Heart Rate and Acceleration Dynamics during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Experimental Fish and Conditions
2.3. Heart Rate and Acceleration Loggers
2.4. Swim-Fitness Test and Respirometry
2.5. Locomotory Behavior during the Swim-Fitness Test
2.6. Stress Challenge Test and Cortisol
2.7. Ultrasound
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
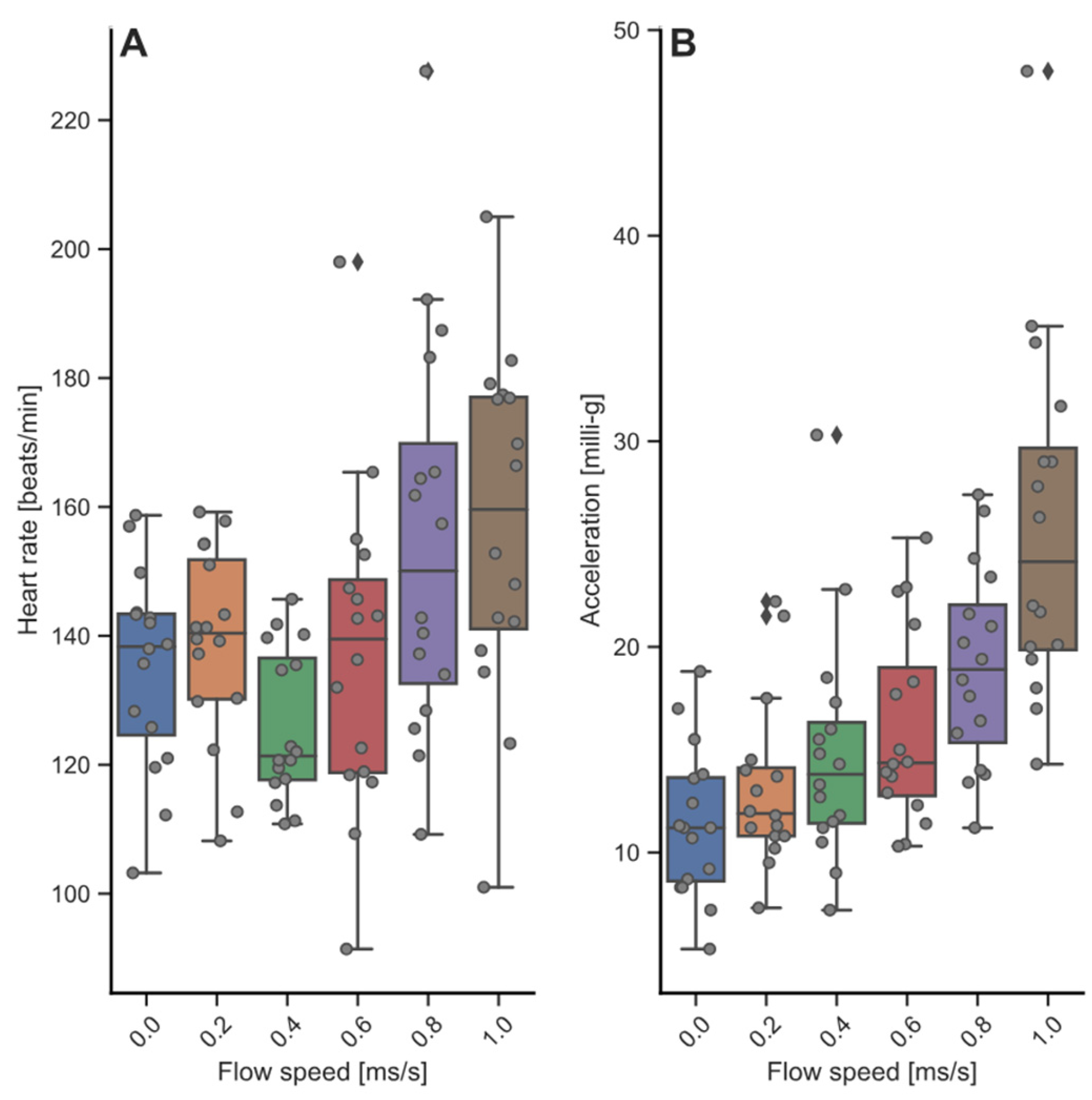
3.1. Swim-Fitness
- 550 ± 101 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for implanted fish and 555 ± 93 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for controls, when swimming at 0.2 m·s−1;
- 550 ± 109 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for implanted fish and 573 ± 115 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for controls, when swimming at 0.4 m·s−1;
- 566 ± 125 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for implanted fish and 561 ± 92 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for controls, when swimming at 0.6 m·s−1.
