regulation
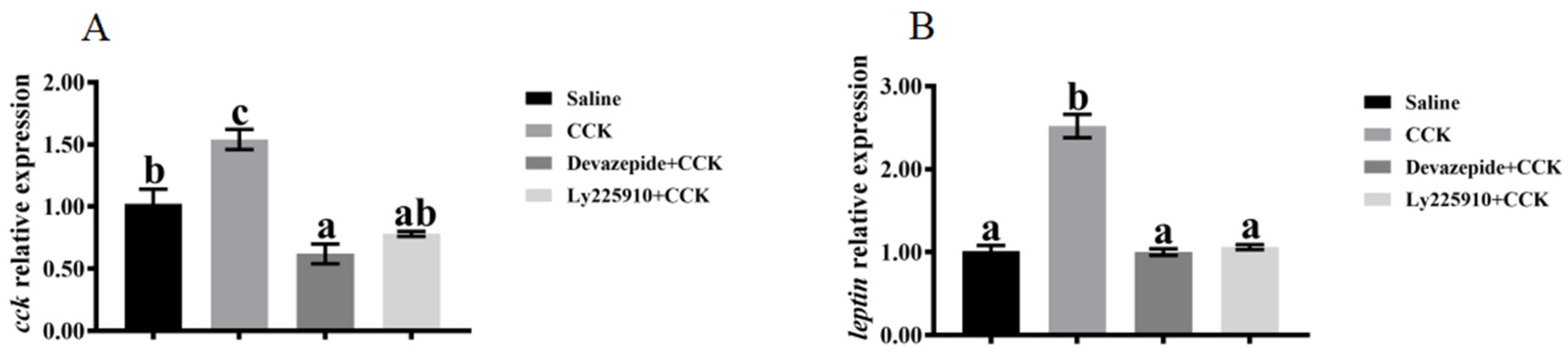
3.3. Effects of Injecting Exogenous CCK Peptide on Feeding Regulation
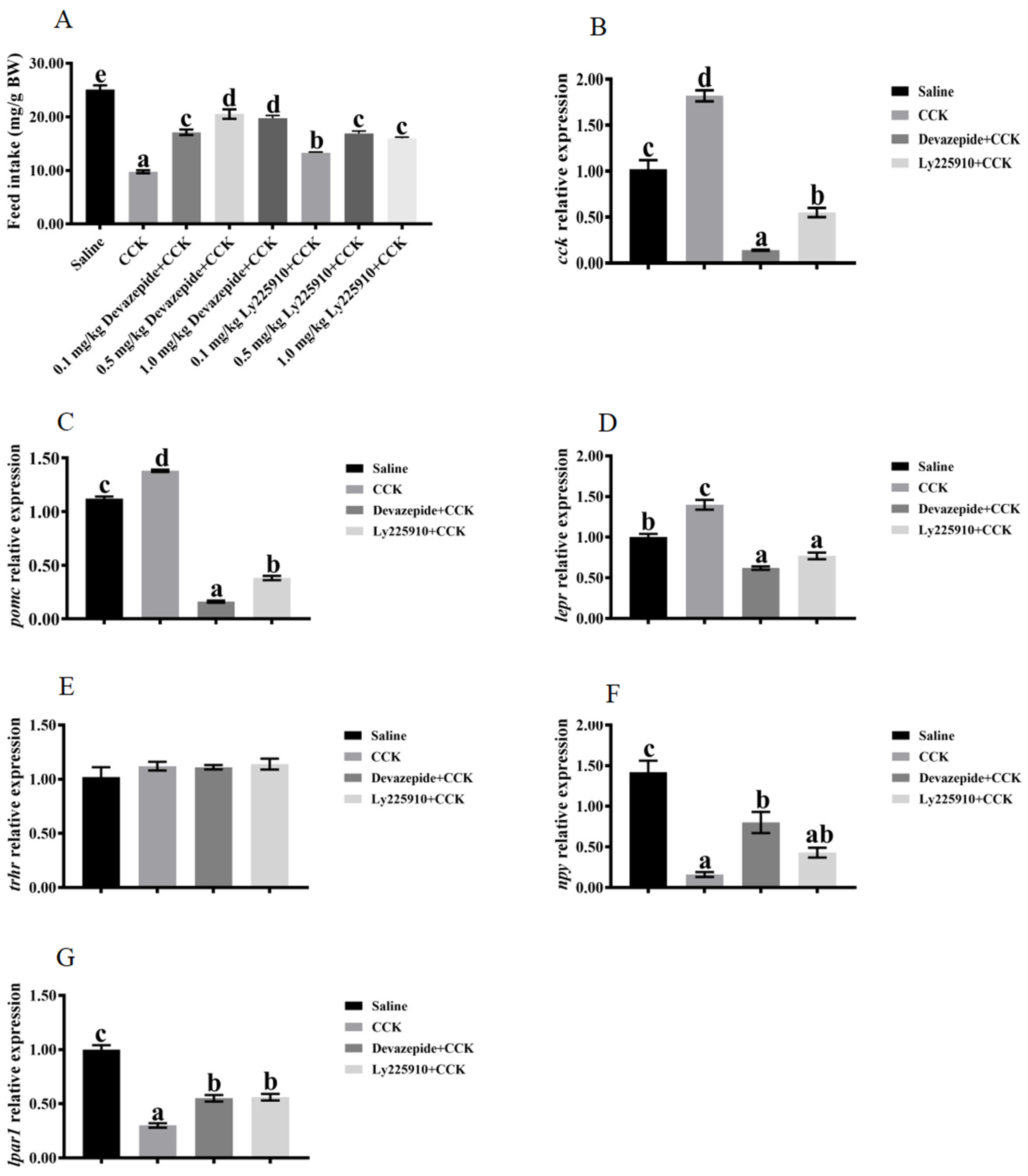
3.4. Effects of Co-Injecting Exogenous CCK Peptide and CCK Receptor Antagonists on Feeding Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strader, A.D.; Woods, S.C. Gastrointestinal hormones and food intake. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.J.; Bloom, S.R. Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 21, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, S.C.; Cachero, A.P.; Jiménez, L.P.; Barrios, V.; Ferreiro, E.A. Peptides and food intake. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Sieira, M.; Soengas, J.L. Nutrient sensing systems in fish: Impact on food intake regulation and energy homeostasis. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, J.I.; Blanco, A.M.; Sundarrajan, L.; Rajeswari, J.J.; Velasco, C.; Unniappan, S. Nutrient regulation of endocrine factors influencing feeding and growth in fish. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehfeld, J.F. Cholecystokinin—From local gut hormone to ubiquitous messenge. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himick, B.A.; Peter, R.E. CCK/gastrin-like immunoreactivity in brain and gut, and CCK suppression of feeding in goldfish. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, R841–R851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Hashimoto, H. Identification of gastrin and multiple cholecystokinin genes in teleost. Peptides 2003, 24, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Ping, H.C.; Wei, K.J.; Zhang, J.R.; Shi, Z.C.; Yang, R.B.; Zou, G.W.; Wang, W.M. Ghrelin, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and cholecystokinin (CCK) in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala): cDNA cloning, tissue distribution and mRNA expression changes responding to fasting and refeeding. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 223, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashita, K.; Fukada, H.; Hosokawa, H.; Masumoto, T. Cholecystokinin and peptide Y in yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata): Molecular cloning, real-time quantitative RT-PCR, and response to feeding and fasting. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 145, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Wang, T.; Zhou, C.; Lin, F.J.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.W.; Wei, R.B.; Xin, Z.M.; Li, Z.Q. Leptin and cholecystokinin in Schizothorax prenanti: Molecular cloning, tissue expression, and mRNA expression responses to periprandial changes and fasting. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 204, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, E.; Volkoff, H. Neuropeptide Y (NPY), cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and cholecystokinin (CCK) in winter skate (Raja ocellata): cDNA cloning, tissue distribution and mRNA expression responses to fasting. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, V.; Campo, S.; D’Ascola, A.; Guerrera, M.C.; Levanti, M.B.; Germanà, A.; Muglia, U. Cholecystokinin in white sea bream: Molecular cloning, regional expression, and immunohistochemical localization in the gut after feeding and fasting. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wank, S.A.; Pisegna, J.R.; De Weerth, A. Brain and gastrointestinal cholecystokinin receptor family: Structure and functional expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8691–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.; Parker, J.; Plumer, J.; Bloom, S. CCK, PYY and PP: The control of energy balance. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 209, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosue, Y.; Inui, A.; Teranishi, A.; Miura, M.; Nakajima, M.; Okita, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Himori, N.; Baba, S.; Kasuga, M. Cholecystokinin octapeptide analogues suppress food intake via central CCK-A receptors in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, R481–R486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, J.; Tang, N.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Chen, H.; Tian, Z.Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.F.; Li, Z.Q. Intraperitoneal injection of nesfatin-1 primarily through the CCK-CCK1R signal pathway affects expression of appetite factors to inhibit the food intake of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Peptides 2018, 109, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.J.; Wu, M.J.; Lu, S.D.; Li, X.J.; Dong, Y.; Jin, Z.B.; Zhou, Z.Y. Effects of replacing fishmeal protein by hemoglobin powder protein on growth performance, food intake, feeding-related gene expression and gut histology of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus lanceolatus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2018, 88, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.F.; Yu, X.T.; Han, J.; Yu, H.H.; Chen, P.; Wu, X.F.; Zheng, Y.H.; Xue, M. Effects of dietary protein sources on growth performance and feed intake regulation of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 2019, 510, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.; Sáez, A.; Caballero-Solares, A.; Fernández, F.; Baanante, I.V.; Metón, I. Effect of dietary macronutrients on the expression of cholecystokinin, leptin, ghrelin and neuropeptide Y in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 240, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasubong, K.P.; Cheng, H.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, W.B.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhu, X.H.; Jiang, G.Z. Effects of replacing fish meal with plant proteins at different dietary protein levels on growth and feed intake regulation of juvenile channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4911–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabioni, R.E.; Lorenz, E.K.; Cyrino, J.E.P.; Volkoff, H. Feed intake and gene expression of appetite-regulating hormones in Salminus brasiliensis fed diets containing soy protein concentrate. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 268, 111208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.J.; Lutz-Carrillo, D.J.; Quan, Y.C.; Liang, S.X. Taxonomic status and genetic diversity of cultured largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in china. Aquaculture 2008, 278, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, J.H.; Coyle, S.D.; Bright, L.A. Largemouth bass aquaculture. In Largemouth Bass Production in China; 5M Published Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2019; pp. 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.Z.; Liang, H.L.; Ge, X.P.; Xia, D.; Pan, L.K.; Mi, H.F.; Ren, M. A study of the potential effect of yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) substitution for fish meal on growth, immune and antioxidant capacity in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 120, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ge, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.R.; Ren, M.C.; Liang, H.L. Transcriptome analysis reveals the feeding response and oxidative stress in juvenile Micropterus salmoides fed a low-fish-meal diet with enzyme-hydrolysed intestinal mucosa protein substitution. Aquaculture 2023, 570, 739441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasar, E.; Harro, J.; Lang, A.; Pôld, A.; Soosaar, A. Differential involvement of CCK-A and CCK-B receptors in the regulation of locomotor activity in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 1991, 105, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballaz, S.J.