- At the higher swim speeds, MO2 levels increased up to:
- 595 ± 96 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for implanted fish and 590 ± 108 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for controls, when swimming at 0.8 m·s−1;
- 713 ± 94 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for implanted fish and 786 ± 264 mg O2·kg−1·h−1 for controls, when swimming at 1.0 m·s−1.

3.2. Locomotory Behavior
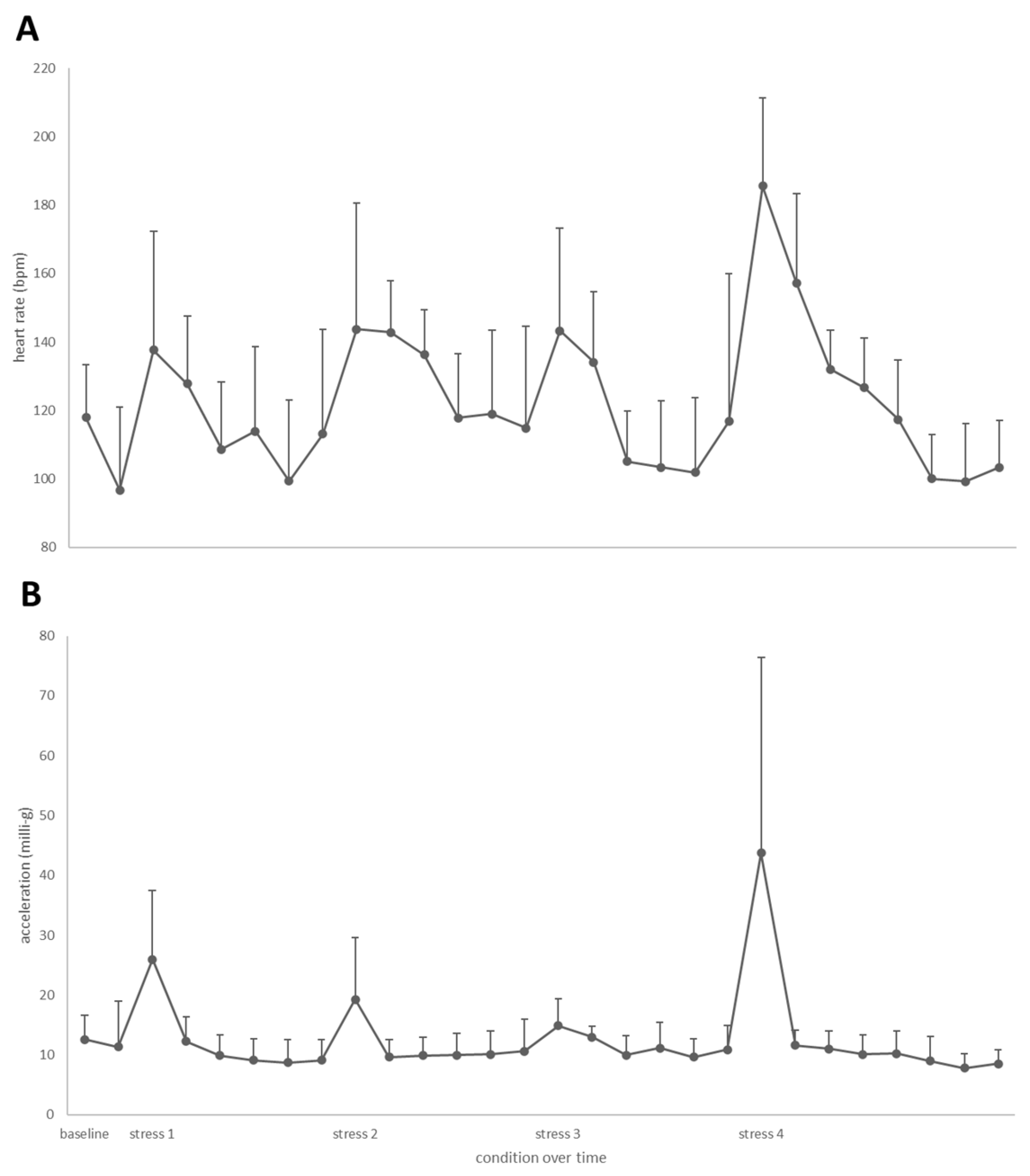
3.3. Heart Rate and Acceleration during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests
3.4. Cortisol Concentrations during the Stepwise Stress Challenge Test
3.5. Correlations between Parameters during the Swim-Fitness Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gillanders, B.M.; Ferrell, D.J.; Andrew, N.L. Estimates of movement and life-history parameters of yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi): How useful are data from a cooperative tagging programme? Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 52, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco Garcia, A.; Partridge, G.J.; Flik, G.; Roques, J.A.C.; Abbink, W. Ambient salinity and osmoregulation, energy metabolism and growth in juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi Valenciennes 1833) in a recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2789–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, J.E.; Walker, S.P.; Pether, S.; Gublin, Y.; McQueen, D.; King, A.; Irvine, G.W.; Setiawan, A.N.; Forsythe, J.A.; Bruce, m. Developing yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) and hāpuku (Polyprion oxygeneios) for New Zealand aquaculture. N. Z. J. Mar. Fresh. 2014, 48, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstra, A.P.; Planas, J.V. Fish under exercise. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.J.; Palstra, A.P.; Planas, J.; MacKenzie, S.; Bégout, M.-L.; Thorarensen, H.; Vandeputte, M.; Mes, D.; Rey, S.; De Boeck, G.; et al. Aerobic swimming in intensive aquaculture: Applications for production, mitigation and selection. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 13, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstra, A.P.; Mes, D.; Kusters, K.; Roques, J.A.C.; Flik, G.; Kloet, K.; Blonk, R.J.W. Forced sustained swimming exercise at optimal speed enhances growth of yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Front. Physiol. 2015, 5, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstra, A.; van Ginneken, V.; van den Thillart, G. Cost of transport and optimal swimming speeds in farmed and wild European silver eels (Anguilla anguilla). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2008, 151, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstra, A.P.; Tudorache, C.; Rovira, M.; Brittijn, B.; Burgerhout, E.; van den Thillart, G.E.E.J.M.; Spaink, H.P.; Planas, J.V. Establishing zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a novel exercise model: Swimming economy, swimming-enhanced growth and regulation of muscle growth marker gene expression. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videler, J.J. Fish Swimming, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Arends, R.J.; Mancera, J.M.; Munoz, J.L.; Bonga, S.W.; Flik, G. The stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) to air exposure and confinement. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 163, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga, R.; Montero, D.; Gordon Bell, J.; Atalah, E.; Ganuza, E.; Vega-Orellana, O.; Tort, L.; Acerete, L.; Afonso, J.M.; Benitez-Sanatana, T.; et al. Stress response in sea bream (Sparus aurata) held under crowded conditions and fed diets containing linseed and/or soybean oil. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsdóttir, I.E.; Nilssen, K.J. Stress responses of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) elicited by water level reduction in rearing tanks. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1996, 15, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaro, A.; Olsen, R.E.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Ebbesson, L.O.; Flik, G.; Gorissen, M. A comparative study of the response to repeated chasing stress in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr and post-smolts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2016, 192, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, E.; Føre, M.; Økland, F.; Gräns, A.; Hedger, R.D.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Uglem, I.; Rosten, C.M.; Frank, K.; Erikson, U.; et al. Heart rate and swimming activity as stress indicators for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.M.; Piper, A.T.; Aarestrup, K.; Azevedo, J.M.; Cowan, G.; Don, A.; Gollock, M.; Rodriguez Ramallo, S.; Velterop, R.; Walker, A.; et al. First direct evidence of adult European eels migrating to their breeding place in the Sargasso Sea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Thorstad, E.B.; Aarestrup, K. Overlooked aspects of the Salmo salar and Salmo trutta lifecycles. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 2019, 29, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevé, N.W.; Vis, H.; Houben, B.; Breukelaar, A.; Acolas, M.L. Outmigration pathways of stocked juvenile European sturgeon (Acipenser sturio L., 1758) in the Lower Rhine River, as revealed by telemetry. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, B.A.; Whitlock, R.; Schallert, R.J.; Wilson, S.; Stokesbury, M.J.; Castleton, M.; Boustany, A. Estimating natural mortality of Atlantic bluefin tuna using acoustic telemetry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, G.; Agustines, A.; Tracey, B.; Snow, S.; Labaja, J.; Ponzo, A. Photo-ID and telemetry highlight a global whale shark hotspot in Palawan, Philippines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarevic, J.; Aas-Hansen, Ø.; Espmark, Å.; Baeverfjord, G.; Terjesen, B.F.; Damsgård, B. The use of acoustic acceleration transmitter tags for monitoring of Atlantic salmon swimming activity in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS). Aquacult. Eng. 2016, 72, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Føre, M.; Frank, K.; Norton, T.; Svendsen, E.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Dempster, T.; Eguiraun, H.; Watson, W.; Stahl, A.; Sunde, L.M.; et al. Precision fish farming: A new framework to improve production in aquaculture. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 173, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, L.; Aspillaga, E.; Palmer, M.; Saraiva, J.L.; Arechavala-Lopez, P. Acoustic telemetry: A tool to monitor fish swimming behavior in sea-cage aquaculture. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstra, A.P.; Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Xue, Y.; Roque, A. Accelerometry of seabream in a sea-cage: Is acceleration a good proxy for activity? Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Lankheet, M.; Diaz-Gil, C.; Abbink, W.; Palstra, A.P. Swimming activity of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) in swim-tunnels: Acoustic accelerometry, oxygen consumption and body motion. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 679848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Sosa, J.; Ramos-Valido, D.; Bravo, F.J.; Carmona-Duarte, C.; Gomes, H.L.; Calduch-Giner, J.