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. The CCK-system mediates adaptation to novelty-induced stress in the rat: A pharmacological evidence. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 428, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, N.; Qi, J.; Wang, S.Y.; Hao, J.; Wu, Y.B.; Chen, H.; Tian, Z.Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.F.; et al. CCK reduces the food intake mainly through CCK1R in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii Brandt). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.Q.; Li, S.J.; Du, J.X.; Dong, C.J.; Lei, C.X.; Song, H.M.; Jiang, P. Fasting and refeeding on the expression of cholecystokinin and its receptor gene in Largemouth Bass. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2023, 47, 1220–1227. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, J.J.; Li, S.J. Cloning and Analysis of DNA and cDNA Sequence in NPY Gene of Northern and Florida Subspecies of Largemouth Bass. Biotechnol. Bull. 2016, 32, 99–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Lai, J.S.; Song, M.J.; Li, F.Y.; Gong, Q. Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of cholecystokinin and its receptor in Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus) and their response to different feeding conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 265, 111129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyon, P.; Saied, H.; Lin, X.; Peter, R.E. Postprandial, seasonal and sexual variations in cholecystokinin gene expression in goldfish brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 74, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, G.R.; Wei, K.J.; Xiong, B.X.; Liang, T.; Ping, H.C. Molecular characterization of cholecystokinin in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus): Cloning, localization, developmental profile, and effect of fasting and refeeding on expression in the brain and intestine. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.W. Central nervous system regulation of food intake. Obesity 2006, 14, 1S–8S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Tovar, S.; Vazquez, M.J.; Williams, L.M.; Diéguez, C. Peripheral tissue–brain interactions in the regulation of food intake. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddle, R.A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Rosen, M.S.; Taplitz, R.A.; Williams, J.A. Cholecystokinin bioactivity in human plasma. Molecular forms, responses to feeding, and relationship to gallbladder contraction. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 75, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.C.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Riley Jr, L.G.; Upton, K.R.; Kobayashi, Y.; Small, B.C. Pre-and postprandial changes in orexigenic and anorexigenic factors in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 176, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valen, R.; Jordal, A.E.O.; Murashita, K.; Rønnestad, I. Postprandial effects on appetite-related neuropeptide expression in the brain of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 171, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Pandit, N.P.; Fu, J.J.; Li, D.; Li, J.L. Molecular cloning, expression analysis, and potential food intake attenuation effect of peptide YY in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 187, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Unniappan, S. Molecular characterization, appetite regulatory effects and feeding related changes of peptide YY in goldfish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 166, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, J.C.; Fenn, C.M.; Small, B.C. Elucidating the roles of gut neuropeptides on channel catfish feed intake, glycemia, and hypothalamic NPY and POMC expression. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 188, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhri, O.; Small, C.; Bloom, S. Gastrointestinal hormones regulating appetite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkoff, H.; Eykelbosh, A.J.; Peter, R.E. Role of leptin in the control of feeding of goldfish Carassius auratus: Interactions with cholecystokinin, neuropeptide Y and orexin A, and modulation by fasting. Brain Res. 2003, 972, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D., Jr.; Cerdán, M.G.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Cone, R.D.; Low, M.J. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 2000, 404, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Rubinstein, M.; Cerdán, M.G.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Cone, R.D.; Low, M.J. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 2001, 411, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baver, S.B.; Hope, K.; Guyot, S.; Bjørbaek, C.; Kaczorowski, C.; O’Connell, K.M.S. Leptin modulates the intrinsic excitability of AgRP/NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, A.M.; Soengas, J.L. Leptin signalling in teleost fish with emphasis in food intake regulation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 526, 111209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffersen, B.Ø.; Skyggebjerg, R.B.; Bugge, A.; Kirk, R.K.; Vestergaard, B.; Uldam, H.K.; Fels, J.J.; Pyke, C.; Sensfuss, U.; Sanfridson, A.; et al. Long-acting CCK analogue NN9056 lowers food intake and body weight in obese Göttingen Minipigs. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | Accession No./Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| cck | TAAAGGGAAGTCACGGCTCATAC | CGGTTATTCTCAACAGACCCTGA | XM_038724067.1 |
| cck1r | CCGTGCTGGTGAGGAACAGG | GCCAGTGCCGAAGACGAAGT | [31] |
| cck2r | GCGCGCCCATCTCCTTCATC | GCCTCCCTCTTCCTGCACCA | [31] |
| leptin | CTTTTCATTCACGTGTTTCGCTG | CCTCTGACTGCAAACAACCTTAC | MN887534.1 |
| lepr | TTGTCCCACAAAGAAGACACAGA | AGTGTAAAATCAGCTCAGCCTCA | XM_038715328.1 |
| pomc | GTGAAAGGAGAGGGAAGAGACAG | AGAACACGACATCAACTCTGGAA | XM_038725660.1 |
| trhr | GCCACAGAGTAAGCAGAAT | TCACATCACATCACATCACA | XM_038705006.1 |
| npy | GTCATCAGTGTTGGCTCCACCTCA | CAACATGCCCTCCTCCACTTTACT | [32] |
| lpar1 | CCACCATAACGAACACTCT | GCTCATCATCAACTCTACCT | XM_038733709.1 |
| β-actin | ATGCAGAAGGAGATCACAGCCT | AGTATTTACGCTCAGGTGGGG | AF253319.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Mi, H.; Yu, H.; Huang, D.; Ren, M.; Zhang, L.; Teng, T. Role of Cholecystokinin (cck) in Feeding Regulation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): Peptide Activation and Antagonist Inhibition. Biology 2024, 13, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080635
Liang H, Mi H, Yu H, Huang D, Ren M, Zhang L, Teng T. Role of Cholecystokinin (cck) in Feeding Regulation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): Peptide Activation and Antagonist Inhibition. Biology. 2024; 13(8):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080635
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Hualiang, Haifeng Mi, Heng Yu, Dongyu Huang, Mingchun Ren, Lu Zhang, and Tao Teng. 2024. "Role of Cholecystokinin (cck) in Feeding Regulation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): Peptide Activation and Antagonist Inhibition" Biology 13, no. 8: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080635
APA StyleLiang, H., Mi, H., Yu, H., Huang, D., Ren, M., Zhang, L., & Teng, T. (2024). Role of Cholecystokinin (cck) in Feeding Regulation of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): Peptide Activation and Antagonist Inhibition. Biology, 13(8), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080635