À.; Cabruja, E.; Vega, A.; Ferrer, M.Á.; et al. Ultra-low power sensor devices for monitoring physical activity and respiratory frequency in farmed fish. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Yonemori, Y.; Musiya, K.; Maita, M.; Shibuya, T.; Ren, H.; Hayashi, T.; Mitsubayashi, K. A needle-type optical enzyme sensor system for determining glucose levels in fish blood. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shinoda, R.; Murata, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Ohnuki, H.; Endo, H. Real-time fish stress visualization came true: A novel multi-stage color-switching wireless biosensor system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, E.; Føre, M.; Randeberg, L.L.; Olsen, R.E.; Finstad, B.; Remen, M.; Bloecher, N.; Alfredsen, J.A. ECG augmented pulse oximetry in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)—A pilot study. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2023, 212, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, Á.; Gunnarsson, A.; Árnason, T.; Oddgeirsson, M.; Sigmarsson, A.B.; Gunnarsson, Á. Validation of ECG-derived heart rate recordings in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) with an implantable data logging system. Anim. Biotelemetry 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouyer, T.; Bonhommeau, S.; Bernard, S.; Kerzerho, V.; Derridj, O.; Bjarnason, Á.; Allal, H.; Steffensen, J.F.; Deguara, S.; Wendling, B.; et al. A novel protocol for rapid deployment of heart rate data storage tags in Atlantic bluefin tuna Thunnus thynnus reveals cardiac responses to temperature and feeding. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Thillart, G.E.E.J.M.; Van Ginneken, V.; Körner, F.; Heijmans, R.; Van der Linden, R.; Gluvers, A. Endurance swimming of European eel. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, W.H.; Terhune, L.D.B. Water tunnel design for fisheries research. Fish. Res. Board. Can. Tech. Rep. 1970, 195, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, N.A.; Kadri, S.; Huntingford, F.A. A moving light stimulus elicits a sustained swimming response in farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 37, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.D.; Seymour, R.S. Cardiorespiratory physiology and swimming energetics of a high-energy-demand teleost, the yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3940–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J.R. The metabolic demand for oxygen in fish, particularly salmonids, and a comparison with other vertebrates. Resp. Physiol. 1972, 14, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, R.W.; Bushnell, P.G. Metabolic and cardiac scope of high energy demand teleosts-the tunas. Can. J. Zool. 1991, 69, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, R.W.; Bushnell, P.G. The cardiovascular system of tunas. Fish Physiol. 2001, 19, 79–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lillywhite, H.B.; Zippel, K.C.; Farrell, A.P. Resting and maximal heart rates in ectothermic vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1999, 124, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.P. Features heightening cardiovascular performance in fishes, with special reference to tunas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1996, 113, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, P.G.; Brill, R.W. Oxygen transport and cardiovascular responses in skipjack tuna (Kutsuwonas pelamis) and yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacores) exposed to acute hypoxia. J. Comp. Physiol. 1992, B162, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenroth, D.; McArley, T.; Danielo, Q.; Harford, A.; Hickey, A.J.; Khan, J.; Sandblom, E. Kingfish (Seriola lalandi) adjust to low salinity with only subtle effects to cardiorespiratory and growth performance. Aquaculture 2022, 556, 738268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrelli, R.M.; Gamperl, A.K. The upper temperature and hypoxia limits of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) depend greatly on the method utilized. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb246227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignucci, A.; Bourjea, J.; Forget, F.; Allal, H.; Dutto, G.; Gasset, E.; McKenzie, D.J. Cardiac and behavioural responses to hypoxia and warming in free-swimming gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantin, F.T.; Gesser, H.; Kalinin, A.L.; Guerra, C.D.R.; De Freitas, J.C.; Driedzic, W.R. Heart performance, Ca2+ regulation and energy metabolism at high temperatures in Bathygobius soporator, a tropical marine teleost. J. Therm. Biol. 1998, 23, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, K.E.; Lai, N.C.; Shadwick, R.E.; Graham, J.B. Heart rate and stroke volume contributions to cardiac output in swimming yellowfin tuna: Response to exercise and temperature. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.N.; Røn, Ø.; Plebaniak Hagen, P.; McGurk, C. Monitoring fish welfare using heart rate bio-loggers in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): An insight into the surgical recovery. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbeti, W.E.K.; Palstra, A.P. Heart Rate and Acceleration Logging during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2024; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Tomàs, J.; Palstra, A.P. Heart Rate and Acceleration Logging during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in European Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2024; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Brønstad, A. Good Anesthesia Practice for Fish and Other Aquatics. Biology 2022, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.A.; Rodnick, K.J. Differential effects of anesthetics on electrical properties of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) heart. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2006, 145, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.J. Effect of an anaesthetic on the heart and respiration of teleost fish. Nature 1962, 195, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.V.; Davison, W.; Forster, M.E. The effects of fish anaesthetics (MS222, metomidate and AQUI-S) on heart ventricle, the cardiac vagus and branchial vessels from Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 27, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoul, B.; Geffroy, B. Measuring cortisol, the major stress hormone in fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.D.; Sandblom, E.; Hinch, S.G.; Patterson, D.A.; Frappell, P.B.; Farrell, A.P. Simultaneous biologging of heart rate and acceleration, and their relationships with energy expenditure in free-swimming sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2010, 180, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.C. Heart rate as an indicator of metabolic rate and activity in adult Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. J. Fish Biol. 1994, 44, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarensen, H.; Gallaugher, P.E.; Farrell, A.P. The limitations of heart rate as a predictor of metabolic rate in fish. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 49, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.P.; Eliason, E.J.; Sandblom, E.; Clark, T.D. Fish cardiorespiratory physiology in an era of climate change. Can. J. Zool. 2009, 87, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.; Jonz, M.; Gilmour, K. Oxygen sensing and the hypoxic ventilatory response. Fish Physiol. 2009, 27, 193–253. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, W.; Wang, T. Regulation of heart rate in vertebrates during hypoxia: A comparative overview. Acta Physiol. 2022, 234, e13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenroth, D.; Kvaestad, B.; Økland, F.; Finstad, B.; Olsen, R.-E.; Svendsen, E.; Rosten, C.; Axelsson, M.; Bloecher, N.; Føre, M.; et al. Under the sea: How can we use heart rate and accelerometers to remotely assess fish welfare in salmon aquaculture? Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Brownscombe, J.W.; Raby, G.D.; Broell, F.; Hinch, S.G.; Clark, T.D.; Semmens, J.M. Remote bioenergetics measurements in wild fish: Opportunities and challenges. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2016, 202, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaji, H.; Hamada, K.; Naito, Y. Identifying spawning events of greater amberjack using accelerometers. Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.M.; Whitmarsh, S.K.; Hounslow, J.L.; Gleiss, A.C.; Payne, N.L.; Huveneers, C. Using tri-axial accelerometer loggers to identify spawning behaviours of large pelagic fish. Movement Ecol. 2021, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.M.; Whitmarsh, S.K.; Jaine, F.R.; Taylor, M.D.; Brodie, S.; Payne, N.L.; Butcher, P.A.; Broadhurst, M.K.; Davey, J.; Huveneers, C. Environmental drivers of yellowtail kingfish, Seriola lalandi, activity inferred through a continental acoustic tracking network. Aquatic Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2023, 34, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Swimming Speed (m·s−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
| ACC | TBA | −0.960 | |||||
| ACC | TBF | 0.981 | |||||
| SL | HR | 0.615 | |||||
| HWA | HWF | −0.582 | −0.546 | −0.679 | −0.670 | −0.550 | |
| TL | TBF | −0.382 | −0.604 | ||||
| SL | TBA | 0.386 | 0.447 | 0.416 | |||
| MO2 | TBF | 0.502 | |||||
| HR | TBF | 0.716 | |||||
| MO2 | HR | 0.810 | 0.606 | ||||
| TL | TBA | 0.431 | 0.496 | ||||
| SL | TBF | −0.621 | |||||
| BW | TBF | −0.543 | |||||
| BW | TBA | 0.367 | 0.437 | ||||
| BW | HR | −0.529 | |||||
| ACC | HWA | −0.662 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palstra, A.P.; Abbink, W.; Agbeti, W.E.K.; Kruijt, L.; Jéhannet, P.; Lankheet, M.J. Heart Rate and Acceleration Dynamics during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Biology 2024, 13, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030189
Palstra AP, Abbink W, Agbeti WEK, Kruijt L, Jéhannet P, Lankheet MJ. Heart Rate and Acceleration Dynamics during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Biology. 2024; 13(3):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030189
Chicago/Turabian StylePalstra, Arjan P., Wout Abbink, Wisdom E. K. Agbeti, Leo Kruijt, Pauline Jéhannet, and Martin J. Lankheet. 2024. "Heart Rate and Acceleration Dynamics during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi)" Biology 13, no. 3: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030189
APA StylePalstra, A. P., Abbink, W., Agbeti, W. E. K., Kruijt, L., Jéhannet, P., & Lankheet, M. J. (2024). Heart Rate and Acceleration Dynamics during Swim-Fitness and Stress Challenge Tests in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Biology, 13(3), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030189







